What is Penoplex?
Under penoplex
traditionally, it is understood a material obtained from polystyrene by means of foaming, as well as extrusion with compression. It is actively used as a heat-insulating material in the field of construction.
The structure of the foam is represented by a large number of isolated cells that are filled with air. They are usually less than a millimeter in size. The material is highly durable. The density of the foam is about 29-35 kg / cu. m, the thermal conductivity index is about 0.029-0.039 W / (m * K). The material has low water absorption and vapor permeability.
What is expanded polystyrene?
Under expanded polystyrene
, or foam, is understood as a material that, like penoplex, is made of polystyrene by foaming, but without using extrusion with pressing. As a result, much larger cells are formed in the structure of the material - a few millimeters in diameter.
Foam plastic can, in principle, be used for the same purposes as penoplex - as a heat-insulating material. In addition, expanded polystyrene is often used in the factory packaging of household appliances - due to the combination of lightness, softness and elasticity.
Expanded polystyrene is much less durable than penoplex, has a higher thermal conductivity. The density of the foam is about 17-18 kg / cu. m. Its water absorption is noticeably higher than foam, but the vapor permeability of both materials is approximately at the same level.
Comparison
The main difference between foam and polystyrene foam is that the first material is produced using extrusion with pressing, as a result of which small cells are formed in its structure. Polyfoam is produced without using the noted technology - and therefore its cells are larger. The specificity of the manufacture of materials predetermines the difference in the indices of their density, thermal conductivity, water absorption.
Having determined what is the difference between penoplex and expanded polystyrene, we will reflect the conclusions in the table.
Table
| Penoplex | Expanded polystyrene |
| What do they have in common? | |
| Both materials are made of polystyrene foam, in many cases interchangeable | |
| Comparable in terms of vapor permeability | |
| What is the difference between them? | |
| Manufactured using press extrusion | Manufactured without extrusion pressing |
| The structure of the material is represented by small cells | The structure of the material is represented by significantly larger cells |
| Has lower thermal conductivity | Has a higher thermal conductivity |
| Has a higher density | Has a lower density |
| Has less water absorption | Has great water absorption |
The main characteristic of any heat-insulating material is the coefficient of thermal conductivity. The lower it is, the better. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the moisture absorption of the material.
Ursa
Coating German production... It is a mineral wool based on durable stamped glass fiber. The company has developed separate series of coatings intended for thermal insulation of premises at each stage of construction.

The manufacturer produces several categories of goods that differ in size, characteristics, and scope.
- URSA GEO... The fiberglass product is used in sustainable construction. The range of URSA GEO includes 20 product names, designed for use in specific conditions.On the domestic market, the most popular coating is M-11. Due to its versatility, it is suitable for installation on most objects.
- URSA Pure On... Visually similar to cotton or wool fabric. Like the previous material, it is made of mineral wool. Free from irritating properties. On the domestic market it is represented by the following types: 34 PN. 25 QN. 37 RN.
- URSA Terra... Ideal for thermal insulation of industrial facilities, sloping roofs, facades. The series is released in several versions: noise protection. technical mat. 34 PN.
- URSA Seko... It is produced in the form of rolls, differing in length and thickness. Designed for installation of thermal insulation of sloping roofs, external walls, ceilings. The assortment is presented in 4 types: AM. A. B. D.
- URSA XPS... Made on the basis of extruded polystyrene foam. They insulate roofs of any design, ceilings, walls, foundations. Available in 3 types: N-V. N-III-G4. N-III.


Which is better to choose - polystyrene or penoplex?
Do you want to understand what is the difference between polystyrene and polystyrene foam? Although these materials are similar in composition, they still have significant differences. After reading this article, you will learn about the manufacturing technology of both materials, their properties, advantages and disadvantages, as well as what are their differences.
The problem of choosing a heat-insulating material arises when the turn has come to insulate the walls. The insulated balcony, walls, even the ceiling and roof are the border that protects us from the effects of cold in the winter, and from the destructive heat in summer. The effectiveness of thermal insulation depends on the materials used in the construction. So that you do not have to "defrost" your summer cottage for a long time, and the heat in the house remains as long as possible, we advise you to insulate the surfaces using foam or polystyrene foam. Both materials are of synthetic origin, safe for human health, and can be used in the construction of industrial and residential buildings.
URSA XPS or Penoplex which is better
Penoplex is, in fact, the same extruded polystyrene foam, but only from another manufacturer. Which is better - penoplex or URSA XPS, depends on the cost of insulation in your city, the cost of delivery, and in terms of their characteristics in thermal conductivity in practice, they differ little from each other. In terms of cost, URSA XPS boards are considered the more expensive material.
