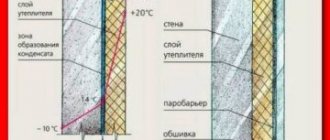
Dry insulation is a guarantee of 100% protection against heat leakage. Due to natural diffusion, moisture vapors move from the walls of the house, which normally evaporate from the surface. And if the house is insulated and the thermal insulation is closed with dense materials, the movement of flows is disrupted. As a result, the thermal insulation can get wet and lose its insulating properties. How to make the evaporated moisture leave the insulation freely, let's figure it out together!
What are the types of external insulation with a ventilated gap?
Thermal insulation materials are always covered with decorative trim or external cladding of panels and slabs. The finishing layer performs not only a decorative function, but also protects the insulation from getting wet, weathering and damage. Most often, there are two systems of external thermal insulation, for which an air gap is structurally necessary:
- Ventilated facade systems;
- Brick cladding.
Both systems are different from each other in the way of the device, the composition of the structure and the external finish, therefore the approach to the ventilation device is different. For the installation of a hinged ventilated facade, our experts recommend:
| Rockwool LIGHT BATTS SCANDIC | Basvul VentFacade | Rockwool Venti BATTS |
Insulation materials
Despite the huge variety of thermal insulation materials, for many years, builders have preferred to insulate the walls of cottages, mainly with 2 types: foam or mineral wool. These materials have worked well.

The texture of the mineral wool allows air to move freely and therefore does not form condensation on the walls. Polyfoam is easier to install, but when using it, it is necessary to think over the ventilation system, since it is a vapor-tight material, which means that condensation can form on it.
Also, plaster and polyurethane are used as insulation of aerated concrete walls. After insulating the facade of the building with polystyrene plates, it can be almost immediately plastering on the mesh using a hydrophobic composition and painted.
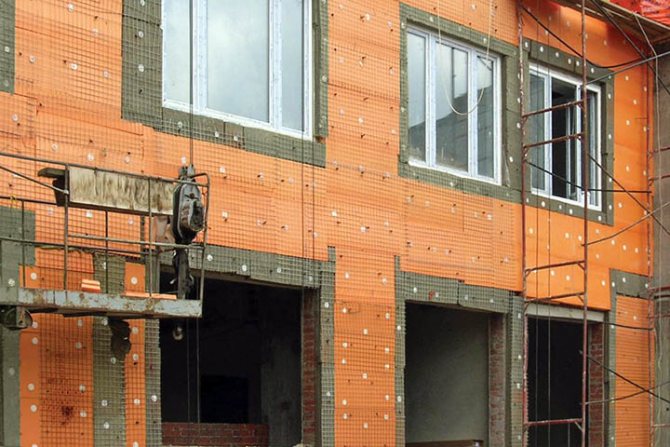


How to provide ventilation in the space under the cladding?
When facing a wall made of foam or aerated concrete blocks with a facing brick, a wall is formed on the outside that allows water vapor to pass through much worse than blocks of aerated concrete. In these cases, a ventilated air gap is arranged in the walls, located closer to the outer part of the wall between the cladding or protective wall and the cold surface of the insulation.
- Ventilation of the air gap is carried out through special vents made in the lower and upper parts of the wall, through which vaporous moisture is removed to the outside. Recommended area of ventilation openings is 75 cm2 per 20 m2 of wall surface.
- The upper ventilation ducts are located at the cornices, the lower ones at the plinths. In this case, the lower holes are intended not only for ventilation, but also for water drainage.
- For ventilation of the layer in the lower part of the wall, a slotted brick is installed, placed on the edge, or in the lower part of the wall, brick or blocks are laid not close to each other, and not at some distance from each other, and the resulting gap is not filled with masonry mortar.
How and how to insulate the ceiling in a private house?
Most of the owners of private houses are interested in reducing the consumption of heat resources, the cost of which is constantly increasing. Trying to create a comfortable microclimate in the house without increased costs, they insulate the walls of the building.However, about half of the thermal energy leaves the building through the ceiling, since, according to the laws of convection, warm air tends to rise and go outside. Knowing how to insulate the ceiling, you can achieve a comfortable temperature, as well as reduce the level of humidity, which is the cause of damage to property due to the formation of fungal colonies and mold.
How to insulate the ceiling in a private house - types of materials
What kind of thermal protection should be used to insulate ceilings, it is advisable to think over even at the construction stage. However, in most cases it is necessary to deal with this serious problem in an already constructed building. The problem of choosing materials should be approached with special responsibility if the roof of the building is not insulated.


