- A little about polypropylene pipes
- Classification of polypropylene pipes
- Soldering polypropylene pipes
- Soldering process
- Nuances when soldering polypropylene pipes
- Conclusion
Today the pipeline takes a very important place in our life. A variety of materials are used for its manufacture. Today, thanks to the development of the polymer industry, one of the most used materials is plastic. It's lightweight, practical, durable and, most importantly, cheap.
But plastic also has its own varieties, and they are very different from each other. Among them there is one very-very, which is called polypropylene. It has the best price-quality-life ratio. At the same time, polypropylene pipes are quite easy to install. Naturally, for this procedure, you need to have a special device. Consider what temperature a polypropylene pipe can withstand, under what conditions it is used and how it is installed.
A little about polypropylene pipes
From the outset, it should be said that the manufacturer's declared service life of 50 years is very impressive, but this condition is maintained only under the right operating conditions.
Polypropylene pipe
However, polypropylene can easily work at elevated pressures. The main thing is that the temperature of the liquid transported through pipes made of this material does not exceed the permissible standards (it is desirable that it be much lower). The same can be said about working at elevated temperatures - pipes can withstand exorbitant norms if the pressure is very low.
Even if polypropylene pipes are correctly installed, this will not help extend their service life if the operation is carried out under extreme conditions. In this case, the service life is reduced to 1-5 years. But all this has nothing to do with the use of polypropylene pipes in the house, since all conditions here are absolutely acceptable. If there are drops, then they are short-term, and this does not cause any harm.
So, the working temperature of polypropylene pipes varies widely. It all depends on several parameters that are indicated in the marking. Let's consider them.
Benefits of Reinforced Polypropylene
- The linear dimensions of these pipes are less susceptible to changes under the influence of temperature. This is true when, in the process of work, the pipes are recessed into the screed. The use of reinforced polypropylene pipes in the heating system avoids damage due to temperature deformations.
- The service life of a reinforced pipeline in conditions of constantly high operating temperatures is much longer.
- The melting temperature of polypropylene pipes with and without reinforcement is the same. But at a temperature just below the melting point, under the influence of pressure, the pipe will burst without reinforcement, but not with reinforcement. The maximum pressure in polypropylene pipes is 10 bar. The higher the temperature of the coolant, the lower the pressure in the pipeline should be.
Conclusion: In systems with a constantly high coolant temperature, it is better to use reinforced polypropylene pipes than the same unreinforced ones.
There is a lot of controversy among consumers about what temperature plastic pipes can withstand. Some say 95 ° C, while others say 120 ° C. This is due to the fact that the group of plastic pipelines includes cross-linked polyethylene pipes.Their operational parameters are slightly different. The optimum operating temperature for a plastic pipe of this type is exactly 120⁰С. The melting point of XLPE plastic pipes is 200 ° C.
The cost of cross-linked polyethylene pipes is several times higher than the price of polypropylene pipes. Therefore, the use of polypropylene pipes is economically justified in systems with suitable performance characteristics. They tolerate short-term increases in the maximum operating temperature declared by the manufacturer. In addition, cases of leaks of polypropylene water pipes after assembly are quite rare.
Plastic pipelines are gradually replacing household communications made of metals. These materials are popular with both professional builders and owners of houses and apartments. Plastics are reliable, strong enough, affordable, easy to install.
The building materials market offers a variety of polypropylene products. To select what works best for one particular pipeline, you need to have at least a minimum of information.
Characteristics of polypropylene
Pure polypropylene is a white powder that is produced from propylene gas using metal catalysts. Manufacturers purchase it in the form of granules. It is quite hard, softens at 140 ° C, the melting point of polypropylene pipes is 176 ° C, they do not like oxygen and light.
A stabilized version of this plastic is used for production. The products are waterproof and chemically resistant; rust or any other deposits do not form on the inner walls. All materials made of this type of plastic can withstand boiling, since the maximum temperature of polypropylene pipes during operation is 120 - 140 ° C.
For production (according to GOST P 52134-2003) you can use:
- - homopolymer - PP-H (PP type 1 or PP-G);
- - block copolymer - PP-B (PP type 2 or PP-B);
- - random copolymer - PP-R (PP type 3 or PP-R).
However, the most commonly used PP-R is the most versatile. When purchasing materials from plastics, the class of operation indicated in the marking should be taken into account. Each manufacturer determines the temperature characteristics of polypropylene pipes and the pressure, subject to which they can last 50 years.
