Expanded polystyrene was invented back in the 19th century by the Russian chemist I.I. Ostromyslensky, but France became the country that patented the material. Since the receipt of the patent, the mass production of expanded polystyrene as a building material began.
Currently, the insulation of the facade with expanded polystyrene is the most common type of thermal insulation for external use. Expanded polystyrene has undergone many tests and improvements to be awarded the title of a world-class facade heat insulator.
Experts advise to insulate buildings with expanded polystyrene, and reviews of owners of private houses with such thermal insulation only support their opinion.
From which side to insulate the house?
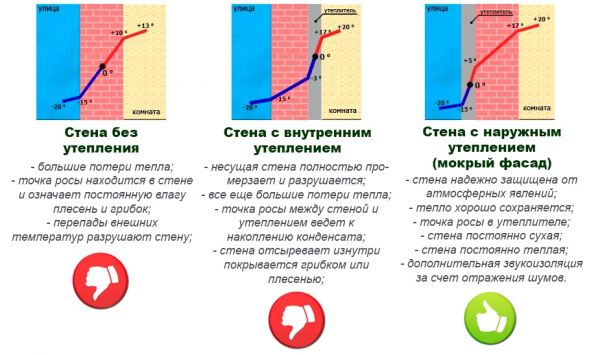
For the most efficient dew point output, it is best to use outdoor insulation walls. The reason for this is that the layer of insulation installed outside excludes direct contact of the wall with the outside cold air, which is why the outer surface of the wall ceases to give off heat to the atmosphere.
Wherein, the inner surface of the wall heats up from the warm air of the house and loses its ability to condense moisture... The dew point is transferred beyond its limits, deep into the insulation material, which almost completely excludes any harmful processes - inside the insulation (if installed correctly), there is nowhere to get moisture. Therefore, external insulation is much preferable to internal insulation, in which there are great difficulties with cutting off steam.
Dew point
The only serious drawback of the outdoor method of insulation is the complexity of the work - the need to use forests, sometimes you have to resort to the help of industrial climbers, etc. Specific conditions impose their limitations and can cause a lack of quality of work, therefore, the process should be carefully thought out and organized in the most efficient way. In addition, there are restrictions on the outside air temperature - in winter, external wall insulation is not performed.
These types of insulation are suitable for external and internal insulation:
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- penoizol;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- penoplex;
- penofol;
- polyurethane foam.
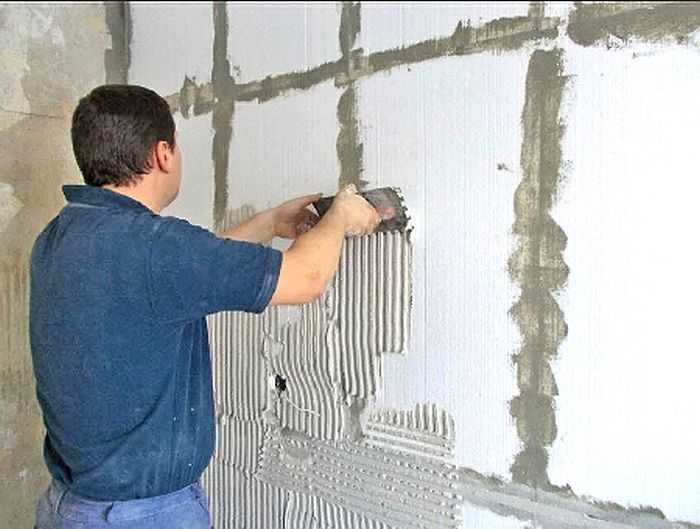
Foam reinforcement and plastering
Sometimes the insulation of the facade with foam must be stretched over two seasons - left to overwinter at some stage. Can be left without harm to materials only after applying the leveling layer. It is not allowed to leave the simply attached foam (EPS). It is recommended to even keep it packed in packs indoors, and not outdoors. So you can only interrupt after plastering.
Reinforcing mesh on corners
The mesh is used for the front, for outdoor work (the inner one will simply crumble from the glue). Density 140-160 g / sq. m. First, the corners are glued. All corners are reinforced - both external and internal, and slopes. Important! From this point on, it is necessary to use a universal composition, and not the one on which the foam was glued. The glue is diluted a little thinner than indicated in the instructions - it should adhere well to the spatula, but it is easy to push through the mesh.
For reinforcement, you can use a ready-made corner with a mesh, you can cut strips from a roll (30 cm wide) and glue them. It's easier to work with a ready-made corner, cheaper - with a piece of mesh. If you make it from a roll, cut the strips across the roll, you get pieces of a meter in length. Fold them in half lengthwise and press the fold well with a spatula.It is necessary to fold so that the edges of the mesh are wrapped inward (it was also in the roll). If it turns out the other way around, they will stick out of the glue layer, it will be hard to work.
Corner reinforcement mesh
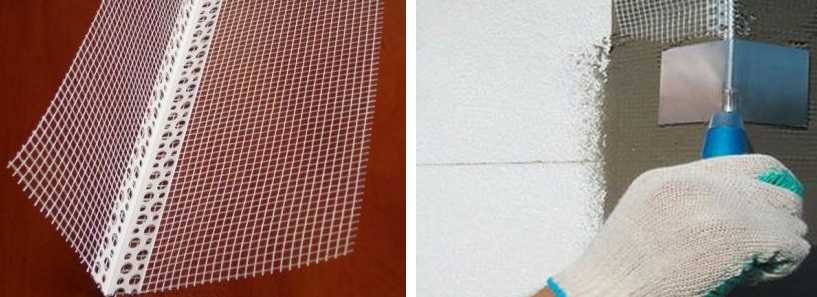

In any case, the work is almost the same. A strip of solution 6-7 cm wide and 2-3 mm thick is applied to the corner on both sides. If you do not glue the finished corner, but the bent strips of the mesh, then the length of the area filled with the solution should be 5-7 cm shorter than the cut piece (93-95 cm).
A corner or a piece of a bent mesh is placed on top. Passing a spatula along the mesh, press it slightly into the glue. Herringbone movements - top-down and sideways.
Approximately half of the mesh on the sides is left without glue. This is normal - it will be easier to dock it with the foam reinforcement in the plane of the wall. Also, without glue, a strip remains at the top if you glue from pieces. Sticking the next piece above, apply the glue directly to this "empty" mesh, cover it on top with the next piece. This gives the joint the same thickness as the entire corner.
When forming a corner, we try to make it even. If it does not work with an ordinary spatula, you can take a corner one (pictured above). It won't be difficult - just lead from top to bottom with one touch.
Foam reinforcement on walls
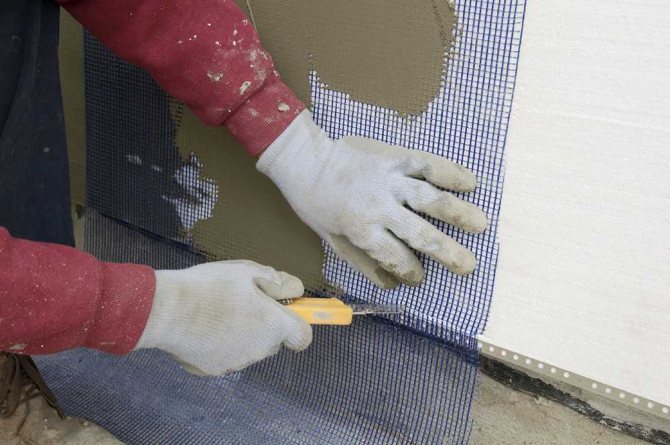
Foam and EPS are reinforced by applying a layer of plastic mesh, which is pressed into the adhesive (universal). The procedure is as follows:
- Apply a layer of glue (universal composition) to the wall with a spatula (width not less than 350 mm). The strip is 5-7 cm wider than the mesh (the mesh is usually 100 cm wide).
- Roll the mesh from top to bottom, so that 5-7 cm from one edge are free of glue.
- They pass with a spatula along the mesh, pressing it into the glue. They try to make the surface even. The mesh is rolled out onto the laid layer of glue, pressed into it with a spatula
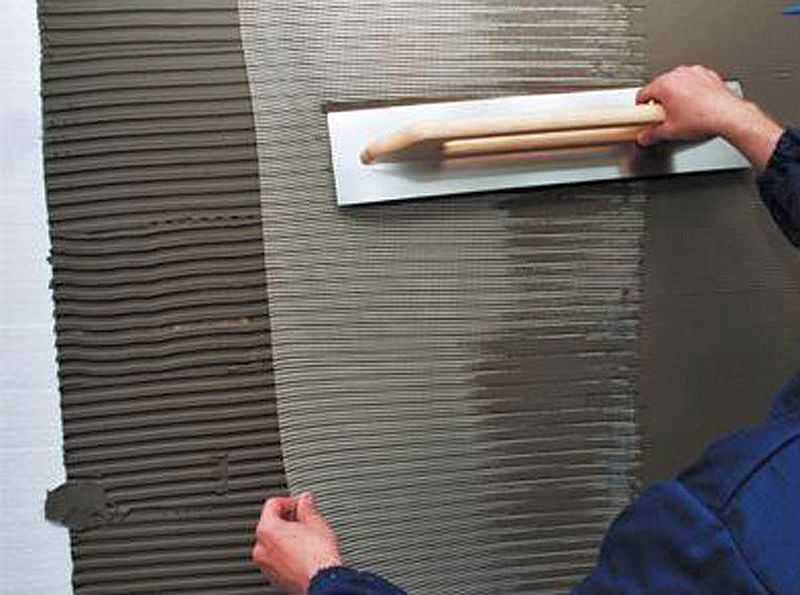


