Features of protective finishing of ovens
With regular use of the oven, all materials from which it is made are exposed to very high temperatures. They depend on the combustion temperatures of the specific substances that are used as fuel. Of course, the walls of the stove are made of refractory materials, but extreme thermal influences change their structure and properties, which leads to gradual destruction. It is to protect against such influences that the lining is used.
The lining will be the best internal protection of your hearth from burnout and other damage.
Purpose of lining
The key and main task is to reduce the impact of an aggressive external environment on the surface of pipes, furnaces, boilers, drums, wells and mills. Since the impact varies, there are several types of finishes: resistant to high temperatures, to chemicals, including acids, which provide thermal insulation.
In the creation of the coating, metal, general industrial rubber, basalt, polymers, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, as well as cement and glue compound are used.
Get a full consultation by number.
In what cases does it apply
If we are talking about a small hearth, which is used periodically - for heating a country house on a weekend or for cooking in the fresh air (barbecue), then additional protection is not needed here. In such cases, if damage occurs, then they are minimal and will not damage the device in the near future.
Mandatory lining is required for the following types of combustion products:
- Large household and industrial.
- Designed for very long-term use - for example, constant heating of the home.
- Heat chambers, which are arranged for regular cooking in "Russian" and other similar stoves.
- Fuel units, the smoke channels of which are arranged directly along the walls of the furnace.
- In cases where high calorific value fuels with an extremely high combustion temperature are used.
Materials used
Having learned what a lining is, it is necessary to consider in more detail the materials for its construction. The materials used for the lining of furnaces and boilers can be divided into three main classes:
- Class A - artificial or natural materials based on silica
- Class B - classic materials based on clay
- Class C - it includes all the remaining options and various refractory solutions
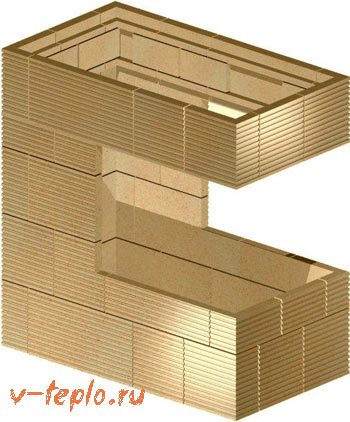
Specific examples
The inner surface of the furnace can be protected by a variety of methods:
- Fireclay brick masonry
- Application of non-flammable mixtures
- Installation of protective screens
It is recommended to install screens when installing metal sauna stoves. In other cases, it is ineffective, as it will lead to a waste of thermal energy.
Having chosen brickwork, it is not recommended to use a classic brick - it quickly collapses and requires replacement. Before the advent of fireclay materials, M-300 brand products were used. They are relatively reliable and durable, but still inferior in efficiency.
It is recommended to use fireclay bricks falling under GOST 390-96.
Lining types
Lining works are carried out directly inside the firebox of metal, stone and brick devices. This can be done in different ways, depending on what effect is expected and what goals should be achieved:
- It is possible to use special protective screens with heat-insulating action.They will affect the percentage of flue gas heating, absorbing a significant part of the radiant heat fluxes and removing most of the heat through the chimneys.
- The use of materials that will take most of the thermal effect on themselves - fire-resistant with low thermal conductivity, slowing down the heating process of the furnace materials and excluding their direct contact with fire.
Lining work in a brick firebox is carried out by laying out brickwork
ATTENTION! Heat-insulating screens significantly reduce heat transfer, therefore they are not used for furnaces intended for heating rooms.
Lining Embodiments
Lining of the fireplace insert with fireclay
The procedure is carried out in different ways, the most suitable is chosen taking into account the material from which the stove or fireplace is made. Also, the choice is influenced by the time of laying the facing layer.
Fireclay materials are considered the most popular method for lining heating appliances. Chamotte is a special clay fired at a maximum temperature of up to 1500 degrees. After the heated natural material is crushed, then panels, bricks or dry mixtures are made from it. Buyers are more likely to choose fireclay materials because of their quality, effective use and affordable cost.
It is advisable to install screens that reflect thermal radiation on the walls of metal sauna stoves. When used in other types of furnaces, the low efficiency of the screens may mean that they were installed incorrectly. The generated heat will not completely warm up the walls and instead will start to go into the chimney, taking into account the modernization of the system.
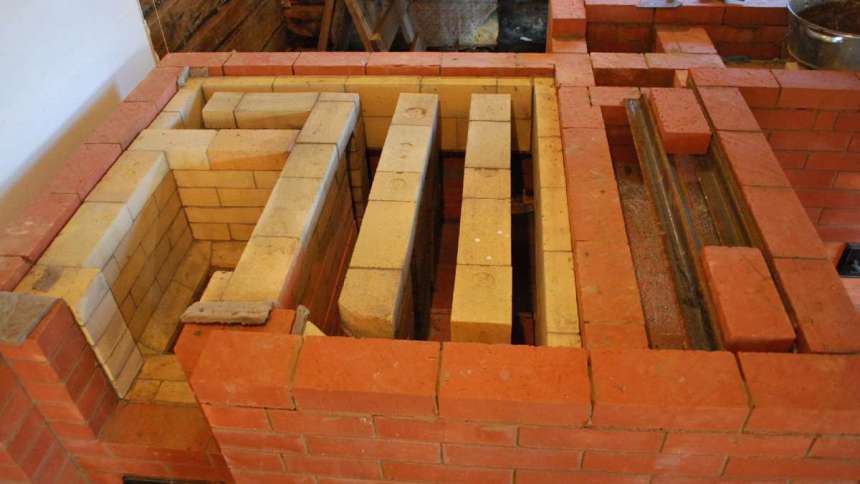


