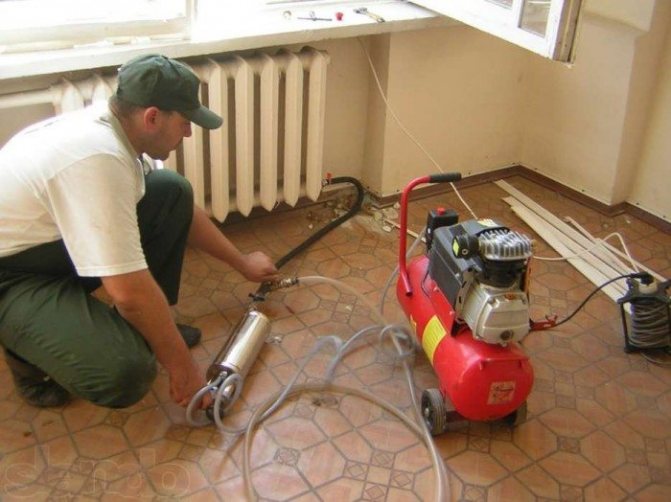
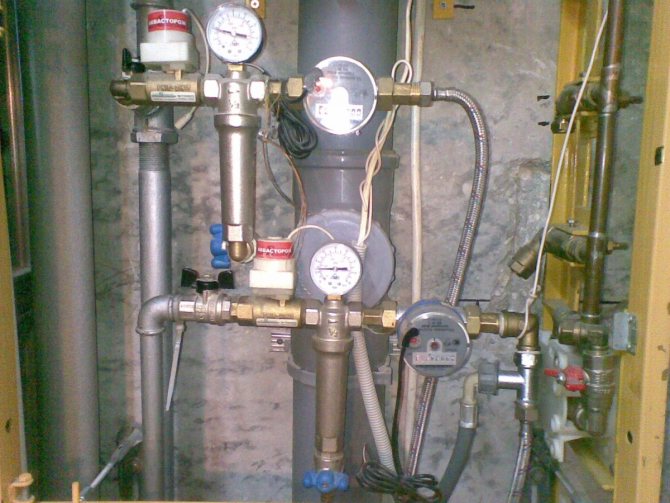
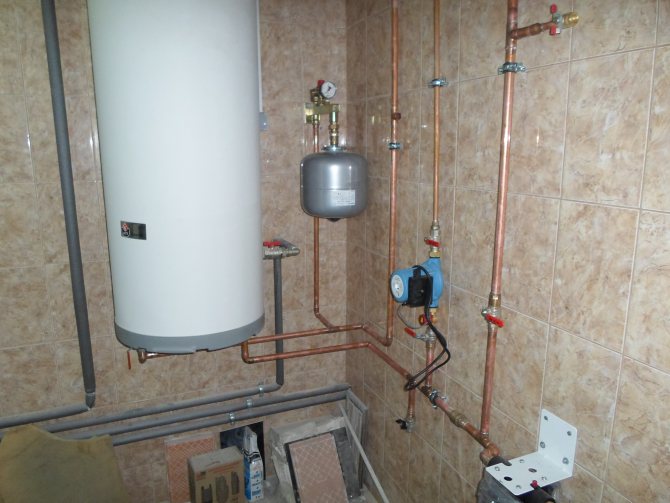
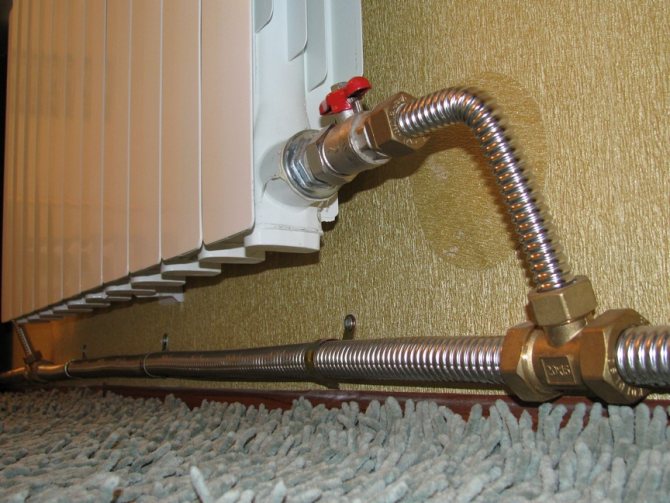
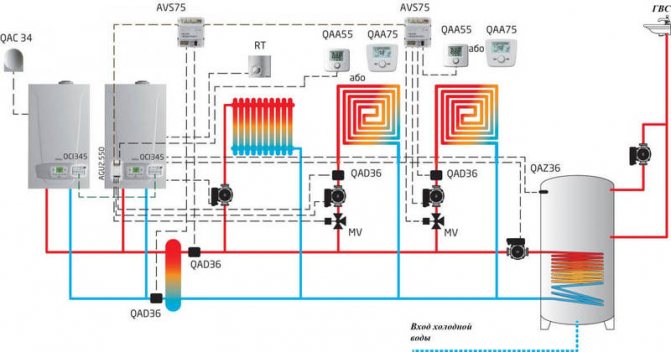
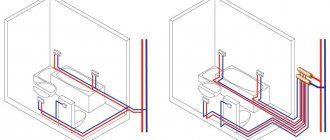
It would seem, what could be difficult in the design of the climate network? In the opinion of the majority, this is either a heating point of the heating system, or an individual boiler that heats a liquid heat carrier. Then water or antifreeze flows through pipes to heating radiators, where a secondary exchange of thermal energy with air in the room takes place.
