For which systems do you need a calculation?
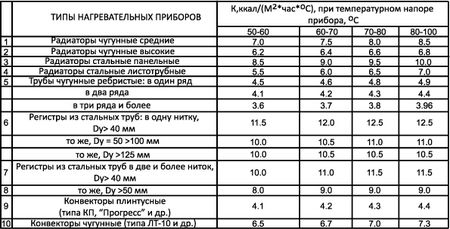
The heat transfer coefficient is calculated for a warm floor. Less and less often, this system is made of steel pipes, but if products from this material are selected as heat carriers, then it is necessary to make a calculation. The coil is another system, during the installation of which it is necessary to take into account the heat transfer coefficient.

Steel pipe radiator
Registers - presented in the form of thick pipes connected by jumpers. The heat transfer of 1 meter of such a design is on average 550 watts. The diameter ranges from 32 to 219 mm. The structure is welded so that there is no mutual heating of the elements. Then the heat transfer increases. If you correctly collect the registers, you can get a good room heating device - reliable and durable.
Main menu
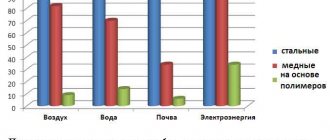
Hello everybody! Perhaps the most expensive, but at the same time, the best heating system will be a copper pipe system. If you are not constrained in funds, then the builders, without hesitation, will offer this material for the pipeline. Not only is it beautiful, it is also reliable. Copper piping can withstand very high temperatures, up to 250-300 ° C, and pressures up to 55-60 kgf / cm2.


In this case, the joints made by soldering will not collapse. Such a pipeline can also be installed in country houses where you do not use heating throughout the winter. The heating system will not defrost, unlike a pipeline made of steel, for example. Heating pipes can be installed outside the house, only good thermal insulation is needed to reduce heat loss. Copper pipes have high thermal conductivity and heat transfer. Resistance to frost, allows builders not to stop the installation of the system in the winter.
Heating a house from copper pipes does not require special care. The outer wall of the pipe will oxidize and become patina. In this case, the bright copper shade will become a noble green color. This is the color of the roofs of ancient churches and castles. It can go well with the design of your room.
The disadvantages of copper piping mainly come down to the financial side and the installation of the heating structure. If you can assemble a heating system made of polymer material almost like a designer, then it will be a little more difficult with copper. The pipes are connected by welding, but, of course, it is not the same as when installing steel pipes. Copper is a noble metal and its soldering will be special.
The most common installation method is capillary brazing. It is based on the capillary effect, the essence of which is that at a certain distance between two surfaces, the liquid fills this space due to the forces of surface tension, in the case of a vertical arrangement, overcoming the force of gravity.


It is this effect that allows the solder to spread evenly over the entire surface of the soldered end, regardless of the position of the pipe (for example, the solder can be fed from the bottom of the joint). Moreover, the strength at the junction is not inferior to the mechanical strength of the pipe itself. Thus, installing copper piping is a job that requires a certain skill and patience. To connect copper pipes with components of the heating system made of a different material, it is necessary to use adapters or brass fittings.
For the installation of heat supply systems, copper pipes of two types are used:
1. unannealed, rigid in the form of straight segments;
2. annealed, soft in the form of coils rolled into rings.
Rigid pipes are convenient for installing risers and heating lines, while soft pipes are used for other pipe sections. The diameter of copper pipes varies from 10 to 28 mm with a wall thickness of 1 mm and from 35 to 54 mm with a wall thickness of 1.5 mm. Pipes of larger diameter are also produced. But, despite the insignificant wall thickness, copper pipes withstand a higher working pressure compared to the same steel pipes.
If you decide to install a copper pipe heating system, then this is definitely a good choice.
How to optimize the heat dissipation of a steel pipe?
During the design process, the specialists are faced with the question of how to reduce or increase the heat transfer of 1 m. Of the steel pipe. To increase, it is required to change the infrared radiation upward. This is done by means of paint. Red color enhances heat dissipation. It is better if the paint is matte.

Calculation
Another approach is to install ribbing. It is mounted externally. This will increase the heat transfer area.
In what cases is it necessary to decrease the parameter? The need arises when optimizing a section of the pipeline located outside the residential area. Then experts recommend insulating the site - isolating it from the external environment. This is done by means of polystyrene, special casings, which are made from special foamed polyethylene. Mineral wool is also often used.
Benefits of using copper pipes
- longer service life than metal-plastic pipes;
- copper pipes are more versatile, in contrast to metal-plastic, they can be used for highways transporting gaseous substances.
- copper pipes have antibacterial properties, thanks to which they can be used in the food industry and in medicine;
- copper pipes have a smoother inner surface;
- copper, more reliable material
The advantages of using metal-plastic pipes:
- connection of pipes is carried out without the use of welding, i.e. a simpler process of installation and repair work;
- the multilayer structure makes it easy to bend metal-plastic pipes, which greatly facilitates the installation work, i.e. more ductile than copper pipes;
- metal-plastic pipes are less susceptible to condensation;
- prices for metal-plastic pipes are much lower than for copper pipes.
We make a calculation
The formula by which heat transfer is calculated is as follows:
Q = K * F * dT, where
- K is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of steel;
- Q is the heat transfer coefficient, W;
- F is the area of the pipe section for which the calculation is made, m2 dT is the value of the temperature head (the sum of the primary and final temperatures, taking into account the room temperature), ° C.
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is selected taking into account the area of the product. Its value also depends on the number of threads laid in the premises. On average, the value of the coefficient is in the range of 8-12.5.


dT is also called temperature head. To calculate the parameter, you need to add the temperature that was at the exit from the boiler with the temperature that was recorded at the entrance to the boiler. The resulting value is multiplied by 0.5 (or divided by 2). The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
dT = (0.5 * (T1 + T2)) - Tк
If the steel pipe is insulated, the resulting value is multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. It reflects the percentage of heat that was given off during the passage of the coolant.