As you can see the characteristics of URSA is the optimal solution for a private developer. Plates are lightweight, easy to cut with a clerical knife and easy to install. For self-warming of a house with URSA XPS plates, no special skills and tools are required. At the same time, you will receive reliable protection from the cold with high mechanical strength and moisture resistance.
(4,75 out of 5)
Polyfoam: features
It is a traditional material for thermal insulation work, which is produced by foaming polystyrene. This technology provides 98% of the air in its composition. Both polystyrene and the resulting polystyrene have:
- good moisture resistance;
- durable;
- wear-resistant;
- not subject to decay;
- they are not affected by sudden temperature changes, exposure to alkalis and acids;
- do not change their properties at high temperatures.
This material is attractive for its low cost and ease of installation. It is used to insulate walls, floors, ceilings and roofs.
Penoplex characteristics
This is a modern and equally popular insulation material.
Penoplex
Due to excellent thermal insulation, zero water absorption, strength, resistance to biodegradation, durability, lightness of the material and ease of installation, it is used for thermal insulation:
- Cellars and plinths. Insulation of foundations of small and deep foundations.
- Floors on the ground, on a concrete slab, when installing a warm floor.
- Walls outside and inside.Thermal insulation of concrete and brick walls, multi-layer walls, walls of frame houses, additional thermal insulation and internal.
- Septic tanks of pipelines, drainage systems.
- Pitched roof and attic floors.
Ursa and Penoplex - modern thermal insulation coatings... The first appeared relatively recently, and polystyrene foam has been used for a long time. Both materials have similar qualities. Light weight, ease of installation, resistance to biodegradation. But on several points Penoplex is more attractive than Ursa. It is moisture-proof, vapor-proof, does not require special protective devices during installation. Ursa is superior only in price, however, the characteristics are sufficient to maintain the demand for coverage at a high level.
Renovation and construction
What is the difference between expanded polystyrene and penoplex?
Penoplex has a low thermal conductivity, so you need a small layer to carry out insulation work. It is also produced from polystyrene using the extrusion method (melting), which provides a single molecular structure. Therefore, penoplex is more elastic and wear-resistant than its foamed counterpart. Such insulation:
- not of interest to rodents, insects;
- not subject to decay, fungus and mold do not take it;
- burns poorly and self-extinguishes;
- weighs little;
- withstands the temperature range from -50 to +75 degrees.
Penoplex is used mainly for insulating loggias and balconies, country houses and apartment walls. Excellent ductility and low compression ratio allow the material to be used as a universal heat insulator. Often it is he who acts as the best option for insulating not only flat surfaces, but also pipes. Ease of installation allows finishing work without special preparation.
A significant advantage of penoplex over polystyrene is that rodents often start in the latter, and this leads to partial or complete deterioration of the material.
Material properties: what is the difference
To choose the most suitable material in terms of price and technical characteristics, let's try to figure out what is the difference between polystyrene (PT of one of the most popular brands PSB-S 25) and penoplex plates (PS).
- PT has a loose and heterogeneous structure, the edges are rough, which can crumble when pressed. Its analogue has a dense and monolithic structure, is not inclined to crumble and collapse when pressed.
- Thermal conductivity with an average air humidity: for PT - 0.045 W / (m × ° C) and for PS - 0.031 W / (m × ° C) (its thermal insulation properties are higher).
- The thickness of the insulation layer in the wall with the same degree of resistance to heat transfer: for PT - 140 mm (minimum), for PS - 100 mm (average, you can use less).
- Indicator of water absorption in 24 hours: PT - 2.13%, its opponent - 0.4% (absorbs moisture 5 times slower).
- Compressive strength: PT - 7 t / m2, PS - 20 t / m2 (almost 3 times stronger).
- Fire safety: PT refers to combustible materials that emit harmful substances during combustion, while the PS extinguishes on its own.
- PT due to its peculiarities has a high vapor permeability compared to PS, which allows the material to "breathe", but does not have the best effect on its thermal insulation properties.
- Service life: PT will last 10-15 years under the correct operating conditions, PS will live up to 50 years.
Do not forget that the price of penoplex is much higher than that of foam. Therefore, if you want to save money, then it is better to choose the second option.
Differences in laying technology
The main thing to pay attention to when laying is the elasticity and tendency of the material to crumble. Be careful with styrofoam as it breaks easily and can crumble.It is used only if any significant mechanical damage and certain loads are excluded. Otherwise, choose a more flexible and stable foam.
There is an opinion that more airy foam is best for insulating external walls, and thinner foam is best for balconies and loggias. If you started interior decoration of the room, then both one and the other material should be abandoned. The main reason is a possible displacement of the dew point, which threatens to be ineffective in the design.
