A well-arranged heating system will provide housing with the required temperature and will be comfortable in all rooms in any weather. But in order to transfer heat to the air space of living quarters, you need to know the required number of batteries, right?
Calculating this will help the calculation of heating radiators, based on calculations of the thermal power required from the installed heating devices.
Have you ever done such a calculation and are you afraid to make mistakes? We will help you figure out the formulas - the article describes a detailed calculation algorithm, the values of individual coefficients used in the calculation process are analyzed.
To make it easier for you to understand the intricacies of the calculation, we have selected thematic photographs and useful videos that explain the principle of calculating the power of heating devices.
Simplified calculation of heat loss compensation
Any calculations are based on certain principles. The basis for calculating the required thermal power of batteries is the understanding that well-functioning heating devices must fully compensate for the heat losses that arise during their operation due to the characteristics of the heated premises.
For living rooms located in a well-insulated house, located, in turn, in a temperate climatic zone, in some cases, a simplified calculation of compensation for thermal leaks is suitable.
For such premises, calculations are based on a standard power of 41 W required for heating 1 cubic meter. living space.

In order for the heat energy emitted by heating devices to be directed specifically to heating the premises, it is necessary to insulate walls, attics, windows and floors.
The formula for determining the thermal power of radiators required to maintain optimal living conditions in a room is as follows:
Q = 41 x V,
Where V - the volume of the heated room in cubic meters.
The resulting four-digit result can be expressed in kilowatts, reducing it from the calculation of 1 kW = 1000 W.
Parameters of bimetallic radiators
The technical parameters of bimetallic radiators are determined by the specifics of their design - in a light aluminum casing there is a rod made of anti-corrosion steel in contact with the coolant. This symbiosis of materials gives them anti-corrosion resistance, high heat transfer and low weight, which makes the installation process easier.
The disadvantages include high cost and low bandwidth.
Based on the foregoing, semi-metal radiators can be used for private houses with individual heating, but only bimetallic radiators can withstand the aggressive aqueous medium of central heating.
Structurally, these types of heating devices are divided into monolithic and sectional. The first ones are twice as long as the second type in terms of service life and three times - in terms of working pressure. And as a result, at a cost.

