Soldering flux for copper pipes

Few people know what soldering flux means. Gumboil is a substance composed of chemical elements that helps the solder to better fill the joint space. In addition, one of the functions of the flux is to remove dirt and products from the oxidation process, such as boric and hydrochloric acids. Apart from everything, it forms a layer of protective film against air oxygen... It is taking these features into account that it is necessary to correctly choose the types of metal products that need to be connected and substances that will fill the connecting gap, as well as keep the indicators of the temperature heater under control.
Types of flux
- The first type of chemical assistant includes substances that do an excellent job of preventing corrosion. This connective substance consists mainly of substances that dissolve liquid and an element such as phosphorus. As a result of their mutual work, an integral connecting substance is formed. When using this type, the need to use substances that are designed to clean up after the soldering process disappears. It is very profitable and not at all troublesome.
- The second type of flux is a substance consisting of salicylic acid, which is perfectly soluble in organic solvents. In addition to this component of the connecting substance, petroleum jelly, alcohol and gold derivatives can also serve as the basis. If you use this type of flux in use, you can achieve an excellent result in relation to the seams, in addition to cleanliness, they will acquire a neat appearance.
- The third type of soft connector is rosin and sodium boric acid. Sodium salt begins to melt at temperatures ranging from 70 degrees Celsius. It is necessary to pay special attention to the fact that this substance and its melting products are absolutely not harmful to human life and health. You can create connecting substances yourself by mixing all the components into one whole.
Submerged-arc copper soldering
What is the difference between flux soldering?
First you need to understand its differences from conventional arc soldering. So, compared to hand welding, the flux soldering process becomes more efficient. The recoil level increases by about 4-5 times... And this is understandable, since the electric current passes through the electrode wire only at its exit. Therefore, the use of flux in the welding process of copper makes it possible to use a current with increased density. You do not even have to worry about the fact that the electrode will be exposed to prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which will lead to the detachment of the coating material.


Brazing materials for copper pipes
In addition, in the process of applying high currents, the melting depth of the metal product rises to sufficiently high. Even because of this, the soldering process can be carried out without cutting the thickened edge. It is necessary to give credit for the fact that providing high protection of the metal in the molten state from contact with air currents, metal seams and joints are of high quality.

Soldering copper pipes with your own hands
The minimum amount of foreign inclusions is achieved by the absence of pores in the metal seams. There is an explanation for this, the rate of formation of metal crystals increases, since slag formations are present on the coating of the connecting seams.
The disadvantage of using soft connectors is that the molten metal becomes as liquid and fluid as possible.
Before purchasing a flux for copper products, pay attention to its special features. First of all, in order to avoid the formation of a film of oxides, it is necessary to carry out some measures:
- Constantly keep under control the limits of the temperature indicators of the soft connector and solder, it is necessary to ensure that they are the same. When choosing a flux, focus on its performance, depending on the type of solder.
- In the event that an ideal coincidence of temperature indicators is achieved, it becomes possible to use it as a device for measuring temperature changes during the soldering process. Therefore, overheating of the elements during soldering is impossible.
Today, there are dry, pasty and liquid fluxes on sale. In most cases, connectors in a liquid state find their use in a liquid solder process. Dry flux is inconvenient to use. Pasty flux for copper products is quite convenient, since it does not require delay in its application. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of the flux in order to get a high-quality result of the work done.