There is no significant difference between the materials during installation on the roof, ceiling and floor. However, thanks to its stronger structure, penoplex will allow you to refuse to install floor coverings when working in the attic. Its versatility allows it to be installed with thermal insulation of foundations, plinths and pipes.
In modern professional construction, the use of both foam and foam is almost abandoned. The first is short-lived, the second is too expensive. In most cases, mineral wool is used for insulation.
Verdict
You should always make informed choices and know what you are agreeing to. Having chosen foam as the most economical and cheapest option, remember that you will need 1.5-2 times more material than foam. You will be able to significantly save only with large-scale construction work. In this case, you also run the risk of getting the wrong thermal insulation properties that you expected. After all, the slightest error in laying the foam can lead to dampness, and such insulation does not retain heat well and can become covered with fungus and mold.
Polyfoam is less durable and lends itself to the destructive influence of the environment, so in a dozen years a new, no less expensive, repair awaits you. So it is unlikely that it will be possible to get at least some significant benefit from the use of foam. Turn to a more durable and economical material in the future - penoplex.
There are exceptions, so each individual case should be weighed: is the use of more expensive polystyrene foam justified, or is it possible to get by with budget foam.
Video: Polyfoam and penoplex - check for flammability
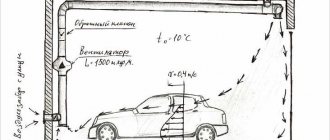
How to make external insulation of the ceiling in a wooden house?
Innovations in modern building technology include the use of insulation to save other building materials and energy. There are enough types of insulation materials on the market, and the most popular are penoplex or polystyrene, which are made from artificial components. Penoplex is one of the variable transformations of polystyrene, and their parameters are in many ways similar, but somewhat different. Therefore, when choosing, foam or penoplex is better for warming a house, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself in detail with their parameters and performance characteristics.
Styrofoam or expanded polystyrene
Most common users don't know what the difference is between Styrofoam and Styrofoam. This situation is most likely due to the fact that both materials are made from polystyrene. The areas of application are also the same - insulation and sound insulation of various surfaces.


Many people assume that Styrofoam and Styrofoam are the same thing. However, this is not the case. In order to choose the material you need, you must carefully study all the properties.
Polyfoam - technical and operational characteristics Very many people believe that it is foam that is best used for insulation. This opinion is due to its characteristics:


Foam production scheme.
- 98% air;
- thermal conductivity (0.038-0.050 W / m K) is 3 times lower than that of wood, and 17 times lower than that of brick, which allows replacing a brick wall with a thickness of 210 cm with a layer of foam plastic 12 cm thick;
- for complete sound insulation, a foam plate with a thickness of 2-3 cm is enough;
- under no circumstances is it able to absorb a volume of moisture exceeding 3% of its mass, while the volume and thermal insulation properties do not change;
- has a low weight and does not require special tools for cutting, which facilitates installation;
- during work, the use of protective equipment is not required, since the foam is odorless, non-toxic, and dust does not form during cutting;
- during operation, it does not move or shrink, it is resistant to microorganisms and mold;
- resistant to lime, gypsum, cement, acids, alkalis, water-soluble paints, but does not tolerate benzene and acetone;
- ignites only when exposed to open fire and dies out after 4 seconds;
- environmentally friendly during operation and disposal, therefore it is used in the production of toys and food packaging.
The disadvantages include increased fragility, which complicates transportation and installation in windy weather.
It should be borne in mind that the foam will serve for a long time, provided that during operation a temperature close to the destruction temperature for a particular type of material is not allowed.
Expanded polystyrene - technical and operational characteristics


Table of characteristics of foams of various grades Table of characteristics of foams of various brands.
- the thermal conductivity of expanded polystyrene (0.028 W / m K) is much lower than that of wood, brick or expanded clay (12 cm of this material can replace a wooden wall 45 cm thick);
- unable to absorb moisture in excess of 1.5-3% of its own weight;
- when exposed to moisture, strength, structure and thermal insulation properties do not change;
- resistant to microorganisms;
- has high compressive and bending strength;
- complete sound insulation is provided by a foam polystyrene plate with a thickness of 2-3 cm;
- does not support combustion, as it is processed with fire retardants;
- does not crumble during processing (unlike foam);
- collapses when exposed to acetone, benzene, dichloroethane (when finishing, the use of varnishes and paints based on ketones is excluded).
At first glance, in terms of operational characteristics, polystyrene foam practically does not differ from foam plastic.