- The second strip of glue is applied starting from the “empty” mesh section. A new piece of reinforcement is applied close to the one already laid. It turns out at the junction of two layers of stacks, but the thickness of the glue is the same as on the rest of the wall. It can be seen that part of the mesh remains without solution.


The glued mesh is left to dry. It should take half a day at least, or better - a day. Then they take a grater with emery and level out all the irregularities.
Foam plaster (applying a leveling layer)
The technique of applying plaster to polystyrene is no different from the standard one. Determine the thickness of the leveling layer based on the result of the previous work. If the previous layer was applied evenly, the leveling layer can be very thin - a few millimeters.
There is only a feature - the mixture should be slightly watery. Slightly thinner than mesh. It is easier to level with such a consistency.
The applied leveling layer is left to dry. Time depends on temperature and layer thickness. Wait until it is completely dry, otherwise the emery will clog. By the way, at this stage it is better to use it already shabby - the surface will be smoother. Decent scratches remain from the new one. This is critical if further you plan to simply paint the facade, and you can work with new ones for applying decorative plaster.
This completes the insulation of the facade with foam. Next - finishing work. What they will be - you choose.
The video demonstrates all the stages. There is only one mistake: when gluing the mesh, it rolls out onto the laid layer of glue, and not onto a dry wall. With technology like the one in the video, the chances are high that the entire trim will fall along with the mesh.
Which foam to choose for thermal insulation on the outside?
The following are currently being produced types of foam :
- PBS-S-15. Has the lowest density, used in secondary objects.
- PBS-S-25. The most used material has optimal characteristics and price.
- PBS-S-35.Material used for insulation and waterproofing of underground structures - foundations, plinths.
- PBS-S-50. The densest type used in critical facilities with difficult operating conditions.
IMPORTANT!The declared density of the material often does not match the actual, therefore, when purchasing material, it is better to insure yourself and buy a more dense one.
In addition, there are modified foam samples - for example, extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). It has a higher strength, does not crumble. Moreover, it is flammable and has a lower vapor permeability than conventional foam. In addition, it is more expensive, which somewhat limits its scope.
A Few Tips
- All work when using expanded polystyrene should be carried out in dry weather.
- Monitor the temperature outside. All work at t + 50 C and below is not carried out.
- Be sure to wait for the previous coat to dry before applying the next one.
- Plates should be impregnated with anti-foam, a substance that reduces the likelihood of fire.
- Purchase all materials from the same manufacturer so that they fit better with each other.


Foam thickness
An insufficient layer of insulation is fraught with a shift in the dew point
As already mentioned, the quality of thermal insulation is very significantly affected by the thickness of the foam for insulating the wall from the outside. After all, if the insulation layer is of insufficient thickness, then it is possible that the building will freeze during the cold season. This is fraught with displacement of the "dew point" inside the dwelling, and, consequently, increased humidity and fogging of windows and walls.
Many novice builders believe that the thicker the foam, the better. This is an erroneous opinion, since there are also nuances here. For example, the desired effect will not be achieved, and material costs will increase significantly.
The best way is to correctly calculate the optimal thickness of the insulation. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the building material used in the construction of the dwelling, and the features of the climate.
Insulation will save on energy
The listed advantages will tell you how to choose foam:
- significant reductions in costs, material and installation work;
- saving heat for energy resources;
- there is no need to use additional heating devices, which also saves the family budget;
- due to the insulation of the walls with foam, it is possible to reduce the thickness of the walls from the main building material;
- stabilization of the temperature regime in the room;
- achieving the state of the ecology of the building;
- an increase in the service life of the structure, since the foam will reliably protect the walls from the influence of climatic factors.
Installation process
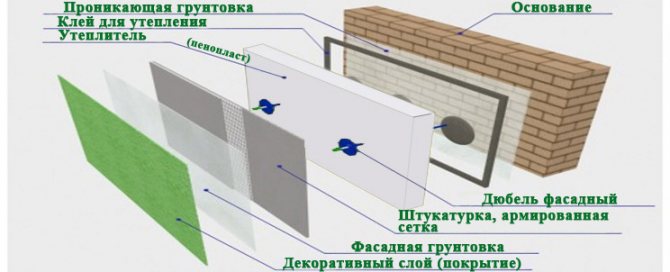
Facade insulation technology is simple, but, as in any other business, you definitely need to know the sequence of actions, installation and processing rules, as well as other subtleties of this matter.
Most often, "wet" facades are subject to foam insulation, because due to the low vapor permeability of the material, the use of a hinged ventilated structure will not be rational, and otherwise condensation will form on the surface. Therefore, you will have to install an additional forced ventilation system, which costs a lot of money. With "wet" facades, things are much easier because to install them you need to do the following:
- wall surface treatment;
- installation of basement profiles;
- mount insulation;
- reinforce the surface.
How to determine thickness
The thermal resistance of the material (R) plays a significant role in calculating the thickness of expanded polystyrene. The quality of the building's thermal insulation depends on it. This value is individual for each region. Some of them can be viewed in the table below.
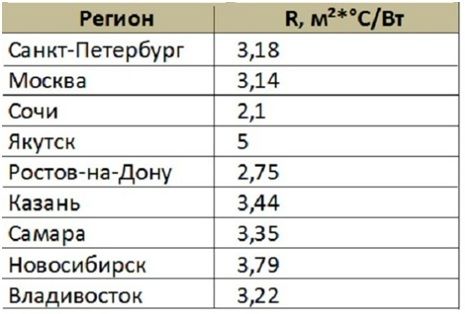

If the walls consist of several layers, then it is necessary to summarize the thermal resistance values for each material.
The calculation of the thickness of the foam is made by multiplying the indicators of thermal resistance and the coefficient of thermal conductivity, which can be found from the table.