Stones made from natural rocks belong to class A materials, most often sandstone, quartz or granite is used for facing. It is recommended to use them for lining fireplace inserts, not stoves, since these materials have a low level of thermal conductivity and crack under the influence of strong fire.
Special plates and roll materials are suitable for surfaces with low thermal conductivity. Lining of this type can be carried out during the construction of the furnace or in an already finished heating device.
Substances or solutions with increased resistance to fire are applied to the inner surfaces of the walls of furnace furnaces. These can be dry mixes, from which a fire-resistant mortar must be prepared, or a heat-resistant adhesive mass, also used for fireclay masonry and brick walls.
Lining mortar Silicon carbide refractory Heat reflective shield
Methods of execution
The lining of the hearth is usually carried out with the help of so-called "fireclay" materials - specially treated substances and their mixtures with the inclusion of firing elements, destroying the plastic properties and bringing their particles to sintering, as well as other refractory products. It can be:
- Hewn stone made of natural rock such as sandstone or quartz, or conglomerate, resistant to particularly high temperatures.
- Finished fireclay bricks, from which the inner wall is laid. Their refractory properties are achieved due to a special manufacturing technology with the addition of powder from pre-fired clay and other substances that improve the properties of the final product. Protection from such a brick is very popular, as it can withstand almost any temperature of the heating furnace and is relatively cheap.
- Roll materials, plates and mats: basalt fiber,
- vermiculite boards,
- kaolin in the form of paper or cardboard, consisting of mineral white clay.
- fireclay, which are refractory concretes with the addition of a lean component,
Vermiculite finishes can be a great alternative to brick and stone
What is liner?
The lining of the furnace is the internal lining of the furnace structure, in which lining bricks are used. The main quality is heat protection, fire resistance and prolongation of the service life of the furnace and firebox. Lining is carried out not only from bricks, other materials are used. The classification depends on the substances that the furnace produces in the course of its work. There are 3 types of refractory materials:
- sour;
- basic;
- neutral.
All finishing works are carried out only after project approval of drawings and selection of materials by a civil engineer. The materials for the lining of the product are the protectors of the fuel part and the furnace itself from mechanical and chemical effects. Thus, this facing of a stove, fireplace or boiler serves to protect the walls and roof of the structure from the effects of high temperatures during the operation of the mechanism.
Comparison table of lining materials
IMPORTANT! In production conditions - at metallurgical and other enterprises where the processing of raw materials and finished products by the hot method is used, the furnace protection is most often made of stone or fireclay bricks. In a “cramped” home, alternatives are more acceptable.
Features of lining protection
Furnace lining is a special surface finish of the product to protect it from possible damage during operation, which is the result of thermal, mechanical, chemical and other effects. Furnace equipment lining is designed to extend the service life of the walls and other parts of the furnace.
With regular use of the oven, all materials from which it is made are exposed to very high temperatures. They depend on the combustion temperatures of the specific substances that are used as fuel.
Of course, the walls of the stove are made of refractory materials, but extreme thermal influences change their structure and properties, which leads to gradual destruction.
It is to protect against such influences that the lining is used.
The lining will be the best internal protection of your hearth from burnout and other damage.
If we are talking about a small hearth, which is used periodically - for heating a country house on a weekend or for cooking in the fresh air (barbecue), then additional protection is not needed here. In such cases, if damage occurs, then they are minimal and will not damage the device in the near future.
Mandatory lining is required for the following types of combustion products:
- Large household and industrial.
- Designed for very long-term use - for example, constant heating of the home.
- Heat chambers, which are arranged for regular cooking in "Russian" and other similar stoves.
- Fuel units, the smoke channels of which are arranged directly along the walls of the furnace.
- In cases where high calorific value fuels with an extremely high combustion temperature are used.
Lining types
Lining works are carried out directly inside the firebox of metal, stone and brick devices. This can be done in different ways, depending on what effect is expected and what goals should be achieved:
- It is possible to use special protective screens with heat-insulating action.They will affect the percentage of flue gas heating, absorbing a significant part of the radiant heat fluxes and removing most of the heat through the chimneys.
- The use of materials that will take most of the thermal effect on themselves - fire-resistant with low thermal conductivity, slowing down the heating process of the furnace materials and excluding their direct contact with fire.
Lining work in a brick firebox is carried out by laying out brickwork
Methods of execution
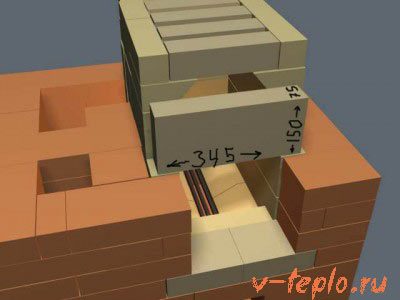

