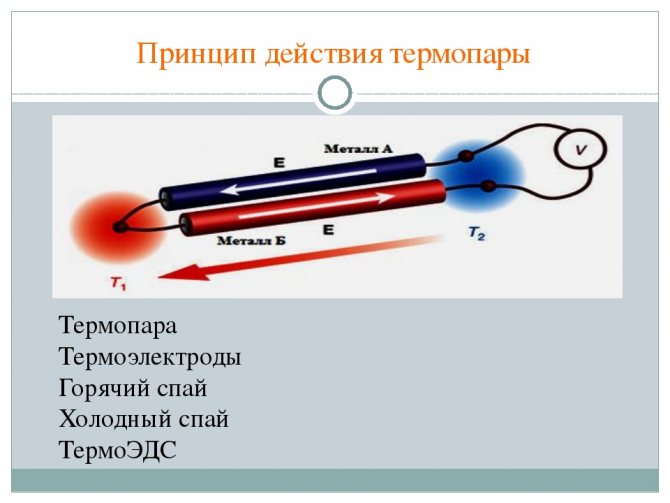
The principle of operation and design of a thermocouple is extremely simple. This led to the popularity of this device and its widespread use in all branches of science and technology. The thermocouple is designed to measure temperatures in a wide range - from -270 to 2500 degrees Celsius. The device has been an indispensable assistant for engineers and scientists for decades. It works reliably and flawlessly, and the temperature readings are always true. A more perfect and accurate device simply does not exist. All modern devices operate on the thermocouple principle. They work in difficult conditions.

Thermocouple assignment
This device converts thermal energy into electrical current and allows temperature measurement. Unlike traditional mercury thermometers, it is capable of operating in conditions of both extremely low and extremely high temperatures. This feature has led to the widespread use of thermocouples in a wide variety of installations: industrial metallurgical furnaces, gas boilers, vacuum chambers for chemical heat treatment, oven for household gas stoves. The principle of operation of a thermocouple always remains unchanged and does not depend on the device in which it is mounted.
Reliable and uninterrupted operation of the thermocouple depends on the operation of the emergency shutdown system of devices in case of exceeding the permissible temperature limits. Therefore, this device must be reliable and give accurate readings so as not to endanger people's lives.
Benefits of using thermocouples
The advantages of using such devices for temperature control, regardless of the application, include:
- a large range of indicators that can be recorded using a thermocouple;
- the soldering of the thermocouple, which is directly involved in taking readings, can be placed in direct contact with the measuring point;
- simple process of manufacturing thermocouples, their strength and durability.
How the thermocouple works
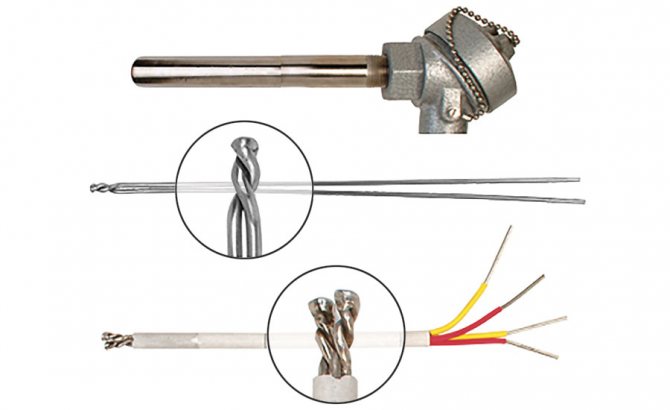
A thermocouple has three main elements. These are two conductors of electricity from different materials, as well as a protective tube. The two ends of the conductors (also called thermoelectrodes) are soldered, and the other two are connected to a potentiometer (temperature measuring device).
In simple terms, the principle of operation of a thermocouple is that the junction of thermoelectrodes is placed in an environment, the temperature of which must be measured. In accordance with the Seebeck rule, a potential difference arises on the conductors (otherwise - thermoelectricity). The higher the temperature of the medium, the more significant the potential difference is. Accordingly, the arrow of the device deviates more.

