Any pipeline is not complete without special fittings. It is designed to open and close the flow of the working medium (liquid, gas, powdery substances). It can also be used to regulate temperature, pressure, flow. According to their purpose, such types of valves are distinguished as control, drive, safety and shut-off valves. All devices also differ in design. Consider and compare ball valves with check valves.
The first step is to clearly define each of the devices. A crane is a drive valve with a shutter element rotating perpendicular to the working medium. The simplest crane consists of two components - a body and a plug moving around its axis. A shut-off valve is a type of fitting in which the shut-off element moves in the direction of the working medium, while dropping into the seat. It consists of a body, a spindle, a yoke assembly and a spool.
Today, both shut-off valves and ball valves are almost universal and can be used in any conditions. Still, there are fundamental differences between these two devices. Each of them has certain advantages in a specific application. The first and main difference is the more complex design. shut-off valve
compared with
ball valve
... It can also work in a partially open position. The valve can control the flow, which is not possible with the valve application.
Such features directly depend on the design of the devices. Ball valves are equipped with a spherical shut-off element, which, when not fully turned, changes the pressure, and the valves are equipped with a ground axle box, the stem which is unscrewed and twisted. Thus, in the latter system, the valve, when lifting or lowering, blocks or opens the flow of the working medium. The most suitable application of the shut off valve is in systems with manual flow control. But in comparison with a ball valve, large head losses occur in it, and the flow moves in only one direction, which leads to a breakage of the spool. Shut-off valves
are characterized by a more complex design and less operational reliability. They are also somewhat cheaper than other types of locking fittings, the seals in them wear out more slowly.
Ball Valves
in turn, they can be used longer without emergencies.
Our experts can help in the selection of equipment. To do this, you need to send an email. mail website
We will be glad to receive your comments, orders through the website and mail requests!
All pipelines are supplied with appropriate fittings. Its purpose is to open and close the flow of liquid (gas), regulate its temperature, pressure or flow rate, and also protect equipment from off-design modes. In accordance with the purpose, valves can be shut-off, control, safety, drive, etc. To what type of valves are taps and valves, and what is the difference between them?
Definition
Crane
- a type of pipeline power fittings in which the valve body rotates around its own axis, located perpendicular to the direction of flow. A typical crane consists of two main elements: a stationary body and a rotating plug.
Ball valve
Valve
(shut-off valve) is a type of actuator valve in which the shut-off element, moving in the direction of flow, sits on the seat. The valve is designed to open, close and regulate gas or liquid flows.
Valve
The specifics of the angle gas valve
Like a water faucet, an angle gas faucet is made of brass; Saddles-seals around the shut-off ball are made of fluoroplastic or nitrile-butadiene rubber (less commonly). But gas is more fluid than liquid; to ensure better closure, the surfaces of the locking elements are subjected to more thorough processing: grinding and, in some cases, polishing.

Angle Gas Faucet Giacomini
Gas taps are operated at lower pressures and temperatures than water ones: usually the pressure does not exceed 5 atm., The temperature of the pumped gas is up to + 60 ° C.
The property of some gases is known to ignite from a spark: therefore, steel parts are not used in the construction of gas taps; handles are made of brass or aluminum (or plastic valves are used).
Currently, ball valves are usually used both as water taps and as gas taps. An article on our website "Ball valve device" will tell you about these gadgets and their operation
For a more detailed description of shut-off valves, read here: https://remontspravka.com/valves/
In the event that the valve is part of a flange transition between pipes, it is called "flanged". You can also find out more about this type of locking mechanisms on our website.
It is easy to distinguish a gas tap from a water tap by the handle: they are made yellow for gas taps, while blue, black, red, etc. for water taps.


Tiemme angle gas valve made in Italy
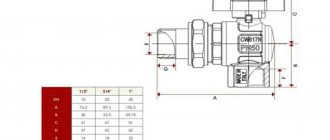
In public utilities, large-diameter pipes are not used to transport gas, and therefore gas valves are mainly produced in two standard sizes: for ½ "thread and for ¾" thread.
