The use of heating systems with a liquid heat carrier in private houses today is based on several schemes of the system. One of the most reliable, simple and time-tested schemes is the gravitational heating system. Based on the laws of thermodynamics, gravitational heating has become widespread due to the small number of elements and the simplicity of work, both in terms of project calculation and practical installation. But, despite the seeming simplicity, for correct operation, it is necessary to take into account many points, which will be discussed in this article.
The principle of operation of the gravitational heating system of a private house
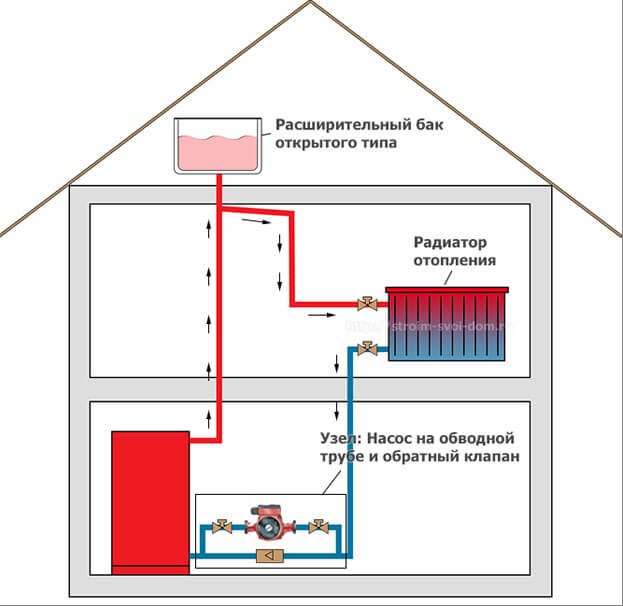
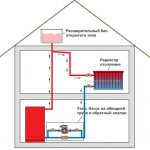
The gravitational heating system of a private house is based on two physical principles. The first is that substances have different densities at different temperatures. The second is that the pressure in the system is created due to the difference in the levels of the liquid, and the greater the difference between the upper and lower points, the higher the pressure in the system.
The first principle of a gravitational heating system is expressed in the fact that when heating a liquid heat carrier, and it does not have to be water, it changes its density. Water in its normal state at a temperature of 20 degrees has a density greater than that heated to 45 degrees; when heated to 80 degrees, the difference will be such that additional volume is required for water. In this case, the coolant of the same mass will occupy a different volume, because of which it begins to expand and be displaced outside the heat exchanger. In a confined space, after the start of the movement of the heated coolant, its place is taken by the cooled coolant. So, under the influence of heating, a flow arises, and the gravitational heating system begins to work.
The second principle of operation of this circuit begins to work from the moment the coolant begins to move. As it heats up, near water or antifreeze, the speed of movement increases, since the temperature rises quickly and the expansion of the volume forces the liquid to be forced out of the boiler water jacket at a higher speed. Leaving the volume of the boiler, the liquid escapes along a vertical pipe to the expansion tank. Having reached the level of the branch, the liquid fills the volume of the pipe and rushes along the pressure loop to the pipelines leading to the heating radiators, creating the necessary pressure. Taking into account the difference in height between the point of entry of the liquid into the pressure loop and the lower point of discharge, the created pressure additionally affects the cold heat carrier.
Gradually warming up, the system reduces the temperature difference between the cold and hot coolant, and thus, the speed of fluid movement in the system increases to maximum and can even reach 1 meter per second.
Underfloor heating installation using a double-circuit floor boiler


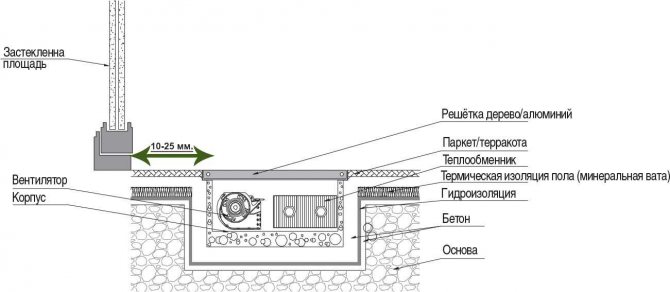
Design warm floor consists of the following layers:
- Floor slab or sub-base.