Wall insulation with foam
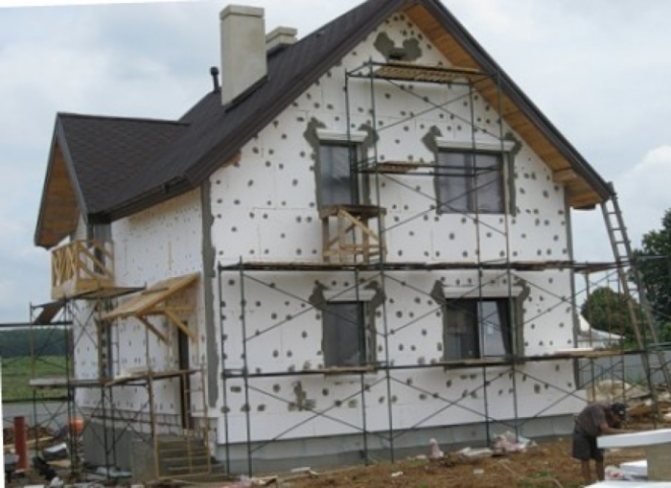
Polyfoam is a good insulation for walls. The walls are insulated with polystyrene, both inside and outside. But most often they produce insulation from the outside. When insulating from the outside, it is possible to move the largest freezing point to the outside of the wall, thereby preventing the cold from entering the room.
It is not correct to make internal insulation of walls that face the street. The fact is that the wall that goes out has to warm up thanks to the internal heating. When laying polystyrene on the inner surface of the wall, the wall will be insulated from both sides, that is, the wall will not only be insulated from the outside, but also will be insulated from the inside of the room, which will prevent it from being heated by heating.
As a result, the "dew point" will move inside the wall, or this point will be between the wall and the foam layer. Moisture will accumulate in these places and soak the wall, in addition, this moisture can freeze in frosts, that is, all this will lead to a violation of heat transfer, and the walls will gradually collapse.
Therefore, the best option would be to insulate the walls from the outside, but you will definitely need to finish the foam on top with a layer of strong plaster. Polyfoam does not have increased mechanical strength, therefore, strengthening the walls is imperative for the durability of the structure.
Insulation of walls outside with foam. Photo lpinists.com.ua
Insulation of the walls of the house with expanded polystyrene outside - stages of work
The main task of cladding insulation of a brick wall with polystyrene foam with your own hands outside is to reduce the cost of energy resources necessary to maintain an optimal microclimate inside a residential building.


Preliminary preparation of the wall
First, you should inspect the surfaces to assess the amount of work. Revealed cavities and cracks should be repaired with a cement-sand mixture. If the walls are painted, the old layer must be removed.
For accurate wall insulation outside the frame house, it is necessary to prepare the surfaces with high quality - eliminate irregularities and dry wet areas.
We insulate the slopes
Windows and doorways are the main areas of the square where significant heat loss occurs. Therefore, it is necessary to organize the thermal insulation of the slopes. This process consists of several steps:
- cleaning the surface from dirt;
- primer of slopes in two layers to improve adhesion;
- leveling by grouting;
- insulation cutting;
- applying a layer of glue;
- installation of plates;
- foaming of the formed cracks;
- plastering.
Finishing can be done later when finishing the walls.
Pasting the cornice
Before insulation, the cornice should be processed. In this case, it is important to follow several rules:
- choose a material of the minimum thickness so that it can adhere to the glue layer;
- strips of insulation must be started to glue from the wall;
- first, the vertical elements are fixed, and then the horizontal ones.
When the cornice is pasted over, they move on to the organization of steam and waterproofing.
Vapor barrier and waterproofing for insulation with expanded polystyrene
Even taking into account the fact that expanded polystyrene is considered a vapor-permeable material, it requires the installation of a vapor barrier layer to prevent the formation of condensation in the voids between the wall and the insulation layer. An excellent solution is the use of membrane films. They are installed with an overlap only on completely dry surfaces. If you insulate wooden walls, the film can be fixed with a construction stapler. When working with concrete or brick buildings, glue can be used to bond the films to the frame.
The process of preparing insulation when using extruded polystyrene foam
Before installation, you should take care of the preliminary preparation of the insulation itself. If it is not corrugated, it should be processed with a needle roller on both sides. Then you should cut out the blanks for pasting the slopes and cornice. Cutting can be done with a jigsaw or a metal hacksaw.
Preparing the wall for insulation with expanded polystyrene
In order to perform this operation yourself, you must first prepare the outer wall. Slightly protruding parts must be cut down or otherwise removed, if there are structural elements protruding beyond the facade - they will have to be pasted over separately.


Then all the potholes are closed. It is not necessary for the wall to be perfectly flat - but the expanded polystyrene must adhere to it tightly and in compliance with the vertical level. It is also advisable to clean the surface of old peeling paint and loose plaster, otherwise they will then fall off along with the sheets of insulation. If the wall is completely loose, perhaps it should be primed with a special compound. In some, especially difficult, cases, the plaster has to be cleaned up to the surface of the wall itself.
After all these works, it is necessary to check how flat the wall is - a drop of up to about 3-4 cm can be leveled by the solution to which the foam will be glued, large drops are undesirable. Next, you should measure and mark the level of the first row of insulation - the laying is always carried out from the bottom up, in horizontal rows.
What are the parameters for choosing foam
When choosing polystyrene, they take into account the physical and technical characteristics that contribute to the performance of the functions assigned to the insulation:
- keeping warm (coolness);
- ease of installation;
- the chosen method of insulation;
- environmental friendliness for nature and safety for human health.
Let's consider the characteristics in more detail.
Thickness of slabs
In stores, there are sheets with a thickness of 10 to 100 mm in increments of 10 mm. The choice of thickness depends on the region and the purpose of the building. Sheets of 40, 50, 100 mm are in demand and are most often found in retail outlets, but the manufacturer is ready to make products of 20, 60, 70, 80 up to 500 mm to order. The price will remain the same in terms of cubic meters.
To make it easier to understand, on average, 10 cm thick foam polystyrene retains heat in the same way as 45 cm thick timber, 73 cm foam concrete masonry, 150 cm brick wall or 300 cm concrete wall. This is enough to insulate walls in any region of the country.
The size
The length and width of the sheets are more difficult to choose. Here, the standard dimensions are 500x1000, 1000x1000 and rarely 1000x2000 mm. To install insulation around window and door openings, the sheets are cut with a sharp knife or file with fine teeth.
For large objects, electric cutters are purchased and made on their own - this way the material crumbles less, the edges remain even, which is convenient for further finishing.
Density
The main parameter characterizing the field of application is density.
For use in construction, manufacturers produce products of three varieties, which are conventionally designated by numbers in the name - 15, 25, 35. Their brief comparative characteristics are given in the table.
Table. Characteristics of different brands of foam.
| Brand | Specific weight, kg / m3 | Thermal conductivity, W / (m * K) | Compressive strength, MPa | Retail price, rub / m3 | Appointment |
| PSB-S-15 | 10 — 11 | 0,04 | 0,05 | 1700 | Thermal insulation by the "frame" method or between the main wall and the facing brick |
| PSB-S-25 | 15 — 16 | 0,035 | 0,1 | 2500 | Insulation "wet" facade |
| PSB-S-35 | 25 — 27 | 0,033 | 0,16 | 3800 | Thermal insulation of horizontal surfaces "under the screed" |
If we compare thermal conductivity, then the values for different types of expanded polystyrene do not differ much, unlike the price, so you should not overpay "for density".
Flammability
Styrofoam burns only when exposed to open fire. The freezing time (self-burning) is 3 - 4 seconds.
At the same time, during the combustion of polystyrene, highly poisonous substances are released, causing death from suffocation.
Foam installation technology on walls
For a normal result, the foam is first glued to the walls, then nailed. Exactly so, and not otherwise. Glue starts from the bottom, usually from the left corner. If the house is insulated with foam, then the first row is supported on the installed ebb, if the thermal insulation is improved in an apartment building, the starting bar is nailed. Without it, there is a high probability that the foam will creep down.
Materials and tools
You will need two spatulas to stick the styrofoam on the walls. One is about 100 mm wide, the second is 180-200 mm. The narrow ones take glue from the container, and the wide ones apply it to the walls. You may also need a saw with a fine-toothed blade to trim the material. All of the tools at this stage. We'll need some more glue. It requires a special one, on the bag it should be written "for polystyrene plates" or something similar. There are two types of this glue:
- Universal compound for polystyrene and subsequent facade finishing (gluing mesh and leveling layer).
- Composition only for gluing polystyrene on walls. For other layers, universal is required.
If you approach the issue from an economic point of view, it is more profitable to buy two different compositions - the universal one is decently more expensive. A number of operations can be done with glue:
- glue polystyrene to the wall and to the slopes;
- grease the joints of the insulation;
- grease fixing mushrooms;
For gluing polystyrene on walls, you need a special glue