In modern measuring complexes, digital temperature indicators have replaced the mechanical device. However, the new device is far from always superior in its characteristics to the old devices of the Soviet era. In technical universities, and in research institutions, to this day they use potentiometers 20-30 years ago. And they exhibit amazing measurement accuracy and stability.
Types of devices
Each type of thermocouple has its own designation, and they are divided according to the generally accepted standard. Each type of electrode has its own abbreviation: TXA, TXK, TBR, etc. Converters are distributed according to the classification:
- Type E - is an alloy of chromel and constantan. The characteristic of this device is considered to be high sensitivity and performance. This is especially suitable for use at extremely low temperatures.
- J - refers to an alloy of iron and constantan. It features high sensitivity, which can reach up to 50 μV / ° C.
- Type K is considered the most popular chromel / aluminum alloy. These thermocouples can detect temperatures ranging from -200 ° C to +1350 ° C. The devices are used in circuits located in non-oxidizing and inert conditions with no signs of aging. When the devices are used in a rather acidic environment, chromel quickly corrodes and becomes unusable for measuring the temperature with a thermocouple.
- Type M - represents alloys of nickel with molybdenum or cobalt. The devices can withstand up to 1400 ° C and are used in installations operating on the principle of vacuum furnaces.
- Type N - nichrosil-nisil devices, the difference of which is considered to be resistance to oxidation. They are used to measure temperatures in the range from -270 to +1300 ° C.
It will be interesting to you The device, the principle of operation and the application of the supercapacitor
There are thermocouples made of rhodium and platinum alloys. They belong to types B, S, R and are considered the most stable devices. The disadvantages of these converters include high price and low sensitivity.
At high temperatures, devices made of rhenium and tungsten alloys are widely used. In addition, according to their purpose and operating conditions, thermocouples can be submersible and surface.
By design, the devices have a static and movable union or flange. Thermoelectric converters are widely used in computers, which are usually connected via a COM port and are designed to measure the temperature inside the case.
Seebeck effect
The principle of operation of a thermocouple is based on this physical phenomenon. The bottom line is this: if you connect two conductors made of different materials (sometimes semiconductors are used), then a current will circulate along such an electrical circuit.
Thus, if the junction of the conductors is heated and cooled, the potentiometer needle will oscillate. The current can also be detected by a galvanometer connected to the circuit.
In the event that the conductors are made of the same material, then the electromotive force will not occur, respectively, it will not be possible to measure the temperature.
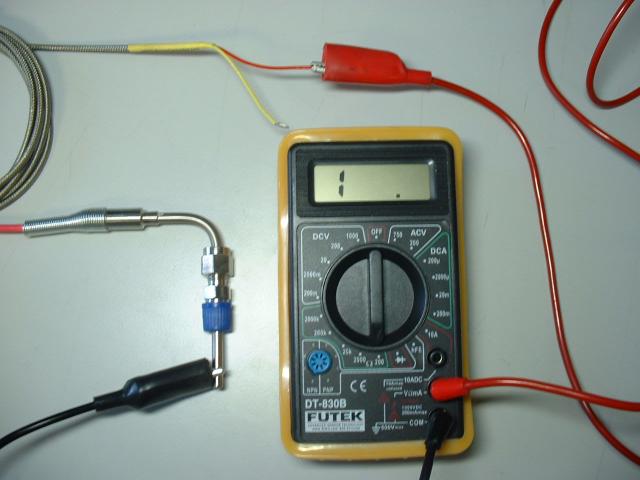


Thermocouple connection diagram
The most common methods for connecting measuring instruments to thermocouples are the so-called simple method, as well as the differentiated one. The essence of the first method is as follows: the device (potentiometer or galvanometer) is directly connected to two conductors. With the differentiated method, not one, but both ends of the conductors are soldered, while one of the electrodes is "broken" by the measuring device.