- Vapor barrier - polyethylene film for the floor of the 1st floor.
- Heat insulator - penoplex.
- Waterproofing agent - polyethylene film.
- Reinforcing mesh with an underfloor heating pipe attached to it.
- Cement-sand screed.
- Finishing floor covering.
Gravity heating the advantages of a gravity heating system

Before considering the positive qualities of gravity heating systems with natural water circulation, it is worth considering separately all the disadvantages of the system. For many, the first and main drawback of the gravitational heating system is its archaism.Indeed, this is one of the most ancient heating systems using a liquid heat carrier. It was from this system that one and two-pipe wiring schemes were later developed, it was this system that was used for mass installation, when the industry mastered solid fuel heating and, a little later, gas heating boilers. But on the other hand, the gravitational heating system is also one of the most reliable - its service life is on average 45-50 years. That is, exactly as long as it takes for the metal pipes to lose their tightness under the influence of the coolant.
The second point is the low efficiency of the gravitational heating system. Indeed, the scheme itself, based on the natural circulation of water, implies the inertia of the process of heating the room, until the heating boiler picks up the required power, and the temperature difference between the heated and cooled coolant reaches a minimum, it will take quite a long time. But on the other hand, even after the boiler stops supporting combustion, the circulation process continues, while a large volume of water in the system will cool down much longer than in a forced circulation system.
Another disadvantage can be written into its asset by the gravitational heating system due to its bulkiness. In practice, with the same area of the heated room, a system with forced circulation compared to gravity will take up much less space. In the gravitational heating system, in addition to batteries, pipes of the upper distribution will also be placed, without which the creation of the necessary fluid pressure is impossible.
And of course, the issue of temperature control in individual radiators, and the possibility of adjusting it. A gravitational heating system in the classic form with a one-pipe construction scheme cannot provide such a function due to the impossibility of shutting off a separate radiator.
But on the other hand, it is an ideal system for installation in homes where there is no electricity or constantly having problems with its supply. The gravitational heating system is capable of operating without electricity, since the main force of movement of the coolant through the system is not the circulation pump, but the thermal expansion of the volume of the coolant.
A large volume of coolant in the system allows for smooth heating of the room. On the other hand, such a volume of heated coolant cools down much more slowly than the volume of a forced circulation system. This is especially pronounced when there is a power outage or damping of fuel in the furnace. A forced circulation system cools down 3-4 times faster than such an archaic gravity heating system.
This property is often used when temporarily staying in the house - just instead of ordinary water, antifreeze is poured into the system, and even after complete cooling, neither pipes nor radiators are threatened with rupture due to freezing of water.
And of course, it just needs to be noted that such a system is simply trouble-free in operation. With proper operation, it can last for about 50 years, while it has only two risk factors. The first is the threat of boiler overheating, but even here it mainly depends on the human factor, and not on the system. The second is the freezing of the coolant, but in this case, the use of antifreeze reduces the risk of this accident to almost zero.
Water heating system
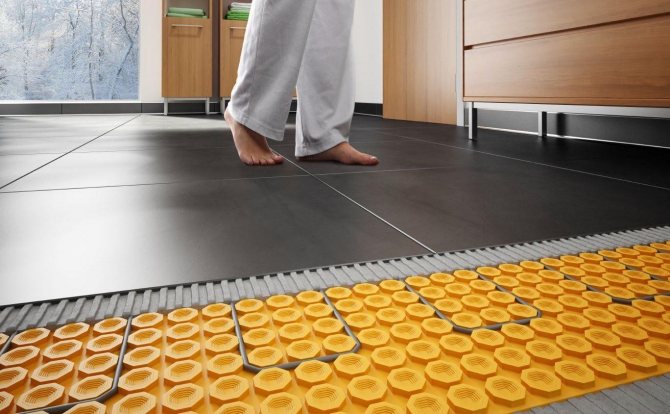
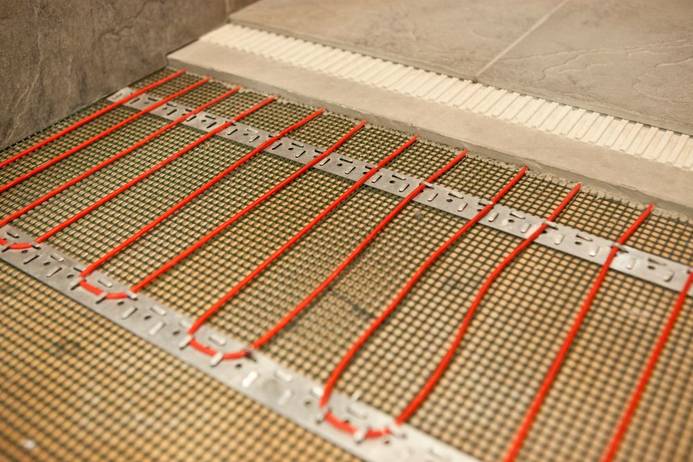