The list of works for which universal glue is required is as follows:
- gluing mesh to corners (and slopes too) and walls;
- applying a leveling layer.
The consumption of both compositions is approximately the same and amounts to 4-6 kg per square meter. Consumption can be less if the walls are initially flat and a smaller layer of glue is required (no need to level the depressions). The consumption for the leveling layer (after gluing the mesh) depends on how smoothly the polystyrene is fixed, whether its corners stick out or not.
For additional fixing of polystyrene to the wall, fungi are needed
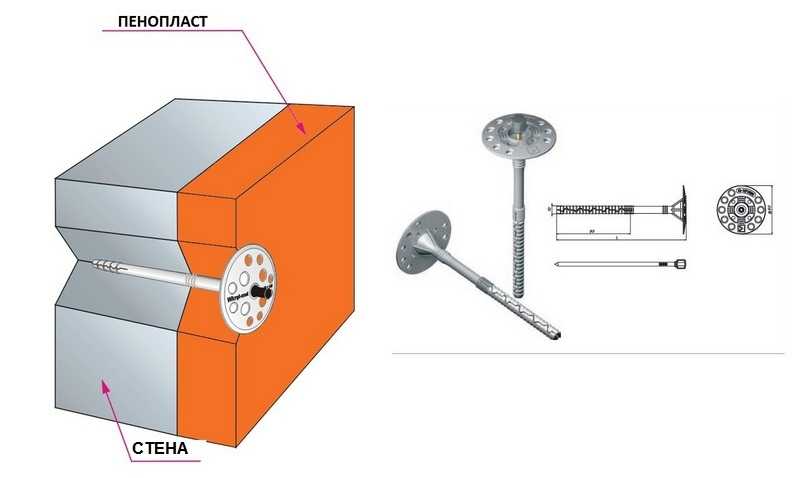

For the second stage - fixing polystyrene on the walls - fungi will be needed. These are special shaped dowels with a large plastic cap and a long leg. Steel or plastic dowel nails are inserted into the dowels. When insulating the facade with polystyrene, it is better to use plastic. They do not conduct cold, do not corrode, cost less, and a large insulated facade does not create loads.
You will need a drill and a hammer to install the fungi. To apply the mesh and leveling layer, you will need an even wide spatula - 300-350 mm or even more. To sand the leveling layer, you will need a plastic float and sandpaper with a grit of 400-500.
Technique of gluing polystyrene on walls
The glue is mixed with water according to the manufacturer's recommendations (stir with a drill with a nozzle or mixer). It is more convenient to work when it is a little thicker than it turns out if you follow the recommendations. Therefore, we do not add a little less water, but there we see how convenient it is to work.
If the wall is uneven, apply the glue to the wall. This makes it easier to correct irregularities - put more in the grooves and less on the humps. If there is too much hump left to reduce glue consumption, a notch can be made in the foam. With EPS, this trick will not work.
Apply glue like this, but only on walls, not on foam


Lay the solution with "cakes" up to 9-10 in area, and also make a roller (not continuous) around the perimeter of the slab, stepping back 3-4 cm from the edge. The sizes of the lozenges are not necessarily the same. It is only important to level the surface as much as possible. After laying out the glue, apply the foam, press down, clap with the palm of your hand (not hard so as not to crush). Sausages spread out along the edges can crawl out of the seams or "float" under other sheets. The fact that they crawl onto other sheets is normal and even good, it will hold on more firmly. But the glue that has come out is better to pick up. Then there will be less alignment.
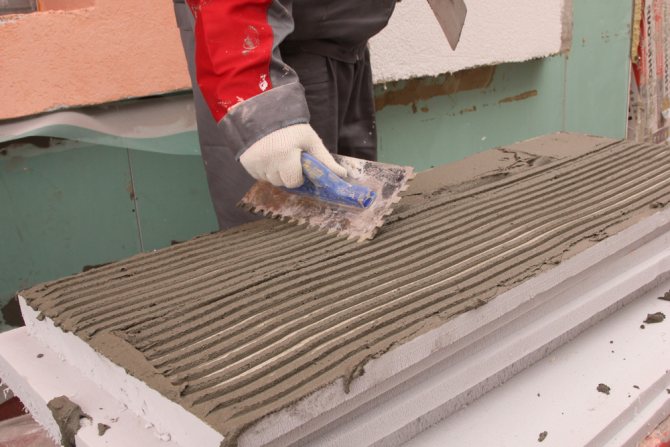
There is a second technique - to apply glue to the foam, level it with a comb (notched trowel) and glue it like that. But this method is suitable only on flat facades without drops.
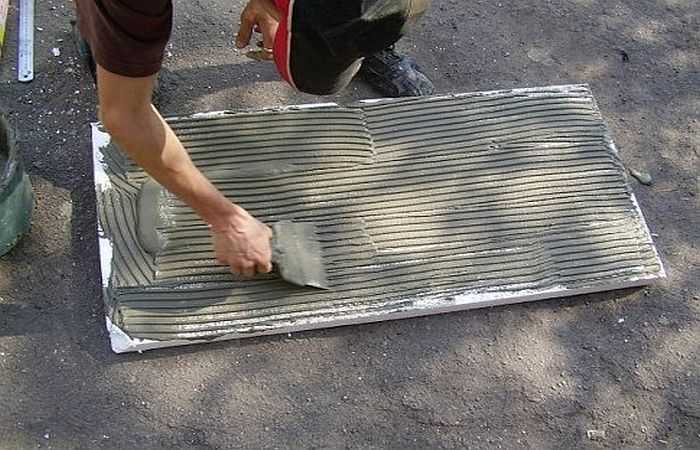
If the wall is even, apply it in a continuous even layer on the foam


When laying the second row, the sheets are positioned so that the seams are not continuous (with an offset, such as brickwork). All subsequent rows also make sure that the seams do not match. We leave the styrofoam glued to the facade for 3 days - this is about how much the glue dries. In the meantime, we glue it in the second section.
A few words about how it is more convenient to glue foam on the facade and what kind of site. If a private house is insulated with foam, the area of work is significant, as is the height. Some of the work will be done from the ground, some will have to be done from the scaffold. To carry them less, it is more convenient to carry out work in sections. One section is done completely - from gluing the foam to the leveling layer, go to the next. In this order of work, there is another plus: less polystyrene remains open (it reacts poorly to ultraviolet light).
Divide the house into sections with different stages of work


We nail down polystyrene (EPS)
So, after the glue has dried (3 days have passed after it was glued), we take plastic fungi (those that are more expensive, they are hard and clog well). Their length depends on the thickness of the insulation. To it (thickness) it is necessary to add 4-5 cm, by which the fungus should enter the wall. If you have a foam layer of 50 mm, then the fungi should be no shorter than 9-10 cm.
The fungi should go into the wall by 4-5 cm. The figure is inaccurate - the mesh is glued over the fungus
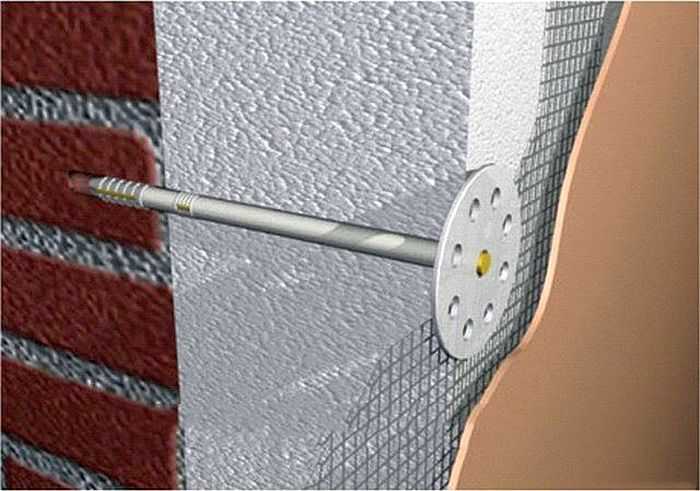

One plate requires 5-6 fungi. In the selected places, holes are drilled (drill 10 mm) 2-3 cm deeper than the length of the legs of the fungus. If the holes are made shorter, they become clogged with material dust and do not fit completely. The location of the fungi is one in the center of the slab and several at the joints. This position allows you to nail down the foam and level the wall at the same time (pull the coal to the desired position).
The layout of fungi when insulating the facade with foam