When deciding on a heat insulator that provides a favorable microclimate, please note that it must perform the following functions:
- hinder the penetration of extraneous noise, providing silence in rainy and windy weather;
- maintain a comfortable temperature in winter, preventing the escape of heated air;
- hinder the access of air masses heated in summer to the rooms, keeping them comfortable cool.
When deciding to purchase a heat insulator to insulate the ceiling with your own hands in a private house, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- coefficient of thermal conductivity. With a decrease in the indicator, the protection of the room from heat loss increases;
- resistance to moisture absorption. The parameter is especially relevant for thermal insulators installed from the attic side;
- fire safety. The use of non-flammable and high temperature resistant materials will avoid unforeseen situations;
- resource of operation. The use of heat insulators with an increased service life will avoid additional costs for repairs;
- harmlessness to human health. Environmentally friendly raw materials used in the manufacture of a heat insulator will not have a negative impact;
- mass. Installing lightweight thermal protection will reduce the stress on the ceiling elements.
In specialized construction shops, a variety of high-quality materials are offered that allow you to effectively insulate the ceiling and perform thermal insulation of the attic floor in a residential building.
Despite the differences in operational characteristics, the following are used to accomplish the assigned tasks:
- thermal insulation wool on a mineral basis. Possesses increased thermal protection characteristics, but is susceptible to moisture;
- cellulose-based ecowool. It is environmentally friendly, used for insulation of the ceiling surface;
- expanded clay granules of various sizes. They are distinguished by fire resistance, as well as environmental safety;
- woodworking waste in the form of shavings and sawdust. They prevent the penetration of cold, but they are afraid of high temperatures;
- gas-filled polyurethane. It is applied to the prepared surface in a foamy form. It absorbs noise well, is not afraid of moisture;
- sheet expanded polystyrene in extruded form. Differs in durability, does not burn, has a long service life.


The peculiarity of these heaters is lightness, since increased loads should not occur in the load-bearing floor beams.
The range of materials offered on the market is complemented by the following thermal insulators:
- vermiculite. Bulk heat insulator made from clay. The granules fill the space between the ceiling beams or the attic floor;
- Styrofoam. Reliable protection with internal insulation. However, it is susceptible to high temperatures and fire and needs to be protected with plaster;
- foam glass. In structure, it resembles pumice, characterized by a cellular structure and low weight. Suitable for lightweight structures.
Attention should be paid to the inexpediency of using the following heat insulators for thermal insulation of the ceiling surface:
- heavy expanded clay concrete, cellular blocks on a ceramic basis and foam concrete, which create an additional load on the floor system;
- slag-filled concrete blocks and glass wool, environmentally unsafe for the health of people in the room;
- heaters, the structure of which does not allow vapors formed in the process of human activity to freely leave the room;
- straw and hay, which are combustible and tend to spontaneously ignite at elevated temperatures.
Let's dwell in more detail on the characteristics of the most common materials that allow you to insulate the ceiling.
Mineral wool
Certain varieties of mineral wool are widely used for thermal insulation of the ceiling surface. They are laid between the beams inside the attic space, as well as from the side of the rooms. Depending on the raw materials used in the manufacture of mineral wool, the following types are distinguished:
- slag. It is produced on the basis of blast furnace slags. Differs in low cost compared to other types of mineral wool. Slag wool is rarely used for thermal insulation of residential premises, as it loses its thermal insulation properties at high humidity. Slag wool has a brittle structure, contains prickly fibers, which, in suspension, pose a danger to the respiratory system;
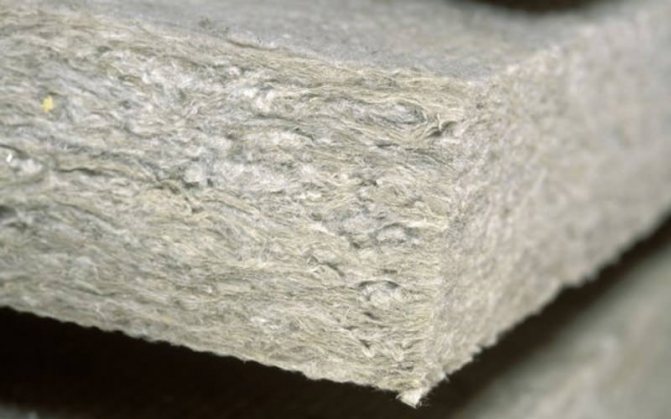