Underfloor heating This is a type of radiator heating, where the radiator is very large - the floor over the entire area. Accordingly, the temperature of the coolant should be much lower than radiator heating and is: - 30 - 35 ° С with concrete flooring - 45 - 55 ° С with a wooden floor. More than 50% of the heat in underfloor heating is transmitted by radiation and is distributed evenly over the entire area of the room.Since the temperatures of the heating medium are relatively low, it is convenient to use condensing boilers and heat pumps as heat sources. According to the principle of the device, two types of underfloor heating can be distinguished:
- concrete underfloor heating device - when the coolant heats the concrete mass, and from its heat is transferred to the floor covering. The cover is ceramic tiles, linoleum or parquet.
- wooden underfloor heating device - when the coolant heats directly the wooden floor boards. In both cases, the coolant moves in a closed loop in the floor structures. The configuration of pipe laying in floor structures can be of 3 types: parallel arrangement of pipes in the form of a "snake". In this case, the heating of individual parts of the floor is not uniform.
- spiral arrangement of pipes. The pipe is laid from the collector in the direction of the outer walls and is laid in a spiral form along the perimeter at a distance of two steps to the center of the room. After turning, the return pipe is laid in the middle of the gap of the supply pipes up to the collector. The reverse way of laying the pipe is also possible - from the center to the collector. In this case, the supply and return pipes are laid at the same time. With the spiral arrangement of the underfloor heating pipes, uniform heating of all floor surfaces is achieved.
- parallel arrangement of pipes in the form of a double "snake". This method, like the first, is intended for the construction of wooden floors, and in terms of thermal characteristics is close to the second method.
According to sanitary standards, the temperature of the floor surface should not exceed 29 ° C in living quarters, 33-35 ° C in bathrooms and in cold areas near the outer walls. To achieve these parameters, the following guidelines should be followed:
- For underfloor heating, use special PEX underfloor heating pipes with a diffuse oxygen barrier or PEX-Al-PEX pipes with a diameter of 16 - 20 mm and lay them from 150 - 250 mm. step between branches.
- With an increase in the diameter of the pipes, the step increases, but unevenly heated floor zones appear. Too thin a layer of concrete over the pipe leads to the same consequences. The optimal concrete layer above the pipe is 60 mm.
- The length of the underfloor heating circuit should not exceed 90 - 100 m, which corresponds to 20 - 25 m² of the heated area. With a longer circuit length, local resistances increase, which the circulation pump may not be able to overcome.
- In "cold zones" the pipe spacing is reduced to 50 - 100 mm.
- With concrete underfloor heating, the entire pipe must be surrounded by concrete, i.e. before pouring, it must be raised 10 - 20 mm above the base (usually foam polystyrene shields).
- The thickness of the thermal insulation layer depends on the temperature difference above and below the overlap: with a difference of 5 ° C, the layer thickness is 50 mm, with a difference of 10 ° C or more, the thickness of the thermal insulation layer is at least 100 mm. Waterproofing (usually a polyethylene film) is desirable but not required.
Fig. Underfloor heating of wooden floors is significantly different due to the poor thermal conductivity of wood. Therefore, the pipe is embedded in special channels of the aluminum reflector and in the space between the loungers it is tightly pressed against the boards. The flowing water heats the surfaces of the reflectors, which transfer heat to the floor. Depending on the material and thickness of the coating, the water temperature varies within 45 - 55 ° C. When concrete is heated, it expands and can destroy the building structures of buildings. To avoid these unpleasant phenomena, compensating damping tapes with a thickness of 5 - 8 mm, located along the entire perimeter of the walls, help.