However, there are differences:
- the intermolecular compound in expanded polystyrene is much stronger;
- density in kg / m3 - 28-45 (for foam 15-35);
- compressive strength 0.08-0.10 MPa (competitor's 0.05);
- bending strength 0.4-1.0 (competitor's 0.07-0.20);
- resistance to temperature fluctuations in expanded polystyrene is 30% higher than that of expanded plastic;
- polystyrene foam costs 2.5-3.5 times more than polystyrene foam.
But it should be noted that some manufacturers have managed to make foam, which has characteristics that do not differ from the characteristics of expanded polystyrene.
The differences are due to the production method. To make foam, polystyrene granules are treated with steam, which leads to their "adhesion" and the formation of many micropores. Expanded polystyrene is produced by extrusion, that is, polystyrene granules melt and form a bond at the molecular level. That is, the structure of polystyrene foam is homogeneous. It is for this reason that it does not crumble during processing and is stronger for bending. Features of the structure also determine the indicators of moisture permeability - they are lower in expanded polystyrene.
Thus, to the question of what is better than polystyrene or expanded polystyrene, the answer suggests itself - expanded polystyrene. But before choosing, you need to weigh some more nuances well.
Compliance with normative acts DSTU BV.2.6.36-2008 "Structures of external walls with facade insulation" determines that the thermal conductivity of the insulation should not be higher than 0.039 W / m K, vapor permeability - up to 0.05 mg / m h Pa. For some types of expanded polystyrene, these indicators do not meet the requirements, that is, the material cannot be used for external wall insulation.The strength of expanded polystyrene is also much higher than required. It's not bad in terms of operation, but bad in terms of cost.
Polystyrene foam has a lower thermal conductivity than foam. If, for example, an indicator of 2.8 m2K / W is needed, then the thickness of the foam must be 106 mm, and the foam polystyrene - 76 mm. If you calculate the cost of one square meter, then the foam will be cheaper.
If you want to make the insulation layer thinner, then it is better to buy expanded polystyrene. If you need to save money, then preference should be given to foam. With correct calculations of the thickness of the insulation layer, the effect of the choice of material will not depend.
General information
It is possible to compare which of these products works best for insulation, only after their operational characteristics have been studied. What does the marking of the material PSB or PSB-S mean:
- PS - expanded polystyrene;
- B - unpressed manufacturing;
- C - self-extinguishing non-combustible material;
- The numbers in the marking indicate the density and resistance to mechanical stress.
| Characteristics | PSB-S-15 | PSB-S-25 | PSB-S-35 | PSB-S-50 |
| Density, kg / m 3 | ≤ 15 | 15,1-25 | 25,1-35 | ≥ 35,1 |
| Compressive strength at deformation 10%, ≥ MPa | 0,041 | 0,032 | 0,15 | 0,15 |
| Flexural strength, MPa | 0,065 | 0,17 | 0,21 | 0,32 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25 0 С +/- 5 0 С, ≤ W (m K) | 0,042 | 0,042 | 0,032 | 0,032 |
| Burning time, ≤ seconds | 4,01 | 4,01 | 4,01 | 4,01 |
| Humidity, ≤ | 12,15% | 12,15% | 12,15% | 12,15% |
| Moisture absorption per day, ≤ | 4,15% | 3,1% | 2,2% | 2,3% |
Polyfoam is made from artificial substances, making them react to the addition of gaseous fillers and foaming agents. The resulting gas bubbles expand during the manufacturing process, turning into foam balls of light weight and high heat resistance. These balls are then pressed or fused into slabs of different densities and used in construction and renovation. So, the insulation of a frame house with penoplex is considered one of the most effective and cheapest methods of insulation.
Penoplex is a variant of polystyrene with much better characteristics. Penoplex is also called extruded polystyrene foam, since it is made by melting or extrusion in special equipment - an extruder (high pressure thermal furnace). In the extruder, the balls are fused into a molded preform, which is a cooled and solid foam, similar to assembly building foam after solidification.
An obvious negative point in the characteristics of foam is high flammability, since it does not burn, but supports combustion.
Features and characteristics of Penoplex insulation
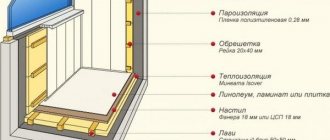
Penoplex (extruded polystyrene foam) and polystyrene differ in many respects, and above all - in the manufacturing method. Penoplex is a denser and harder thermal insulation, the surface of plates covered with extruded polystyrene foam remains strong and warm in any conditions, even with floor insulation, which cannot be said about the foam layer of thermal insulation. When insulating the EPSP floor, you don't even have to assemble the frame for its fastening, but lay the slabs directly on the rough concrete or wooden floor. The upper decorative laminate coating (when laying linoleum or carpet, chipboard or OSB is first laid) will not allow the weight of residents or furniture to push through the surface of the expanded polystyrene. In addition, the increased ability to retain heat is reflected in the quantitative indicator - expanded polystyrene will be required much less than other types of thermal insulation in order to obtain not only a warm, but also a durable floor.