The lining of the hearth is usually carried out with the help of so-called "fireclay" materials - specially treated substances and their mixtures with the inclusion of firing elements, destroying the plastic properties and bringing their particles to sintering, as well as other refractory products. It can be:
- Hewn stone made of natural rock such as sandstone or quartz, or conglomerate, resistant to particularly high temperatures.
- Finished fireclay bricks, from which the inner wall is laid. Their refractory properties are achieved due to a special manufacturing technology with the addition of powder from pre-fired clay and other substances that improve the properties of the final product. Protection from such a brick is very popular, as it can withstand almost any temperature of the heating furnace and is relatively cheap.
Roll materials, plates and mats:
- basalt fiber,
- vermiculite boards,
- kaolin in the form of paper or cardboard, consisting of mineral white clay.
Solutions and substances that cover the walls of the furnace:
- fireclay, which are refractory concretes with the addition of a lean component,
- mullite - silicate liquid glass mixtures with different compositional variations.
| Materials (edit) | Specific weight of the product (density), kg / m3 | Possible operating temperature, max., 0C |
| Ordinary clay brick | 1600 | 700 |
| Basalt cotton wool | 100 | 750 |
| Vermiculite layer | 150-250 | 1100 |
| Chamotte (mortar or ready-made brick) | 1800-2000 | 1300 |
| Kaolin is dense | 2400-2500 | 1400 |
| Mullite (clean / mats) | up to 3030 | 1800 / 1600 |
IMPORTANT! In production conditions - at metallurgical and other enterprises where the processing of raw materials and finished products by the hot method is used, the furnace protection is most often made of stone or fireclay bricks. In a “cramped” home, alternatives are more acceptable.
My own master
Of course, for the installation of a lining layer in a home, you can resort to the services of specialists, but with some work skills and appropriate knowledge, this operation can be carried out independently.
Do-it-yourself lining of the furnace from fireclay bricks is performed taking into account the following features:
- The brick is neatly laid out "edge to edge", without shifting the masonry elements relative to each other, along all the walls of the internal firebox.
- The joints between the individual bricks are filled with a mortar based on chamotte and clay.
- If the main masonry is also made of bricks, then the lining and the main layer are joined by means of one vertical seam, but without bandaging.
- If the material of the furnace itself is metal (cast iron or steel), then a small gap should be left between its walls and the masonry, designed for the thermal expansion of the metal, otherwise regular heating and cooling can soon destroy it.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with the Rating of solid fuel heating boilers for a private house: top-13
Finishing with fireclay bricks occurs according to the scheme - along all walls with a gap, taking into account the expansion of materials
ATTENTION! It is also possible to masonry with fireproof red bricks, but it is impossible to mix types of bricks (fireclay plus refractory), since they have different indicators of linear expansion and thermal conductivity, which will make the building short-lived.
Old fireclay brick masonry is subject to regular inspection and repair of worn-out areas, which is carried out by grouting with a mortar of fireclay and alumina cement.
The advantage of using roll materials (as well as plates and mats) is that they take up very little space and do not "steal" the total volume required for fuel filling and smoke passage. The standard thickness of most of them does not exceed 1 cm (for example, thick kaolin cardboard is up to 7 mm thick). To carry out the necessary work, you need to remember that:
- The amount of materials required for the lining is calculated taking into account their linear expansion during heating.
- In some cases, it is possible to lay the canvas in 2 layers, but for household needs this is not at all necessary.
- The individual plates are attached with reinforcement elements - metal pins that are inserted into pre-made grooves.
- When finishing with refractory mats or plates, the sequence of their attachment should be observed: first, the bottom is covered, then the side surface, and then the “ceiling” of the furnace section.
Coating with solutions
Coating with refractory mortars results in an even thinner lining layer. This method is characterized by the following nuances:
- For the preparation of solutions, dry compositions of chamotte, mullite or corundum mixtures are usually used, which are then diluted with water to the desired consistency.
- After application, the solution must be fired under natural conditions (when the oven is operating) or using a blowtorch. In the second case, work is carried out until a hard crust appears.
Any coating can wear out over time. Even the strongest liner inside your firebox can gradually lose its initial tightness. To preserve it, consider the following:
- The internal protection of the oven needs periodic inspection for integrity. Damage should be repaired in time with solutions prepared from a mixture of chamotte and clay.
- Surfaces that are initially made of better quality (even sealed layer of uniform thickness without cracks and other damage) will last much longer.
ATTENTION! The installation of the lining is a complex engineering task that is best entrusted to knowledgeable people, that is, to carry out the work under the supervision of a specialist or to leave it completely in the hands of professionals. High-quality performance of this important work will allow you to forget about repairing the hearth for a long time.
Furnaces designed for heating residential premises can have different shapes, sizes, and other design features. Based on the purpose and technical characteristics, a decision is made on the need for facing the fireboxes.
When required
Fireplaces of small household stoves that operate in the usual mode are not recommended to be lined - this way they better cope with the tasks of heating the premises with low fuel consumption.
Furnace lining may be required for the following product types:
- Furnaces designed for long-term use.
- Furnaces that use high-calorific fuel.
- Large household stoves.
- The fire chambers of Russian stoves, which are used for cooking.
- Stoves in which smoke channels are located along the walls of the firebox.
The ways
Furnace cladding can be internal or external. The inner one protects the firebox of the stove from overheating, the outer one is designed to give a decent appearance.
The interior is made of refractory materials that can withstand high temperatures for a long time.
The brick is laid out on the edge along the walls of the firebox, while the masonry of refractory bricks is joined to the main masonry of the firebox with one vertical seam, but is not tied.
This method allows you to protect the walls of the firebox from overheating and significantly extends the life of the stove.
Depending on the purpose of the furnace for finishing, protective screens can be used that can absorb radiant fluxes. If the stove is used for cooking, such screens are installed inside the firebox, where they contribute to the rapid heating of flue gases or air supplied to the firebox.
Brick lining
Do-it-yourself lining of the furnace from fireclay bricks is performed taking into account the following features:
- The brick is neatly laid out "edge to edge", without shifting the masonry elements relative to each other, along all the walls of the internal firebox.
- The joints between the individual bricks are filled with a mortar based on chamotte and clay.
- If the main masonry is also made of bricks, then the lining and the main layer are joined by means of one vertical seam, but without bandaging.
- If the material of the furnace itself is metal (cast iron or steel), then a small gap should be left between its walls and the masonry, designed for the thermal expansion of the metal, otherwise regular heating and cooling can soon destroy it.
Finishing with fireclay bricks occurs according to the scheme - along all walls with a gap, taking into account the expansion of materials
ATTENTION! It is also possible to masonry with fireproof red bricks, but it is impossible to mix types of bricks (fireclay plus refractory), since they have different indicators of linear expansion and thermal conductivity, which will make the building short-lived.
Old fireclay brick masonry is subject to regular inspection and repair of worn-out areas, which is carried out by grouting with a mortar of fireclay and alumina cement.
Do-it-yourself furnace lining
Do-it-yourself lining of the furnace, made with fireclay products, will be strong, durable and effective, only with the use of a special solution. The best option is ready-made dry mixtures for lining furnaces with your own hands, adapted for chamotte and tested for laboratory operation. Heat-resistant and refractory compositions for masonry are available on the market in an assortment, and prices are quite affordable, and experiments with lining are more expensive, since the repair and restoration work of heating structures is a laborious and time-consuming business.
Lining with fireclay bricks
Ready-made dry mixes for lining have manufacturer's instructions on the packaging and information on the exact purpose of the composition. The cladding of furnace sections of furnaces requires refractory mixtures, and for other sections, heat-resistant solutions can also be used. Refractory compositions are much more expensive, but only they should be used for lining furnaces, especially since a little solution is required - you can take at the rate of 70 kg of dry matter per 100 pieces. bricks.
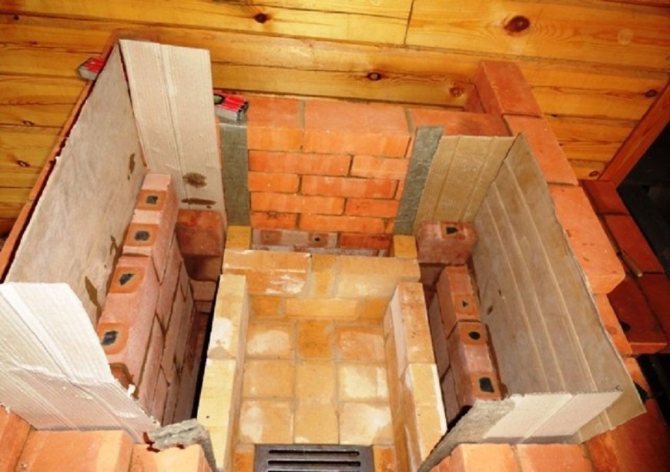


