The topic of this article is the calculation of water supply networks in a private house. Since a typical small cottage water supply scheme is not very complex, we do not have to go into the jungle of complex formulas; however, the reader will have to assimilate a certain amount of theory.
Fragment of the water supply system of a private house. Like any other engineering system, this one needs preliminary calculations.
Features of the wiring of the cottage
What, in fact, is the water supply system in a private house easier than in an apartment building (of course, in addition to the total number of plumbing fixtures)?
There are two fundamental differences:
- With hot water, as a rule, there is no need to provide constant circulation through risers and heated towel rails.
In the presence of circulation inserts, the calculation of the hot water supply network becomes noticeably more complicated: the pipes need to pass through themselves not only the water disassembled by the residents, but also the continuously circulating masses of water.
In our case, the distance from the plumbing fixtures to the boiler, column or tie-in to the line is small enough to ignore the rate of hot water supply to the tap.
Important: For those who have not come across DHW circulation schemes - in modern apartment buildings, hot water supply risers are connected in pairs. Due to the pressure difference in the tie-ins created by the retaining washer, water is continuously circulated through the risers. This ensures a fast supply of hot water to the mixers and year-round heating of heated towel rails in the bathrooms.

The heated towel rail is heated by continuous circulation through the hot water risers.
- The water supply system in a private house is divided according to a dead-end scheme, which implies a constant load on certain sections of the wiring. For comparison, the calculation of the water supply ring network (allowing each section of the water supply system to be powered from two or more sources) must be performed separately for each of the possible connection schemes.
Other parameters
The above criteria for choosing a boiler are the main ones, but there are other characteristics that can affect the choice of a particular model, such as workmanship and material, as well as the cost of equipment. The most durable tanks are considered to be made of stainless steel. An important advantage is the presence of a removable heat exchanger so that you can descale it yourself. You should avoid purchasing devices using foam rubber as insulation, as this material is very short-lived. In addition, the price of a boiler directly depends on the manufacturer and the country where the equipment was assembled.
The hot water system makes your home comfortable and cozy. This is easy to achieve with a quality water heater. The choice of models is currently great and, after calculating the necessary parameters, everyone can choose equipment with a good price-quality ratio.
What do we think
We have to:
- Estimate water consumption at peak consumption.
- Calculate the cross-section of the water pipe that can provide this flow rate at an acceptable flow rate.
Note: the maximum water flow rate at which it does not generate hydraulic noise is about 1.5 m / s.
- Calculate the head at the end fixture. If it is unacceptably low, it is worth considering either increasing the diameter of the pipeline, or installing an intermediate pump.


The low pressure on the end mixer is unlikely to please the owner.
The tasks are formulated. Let's get started.
Consumption
It can be roughly estimated by the consumption rates for individual plumbing fixtures. Data, if desired, can be easily found in one of the annexes to SNiP 2.04.01-85; for the convenience of the reader, we present an excerpt from it.
| Device type | Cold water consumption, l / s | Total consumption of hot and cold water, l / s |
| Watering tap | 0,3 | 0,3 |
| Toilet bowl with a tap | 1,4 | 1,4 |
| Toilet with cistern | 0,10 | 0,10 |
| Shower cubicle | 0,08 | 0,12 |
| Bath | 0,17 | 0,25 |
| Washing | 0,08 | 0,12 |
| Washbasin | 0,08 | 0,12 |
In apartment buildings, when calculating the consumption, the probability coefficient of the simultaneous use of devices is used. It is enough for us to simply sum up the water consumption through devices that can be used simultaneously. Let's say a sink, a shower stall and a toilet bowl will give a total flow of 0.12 + 0.12 + 0.10 = 0.34 l / s.


The water consumption through devices capable of operating simultaneously is summed up.
Which water heater to choose?