As an example, one can cite, in which foam plastic plates with a thickness of 8-12 cm were used, while the thickness of the EPSP was enough to insulate the floor with a thickness of 3-4 cm. It will turn out warmer. Such high rates allow the use of extruded polystyrene foam even in the Far North. This quite accurately indicates that foam or foam is better.
Of the negative aspects of the operation of expanded polystyrene, high vapor permeability and cost can be noted. But the price justifies the quality that you get when using EPS, and for a good layer of thermal insulation, which will help save on energy during the heating season, and on the use of other materials and methods of building insulation, you can slightly increase the one-time costs for finishing the premises.
Main settings:
- Thermal conductivity: 0.029-0.031 W / m;
- Operating temperatures: -50 / + 75 0 С;
- Compression density: - 20,000-22,000 kg / m 2;
- Moisture absorption: 0.5%;
- Flammability class G3;
- Service time: ≥ 50 years;
- Practical board thickness in use: ≥ 3 cm.
Environmental friendliness
Depending on the type, mineral wool can be produced on the basis of cullet (glass wool), basalt (stone wool) or blast furnace slag (slag wool). All 3 types of materials are characterized by a low degree of environmental friendliness: some contain hazardous formaldehyde, others form harmful dust. It is forbidden to use glass wool and slag wool when insulating kindergartens, bedrooms and a number of other rooms. Eco-friendly PIR insulation made of polyisocyanurate does not contain harmful substances and does not form hazardous chemical compounds even under the influence of high temperatures and humidity.


Comparison of Styrofoam and Styrofoam
As you can see, the question of whether foam or foam is better remains on the developer's conscience, since the operational characteristics of each of the heaters presented should be used to the maximum, but this often requires different initial conditions. Penoplex clearly wins at first glance, except for the cost, since the main indicators that are of interest to the owners of private housing construction are the thermal conductivity coefficient, which is almost twice as good for EPS.
In addition, penoplex (aka extruded polystyrene foam) retains moisture almost four times stronger, not allowing it to pass through the material, which means that water almost never passes through the foam layer. The material is almost non-combustible, and compared to foam, this is its clear advantage. Although polystyrene is usually protected from fire by plastering.
The next parameter of expanded polystyrene is density (physical strength), which is 2.5 times higher than that of expanded polystyrene. In practice, this is expressed in the fact that the EPS, when insulating the floor, can not even be protected with denser sheets, but immediately lay the finishing layer of the floor covering on it. The polystyrene is sold immediately under similar loads. Therefore, there is no question of insulating the floor with foam plastic - only the walls and the ceiling are insulated with it, and it is recommended to insulate only the outer walls, since the inner surfaces can be easily damaged by furniture or just an accidental blow.
But if it is necessary to insulate these particular surfaces without insulating the floor, polystyrene is, of course, preferable precisely because of its cheapness and ease of use. For the insulation of external walls, the thickness of the heat insulator layer does not play any role, as does the degree of moisture absorption - after all, the foam layer will still be closed, for example, with siding or clapboard, tiles or facing bricks.
Perhaps the most well-known material for external and internal wall insulation today is expanded polystyrene (polystyrene). Extruded polystyrene foam, known as penoplex and some others, competes with it. Let's set ourselves the task of comparing penoplex and polystyrene and decide - what should we still prefer for thermal insulation of a private house.
Difference between Styrofoam and Penoplex
Before starting to compare the properties of foam and foam, let's clarify what is the difference between these materials. Both of them are made from polystyrene, but using different technologies.Polyfoam (expanded polystyrene) is obtained by foaming polystyrene, it is a plate of sintered gas-filled granules. There are micropores inside them, and there are voids between the granules. The denser the granules are compressed, the greater the density of the foam, the lower its vapor permeability and water absorption. Compared to polystyrene foam, penoplex, or extruded polystyrene foam, is produced in a different way - by extrusion, using increased temperature and pressure, as a result of which the finished material has a uniform structure with closed pores, the diameter of which does not exceed 0.2 mm.
Comparison of heaters. Advantages of PIR boards
Today, in the assortment of large stores, you can find a number of such building materials that are used for similar purposes, but still differ in their characteristics.
Penoplex is one of the most demanded foam materials, the properties of which have been improved as a result of additional processing - extrusion.
