When installing pipelines for supplying hot water or heating systems, the question often arises of finding an alternative to expensive pipes made of copper and other types of metal. As their counterpart, products made of polypropylene are best suited. But conventional polypropylene structures have many disadvantages. Therefore, modern manufacturers began to produce another type of PP pipes - products with fiberglass reinforcement.

Reinforced PP pipes are one of the best options for installing heating systems
What is polypropylene?
Polypropylene is a material that, by its very nature, undergoes significant elongation and expansion during heating.
Example:
The hot water supply system, 10 m long, is mounted at a temperature of 200C, and water with a temperature of 1000C will pass through the pipe. With such a temperature difference, each meter of the pipe can lengthen by 12 mm, respectively, with a pipe length of 10 m, the pipe will stretch by 12 cm.
That is why, during the design and installation of heating or hot water supply systems, this property of polypropylene cannot be ignored for a number of reasons:
- a straight pipe will go in ugly waves. Especially if there is a long section;
- If the pipes are hidden in the wall, then there is a high probability of violation of the decorative coatings on the wall.
Reinforcement of polypropylene pipes is done just in order to reduce linear expansion during heating. In this case, something like a rigid frame is formed, which prevents the pipe from lengthening. In this case, the reinforced pipe does not become stronger, the frame only serves to reduce the linear elongation. Should you choose this kind of polypropylene? We read further about the types of reinforcement.
https://youtu.be/DvxUX-nmuKs
Polypropylene problems
There is a silver lining. A great example of positive thinking. Unfortunately, the opposite is also true: there is no good without a silver lining. There have already been so many praises addressed to polypropylene pipes that they simply cannot but have drawbacks.
Indeed, there are circumstances in which other materials are better preferred over polypropylene.
The reasons lie in the properties of the material itself:
- Polypropylene - low-melting plastic;
- It has a large coefficient of thermal expansion.
Let's focus our attention on his problems.
Temperature
The melting point of polypropylene is 175 C. However, it begins to soften at much lower 140 C. As for the guaranteed temperature at which the polypropylene pipe must work guaranteed - it is only 95 degrees Celsius (and even less for some varieties) ...
What is the reason for such a significant reassurance with temperature - has already been written more than once. Now we will only note that at high pressure and high temperature acting on the material at the same time, it is much less stable than under the influence of each of the factors separately.

Melts, how it melts
Heat elongation
All materials expand when heated. Some are less, others more. Polypropylene expands very strongly.
This is inconvenient for the following reasons:
- Aesthetics... A long straight pipe, elongated, travels in untidy waves.
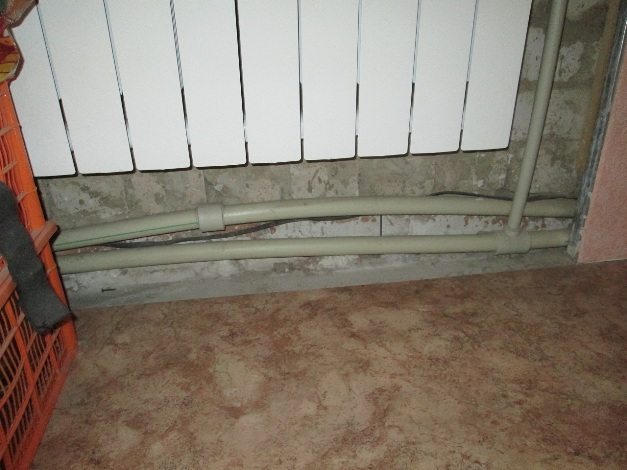


Obvious deformation when heated. The pipe has become too long for the area where it is installed
- Integrity of decorative coatings... If the pipes are recessed under the screed on the floor or in the wall covering, then when lengthened, they will inevitably cause the covering to crack after some time.


Nothing pretty, right?
Aluminum on the outside of the pipe
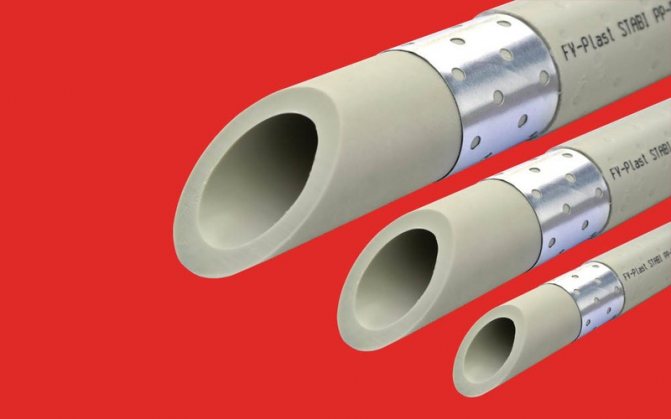