- If the area of the room is more than 40 m², the concrete monolith is divided into parts with transverse expansion tapes. And also when moving from one room to another.
- Concrete work is carried out only after a hydraulic test, leaving the working water pressure in the pipe. Finishing work can be performed only after slowly heating the concrete to 50 ° C and slowly cooling it to 20 ° C.
Underfloor heating of wooden floors is significantly different due to the poor thermal conductivity of wood. Therefore, the pipe is embedded in special channels of the aluminum reflector and in the space between the loungers it is tightly pressed against the boards. The flowing water heats the surfaces of the reflectors, which transfer heat to the floor. Depending on the material and thickness of the coating, the water temperature varies within 45 - 55 ° C.
- Aluminum reflectors should cover 70 - 90% of the floor area.
There are no problems with underfloor heating of all rooms of the house, especially when heat sources operate on gas, liquid or electric fuel, but this type of heating is not desirable in bedrooms, children's rooms. If, in addition to the underfloor heating, there is also a radiator heating in the heating system, it is necessary to prepare the required water temperature for the underfloor heating system by mixing the supply and return water. Below are a few tricks to achieve the desired result:
- "Wild way" - The return water from the last radiator is passed through the underfloor heating circuit.
- "Cheap way" - used with a small number of heating circuits (2 - 4) underfloor heating. Then on each return water circuit, but not closer than 150 mm from the return manifold, a thermostatic valve (RTL) is installed, which releases water from the circuit at the set temperature, and the incoming hot water raises the temperature in the circuit and the valve closes
- "Classical method" - the unit prepares water of a certain temperature by mixing the supply and return water through a check valve or a three-way valve. In this case, the water in the circuit circulates constantly, and the room thermostats change the flow rate in the circuits, thereby also the temperature level in the room. The flow rate can also be changed by collector servo motors, which are controlled by mini electric motors, receiving a signal from a central console, to which room sensors transmit information by radio waves.
R.S. Payvin floor heating systems
A simplified version of the heating system with natural circulation of the heat carrier
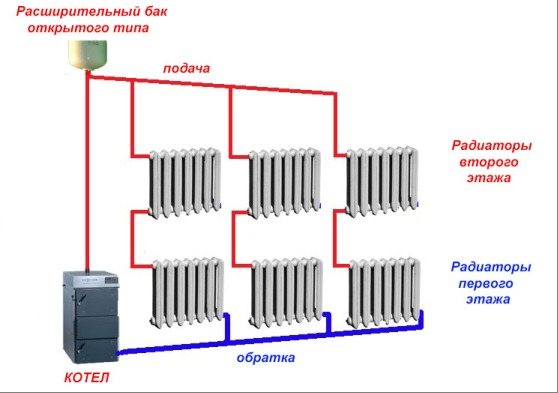

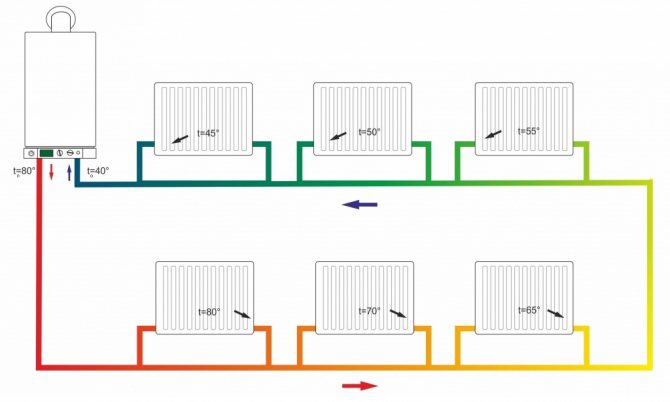
When choosing a private gravitational heating system, it is necessary to carry out a number of calculations in order to understand how the system will provide heating of the room. Under normal conditions, the volume of individual rooms and the power of heating radiators installed in them are taken into account in the layout of the piping layout. When installing radiators of the same rating, the gravitational heating system will heat up the rooms unevenly. The first radiator closest to the boiler will heat up more, and in the radiator farthest from the boiler, the coolant temperature will be significantly lower. That is why, when selecting heating devices, the former are installed with lower power, and those that are further must be more powerful.