Comparison
The main difference between a valve and a tap is that a valve can regulate the pressure of a working flow, but a tap cannot (besides, adjustment by a tap is strictly prohibited according to the rules of operation). The valve performs only two functions, having only the position "open" or "closed", and the valve can easily adjust the pressure of the working flow.
It's all about the design differences between the valve and the crane. In valves, the shut-off element sits on the seat, moving in the direction of flow, and in valves, it turns around its own axis. In addition, cranes are usually ball-type, that is, when the ball is turned, the diameter of the hole changes, and the valves are equipped with a ground axle box (by unscrewing or twisting the stem of the ground axle box, they raise or lower the valve attached to the stem, thereby opening or closing the hole located in saddle).
Ball valve and valve: difference and product features!
What is better to buy: a faucet or a device such as a valve? It is actually unrealistic to answer such a question exactly. Indeed, in some situations it is necessary to use a ball valve, but in others - a special valve. Additionally, it is recommended to note here the fact that the crane is considered a more convenient device to use. In this situation, the handle can be rotated all 90 degrees. Due to this, the incoming water is shut off. But the shut-off valve present in the valve must be turned in order to close or open the water supply.
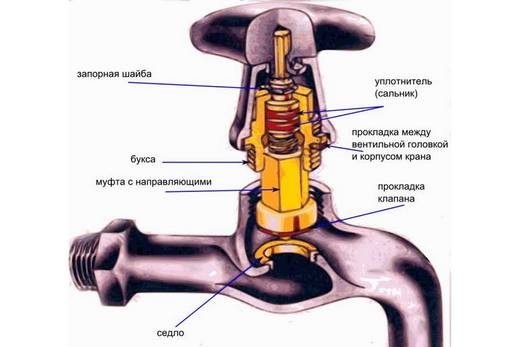

Additionally, there are special valves with gaskets on the valve. When they are worn out, it is enough to simply change them to a new version. It is also recommended to periodically replace the oil seal itself. But with a ball valve, such problems do not really exist. Only constant and thorough care of the surface itself is recommended here. She should always be in the most perfect condition.
In general, if enough hard water is supplied to the room, then the installation of a valve is recommended.After all, such a product is subject to, albeit partial, but still repaired. In a situation where the crane is damaged for some reason, then you cannot do without its full replacement.
With all this, the valve can most often be purchased at a lower cost, if taken in comparison with the second type of product. Such a not too high price is primarily due precisely to the fact that the device has a simple design of such an element as a shut-off valve.
In any situation, a shut-off type of fittings in modern times is used to create a variety of sewer and gas pipeline systems. It is also commonly found in general purpose pipelines. The device is designed to shut off a gas or water flow. For this purpose, it is possible to install not only valves and gate valves, but also such devices as taps and valves. All of them have a huge number of advantages, and some negative characteristics. It all depends on the situation.
Thus, the difference between a valve and a tap initially lies in the fact that with the use of a tap it is impossible to regulate the pressure of the working flow. But the second product allows for such an action.
Conclusions site
- The valve has two positions - this is the "open" position and the "closed" position.
- The design of the valve, in addition to switching on / off, also allows you to regulate the pressure of the working flow.
- Visually, the valve differs from the valve in the following way: if the handle is simple and its end is attached to the stem, it is a valve; if there is a "lamb" on the stem instead of the handle, this is a valve.
Since such a discussion has begun, it's time to refresh for the next issue of linguists. Here is just the question of the bolt / screw will arrive in time.
1. Industrial pipeline fittings A device installed on a pipeline and a vessel and providing control of the flow of the working medium by changing the flow area. Note. The term "industrial pipeline valves" may also be applied to a set of devices installed on pipelines and tanks that meet this definition.
2. Shut-off valves Industrial pipeline valves designed to shut off the flow of the working medium.
3. Control valves Industrial pipeline valves designed to regulate the parameters of the working medium by changing its flow rate.
