Each of us has repeatedly witnessed the formation of water droplets on surrounding objects and structures. This is explained by the fact that the surrounding air cools over an object brought from frost. Saturation with water vapor occurs, and dew condenses on the object.
The fogging of windows in the apartment has the same nature. The reason windows cry is due to condensation processes that are influenced by humidity and ambient temperature.

Condensation is closely related to dew point. For a better understanding of the described phenomena, it is simply necessary to consider this factor in more detail.
Dew point. What is it?
The dew point is the temperature at which the ambient air is cooled, at which the water vapor that it contains begins to condense, forming dew, that is, it is the temperature of condensation.
This indicator depends on two factors: air temperature and its relative humidity. The dew point of a gas is the higher the higher its relative humidity, that is, it approaches the actual ambient temperature. Conversely, the lower the humidity, the lower the dew point.
Dew point - formula, calculation and visualization
What is dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which the air must cool in order for the water vapor contained in it to reach saturation and begin to condense into dew. Simply put, it is the temperature at which condensation occurs.
The dew point temperature is determined by only two parameters: temperature and relative humidity. The higher the relative humidity, the higher the dew point and closer to the actual air temperature. The lower the relative humidity, the lower the dew point of the actual temperature.
Dew point table
A table with the dew point temperature for various temperatures (from -5 ° C to 35 ° C) and relative humidity (from 40% to 95%) of indoor air can be found in reference Appendix R to SP 23-101-2004 "Design of thermal protection of buildings ". Unfortunately, several typos have crept into this table. I have prepared a file with a table for you; typos are corrected there.
Dew point formula
You can use the formula to roughly calculate the dew point Tr (° C) depending on the air temperature T (° C) and its relative humidity Rh (%):
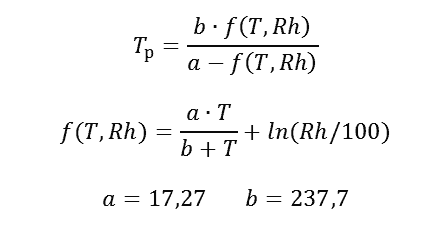
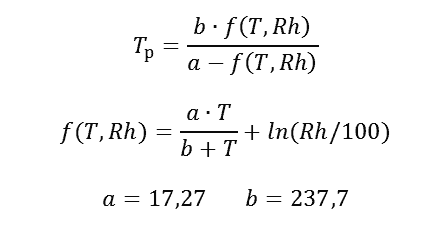
The formula has an error of ± 0.4 ° C in the range of air temperature T from 0 ° C to 60 ° C, dew point temperature Tr from 0 ° C to 50 ° C, relative humidity Rh from 1% to 100%.
Dew point devices
Psychrometer (hygrometer psychrometric) - a device for measuring air humidity and temperature. The psychrometer consists of two alcohol thermometers, one of them is an ordinary dry thermometer, and the other has a humidification device. Due to the evaporation of moisture, the humidified thermometer cools down. The lower the humidity, the lower its temperature. At 100% humidity, the thermometer readings are the same. A psychrometric table is used to determine the relative humidity. Such devices are currently used only in laboratory conditions.
The most convenient in the practice of building inspection are portable electronic thermohygrometers with indication of temperature and relative humidity on a digital display. Some models of thermo-hygrometers also have a dew point indication.