It is important to choose the right expansion tank in the choice of structural elements. When calculating the volume of the expansion tank, it is customary to take the ratio 1/10 as the basis. That is, when the volume of water in the system is about 250 liters, the volume of the tank must be at least 25 liters.
The gravitational heating system is very demanding on the materials of construction. First of all, this applies to pipes and pipelines. The large volume of the coolant and the low pressure in the system require that the circulation be carried out with the lowest losses, and this is possible, either in steel or in polypropylene pipes. But here, too, there are certain limitations.So, steel pipes must be connected either by gas or electric welding, or by means of threaded connections. And if the first type allows you to provide a reliable connection practically without obtaining a weld inside the pipe, then the threaded method can create a large number of irregularities inside the pipeline. As for the polypropylene pipe, it has one significant drawback. This disadvantage concerns the ability of the pipe to withstand high temperatures - the maximum temperature that such a pipe can withstand is +95 degrees, which is not suitable for a pipe installed immediately after the boiler.
But even with all these caveats, the simplified diagram of a gravitational heating system is significantly different from a forced circulation system.
Such a system must necessarily include:
- Heating boiler (a prerequisite for such systems is the presence of a boiler with a large volume of a hot water jacket);
- Large diameter water pipes 11/2 inches;
- Expansion tank with a capacity of 1/10 of the volume of liquid in the system;
- Supply pipes with a diameter of 1 inch;
- Radiators of different sizes to ensure uniform heating of the premises;
- Return pipe;
- Liquid drain cock;
- A thermometer and a pressure gauge in the boiler, and Mayevsky's taps in the radiators are installed as control devices in the system.