When lining with fireclay bricks, it should not always be soaked before laying, but in certain cases:
- Dry brick quickly absorbs water from the mortar, as a result, the mortar seam sets faster and loses its plasticity. It is very difficult to tweak something, so a good masonry skill is required. If the brick is soaked before work, then it is possible to obtain an additional resource for correcting errors in the masonry by extending the mobility of the mortar mixture.
- When reusing bricks from dismantling old stoves, soaking opens the capillaries and pore structures of the brick, into which dust and solutions have gotten during the service. Moisture and solutions as a result of moistening more easily penetrate into the brick, the adhesion and strength of the masonry increases.
- During summer masonry work, when the air temperatures are high, it is recommended to soak the brick for a short time before laying it.In autumn and winter, this procedure becomes unnecessary and harmful, since waterlogged bricks in the masonry must be dried, and it is unacceptable to heat the stove before natural drying and setting of the mortar in the seams of the masonry - this can cause deformations in the seams of the masonry and reduce its strength. Sometimes drying is carried out using heat from a powerful electric incandescent lamp with all the doors of the stove fully open.
Dry fireclay brick for masonry is preferable, therefore, instead of soaking the brick, you can make the mortar mixture a little less thick in order to have a short time to straighten out possible flaws in masonry work.
Lining with refractory adhesives and pastes
Alternatively, the use of refractory aluminosilicate glue rather than fireclay mortars for linings has invaluable advantages. These compositions are used not only for linings of household furnaces as masonry and coating solutions, but also in metallurgy. use high-temperature adhesives for the installation of products made of basalt and kaolin fiber, ceramic fiber, fireclay products, with excellent adhesion in the end.
Aluminosilicate glue is sold ready-to-use, in sealed plastic containers of different packaging, at least 2 kg.
Lining using refractory glue includes the following steps:
- Before work, the glue is thoroughly mixed until completely homogeneous.
- Apply glue to the pre-moistened surfaces with steel spatulas. On the walls of the furnace section and / or other elements of the lining, the glue is applied in a thin layer - no more than 3 mm. In the case when the lining is carried out only with an adhesive layer, without sticking cardboard or other materials, then the glue is applied 3-4 times, with an exposure of each layer for about 15 minutes.
- When fixing basalt cardboard on horizontal surfaces, the adhesive mass can be diluted with water up to 15%. The consumption of the adhesive is influenced by the quality of the surfaces to be treated and the thickness of the applied layers, the glue can be consumed per square meter. Meter within 2-4 kg.
- The glue layer dries completely in a day, if the temperature is not lower than 25⁰С and the thickness of the application is not more than 3 mm. At high temperatures (over 85⁰C), complete drying occurs in 5-7 hours.
Lining of furnaces for brick stoves and fireplaces
When lining the walls of furnace sections, it is imperative to take into account the inevitable thermal expansion of materials under temperature influences when furnaces, fireplaces or boilers are operating. Internal protection from a layer of chamotte and an external masonry layer of ordinary red brick should have an expansion gap of 0.7-1.0 cm and / or an interlayer of asbestos board, basalt or kaolin sheet, or roll material. Direct contact of the outer wall of the furnace section with the furnace lining is unacceptable, there must be either a free gap or filling with a heat-resistant material, otherwise the difference in the temperature expansion of the materials will cause deformations and the structure will gradually collapse.
Before the start of laying, the need for materials is calculated. Fireclay bricks with standard dimensions of 250 * 150 * 65 mm are more common. Fireclay products are produced in a large assortment, this makes it possible to select fireclay for a configuration of any complexity - for combustion chambers, fireplace vaults, arches, etc. It is possible to lay out inclined surfaces along the frames of grate grates and form the rear walls of fireplaces, the so-called "tooth" - a heat reflector streams. In fireplaces, the inner walls are made with a slope so that heat goes into the room, and the combustion products are directed into a precisely calculated opening. In the same way as in the furnaces of furnaces, expansion gaps between the fireclay lining and the outer brick walls are required in fireplaces.
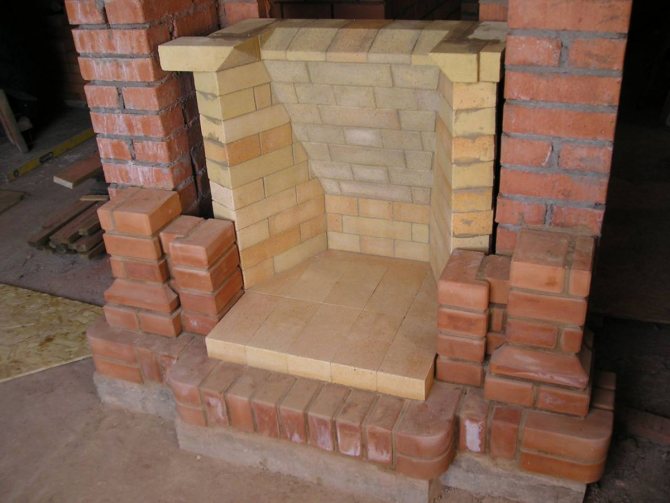