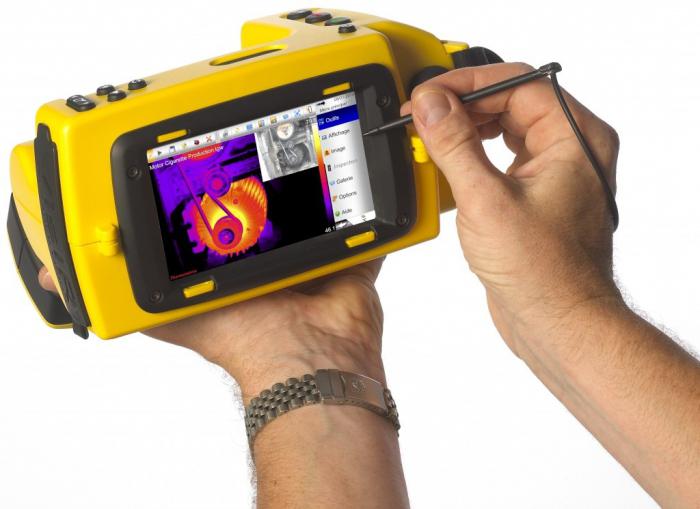
Dew point calculation in thermal imager
Some models of thermal imagers have a built-in function of calculating the dew point in real time and displaying an isotherm on the thermogram, clearly showing the surfaces where the temperature is below the dew point during thermal imaging. Such a function is available, for example, in the FLIR Systems line of thermal imaging cameras for construction purposes (“B” series from “Building”).
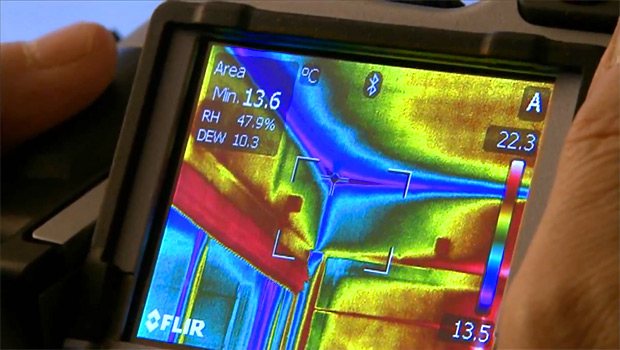

The dew point isotherm can be added to the thermogram later in the processing program on the computer. For the calculation, you will need to set the temperature and humidity.The isotherm will paint over all surfaces on the thermogram, the temperature of which is below the dew point. Please note that this function only shows areas of condensation hazard under the conditions of a thermal imaging survey. If the outside temperature rises, and the humidity inside drops, the danger zones will disappear from the thermogram (the structures will be warmer, and the dew point is lower). Below are screenshots of FLIR and TESTO programs.

Dew point in construction
I will write in one of the following publications about the value of condensation and dew point during the operation of building structures, the position of the dew point or the plane of possible condensation in the walls, the assessment of defective structures by the dew point criterion using thermal imaging.
How to calculate the dew point?
The dew point calculation is important in many aspects of life, including construction. The quality of life in new buildings and premises that have been leased for a long time depends on the correctness of the definition of this indicator. So how do you determine the dew point?
To determine this indicator, use the formula for the approximate calculation of the dew point temperature Tr (° C), which is determined by the dependence of the relative humidity Rh (%) and the air temperature T (° C):
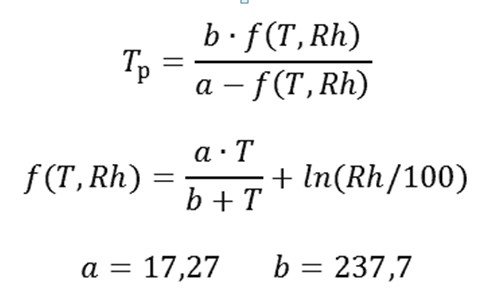
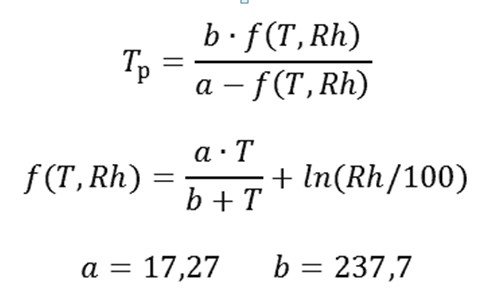
With what devices is it calculated?
So how is the dew point calculated in practice? The determination of this indicator is carried out using a psychrometer - a device consisting of two alcohol thermometers that measures humidity and air temperature. It is used mainly in laboratories these days.