Boiler diagram.
Depending on the task assigned to you, the calculation of the boiler that is right for you can be done in two ways. In the first case, the stored volume of water is taken into account and the capacity of the heat exchanger and the power supply is calculated. In the second, the volume of a water heater is calculated for storing heat generated over a certain time by a source of a certain power.
It should be understood that no matter what technique you use, the accumulating capacity of water is always characterized by its heat capacity. This value is constant and it is equal to 4.187 kJ.kg / ° C. This means that, for example, to heat 1 kg of water by 1 ° C, you need to provide an amount of heat equal to 4.187 kJ. And this requires 1,163 kWh.

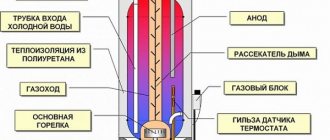
Electric boiler device.
For example, if you have a water heater with a volume of 1000 liters, and you need to heat the water up to 50 ° C, then the heat energy requirement is calculated as follows: 1000 × 50 = 58 kWh.
The power of the heat exchanger depends on the temperature difference between the heated and heated water, as well as on the heat transfer coefficient. For each specific heat exchanger, the heat transfer coefficient will be individual. Therefore, a universal formula for calculating a water heater cannot exist. And the easiest way to choose a heat exchanger is the diagrams that manufacturers indicate in the technical specifications for their water heaters.
Having remembered this simple truth, you can proceed to the consideration of individual characteristics.
Standard electric boiler device
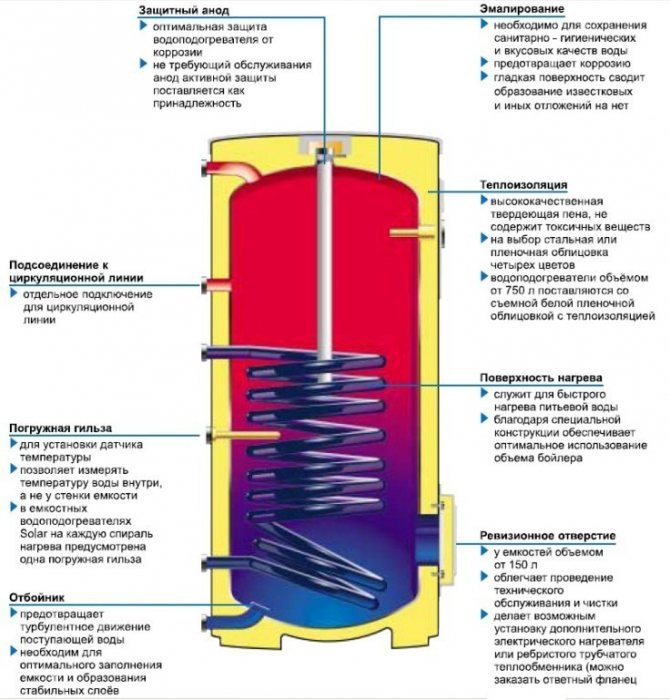

Boiler storage tank diagram.
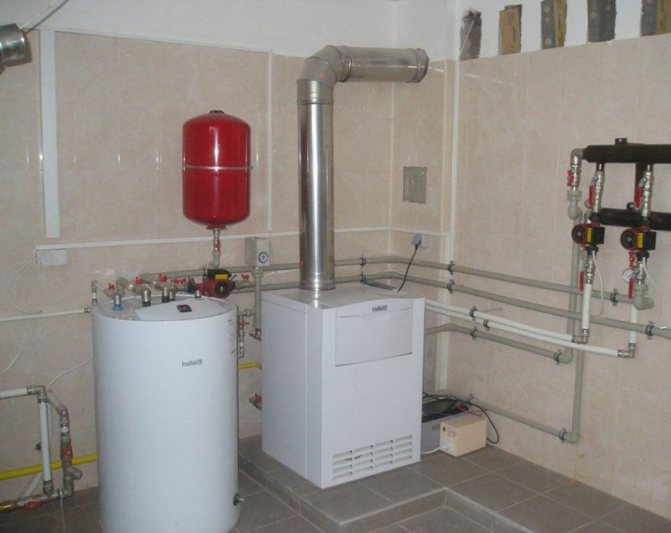
In our country, it is generally accepted that a water heater and a boiler are different devices. But in fact, the whole difference is that the boiler has a storage tank for heating and storing hot water. That is why in the technical literature they are called "storage water heaters". Also, boilers differ in heat source. There are now direct and indirect heating systems. If the device itself generates heat using a thermoelectric heater or a gas burner, then this is a direct heating system. Indirect heating occurs due to the heating agent supplied from the heating boiler to a certain temperature. Most often, storage water heaters are used, you can see their diagram in Image 1.