Quality can be determined by the following features:
- the surface after soldering is completely covered with it;
- has a viscous base and high density, which ensures the availability of solder to the destination;
- protects from the formation of a film, qualitatively cleans it from it;
- has a homogeneous composition of chemicals;
- with its help, all seams are visible during the soldering process;
- using it, the possibility of working in an upright position comes off;
- well removable dirt.
To achieve a high-quality product, it is necessary to get rid of it after the soldering process with the help of solvents intended for this.
Varieties of connections
Low temperature soldering of parts
This technology of brazing copper pipes is used for the installation of utility networks for heating, water supply and other similar systems, where the temperature of the transported liquid does not exceed + 130 degrees Celsius. In this case, the flame from a gas burner heats the product no higher than + 450 degrees Celsius, and the size of the part is 6-108 mm (see also the article "Fittings for polypropylene pipes: types and their technical description").
Various soft metals are used as solder in low-temperature brazing: lead, tin, and so on. It is from here that this method is called "soft soldering". The joint width, depending on the size of the fittings, can be 7-50 mm.
The connection in question is very common when installing various plumbing systems.
This is due to the following factors:
- with low-temperature brazing, copper does not anneal (which affects the strength of the pipeline);
- the process of carrying out work is less laborious and safer;
- applies only to the manufacture of water transport systems;
- cannot be used to connect gas pipelines.

Low temperature brazing uses tin or lead as solder
High-temperature soldering of parts
In this case, the brazing of copper pipes is carried out at a flame temperature exceeding + 450 degrees Celsius.
In this case, a solder is used based on the following metals:
- copper;
- silver;
- other alloys harder than tin.
The use of this technology makes it possible to obtain a permanent connection with increased strength and withstand a much higher temperature of the transported medium.
Another name for the connection is "hard brazing".


The photo shows the high-temperature brazing process
Brazing copper pipes is used in the following cases:
- connection of parts larger than 28 mm;
- docking of parts intended for transporting liquids whose temperature exceeds 130 degrees Celsius;
- manufacturing of heating systems (this method of connection allows you to branch off from an existing engineering network without deteriorating the technical characteristics of the latter).
- the use of solid soldering is provided by instructions for the installation of gas pipeline systems.
Note! During high-temperature brazing, the copper is annealed, as a result of which the pipe loses its strength. To minimize this phenomenon, it is necessary for the joint to cool naturally, and the heating during soldering be as low as possible.
Cold joining of parts
There is also a solderless copper pipe connection. For this, special crimp couplings are used, the design of which is similar to similar products used when working with polymer parts.
Externally, the cold joint is similar to a soldering fitting. However, the former is additionally equipped with rubber seals made of special polymers.
In addition, there is also a detachable connection of copper pipelines. For this, a collet fitting is used.
They are divided into two types:
- for joining hard and medium-hard parts;
- for joining soft and semi-hard products.


Compression fittings can be used for cold connections.
Pastes for soft soldering of copper pipes in Moscow
The "Online Consultant" is available on the seller's website. To go to the site, click "To the store"
One click order is available on the seller's website. To go to the site, click "To the store"
The "Online Consultant" is available on the seller's website. To go to the site, click "To the store"
One click order is available on the seller's website. To go to the site, click "To the store"
A free number 8-800 is available on the seller's website. To go to the site, click "To the store"
The "Online Consultant" is available on the seller's website. To go to the site, click "To the store"
What kind of solder for brazing copper pipes is better to use, types and features of materials
Copper tubular products are used in a wide variety of industries. Gas, oil products, water and other media are transported through pipelines made of it. For the installation of the lines, solder is used for welding copper pipes.


The conditions in which such pipelines are operated can be different - they influence the choice of the type of solder for connecting structural elements.
What is soldering and soldering?
Solder is an alloy or metal that is used to join separate metal parts in order to equip a single system. The technology of joining two parts into a one-piece structure is usually called soldering.
Since solders are used in many industries, they are produced in a variety of forms - this can be wire, rods, foil, etc. The chemical composition of the solder for brazing copper pipes directly depends on the temperature of melting, on the type of elements used, on their parameters and other nuances.


The basis of the solder is the following chemical elements:
For solder, the melting temperature should be lower than for the metals from which the butted parts are made, which are slightly heated during the soldering process and cannot be deformed. Soldering is considered to be a more profitable connection method compared to welding.