The thickness and materials for the lining are selected based on the operating mode of the furnace or boiler unit. In order to strengthen the fireclay masonry, reinforcement is also used.The seams are reinforced with steel wire with a diameter of 3 - 5 mm in every second row. When the furnaces are erected according to the schemes-orders, then the lining is made in parallel, and all the dimensions have already been calculated and painted in the order, as well as the shapes and sizes of fireclay products.
But if you need to lining the furnace of an already built furnace, the stages of the process are as follows:
- The first row of fireclay bricks is laid around the grates, and a brick with an inclined edge is preferred to provide a slope in the direction of the grates.
- In finished furnaces, it is extremely difficult to lay out the back wall with an inclination, so you have to make them even. The back and side walls of the lining are raised simultaneously.
- With small sizes of furnaces and the need for their lining, not fireclay bricks are used, but thin-walled fireclay panels or plasters with a pasty refractory composition. When applying coatings, it is necessary that the entire surface has been processed. Before work, arrange the top lighting by removing the cast-iron rings from the burners.
When lining furnaces of any size, as well as during laying, it is unacceptable to combine ceramic heat-resistant bricks and refractory fireclay bricks. These materials vary greatly in density and linear expansion, and in addition, they have a different coefficient of thermal conductivity. The combination of chamotte and red brick will give masonry, subject to deformation when heated, unstable and unreliable, and the main red brick is the first to crack and collapse. To compensate for thermal expansion, gaps with a refractory sheet made of asbestos, basalt or kaolin are always needed between chamotte and ceramics. In small furnaces with lining, it is also difficult to arrange gaps, but this is necessary, at least with a minimum size of half a centimeter.
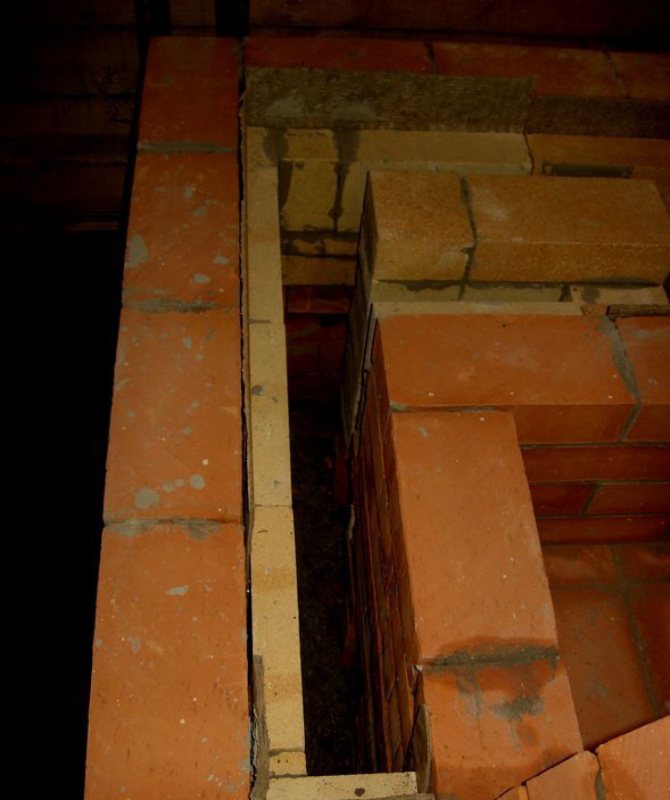


Metal furnace firebox lining
The linear expansion of metal and chamotte is incomparable with similar parameters of bricks of different types, therefore, when lining steel furnaces, the question of gaps does not even arise. The thermal gaps between the steel sheet of the furnace and the fireclay are filled with asbestos, but kaolin or basalt wool or mats are preferred.
The lining of metal heating furnaces inevitably reduces the heating efficiency, since part of the heat from the combustion of the fuel will go not to warm up the walls, but to the chimney. Therefore, in the presence of the inner lining of the furnaces, it is completely unnecessary to make the outer lining of the steel stove with ceramic bricks - the high heat capacity and low thermal conductivity of the ceramics will greatly reduce the heat transfer from the furnace.
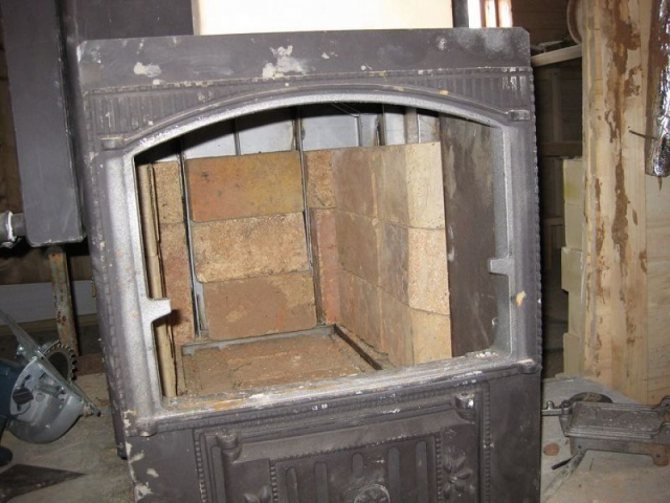


They begin to veneer the metal firebox from the bottom to the top, just like a brick one - they lay out the bottom, on a flooring made of, for example, basalt cardboard no thinner than 1 cm.Cardboard or sheets of other heat-resistant material are fixed with refractory glue.
Differences in the lining of solid fuel boilers
The peculiarities of the lining of boilers are in taking into account the specifics of the work - the boiler unit must generate heat energy and continuously transfer it to the heat exchange circuit to the circulating coolant, and heat dissipation through the outer casing by the boiler structures is reduced to a minimum, since in the context of boilers, heat transfer to the outside is heat loss. All this determines the differences between the lining of various boilers, depending on their shielding.
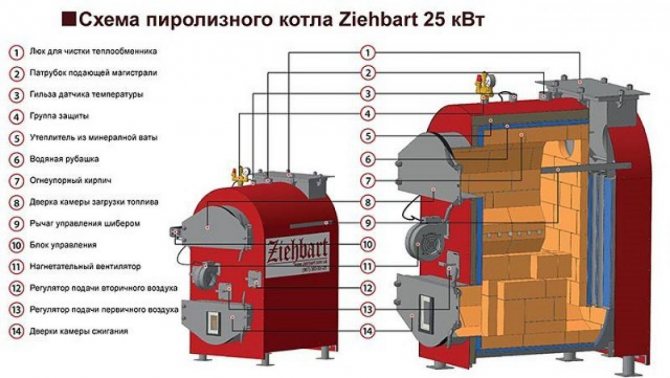