It is impossible not to mention the so-called remote method of connecting a thermocouple. The principle of operation remains unchanged. The only difference is that extension wires are added to the circuit. For these purposes, an ordinary copper cord is not suitable, since the compensation wires must necessarily be made of the same materials as the thermocouple conductors.

Disadvantages of measuring temperature with a thermocouple
The disadvantages of using a thermocouple include:
- The need for constant monitoring of the temperature of the "cold" contact of the thermocouple. This is a distinctive feature of the design of measuring instruments, which are based on a thermocouple. The principle of this scheme narrows the scope of its application. They can only be used if the ambient temperature is lower than the temperature at the measuring point.
- Violation of the internal structure of metals used in the manufacture of a thermocouple.The fact is that as a result of the influence of the external environment, the contacts lose their homogeneity, which causes errors in the obtained temperature indicators.
- During the measurement process, the thermocouple contact group is usually exposed to negative environmental influences, which causes malfunctions during operation. This again requires sealing the contacts, which causes additional maintenance costs for such sensors.
- There is a danger of electromagnetic waves affecting the thermocouple, which is designed with a long contact group. This can also affect the measurement results.
- In some cases, there is a violation of the linear relationship between the electric current arising in the thermocouple and the temperature at the measurement site. This situation requires calibration of the control equipment.
Conductor materials
The principle of operation of a thermocouple is based on the occurrence of a potential difference in conductors. Therefore, the selection of electrode materials must be approached very responsibly. The difference in the chemical and physical properties of metals is the main factor in the operation of a thermocouple, the device and principle of operation of which are based on the occurrence of an EMF of self-induction (potential difference) in the circuit.
Technically pure metals are not suitable for use as a thermocouple (with the exception of ARMKO iron). Various alloys of non-ferrous and precious metals are commonly used. Such materials have stable physical and chemical characteristics, so that temperature readings will always be accurate and objective. Stability and precision are key qualities in the organization of the experiment and the production process.
Currently, the most common thermocouples are of the following types: E, J, K.


The principle of operation and structure of thermocouples
The thermocouple consists of two conductors and a tube that serves as a protection for thermoelectrodes. Thermoelectrodes consist of base and noble metals, most often alloys, fixed to each other at one end (working end or hot junction), thus they form one of the parts of the device. The other ends of the thermocouple (risers or cold junction) are connected to the voltage meter. An EMF appears in the middle of two unconnected terminals, the value depends on the temperature of the working end.
Identical thermocouples combined in parallel close the circuit, according to the Seebeck rule, we will consider this rule further, a contact potential difference or thermoelectric effect is formed between them, electric charges appear on the conductors when they touch, a potential difference arises between their free ends, and it depends on the temperature difference. Only when the temperature between the thermoelectrodes is the same, the potential difference is equal to zero.
For example: By placing a junction with coefficients different from zero, in two boiling pots with liquid, the temperature of the first is 50, and the second is 45, then the potential difference will be 5.
The potential difference is determined by the temperature difference between the sources. The material from which the thermocouple electrodes are made also depends. Example: A thermocouple Chromel-Alumel has a temperature coefficient of 41, and a Chromel-Constantan has a coefficient of 68.
Thermocouple type K
This is perhaps the most common and widely used type of thermocouple. A pair of chromel - aluminum works great at temperatures ranging from -200 to 1350 degrees Celsius. This type of thermocouple is highly sensitive and detects even a small jump in temperature. Thanks to this set of parameters, the thermocouple is used both in production and in scientific research. But it also has a significant drawback - the influence of the composition of the working atmosphere. So, if this type of thermocouple will work in a CO2 environment, then the thermocouple will give incorrect readings.This feature limits the use of this type of device. The scheme and principle of operation of the thermocouple remain unchanged. The only difference is in the chemical composition of the electrodes.