A fungus is inserted into the drilled hole, then hammered in with a hammer. His hat should fit snugly against the insulation. If not, take out, deepen the hole. Sometimes, after a certain amount of established fungi, they stop clogging. This means that the drill has worn off - it has become smaller in diameter - and it is time to change it.
We hammer plastic dowels into fungi
They clog the fungi so that the cap is slightly recessed in the foam - it leaves about 1 mm. Then the consumption of glue for the leveling layer will be less. It is easy to score with foam, but it is more difficult with expanded polystyrene (EPS).
If there are two layers of insulation
If the required thickness of the insulation is more than 50 mm, but less than 100 mm, two layers are applied. In this case, one layer is glued, as described above, the sheets of the second are positioned so that they do not coincide with the joints of the first. When applying the second layer, it is more convenient to apply the glue to the sheet rather than to the wall. The joints of the first one can not be overwritten or foamed - they will overlap.
If you have time, it is advisable to wait until the first one is dry before applying the second layer. If this is not possible, you can immediately glue the second one, but to a height of no more than 2 m, otherwise the sheets may move.
The seams of the first and second layers must not match


We begin to nail down the foam with fungi after the glue dries (the same 3 days). Just do not be mistaken in calculating the length of the fungus - the total thickness of the insulation + 1 cm for glue + 4-5 cm for the wall. The depth of the hole is another 2-3 cm more, the diameter is the same 10 mm. When the foam is nailed to the facade, you can move on.
Sealing joints and fungi
First, we align the section of the facade, pasted over with foam. It often happens that the edges of the foam stick out somewhere.They can be cut off with a stationery (wallpaper) knife. There are also special graters for foam. They are convenient for leveling the surface. You can also try to do this with EPS, but only with a knife, and then it is cut badly. The work takes a lot of time, but it is worth spending time on it - this will greatly reduce the consumption of expensive compounds for subsequent finishing layers.
Then, in order to exclude the ingress of cold air between the plates, the seams are rubbed. They take on the spatula the same composition with which the foam was glued to the facade, fill the seams. If there are seams larger than 3 mm, we put a narrow strip of insulation in them, then rub with glue. You can fill the seam with polyurethane foam. We leave it for 4-5 hours, then cut off the excess with a knife and rub it with glue on top. The caps of the fungi are recessed, we also gloss over them, leveling them with the main surface.
Rubbed Styrofoam Seams


When grouting joints and caps, we try to make the surface even - the glue should not protrude. If you have looked somewhere, after drying we take a grater, fix the sandpaper (grain 400-500) and level it. You just need to wait until it dries completely - once it gets into wet glue, the emery immediately clogs up, you just need to change it (the mesh is not suitable for this work).
Material advantages
We have already understood that polystyrene is an excellent material that is used to insulate walls, as well as soundproof a room. It doesn't matter what size it is. This material is very light and compact, which does not cause any big problems during transportation. It is very well cut to the required dimensions, so it can be used for insulation of various sizes and shapes. Poor sound conductivity allows the use of this material not only for insulation and sound insulation of residential buildings, but also significantly expands the scope of its application.
Thermal insulation of ceilings: polystyrene is suitable for ventilated rooms
When insulating the ceiling, it is important to remember not only about the thermal insulation properties of polystyrene, but also about moisture resistance. After all, hot air and vapors from the kitchen, bath, etc. will tend upward. If you lay these heaters, then the steam will not go beyond the ceiling ceilings, but may settle on them in the form of condensation. But if natural and forced ventilation works well in the house, then lay any of the options boldly. The thermal insulation will be top notch.


In non-insulated rooms (balconies, summer verandas), the expanded polystyrene ceiling will be an excellent insulator against moisture
Corresponding Foam Advantages and Disadvantages
In the information disseminated by manufacturers and traders of this material, there is not a word about its shortcomings, there is only a list of advantages. This is quite understandable, because the ultimate goal of an enterprise and a store is to make a profit from the sale of goods. But since polystyrene has been used as a heater for more than 50 years, over such a long period of practical application, it was possible to identify its weaknesses.


They are not widely publicized, but in order to choose the right material for facade insulation, this information is very valuable. After all, foam has both nuances and restrictions on the scope of application.
Styrofoam and pests
One of the advantages of this type of insulation material is the fact that the foam granules are not suitable for food for rodents. The facts are not so straightforward. The practice of using this type of material in construction shows that rodents really do not accept PPP as a food source. But at the same time, they are able to gnaw the insulation, significantly damaging it.
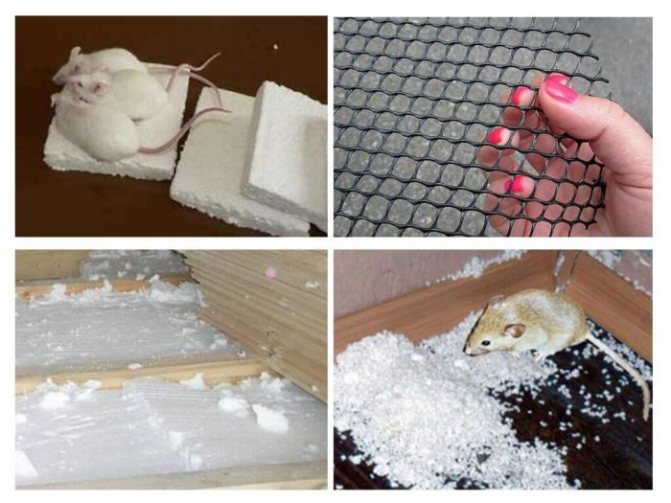


There is only one sure way to escape this misfortune - to block any access to the foam sheets for rodents. A practical homeowner would do just that.
The effect of ultraviolet radiation on foam
Manufacturers of foam products do not advertise information that the material is not resistant to ultraviolet rays.The direct rays of the sun are especially dangerous for him. Often the consumer remains unaware that this radiation changes the coefficient of chemical stability of expanded polystyrene and contributes to its intensive aging. Styrofoam is a polymer material that is subject to gradual degradation. Exposure to ultraviolet light contributes to a significant acceleration of this process.


This disadvantage can be attributed to not too significant, since it is possible to protect the insulation material from the effects of UV rays, simply by hiding it from the direct sun. When the insulation foam layer is already fixed on the facade of the building, you need to start finishing work on the cladding as soon as possible.
Soundproofing qualities of PPP
Assurances of expanded polystyrene sellers about the high quality of sound insulation of the material are very doubtful. The owners of frame houses who have used polystyrene foam to insulate their homes, massively complain that the level of sound absorption was much lower than expected.


This fact lends itself to a simple explanation: more than 90% of air is present in the composition of expanded polystyrene. It perfectly accumulates heat and at the same time successfully conducts sound. This means that you should not place too high hopes on the fact that this material will help reduce the permeability of the walls of the building for sounds from the outside.
Water vapor permeability of PPP
The reduced level of vapor permeability of expanded polystyrene in a practical sense means that an obstacle from expanded polystyrene plates will appear on the path of vapor flows from the inside of the dwelling to the outer contour of the building. Often the air temperature outside is much lower than in an apartment or house. Condensation will inevitably fall out, and as a result, the accumulation of moisture in those places where the joints of the heat insulator with the wall structure are located. This will significantly increase the risk that adjacent materials may become damp.
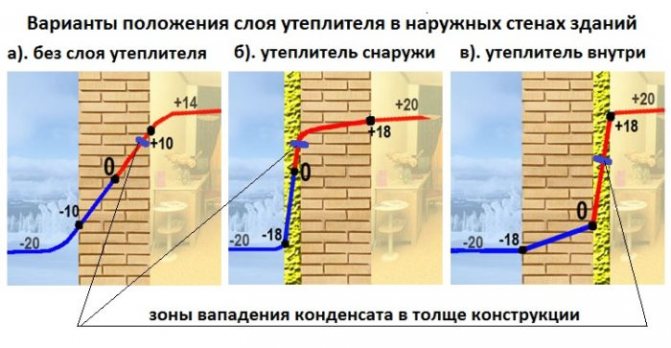

The only reasonable solution would be to correctly calculate the dew point, the design thickness of the insulating material. The dew point should not coincide with its limits. The right solution in this case will be the arrangement of the ventilation facade. It is worth taking into account the following information - the ability of the insulation to pass steam can only be considered in conjunction with a detailed overview of the structure as a whole. The material for the construction of the walls, the presence or absence of steam and waterproofing, the height of the foundation of the building and many other factors affect.
The choice of foam in terms of heat conductivity
The best thermal insulation qualities are shown by insulation materials based on polystyrene foam with a low density level, such as extruded polystyrene foam. Its thermal conductivity is one of the lowest, since the material is low-density (from 25 to 35 kg * m3).