- glass wool. The canvases are formed from the finest fibers made from molten glass. Glass wool is supplied in rolls or in separate layers. Has a reduced thermal conductivity compared to slag and basalt heat insulator, is capable of absorbing moisture up to 800 grams per square meter. Glass wool, in combination with other thermal insulators, is used to insulate attic floors;
- basalt wool. The use of plastic rocks based on basalt makes it possible to reduce the fragility of fibers and makes it possible to use basalt material for internal thermal insulation of a room. The compacted array has increased strength, is not afraid of mechanical stress and moisture. Sold in rolls and mats, installed from the inside and outside of the room.
The presence in the structure of all varieties of mineral wool resins based on phenol-formaldehyde, which are a binder component, does not allow the specified heat insulator to be classified as an environmentally friendly raw material.
Ecowool
A thermal insulator based on small cellulose fibers is less common than expanded polystyrene or mineral wool, but is gradually gaining wide popularity. Insulation is laid on the outside of the room using one of the following methods:
- dry. The space between the floor beams is evenly filled with ecowool, followed by the compaction of the array;
- wet. It is realized with the help of special equipment that supplies fibers mixed with glue under pressure into the space between the logs.
The main features of cellulose-based cotton wool:
- the possibility of forming an insulating array of any thickness;
- insignificant mass, which does not allow cotton wool to weigh down the overlap;
- porous structure providing effective thermal insulation;
- no negative impact on human health;
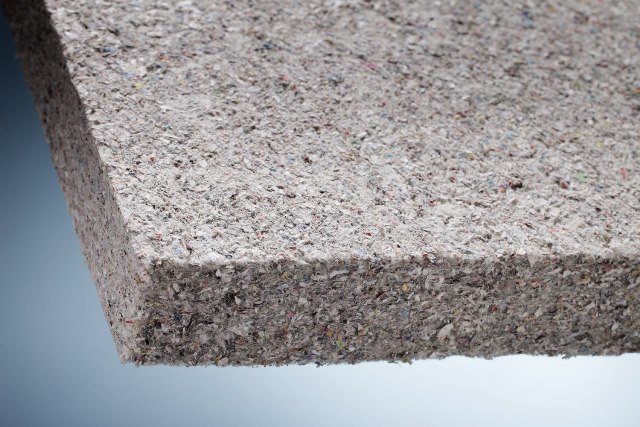


- reliable preservation of the surface, which impedes the development of microflora;
- extended period of operation with preservation of operational properties;
- accelerated installation of a thermal insulator using special equipment;
- the possibility of increasing the thickness and compaction of the existing layer;
- reduced flammability and self-extinguishing properties of the insulation;
- the formation of a sealed array, in which there are no seams and joints;
- free exit of warm air vapors through the cellular array.
Depending on the applied installation method and the thickness of the protective layer, the payback period is 2–2.5 years.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay granules are made by high-temperature clay firing. They are used for thermal insulation of attic floors.
The main characteristics of expanded clay:
- ecological cleanliness. Granules are made from raw materials that are safe for health;
- Fire safety. When heated, expanded clay does not release harmful components;
- different density. Thermal insulation properties are determined by the size of the granules;
- durability. During the period of operation, the properties are preserved;
- insulation. Expanded clay grains impede the penetration of noise into the room.
For thermal insulation, it is necessary to use expanded clay with a grain size of 0.4–1 cm, which is poured onto a surface covered with glassine with a previously installed reinforcing mesh. The formed thermal layer is poured with a cement screed.


Sawdust
Wood sawdust and small shavings are applied at the same time. In this case, the shavings provide a porous structure, and the sawdust increases the density of the massif. The popularity of the obsolete, but still popular insulation is due to its properties:
- cheapness;
- environmental friendliness;
- reliability of thermal insulation.
The effectiveness of thermal protection is determined by the thickness of the thermal insulation layer, which depends on the winter temperature in the region. With a backfill thickness of 6–8 cm, reliable thermal insulation is provided at outdoor temperatures up to minus 25 degrees Celsius.
The disadvantages include:
- flammability at elevated temperatures;
- significant shrinkage during compaction;
- the need to mix with fire retardants, cement or clay.
When insulating the ceiling covering with a mixture of sawdust and shavings, place the power supply cables in the corrugated hoses, and also provide a safe distance to the chimney that heats up during heating.
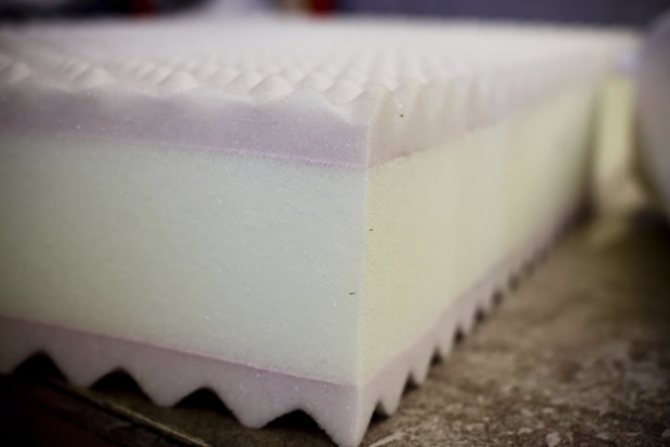