Calculation table for a storage water heater.
Before deciding on the purchase of a specific water heater, it is necessary to calculate all the parameters and take into account the features of your home and the conditions of future use. Be sure to evaluate the following parameters:
- condition of electrical wiring;
- possible load on electrical wiring;
- availability of the ability to connect to gas communications;
- serviceability of all equipment serving the house (including water pumps, if any).


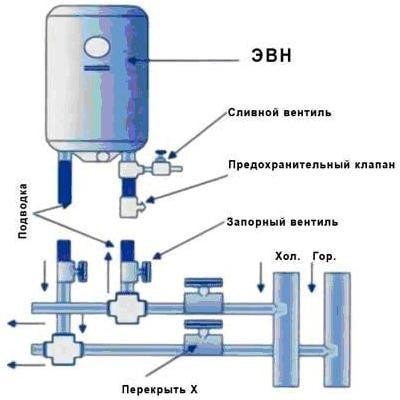
Installation of a storage water heater (boiler).
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the number of people who will use the water heater and roughly plan how much hot water they will consume every day. After that, you can start choosing a specific model.
In order to choose a water heater that is right for you, you should first decide on its main characteristics, namely:
- the most suitable energy source;
- required volume of heated water;
- coolant consumption;
- heating time.
According to these parameters, the water heater is calculated.
Energy source for heating water


Boiler heating circuit.
Gas and electricity are used as the main sources of energy for water heaters. There are also more exotic sources like solar panels, but they are not very common in our country. Therefore, in order to carry out an accurate calculation, it is necessary to compare the advantages and disadvantages of gas and electricity.
- Electric water heaters are available in capacities from 1 to 6 kW. The power of a gas boiler starts from 4 kW.
- As a rule, storage-type gas water heaters have a larger hot water tank (up to 150 liters), while electric ones rarely exceed 100 liters.
- The cost of gas in Russia is much cheaper than electricity.


Diagram of a pressure water heater device.
It seems that the choice is obvious and there is no need to make complex calculations. It will take about half the time to get 100-150 liters of hot water using a gas water heater than using a system powered by electricity. But electrical devices do not require additional power line equipment - a simple outlet is enough for them. It is not required to invite specialists for the installation of such a boiler. Whereas a gas water heater must be connected to a gas pipeline, which is not available in every summer cottage. In addition, a chimney is required for the safe installation of a gas-fired water heater.
It is impossible to compare prices for boilers with different power sources. The cost of electrical systems depends primarily on the power of the heating element and the volume of the tank. The price for gas-fired water heaters is formed depending on the type of combustion chamber. They are internal and external. Installation of equipment with an internal chamber requires minimal effort and time. But such devices cost about twice as much as boilers with an external chamber.
One more condition must be taken into account. Gas boilers are capable of significantly heating the air. In the conditions of summer cottages and small rooms, such a feature can become a real problem if you place a water heater, for example, in the kitchen.
Therefore, it is impossible to give unambiguous recommendations for choosing a boiler with a specific energy source.
Cross section
Calculation of the cross-section of a water supply pipe can be performed in two ways:
- Selection according to the table of values.
- Calculated according to the maximum permissible flow rate.
Selection by table
Actually, the table does not require any comments.
| Nominal pipe bore, mm | Consumption, l / s |
| 10 | 0,12 |
| 15 | 0,36 |
| 20 | 0,72 |
| 25 | 1,44 |
| 32 | 2,4 |
| 40 | 3,6 |
| 50 | 6 |
For example, for a flow rate of 0.34 l / s, a DU15 pipe is sufficient.
Please note: DN (nominal bore) is approximately equal to the inner diameter of the water and gas pipe. For polymer pipes marked with an outer diameter, the inner one differs from it by about a step: say, a 40 mm polypropylene pipe has an inner diameter of about 32 mm.