According to experts, a 20-cm layer of expanded polystyrene produced by extrusion is comparable in terms of the level of heat savings with a 30-cm layer of foam, having a density of 15 kg * m3 and 25 kg * m3.
Summary of characteristics
Polyfoam or expanded polystyrene is produced from a polymer mass that is exposed to water vapor under high pressure.
As a result, the polymer granules increase tenfold, and a foam material is obtained. In fact, these are millions of air bubbles enclosed in the thinnest polystyrene shells, which account for only 2-3% of the total volume of the material. Expanded polystyrene is a solid and fairly durable foam, created with one purpose - to keep the heat in the room.
The main characteristics of expanded polystyrene:


Thermal conductivity - mineral wool is the main competitor to expanded polystyrene, but if we compare the indicators of their thermal conductivity, it becomes clear that mineral wool loses significantly.
At the same time, the level of thermal conductivity of expanded polystyrene can be varied by choosing a material of different density - the denser the structure, the higher the thermal conductivity. Vapor permeability - ordinary foam has zero vapor permeability, since dense polystyrene shells of air bubbles are not able to pass wet vapor. Extruded polystyrene foam differs from ordinary polystyrene, since the cutting method is used to form it, which means that steam can be taken in through the cuts. Moisture absorption - the situation with moisture absorption is somewhat different. Regular polystyrene foam, immersed in water, absorbs 10 times more water than dense extruded polystyrene foam.
For this reason, it is recommended to use extruded polystyrene foam for exterior decoration of houses. In order for the foam to serve for a long time and continue to retain high-quality heat, it must be properly protected from getting wet. Durability - extruded polystyrene foam is ten times stronger than usual, since it has a denser structure, and, accordingly, the bond between molecules is stronger. The flexural strength is from 0.4 to 1 kg / cm², while in ordinary polystyrene foam it is equal to 0.02-0.2 kg / cm². Soundproofing - many foam vendors claim that it protects equally well from cold, and from the noise, but this is not true.


Air bubbles are only able to dampen impact noise to a small extent and only if the foam is laid in a thick layer and in compliance with the technology. Foam plastic cannot cope with airborne noise, which usually gives us discomfort. Environmental friendliness - there is an opinion that insulation with expanded polystyrene from the inside, and in general, the use of this material in the construction of a residential building will have a detrimental effect on human health and the environment. In environmental terms, expanded polystyrene is safe, but there are several reservations.
First, the material oxidizes in the open air, which happens especially quickly with conventional non-extruded foam. During oxidation, toxic substances are released into the atmosphere: toluene, formaldehydes, acetophenone, ethylbenzene, methyl alcohol, etc.
That is why, after laying, the foam insulation must be immediately covered with insulation and trim. Flammability - if you look closely at the advertising of expanded polystyrene in the construction market, you will notice that many manufacturers focus on the fact that their products are more harmless than wood in terms of fire safety. In fact, wood needs a lower temperature to ignite than polystyrene foam. But before it ignites, it will melt and release toxic smoke.


If the manufacturer claims that his expanded polystyrene is capable of decaying on its own, do not believe it. To make sure that such a statement is false, it is enough to familiarize yourself with the Russian GOST 30244-94, which states that expanded polystyrene belongs to the group of the most dangerous materials in terms of flammability - G3 and G4. Many manufacturers, presenting their products, use European standards for determining flammability for biological, chemical and complex characteristics. Therefore, it turns out that the most dangerous and flammable material is wood.
The toxicity of expanded polystyrene is determined approximately, since it is not possible to accurately compare the combustion products of foam and wood. As for the due diligence, which can provide reliable information about the product, it is simply not included in the general list of technical characteristics. The consumer receives only part of the information, that is, inaccurate chemical characterization and nebulous biological analysis.
It should also be borne in mind that over time, any foam, even with flame retardant additives, literally gets old and loses its quality indicators, including the flammability class (it becomes more prone to fire) Durability - this indicator depends on many factors, starting from the quality of the material itself , ending with operating conditions and climate. Compliance with the installation technology and the use of suitable adhesive and protective mixtures play an important role. If the walls are insulated with expanded polystyrene according to all the rules, the material is guaranteed to last 25-30 years.
The most important mistake when choosing polystyrene foam for insulation is the incorrect calculation of the thickness of the plates. Many people think that the thicker the insulation, the better, but not only does this lead to an increase in money spending, it also reduces the service life of the insulation itself and the walls.
Polyfoam is one of the cheapest insulation materials, which can be installed without professional skills. That is why the demand for it is so great, and since demand creates supply, there are very many types of expanded polystyrene, if not too many. An ignorant person will immediately get confused in such a variety, and he will have no choice but to trust a sales consultant. Many manufacturers are cleverly playing on this, promoting not what is right for you, but what needs to be sold.
Therefore, before you go for polystyrene, conduct a detailed analysis: what you will insulate, for what purposes, climate features in your region, financial capabilities, etc. If you need to insulate the walls of the house from the outside, choose PSB-S expanded polystyrene of at least grade 40 .If you see the number 25 or less on the marking, such material is unsuitable for any construction work. After determining the grade, select the density of the material - for PSB-S40 it can vary from 28 to 40 kg / m³.


Be sure to pay attention to the density, and not only to the brand! Helpful advice: If you are assured that the density of the selected polystyrene foam is not lower than 35 kg / m³, specify how it was produced. The usual method allows you to get foam with a density of no more than 17 kg / m³, while a higher quality material can only be made by extrusion (strong pressure). Finally, break off a small piece from the corner of the polystyrene foam - if the edge breaks off unevenly and small balls are visible on scrapped, then the quality of the product is low. High-quality extruded polystyrene foam breaks off smoothly, and on break you will see regular polyhedrons.
Classes and brands of foam
Polyfoam as a material for decoration and insulation of the facade can have different brands, corresponding classes - each of them has its own purpose, composition and characteristics.
Styrofoam classes
There are two classes of finishing materials on the modern construction market:
- Pressed - it is made by pressing equipment.
- Non-pressed - materials are sintered at high temperatures.
To which class a particular finishing material belongs can be determined, so to speak, by eye, visually. So unpressed sheets of material are granules of a round or oval shape firmly glued together with a special composition, while the structure of the sheet itself is porous. The overlapped sheets are smooth, but the density can be different, depending on the brand of the product itself.
Styrofoam grades


Figure 3. Storage of facade foam
Non-pressed polystyrene is abbreviated as PSB, but pressed - PS. Although the material itself has different letter designations.
- A - the canvas is made in the correct geometric shape, namely in the parallelepiped format, with a flat edge;
- B - the edge of the sheet itself has a cut in the form of the letter L;
- R - cutting of the canvases is carried out using a hot stream;
- F - facade type or it is applicable using decorative elements;
- C - self-extinguishing type of finishing material;
- H - the material is applicable for outdoor decoration.
So the numbers in the name of the PPP will coincide with the density indicators.
Extruded foam grades
Picture 3 - BPP stamps
- PSB - 15 is the most expensive material with high brittleness. It is used as a heat-insulating and packaging material, characterized by low levels of hygroscopicity. They are used for finishing and insulating balconies, summer cottages, outbuildings.
- PSB - 25, often in the marking is supplemented with the letter F and is applicable for facade insulation.Due to its density, it is also applicable for the manufacture of decorative elements.
- PSB - 35 is a material widely used in construction and decoration. For example, for insulation of pipelines carrying heat and gas, it is applicable in the process of manufacturing a multi-layer type of panels as a heat-insulating gasket.
- PSB - 50 has the highest density, perfectly insulates heat and sound, therefore it is used on all objects, regardless of purpose.
What else do you need to know about the material?
The structure of expanded polystyrene can be called truly unique. It is developed using inflating polystyrene granules with air... It is this process that becomes the basis for the unique properties of the expanded polystyrene itself. Polyfoam is small granules that are interconnected.
In general, the material is also different. high sound insulationbecause it itself converts sound energy into heat energy. A slab of 2-3 centimeters is enough to achieve high performance in this parameter.
Insulation properties do not change even under the influence of too low or too high temperatures. The structure is not deformedeven if the material is exposed to large amounts of water.
Where is it used depending on the size?