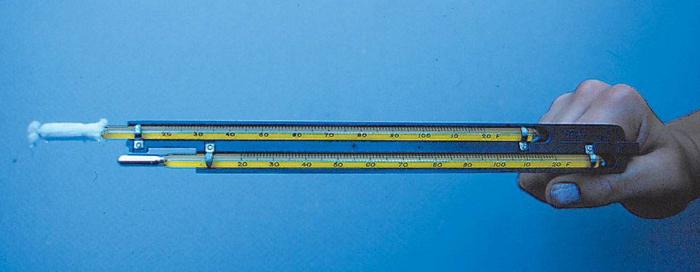

To inspect buildings, portable thermo-hygrometers are used - electronic devices, on a digital display of which data on relative humidity and air temperature are displayed. On some models, even the dew point is displayed.
Also, some thermal imagers have the function of calculating the dew point. At the same time, a thermogram is displayed on the screen, on which surfaces with temperatures below the dew point are visible in real time.


About heaters and their role in moisture condensation
Some heaters release moisture when the humidity drops. Cellulose: Ecowool and its natural counterparts, which come on the market with another brand, have a fibrous structure capable of absorbing moisture without condensation, and then easily giving it away. And some accumulate it, while losing their insulating properties. It is very difficult to dry mineral wool, polyurethane foam boards, PPP boards. By regulating the air humidity in the room without compromising its thermal insulation properties, ecowool reduces the risk of dew point at the surfaces and inside the wall. Having no seams, it does not allow warm air to pass to cold surfaces, cold streams to internal partitions.
How is the dew point in construction determined?
Dew point measurement is a very important stage in the construction of buildings, which must be carried out even at the stage of project development. The possibility of air condensation inside the room depends on its correctness, and, consequently, the comfort of further living in it, as well as its durability.
Any wall has a certain moisture content. That is why, depending on the material of the wall and the quality of the insulation, condensation can form on it. The dew point temperature depends on:
- indoor air humidity;
- its temperature.
So, using the above table, you can determine that in a room with a temperature of +25 degrees and a relative humidity of 65%, condensation will form on surfaces with a temperature of 17.5 degrees and below. A rule should be remembered: the lower the humidity in the room, the greater the difference between the dew point and the temperature in the room.


The main factors that affect the location of the dew point are:
- climate;
- indoor and outdoor temperature;
- humidity inside and outside;
- mode of living in the room;
- the quality of the functioning of the heating and ventilation systems in the room;
- wall thickness and material;
- insulation of floors, ceilings, walls, etc.
Dew point
The dew point at a given pressure is the temperature to which the air must cool in order for the water vapor contained in it to reach saturation and begin to condense into dew.
The dew point is determined by the relative humidity and air temperature. The higher the relative humidity, the higher the dew point and closer to the actual air temperature. The lower the relative humidity, the lower the dew point of the actual temperature. If the relative humidity is 100%, then the dew point is the same as the actual temperature.
Real life example
- any object is brought into a warm room from frost. The air above the surface of such a thing cools below the dew point (for the current humidity and temperature) and “dew” forms on the surface. The higher the moisture content in the air, the less the temperature difference between the air temperature and the temperature of the same object is needed in order for the condensation process to begin. Subsequently, the object heats up to room temperature, and the condensate evaporates. Actually, this is the reason for the recommendation not to immediately turn on household appliances brought in from the cold.
The dew point of the air is the most important parameter, which indicates the humidity and the possibility of condensation in the room, but it cannot be controlled. This is a physical term. The dew point can be found on the graphs showing the relationship between humidity and room temperature.
If the temperature of the internal glass in the glass unit is equal to or lower than the dew point temperature at the current relative humidity of the internal air, then condensation may appear on the glass.
There are several ways to lower the humidity in the room:
1. It is recommended to maintain the air temperature in the room not lower than 20 ° С, and the relative humidity not higher than 30-40%. 2. It is recommended to ventilate the room at least 3 times a day for 10-15 minutes. When buying plastic windows, ask the managers about the additional capabilities of the microclimate regulators: combs, micro-ventilation, winter ventilation, ventilation valves allow you to choose the most comfortable and effective way to ventilate the room. 3. The ventilation hood must have a draft. It is recommended to keep the interior doors open. (provide a gap of 15-20mm between the door and the floor) 4. Heating devices (radiators) should be freed from obstructing objects (sofas, furniture, blackout curtains, etc.)