As you can see, the system has a small number of structural elements and is quite suitable for assembling it yourself.
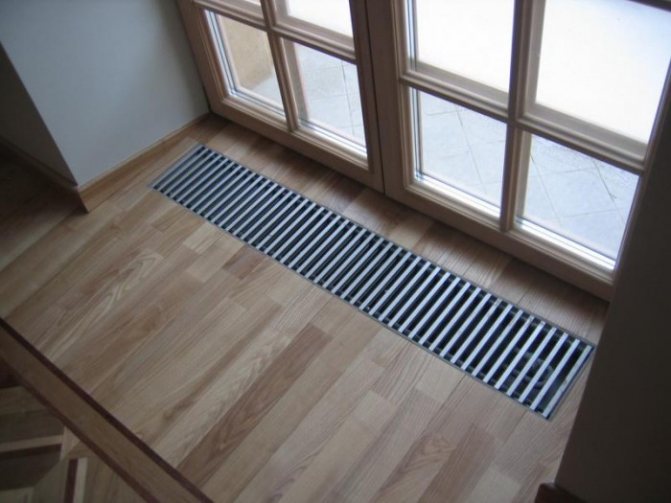
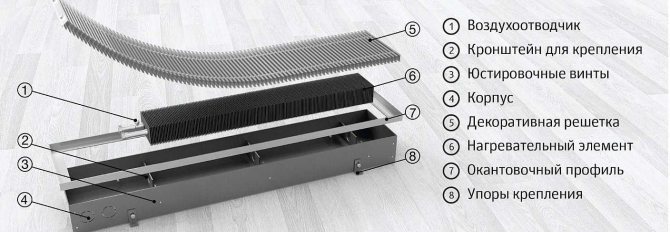
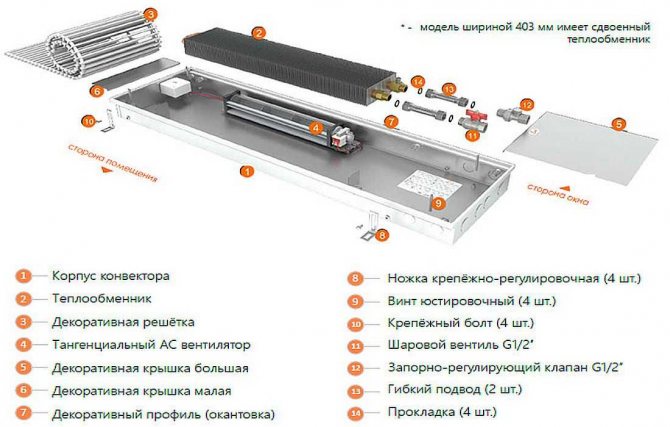
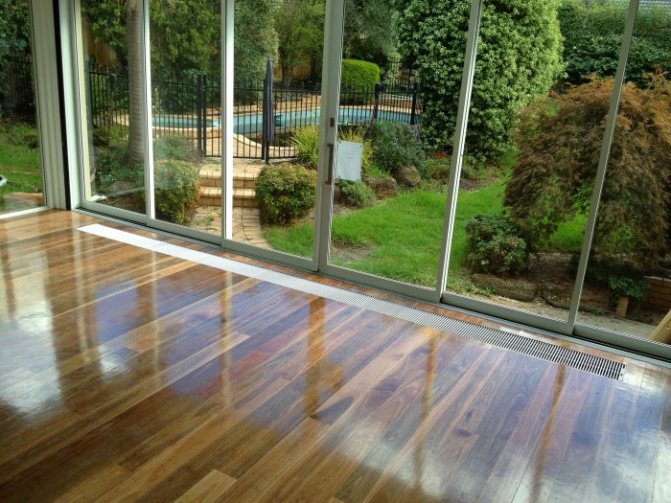
What is a floor convector?
Water built-in heating convectors are modern equipment that will help you warm up your home quickly enough. As the name implies, built-in heating convectors are mounted directly into the floor - that is, even during the construction of a house, special niches should be prepared, where built-in heating batteries are placed. You can lead the coolant circuit to them through shallower channels.
It should be noted that underfloor heating radiators may be the only source of heat.
Appliances such as floor convectors are based on simple laws of physics. Cold air, sinking into the lower part of the room, freely penetrates through a special grate to the heating element. There it heats up and rises, thus warming up the whole room. Warm air circulates continuously, thus providing constant warmth in the room.
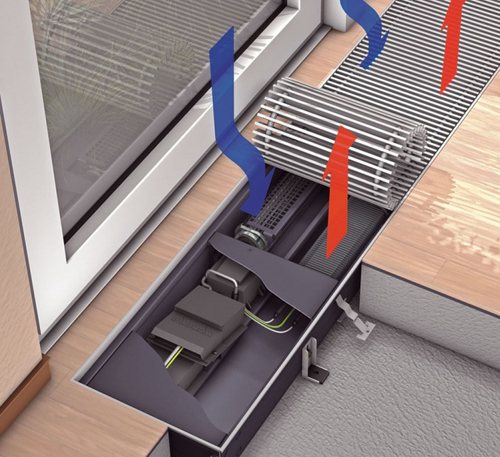

Air circulation in the floor convector
Floor convectors are the perfect solution for large rooms. In them, installing radiators near windows is ineffective, since these devices simply cannot warm up a large area. At the same time, built-in heating convectors can be located in any part of the room - and at the same time they will not interfere with movement around the room. Floor heating radiators can be used to heat large supermarkets, school and medical facilities, warehouses.
Water floor heating convectors
Each built-in floor heating convector is equipped with a power regulator, which means that you can adjust the degree of heating of the element at any time.
This function makes it permissible to use underfloor heating convectors even in those rooms in which the temperature of a certain level must be maintained (library, greenhouse, children's room).