Penoplex use: attics, facades, roofs and building foundations. For each of these objects there is a separate, most suitable type of slabs.
It is also worth noting such pros and cons of penoplex: materials of this type require maintaining a certain, not too high temperature.
If this condition is violated, they deform and may even ignite. There are a number of foam-type slabs for insulation. They are made using a similar technology, therefore, they are similar in structure and properties, but, as a rule, have a different scope. Plates are made using a similar technology and have been produced in Russia from year to year.
They do not shrink, are resistant to chemical attack, but are afraid of gasoline and solvents, and are also used inside buildings.
It is mainly used in industrial and civil construction and road construction. A range of materials used to insulate three-layer walls, flat and pitched roofs, plinths, underground parts of the building.
Also used in the manufacture of sandwich panels, on highways and airfields.
Penoplex and polystyrene: what's the difference?
It is used for sound and heat insulation of basements, ceilings, foundations, walls, roofs of all types, in the construction of roads, underground parking lots and industrial facilities. Has one of the lowest thermal conductivity coefficients among similar materials.
Ursa xps expanded polystyrene insulates flat and pitched roofs, foundations, basement walls, and is also used for underfloor heating. Since the foam granules foamed during the production process do not adhere too tightly to each other, its properties as a heat insulator are much lower than that of foam.
For an equal degree of protection from the cold, foam will have to be purchased 25 percent more than foam. Penoplex is more moisture resistant. Its water absorption rate is approximately 0.35 percent, versus two percent for foam.
Comparative characteristics of foam and foam
Now let's look at the comparative characteristics of foam and foam. The most important of the qualities that heat insulators must possess are thermal conductivity and vapor absorption. It is useful, when comparing foam and polystyrene foam, to give the values of compressive strength.
Thermal conductivity
A comparative table of thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam (for example, materials of the same density) shows the following figures: foam - 0.04 W / mK, penoplex - 0.032 W / mK. This means that there is approximately 25 mm of foam on a 20 mm thick extruded polystyrene foam board. We will not describe the table in detail, since the comparison of the thermal conductivity of foam and foam must be carried out taking into account the density of a particular brand of insulator, and we do not set such a task.
Moisture permeability
The next characteristic that interests us is a comparison of the properties of foam and foam in terms of moisture permeability. While the water absorption of the first does not exceed 0.4%, the second material reaches 2% in this characteristic. In other words, a comparison of this characteristic of foam and foam is in favor of the latter. When using extruded polystyrene foam, it is quite possible that there is no vapor barrier, but with proper insulation with foam, this is undesirable.
Strength
It is indicative to compare penoplex and polystyrene in terms of compressive strength. In the first case, this value reaches 0.5 MPa, in the second - only 0.2 MPa. It should be borne in mind that the comparative characteristics of foam and foam of the same thickness and density make an almost fourfold difference obvious! That is why penoplex is good for the system of floor insulation in structures with high loads - it is used in garages, on skating rinks and even in the construction of runways.
Price
Of course, the comparative table of thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam, the difference between other technical characteristics is important. However, for a common man in the street, there is another important factor that he will certainly take into account when comparing foam and foam. This is the price. It is obvious that Penoplex insulation is in a higher price category than polystyrene; a cubic meter of extruded polystyrene foam is about one and a half times more expensive. Here is a stumbling block for many owners: is it cheaper to insulate, but worse, or more expensive, but of better quality? Many, having compared the prices of penoplex and polystyrene, choose the latter because of the cost.
In conclusion, we note that in construction, extruded polystyrene foam is increasingly replacing foam. In the United States and in many European countries, the use of foam plastic for finishing the facades of buildings is generally prohibited due to the poisonous toxins that it releases during combustion. In Russia, when building houses, they also gradually abandon the use of this material, replacing it with penoplex (which, by the way, is also quite fire hazardous) or non-combustible mineral wool.
What should the owner of an end apartment do if it blows from the walls ... cold in winter and hot in summer? Or is there a need to actively use not only the useful, but also the total area of the apartment, for example, a small balcony or a large "cold" loggia?
Yes, there are many more such "if" and "or" ... And there is only one way out - insulation. The next question that arises before the owner of the premises is which insulation is better to choose.
An unprepared buyer may simply get confused among the names of various modern heaters presented on the building materials market.
What do such concepts related to insulation as expanded polystyrene, extruded (extruded) expanded polystyrene or expanded polystyrene mean? Let's figure it out.
Description of materials and their differences
Expanded polystyrene is expanded polystyrene (styrofoam). Depending on the manufacturing method, expanded polystyrene is divided into expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) and extruded polystyrene foam (XPS).