Polyurethane foam
It is a foamy heat insulator obtained as a result of the interaction of polyester ingredients and special emulsifiers. When spraying, it hermetically fills cavities and crevices, forming a seamless coating that is distinguished by its tightness. For the application of polyurethane foam protection, special equipment is needed to supply a foamy heat insulator under pressure.
Polyurethane foam thermal protection has a set of advantages:
- increased density. The solidified massif does not deform under load, and also does not crack;
- reduced water absorption. Polyurethane foam retains its properties at high humidity;
- low thermal conductivity. Thermal insulating properties are retained regardless of temperature and moisture concentration;
- ease of processing. Excess polyurethane foam can be easily removed with a knife, which makes it possible to achieve flatness;
- provides waterproofing and vapor barrier. There is no need to use auxiliary protection;
- high noise absorption. Polyurethane foam spraying significantly reduces the noise level entering the room.
Polyurethane foam quickly polymerizes, spreading over the surface, after pouring or spraying.
Expanded polystyrene
For a long period of use as a heat insulator, expanded polystyrene has established itself on the positive side, although it has a number of disadvantages.
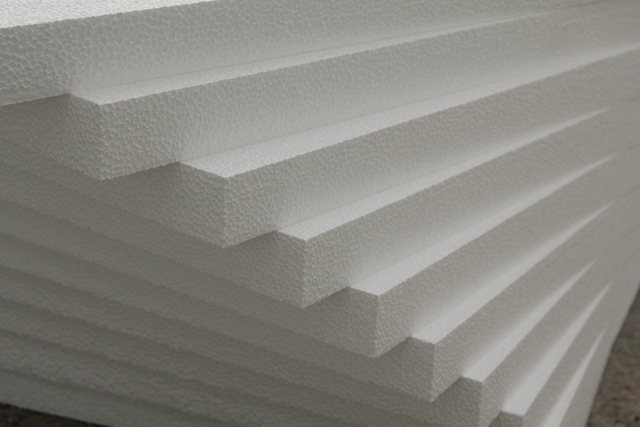