A practical example of calculating heat output
Initial data:
- A corner room without a balcony on the second floor of a two-story cinder block plastered house in a windless region of Western Siberia.
- Room length 5.30 m X width 4.30 m = area 22.79 sq. M.
- Window width 1.30 m X height 1.70 m = area 2.21 sq. M.
- Room height = 2.95 m.
Calculation sequence:
| Room area in sq.m .: | S = 22.79 |
| Window orientation - south: | R = 1.0 |
| The number of external walls is two: | K = 1.2 |
| Insulation of external walls - standard: | U = 1.0 |
| Minimum temperature - down to -35 ° C: | T = 1.3 |
| Room height - up to 3 m: | H = 1.05 |
| Upstairs room - not insulated attic: | W = 1.0 |
| Frames - single-chamber double-glazed windows: | G = 1.0 |
| The ratio of the area of the window and the room - up to 0.1: | X = 0.8 |
| Radiator position - under the windowsill: | Y = 1.0 |
| Radiator Connection - Diagonal: | Z = 1.0 |
| Total (don't forget to multiply by 100): | Q = 2 986 Watt |
Below is a description of how to calculate the number of radiator sections and the required number of batteries. It is based on the obtained results of thermal power, taking into account the dimensions of the proposed installation sites for heating devices.
Regardless of the outcome, it is recommended to equip not only window niches with radiators in corner rooms. The batteries should be installed near “blind” external walls or near corners, which are exposed to the greatest freezing due to the outdoor cold.
How to choose a cast iron radiator
What performance characteristics of a radiator should you pay attention to when choosing radiators? First of all, these are:
- operating pressure;
- operating temperature in the heating system for which heat transfer is calculated;
- heat transfer;
- the area of the heat-emitting surface;
The first of these indicators determines the pressure of the coolant (water) that the radiator can withstand. The higher the number of storeys in a building, the stronger it should be. The second designates with what temperature the coolant is supplied to the radiator and with what it comes out of it for subsequent heating. So the indicator 90/70 means that the water entering the first section of the battery has a temperature of 90 degrees. and coming out of its last section - 70 degrees. Heat transfer is an indicator indicating how much heat a radiator section gives up during the time while the water in it cools down from the inlet temperature (for example, 90 degrees) to the outlet temperature (for example, 70 degrees).
The shape of the acquired radiator deserves special attention. It is no secret that the prejudice towards cast-iron radiators is caused by the fact that when they mention them, many people remember the "cast-iron accordion" familiar from childhood under the window. Indeed, the usual "ribbed batteries" have a small and ineffective heating area (heat transfer) - so for the section of the familiar MC 140 radiator this figure is 0.23 sq. M.
Part of the heat of the incoming heat carrier is lost “on the way” from the heating boiler to the hot water heating battery, because massive supply pipes are used for such systems. In addition, for heating water to a design temperature of 90 degrees. only steam boilers of high power are suitable. Therefore, in private houses, the heating system sometimes operates at a lower temperature mode.
However, modern cast-iron radiators both in appearance and, accordingly, in parameters can differ significantly from their predecessors - "accordions". While retaining all the advantages of traditional cast iron batteries, it is devoid of many of their disadvantages. So, the radiator of Minsk production 1K60P-500 is assembled from flat plates, each of which has a small heating area (0.116 m) and low power (70 W).
However, a radiator assembled from them, in fact, is a heating panel, which (unlike ribbed batteries) gives a wide directional heat flux. Other manufacturers also provide a wide selection of such radiators.
The advantage of modern cast iron radiators is that many models allow assembling batteries of the required power from separate sections.
Radiators sold in assembly (for example, Conner, STI Breeze and some others) are formed from the number of sections designed for rooms of various sizes based on the engineering calculation of the required thermal power per square meter of the room.
For example, you can purchase one radiator of 4-6-8-12 sections or two radiators of 4 (6, 8, sections).
Specific thermal power of battery sections
Even before performing a general calculation of the required heat transfer of heating devices, it is necessary to decide which collapsible batteries from which material will be installed in the premises.
The selection should be based on the characteristics of the heating system (internal pressure, heating medium temperature). At the same time, one should not forget about the greatly differing cost of purchased products.
How to correctly calculate the required number of different batteries for heating will be discussed further.
With a coolant of 70 ° C, standard 500 mm radiator sections made of dissimilar materials have an unequal specific heat output “q”.
- Cast iron - q = 160 Watt (specific power of one cast-iron section). Radiators made of this metal are suitable for any heating system.
- Steel - q = 85 Watt... Steel tubular radiators can withstand the harshest operating conditions. Their sections are beautiful in their metallic luster, but have the least heat dissipation.
- Aluminum - q = 200 Watt... Lightweight, aesthetic aluminum radiators should be installed only in autonomous heating systems, in which the pressure is less than 7 atmospheres. But in terms of heat transfer, their sections have no equal.
- Bimetal - q = 180 Watt... The insides of the bimetallic radiators are made of steel, and the heat-dissipating surface is made of aluminum. These batteries will withstand all kinds of pressure and temperature conditions. The specific thermal power of the bimetal sections is also at a height.
The given values of q are rather arbitrary and are used for preliminary calculations. More accurate figures are contained in the passports of purchased heating devices.
Image gallery
Photo from
The advantages of the sectional assembly principle
Basic rules for assembling heating devices
Obsolete Cast Iron Battery Sections
Powder coated colored sections
How much does a copper radiator VAZ 2106 weigh?
If a native copper radiator dies on an old penny, finding a replacement for it is very simple and not as expensive as if you take the original one.
You can safely put aluminum for the VAZ 2103-2106.
Personally, I took myself from the manufacturer LUZAR.
Refinement requires additional purchase of branch pipes (2106 alum), straight arms and a couple of hours of free time.
Saving finance by 2.5 times.
Luzar code LRc 0106
OEM number: 2106-1301012
Core size, mm: 450 * 342 * 32
Where can I buy
Applicability for A / M
Brand Name - LRc - Luzar Radiator cooler
We manufacture hundreds of models of engine cooling radiators for automobiles. Radiators are produced for almost any brands on the Russian market, of various modifications, with various motors. Dozens of new cooling radiators are constantly in development - for popular and newest cars, which can be bought in Russia and the CIS.
Cooling system radiator Is a heat exchanger that prevents the engine from overheating during operation. The cooling radiator dissipates excess. more details
Brand Name - LRc - Luzar Radiator cooler
We manufacture hundreds of models of engine cooling radiators for automobiles. Radiators are produced for almost any brands on the Russian market, of various modifications, with various motors. Dozens of new cooling radiators are constantly in development - for popular and newest cars, which can be bought in Russia and the CIS.
Cooling system radiator Is a heat exchanger that prevents the engine from overheating during operation. The cooling radiator dissipates excess heat from the car engine through the coolant, thereby maintaining an optimal temperature of 85-100 ° C (depending on the car brand).
The design of the cooling system radiators from LUZAR
LUZAR cooling radiators can be divided into three types:
- Tubular-lamellar, prefabricated, aluminum. It consists of aluminum plates through which aluminum tubes pass through which coolant flows. The tanks on these radiators are made of plastic. Cooling radiators of this type are used for engines with small cubic capacity - due to limited heat transfer; have the best rigidity and low weight, as well as the lowest cost.
- Tubular tape, non-assembled (brazed), aluminum. The corrugated aluminum tape in such a radiator is located between the aluminum flat-oval tubes. Radiator tanks of this type can be made of both plastic (the most common) and metal (most often used for cargo cooling radiators). The design of non-assembled (brazed) aluminum cooling radiators is the most versatile, allowing you to create heat exchangers with any given characteristics. They have low weight and relatively high rigidity, as well as an optimal price.
Tubular tape, non-assembled (brazed), copper-brass. The design is very close to type 2 - between the copper flat-oval tubes there are copper strips folded in the form of an "accordion". In this case, the tanks on such cooling radiators are used brass - in order to increase the overall rigidity of the structure. Copper cooling radiators - due to the high specific heat capacity of copper - have excellent heat transfer rates. However - due to the high softness of copper - cooling radiators made of this metal are forced to have a narrow tube and a large interval (pitch) between the tubes, which imposes serious restrictions on maximum efficiency. Also, copper radiators have the highest prices and the lowest torsional, kink and internal pressure stiffness. In this regard, copper radiators are "outdated" and are gradually being phased out.
LUZAR: guarantee and reliability
We manufacture radiators according to the standards of car manufacturers. Each piece is tested by overpressure and an aggressive environment, so that at the production stage it was possible to identify corrosive defects and leaks.
LUZAR products are distributed through partner stores, the list of which can be found in the "Where to buy?" Section. In the same stores, you can exchange the cooling radiator if you find a defect or incompatibility with your car.
Questions about production, packaging, installation and sales are answered by our managers by phone 8-800-555-8965.