4. Distribution and mixing valves Industrial pipeline valves designed to distribute the flow of the working medium in certain directions or to mix flows.
5. Safety valves Industrial pipeline valves designed for automatic protection of equipment from emergency changes in parameters.
6. Backflow fittings Industrial pipeline fittings designed to automatically prevent backflow of the working medium.
7. Phase separation valves Industrial pipeline valves designed for automatic separation of working media depending on their phase and state.
8. Gate valve Industrial pipeline fittings, in which the shut-off or regulating body moves reciprocally perpendicular to the axis of the flow of the working medium.
9. Ndp valve. Valve Industrial pipeline fittings, in which a shut-off or regulating body moves reciprocally parallel to the axis of the flow of the working medium.
10. Crane Industrial pipeline fittings, in which the shut-off or regulating body has the shape of a body of revolution or part of it, which rotates around its own axis, arbitrarily located to the direction of flow of the working medium.
eleven.Valve Industrial pipeline fittings in which a valve or regulator is rotated about an axis other than its own axis.
12. Straight-through fittings Industrial pipeline fittings in which the working medium does not change its direction of movement at the outlet as compared to its direction at the inlet.
13. Angle fittings Industrial pipeline fittings, in which the working medium changes its direction of movement at the outlet compared to its direction at the inlet.
14. Flanged fittings
15. Coupling fittings
16. Pin reinforcement
17. Choke fittings
18. Weld-on fittings
19. Stuffing box fittings Industrial pipeline fittings, in which the sealing of moving elements relative to the environment is carried out by stuffing box packing.
20. Bellows fittings Industrial pipeline fittings, in which the sealing of moving elements relative to the environment is carried out by a bellows.
21. Diaphragm fittings Industrial pipeline fittings, in which the sealing of moving elements relative to the environment is carried out by a membrane.
22. Wedge gate valve A gate valve with a shut-off or regulating body, in which the sealing surfaces are located at an angle to each other.
23. Parallel gate valve A gate valve with a shut-off or regulating body, the sealing surfaces of which are parallel to each other.
24. Gate valve with a rising stem (stem) A gate valve, when opened and closed, the spindle (stem) makes a translational or rotational-translational movement.
25. Gate valve with a non-rising spindle A gate valve, when opening and closing of which the spindle makes a rotational movement.
26. Shut-off valve A valve designed to shut off the flow of the working medium.
27. Regulating valve A valve designed to regulate the parameters of the working medium by changing its flow rate and controlled from an external power source.
28. Single-seat control valve
29. Double-seated control valve
30. Mixing valve A control valve designed for mixing two or more working media of different parameters.
31. Distribution valve A valve designed to distribute the flow of the working medium in certain directions.
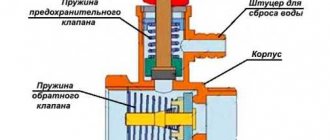
32. Safety valve A valve designed to protect the equipment from unacceptable pressure by relieving excess operating fluid and ensuring that the relief stops at the closing pressure and that the operating pressure is restored.
33. Non-return valve A valve designed to automatically prevent backflow of the working medium.
34. Non-return shut-off valve
35. Non-return valve A non-return valve with forced opening and closing.
36. Regulator Industrial pipeline fittings designed to regulate the parameters of the working medium by changing its flow rate and controlled directly from the working medium.
37. Condensate drain Industrial pipeline fittings designed to drain condensate of water vapor.
38. Float-type steam trap A condensate drain with a float-operated shut-off element.
39. Thermostatic condensate drain A condensate drain, the shut-off element of which is controlled by a thermostat.
40. Thermodynamic condensate trap Condensate trap, the shut-off element of which is controlled due to the aerodynamic effect of the thermodynamic properties of the working medium.
41. Distribution valve A crane designed to distribute the flow of the working medium in certain directions.
42. Cylindrical valve A valve, the shut-off or regulating body of which is in the form of a cylinder.
43.Cone valve A valve, the shut-off or regulating body of which is in the form of a cone.