What temperature can polypropylene pipes withstand?
Deformation of the pipeline threads is not yet the biggest nuisance that owners of houses with hot water systems mounted from polypropylene can expect. Of course, curved and sagging pipes do not add aesthetics to the interior, but such a nuisance can still be masked, for example, with decorative boxes.
The permissible temperature regime at which the operation of PPR pipes is possible is approximately + 90-95оС.
In general, polypropylene begins to acquire excessive plasticity already at + 120-130 ° C, and at + 170-175 ° C it turns into a liquid state. Why, according to the standards, the recommended operating temperature is only 95 degrees, and not 100 or 110? Indeed, with such heating, the PP-pipe continues to remain quite solid. The answer here lies in another technological feature: water in pipelines is always supplied under a certain pressure.
It doesn't matter whether the hot pipeline is heating, or is connected to a washbasin, there is always a certain pressure in it, sometimes reaching tens of atmospheres. Therefore, it is impossible to consider the permissible temperature regime in isolation from the working water pressure inside the line. The higher the pressure, the lower the permissible pipeline heating values.
Illustrative example
As an example, consider a simple case. In the regions located in Siberia, the Far East and the European north of the Russian Federation, in winter, frosts can reach 35-40 degrees or more below zero. Heat losses of buildings at such a time are very significant, and to compensate for them, boiler houses and thermal power plants increase the supply temperature to 110-130 ° C. And so that the water does not boil in the system, the pressure rises to several tens of atmospheres. Under these conditions, the water does not pass into a vaporous state.
At the entrance to the house, due to the loss of heat energy along the way, the water temperature already drops to the set by GOST + 70 ... 75 degrees, but the pressure in the system continues to remain elevated. As a result, there is an increased likelihood of rupture of a polypropylene pipe, since its plasticity increases when heated. Therefore, it is not advisable to use polypropylene for heating systems for this reason. However, modern industry produces polypropylene pipes intended for hot water supply, but they also have their own operational limitations.
Temperature table for PP pipe marking
In the domestic building materials market, you can find several varieties of polypropylene pipes. They differ in marking and color. The color scheme usually includes four primary colors - white (the most common), green, gray and black. Black PCBs are highly resistant to ultraviolet solar radiation. The rest of the colors do not have any technological function, being purely decorative.
Another thing is the marking of PP-pipes. It carries a direct informational load, indicating by what technology and with what types of polypropylene this product is produced. The technical and operational characteristics of the pipe directly depend on this.
The table below shows the markings found on our market, working pressure and maximum temperature:
| Marking | Appointment | Mach. working to | Working pressure in the system (atm.) |
| PN-10 | Cold water supply | +40 оС | 10,2 |
| PN-16 | Universal | +60 оС | 16,3 |
| PN-20 | Universal | +95 оС | 20,4 |
| PN-25 | Hot water supply | +95 оС | 25,5 |
When choosing a material for installing a pipeline, it should be borne in mind that exceeding the operating parameters established by the manufacturer leads to a reduction in the service life of the pipe.
Features of installing pipes for hot water (heating and water supply): the issue price is not high
Installation of reinforced polypropylene pipes is quite simple and effective. It consists in sequential welding (or soldering) of individual elements.
A standard set of tools that you may need:
- A soldering iron (or a specific welding machine) - useful when soldering sockets.
- Pipe cutter or suitable cutting pliers.
- The device with which the chamfer is removed.
- A device for removing aluminum foil (shaver).
- Special attachments.
Before proceeding with the direct assembly of the line, the following sequence of actions should be performed (preparatory stage):
- Measure the required length and cut off the desired section.
- Chamfer the outer edge using a chamfer.
- Clean (degrease) the joints - the places where the elements will be connected to each other.
Plastic pipe for water stands out from the rest with a variety of fittings and diameters
Polypropylene pipes reinforced with aluminum for heating require an additional preparatory operation - stripping, so that the reinforced pipe does not begin to delaminate. In addition, this will help protect aluminum from electrochemical destruction and possible leaks.

You can remove the foil under the decoratively applied propylene (microscopic thickness) fixed from the outside by installing it in a simple device (a sleeve with knives) and performing 1 ... 2 turns.
The cleaning of three-layer elements (the reinforcing frame is located between the plastic layers) is a little more difficult - you need a special facing tool that removes the inner layer (about 1 mm) located near the very end.
Does a glass fiber reinforced pipe need such an operation? The unequivocal answer is no! After all, the inner layer differs little from propylene.
The next step is to prepare the soldering iron, for which it is necessary:
- Fix the device on a special stand.
- Turn on the heating element - the soldering iron should heat up to 260 ° C.
Now you can proceed to the soldering process. Welding of polypropylene pipes reinforced with fiberglass consists in tightly joining two products, the edges of which are preliminarily softened, as a result of which a monolithic joint is formed at the junction (mutual diffusion of the molecules of the connected elements occurs).
Sequencing:
- Take two prepared parts and install them on the sleeve and mandrel (tapered cylindrical surface).
- Warm them up until the material starts to "melt". The time spent on warming up depends on the type of parts and wall thickness (specific values can be easily found in special tables).
- Remove the elements from the heater (the action must be performed simultaneously) and quickly connect to each other, ensuring their immobility for two to three seconds. This time is enough for the material to harden and form a monolith.
Read more: Do-it-yourself piping in the bathroom: serial and parallel circuits