Specifications
Product description
Catalog group. Cooling system Engine
Description Radiator
LLC "Orenburg Radiator" is engaged in the development, implementation and serial production of radiator products, which are used in the production of tractors, combines, agricultural machinery, as well as domestic cars and trucks.
Already, among the manufactured products there are more than 500 items of products that are in demand not only in Russia, but also abroad (in Belarus, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Poland, Hungary, Turkmenistan, Germany, Czech Republic, Pakistan, etc.).
automotocity.com
Calculation of the number of radiator sections
Collapsible radiators made of any material are good in that individual sections can be added or subtracted to achieve their design thermal power.
To determine the required number of "N" sections of batteries from the selected material, follow the formula:
N = Q / q,
Where:
- Q = the previously calculated required heat output of the devices for heating the room,
- q = heat specific power of a separate section of the batteries intended for installation.
Having calculated the total required number of radiator sections in the room, you need to understand how many batteries you need to install. This calculation is based on a comparison of the dimensions of the proposed installation sites for heating devices and the dimensions of the batteries, taking into account the supply.


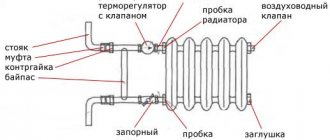
battery elements are connected by nipples with multidirectional external threads using a radiator wrench, at the same time gaskets are installed in the joints
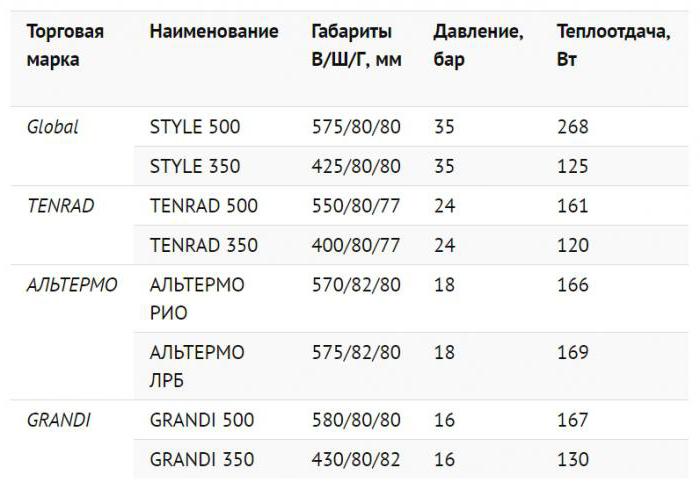
For preliminary calculations, you can arm yourself with data on the width of the sections of different radiators:
- cast iron = 93 mm,
- aluminum = 80 mm,
- bimetallic = 82 mm.
In the manufacture of collapsible radiators from steel pipes, manufacturers do not adhere to certain standards. If you want to put such batteries, you should approach the issue individually.
You can also use our free online calculator to calculate the number of sections:
Enlarged cooling radiator - DRIVE2
Hello everyone, at last we have embodied our old idea in metal, or rather in copper. Enlarged cooling radiator.