44. Ball valve A valve, the shut-off or regulating body of which has a spherical shape.
45. Reverse shutter. Ndp. Check valve A shutter designed to prevent backflow of the working medium.
46. Butterfly valve A valve, the shut-off or regulating body of which is made in the form of a disk.
Among the most common locking devices are gate valves and taps. What is the specificity of both?
Design features
Many do not understand how a crane differs from a valve, so this issue should be given special attention, we will consider the main design and operational differences, and also touch on the advantages and disadvantages of each of the elements. (See also How to Choose a Basin Faucet: Features.)
Comparative analysis of valve and faucet
Let's consider the most important nuances as a comparison:
- The valve is designed to shut off the flow of the working medium and adjust its intensity, while the valve can only be used in open-closed positions... Any adjustments using a crane are not only inconvenient, but also undesirable - the structure wears out and breaks down very quickly. That is, the main difference between a valve and a tap in a functional sense is the possibility of adjustment.
This is how the valve works - opening and closing is carried out in the direction of movement of the working medium, and not perpendicular to it
- The valve and the crane can perform the same functions, but their scheme of work is different.... If a disk or a ball in the tap moves on an axis perpendicular to the flowing water flow, then in the valve the valve moves along the axis of movement of the working medium. If the valve can be closed in half a turn, which can be considered an advantage, then the valve will require 5-6 turns, which is not very convenient in case of frequent use.
Advice! It is very easy to distinguish a valve from a tap, even if you do not understand anything about these types of devices. In the crane, the main control element is a lever or a small butterfly flag, while in the valve the control is carried out by a handle in the form of a diamond or in the form of several rings.


The knobs of the valves are made so that it is convenient to twist them
- The main advantage of cranes is their simplicity, because they are very easy to use.... But if the product is rarely used, then the disc or ball valve is covered with limescale and eventually sticks to the body, which makes it impossible to close or open them. In this case, the only solution is to replace the entire assembly, which is not very desirable, since its price is quite high.
With infrequent use, the ball sticks, and the faucet becomes unusable.
- Choosing between the valve or ball valve options, one very important nuance should be noted - the first option can be repaired by hand, while the second cannot be repaired... But it is worth noting the fact that the valves have a shorter resource, so from time to time it will be necessary to replace consumables.
What to look for when choosing a valve
In order not to purchase a low-quality product that will quickly fail, you need to remember a few simple recommendations:
- It is important to know the size of the required nodes, for plumbers they are designated 1 2, 3 4 and so on. You, however, need to measure the diameter of the pipe, and the seller will select the required one; you should not rely on an eye gauge, since it is very easy to make a mistake.
- The ideal option is to purchase devices from well-known manufacturers, the quality of which is known to a wide range of users. The necessary information can be gleaned from consultations with specialists, as well as on specialized resources on the Internet. (See also How to Install a Sink: Features.)
Advice! The seller must have a quality certificate for all products, ideally if they comply with GOST standards, this guarantees their good work.
- Externally, the structure should look neat: the coating should be uniform, from the inside, the surface should not have sagging and seams. Any flaws indicate low quality.
- The weight of solid cranes is very large, this confirms the thickness of the walls and the quality of the raw materials used.


Brass is an excellent material for making valves
What is a gate valve?
Under gate valve
it is customary to understand a shut-off mechanism on a pipeline, which involves shutting off the flow of a liquid or gas by means of a partition. It can move across the pipe up and down or left and right. The valve in many cases also allows you to adjust the flow rate of the liquid or gas. For example, if the baffle of a valve is half-shifted, the flow rate is reduced by 50%. As it moves higher or to the left (or lower or to the right - depending on its initial position), the flow intensity can increase or decrease.
The baffle on the valve is most often made in the form of a disc, sometimes a wedge or a sheet. There are valves in which the partition consists of one element, but in some cases it is represented by several details. For example, if there are two of them - an increase in intensity, or an opening of a stream, it can be carried out by means of their expansion. Reducing the dynamics, or closing the flow, on the contrary, is carried out by closing the components of the valve baffle.