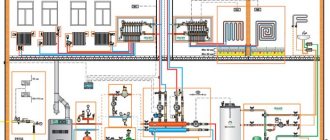
But behind the external simplicity, very complex engineering solutions are hidden, the operation and maintenance manual of which takes more than a dozen pages.
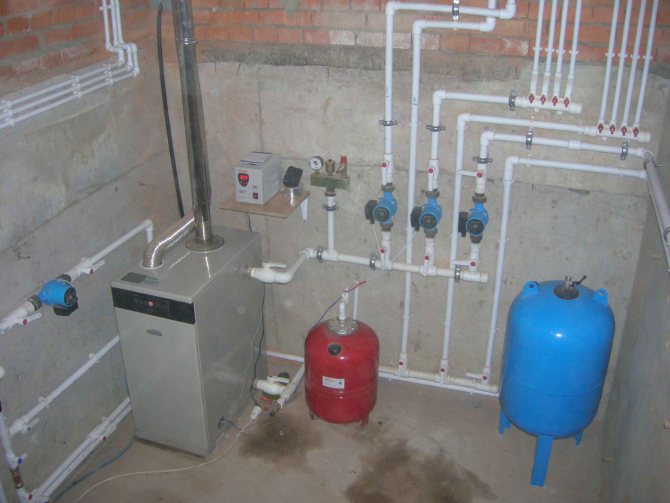

The heat in the house depends on the correct installation and periodic maintenance of the heating system
Water heating
Most widespread, despite the emergence of more modern systems. The main division is dependent and independent heating. Wiring types:
- One-pipe (this system is also called bifilar)
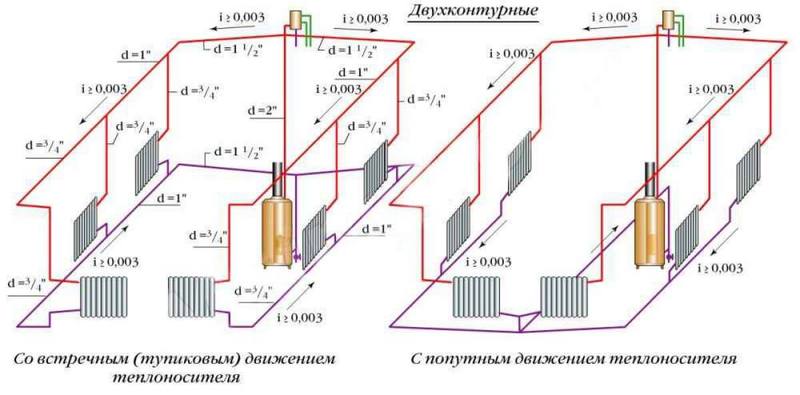
- Multi-circuit: one of the wiring - two-pipe - is a common system in this category, along with four - and three-pipe heating systems
- A wiring called a manifold
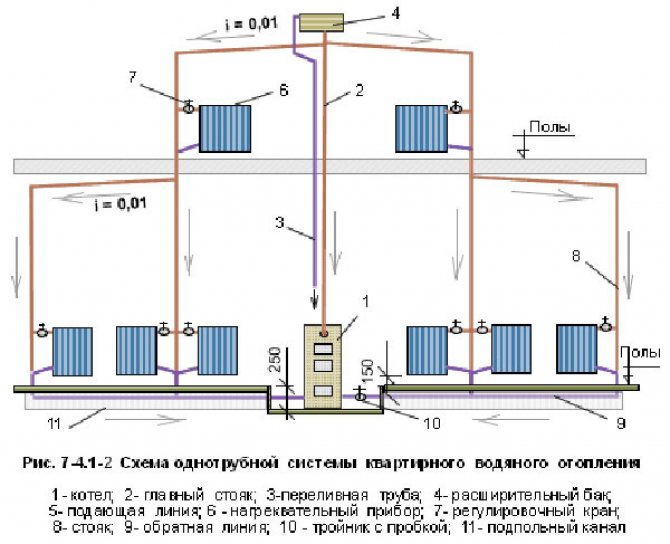
Single-pipe system operation
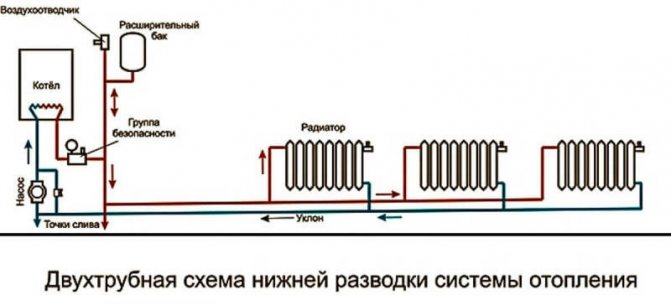
The heat carrier in this system is water. After heating, the coolant passes through the guide pipes. In terms of the level of operating temperature conditions of this system are different. A basic example: the heating scheme of a riser system will be one-pipe with hydraulic connection, and two-pipe in the context of heating devices (radiators) operating in it. The connection diagram is dependent, or open, that is, it has a vertical or horizontal riser, as is the case with a bifilar system. The coolant is heated by means of autonomous energy elements, which are divided into coils. The connection is optimally made to the ascending or descending section of the pipeline.
Horizontal bifilar systems have tubular heating devices (convectors, heating ribbed or smooth pipe, steel or cast iron radiator, etc.) When using a horizontal heating system, it is impossible to adjust the temperatures of one or more heating devices - those that need heating at the moment. Adjustment is only possible for the entire heating circuit. These systems are mainly used for heating agricultural facilities.