Nominal bore is approximately equal to the inner diameter.
Flow rate calculation
Calculation of the diameter of the water supply system by the flow rate of water through it can be performed using two simple formulas:
- Formulas for calculating the area of a section along its radius.
- Formulas for calculating the flow rate through a known section at a known flow rate.
The first formula is S = π r ^ 2. In it:
- S is the required cross-sectional area.
- π is pi (approximately 3.1415).
- r is the section radius (half of the DN or the inner diameter of the pipe).
The second formula looks like Q = VS, where:
- Q - consumption;
- V is the flow rate;
- S is the cross-sectional area.
For the convenience of calculations, all values are converted to SI - meters, square meters, meters per second and cubic meters per second.


SI units.
Let's calculate with our own hands the minimum DU of the pipe for the following input data:
- The flow through it is all the same 0.34 liters per second.
- The flow velocity used in the calculations is the maximum allowable 1.5 m / s.
Let's get started.
- The flow rate in SI values will be equal to 0.00034 m3 / s.
- The cross-sectional area according to the second formula must be at least 0.00034 / 1.5 = 0.00027 m2.
- The square of the radius according to the first formula is 0.00027 / 3.1415 = 0.000086.
- Take the square root of this number. The radius is 0.0092 meters.
- To get DN or inner diameter, multiply the radius by two. The result is 0.0184 meters, or 18 millimeters. As you can easily see, it is close to that obtained by the first method, although it does not exactly coincide with it.
Power consumption
Having come to a decision about the need to purchase and calculating the volume of an indirect heating boiler, you need to calculate how much warm water is needed for normal existence. Imagine a family of 4 and carry out an average daily analysis for a week and a peak (morning of the working day) study of hot water consumption.
- Weekly analysis
- In order to wash the dishes, you will need about 5 liters of warm water per minute. The rinsing time is taken into account, this is about 5 minutes. I wash my plates twice a day, we get 50 liters of warm water used for kitchen utensils per day. We multiply by 7 days a total of 350 liters per week.
- Each person takes a bath 2-3 times a week, while spending about 170 liters. 4 * 2.5 = 10 * 170 = 1700 liters in 7 days.
- Shower 4-5 more times for 10 minutes at a flow rate of about 12 l / min. 4.5 * 10 * 12 = 540 per family member, respectively, for all 2160 liters per week.
- Small hygiene (wash hands, shoes, clean the house) - about 10 liters per person per day will amount to 280 liters for the study period.
Total - 350 + 1700 + 2160 + 280 = 4490 liters per week. Let's add guests who came in and just in case we get an approximate figure of about 5000 liters per week. But the boiler counts in hours, you need to translate into its units. 5000/7/24 = 30 liters per hour of warm water is the average consumption of a family of 4 people.
Based on our figures for the ratio of temperature and power, we obtain the required average power consumption - 30 * 0.0375 = 1.125 kW / h.
Pressure
Let's start with a few general notes:
- Typical pressure in the cold water supply line is from 2 to 4 atmospheres (kgf / cm2)... It depends on the distance to the nearest pumping station or water tower, on the terrain, the state of the mainline, the type of valves on the main water supply, and a number of other factors.
- The absolute minimum pressure that allows all modern plumbing fixtures and household appliances using water to work is 3 meters... The instruction for Atmor instantaneous water heaters, for example, directly says that the lower response threshold of the pressure sensor that includes heating is 0.3 kgf / cm2.