The main advantage of the gate valve is the ability to open or close the flow relatively quickly and at relatively low energy consumption (or set the required flow rate).
Gate valves can be installed on high pressure pipelines - for example, heating, plumbing. They are among the most sealed shut-off elements.
With frequent use, the valve can wear out rather quickly - this is due in many cases to a rather large frictional force between the edges of the partition and the block, in which it moves left-right or up-down.
Another drawback of the valve is the need to allocate additional space outside the pipeline cross-section in order to temporarily place the moving part of the partition. Installation, maintenance and repair of the shut-off element in question can also be quite labor-intensive.
Thus, taking into account the noted advantages and disadvantages, the valve is most often used not as a regulating element, but as a shut-off element, which is supposed to be placed in the "open", "closed" position or in another static position for quite a long time. In order, in turn, to frequently adjust the flow of liquid or gas on pipelines, another shut-off device, a tap, can be successfully used. Let's consider its features.
Varieties of valves and taps
Such significant design differences between the valve and the ball valve determine the principle of their operation. The first type is applicable not only for opening / closing the flow of substances moving inside the pipe, but also for regulating it. The second type is used to feed or shut off substrates in a pipeline.
Varieties of ball valves


The main difference between a valve and a tap is that the latter are represented by models of products that can not only stop, but also change the direction of movement of substances:
- two-way - used to shut off or open the movement of substances transported to one of the sides of the pipeline;
- three-way L-shaped - are distinguished by their ability to change the direction of flow of substrates and to completely stop their movement in the pipe;
- T-shaped - used to disconnect the stream, combine or change its direction.
It should be noted that the taps are also designed to open or close the flow. If in a certain section of the pipe it is necessary to reduce the flow force, a device is selected with the appropriate section of the hole in the sphere:
- full bore - the locking mechanism does not affect the substrates flowing through it, which is ensured by matching the diameter, inside the hole, to the existing pipe;
- standard bore - the lumen of the shut-off ball has a 20–30% narrowing in comparison with the cross-section of the connected pipeline;
- partial bore - the restriction value provides a pressure reduction by 30-60% of the initial value.
Depending on the material of manufacture of the ball valve, its technical characteristics differ.
- Brass. Suitable only for operation in systems with neutral substances, the temperature value of which does not exceed 150 ° C, and the pressure of 40 bar. The nominal cross-sections of the cranes are in the range from 8 to 100 mm. They are distinguished by their ability to effectively withstand temperature changes, and are immune to corrosion.
- Steel. They are susceptible to corrosion, quickly collapse when interacting with aggressive compounds, therefore they are mounted on pipes, the main medium is water or other non-aggressive compounds. The ultimate flow force that steel cranes can withstand is 160 bar and a temperature of 200 ° C. They differ in the production of products in a wide range of nominal cross-sections from 15 to 600 mm.
- Corrosion-proof. They are distinguished by resistance to aggressive substances and the absence of corrosive destruction. They are able to withstand a pressure of up to 60 bar, provided that the temperature of the substances in the pipe does not exceed 210 ° C.
- Cast iron. Shut-off valves used only in piping systems for hot or cold water supply.
Types of valves


To understand how the valve differs from the valve, you need to understand the differences in the materials from which the body is made. Valves are characterized by the following types of metals:
- cast iron - the nominal cross-section of products made of this material has a range of 15–300 mm, and the maximum pressure that it can withstand is 16 bar;
- steel - here the valve passage diameter ranges from 3 to 200 mm, and the maximum flow force and medium temperature are 220 bar and 450 ° C, respectively;
- stainless steel - used on pipelines with a cross section of 3–200 mm, while the pressure of the substance is not more than 220 bar, and its temperature is 570 ° C.
