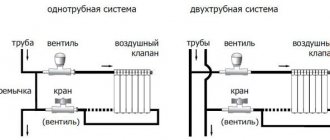
In the construction of any heating system, different types of radiators are used. Any heating system must be designed taking into account the number of radiators and their internal volume. Each radiator section has a certain volume, and when installing the heating system, you need to know for certain the number of sections in the battery. The efficiency and correct operation of the heating system depends on the correct calculation of the number of sections.
What types of radiators are there?
Today the following types of radiators are most commonly used:
- cast iron radiators;
- aluminum alloy radiators;
- bimetallic radiators.
Varieties of heating batteries
Standard


These devices are available in a range of heights, typically from 300 to 750 mm, with the largest range of lengths and configurations in heights from 450 to 600 mm in height. The length ranges from 200 mm to 3 m or more, with the greatest range from 450 mm to 2 m in length.
Panels and convectors


Such radiators usually consist of one or two panels, but sometimes 3-panel ones are found. Modern single-panel radiators have a corrugated panel that forms a series of fins (called "convectors") attached to the rear (wall-facing) side of the panel, which increases the convection power of the battery. These are commonly known as "single convector" (SC). Radiators consisting of two panels with fins stacked on top of each other (with fins in the middle) are known as "dual convector" (DC) radiators. There are also double radiators, consisting of one finned panel and one non-finned panel. The old-style radiators consisted of one or two panels without any convection fins.
A traditional standard heat sink has seams at the top, sides, and bottom of each panel (where pressed steel sheets are joined together). Nowadays, most seam batteries are sold with decorative panels installed on the top and sides (the top ones have vents for air circulation), and these are known as "compact" batteries. The top seam radiator alternative uses a single sheet of pressed steel and this sheet is rolled together at the top of the radiator.
Low surface temperature batteries
Most of these radiators are designed so that their radiating surfaces have relatively low temperatures at normal heating system temperatures. They are used wherever there is a risk of burns - most often in child care facilities, nursing homes, hospitals and hospitals.
Designer batteries
There is a huge selection of radiator designs available that can be more pleasing to the eye than their regular counterparts. Some designer batteries are available in tall, narrow configurations that may be suitable for rooms with, for example, narrow walls next to doors, where conventional radiators cannot provide sufficient power with limited wall space available.
Skirting radiators
These devices are usually disguised as skirting boards. The operation of these radiators is similar to the “warm floor” effect, as the user eye does not notice any radiator sections on the walls. Installation of skirting boards allows you to save the interior space of the room.
Heated towel rails
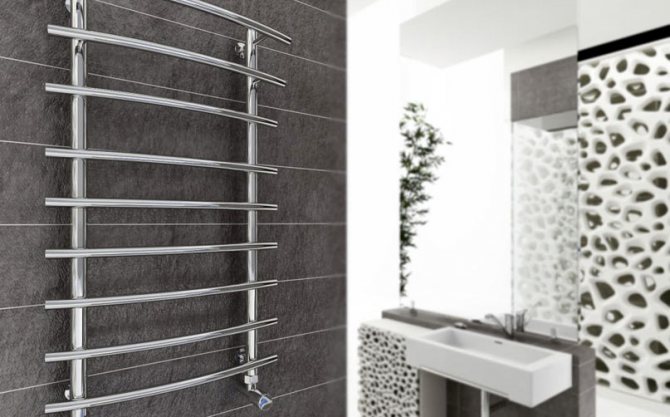