Floor convectors are used for heating any premises
Basic schemes for heating houses
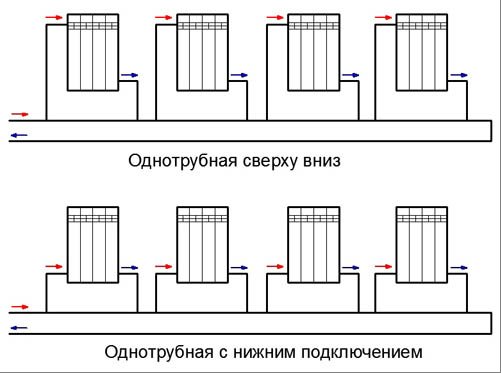

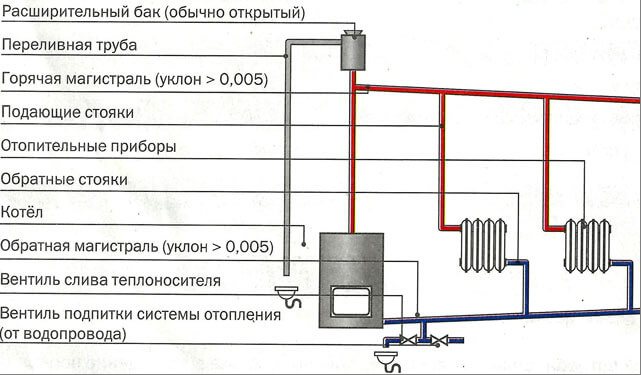
Today there are several types of gravitational heating systems. The most popular is the simplest system with a pressure loop and a slope of supply and return pipelines.Here, a scheme is implemented in which the coolant circulates in a natural mode, and the expansion tank has an open top. The disadvantage of this type of gravitational heating system is its inertia and complexity in implementation. The complexity of implementation in this case means the need to maintain all parameters of pipe slopes. So, after the pressure loop is mounted, the piping should be done with an inclination of 0.05 degrees to the side of the boiler. This slope is sufficient to provide initial fluid movement. The same slope is ensured when laying the return pipeline.
Such schemes imply one-pipe options for building a security system. More advanced gravitational heating systems imply a two-pipe piping scheme. But for this it is necessary to ensure the correct laying of the main pipeline. For the normal functioning of such a system, the total length of the supply pipe should be about 25 meters, the maximum size of such a pipe can be 35 meters. A long pipe length will reduce the temperature of the coolant supply; for its laying, an additional slope will be required, which will require an additional volume of the attic space or volume inside the room in the project.
How to make a heating system yourself in a private country house
Installation process divided into several stages: laying insulation, laying pipes, concreting and laying flooring.
Insulation laying


- Fasten the damping tape to the walls around the perimeter of the base.
- Lay the vapor barrier (plastic wrap) on the base 1 floor with wall allowance 20 cm... Glue the joints of the film with tape.
- Lay the foam boards on the base end-to-end, filling the entire area.
- Attach the foam boards to the base with mounting mushrooms.
- Lay waterproofing (plastic wrap) on the penoplex with an allowance for the wall 15 cm. Glue the joints of the film with tape.
Installing pipes under a wooden or other type of floor
- Lay the reinforcing mesh on the waterproofing, taking care not to damage the plastic wrap. Lay the mesh with a mesh size that is a multiple of the laying step according to the drawing (if the laying step 20 cm, then the grid cell size is 10 cm).
- Place foam trims under the net, lifting the net above the film surface by 10-15 mm.
- Lay the pipe in accordance with the drawing.
- Fasten it to the bars of the reinforcing mesh with a cable tie.
- Connect the system to the manifold.
- The collector itself is connected to a single-circuit or double-circuit boiler.
Important:
- Observe the minimum bending radius when bending 15 cm.
- When laying through walls or expansion joints, put a piece of thermal insulation (polyethylene foam) on the pipe and enclose it into a section of larger diameter (to avoid mechanical damage).
Concreting


Before concreting, the circuits are pressurized with high pressure 2 atmospheres during the day.
Pressure testing and connection to the manifold must be carried out by plumbing specialists. During concreting, the water in the pipes must also be under pressure.
- Install beacons (the height of the screed must be not less than 5 cm).
- Prepare screed mixture.
- Distribute the mixture between the beacons, trying to fill all the voids as much as possible.
- Tamp the mortar with a hoe.
- Align the solution with the rule of the beacons.
- Cover the screed with plastic wrap to keep it from drying out.
Important:
- Fortress recruitment takes place within 28 days.
- When concreting in dry weather, the screed under the film is moistened (moderately watered from a watering can) 2-3 times a day during the week.
- The plastic film is peeled off In 2 weeks.
Laying the floor covering
Selected flooring (tiles, linoleum, laminate) is installed in 5-6 weeks after laying the screed.If necessary, additional leveling of the screed surface is carried out with self-leveling mixtures.