Dew point table. Example: if the room temperature is + 20 ° С, and the relative humidity is 40%; dew point at which condensation can occur on glass is + 6 ° С
| Ow. / T | 0 | 2,5 | 5 | 7,5 | 10 | 12,5 | 15 | 17,5 | 20 | 22,5 | 25 |
| 20 | -20 | -18 | -16 | -14 | 12 | -9,8 | -7,7 | -5,6 | -3,6 | -1,5 | -0,5 |
| 30 | -15 | -13 | -11 | -8,9 | -6,7 | -4,5 | -2,4 | -0,2 | 1,9 | 4,1 | 6,2 |
| 40 | -12 | -9,7 | -7,4 | -5,2 | -2,9 | -0,7 | 1,5 | 3,8 | 6,0 | 8,2 | 10,5 |
| 50 | -9,1 | -6,8 | -4,5 | -2,2 | 0,1 | 2,4 | 4,7 | 7,0 | 9,3 | 11,6 | 13,9 |
| 60 | -6,8 | -4,4 | -2,1 | 0,3 | 2,6 | 5,0 | 7,3 | 9,7 | 12,0 | 14,4 | 16,7 |
| 70 | -4,8 | -2,4 | 0,0 | 2,4 | 4,8 | 7,2 | 9,6 | 12,0 | 14,4 | 16,8 | 19,1 |
| 80 | -3,0 | -0,6 | 1,9 | 4,3 | 6,7 | 9,2 | 11,6 | 14,0 | 16,4 | 18,9 | 21,3 |
| 90 | -1,4 | 1,0 | 3,5 | 6,0 | 8,4 | 10,9 | 13,4 | 15,8 | 18,3 | 20,8 | 23,2 |
| 100 | 0,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 7,5 | 10,0 | 12,5 | 15,0 | 17,5 | 20,0 | 22,5 | 25,0 |
The partial pressure of water vapor contained in the air of the room (absolute humidity of the indoor air eв) depends on the temperature of the indoor air tв and its relative humidity \ varphiв as
ev = E (t) \ varphi
The dependence is presented graphically in Figure 1:
At a low outside temperature, the temperature on the inner surface of the glazing (τv.p.) will be significantly lower than the air temperature inside the room (in the middle of the room at a height of 1.5 m from the floor). In this case, the limiting value of the partial pressure of water vapor E, corresponding to the temperature τw.p., may be lower than the calculated value e = f (tw, \ varphiw), which will lead to the loss of "excess" water vapor on the cold inner surface of the glazing in the form condensation or frost. The temperature value at which E = f (τv.p.) And ev = f (tv, \ varphiв) will be equal, corresponds dew point temperature.Let's determine the probability of condensation on the inner surface of a single-chamber glass unit 4-12-4, installed with an internal air temperature tв = 20 ° C and an internal air humidity \ varphiв = 60%, provided that the outside temperature drops to tn = -30 ° C.
- According to GOST 24866-99 "Glued double-glazed windows", the reduced heat transfer resistance of a 4-12-4 double-glazed window is Ro = 0.30 m 2 ° C / W
- Determine the dew point at indoor air temperature tв = 20 ° С and relative humidity \ varphiв = 60%. In accordance with Figure 1, the limiting value of the partial pressure of water vapor E at a temperature of tв = 20 ° C is 17.53 mm Hg. According to the equation ev = E (t) \ varphi absolute air humidity e = 17.53 * 0.6 = 10.52 mm Hg, which corresponds to the dew point t = 12.0 ° C
- Determine the temperature on the inner surface of the glass unit.
τv.p. when the outdoor temperature drops to -30 ° С. The total temperature difference in this case is δT = Tv-Tn = 20 + 30 = 50 ° C.
Proceeding from the fact that the temperature drop in the thickness of the enclosing structure from the inside to the outside is proportional to the change in thermal resistance, namely
δtв = (δ.Т / Ro) xRв where
Rw = 0.12 - resistance to heat transfer at the inner surface of the glazing.