Full size
There are a lot of people on the Internet, and just in personal communication, who complain about the heating of engines, especially in the mountains. Basically, these are the owners of "automatic" cars with different motors.
It was decided to start with the manufacture of the largest radiator with three rows of honeycombs (there is an option with two) 70 mm thick along the honeycombs (two-row has a thickness of 46 mm along the honeycombs)
The standard aluminum is 35mm thick in honeycombs.
There were fears that such a thickness would not fit into the standard engine compartment, but as it turned out, everything fits, not without some effort, of course.
We put this radiator on a patrol in a configuration with a td42t engine and automatic transmission. Technical data of the car Lift 2 ″, 35 ″ m / t tires, the main pairs in gearboxes are 4.375.
A story in small details does not make much sense here, because a kind of installation instruction with a photo will be compiled for the product and sent to those who are going to install our product
In short, you need to carefully, without peeling, and just a little bit, bend the lower edges of the "mudguards" (arches) in the area of the lower part of the radiator, cut the diffuser in several places (if it is saved) and cut the upper and lower cooling pipes to compensate for the thickness radiator (in the case of a two-row radiator, everything is simpler).
We also conducted tests by hanging temperature sensors at the inlet and outlet of the radiator in order to have an objective assessment of what is happening and understand whether the game is worth the candle and the money spent. And of course both of them weighed))). The standard radiator has a weight of 8 kg Copper 23 kg.
To begin with, we measured the work of a regular radiator, then an enlarged copper one.
And so the first photo, this is the work of a regular radiator, the air temperature outside is minus 5
The second photo, the temperature of the copper radiator, the outside air temperature is 0, a trailer with a load of 400 kg is attached to the car.


Full size
Uniform driving at speeds of 60-80 Standard radiator.


Full size
Smooth ride at speeds of 60-80 Increased radiator


Are full
www.drive2.ru
Improving the efficiency of heat transfer
When the room is heated by a radiator, the outer wall also intensively heats up in the area behind the radiator. This leads to additional unnecessary heat loss.
It is proposed to shield the heater from the outer wall with a heat-reflecting screen to improve the efficiency of heat transfer from the radiator.
The market offers a variety of modern insulating materials with a heat-reflecting foil surface. The foil protects the warm air warmed up by the battery from contact with the cold wall and directs it inside the room.
For correct operation, the boundaries of the installed reflector must exceed the dimensions of the radiator and protrude 2-3 cm on each side. The gap between the heater and the thermal protection surface should be 3-5 cm.
For the manufacture of a heat-reflecting screen, you can advise Isospan, Penofol, Aluf. A rectangle of the required dimensions is cut out of the purchased roll and fixed on the wall at the place where the radiator is installed.
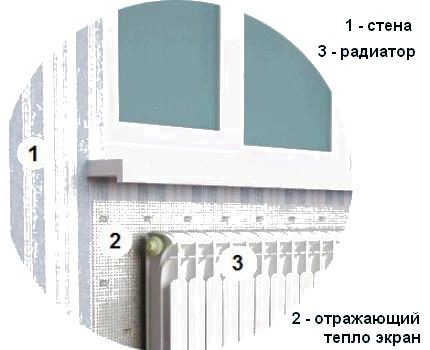