These radiators are specially designed for drying towels, as well as for draining bathtubs and showers.However, the heat output of towel warmers is significantly reduced when covered with towels, and even if they are not covered with towels, towel warmers are able to dissipate much less heat than conventional batteries of a similar size. Usually, heated towel rails are not enough to heat the premises. They are used only in relatively small and well insulated bathrooms. Some towel radiator designs contain a conventional radiator with towel racks above and sometimes on the sides of the radiator. Such devices have the best heat output.
Thermal output of radiators with different center distances
The second key characteristic of bimetallic radiators is thermal power... Using this parameter, determine how many sections of the radiator are needed to effectively heat a room of a certain area. This characteristic of a bimetallic radiator directly depends on the value of the center distance:
- 500 mm - heat output is from 170 to 200 W.
- 350 mm - from 120 to 140 W.
- 300 - from 100 to 145 W.
- 200 - about 100 watts.
The exact value of the thermal power depends on the modification of the device, this characteristic of the bimetallic radiator is indicated in the technical passport for the product. It is calculated as follows: the amount of heat given off by the radiator at a working environment temperature of +70 degrees Celsius is estimated. Recall that the following standard is used in Russia: to heat a room with an area of 10 square meters, a thermal power of 1 kW is required.
To determine the number of sections required, you can use the following formula: N = S * 100 / Qwhere:
- N is the optimal number of sections.
- S is the area of the room.
- Q - passport index of the section.
The amount of coolant in the heating battery
Correctly selected volume of coolant in the section allows the heating radiator to work most optimally. The amount of water in the radiator affects not only the operation of the boiler, but also the efficiency of all elements of the heating system. The most rational selection of the rest of the equipment that is included in the heating system also depends on the correct calculation of the volume of water or antifreeze.
The volume of the coolant in the system also needs to be known in order to choose the right expansion tank. For houses with a central heating system, the volume of radiators is not so important, but for autonomous heating systems, the volume of water in the radiator sections needs to be known for certain. You also need to take into account the volume of pipelines of the heating system so that the heating boiler works in the correct mode. There are special tables for calculating the internal volume of pipelines in the heating system. It is only necessary to correctly measure the length of the heating circuit pipes.
Today, the most demanded radiators are made of bimetal and aluminum alloy. The bimetallic radiator section with a height of 300 millimeters has an internal volume of 0.3 l / m, and the section with a height of 500 millimeters has a volume of 0.39 l / m. The same indicators are for the radiator section made of aluminum alloy.
Also, cast iron radiators are still in use. The imported cast iron section, 300 millimeters high, has an internal volume of 0.5 l / m, and the same section with a height of 500 mm already has an internal volume of 0.6 l / m. Domestic-made cast iron batteries with a height of 300 mm have an internal volume of 3 l / m, and a section with a height of 500 mm has a volume of 4 l / m.
Water or antifreeze
Ordinary water is most often used as a heat carrier, but antifreeze and distillate are also used. Antifreeze is used only if the residence is not permanent. Antifreeze is needed when the heating system does not work during the winter. Using antifreeze as a coolant is much more expensive than using ordinary water.In order not to spend extra money when using antifreeze as a coolant, you need to know exactly the volume of the heating system. The number of radiator sections should be counted, and the volume of the radiators should be calculated using the above parameters. The volume of the pipeline is determined using a special table. But for this, you first need to measure the length of the pipes with an ordinary tape measure.
At the end of the calculations, the volume of pipelines and the volume of heating radiators are added together, and already on the basis of these data, the required amount of antifreeze is purchased. Also, this data will be useful for determining the amount of water that will be used in the heating system. This information will allow the most flexible setting of the boiler, as well as other elements of the heating circuit.
What is a bimetal radiator
Despite the large assortment of heating batteries, modern bimetallic radiators are now very popular, due to their advantages. First, let's consider what this device is.

Device
The structure can be solid or sectional, consisting of two metals. All products fall into 2 groups, depending on the materials used: steel and aluminum, copper and aluminum.
The heating device of the first type has the following design: a steel pipe with horizontal collectors and vertical columns, with a fixed aluminum radiator. Since the coolant has to come into contact only with steel, the maximum temperature in such batteries does not exceed +110 ° C, and the permissible pressure should be no more than 40 bar. Each joint is reliably sealed to minimize the likelihood of leakage. The heater can always be enlarged, since it is permissible to build up additional sections.
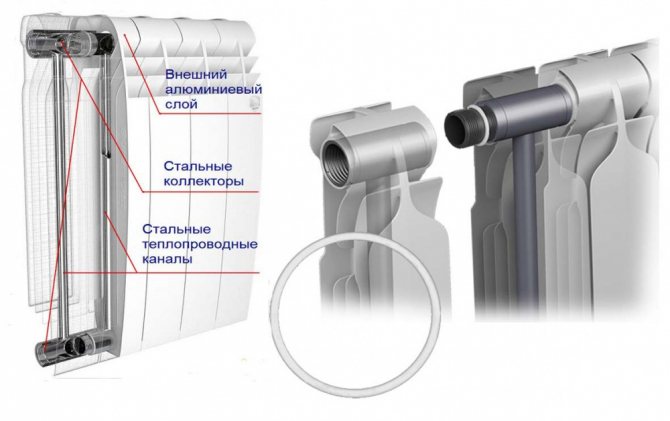

Each section has a tubular steel core through which the heating medium is transported. The core refers to 2 tubes connected by a thin column. They have a thread required to connect the sections. The aluminum heat exchanger has a rather complex shape and many convection air ducts.
Batteries made from aluminum and copper are one-piece construction. In the aluminum case, there is a copper coil, for the manufacture of which the soldering method is used. It is capable of withstanding operating pressures of up to 50 bar. In such batteries, the coolant will come into contact with copper. This metal has a higher thermal conductivity than steel, in addition, it is not afraid of deposits, since the inner surface of the pipe is practically without roughness. This makes it possible to use any coolant, not only water.
The bimetallic battery has a unique design to reduce weight and increase thermal conductivity. Due to their low weight, the installation of such radiators can be carried out even on plasterboard walls. A special protective layer is provided on the outer surface, which improves the product's resistance to mechanical and chemical damage. In short, the design incorporates the merits of two different metals.
Specifications
Modern heating devices are lightweight, reliable and perfectly conduct heat energy. Thanks to the metal surface, products easily absorb heat and give it to the surrounding space, quickly warming it up.
Before choosing such radiators, you need to familiarize yourself with their technical characteristics. This will allow you to make the right decision when organizing heating for your home. Any battery must be strong to maintain pressure in the system with ease. And in this regard, bimetallic radiators come out on top: the maximum permissible pressure threshold is 50 bar.On average, their service life reaches 20 years. They are extraordinarily robust and come in a modern, elegant design.
With a center-to-center distance of 500 mm, the system shows high heat transfer: heat output varies from 170 to 190 W. Since the coolant has to come into contact with steel and not aluminum, the maximum allowable working pressure increases.
It should be noted that in systems this indicator rarely exceeds 15 bar. Nevertheless, bimetallic radiators serve as a kind of quality guarantor, since they are the best resistant to water hammer. And the buyer appreciates this reliability.
Due to the small diameter of the channels in the radiators, the volume of the coolant is easily reduced by 2-3 times. This allows the batteries to respond faster to thermostat commands - the heating process will become even more comfortable.
Benefits
Compared to popular traditional solutions, the produced bimetallic radiators have a lot of positive qualities.