The main three methods of boiler lining
- Rarely used for domestic boilers - heavy linings. If the boiler has weak shielding, and heats up during operation above 1200⁰C, then there are risks that the walls of sheet steel will quickly burn out. In addition, it is no longer safe to service such a unit, and fires are possible. When making heavy linings, fireclay bricks are laid with a spoon in two or even three layers. As a result, the temperature of the outer surfaces of the boiler drops to 80⁰C.
- A single-layer fireclay lining is considered lightweight.At the same time, the outside of the surface of the boilers is additionally lined with non-combustible material based on the specific temperatures to which the unit is heated, and from above, sheathing with sheet steel is also possible.
- The outer lining is made of refractory compounds - glue, viscous coatings or pastes in order to thermally insulate the pipes from above. This simple method of lining is used in areas where it is difficult or impossible to use other heaters due to strong heating. Apply a coating lining with brushes two, less often three or four times, laying a reinforcing fiberglass mesh. Steel meshes are not used, since they give too much linear expansion when heated. The mesh provides protection against possible through mechanical damage to the lining layer. This thickened multi-layer lining prevents heat loss through the pipes.
Features of the lining of the furnaces of molded clay stoves
The molded adobe stove is now in great fashion, and the variety of such stoves, both in design, in structure and in size, is growing, despite the huge range of cast iron and steel stoves and all the necessary building materials for the construction of brick stoves. Stucco ovens are special - they are very ancient, time-tested and highly functional, and they heat and "heal" and create an exclusive chic. The quirky stucco stove with stove benches is now an undeniable powerful trend. The furnace of a molded adobe oven also needs protection - lining.


For stucco furnaces, experts recommend using fireclay as linings. A small exception - if the stove is composed of a mortar mixture with stone reinforcement (a rather complex technology on the verge of art), then it is possible to limit oneself to a lining with refractory glue or pastes. The same compositions are used as for furnaces and boiler pipes - mullite or corundum mixture, special expanding alumina cements, chamotte mortar mixtures or marls, as well as adhesive aluminosilicate compositions.
Lining with pastes and viscous adhesives is simple and does not require high qualifications, but only accuracy and attention. When the refractory mixture hardens, it forms a monolithic protective shell and will not allow the main clay walls of the furnace to crack under strong heating.
Lining, repair and restoration of furnace chambers
All ovens are subject to revision checks before starting a new season of operation after the summer months. During the summer downtime, impacts are possible, the results of which are not immediately noticeable, but will lead to cracks and chips at the beginning of the furnace. These phenomena not only reduce the efficiency of heat transfer from the stove, but can also become very dangerous - these are the risks of carbon monoxide in the residential area. Carbon monoxide, or carbon monoxide, gas without taste, color and smell, extremely dangerous to health and life - this information is trivial and familiar to everyone. Revisions of the furnace after downtime are carried out on the outer brick (lined, plastered, tiled, etc.) layers, as well as, without fail, and on the inner surfaces of the existing lining. All cracks and damage are carefully repaired.


The lining is repaired with refractory coatings - mastic, glue, mortar. It is enough to restore the outer surfaces with a heat-resistant material. After repair work, the furnace should be heated no earlier than the refractory and heat-resistant material has completely dried and set, and only by natural drying. Deformations in the areas of the embedments occur if the furnace is started to heat immediately after repair.
Independent lining of the furnace and boiler is possible, but it requires knowledge and some experience, therefore, they often turn to professionals about these issues. After all, it is not enough just to carry out work, you also need to calculate the required lining thickness and choose the right material from a considerable range of materials.
From roll material
The advantage of using roll materials (as well as plates and mats) is that they take up very little space and do not "steal" the total volume required for fuel filling and smoke passage. The standard thickness of most of them does not exceed 1 cm (for example, thick kaolin cardboard is up to 7 mm thick). To carry out the necessary work, you need to remember that:
- The amount of materials required for the lining is calculated taking into account their linear expansion during heating.
- In some cases, it is possible to lay the canvas in 2 layers, but for household needs this is not at all necessary.
- The individual plates are attached with reinforcement elements - metal pins that are inserted into pre-made grooves.
- When finishing with refractory mats or plates, the sequence of their attachment should be observed: first, the bottom is covered, then the side surface, and then the “ceiling” of the furnace section.
INTERESTING! Many modern factory-made furnaces already have a lining layer on the walls of the furnace sections and do not require additional processing. In particular, steel aggregates are often treated with vermiculite.
Interior finishing can be done with basalt cardboard
What materials are better for making a lining for a muffle furnace
Furnace lining materials are divided into several classes. Their main difference is the features of the ingredients that make up:
- "A" - the footer is created from components of natural origin. This also includes synthetic materials with a silicone binder.
- "B" - the main ingredient of the cladding is specially processed clay - chamotte. Blocks and bricks are created from it, which are used in the construction of a stove.
- "C" - this class includes materials created on the basis of other components.
The most popular raw material for the lining of muffle furnaces is the B-class raw material, since it is readily available and relatively inexpensive.
To improve the heat-resistant qualities of chamotte, quartz sand, crushed sandstone and other rocks are added to it, which do not change with significant heating.