According to the method of moving the coolant, internal heating systems are divided into systems with natural and forced circulation (the pressure in the system is maintained by means of a circulation pump). In the case of natural circulation, there are subspecies - with top filling and with bottom filling. Installations with top filling work according to the scheme: lifting the heated coolant upward along the supplying vertical riser and distributing it into horizontal pipelines and then to radiators. After the heat energy is transferred to the devices and further into the room air, the heavier cooled water goes to the boiler unit.


Through the main pipeline, the coolant can be directed in various ways, in a dead-end or a passing scheme. When using a dead-end scheme, the heated coolant from the boiler has the opposite direction relative to the cooled water. The "sign" of this system is the presence of one or more loopbacks, or circulation rings. In the case when the heating radiators are located next to the boiler, the lengths of the loops are reduced. Accordingly, with distance from the main riser, the lengths of the circulation rings increase.Therefore, the most appropriate scheme is in which the circulation rings are minimally removed from the autonomous boiler unit. Ideally, this is not one extended system, but several shorter ones.

Pipes
What pipes can be used for heating and hot water supply?
Let's separate, so to speak, flies from cutlets: centralized (with elevator nodes) and autonomous engineering systems put forward completely different requirements for materials.
For central heating, the normal temperature is up to + 95 ° C at a pressure of 4-5 atmospheres, which is already very close to the boundaries of the possibilities of polymeric materials. On hot water supply, the nominal temperature is lower (75 ° C), but the pressure is higher (up to 6 kgf / cm2). The picture is aggravated by the high probability of deviations from the standard values, and the occurrence of water hammer.


Pipe rupture during water hammer
In autonomous heating systems, pressure is maintained up to 2.5 kgf / cm2 at temperatures up to 75-80 ° C, on autonomous hot water supply - up to 4.5 kgf / cm2 at 60-75 ° C. The parameters are stable, water hammer is excluded (more precisely, they can only be created by the owner of the house, which is not in his interests).
In this video you will learn about pipes for heating and water supply.