Solders in accordance with the melting point are of several types:
- Fusible - from 150 to 450 degrees.
- Medium melting - no higher than 1100 degrees.
- High melting point - up to 1850 degrees.
The first type of solders is used for soft soldering, and the second and third for hard soldering.
What do you need to solder copper pipes? When joining products, in addition to solder, flux is required. It is necessary to protect the bonded surfaces from oxidation.To make the connection strong, you must choose the right solder and flux. The purpose of using solders is to obtain a reliable seam. It is often impossible to do without it when joining pipes for different purposes, including copper products.
What you need to have to solder copper
No expensive copper soldering equipment or special consumables are needed, everything is very simple.
To solder copper pipes for home use, you will need the following:
- Heating element in the form of a gas burner for heating and melting the solder. The most commonly used propane gas is regulated pressure. You can use a more powerful soldering iron or a hair dryer with decent power.
- Special cutter for copper products. Copper is a very soft metal, so you need to cut it with tenderness because of the risk of crushing the walls. Such cutters are called pipe cutters, they are of a huge variety - for every taste. There is a wide variety of models on the market, including devices for cutting in the most inaccessible places.
- Solder fittings if bends of unannealed tubing are expected.
- A pipe expander is also a special device to enlarge the diameter of a copper pipe before heating, if necessary. This possibility is extremely important when products with dimensions that are slightly different in size are joined.
- The so-called "beveling device" is a device where the name speaks for itself. It's about chamfering from the end sides of the tubes. The fact is that after cutting, metal burrs can form at the ends. They are not at all harmless, but on the contrary, they will not allow to form a strong and beautiful butt joint. Bevellers are of two types: pencil-shaped or round in shape. Round are preferable and more convenient to use: they can be used to remove burrs from soft copper products with a diameter of up to 36 mm.
- Brushes and brushes with steel bristles for preparing copper parts: removing dirt and oxide film.
- Consumable material for the solder itself. Solders for brazing copper pipes can be of two types of wire: copper wire with a high melting point, which contains a small proportion of 6% phosphorus. The second option is tin wire, whose melting point is much lower - about 350 ° C.
- Pastes and special flux mixtures to protect metal from the formation of defects in the form of air bubbles and better adhesion between the copper of parts and the solder.


Additional things to the basic tools for brazing copper pipes will be non-specific tools:
- measuring tape or tape measure;
- building level;
- marker and brush;
- hammer.
Before starting pipe soldering, it is necessary to solve a fundamental technological question: what kind of solder will be soldered? Copper wire hard solder, which is more commonly used in air conditioners and refrigerators?
Or use tin wire that works great with heating pipes or plumbing?
Brazing copper pipes
Due to the fact that copper is weakly susceptible to corrosive processes, it is easy to solder. Tin, silver, other alloys and metals are the best in contact with it during the docking process.
Capillary soldering is used to connect copper products. It is based on the ability of a liquid, due to adhesion, to move along narrow channels, including against the direction of gravity. Due to the phenomenon of capillarity, the solder is able to uniformly fill the gaps, regardless of how the pipes are positioned.

In this case, the soldering process can take place using light-, medium- and high-melting alloys. Due to the first type, low-temperature brazing is performed, and the other two - high-temperature.The choice of solder is based on the conditions in which the finished pipeline will be used.
The low-melting type, also called soft solder for brazing copper pipes, includes tin and its alloys: tin-copper, tin-silver, tin-copper-silver. Solders, the main component of which is lead, belong to the same type, but they are toxic and for this reason they cannot be used when laying pipelines for supplying drinking water.
Brazing technology for copper piping
Copper pipes are used for the installation of various communications: water pipes, heating systems and gas pipes. They have a number of advantages, such as:
- are resistant to the destructive effects of corrosion;
- the surface of the copper pipes is rather smooth;
- resistant to ultraviolet radiation;
- have a high coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- able to withstand high temperatures;
- have good strength;
- the operational life of a copper pipeline reaches 50 years.
Note! The main disadvantage of such a pipeline is its relatively high cost, however, copper material remains popular as it is very reliable and durable.
Soldering is used to connect the individual elements of the copper structure. Its varieties are as follows:
- high temperature soldering;
- low temperature soldering.
The high-temperature brazing option is used to obtain a joint with increased strength. Low-temperature brazing is used in all other cases.
How to choose a solder
Despite the fact that soft solders are considered not strong enough, when using capillary welding, a high-quality sanitary structure can be obtained. Low-melting solders are used for joining copper pipe products with a diameter of 6-180 millimeters. They are preferred because they work at low temperatures. The fact is that copper at high temperatures is capable of losing strength.
All solders belonging to the medium and high melting type are of the solid type. For high-temperature brazing of copper products, solders based on copper, silver and other metals are used. Thanks to their use, a seam is obtained that is durable and resistant to high pressure and high temperatures.