The lining of the kiln with fireclay bricks or ceramics is sometimes carried out in combination with other materials containing white clay. They are available in the form of rolls, sheets or plates and are inserted between layers of ceramic or heat-resistant masonry. Most often used:
- Basalt wool.
- Kaolin.
- Mullite-silica mats.
- Vermiculite.
If the furnace is lined with bricks, then dry mixtures are almost always used. They are used to prepare a solution that is resistant to high temperatures. The masonry is coated with this composition and the cavities and cracks formed during the construction of the muffle are filled.
Semi-fluid formulations help create a cohesive design and prevent heat leakage


Coating with solutions
Coating with refractory mortars results in an even thinner lining layer. This method is characterized by the following nuances:
- For the preparation of solutions, dry compositions of chamotte, mullite or corundum mixtures are usually used, which are then diluted with water to the desired consistency.
- After application, the solution must be fired under natural conditions (when the oven is operating) or using a blowtorch. In the second case, work is carried out until a hard crust appears.
IMPORTANT! The advantage of the mortar method is also the creation of absolutely monolithic surfaces, which give the best protection of materials from the effects of fire. However, such a monolith will require repairs faster than masonry and brickwork.
The well-thought-out protection of the stove will guarantee warmth and comfort for many years
Glue and mortar


Refractory mortar for laying fireclay bricks
In addition to the quality and characteristics of materials, the effectiveness of the lining procedure is also influenced by their correct installation with the use of special substances.
Solution
Heat-resistant solutions form a monolithic thin layer on the walls of the furnace, which protects the working surface from the effects of flame. This monolith may require repair as it wears out. When working with a solution, you must follow the basic rules:
- Solutions are prepared from dry mixtures of corundum, mullite or chamotte type, which are diluted with water to a creamy consistency. The proportions of the components and the characteristics of the mixtures are usually indicated on the packaging.
- First, the solution layer is fired with a blowtorch or heated in an oven to form a hard coating during firing.
- If the lining is carried out with fireclay bricks, the joint seams must be filled to the full height of the masonry.
For 1 m3 of brickwork, at least 100 kg of ready-made mortar from any type of mixture is usually required.
Refractory adhesive


Refractory glue for laying the firebox
Refractory glue is considered to be the stronger component, it is sold in containers weighing from 2 to 50 kg and is most often used for lining. Before starting work, the container is opened and mixed until smooth, then applied to the surface, observing the basic rules:
- The glue mass is applied to the moistened surface with a spatula with a layer of no more than 3 mm.
- When covering the entire furnace cavity with glue, the procedure is carried out in layers, observing intervals of 15 minutes after each application.
- To glue basalt cardboard to horizontal sections, the composition with glue is diluted with water by 15% no later than 12 hours before starting work.
- The consumption of glue is from 1 to 4 kg, depending on the structure of the surface to be processed and the thickness of the adhesive layer.
The glue mass solidifies completely at a temperature of more than 25 degrees within 24 hours, if temperatures are more than 90 degrees - after 6 hours.
Optimal solution preparation technology
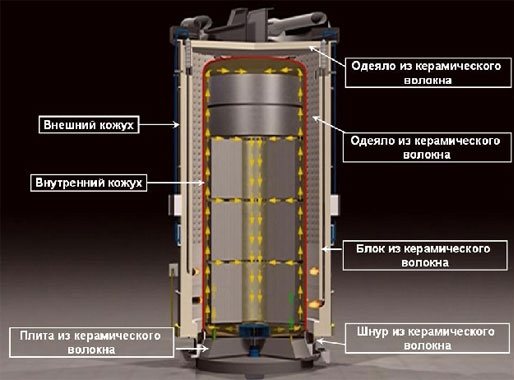