Extruded (extruded) expanded polystyrene - expanded polystyrene obtained by extrusion.
Penoplex is a trademark of a Russian manufacturer, under which extruded (extruded) expanded polystyrene is produced. Therefore, in relation to one manufacturer, penoplex or extruded polystyrene foam is one and the same heat-insulating material.
With regard to various enterprises for the production of extruded polystyrene foam, all consumer properties of extruded polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene remain unchanged.
Comparison of foam and polystyrene foam
The first question that the buyer asks before purchasing insulation is - which is better than penoplex or expanded polystyrene? What is common and what is the difference between expanded polystyrene and expanded polystyrene?
The common thing for these two heaters is that they are both used in the construction industry as a thermal insulation material and are made from polystyrene, both materials are durable, biological resistance to microorganisms, light weight and ease of installation.
Differences between foam and polystyrene foam:
- Manufacturing technology
... Expanded polystyrene is created by processing polystyrene microgranules with water vapor, increasing their size under a high steam temperature until the mold is completely filled with expanded polystyrene foam. Extruded polystyrene foam is produced using the extrusion method - mixing polystyrene microgranules at elevated pressure and temperature using a foaming agent and extruding from an extruder. - Appearance and structure
... The foam board looks like a very hard foam rubber with a uniform closed-cell structure. Expanded polystyrene has a granular structure. - Thermal conductivity
... The thermal conductivity of the penoplex is somewhat better than that of the expanded polystyrene. - Air permeability
... Expanded polystyrene has good air permeability, in contrast to almost airtight foam. - Water vapor permeability.
The vapor permeability characteristic of foam is 5 times worse than that of expanded polystyrene. - Flammability
... Flammability class for G3-G4 foam (high flammability), for G1 expanded polystyrene (low flammability). - Mode of application
... Expanded polystyrene is best used for external insulation of facades and external walls. Penoplex is indispensable for insulating interior walls and balconies, roofs, as well as foundations of buildings and structures.
Advantages and disadvantages of Penoplex insulation


"Penoplex", unlike its predecessor, is made from extruded polystyrene. Therefore, it also has excellent thermal insulation properties, is characterized by ease and ease of installation. However, the use of extruded polystyrene slightly changes the scope of this heat insulator.
Now there are four lines of this coating on the market:
"Wall" ("31" with fire retardant). Used to insulate walls (both external and internal) and basement;
"Foundation" ("35"). Installed on the basement and foundation of the building;
"Roof" ("35"). Installed on roofs - flat, sloping and even inversion;
"Comfort" ("31C"). A universal solution that is suitable for insulating any part of the building.
Fire retardant is a special substance that prevents the heat insulator from burning. Therefore, the wall versions of "Penoplex" are supplemented with them in the composition, which increases fire safety, but negatively affects the price.
What to look for when choosing
Extruded polystyrene foam Penoplex is produced in the form of plates of various markings - Penoplex 35, 31, 31C, 45C, 45, 75. Moreover, recently the marking of plates 35, 31, 31C has been replaced with new types:
- 35 (without fire retardants) - Penoplex-Foundation;
- 35 - Penoplex-Roofing;
- 31 - Penoplex-Wall;
- 31C - Penoplex Comfort.
The average consumer is unlikely to be interested in superdense plates marked 45C, 45, 75 to solve the pressing problems of insulation.
Plates with increased strength are used for thermal insulation of load-bearing structures of buildings and structures, roadways, loaded structures and airfield runways. The thickness of the slabs is 40, 50, 60, 80 and 100 mm, and the size is 600 by 2400 mm.
Therefore, the question of choosing between the materials expanded polystyrene and expanded polystyrene 45 or 75 is raised only on an industrial scale.
An ordinary buyer, as a rule, needs to opt for one of two options - expanded polystyrene or Penoplex 35? Or, in light of the latest innovations from the penoplex manufacturer - Penoplex-Foundation, Penoplex-Roof, Penoplex-Wall and Penoplex-Comfort.
The new labeling of thermal insulation boards speaks for itself here. Extruded polystyrene foam or penoplex 35 is divided by the manufacturer into two types - without the use of special treatment to reduce flammability for Penoplex-Foundation and impregnated with fire retardants for Penoplex-Roof.
Expanded polystyrene Penoplex-Comfort is the most versatile material grade. Plates are used for thermal insulation of balconies and loggias, roofs, walls, plinths, foundations and floors, as well as for insulation of garages and outbuildings.
The almost complete waterproofness of the slabs makes it possible to use them for thermal insulation of baths, saunas and swimming pools with a high level of humidity. The thickness of the slabs is 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80 and 100 mm, and the size is 600 by 1200 mm.