Among them, the most in demand:
- copper-phosphorus;
- copper-silver-phosphorus;
- silver.
In the latter case, not only solder is required, but also a flux paste for brazing copper pipes.
The essence of the process
The pipeline, created in this way, due to the use of copper pipes during its installation, is distinguished by high reliability and exceptional durability. Of course, such a system has a fairly high cost, but it is fully justified by the unique characteristics it possesses. What is important, copper pipes can be used both in plumbing and heating systems. And in fact, and in another case, they demonstrate the highest reliability and durability.
The simplest and most reliable way to install such systems is to braze copper pipes. This connection technology has been used for a long time, it is well studied and does not cause any particular problems in practical implementation. The essence of this method is that the joint between the parts to be joined is filled with a special compound called solder. In order for the solder for brazing copper pipes to enter and fill the joint between the parts, it is melted under the influence of high temperature. After the heating of the solder stops, and it has already completely filled the future seam, it solidifies, forming a reliable, sealed and durable connection.
Brazing copper is also convenient in that, if necessary, the connected elements of the pipeline can always be easily disconnected.To do this, it is enough to heat the joint to make the solder soft and pliable.


Copper pipe brazing process
Pros and cons of different types of solders
An important advantage that brazing alloys have is directly related to the strength of the resulting seams and their resistance to high temperatures. Using high-temperature brazing, copper pipes with a diameter of 6 to 159 millimeters are joined. When laying water supply lines, the cross-section of pipe products connected by this type of soldering cannot be less than 28 millimeters.


As practice shows, of the soft solders for joining copper pipes, tin-copper is the most popular, and among hard solders, copper-phosphorus is often used. Different companies have different manufacturing technology and the percentage of components.
Before you start creating a copper pipeline, you should make sure that there are no defects on the surface, which can often be found when cutting pipes. The reliability of the seams largely depends on the cleanliness of the products that are used in the working process. For products with a diameter of 6-108 millimeters, the width of the joint can be 7-50 millimeters.
Gas stove
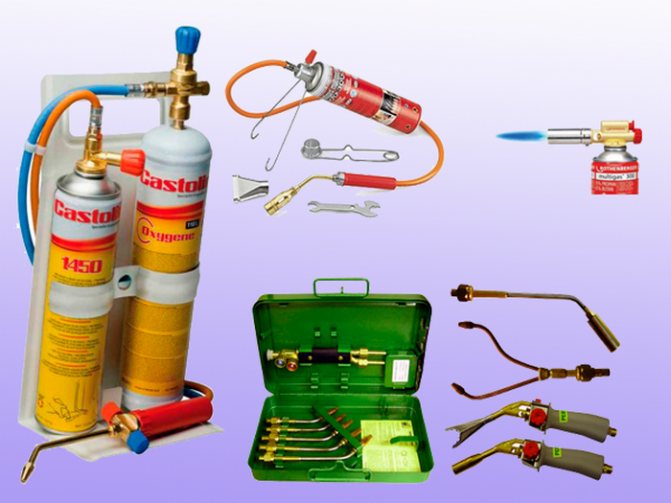