Advantages of expanded polystyrene:
- affordable price;
- ease of installation;
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to damage by microorganisms;
- different density of the material;
- choice of thickness.
Weak sides:
- the possibility of ignition at elevated temperatures;
- the release of toxic substances and poisonous smoke when heated;
- the need for frequent ventilation of the room.
The installation process involves filling the surface with sheets with sealing of the joint areas with polyurethane foam.
Calculation of the thickness of the insulation
It is possible to ensure the required reduction in heat transfer of the floor located under the attic space by correctly calculating the minimum possible thickness of the heat insulator. This requires:
- independently perform complex calculations;
- take advantage of the online calculator.
The second option is much simpler, since it allows you to accurately and in a limited time determine the thickness of the heat-insulating layer. A previously prepared diagram, which indicates the materials used and their dimensions, will facilitate filling in the necessary columns of the online calculator.
Initial data for calculations:
- type of applied thermal protection;
- ceiling thickness and size of the protective layer;
- the presence and size of the air gap;
- heat transfer resistance corresponding to the region of residence.
Depending on the design features of the floor, the characteristics of the insulation, the thickness of the protective material varies:
- mineral wool - 5–20 cm;
- foam plastic - 4–18 cm;
- expanded polystyrene - 10-14 cm;
- expanded clay - 12-16 cm.
Having filled in all the necessary fields and clicking the "Calculate" button, the calculator will calculate the thickness for a specific type of ceiling insulation.
How to properly insulate the ceiling in a private house
The implementation of measures for thermal insulation of the ceiling of a residential building can be performed in different ways:
- by means of internal, vapor-permeable thermal insulation. Reducing heat losses is ensured if an attic is located above the ceiling, and not a cold attic. The technology provides for the manufacture of frame elements, which are fixed to the ceiling and filled with heat-insulating material. It is obligatory to place a vapor barrier layer between the ceiling surface and the heater, followed by sheathing of the insulated structure with plasterboard. The disadvantages of the method are the loss of part of the volume and the complexity of the work;
- by the method of external, vapor-tight ceiling insulation. The work is carried out from the side of the attic. The effectiveness of the implementation of thermal insulation measures and their technology are determined by the type of insulation used and the characteristics of the ceiling structure. The pace of work is slowing down due to the need to clean the attic from debris, special preparation of the surface to be treated and additional protection of utilities above the ceiling.
Having decided on the method of thermal protection, you can start preparatory measures.
Preparatory work
The technological sequence of operations and the labor intensity of the work is determined by the material of the ceiling surface.
Processing of a wood ceiling provides for:
- antiseptic treatment with a primer with a fire retardant effect. The coating is applied with a brush, carefully filling the gaps between the boards;
- filling small cracks and sealing cavities in wood with polyurethane foam. Excess foam after hardening is carefully removed with a sharp knife.
The concrete surface is prepared as follows:
- the existing coating is removed;
- peeling plaster is eliminated;
- small cracks expand;
- defects are treated with soil;
- cracks are plastered or sealed with foam;
- the surface is covered with a concrete primer.
We insulate the ceiling from the attic
Insulation technology from the outside changes depending on the materials used:
- a roll or sheet thermal insulator spreads without gaps between the beams;
- foamy polyurethane and ecowool are sprayed on the attic base;
- The prepared base is filled with expanded clay granules and sawdust.
The roll insulation is laid between the beams as follows:
- A vapor barrier is attached in the interbeam space.
- Insulation fits tightly.
- Waterproofing overlaps.
- Support rails are attached.
- Wooden flooring is nailed.
Polyurethane foam does not need a vapor barrier membrane, unlike ecowool. Both materials, when sprayed in liquid form, form a seamless array. A variant of layer-by-layer dry laying of ecowool on a vapor barrier membrane with intermediate sealing of each layer is possible.
Warming with expanded clay does not cause problems and is carried out in the following order:
- A vapor barrier is spreading.
- The cracks are covered with a solution of clay.
- The space is filled with expanded clay.
- The heat insulator is covered with a boardwalk.
How to insulate the ceiling in a private house indoors
Internal insulation can be done by one of the following methods:
- gluing a sheet heat insulator with fixation with special elements with a mushroom head;
- laying insulation in cells of a metal or wooden lathing attached to the ceiling.
Carry out the sticker, observing the sequence of operations:
- Prepare the required amount of glue.
- Apply the adhesive with a spatula to the insulation.
- Press the heat insulator against the ceiling for a couple of seconds.
- Drill the mounting holes.
- Insert the mushrooms and hammer in the spacer.
- Fill the gaps with foam.
Fasten the insulation to the crate cells as follows:
- Mark out the ceiling surface.
- Cut and fasten the frame parts.
- Lay and secure the insulation.
- Fill the crevices with foam.
- Cover the surface with a vapor barrier.
- Sheathe the frame with drywall.
- Reinforce the seams and putty the sheets.
- Apply a fine finish.
Summing up
Based on the recommendations presented, you can choose a material for thermal insulation of the ceiling surface. It is not difficult to carry out ceiling insulation with your own hands in a private house, adhering to the technology. A well-insulated home will delight you with a comfortable microclimate and will reduce heating costs.
Table: Comparison of the properties of popular heaters for a ventilated facade
| Parameter | VENTY BATTS | VENTY BATTS D | Value |
| Density | 90 kg / m3 | Top layer 90 kg / m3 Bottom layer 45 kg / m3 | 37 kg / m3 |
| Thermal conductivity | λ10 = 0.034 W / (m K) λ25 = 0.036 W / (m K) λA = 0.042 W / (m K) λB = 0.045 W / (m K) | λ10 = 0.035 W / (m K) λ25 = 0.037 W / (m K) λA = 0.038 W / (m K) λB = 0.040 W / (m K) | λ10 = 0.036 W / (m K) λ25 = 0.037 W / (m K) λA = 0.039 W / (m K) λB = 0.041 W / (m K) |
| Flammability group valve butts | NG | NG | NG |
| Tensile strength for separation of layers, not less | 4 kPa | 4 kPa | 6 kPa |
| Water absorption at full immersion, no more | 1.5% by volume | 1.0% by volume | 1.0 kg / m2 |
| Water vapor permeability, not less | μ = 0.30 mg / (m h Pa) | KM0 | KM0 |
Heat saving as an addition to insulation
To reduce heat loss in a frame house, as in any other structure, one should be guided by the generally accepted rules for saving energy spent on heating:
- An excessively large volume of heated air in the room leads to an overestimation of the energy consumption for the heating system;
- Well-sealed windows and doors will help to keep warm;
- Correct air circulation in a house with a ventilation device also helps to save energy;
- The entrance vestibule or the entrance to the room through the veranda is also a reduction in heat loss;
- Short-term ventilation of the room is more rational and economical than a slightly opened window or window for a long time;
- Traditional installation of heating devices under window openings is not the best solution for saving heat: it is better to place them against the inner walls;
- The distance between the wall and the radiator must be at least 4 cm so as not to disturb air convection.
How to equip a ventilated layer in facade insulation?
If the outer cladding is made of dense vapor-tight sheets, then a ventilated air gap is arranged in the wall. The thickness of the ventilation gap is 60 mm, this is the distance between the outer skin and the insulation boards. Vapor-permeable mineral wool must be covered with a windproof vapor-release membrane.
One of the options for decorating the walls of low-rise buildings is to install a siding protective screen.These thin profiled "boards" are made from metal (metal siding) or PVC (vinyl siding, plastic paneling).
Decorative siding panels can imitate wood planks, masonry, etc. A ventilated air gap is provided between the decorative siding screen.
- When installing siding, vertical guides with a step of 600 mm are attached to the existing frame or wall: from wooden slats 4x6 cm, 5x5 cm, special profiled strips made of PVC or galvanized steel.
- The guides are installed strictly vertically. If the walls are uneven, they are leveled using spacers made of wood, plywood, or the size of the slats is reduced.
- The space between the rails is filled with rockwool LITE BATTS® or Venti Butts thermal insulation boards. If the required thickness of the insulation layer is greater than the thickness of the slats, then they are installed in 2 rows - horizontally and vertically.
- The slats and insulation should be installed so that an air gap remains between the surfaces of the insulation and siding.