Key advantages of heating equipment.
- Long service life... It is explained by high-quality assembly and the use of two different metals in the structure.
- High strength index... This advantage was achieved through the use of a steel core, which not only perfectly resists high pressure, but also is not afraid of water hammer possible in the heating system. Connection diagrams are different, but this work should be entrusted to specialists.
- Good heat dissipation... The heat will quickly spread throughout the room, because the outer casing of the device is made of aluminum. Even the standard model is capable of a heat dissipation of 190 watts, which is more than the capabilities of a single-element radiator.
- Corrosion resistant... The coolant comes into contact with steel, which is not afraid of corrosive processes, thereby extending the service life.
- Fast response to thermostat... Bimetallic devices have a smaller heating medium volume, which allows the thermostat to react more quickly to changes in settings.
- Attractive design... Aluminum, as a metal, is easy to cast, so a wide variety of designs are made from it, suitable for any interior.
Bimetal batteries have many advantages, but there is simply no ideal material.
disadvantages
Before choosing such batteries, you need to familiarize yourself with their weaknesses.
As for the disadvantages, there are not many of them:
- high price... This is when compared with more traditional solutions. But it should be noted that bimetal is a strong and durable material, therefore such a purchase is a long-term investment;
- cheap models are not protected from corrosion. Over time, they are attacked by rust, spoiling the quality and reducing the service life.
As you can see, there are practically no shortcomings. And if you make a choice once correctly, there will be no more difficulties.
Prices for different models of bimetallic heating radiators
bimetallic heating radiators
Average data


If, for some reason, the user cannot determine the exact volume of water or antifreeze in heating radiators, then averaged data can be used that are applicable to certain types of heating radiators. If, say, we take a 22 or 11 type panel radiator, then for every 10 cm of this heating device there will be 0.5-0.25 liters of coolant.
If you need to determine "by eye" the volume of a section of a cast-iron radiator, then for Soviet samples the volume will range from 1.11 to 1.45 liters of water or antifreeze. If imported cast iron sections are used in the heating system, then such a section has a capacity from 0.12 to 0.15 liters of water or antifreeze.
There is another way to determine the internal volume of the radiator section - to close the lower necks, and pour water or antifreeze into the section through the upper ones - to the top. But this does not always work, since aluminum alloy radiators have a rather complex internal structure. In such a design, it is not so easy to remove air from all internal cavities, therefore, this method of measuring the internal volume for aluminum radiators cannot be considered accurate.
Correct calculation
You also need to take into account the fact that the heat exchanger of the heating boiler also contains a certain amount of heat carrier. The heat exchanger of a wall-mounted heating boiler can hold from 3 to 6 liters of water, and floor heating devices can hold from 9 to 30 liters.
Having found out for certain the internal volume of all heating radiators, pipelines and a heat exchanger, you can proceed to the selection of an expansion tank. This element of the heating system is very important, since it depends on it to maintain the optimal pressure in the heating circuit.
How to calculate the number of sections
Based on sanitary standards, 100 watts of power are required per 1 square meter of the room. The calculation is as follows: the area of housing is considered - the length is multiplied by the width. The resulting figure is multiplied by 100 W and divided by the heat transfer of one section.


For example, let's take a room 3 by 4 meters. You can calculate using the above formula: K = 3 × 4 × 100/200 = 6. Here the figure 200 is the heat transfer rate of one section.
The calculation of sections of bimetallic heating radiators by area is more accurate. The calculations are the same, only the basic data is the heating output for 1 m³. The normalized value is 41 W.
So, the room is 3 by 4 meters, the ceiling height is 2.7 meters. Volume (V) = 3 × 4 × 2.7 = 32.4 m³. Radiator power (P) = 32.4 × 41 = 1328.4 W. Number of sections (K) = 1328.4 / 20 = 6.64. The volumetric method is more accurate, as it takes into account the height of the ceilings, which will achieve optimal heating.
Output
The accurate determination of the total volume of the heating system determines its correct operation and efficiency, as well as the operation in optimal mode of other elements of the system. The most important thing in the correct determination of the volume of the heating circuit is that each boiler is designed for a certain volume of the heating medium. If the volume of the heating system is excessive, then the boiler will work continuously. This will significantly reduce the service life of the heating device, and entail unplanned costs. The volume of the heating circuit must be correctly calculated.