In order to properly solder copper water pipes, you need to prepare the appropriate type of burner. They are divided into several types:
- A device with a disposable cylinder for domestic use;
- Burner with installed stationary cylinder;
- Oxyacetylene torch suitable for brazing copper pipes. It is she who needs to be found to perform the work.
In turn, a torch for melting solder and brazing copper may differ in power. You need to choose depending on what kind of solder you will work with (soft or hard).
- For soft soldering, you can take a low-power semi-professional torch with a hot air gun. Such a tool develops temperatures up to 650 degrees while burning a flame. A distinctive feature of such a device is that here it is possible to regulate the temperature of the flame supply, and at the same time it will remain set-stable.
- Brazing of copper pipes of a water supply system can be carried out only with professional burners.
Copper soldering flux
Copper is recognized as the most reliable metal product and is used in many industries. At the same time, there are obvious drawbacks to the operation of copper, despite the high mechanical and technical characteristics and the flux for brazing copper will help eliminate the problems of malfunction of the same copper plumbing system. The main task of using paste for soldering copper is the formation of a protective film against environmental influences, in particular oxygen.


Features of soldering copper with flux
In many Western European countries, copper pipes have long been used as the main components of the water supply and heating systems. Damage to a copper pipe is an unpleasant little thing, but a flux for soldering copper wires will help get rid of the root cause of the malfunction. Let's try to figure out what types of flux are available in practice:
- The first and main category of the copper soldering flux group includes those components that perfectly cope with the manifestation of corrosion. This group includes all components that dissolve in a liquid, as well as in phosphorus. As a result, a whole substance is formed, which ultimately provides for an exception to the rules for cleaning the surface of the product after the soldering process. In most cases, this copper soldering flux is the less costly and most cost effective option.
- The second group of components of fluxes for brazing copper pipes is presented as a substance where salicylic acid is used in the composition, which is dissolved in organic compounds.In addition, this group includes substances and materials that are components or derivatives of petroleum jelly, alcohol and even gold material. Using this type of flux for soldering copper with our own hands, we can achieve an ideal indicator of the condition of the seams, as well as the cleanliness and neat appearance of the treated surface.
- The third and perhaps the most popular group contains rosin or sodium boric acid. The last chemical component begins to undergo melting, starting from a temperature of +70 C. In this case, both rosin and boric acid do not pose a specific threat to human life and health.
P.S
A few tips for those who decide to use flux when welding (brazing) copper pipes:
- Buy several formulations of different types and shapes and try them to determine which one is best for your activity.
- Do not pursue a low price and choose products from those manufacturers whom you trust.
- You can ask experts with experience for advice (for example, in the comments under this post).
We wish you good luck in choosing and using flux for brazing copper pipes!
What should a copper pipe soldering flux look like?
As you can see from the above, in order to choose a flux for brazing copper, it is necessary to study in detail the specification of each component, and at the same time, it will be necessary to follow some precautions and general rules of application:
- Flux paste for soldering copper must ensure the uniformity of the area of the processed surface of the product.
- The viscosity index of any component of the flux should be much lower than that of the solder, that is, the preparation should melt earlier than the solder and ensure uniform filling of the entire space of the workpiece. Complete replaceability is the main criterion for the indicator of the interaction of flux and solder.
- The oxide film must completely dissolve and protect the metal from the secondary oxidation process.
- The seam processed with solder paste for copper must have a presentable appearance and not create inconveniences for further operation.
- Chemical stability of the substance. During the heating process, the flux should not decompose in any way.
- At the end of the technological work, the sludge residues must be removed.
- It is allowed to use paste for soldering copper pipes in a vertical position.
Flux options for copper materials
The industry today produces several options for fluxes that are used for specific industrial operations. As a rule, these are 3 main groups:
- Liquid category. It is used in special tubes, they go together with soft solders.
- Powder category. They are stored in special containers, used in conjunction with medium and reinforced group solders.
- Gumboil in the form of a pasty substance. This is a ready-made version of the flux that is used as a solder and as a means of processing and applying the solder to the surface.