Aluminum reinforced pipe
The aluminum layer does not impart strength to the pipe, since, unlike metal-plastic pipes, aluminum foil with a thickness of 0.1 to 0.5 mm is used for reinforcing polypropylene. But at the same time it perfectly solves the problem of linear elongation. As mentioned above, if, without reinforcement, 1 m of a polypropylene pipe lengthens by almost 12 mm when heated, then under the same conditions, when reinforced with aluminum from the outside, the pipe will change its length by only 2 mm.
Aluminum foil with polypropylene is bonded with a special glue. Reinforcement with aluminum from the outside occurs in the following sequence:
Polypropylene pipe - adhesive layer - aluminum foil - adhesive layer - polypropylene layer.
The quality of the adhesive joint and of the polypropylene itself affects the durability and service life of such a pipe.
Advantages of external reinforcement with aluminum:
- The linear elongation of the polypropylene pipe is significantly reduced.
Disadvantages of external reinforcement with aluminum:
- Over time, bulges may form in some sections of the pipe.
Outwardly, it seems that the pipe will soon burst, but in reality it is not. Only the outer thin layer of polypropylene, which covers the aluminum foil, is blown up.
Manufacturers of polypropylene pipes allow such bulges, since this does not affect the strength of the pipe itself. The main thick layer of polypropylene remains intact. Bulges can form due to residual moisture during production. You should not be afraid of this drawback, the system will continue to work properly and further in spite of its unpresentable appearance.
- The outer layer must be stripped before welding as the outer diameter of the aluminum-reinforced polypropylene pipe is larger than usual.
Types of reinforced polypropylene pipes. Product marking
At the moment, the market for consumables for heating systems has a rich selection. Noteworthy is the marking of products, thanks to which we can obtain all the necessary information about the operating parameters of the pipe and operational capabilities. For polypropylene reinforced pipes, marking plays a key role. Based on the information, we will be able to correctly and accurately select the required type, type of product.


Let's start with the classification of polypropylene pipes, which is based on the variety of products. Synthetic consumables are divided into the following types:
- The first type - products made of homopolypropylene have the PPH index (H - homopolymer). This type is characterized by high strength. They are commonly used in cold water systems.
- The second type is pipes containing a block copolymer (B - block copolymer). These consumables are marked with PPB indexes and can be used in low-temperature heating systems (warm water floors).
- The third type is the most common. Products are used for underfloor heating and hot water supply. Such pipes are marked with PPR, where R is a random copolymer. Usually, it is this type of product that is made reinforced. The letter C is added to the existing PPR marking, meaning the increased requirements for temperature jumps (up to 950C).
The European abbreviation PP corresponds to the Russian-language version of PP, which means polypropylene.
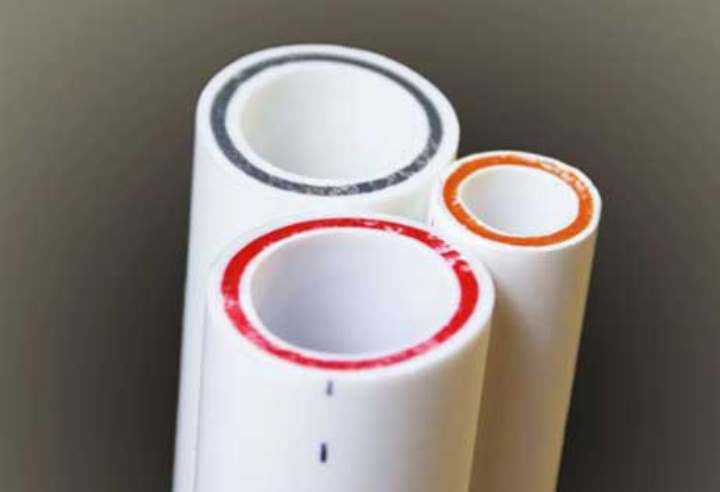
Further, after the designations of the product belonging to the type of material, there are designations characterizing the value of the nominal working pressure. The indices PN are used for this purpose. At the household level, for water supply and heating systems, reinforced pipes with PN20, PN25 indices are usually used.These two types are optimal for heating systems, both for a centralized heating option, and in combination with individual heating devices. The difference is that products with the PN20 index are reinforced with fiberglass, and those with the PN25 index have an aluminum interlayer.
Important!
Unlike conventional PP consumables, both PN20 and PN25 have a low coefficient of thermal expansion. For products reinforced with fiberglass, this figure is 5-7% higher than for foil-clad polypropylene pipes.
The required quality, compliance of the product with the declared parameters can be obtained by purchasing original, branded products. Price is an aspect on the basis of which a counterfeit from a branded consumable can be determined. Reinforcing component - fiberglass can be of different colors, orange, blue, red or green. The color scale does not play any role. Some manufacturers, in addition to the existing designations, apply stripes along the pipe surface:
- red stripe, scope of use - pipelines with hot water or coolant;
- blue stripe, products are used for cold water supply;
- two colors - the versatility of the line.