GOST P 52134-2003 determines what temperature polypropylene pipes of various classes can withstand:
- - ХВ - cold water supply (20о С);
- - first class - hot water supply, polypropylene pipes, operating temperature 60 ° С;
- - second class - hot water supply at 70 ° С;
- - third class - floor heating 60 ° C;
- - fourth class - low-temperature radiator and high-temperature floor heating - 70 ° C;
- - fifth class - high-temperature radiator heating - polypropylene pipes, operating temperature - 90 ° C.
The minimum allowable temperature for storage and operation is minus 20 degrees. Reinforced products are suitable for cold and hot water, as well as for heating. Products with fiberglass are most in demand, since there is no need to clean the ends before soldering. Smooth surfaces, perfectly round shape, uniform wall thickness, absence of cracks, cavities, bubbles, uniform color serve as a sign of the quality of the material.
Applications
SNiP 2.04.05-91 determines that no water system at home should have hotter than 95 ° C (for schools and kindergartens, this parameter has been reduced to 37 ° C). Theoretically, the temperature characteristics of polypropylene pipes allow them to be used for any household pipeline.
But this is only in theory. For example, in the Far East, -50 degrees is not uncommon in winter. It is not difficult to imagine heat loss in a residential building in such weather.In order to ensure proper conditions in the residential sector, the temperature of the coolant in heating systems must be increased beyond a hundred degrees. It becomes necessary to turn on the return pipeline, and manually and in each building. It's time to remember what temperature polypropylene pipes withstand. What will happen to them at 130 ° C? They, of course, will not flow, even if they are not reinforced, but they will not last long.
The role of reinforcement
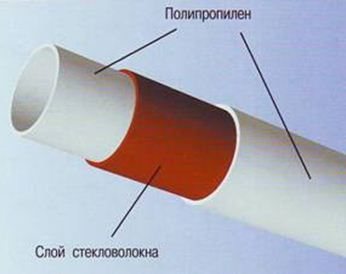
The ability of a polymer to withstand high temperatures is significantly affected by the presence of reinforcement. The most common types are pn20 polypropylene pipe and pn25 polypropylene pipe. The main difference between the two products should be noted - PN25 has aluminum or fiberglass fittings. This means that PN25 has a much lower coefficient of linear expansion, which is important if the system is concreted. In addition, at 120 ° C, unreinforced material will certainly burst, but reinforced material will not.
In a polypropylene system, the temperature of the internal environment should theoretically not exceed 95 ° C, but a short-term violation of this limit will not bring much harm (even in the absence of fittings). When choosing a material for domestic pipelines, it should be borne in mind that the best for transporting hot water and heating is a polypropylene pipe reinforced with pn25 fiberglass - it is welded without stripping and will never delaminate during operation.
Polypropylene pipes reinforced with pn25 aluminum have a lower coefficient of linear expansion, but they require stripping before brazing, and when aluminum is located close to the outer surface, delamination is possible. The polypropylene system must be completed from the materials of the same manufacturer so that the pipes are fully compatible with the fittings. When buying, it will not be superfluous to inquire about the certificate of conformity and the organization that issued this document.
This article is about whether it is possible to use metal-plastic and polypropylene in central heating systems and hot water. Opinions on this matter are controversial, even among practicing plumbers with extensive experience, so do not take the text as an attempt to state the ultimate truth. I just want to express my thoughts on the reliability of different materials and explain to the reader in what real
conditions they have to be exploited.
- SP 40-103-98 directly indicate (I quote): metal-polymer pipes are designed for systems ... with a pressure of up to 1 MPa and a temperature of up to 75 C;
1 megapascal corresponds approximately to ten atmospheres (10 kgf / cm2). When specifying pressure parameters, bars are used along with these values; 1 bar, again with a minimum error, is equal to 1 kgf / cm2.
- SP 41-102-98 pushes the boundaries of the possible and indicates as an acceptable mode for metal-plastic already 90 C at 1 MPa;
- Most of the little-known metal-plastic manufacturers indicate 10 atmospheres and the same 90 ° C as the recommended operating parameters , guarantees 8.6 atmospheres at a temperature of 95 C and a service life of 10 years
... I think that from the products of less famous manufacturers you can expect, at best, the same durability in extreme conditions;
- SP 40-101-96 for polypropylene pipes mentions a service life of at least 30 years at a temperature not higher than 70C
; - The melting temperature of polypropylene pipes, given in the same joint venture, should not be less than 146 degrees;
- Manufacturers of polypropylene pipe products indicate a service life of 50 years at temperatures up to 70 C and 25 years at 80 degrees;
- The working pressure is always indicated for a temperature of 20 C and is equal to 10 - 25 kgf / cm2, depending on the line of pipes and the presence or absence of reinforcement;
- The permissible operating temperature of polypropylene pipes is 90 - 95 degrees (different brands have different ways). However, when approaching the upper boundary, the fracture pressure decreases from 25 - 30 to 8 - 10 kgf / cm2;
Polypropylene without reinforcement is characterized by a large thermal expansion (6.5 mm / running meter when heated to 50 degrees). It is noticeably reduced by pipe reinforcement (up to 3.1 mm / m with fiber reinforcement and up to 1.5 mm / m with aluminum foil).