For central hot water supply and heating, the following are used:
| Picture | Description |
| Galvanized (zinc coated steel pipe). Unlike black steel, it does not overgrow with deposits and does not corrode. For mounting on threads only: welding breaks the anti-corrosion coating. |
| Copper pipe. It mounts on brazed socket, press and crimp fittings. The tensile strength exceeds 200 atmospheres, the heat resistance reaches 150-250 degrees, depending on the type of fittings used. |
| Corrugated stainless steel pipe. With characteristics close to copper, it is 2-3 times cheaper, and much easier to install: the connection on the crimp fitting is assembled with two adjustable wrenches in 30 seconds. |
For autonomous engineering systems, the following can be used:
| Picture | Description |
| Polypropylene pipes (usually with a reinforcing layer - foil or polymer mixed with fiber). Their advantages are the low cost of pipes and fittings themselves for low-temperature welding. |
| Heat-resistant and cross-linked polyethylene (PERT and PEX) are ideal pipes for heating and water supply in the floor for collector wiring systems: they are sold in coils up to 200 meters long, which allows all connections to be brought outside the screed (see Polyethylene pipes for water supply). |
| Metal-polymer pipes (on crimp and press fittings) are also sold in coils, and are supplied with an aluminum welded core glued between two layers of PERT or PEX. Their advantages are wall stiffness and relatively high tensile strength (up to 16 kgf / cm2). |
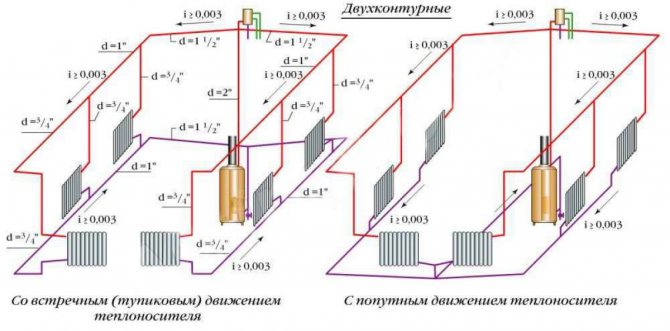
Hot water heating systems are distinguished:
a) according to the scheme for connecting pipes with heating devices:
- one-pipe with serial connection of devices;
- two-pipe with parallel connection of devices;
- bifilar with a serial connection first of all the first halves of the devices, then for the flow of water in the opposite direction of all their second halves;
b) according to the position of pipes connecting heating devices vertically or horizontally - vertical and horizontal;
c) by the location of the highways:
- with top wiring when laying the supply line above the heating devices;
The main advantages of a one-pipe heating system
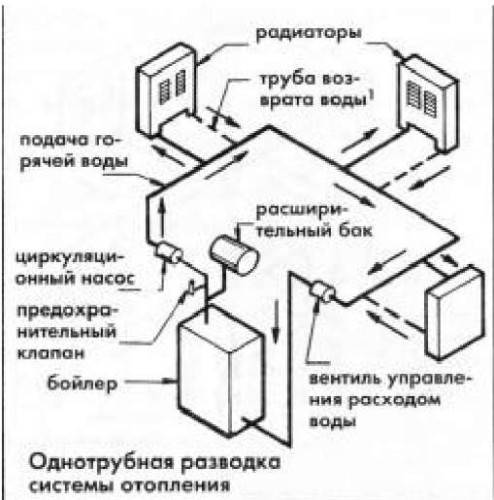

Single-pipe system diagram
The described heating system has several significant advantages:
- The ability to transport the heated coolant around the entire perimeter of a residential building in one circle through the heating pipes. A two-pipe system can only do this in two or even three times;
- The possibility of organizing the heating system below the floor level and under the entrance doors, which greatly simplifies organizational and repair work;
- The presence of only one pipe with a coolant leads to large savings in the construction budget;
- Possibility of quite simple control over the heating of all radiators together and separately.
These qualities of a one-pipe heating system allow for a high-quality and reliable heating system in multi-storey buildings.
Acceleration manifold
Despite all the positive aspects of this type of heating systems, it is worth considering one difficulty in their operation.
A single-pipe heating system of a one-story house works rather poorly without the use of a pump, which will contribute to the correct circulation of the coolant through the pipe and radiators. In order to organize the correct and reliable operation of such a system, it is necessary to install an acceleration manifold.
This determines the constant temperature of the coolant in each radiator and the noise level that is inevitable when using water heating systems.
In the event that this heating system is organized in a two-story building, there is no need to install an acceleration collector. Due to the fact that the heating pipe is located quite high, which contributes to the creation of a large natural pressure, the use of booster pumps and a collector is practically not required.