This durable moisture-resistant insulation is used when performing outdoor work. To insulate the wall with foam, you first need to determine what density, size, type of polystyrene foam will be required for work.
The choice depends on the expected loads that this material will bear during the period of operation.
When insulating a vertical wall, the loads will be minimal; a sheet of any brand will do.
Even PSB-S 15 will give the same result as PSB-S 25 when it comes to wall insulation in areas with mild winters.
This is due to the fact that the principle of operation of the foam is based on gluing polystyrene balls, between which and inside there are multiple air chambers.
It is known that the less mass and more air, the better the effect of thermal insulation is.
It is inconvenient to work with sheets of low density, which are more fragile and break. PSB-S 25 has a high density, it is easier to finish with it.
Expanded polystyrene 25 is often used for external insulation of walls of non-residential premises. They are used to decorate balconies, loggias, garages, shopping centers, and various institutions.


For northern regions with cold winters, it is believed that a leaf thickness of 5 cm is enough to keep warm indoors on the coldest nights.
Polyfoam grade 100 is used for thermal insulation of industrial freezers, as well as for warming houses in the harsh climate of the Far North.
A sheet size of 10 cm will maximize the thermal protection index. When choosing a brand of expanded polystyrene, you can choose a sheet that has various parameters.
A non-standard sheet 500x500 is sometimes much more convenient to work with than a standard long sheet with dimensions of 2000x1000 mm.
For insulation of the walls of the house, sheets of 1000x1000 and 1000x500 mm in size are suitable. It is convenient to work with them, there are fewer joints that will have to be hermetically sealed.
To fill smaller areas, the existing sheets are cut into suitable pieces. For all non-standard situations in finishing, it is better to use a large sheet to make it easier to cut configurations.
In the process of laying, such sheets are adjusted to the desired parameters, cutting the expanded polystyrene into pieces. This material is easily cut.
Expanded polystyrene with dimensions of 2000x1000 mm is more difficult to install. Working alone, it is easier to stack two sheets of 1000x1000 than one sheet measuring 2000x1000 mm.
Advantages and disadvantages of facade insulation with expanded polystyrene


For insulation of facades with expanded polystyrene, it is recommended to choose special sheets that have been treated with flame retardant impregnations.
Such thermal insulation has a number of significant advantages:
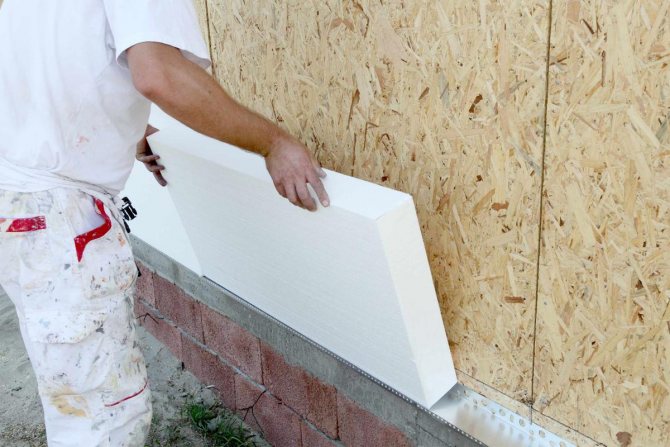
- Extruded EPS boards are easy to work with as they are lightweight and small in size. It is quite possible for one person to insulate a house without helpers.
- Plates can be processed by any means at hand - they are easy to cut and bend well enough.
- Insulation of the house from the outside with expanded polystyrene ensures that the dew point is located outside the load-bearing wall. In this case, moisture will not accumulate, and the walls will freeze.
- The facade of the building, insulated with expanded polystyrene, will act as a temperature stabilizer in terms of thermal inertia. Thus, its daily fluctuations will not affect the microclimate inside the house in any way.
- External thermal insulation with expanded polystyrene will not affect the area of the rooms.
- Walls insulated with this material will not be negatively affected by moisture from the outside, since the heat insulator is hydrophobic.
- The method of thermal insulation with expanded polystyrene is environmentally friendly. The material does not emit harmful toxic chemicals. You can work with him without using personal protective equipment.
- This surface is durable. If you cover the expanded polystyrene with a protective decorative layer, then it can last up to 80 years without losing its properties.
As for the disadvantages of the facade insulation method using expanded polystyrene plates, only the relative flammability of the material should be highlighted. Polymeric additives, which are included in the composition, are "responsible" for the increased fire hazard. However, if this heat insulator is used in accordance with fire safety requirements and the rules for its installation, then the danger can be easily avoided.
Note that the combustion temperature of expanded polystyrene is +491 degrees Celsius. This is more than 2 times higher than paper or wood. In addition, the fire resistance of the material is also determined by its combination with other building materials and the presence of protective coatings.
How is it transported?


The cut and ready-to-sell expanded polystyrene is packed by the manufacturer in transport bags and transported. GOST permits transportation unpacked if there is a guarantee that the sheets will not be damaged on the way.
When forming the package, the requirements of GOST 21929-76 must be observed. The height of the formed package should not be more than 0.9 m. With a slab thickness of 500 mm, the package is formed from two slabs.
On the side edge of the product or package, there must be a marking containing the stamp of the Quality Control Department of the enterprise that manufactured these products, the type and brand of the plate.
Marking must be made in accordance with GOST 14192-77 and contain the name of the enterprise or its trademark, the date of manufacture of the product, its name and batch number.
Indicate the brand and type of plates, their number in the package.
There should be a designation of the standard on the basis of which these products were manufactured.
Wall insulation with foam
Insulation from extruded polystyrene foam is an excellent insulation for wall openings. Most often, installation is carried out from the outside of the wall, which does not allow cold to penetrate into the internal space.
Experts do not recommend equipping internal wall partitions with insulation, as the dew point will shift... Under the internal building material, moisture will systematically accumulate during the heating season, and the wall will be saturated with condensate. Dampness will appear in the inner space, which will freeze during the cold period. When heat transfer is disrupted, the wall ceiling collapses. In this case, the process of internal heating of the wall is absent, which is undesirable.
Installation advantages:
- The installation of the building material will be carried out not only by a specialist, but also by a beginner.
- PPS is well cut with an ordinary knife. It is easy to create any geometric shape from it.
- If the plates are glued to the facade, the total weight of the structure will practically not change, which means that overpayments for strengthening the frame will be avoided.
- The roofing mechanism does not require expansion, since the expanded polystyrene on the wall slightly increases the outer perimeter of the structure.
- The insulation chosen by the owner will not irritate the skin of the hands, so it can be glued without protective devices. Respiratory system, eyes remain in order.
Foam cost
Expanded polystyrene made by extrusion is called polystyrene foam. Such plates are more durable than polystyrene, and their price is much higher. The cost of one plate (1200x600x50 mm) is 183 rubles, in terms of 1 m3 it is 5080 rubles.


On sites selling heaters, you often find such a product name as 50 mm foam. This is an ordinary sheet material with dimensions of 1000x2000 mm. The price of one plate is 180 rubles. Now, in comparison with penoplex, it can be seen that a cube of ordinary foam 50 mm thick costs 1,800 rubles, and this is 3,200 rubles cheaper than extruded polystyrene foam.
So, a cube of ordinary foam, depending on the density, costs:
- PSB-S15 - 2160 rubles;
- PSB-S25 - 2850 rubles;
- PSB-S35 - 4479 rubles;
- PSB-S50 - 6699 rubles.
Insulation of floors: you can't imagine better
Another structural element that is 100% suitable for polystyrene insulation is floors. Thanks to the waterproofing of the slabs, you will save the house from dampness rising from the basement. This is especially beneficial for owners, whose buildings are located on soils with a similar groundwater level. Both materials can be laid both on a concrete base and on a subfloor made of planks, if a system of underfloor heating is planned. Only in the case of a wooden base in the subfloor, ventilation should be made with high quality so that moisture does not soak the boards. Without it, the tree will quickly rot, because on top of it there will be a waterproof material.