- At what temperature the pipes made of polypropylene and metal-plastic burst, their manufacturers, for obvious reasons, do not indicate, but short-term heating is limited to 110 degrees
.
And what conclusions can be drawn from all of the above? What temperature can polypropylene pipes and metal-polymer products withstand, and at what pressure can they work?
Absolutely safe mode, which does not lead to a decrease in the service life - 70 degrees at a pressure of up to 8 atmospheres. The maximum operating temperature of 95 C, although it is the regime guaranteed by the manufacturer, will lead to accelerated degradation of polymers. Pressure surges in this mode can lead to pipeline destruction.
The sewage system made of PVC can be operated at all only at 60 C. Fortunately, household drains reach the comb (intra-apartment sewerage wiring) already somewhat cooled.
Classification of polypropylene pipes
So that when buying polypropylene pipes there are fewer questions to the seller, it is imperative to navigate their labeling. You can find the following on the shelves:
- PN10. The operation of such products is carried out at temperatures up to +20 degrees Celsius. As a rule, this is cold water supply. But in some cases, this marking is also used in the installation of underfloor heating. Their temperature should not exceed 45 degrees, and the working pressure should not exceed 1 MPa;
Features of polypropylene pipes - PN16. This marking applies to products that are designed to operate at low temperatures and high pressures. In some cases, it is possible to use it in central heating with reduced pressure;
- PN20. Products made from this type of plastic can be called truly versatile. They can be used both in cold and hot water supply at a maximum temperature of 80 degrees and a pressure of up to 2 MPa;
- PN25. These are polypropylene pipes for heating, which are additionally reinforced. Products with such markings can withstand rather high temperatures together with high pressure (up to 2.5 MPa). Such pipes differ from metal-plastic pipes in that the aluminum foil in them is perforated and located close to the walls. This makes it possible to fasten the elements without the use of glue.
Is the water hot
Is it a lot or a little?
Let's see what the current regulatory documents say about it.
SNiP 2.04.05-91 ("Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings") plainly states that the water temperature for all systems of the house should not exceed 95 degrees. And in the case of preschool children's institutions - 37.
If so, you can safely put polypropylene pipes: the working temperature is suitable. Is that so?
It would seem that now all the questions have been removed, you can go home. But, as is customary, there is a nuance. Even two.
The cost of globalization
In late Soviet times, not long before the change of the regime to democratic and the disappearance of sausages from stores, in the Far East (undoubtedly, not only there, but in the Far East, the author had a chance to observe this outrage personally), whole neighborhoods of houses were built according to the so-called Leningrad project ...
Triple glazing and triple doors in the entrances are combined with panel walls and very original heating devices.Convectors for hot water heating are simply a coil of a heating riser with a diameter of 3/4 inch with a transverse ribbing of thin steel plates tightly put on it.
In theory, everything should have worked ...
To understand the full scale of the tragedy, you need to have a good understanding of the Far Eastern climate. The temperature is -40 - -45 there, not that every day in winter, but no one is surprised, and -30 in a strong wind is more than an ordinary phenomenon. The amount of heat loss in a panel house is easy to estimate. And now let's compare it with the heat that 50-80 centimeters of pipes with pitiful plates leave in the apartment.
To ensure an acceptable temperature regime in these houses, it was necessary to raise the temperature of the coolant in the heating system much higher than a hundred degrees. Fortunately, the parameters of heating mains in the winter cold allowed it.
We live in Russia
There is no automated control of water supply in residential buildings in our country and will not be massively for a very long time. And now oil on canvas. Winter. On the street -40. Maintaining the temperature schedule, the CHP plant raises the temperature of the heat carrier in the supply pipeline to 130 C. The water in the pipe does not turn into steam only due to pressure.
In order for the residents to have a temperature of no higher than 95 C in the tap, the water supply must be switched to the return pipeline. Manually. In an elevator unit in the basement of every house.
And the locksmith is sick. Or in a binge. Or simply shortened. In what state of housing and communal services in the provinces - you do not need to tell.