Description of the material (video)
Pricing
The production of both expanded polystyrene and polystyrene foam is quite cheap. What is their retail value?
The price of extruded polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam at the very minimum parameters (density, thickness, quantity in a package) starts, respectively, from 1000 rubles. and 1200 rubles. per packing. Conclusion - the trademark of various manufacturers also matters when choosing and purchasing insulation.
The most expensive insulation among all brands of extruded polystyrene foam was Penoplex. And with an increase in the characteristics of thermal insulation boards of different brands, the price also increases accordingly - up to 3000 rubles. and 4200 rubles.
The cost of expanded polystyrene (foam) also depends on the physical characteristics and the manufacturer and is in the range of 1000 - 3000 rubles. per packing. The price of foam and polystyrene foam on the building materials market is slightly different in favor of the latter.
The small price difference between expanded polystyrene and expanded polystyrene is most likely due to a more complex technology for the manufacture of expanded polystyrene ... and maybe the seller's margin is too high.
Installation
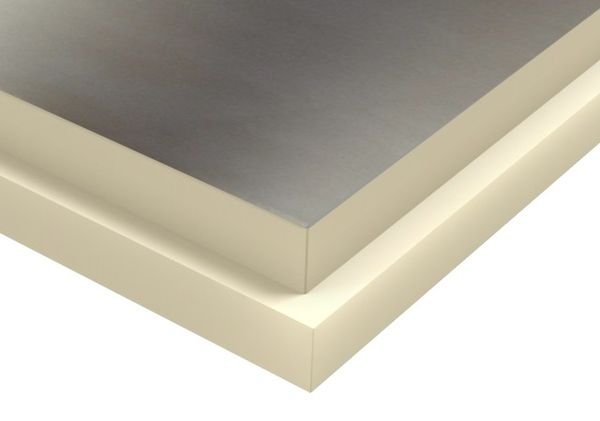
PIR insulation is produced in the form of finished panels coated with kraft paper, foil or as part of sandwich panels. Each option has its own area of application and methods of insulation. In addition to the structural differences, there are ready-made solutions for the insulation of separate walls, ceilings and roofs.
Sandwich panels


This is a ready-made wall structural material for creating insulated one-story buildings or for forming the walls of frame houses with a higher number of storeys. The panels are joined together with a lock connection. The joints are additionally blown out with polyurethane foam or glued with special polyurethane building glue.
It is allowed to connect panels using such structural elements as a frame made of a profiled pipe or a corner. Fastening of the panels is carried out by bolting with wide substrates of sheet steel with a thickness of at least 3 mm, to ensure rigidity and not damage the insulation layer.
Wall panels


The standard size of the PIR wall panel is 600x1200 mm, the thickness is selected depending on the required insulation.
Sheets are stacked end-to-end, using a quarter or a lock. The lathing is not required, the material is attached to the insulated base with special plastic dowels with a wide head, as in the case of EPS.
Additionally, sheets with lining with kraft paper can be glued to the base using any tile or polymer adhesive composition.
For roofing
In fact, this is a kind of sandwich panels, however, the panel is often protected with a steel sheet only from the upper side, where the usual waves are additionally formed at the joints in order to ensure the tightness of the roof.
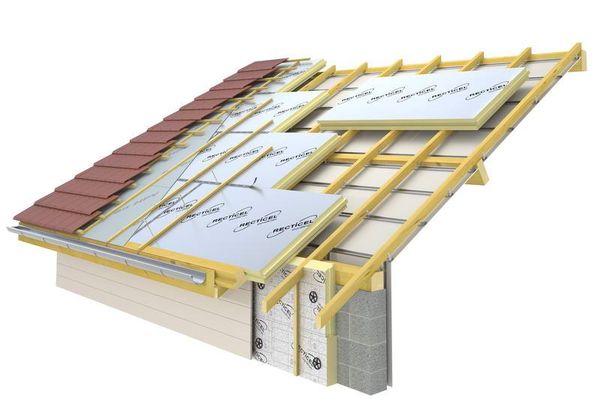


On the underside, the slabs are covered with kraft paper or foil. The installation process is similar to laying a profiled sheet along the rafters. A flat roof surface with the required slope is formed.
Insulation for floors
In fact, a direct analogue of wall material, however, slabs are more often used in a square or rectangular shape with a lock on all four sides. No additional fastening is required.

A mandatory damping tape is laid along the perimeter of the insulated floor, and then the entire area is laid with slabs. A dry or wet screed, underfloor heating system, etc. can be formed on the insulated floor.