Accordingly, we get \ varphitв = (50 / 0.30) x0.12 = 19.99 ° C
The temperature on the inner surface of the glass unit will be equal to τv.p. = 20-19.99 = 0.01 ° C, which is significantly lower than the dew point temperature for a given room (t = 12 ° C)
Thus, the temperature on the inner surface of a single-chamber double-glazed window installed in a room with an internal air temperature of tв = 20 ° С and an internal air humidity \ varphiв = 60%, provided that the outside temperature drops to tн = -30 ° С, will be significantly lower than the temperature dew point, which will lead to abundant condensation and the formation of ice on the glass from the inside of the room.
So, to summarize, we can say that such example conditions are acceptable for some industrial enterprises, parking lots, shopping centers, etc. that is, for premises not intended for permanent residence of people [1]
Window firms all the time
faced with a dew point - the eternal problem of condensation, especially in winter (windows "flow", "cry" in the frost, condensation falls abundantly on glass and frames) does not give anyone rest. This problem especially worries those who have not yet installed windows for themselves and are very afraid to face this problem in the future.
- I.V. Boriskina, A.A. Plotnikov, A.V. Zakharov "Design of modern window systems for civil buildings"
Smirnova Dana
Features of non-insulated walls
In many rooms, wall insulation is completely absent. In such conditions, the following options for the behavior of the dew point are possible, depending on its location:
- Between the outside surface and the center of the wall (the inside of the wall is always dry).
- Between the inner surface and the center of the wall (condensation may appear on the inner surface if the air in the region is suddenly cooled).
- On the inner surface of the wall (the wall will remain wet throughout the winter).
Dew point localization
The location of the dew point depends on which side the insulation is located on. So, in a wall without insulation, it will shift along the thickness of the wall depending on changes in air temperature and humidity. With a minimum temperature difference, it will be located in the thickness of the wall between the center and the outer surface.
Subsequently, the inside of the wall will remain dry. When its position is between the inner surface and the center of the wall, the latter will get wet inside during a sharp cold snap or during a frost period.
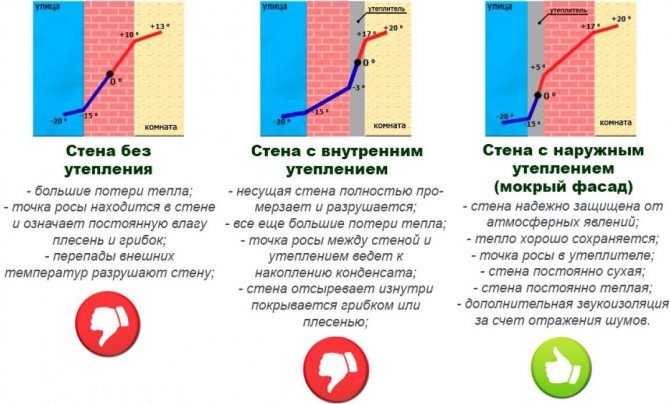

The wall can be insulated from the outside or outside, or it can not be insulated at all.The location of the dew point will depend on this.
In a wall with insulation on the outside, the location of the dew point will be optimal. Indeed, in this case, it will be located inside the insulation, and thus the inner surface of the wall will be dry. This is the best option.
But, if the thickness of the insulation was chosen incorrectly, the dew point may shift, which is fraught with the appearance of fungus, mold, and rapid destruction of the walls.
In a wall with a heater installed from the inside, condensation forms in the wall closer to the living quarters, the temperature of the wall under the thermal insulation layer decreases, creating optimal conditions for the growth of mold.
Localization can be like this:
- between the center of the wall and the insulation, and during frosts or a sharp drop in temperature at their border;
- on the inner surface of the wall, which will be wet throughout the winter period under the insulation;
- inside the insulation, which, like the wall under it, will be wet during the entire cold period.
As you can see, the location of the dew point has a significant impact on human comfort and health.
How to properly insulate the wall?