This is what the standard marking on the product looks like.
Aluminum on the inside of the pipe
This method of reinforcing a polypropylene pipe is one of the solutions to eliminate external blisters. Although there is still a potential risk of puffing up with this method, the only difference is that it will not be visible to the user. With such small bumps, the system will continue to work.
Advantages of inner reinforcement with aluminum:
- The polypropylene layer between the reinforcements is quite large and it is much more difficult for it to swell.
Disadvantages of reinforcement with aluminum on the inside:
- Possible collapse of the weak sections of the polypropylene pipe inward if you make a mistake during the design or operation of the system. which will entail a malfunction and possibly the integrity of the system.
Criterias of choice
Studying the polypropylene pipes on the market, they decide which ones to choose according to the set of basic operating parameters.
Operating pressure
The parameter is designated by the letters PN when marking. The choice of value is determined by the characteristics of the system. In case of frequent water hammering or the need to periodically pressurize conventional pipelines, it is optimal to choose products of the PN20 brand, but for high temperatures typical for heating systems (from + 70 ° C) PN25 pipelines with composite or fiberglass reinforcement are suitable.
The pressure in floor and autonomous heating systems, as a rule, is less (up to 10 atmospheres), therefore, polypropylene pipes PN20 with monolithic or perforated aluminum reinforcement are suitable for their installation.
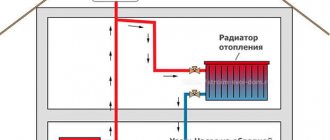
Water supply to the heating radiator with polypropylene pipes
Heating agent operating temperature
Which polypropylene pipes are best for heating depends on the type of system. Due to the fact that the temperature of the coolant in systems such as "underfloor heating" is lower (usually up to + 40 ° C), it is possible to use not only pipes with any type of reinforcement, but also products of a single composition.
In radiator-type systems with a coolant temperature of about + 85 ° C, any reinforced polypropylene pipes can be used.
Pipe diameter
What diameter of a polypropylene pipe to choose for heating? It is important that it meets the needs of the system and ensures the passage of the required amount of coolant per unit of time.
- For large objects (large saunas, hotels, hospitals, etc.), pipes of 200 mm or more will be required.
- For the installation of heating systems in private houses, the required water passage will be provided by pipes of 20-32 mm.It is easy to lay them on your own, including giving the necessary bend.
- Heating polypropylene pipes with reinforcement are also used for the installation of hot water supply lines. In this case, choose a diameter of 20 mm, and for risers, products of 25-32 mm are optimal.
- Central heating systems use 25 mm pipes.
- For a warm floor, 16 mm is enough.
A complex autonomous heating system will require the use of pipes of various diameters.
The recommendations listed above should be considered basic and before purchasing and installing heating pipes, make a choice taking into account the characteristics of a particular object and even individual lines of the system.
- For example, when installing heating in a private house with a one-pipe system, the radiators are connected in series to the main line. For the installation of such a ring, pipes of 32-40 mm will be required, and for outlets to radiators - up to 26 mm.
- With a two-pipe system, the principle of heating is different. The parallel operation of the supply and return lines reduces the pressure in the lines, therefore, pipes of a smaller diameter should be chosen - up to 30 mm.
Diameters of polypropylene pipes for heating - table of correspondence of internal and external dimensions
Polypropylene with fiberglass
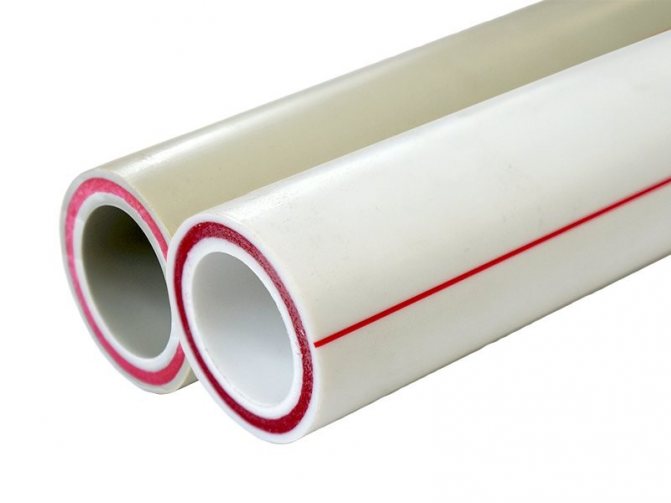