Types of thermocouples
Technical requirements for thermocouples are determined by GOST 6616-94. Standard tables for thermoelectric thermometers - nominal static conversion characteristics (NSC), tolerance classes and measurement ranges are given in the IEC 60584-1.2 standard and in GOST R 8.585-2001.
- platinum-rhodium-platinum - TPP13 - Type R
- platinum-rhodium-platinum - TPP10 - Type S
- platinum-rhodium-platinum-rhodium - TPR - Type B
- iron-constantan (iron-copper-nickel) TLC - Type J
- copper-constantan (copper-copper-nickel) TMKn - Type T
- nichrosil-nisil (nickel-chromium-nickel-nickel-silicon) TNN - Type N.
- chromel-alumel - TXA - Type K
- chromel-constantan TChKn - Type E
- chromel-copel - THK - Type L
- copper-copel - TMK - Type M
- silkh-silin - ТСС - Type I
- tungsten and rhenium - tungsten rhenium - TVR - Type A-1, A-2, A-3
The exact alloy composition of thermocouples for base metal thermocouples is not given in IEC 60584-1. НСХ for chromel-copel thermocouples ТХК and tungsten-rhenium thermocouples are defined only in GOST R 8.585-2001. There is no thermocouple data in the IEC standard. For this reason, the characteristics of imported sensors made of these metals may differ significantly from domestic ones, for example, imported Type L and domestic THK are not interchangeable. At the same time, as a rule, imported equipment is not designed for the domestic standard.
The IEC 60584 standard is currently under revision. It is planned to introduce into the standard tungsten-rhenium thermocouples of type A-1, for which NSX will correspond to the Russian standard, and type C according to the ASTM standard [6].
In 2008, IEC introduced two new types of thermocouples: gold-platinum and platinum-palladium. The new IEC 62460 standard establishes standard tables for these pure metal thermocouples. There is no similar Russian standard yet.
Checking Thermocouple Operation
If the thermocouple fails, it cannot be repaired. Theoretically, you can, of course, fix it, but whether the device will show the exact temperature after that is a big question.
Sometimes the failure of a thermocouple is not obvious and obvious. In particular, this applies to gas water heaters. The principle of operation of a thermocouple is still the same. However, it plays a slightly different role and is intended not for visualizing temperature readings, but for valve operation. Therefore, in order to detect a malfunction of such a thermocouple, it is necessary to connect a measuring device (tester, galvanometer or potentiometer) to it and heat the junction of the thermocouple. To do this, it is not necessary to keep it over an open fire. It is enough just to squeeze it in a fist and see if the arrow of the device will deviate.
The reasons for the failure of thermocouples can be different. So, if you do not put on a special shielding device on the thermocouple placed in the vacuum chamber of the ion-plasma nitriding unit, then over time it will become more and more fragile until one of the conductors breaks. In addition, the possibility of incorrect operation of the thermocouple due to a change in the chemical composition of the electrodes is not excluded. After all, the fundamental principles of the thermocouple are violated.
Gas equipment (boilers, columns) is also equipped with thermocouples. The main cause of electrode failure is oxidative processes that develop at high temperatures.
In the case when the readings of the device are deliberately false, and during an external examination, weak clamps were not found, then the reason, most likely, lies in the failure of the control and measuring device. In this case, it must be returned for repair.If you have the appropriate qualifications, you can try to fix the problem yourself.
And in general, if the potentiometer needle or digital indicator shows at least some "signs of life", then the thermocouple is in good working order. In this case, the problem is clearly something else. And accordingly, if the device does not react in any way to obvious changes in the temperature regime, then you can safely change the thermocouple.
However, before you dismantle the thermocouple and install a new one, you need to fully make sure that it is faulty. To do this, it is enough to ring the thermocouple with an ordinary tester, or even better, measure the voltage at the output. Only an ordinary voltmeter is unlikely to help here. You will need a millivoltmeter or tester with the ability to select a measurement scale. After all, the potential difference is a very small value. And a standard device will not even feel it and will not fix it.