In addition to the material, the valves differ in the form of execution:
- checkpoints - are installed only on flat sections of the pipe and provide smooth regulation or shutdown of the flow of substances moving in the pipe;
- straight-through - they differ in the minimum value of resistance to the moved flow and are mounted in almost any plane;
- corner - have a specific shape that allows their installation on corner pipelines.
What is a crane?
Crane
Is a shut-off element, the main part of which is a shutter, presented in the form of a ball, in the form of a cone or a cylinder. They have a channel with a diameter that is sufficient to ensure the passage of the flow, if the corresponding channel is located parallel to the flow or is located at a slight angle to it. In turn, when the channel is placed perpendicular to the flow (by rotating the ball, cone or cylinder in which it is made) or at a large angle to the flow, the movement of the liquid or gas in the pipe stops or its intensity decreases.
Changing the position of the valve is carried out by rotating a spherical, conical or cylindrical valve around its axis perpendicularly or parallel to the flow (this is not important, the main thing is to achieve the necessary tightness).
The valve, like the gate valve, is characterized by a high degree of tightness. Therefore, it can be installed in high pressure pipelines. At the same time, the main drawback of valves is not typical for cranes - wear. Provided that the locking device in question is properly lubricated and serviced, it can last a long time.
The valve is thus excellent for regulating the rate of movement of a liquid or gas in a high pressure pipe. This is due to its frequent use as a shut-off mechanism in the final section of pipelines. For example, as the main element of household mixers, which are located in bathrooms, kitchens, showers.
The valve, as a rule, does not require a large space outside the section of the pipeline, since its main element - the gate - rotates around its axis within the pipe. However, additional space may be required for the control valve and other mechanisms that complement it.
Varieties of ball valves.
Ball valve for coupling.
They are installed on pipelines supplying water or gas. The main part of the constituent elements is made of steel, so the product is reliable and durable. The valve is connected to the pipe by means of an internal thread. Its dimensions must correspond to the connecting thread. Large diameters are available in sizes from 2.5 to 4 inches. Small: 1/4 and 3/8 inches. Medium: 1/4, 3/4 and up to 2 inches.


Flanged ball valve.
He replaced the valves. They are distinguished with respect to the type of environment where they will be installed: on water, gas, heat pipes. This shut-off device not only adjusts the flow of water and gas, but also blocks them if necessary. It consists of a body and a rotating ball. The valve is attached to the flange, which provides the connection with extra strength. They are presented in a wide range of diameters: from 15 to 1400 mm.


Ball valve full bore.
It is used in all pipeline systems, regardless of their purpose. The valves are durable in use, do not need lubrication. The overlap and passage of the medium is carried out due to the spherical element, which is the main part of the structure. They are able to withstand pressure drops, temperatures. The crane has two functions: it opens and closes, and therefore the same number of positions. The diameter of the full bore device must match the diameter of the pipe on which it is mounted. Their cross section varies from 15 to 1500 mm.
Ball valve brass.
Ball valves made of brass are used in pipelines that pass a non-aggressive liquid. The sealing properties are very high. They can be used in water pipes as brass is safe and does not adversely affect water quality. The crane is very easy to use and available for repair: the adjusting nut is located under its handle.


Nickel plated ball valves.
Nickel ball valves are distinguished depending on their capacity: full bore and reduced. The diameter of the first type must correspond to the cross-section of the pipeline, and the size of the diameter of the last type is one third less than the diameter of the pipe. By the method of connection, the most widespread are products with internal and external threads, welded, flanged and threaded. Nickel-plated valve bodies are either one-piece or collapsible.


Drain ball valve.
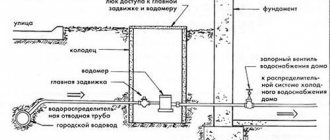
This type of faucet controls the movement of water or gas. It is used, for example, for the arrangement of individual heating. It can be used to shut off some sections of the pipeline. To remove air from the system and remove plugs, a Mayevsky crane is used. It connects to the 1/2 section hole in the top of the battery by screwing it in.