The most popular reinforcing layer at the moment is fiberglass. Choosing polypropylene with fiberglass, you will see that the inside and outside of such a pipe is polypropylene, and the central layer is fiberglass. However, all three layers form a single whole, since the central fiberglass layer is made on the basis of polypropylene mixed with glass fibers. The linear elongation of such pipes is slightly greater than when reinforced with aluminum foil and is about 2.5 mm with a pipe length of 1 m.
Benefits of the new material
Reinforced polypropylene is a modern high-tech material that is successfully used in the manufacture of pipelines. It is much lighter than metal, has elasticity and a high level of chemical and corrosion resistance. In addition, the material is environmentally friendly.
Reinforced polypropylene pipes have a fairly low cost and their installation is not too difficult even for non-professionals. It should be noted that pipelines made of this material are attractive in appearance and very rarely leak. Such a nuisance can only happen due to mistakes made during installation.
In addition to indoor heating and water supply systems, reinforced polypropylene is used in sewerage systems, ventilation, outdoor water supply, in agriculture and industry. There are two varieties of this material. We will consider the advantages and disadvantages of each of them in this article.


Polypropylene with basalt fiberglass
Basalt fiber reinforced polypropylene pipes are the newest type of pipes of the fourth generation. When choosing such polypropylene, keep in mind that the linear elongation of such pipes is the same as for fiberglass reinforcement. However, this type of reinforcement has a number of significant advantages:
- High thermal stability and resistance to pressure drops.
- High durability of the pipe.
- Such a pipe has a larger internal flow section and, accordingly, a smaller wall thickness.
It doesn't really matter which polypropylene pipe you choose, reinforced with fiberglass or basalt, this does not affect the characteristics in any way. The only difference is in the manufacturing technology. There are many companies that produce polypropylene pipes with the same performance but different reinforcement.
So which polypropylene is better?
Pipes without aluminum foil reinforcement are much easier to install. Such pipes do not need pretreatment before welding, do not blow in or collapse.Then the question arises, why, having a number of significant disadvantages, this type of reinforcement is still used? In fact, there is such a thing as "oxygen permeability". Air that penetrates the pipe walls enters the coolant. Air in the heating system can harm it, as the chance of corrosion increases. Polypropylene pipes, reinforced with a continuous layer of aluminum foil, completely impermeable to oxygen. A pipe reinforced with perforated aluminum allows oxygen to pass through, but not in such volumes as a pipe without reinforcement at all.
Now, pipes with a layer of ethylene vinyl alcohol on the outside of the pipe have begun to be used as an oxygen barrier, which prevents oxygen from entering the coolant. It can be concluded that soon pipes with reinforcement with aluminum foil will simply cease to be produced. Because there are other types of reinforcement that do not have the same drawbacks as this one.
Findings:
- Reinforcement is needed to compensate for linear elongation during heating.
- The reinforcement is made of aluminum in the form of a continuous foil on the outside of the pipe and inside. Perforated aluminum - outside.
- Reinforced pipe with fiberglass or basalt replaces aluminum reinforcement in water supply systems. An additional anti-diffusion layer makes it suitable for installation in heating systems.
Installation features
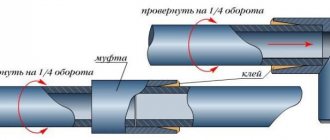
The principle of assembling a plumbing or heating system from reinforced pipes is the same as in the general case: pipes are cut to size, chamfers are removed, pipes and fittings for polypropylene pipes are heated with a special simple soldering iron, after which they are combined at one point in space-time. A few seconds - and instead of two parts, one, absolutely monolithic.
However, there is a difference: aluminum-reinforced polypropylene pipes require one more technological operation. This is a sweep. Before pushing the pipe into the soldering iron nozzle for polypropylene pipes, you need to remove the aluminum layer from it. Nothing complicated: the pipe is inserted into a simple sleeve with knives, one or two turns - and you're done.


Manual stripping for pipes can be like this
For pipes with an aluminum layer inside, a slightly trickier tool is used - a facer. It selects the inner layer from the very end of the pipe so that the end is welded securely to the fitting.
This ensures that the pipe:
- Will not delaminate;
- That aluminum will not be destroyed due to electrochemical processes that begin in the presence of metals and at least some kind of potential difference.
What about glass fiber reinforced polypropylene pipes?
But nothing. From the point of view of welding with a fitting, their inner reinforcing layer is no different from polypropylene. And if so, no additional operations are needed.