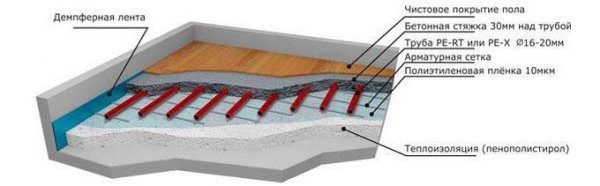

Photo 3. Diagram of the underfloor heating device. The entire construction consists of seven layers.
What to look for when designing a gravitational heating system
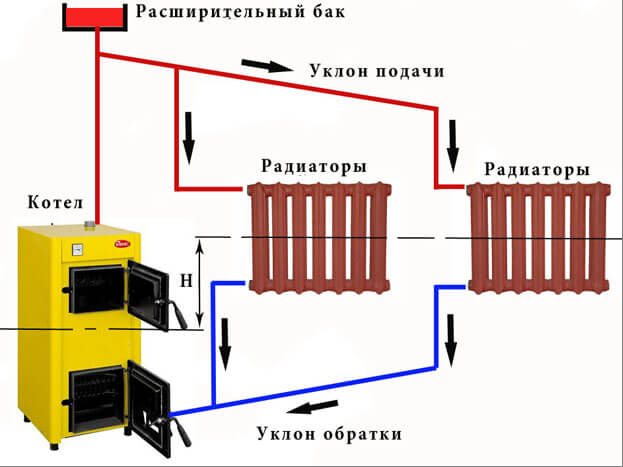

The main problem of the effective operation of the gravitational heating system in low-rise private houses is the incorrect location of the boiler and radiators relative to each other. One of the important parameters of the system is the value of the circulating head. It shows the distance from the center of the heater to the center of the boiler. The higher this indicator, the more efficient the work of the entire system.
The inefficiency and low efficiency of heating boilers, both solid fuel and gas, installed in gravitational systems are often associated with a small difference in heights between the radiator and the boiler. So, under normal conditions, this difference is usually only 0.2-0.3 meters. This situation does not allow saving up to 25% of fuel. Most of the energy is spent on superheating the liquid. At the same time, if you increase the height difference by 0.5 meters and bring it to 0.7-0.8 meters, then the efficiency will increase by 6-11%, and with a difference of 2.0 meters, it becomes possible to save up to 20% of energy ... That is why, when designing gravity-type heating systems, the placement of the boiler is planned at the lowest point, most often in the basement.
At the same time, considering all the options and methods for installing heating systems in a private house, despite the seeming simplicity of implementing this project, it is recommended to entrust it to professionals. Experience and availability of special equipment will help to ensure quick and, most importantly, easy installation of all equipment, minimizing the risk of errors.
Pros and cons of a one-pipe system


The one-pipe system is more suitable for small houses with a small heating area
A single-pipe heating system for any apartment or private house warms up faster when compared to a two-pipe one. Subject to the installation rules, the system will be well balanced, the rooms will be heated evenly. This scheme is chosen for its aesthetic appearance, since only a single pipe is needed for routing. In addition to the main advantages when wiring a one-pipe type, you can connect the tap to the battery, which will allow you to remove it without having to turn off the entire heating system. It is advisable to install a scheme of this type in small private houses, this is a more economical option, in contrast to the two-pipe method.
Of the minuses of the scheme with a single pipe, difficulties are noted with adjusting the temperature regime in the premises. For this purpose, you need to use polypropylene thermal valves or radiator regulators. In addition to regulation, it is necessary to create strong pressure and install powerful pumps with tanks for expansion at the maximum point of the circuit. If the house is two-story, the heat carrier must come from above. In large houses, it is sometimes necessary to increase the number of sections in the batteries, due to which they have to increase their length and spend additional energy on placement.
Benefits of underfloor heating
- Comfort! You will be able to walk barefoot all year round - it is especially pleasant to feel the warmth when you step out of the shower.
- A properly sized unit can heat a larger area than a separate radiator, therefore installing a warm floor will significantly reduce heating bills.
- Your floors will stay warm even when the windows in your home are open.
- The installation is hidden from view - so the interior will not be spoiled by ugly bulky radiators.
- It can be installed under stone, tiles, wood or carpet (provided that the carpet is not too thick - 1.5 cm is usually considered the maximum suitable thickness)
- If you are going to sell or rent your home, the presence of a heated floor will help you set the price higher: housing with heated floors immediately raises its status in the eyes of future buyers or tenants.