Comparison
The main difference between a gate valve and a tap is that the main element of the first shut-off device is a partition that moves perpendicular to the flow of liquid or gas in the pipeline. The main element of the valve is a valve with a channel made in it, which, when placed parallel to the flow or at a slight angle to it, increases the intensity of fluid movement in the pipe, and when placed perpendicular to the flow or at a large angle to it, reduces its intensity.
The difference between the types of closure elements under consideration can also be traced in the aspect:
- wear and tear;
- the need for spaces outside the cross-section of the pipeline;
- scope, prevalence of inclusion in the structure of household mixers.
Having determined what is the difference between the valve and the crane, we fix the conclusions in a small table.
Features of Wedge Gate Valves
Practical application shows that when using gate valves As a control valve, the gate valves fail rather quickly, ceasing to keep the flow of the medium in a closed state, that is, they do not even perform their direct function.
It should be noted that we are talking specifically about steel gate valves, because cast iron gate valves are not even considered here. The main problem is that cast iron injection molding machines are extremely demanding on operating conditions.
For example, cast iron valves cannot be used at temperatures above +350 degrees and below -20 degrees (here we are talking about the best grades of cast iron) on the Celsius scale. There are also restrictions on the type of pumped medium (a cast-iron injection molding machine is practically impossible to safely use in some types of gas pipelines), pressure, diameter of the bore, etc. Although gate valves are still the most common type of injection molding machine in various pipelines, there has been a recent trend towards replacing gate valves with ball valves in many systems.
The main reasons for replacement:
- gate valves require constant monitoring of the technical condition (for example, cleaning the stuffing box seals),
- gate valves do not show themselves well in the event of emergency situations requiring a quick shutdown of the flow of the working medium.
In addition, the design of the valve does not provide good tightness, moreover, this applies to almost all elements: both the valve itself and the body. Further, we note that the wedge gate valves have a fair weight and solid dimensions, and also often break, which leads to the regular occurrence of emergency situations.
Table
| Gate valve | Crane |
| What do they have in common? | |
| Gate valves and valves provide high tightness of blocking the flow of liquid or gas in the pipeline, suitable for pipes with high pressure | |
| What is the difference between them? | |
| The main locking element of the gate valve is a partition that moves left-right or up-down (if it is not represented by a more complex - for example, a two-leaf design) | The main shut-off element of the valve is a shutter that can rotate around its axis and place the channel made in it at a greater or lesser angle relative to the flow of liquid or gas in the pipe |
| Wears more intensively with frequent use | Less wear and tear with frequent use |
| As a rule, it requires significant space outside the pipeline cross-section - to accommodate the outgoing part of the partition | Requires space outside the pipeline only for the purpose of placing control elements - valves and their complementary mechanisms |
| It is mainly used as a typical shut-off element, which is in the "open", "closed" or otherwise static position for a long time | It is used as a regulating element, through which you can set the desired flow rate in the pipeline at any convenient time |
| Generally not used as a component of household faucets | Is one of the main components in household faucets |
The main types of valves
To begin with, consider what types of systems are and what are their main advantages:
| Gate valves | A very common option, which is most used on large-diameter pipelines, as it provides high reliability and ease of operation. The blocking element can be located in two positions: open and closed, the blocking element moves perpendicular to the flow axis. The most common types of gate valves are wedge, gate and parallel |
| Cranes | They can be of two main types: ball and disk. Disk structures in another way are called gates, they are a gate valve, the axis of which is located in the middle of the pipe, a turn of the handle closes the pipeline, to ensure reliability, a lock may be present in the design. The ball valve has the following features: the main locking element is a hollow ball, when turned 90 degree flow closes |
| Gates | This option is used almost everywhere and is a system in which a valve with a gasket is located on the axis of the device. Its movement up and down allows not only to shut off the flow entirely, but also to regulate its intensity, this feature is the most important, which is why valves are in such high demand. |
The disk valve can only be used to open-close the system