Next, we take into account the intended purpose of the component for a specific category of production work, in particular:
- Preparations with anti-corrosion properties. The component of the drug includes solvents, as well as the composition of phosphorus. During the heating procedure, a kind of connection occurs, where organic components are formed. At the end of technological work, it is necessary to remove sludge without using special technologies, that is, in the usual way.
- Drugs with high frequency characteristics. As a component, gold or other materials of the noble group are used - ethanol, petrolatum, and salicylic acid. As a result, a smooth and perfect seam is formed, which does not require additional processing.
- Activated group fluxes. This category includes substances of the most popular groups - borax, as well as rosin.Borax already at a temperature of +70 C begins to melt, without emitting dangerous secretions.
For the latter group, it makes simple requirements, in particular, it is recommended to prepare preparations directly at the site of technological operations. So, rosin must be mixed in portions with salicylic acid or anhydride (the use of diethylamide and aniline is allowed).
Soldering process what you need to know
In the process of soldering, you need to remember the following.
The supplied current will move only at the departure, this will allow at least 5 times to increase labor productivity in comparison with manual arc welding. "
The use of welding currents in this case, which have a high density, will not cause the so-called peeling of the coating, and, consequently, overheating of the working electrodes in the final process of departure. If we use thick metal blanks, then it will not be necessary to carry out the section of the existing edges, since the penetration will be carried out completely to the depth.
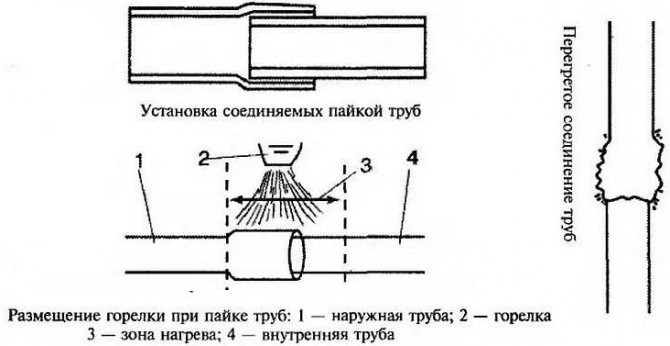
For copper pipes, the following requirements must be observed during the brazing process:
- It is desirable that the flux was originally a derivative of the solder. In this case, it will be possible to achieve maximum uniformity of melting of all components of the flux and solder. This factor allows the specialist to fully control the heating workflow, and thereby regulate the production cycle of welding.
- If you use solder and flux that match in terms of melting temperature, then the last parameter is used to control the temperature of the soldering process. Here we will be able to minimize the loss of the brazing process, as well as possible damage to workpieces and other components.
The best option, albeit an expensive one, will be the use of a flux paste, which is at the same time a propoyem and a material for processing the preliminary soldering of the product surface.
There is one more important point, the formation of slag, which accompanies this process. In this case, the surface of the weld will increase crystallization, which in turn will significantly reduce the number of visible voids, as well as the appearance of deposited particles in the deposited substance. The disadvantage of this process is the increased fluidity. But despite this, the speed and quality of surface treatment will cover all possible disadvantages of soldering copper blanks.
Work process
Given the high cost of soldering copper pipes (in case you hire a specialized team of plumbers for this), it is possible to recommend doing all the work yourself, especially since the price of semi-professional gas burners makes them quite affordable.
Let's consider in more detail each of their connections.
General points
The heating of the pipe and solder during low-temperature brazing of copper pipes is carried out using a gas burner.
Various gas mixtures are used as fuel:
- air-propane-butane;
- air-propane;
- air-acetylene.
Note! In some types of work, the use of an open flame is not allowed. Then heating is done using electricity. This does not affect the speed of work, but this way only small diameter products can be joined.
With regard to solid brazing, here it is possible to achieve the desired temperature only with the use of an open flame.
Sufficient heating can be achieved using the following fuels:
- air-acetylene;
- oxygen-propane;
- oxygen-acetylene
The latter combination is used for direct welding of acetylene pipes (no solder). The flame temperature in this case should reach the melting point of copper (from 1070 to 1080 degrees Celsius).
In hardware stores, there are many devices with which you can solder copper pipes.
They can be divided into two main categories:
- portable burners with disposable cylinder for home use;
- versatile gas burners designed for large capacity and professional work.