10.3. Heating system design sequence
Initial data for design: purpose and technology, layout and building structures of the building; climatic conditions and the position of the building on the ground; heat supply source; room temperature.
Calculation of the thermal regime. Thermal calculation of external fences of structures, calculation of thermal conditions in rooms, determination of thermal loads for heating (see Section I and Chapter 8).
System selection. The choice of the parameters of the coolant and hydraulic pressure in the system, the type of heating devices and the system diagram (with a feasibility study, if necessary).
System design. Placement of heating devices, risers, highways and other system elements. Division of the system into parts of constant and periodic action, for zone and frontal regulation. Appointment of the slope of the pipes; schemes of movement, collection and removal of air; compensation for elongation and insulation of pipes; places of descent and filling of risers and systems with water. The choice of the type of shut-off and control valves, its placement.
The design is completed by drawing a diagram of the system with the application of thermal loads of heating devices and calculated areas.
Thermal hydraulic calculation of the system. Hydraulic calculation of the system. Thermal calculation of pipes and devices (see Ch. 9).
Four-pipe system
The four-pipe system has two independent circuits: one circulates cold water, another hot. An ejection coil with a four-pipe system has two heat exchangers. Cold water is supplied to a two-row heat exchanger, and hot water is supplied to a single-row heat exchanger. Three-pipe and four-pipe systems provide the ability to supply cold or hot water to any ejection coil, depending on the need. However, in comparison with the three-pipe system, the four-pipe system does not have losses from mixing the heat - refrigerant. In addition, the four-pipe system has a more stable hydraulic performance.
| Heat supply scheme from CHP. |
In fig. 1.7 shows a diagram of a four-pipe heat supply system from a quarterly steam boiler house.
Water two - and four-pipe systems are used to supply heat to residential and public buildings. Two-pipe systems can be either closed or open, usually with local heating substations. Four-pipe systems, as a rule, are closed, and up to the central heating substation, heating networks are performed with two-pipe, after the central heating station to buildings - with four-pipe. The mode of operation of two-pipe heating networks is established on the basis of the provision of heat energy to all consumers. In four-pipe networks, heating systems are connected to two mains (supply and return) and hot water supply systems to two (supply and circulation).
| Temperature controller for two-pipe air-water air conditioning system. |
In a four-pipe water-air conditioning system, the amount of primary air is determined in accordance with the requirements of sanitary standards, therefore, in the warm season, the cold introduced by it is not enough to maintain the required air parameters in the room. In this regard, in addition to the coolant piping circuit, another coolant circuit is laid. In fig. IV.77 shows a schematic diagram of a four-pipe system. The operation of the hot water circuit of this system is similar to that of a two-pipe system. The cold water circuit has its own circulation pump /, which pumps water first into the water cooler 4, then into the heat exchangers of the ejection coils.
The connection of a two-pipe heat supply system for heating and ventilation needs with a one-pipe DHW system (open DHW circuit) leads to a three-pipe heat supply system. The three-pipe water system is also used for heat supply of industrial enterprises (industrial areas) that have a technological heat load of increased potential and a closed DHW circuit. In this case, to reduce the initial capital investment and reduce the cost of operation, two lines are used as supply lines, and the third is a common return line, i.e. instead of a four-pipe system, we get a three-pipe system. Each supply line should be connected to consumers that are homogeneous in potential and mode of heat consumption.
The four-pipe system has two independent circuits: one circulates cold water, another hot. An ejection coil with a four-pipe system has two heat exchangers. Cold water is supplied to a two-row heat exchanger, and hot water is supplied to a single-row heat exchanger. Three-pipe and four-pipe systems provide the ability to supply cold or hot water to any ejection coil, depending on the need. However, in comparison with the three-pipe system, the four-pipe system does not have losses from mixing the heat - refrigerant. In addition, the four-pipe system has a more stable hydraulic performance.
The four-pipe system has two independent circuits: one circulates cold water, another hot. An ejection coil with a four-pipe system has two heat exchangers. Cold water is supplied to a two-row heat exchanger, and hot water is supplied to a single-row heat exchanger. Three-pipe and four-pipe systems provide the ability to supply cold or hot water to any ejection coil, depending on the need. However, in comparison with the three-pipe system, the four-pipe system does not have losses from mixing the heat - refrigerant. In addition, the four-pipe system has a more stable hydraulic performance.