The pressure sensor of the device is triggered at a pressure of 3 meters.
Reference: at atmospheric pressure, 10 meters of head corresponds to 1 kgf / cm2 overpressure.
In practice, on an end fixture, it is better to have a minimum head of five meters. A small margin compensates for unaccounted losses in connections, shut-off valves and the device itself.
We need to calculate the head drop in a pipeline of known length and diameter. If the difference in pressure corresponding to the pressure in the main line and the drop in pressure in the water supply system is more than 5 meters, our water supply system will function flawlessly.If it is less, you need to either increase the diameter of the pipe, or open it by pumping (the price of which, by the way, will clearly exceed the increase in costs for pipes due to an increase in their diameter by one step).
So how is the calculation of the pressure in the water supply network carried out?
Here the formula H = iL (1 + K) is valid, in which:
- H is the coveted value of the pressure drop.
- i is the so-called hydraulic slope of the pipeline.
- L is the length of the pipe.
- K is a coefficient that is determined by the functionality of the water supply system.
The easiest way is to determine the K.
It is equal to:
- 0.3 for household and drinking purposes.
- 0.2 for industrial or fire-fighting.
- 0.15 for fire and production.
- 0.10 for a firefighter.


In the photo there is a fire water supply system.
There are no particular difficulties with measuring the length of the pipeline or its section; but the concept of hydraulic bias requires a separate discussion.
Its value is influenced by the following factors:
- The roughness of the pipe walls, which, in turn, depends on their material and age. Plastics have a smoother surface than steel or cast iron; in addition, steel pipes become overgrown with limescale deposits and rust over time.
- Pipe diameter. The inverse relationship operates here: the smaller it is, the more resistance the pipeline has to the movement of water in it.
- Flow rate. With its increase, the resistance also increases.
Some time ago, it was necessary to additionally take into account hydraulic losses on valves; however, modern full bore ball valves create roughly the same resistance as a pipe and can therefore be safely ignored.


An open ball valve has almost no resistance to the flow of water.
It is very problematic to calculate the hydraulic slope on your own, but, fortunately, this is not necessary: all the necessary values can be found in the so-called Shevelev tables.
To give the reader an idea of what is at stake, we present a small fragment of one of the tables for a plastic pipe with a diameter of 20 mm.
| Consumption, l / s | Flow speed, m / s | 1000i |
| 0,25 | 1,24 | 160,5 |
| 0,30 | 1,49 | 221,8 |
| 0,35 | 1,74 | 291,6 |
| 0,40 | 1,99 | 369,5 |
What is the 1000i in the far right column of the table? This is just the hydraulic slope value per 1000 linear meters. To get the value of i for our formula, it is enough to divide it by 1000.
Let's calculate the pressure drop in a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm with its length equal to 25 meters and a flow rate of one and a half meters per second.
- We are looking for the corresponding parameters in the table. According to her data, 1000i for the described conditions is 221.8; i = 221.8 / 1000 = 0.2218.
Shevelev's tables have been reprinted many times since the first publication.
- Substitute all values into the formula. H = 0.2218 * 25 * (1 + 0.3) = 7.2085 meters. With a pressure at the inlet of the water supply system of 2.5 atmospheres at the outlet, it will be 2.5 - (7.2 / 10) = 1.78 kgf / cm2, which is more than satisfactory.
Connection of an indirect heating boiler with recirculation
The piping for various types of indirect heating boilers with recirculation is made in accordance with the drawing. When choosing components, it is important to take into account the features of a home heating system.
For piping the water circuit to the boiler, the following 3 installation systems can be used:
- Installation of three-way valves.
- Installation of a double circulation pump.
- Regulation by means of hydraulic arrows.
The use of liquid recirculation systems significantly increases the performance of heating systems and by increasing the efficiency when heating liquid and rooms from boilers.
When installing indirect winding systems with three-way valves, it should be borne in mind that this method is intended for tanks with increased displacement. When developing such a system, it is calculated how the installation of a two-circuit type of heating will be carried out.


Connecting the boiler to the boiler equipment
Monitoring water temperature information is very important.In a situation where the water in the tanks of boilers has a set heating temperature much higher than in the heating circuits of heating systems themselves, this can lead to incorrect operation of all equipment.
This will prevent switching over to heating the heating circuits. There are also options for installing indirect heating boilers using two circuits. The selection of the required option will also depend on the water in the water supply system. In a situation where the liquid in the main channel is of a high degree of rigidity, it is better to use the installation of systems with three-way valves, since two-circuit systems can quickly break down due to blockages.