Gas burner with disposable cylinder
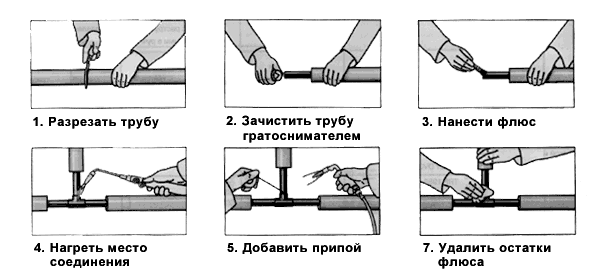
The general scheme for welding copper pipes is as follows:
- cutting the pipe and cleaning the end from the burrs that have appeared;
- cleaning to a characteristic copper luster of the inner and outer part of the pipe on which the fitting will be put on;
- control of the location of the connectors and the gaps between them and the pipe;
- applying flux to the outside of the pipe (not necessary in all cases);
- assembly of the connecting unit;
- heating of the docking point;
- filling a special mounting gap with the used solder;
- stopping heating;
- gradual cooling of the seam;
- removal of flux residues and excess solder.


Copper pipe cutter
Pipe preparation
Copper parts are cut using the following tools:
- a special cutter - it does not form burrs, but can lead to a decrease in the inner diameter of the part due to bending inside the edges;
- hacksaws for metal - does not form a bend, but a lot of burrs appear at the junction, which must be disposed of before soldering.
Note! Edge jamming (when using a cutter) reduces the outer diameter of the pipe and, accordingly, increases the mounting gap. As a result, after soldering, the connection will not be airtight. According to the instructions, the size of the mounting gap can be 0.02-0.4 mm.
The end of the pipe after cutting must have a strictly round shape. A hand-held calibrator helps to achieve this. Its use guarantees the correct size of the mounting gap.


Pipe calibrator
The flux should be applied to the pipe immediately after it has been stripped. It is strictly forbidden to lubricate the inner surfaces of the connecting fitting with this substance.
As soon as you apply the paste, the parts must be connected immediately, otherwise dust or other foreign particles may get on the wet end. It is necessary to push the pipe into the socket until it stops, slightly rotating the fitting around its axis, which allows achieving a more uniform distribution of the flux. Before heating, the remaining paste on the pipe must be removed.
Soldering flux for copper pipes
Features of heating in low-temperature brazing
To work you will need:
- flux for soft soldering;
- propane burner;
- gas mixture.
Soldering copper pipes with tin solder can be done with a special soldering iron, which also heats the fitting.


The flux is applied only to the outside of the pipe
The work is carried out in the following sequence:
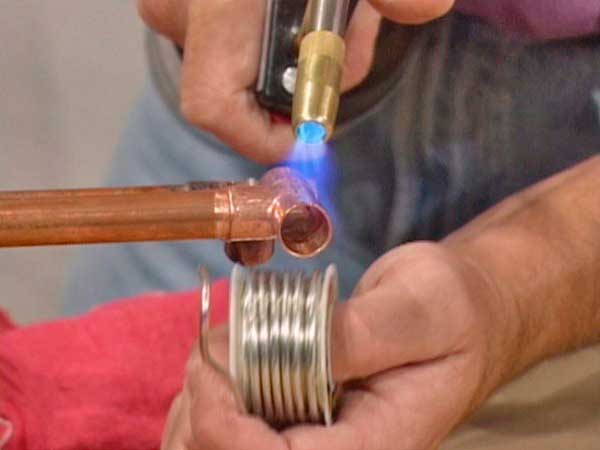
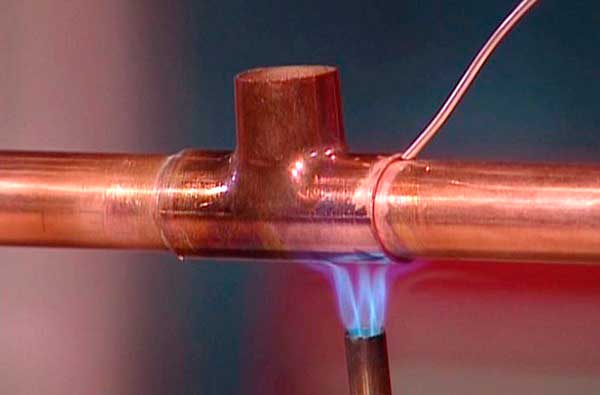
- The flame of the burner must be constantly moved around the joint, performing uniform heating of the entire part.
- Touching the end of the solder to the mounting slot, you need to check if the tin begins to melt. If not, heating continues.
- Once the solder has melted, the heating must be stopped to allow the tin to fill the capillary gap in the fitting.