In an insulated wall, the dew point can be located in different places of the insulation, which depends on a number of factors:
- The thermal insulation properties of the insulation decrease as the level of its moisture increases, since water is an excellent conductor of heat.
- The presence of insulation defects and gaps between the insulation and the wall surface creates good conditions for the formation of condensation.
- Dew drops significantly reduce the thermal insulation properties of the insulation, and are also an aid for the development of fungal colonies.
Thus, one should understand the risk of using materials that allow moisture to pass through walls for wall insulation, since they are susceptible to loss of heat-shielding qualities and gradual destruction.
In addition, be sure to pay attention to the ability of the materials chosen for wall insulation to resist ignition. It is better to opt for materials with an organic matter content of less than 5%. They are considered non-combustible and are most suitable for insulating living quarters.
External wall insulation
The ideal option for protecting a room from dampness and cold is external wall insulation (provided that it is made in compliance with technology).


In the event that the thickness of the insulation is chosen optimally, the dew point will be in the insulation itself. The wall will remain absolutely dry throughout the entire cold period, even with a sharp cold snap, the dew point will not reach the inner surface of the wall.
If the thickness of the insulation has not been calculated correctly, some problems may arise. The dew point will move to the boundary between the insulation material and the outside of the wall. Condensation can form in the cavities between the two materials and moisture can accumulate. In winter, when the temperature drops below freezing, moisture will expand and turn into ice, contributing to the destruction of thermal insulation and partly of the wall. In addition, the constant humidity of the surfaces will lead to the formation of mold.
In case of complete non-observance of the technology and gross errors in calculations, it is possible to displace the dew point to the inner surface of the wall, which will lead to the formation of condensation on it.
Internal wall insulation
Insulating the wall from the inside is initially not the best option. If the insulation layer is thin, the dew point will be at the border of the insulation material and the inner wall surface. Warm air in a room with a thin layer of thermal insulation will practically not reach the inner side of the wall, leading to the following consequences:
- high probability of getting wet and freezing of the wall;
- moistening and, as a result, the destruction of the insulation itself;
- excellent conditions for the development of mold colonies.


However, this method of warming a room can be effective.To do this, you must comply with some prerequisites:
- the ventilation system must comply with regulations and prevent excessive humidification of the ambient air.
- the thermal resistance of the fence structure, according to regulatory requirements, should not exceed 30%.
What is the risk of ignoring condensation in construction?
In winter, when the temperature is almost constantly below zero degrees, warm air inside the room, in contact with any cold surface, is supercooled and falls on its surface in the form of condensation. This occurs provided that the temperature of the corresponding surface is below the dew point calculated for the given temperature and humidity.
If condensation occurs, the wall is damp almost always at a lower temperature. The result is the formation of mold and the development of a wide variety of harmful microorganisms in it. Subsequently, they move into the surrounding air, which leads to various diseases of the residents, who are often in the room, including asthmatic disorders.
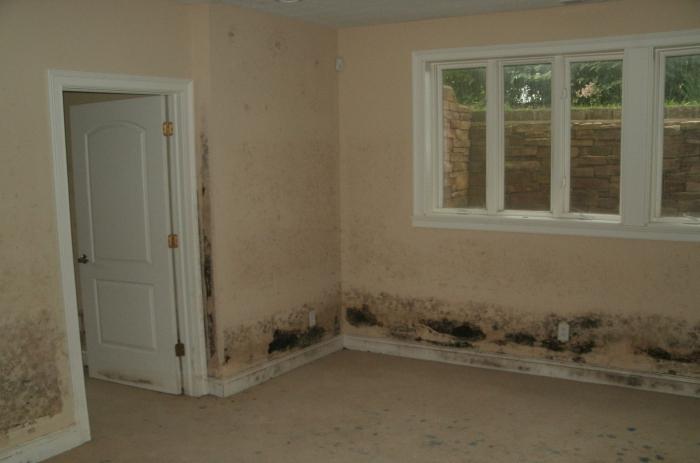


In addition, houses affected by mold and fungal colonies are extremely short-lived. The destruction of the building is inevitable, and this process will begin precisely from the damp walls. That is why it is extremely important to make correctly all calculations regarding the dew point even at the design and construction stage of the building. This will allow you to make the right choice regarding:
- wall thickness and material;
- the thickness and material of the insulation;
- method of wall insulation (internal or external insulation);
- selection of ventilation and heating systems that can provide an optimal microclimate in the room (the best ratio of relative humidity and temperature).