Ceramic lining diagram.
Until the optimal composition of the solution is obtained, many experiments must be carried out. In order to keep the time required for testing to a minimum, several test brick blocks with different mortar compositions should be prepared in advance. The main thing is to designate the blocks in order to determine the optimal combination after testing.
A fairly good option for preparing a solution is a mixture of clay with ground brick dust.
If the stove will be used only for burning firewood, then the use of chamotte materials as a solution is impractical. It is more optimal to use them when using coal as fuel.
Lining methods depending on the type of furnace.
The choice of materials and methods of lining is necessary depending on the type of furnace. There are several types of ovens: 1) Metal; 2) Brick; 3) Steam boiler; 4) Adobe.
- When lining metal furnaces, it must be borne in mind that when heated, in accordance with the laws of physics, the metal will expand, and when it cools, it will shrink again. Therefore, when insulating such a furnace, it is necessary to provide a small gap between the lining layer and the surface of the furnace. The resulting space should be filled with basalt wool or other non-combustible material. - When lining a brick kiln, you should also not put fireclay close to the outer masonry. Otherwise, the heating and expanding lining layer may begin to push out the outer layer. This will lead to its cracking, cracking, which can cause carbon monoxide to leak into the room. - Sometimes a furnace steam boiler also requires lining. In this case, it is usually insulated with fireclay bricks in one or two layers. Alternatively, a so-called on-tube lining can be produced. To do this, coat the boiler pipes in several layers with a special viscous non-combustible mass. And lay a reinforcing mesh on top.- For molded adobe stoves, you can use fireclay bricks, but experienced stove-makers still advise choosing a coating method and using special mullite, corundum or fireclay mixtures.
Brick kiln lining
Problems with the lining of the furnace part arise not only with metal furnaces, brick furnaces also have some features. At high oven temperatures, thermal cracking can occur as heated inner layers push cold outer layers out of their place. The outer walls, which retain the shape of the furnace and play the role of a "bandage", diverge to the sides under the influence of the expanded inner layers. In this case, cracks and destruction of individual bricks are formed, which can also lead to the release of carbon monoxide gases into the room.
Cracking is aggravated by the fact that the clay used to join the outer layer of bricks has low adhesion and expands when heated more than the bricks themselves. Accordingly, when overheated, the seam collapses. It is more correct to use a more plastic mortar when creating a furnace with its separate test, when two bricks are connected together with the resulting mortar and fired at a high temperature. After the test, the adhesion of the mortar, its expansion and cracking are checked. And already on the basis of the results obtained, either the composition of the solution changes, or, if the test result is satisfactory, the solution is used to create the entire furnace.
Laying fireclay bricks.
Before starting to create a fireclay brick lining, some stove-makers soak it in water. Is it really necessary - there is no single opinion on this matter. But most experts believe that it is imperative to wet a brick that has already been in use. Its capillaries and cracks are clogged with dust and mortar residues. It is also recommended to soak fireclay bricks for beginners - so that the solution on a damp surface dries longer and it is possible to correct flaws in the masonry. However, these "water procedures" can be carried out only in summer, in the heat. It is not recommended to soak chamotte in wet weather or in autumn - the brick will dry for a very long time. Experienced stove-makers carry out the laying of fireclay bricks inside the firebox in the following order - first they put a brick around the grate, then raise the side and rear walls. After every two rows, it is recommended to reinforce the masonry with reinforcement such as steel wire. When erecting ordinary household stoves and fireplaces, one lining layer is sufficient. Bricks are fastened with clay mortar, the use of cement-sand, as when laying with ordinary bricks, is strictly prohibited.
However, if a novice stove-maker is not sure of his abilities, it is still not recommended to experiment with mixing the solution - it is better to buy a ready-made one. The stores have an extensive line of special solution packages for every taste and wallet. These are various refractory masonry mixtures, grout, mastic, glue. It should be noted that for lining, preference should be given not to a heat-resistant, but to a refractory mixture. According to rough estimates, laying 100 fireclay bricks will require approximately 55-75 kilograms of dry mix.
2) Natural stone as lining. For lining, a natural stone such as sandstone or quartz is used. These minerals are highly resistant to extreme temperatures and have low thermal conductivity. They are fastened inside the firebox in the same way as fireclay bricks - with the help of mortar or special mixtures.
3) Roll lining. If the volume of the furnace chamber is small, it is recommended to use roll materials for lining - to save space. Most of these materials do not exceed one centimeter in thickness.For roll lining, high temperature insulation boards, mats, modules and fiber are commonly used. They are mainly made from basalt, ceramic fiber, vermiculite. Due to this, they have not only a small thickness, but also a low weight. At the same time, they are distinguished by low thermal conductivity and high temperature resistance - some can withstand temperatures up to 1350 degrees Celsius. You can also use seemingly unsuitable materials such as paper and cardboard. But not ordinary ones, but made from kaolin and mineral white clay. Roll materials are fixed in the combustion chamber, usually using metal pins, which are inserted into specially prepared grooves. Refractory boards or mats are placed first on the bottom, then on the side walls and only at the end on the upper surface of the furnace. You can also use special glue to fix the mats and fibers. High-temperature aluminosilicate glue tightly connects not only basalt slabs, fiber and mats, but also bricks. Sold in plastic buckets weighing from two to fifty kilograms. Consumption per square meter - 1-4 kilograms.
4) Coating with solutions. This is the treatment of the inner surface of the furnace with special fireclay solutions (they are also called refractory concretes), mullite (they are also silicate liquid glass) or corundum solutions. Such a coating turns out to be ultra-thin, but at the same time refractory. These mixtures are sold in packs - ready-made, dry. To prepare the solution, dilute with water to the desired consistency. The prepared mixture is applied to the walls of the combustion chamber and thermally treated - fired. If the oven is still inoperative, you can burn the applied solution with a blowtorch or gas torch.
The complexities of household lining
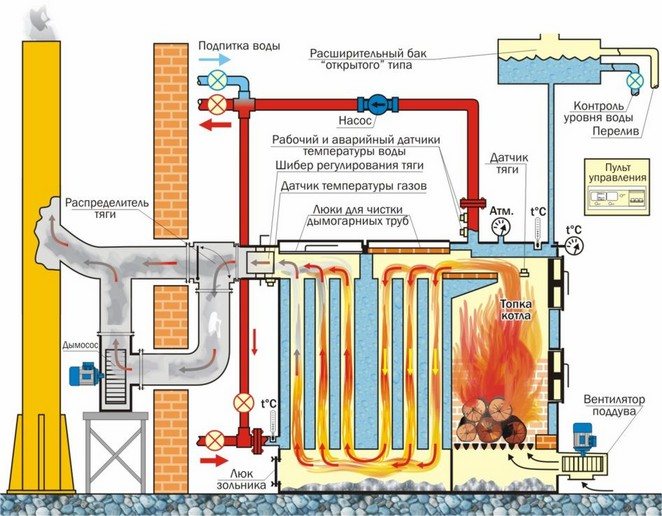

Diagram of a solid fuel heating boiler.
In most cases, when designing stoves, boilers or barbecues, a layer of fireclay bricks is laid. However, it is difficult for a person inexperienced in construction to determine the technological features of the lining:
- how many layers are needed;
- whether there is a gap between the fireclay bricks for their expansion when heated, and what are the dimensions of the gaps;
- how to fix fireclay.
If the dimensions of the firebox allow, then for the lining it is better to use fireclay bricks of a standard size (250 * 150 * 65 mm), laid vertically. Laying horizontally will improve the heat-shielding properties, but it will “eat up” the internal volume of the firebox. No gaps are left between the bricks, since fireclay bricks practically do not expand when heated. You should not use cement mortar to fasten bricks, as it will collapse from temperature extremes, it is easier to make a cut at the junctions of bricks with each other and connect them with a metal spike.
Lining of metal furnaces
Particular attention should be paid to the lining arrangement if the furnace is metal, since the thermal expansion of the metal is much greater than that of the brick, which must be taken into account. There must be a gap for thermal expansion between the lining layer and the metal walls of the furnace, otherwise the lining may simply collapse when the metal is heated. The gap is sealed with basalt wool in the form of bundles or sheets. If the stove is not located in a residential area, asbestos can be used for the same purposes.
Another mistake when using metal stoves is bricking them not only inside, but also outside, explaining this by improving the safety and heating of the stove. However, this approach is flawed because:
- the brick has a high heat capacity and low thermal conductivity, which means that all the heat from the combustion of the fuel will remain inside the furnace and leave with smoke;
- the surface of the furnace will be deprived of air access for heat removal, which will lead to burnout. Burnout of the walls, in turn, promotes the penetration of carbon monoxide into the room, which is dangerous to health.