The solder must completely fill the mounting gap
The tightness of the connection is ensured by the fact that the solder, melting, fills the gap between the fitting and the pipe.
Note! With low-temperature brazing, heating should stop immediately after the substance begins to fill the mounting gap. Failure to do so may overheat the joint, which will reduce the strength of the pipeline.
As soon as the solder melts, it is necessary to allow the joint to cool on its own, since soft tin is a very fragile substance.
During soldering, it is important to avoid overheating of the parts, otherwise the flux may deteriorate and will not be able to remove the resulting oxides.
Instead of a torch, you can use a special electric soldering iron, which consists of electric tongs and a power supply. The sequence of operations in this case does not differ from the above.
Sequence of operations for solid brazing
For operation, burners must be used that run on propane or acetylene mixed with oxygen.
During work, you should pay attention to the following nuances:
- Heating must be done quickly but evenly... The burner must be constantly moved along the entire length of the fitting.
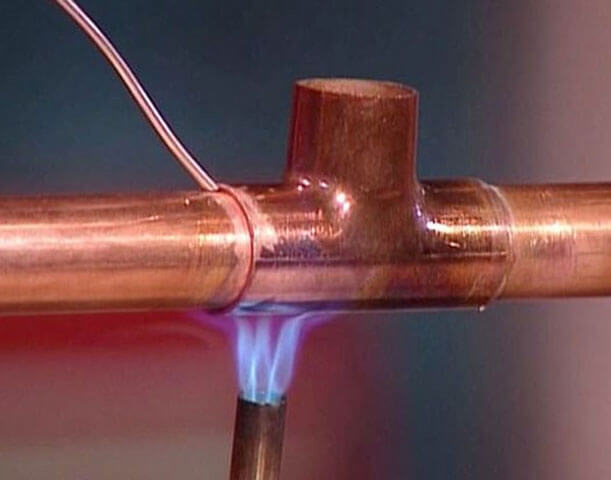
- The flame should be bright blue... The parts are heated to a temperature of 750 degrees Celsius (they acquire a characteristic dark cherry color).


Burner flame should be bright blue
- If the heating has been done correctly, the solder that is being fed to the mounting hole should start to melt.... You can preheat it in a burner flame.
- The essence of the work is that it is necessary to achieve the lowest possible heating temperature at which the solder begins to melt. It is desirable that the solder immediately fills the capillary hole with a single touch of the fitting.
Once the connector has cooled down, carefully remove all flux residues from the pipe. If a water supply system was installed, all pipes must be thoroughly rinsed to remove the flux inside. It is a harsh chemical that can harm human health.


Do not forget to thoroughly clean the junction from the flux
Cold join
The technology of connecting soft copper pipes using press fittings does not cause difficulties and comes down to a few simple sequential steps:
- cutting the pipe to the required size;
- deburring the butt end and giving it a round shape;
- inserting a press fitting into the pipe;
- pipe connection using a slip-on sleeve (special pliers are used).


Connection diagram with press fittings