You can calculate the dew point in the wall yourself. In this case, one should take into account the peculiarities of the climatic region of residence, as well as other nuances given earlier. But still, it is better to contact specialized construction organizations that are engaged in such calculations in practice. And the responsibility for the correctness of the calculations will lie not with the client, but with the representatives of the organization.
Dew point concept
The dew point is the temperature at which moisture falls out or condensation from the air, which was previously in it in a vapor state. In other words, the dew point in construction is the border of the transition from a low air temperature outside the enclosing structures to a warm temperature of indoor heated rooms, where moisture may appear, its location depends on the materials used, their thickness and characteristics, the location of the insulation layer and its properties.
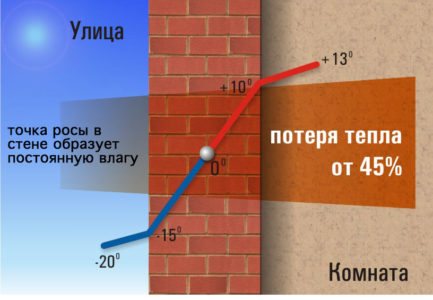

Dew point in the wall without insulation
The normative document SP 23-101-2004 "Design of thermal protection of buildings" and SNiP 23-02 "Thermal protection of buildings" regulate the conditions for accounting and the value of the dew point:
“6.2 SNiP 23-02 establishes three obligatory mutually related standardized indicators for the thermal protection of a building, based on:
"A" - normalized values of resistance to heat transfer for individual enclosing structures of thermal protection of the building;
"B" - normalized values of the temperature difference between the temperatures of the internal air and on the surface of the enclosing structure and the temperature on the inner surface of the enclosing structure above the dew point temperature;
"In" - a standardized specific indicator of heat energy consumption for heating, which allows varying the values of the heat-shielding properties of the enclosing structures, taking into account the choice of systems for maintaining the standardized microclimate parameters.
The requirements of SNiP 23-02 will be met if the requirements of indicators of groups "a" and "b" or "b" and "c" are met when designing residential and public buildings.
Condensation of water vapor occurs most easily on some surface, but moisture can also appear inside the structure. Applied to the construction of walls: in the case where the dew point is located close to or directly on the inner surface, under certain temperature conditions during the cold season, condensation will inevitably form on the surfaces. If the enclosing structures are not sufficiently insulated or were built without an additional insulating layer at all, then the dew point will always be located closer to the inner surfaces of the premises.
The appearance of moisture on the surfaces of structures is fraught with unpleasant consequences - it creates a favorable environment for the reproduction of microorganisms, such as fungus and mold, the spores of which are always present in the air. In order to avoid these negative phenomena, it is necessary to correctly calculate the thickness of all elements that make up the enclosing structures, including calculating the dew point.
According to the instructions of the normative document SP 23-101-2004 "Design of thermal protection of buildings":
"5.2.3 The temperature of the internal surfaces of the building's external fencing, where there are heat-conducting inclusions (diaphragms, through inclusions of cement-sand mortar or concrete, interpanel joints, rigid joints and flexible ties in multilayer panels, window frames, etc.), in the corners and on window slopes should not be lower than the dew point temperature of the air inside the building ... ".
If the surface temperature of the wall inside the premises or window blocks is lower than the calculated value of the dew point, then condensation is likely to appear during the cold season, when the outside temperature drops to negative values.
The solution to the problem - how to find the dew point, its physical size, is one of the criteria for ensuring the required protection of buildings from heat loss and maintaining normal microclimate parameters in the premises, in accordance with the conditions of SNiP and sanitary and hygienic standards.