On a flat concrete screed, the installation of expanded polystyrene plates is carried out very quickly, and the effect of insulation is high
How long will it last
Polyfoam is resistant to moisture, corrosive substances of organic origin, therefore, the service life before replacement is, according to the assurances of manufacturers, 700 freeze-thaw cycles. This is much more than the service life of the plaster layer, in which, in addition to the composition itself, the polymer network is destroyed.
Based on the recommended operating parameters, you can count on the service life of external foam insulation from 20 to 40 years. It all depends on the quality of building materials and the careful work carried out.
Insulating the walls of the house with foam is one of the available ways to keep warm in winter and cool in summer. The simple installation process, which any person can master, makes foam polystyrene insulation a popular way, which allows you to significantly save money on the purchase of materials and pay for builders.
Source: otdelkasten.com
Material characteristic
Polyfoam has a rigid foam structure, consisting of only 2% polystyrene, the rest of the volume (98%) is filled with air.


This factor, as well as a special manufacturing technique (foaming polystyrene granules), give the material excellent performance characteristics:
- Low thermal conductivity. It is due to the fact that the foam cells have the shape of a polyhedron with a size of only 0.5 mm, moreover, they have a closed structure. This makes it possible to significantly reduce heat transfer, and also serves as an obstacle to the penetration of cold air currents.
- Soundproofing. It is also provided with a cellular insulation structure. To arrange high-quality insulation of the room from extraneous noise, a two-centimeter foam layer is sufficient.
- Hygroscopicity. It is at a low level, since even in direct contact with water, the foam absorbs a minimum amount of it. This property can be explained by the fact that water absorption does not occur through the closed cells themselves, water can only partially seep through small channels, which serve as a connection between the cell cycles.
- Despite its low density, the product has a fairly high strength. It can maintain its original dimensions for a long time even under the influence of heavy loads.This property is due to the demand for foam at airports during the construction of runways.
- Resistant to chemical and biological effects. The material continues to maintain its performance characteristics even after prolonged contact with many chemicals.


For example, with various salts, including seawater, soap and bleaching solutions (hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorite), with some acids except concentrated nitric and acetic acids, with gypsum, bitumen, lime, non-aggressive adhesives, and much more.
- Fire safety. Polyfoam can ignite only at a temperature that is twice as high as, for example, wood, while the product does not support combustion, it can ignite only in direct contact with an open fire.
- Simple and convenient installation. Foam-based heaters are lightweight, and therefore, as a rule, there are no problems with transportation. Lightweight and free to cut (without the use of special equipment), easy to use and easy to install.
Due to the fact that the foam is a synthetic product, it perfectly resists infection by fungus, mold or other bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms. However, with all this, this insulation is a "tidbit" for rodents.
Orange foam deserves special attention, which stands out against the background of its “brothers” with its color scheme. This marketing technique is used by many well-known manufacturing brands.
You can also often hear doubts about the safety of foam, many are not sure that the foam is safe, whether it is harmful to human health. There is no unequivocal answer how dangerous it is, in many respects the "degree of harm" depends on the observance of the insulation technology and the rules of operation.
Do-it-yourself insulation of a frame house with polystyrene foam
Insulation with expanded polystyrene can imply fastening the material in the following ways:
- using special glue (glue is intended specifically for expanded polystyrene, it is not universal);
- with dowels. The scheme of fastening the insulation to the wooden wall of the house
Experts recommend using 2 methods at once at the same time: the insulation in this way will be fixed on the wall of the building just tightly.
The glue is used first:
- The starting aluminum profile is mounted. It is designed so that the expanded polystyrene tiles do not subsequently slide down due to the glue (then they simply have to be re-glued, which is undesirable);
- The glue is applied around the perimeter of the entire heat-insulating sheet at different points, but only in the center (for example, 10 drops of glue in the center of the sheet). By the way, with the help of the thickness of the adhesive base, you can level out small microcracks and irregularities of the surface itself (but only small ones: if they are huge, then the glue will obviously not help here, as noted above);
- The sheet is pressed against the wall, after which you can start applying a new sheet of insulation. Scheme of applying an adhesive composition to a foam sheet
After gluing the boards, it is necessary to wait at least 3 days so that the tile adhesive seizes as reliably as possible. By and large, it is not a problem to withstand such a period: it is unlikely that a person on his own will quickly paste over all the outer walls of the building.
After the glue has set, you can already proceed with the additional fastening of the insulation with dowels. It is easy to calculate the number of dowels: for every square meter of wall area, there must be at least 5 dowels.
As for the length of the dowel, the rule also applies here: they must enter the wall with their main part (up to the cap) by at least 5 centimeters. Less is impossible, since the tiles of the heat-insulating material can simply slide off.
In this case, then it is generally not recommended to use dowels: let the insulation be kept on one glue. The dowels themselves should be centered with a slight offset.
What else you need to know when insulating a house with expanded polystyrene:
- all cracks with a size of more than 5 millimeters are foamed without fail;
- using a special trowel for foam plastic, small irregularities and differences in the level of the wall are eliminated;
- if 2 layers of insulation are used at once, then the second, outer layer, necessarily comes with an overlap of the seams both vertically and diagonally (by the way, if you carry out installation using this technology, then it is no longer necessary to foam the first layer). General scheme of wall insulation of a frame house
Output
The use of extruded polystyrene for insulating houses and other buildings is the best option of all. Such an affordable and high-quality heat insulator guarantees high levels of comfort and coziness in the house, protects the building from moisture ingress, and significantly saves money on heating.
Currently, the choice of polystyrene in the domestic market is simply huge. Many companies offer materials with unique characteristics and at different prices, which opens up wide opportunities for consumers. In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic.
Stages of work during finishing
Below we will look at the main points when working with insulation.
Exterior wall preparation
Aerated concrete walls, before insulating, you need to prepare:
- remove mortar residues, debris, dust;
- fill in irregularities, seams, grooves, recesses in foam blocks;
- Level the surface by removing the protruding parts;
- prime the walls with several layers of a moisture-repellent emulsion.
Methods for fixing expanded polystyrene
There are several options for fastening the insulation:
- with glue;
- using self-tapping screws;
- installation of slabs on the crate.
Fastening polystyrene foam outside the house with glue
Before insulating, you need to make sure that the surface of the aerated concrete wall is as flat on the outside as possible. It is unacceptable that air pockets form in any places, grooves, potholes. It is there that condensation can subsequently accumulate, and this will lead to the formation of mold, fungal spores.
Sequence of work
- Glue preparation. Manufacturers offer special glue for expanded polystyrene. For work, you need to purchase glue for outdoor use. Stir according to the instructions on the package. It is unacceptable that there are dry and solid particles in the finished mixture.
- Bonding several lower rows. Each row is glued with a displacement of the seam of the joints, that is, "apart". A spatula with 8 mm wide notches is required to apply the adhesive.
- Only after complete drying do they start gluing the next rows. If you ignore this point and immediately glue subsequent rows, the plates will begin to slide down.
- After sheathing the main surface from the outside, they begin to fix the expanded polystyrene to the slopes.
- For the reliability of the structure, it is necessary to additionally attach each plate using five self-tapping screws with large caps. To do this, you need to make through holes in the slab and in aerated concrete by 4-5 cm in the four corners and in the center. In order to save money, the dowels can be fixed at the joints of the plates. Hats need to be "drowned" in expanded polystyrene.
Finishing work
As soon as the glue dries and additional reinforcement with dowels is installed, it is necessary to glue the reinforcing mesh onto the sheathing. For this, the same adhesive is used for expanded polystyrene. A layer of glue is applied over a width slightly larger than the width of the mesh. Next, the mesh itself is applied and recessed with a roller in the adhesive mixture. The mesh must be closed; for this, another layer of glue is applied from the outside.
The final step will be the application of decorative plaster.You can also prepare the wall for painting. To do this, a leveling layer is applied to the surface, everything is primed and painted after drying.
The second way to insulate a house from foam blocks only with the help of self-tapping screws provides for the same work, but without gluing it to the wall. However, the reliability of this design is reduced. In case of strong winds, there remains the danger of the foam boards tearing off the blocks.
The third method is the installation of slabs outside the house on a wooden crate, which is rarely used due to laborious work.
Thermal insulation of walls made of aerated concrete with expanded polystyrene is a simple process that the homeowners of one-, two-story houses themselves can do.
obloke.ru