It is best to fix the screen that reflects the heat of the heater on the wall with silicone glue or with liquid nails
It is recommended to separate the insulation sheet from the outer wall with a small air gap, for example, using a thin plastic grating.
If the reflector is joined from several pieces of insulating material, the joints on the foil side must be glued with metallized adhesive tape.
Steel radiators
Heating devices made of steel are presented on the market in a wide range. Structurally, they are divided into panel and tubular.
In the first case, the panel is mounted on the wall or on the floor. Each part consists of two welded plates with a coolant circulating between them. All elements are connected by spot welding. This design significantly increases heat transfer. To increase this indicator, several panels are connected together, but in this case the battery becomes very heavy - a radiator of three panels is equal in weight to cast iron.
In the second case, the structure consists of lower and upper collectors connected to each other by vertical pipes. One such element can contain a maximum of six tubes. To increase the surface of the radiator, several sections can be joined together.
Both types are durable heating devices with good heat dissipation.
For design purposes, tubular steel radiators can be produced in the form of partitions, stair railings, mirror frames.
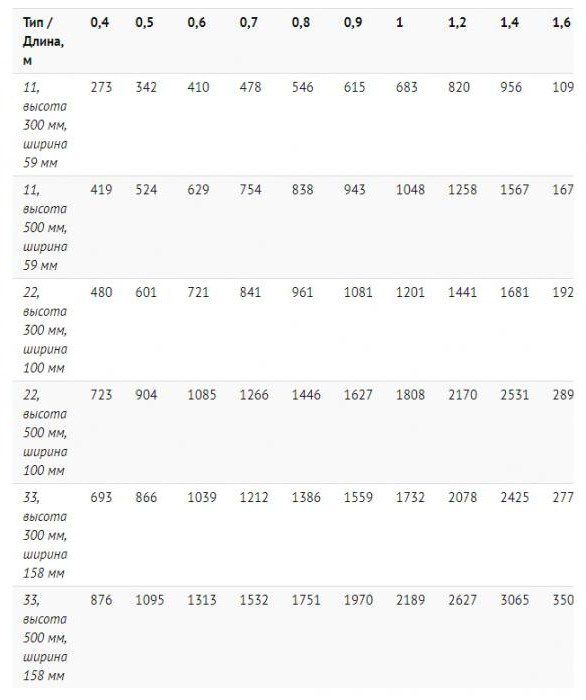
The heat transfer table of steel heating radiators is posted later in the article.

Strengths and weaknesses of aluminum radiators
List of positive characteristics of aluminum batteries:
- Profitability.
- Light weight. How much the aluminum battery weighs greatly simplifies the installation and removal of devices.
- Possibility of temperature adjustment.
- The highest efficiency among all household radiator heaters.
- Presentable appearance, allowing the use of aluminum radiators both in ordinary homes and in prestigious institutions.


Weak sides:
- Weakness of intersection joints (leaks sometimes occur there).
- Uneven heat distribution: it is mainly accumulated by the ribbed part of the sections.
- Weak convection circulation.
- Low service life. The same cast iron batteries last much longer than 15-20 years.
- Internal gases may form.
- Excessive reactivity of aluminum. This is the biggest drawback of this type of battery, because of which the presence of the slightest impurities in the coolant can provoke destructive processes on the inner walls.
- Low resistance to pressure drops.
Considering all these disadvantages, the scope of application of aluminum radiators is limited to autonomous heating systems, which have a stable low pressure and a chemically neutral coolant. As for the installation of batteries of this type in ordinary apartments, there is even a special prohibition on this from the relevant authorities.
Heating radiator, comparison of several types
for each of them there are certain conditions
- Sectional cast iron radiator.
- Aluminum heating device.
- Bimetallic sectional heating devices.
We will compare different types of heating devices in terms of parameters that affect their choice and installation:
- The value of the heat output of the heating device.
- At what operating pressure. effective operation of the device occurs.
- Required pressure for crimping battery sections.
- The occupied volume of the heat carrier by one section.
- What is the weight of the heater.
It should be noted that in the process of comparison, one should not take into account the maximum temperature of the heat carrier; a high indicator of this value allows the use of these radiators in residential premises.
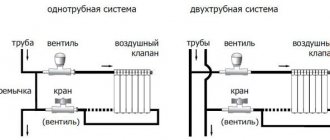
In urban heating networks, there are always different parameters of the operating pressure of the thermal carrier, this indicator must be taken into account when choosing a radiator, as well as the parameters of the test pressure. In country houses, in villages with cottages, the coolant is almost always below 3 bar. but in urban areas, centralized heating is supplied with a pressure of up to 15 bar. Increased pressure is necessary as there are many buildings with many floors.