So what?
If the water has such a temperature, should the polypropylene pipes flow down?
Fortunately, this does not happen. Up to a point of 140-150 degrees, even unreinforced polypropylene pipes are not yet deformed. But their service life is, in fact, shrinking.
The fact is that manufacturers are big reinsurers. If at a temperature of 94 degrees a pipe bursts, for which an operating temperature of 95 is declared, the manufacturer will be sued. Since the thickness, strength of plastic and other physical properties of pipes inevitably change slightly from batch to batch, all decent manufacturers indicate greatly underestimated parameters for products, which are guaranteed to fit all batches of goods.
Soldering polypropylene pipes
To form joints of polypropylene pipes, special sockets, or couplings, are used. They act as a kind of mediator between several elements (in some cases there may be 4 of them). Connections can be both detachable and non-detachable. The latter type is the most common, since later the pipes are laid into the wall, where access is very limited.
Soldering a polypropylene pipe
It is also worth noting that the creation of permanent joints gives a fairly good result thanks to the plastic itself, which can very easily form a monolith with sockets or fittings.
So, for soldering plastic pipes, we definitely need the following elements:
- pipes of the same diameter;
- fitting;
- special soldering iron with nozzles of standard diameters.
For welding with a soldering iron and creating a monolithic joint, the melting temperature of polypropylene pipes must be known. It lies within 230-260 degrees. It is exposed on the device, after which you need to wait 10-20 minutes (it all depends on the size of the nozzle). The soldering iron must first be placed on a flat surface.
One of the recommendations of specialists is a ban on welding polypropylene at negative ambient temperatures. It should also be borne in mind that on a hot day, the heating of the elements and the plastic itself is carried out much faster than the established standard time frames.
Polypropylene pipe preparation
While the soldering iron is warming up, you can prepare the elements to be welded themselves. To do this, cut off the edge with a pipe cutter or regular scissors. It is advisable to do this at a right angle.All connected elements must be cleaned of debris, dust and dirt, as they can further interfere with the creation of a full-fledged connection, provoking the further appearance of a leak.
With the help of a special device, the top is removed from the pipe. Fittings are manufactured in such a way that without such stripping, the pipe simply will not enter them. So, the pipe was cleaned and the soldering iron warmed up. Let's start creating a connection. Note that the heating temperature of polypropylene pipes during operation must necessarily be less than the melting temperature, since in the future the connection may simply disperse.
Soldering process
Two prepared parts - the fitting and the pipe are placed on the heated nozzles. Having held them for a specified time (for each type of pipes it is different), the elements are connected. It is very important to note that the fitting heats up from the inside and the pipe from the outside. Next, you need to turn these elements slightly relative to each other so that the molten plastic from two surfaces mixes and becomes one whole. It is recommended to do this as quickly as possible before the material begins to crystallize. Well, if everything is done correctly, then we get a one-piece monolithic connection.
Experts recommend to additionally withstand the cooling time and pay special attention to thin-walled elements.
The thing is that, when heated and soldered, they are easily deformed for a long time. Therefore, it is advisable to leave the connections alone for 20-30 minutes (it all depends on the ambient temperature).
Nuances when soldering polypropylene pipes
When creating a permanent connection, the first thing you need to know is what temperature the polypropylene pipe can withstand. This is very important, since in the future, if the material is incorrectly selected, it is necessary to change the unusable part. Remember that PN10 and 16 are designed for low temperature operation (up to +20 degrees). PN20 and 25 - for a medium with a maximum temperature of up to +80 (with constant supply) and short-term up to +120 degrees.
The welding machine (soldering iron) must be turned on throughout the entire process of creating communications. In this case, the heating of the parts must be started at the same time.
It is imperative to observe the heating time frame, since underheating is fraught with the creation of an unreliable connection due to very weak diffusion, and overheating is a complete deformation of the pipe edge.
The armature decides
When discussing polypropylene pipes what temperature they can withstand, one cannot but recall another factor that strongly affects the ability of pipes to withstand high temperatures.
The two common types of pipes - PN20 and PN25 - differ primarily in that the latter are reinforced with aluminum foil or fiberglass.
What does this mean from a practical point of view?
- If you have reinforced polypropylene pipes, the temperature affects to a lesser extent the change in the linear dimensions of the pipe. However, this is only relevant for those cases when the pipes are recessed into the screed. Flexibility allows them not to be damaged during thermal deformations.
- When the water supply system has a constantly high operating temperature, polypropylene pipes with reinforcement last much longer. However, the difference between 40 and 60 is hardly important to most middle-aged people.