Design features
If we are more scrupulous about the process of measuring the temperature, then this procedure is carried out using a thermoelectric thermometer. The main sensitive element of this device is a thermocouple.
The measurement process itself occurs due to the creation of an electromotive force in the thermocouple. There are some features of a thermocouple device:
- The electrodes are connected in thermocouples to measure high temperatures at one point using electric arc welding. When measuring small indicators, such a contact is made using soldering. Special compounds in tungsten-rhenium and tungsten-molybdenum devices are carried out using tight twists without additional processing.
- The connection of the elements is carried out only in the working area, and along the rest of the length they are isolated from each other.
- The insulation method is carried out depending on the upper temperature value. With a value range from 100 to 120 ° C, any type of insulation is used, including air. Porcelain tubes or beads are used at temperatures up to 1300 ° C. If the value reaches 2000 ° C, then an insulating material of aluminum oxide, magnesium, beryllium and zirconium is used.
- An outer protective cover is used depending on the environment of use of the sensor in which the temperature is measured. It is made in the form of a metal or ceramic tube. This protection provides waterproofing and surface protection of the thermocouple from mechanical stress. The outer cover material must be able to withstand high temperature exposure and have excellent thermal conductivity.
It will be interesting for you Installation of an electrical panel under the meter and machines
The design of the sensor largely depends on the conditions of its use. When creating a thermocouple, the range of measured temperatures, the state of the external environment, thermal inertia, etc. are taken into account.
Thermocouple Benefits
Why have thermocouples not been replaced by more advanced and modern temperature measurement sensors over such a long history of operation? Yes, for the simple reason that until now no other device can compete with it.
First, thermocouples are relatively cheap. Although prices can fluctuate in a wide range as a result of the use of certain protective elements and surfaces, connectors and connectors.
Secondly, thermocouples are unpretentious and reliable, which allows them to be successfully operated in aggressive temperature and chemical environments. Such devices are even installed in gas boilers. The principle of operation of a thermocouple always remains the same, regardless of operating conditions. Not every other type of sensor will be able to withstand such an impact.
The technology for the manufacture and manufacture of thermocouples is simple and easy to implement in practice.Roughly speaking, it is enough just to twist or weld the ends of wires from different metal materials.
Another positive characteristic is the accuracy of the measurements and the negligible error (only 1 degree). This accuracy is more than enough for the needs of industrial production, and for scientific research.
Types of thermocouple junctions
The modern industry produces several designs that are used in the manufacture of thermocouples:
- with an open junction;
- with an isolated junction;
- with a grounded junction.
A feature of open junction thermocouples is poor resistance to external influences.
The following two types of construction can be used when measuring temperatures in aggressive media that have a destructive effect on the contact pair.
In addition, at present, the industry is mastering schemes for the production of thermocouples using semiconductor technologies.


Disadvantages of Thermocouple
There are not many disadvantages of a thermocouple, especially when compared with its closest competitors (temperature sensors of other types), but still they are, and it would be unfair to keep silent about them.
So, the potential difference is measured in millivolts. Therefore, it is necessary to use very sensitive potentiometers. And if we take into account that metering devices can not always be placed in the immediate vicinity of the place of collection of experimental data, then some amplifiers have to be used. This causes a number of inconveniences and leads to unnecessary costs in the organization and preparation of production.
Types of thermocouples
- Chromel-aluminum
... They are mainly used in industry. Characteristic features: wide temperature range of measurements -200 ... + 13000 ° C, affordable cost. Not approved for use in shops with a high sulfur content. - Chromel-copel
... The application is similar to the previous type, the feature is the preservation of performance only in non-aggressive liquid and gaseous media. Often used to measure temperatures in open-hearth furnaces. - Iron constant
... Effective in a rarefied atmosphere. - Platinum-rhodium-platinum
... Most expensive. They are characterized by stable and accurate readings. Used to measure high temperatures. - Tungsten-rhenium
... Usually, they have protective covers in their design. The main area of application is the measurement of media with ultra-high temperatures.