To ventilate the air gap and remove diffusion moisture, there are special ventilation holes in the lower edges of the siding panels through which vaporous moisture is removed to the outside.
Note! From the outside, light butts stone wool insulation should be protected with a windproof vapor-permeable material. Siding panels are installed taking into account possible temperature deformations. Therefore, when installing the siding, strengthening the panels to the chamfers and edges, they leave a gap in the winter - 10 mm, in the summer - 6 mm.
Scheme and drawing
A detailed drawing with a supporting element of a frame house in section will help you better understand the technology of its device, determine for yourself the sequence of installation of each layer of the "sandwich" and the location of materials. Also, the diagram will help prevent mistakes when installing such important elements as load-bearing walls and interior walls.


In the drawings, in addition to the connection nodes, the communication wiring diagrams are clearly indicated.
Today, many projects of frame-type buildings with diagrams are made in special programs for a PC, where it is enough to enter some data and the system itself will make a detailed drawing.
The program requires the following parameters:
- the exact location of the external and internal walls;
- the number of indoor spaces;
- the thickness of future walls and materials for their construction;
- type of soil and moisture level, climatic and geological features of the region.
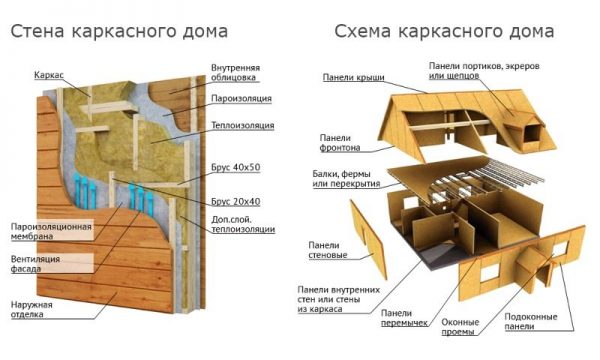

Frame house scheme
The diagram of the future wall includes the following:
- area and type,
- location of openings for doors and windows,
- method of fastening and connecting modules,
- sandwich.
The last point includes the sequence of layers of the "sandwich" and the parameters of the materials used (type, thickness, method of attachment, etc.).
The disadvantage of a drawing developed on a computer is that the electronic brain will not make an estimate for the work and will not analyze the characteristics of the soil and climate to draw up the correct project.