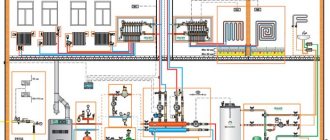
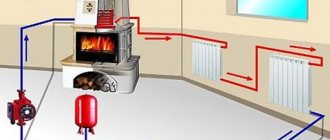
The heating system consists of many mandatory components, each of which performs its own specific functions. One of these elements is a mud filter for water, which is used to clean the coolant from foreign particles. This simple device has a significant impact on the efficiency of the heating system. This is especially noticeable in complex systems with a large number of control valves.
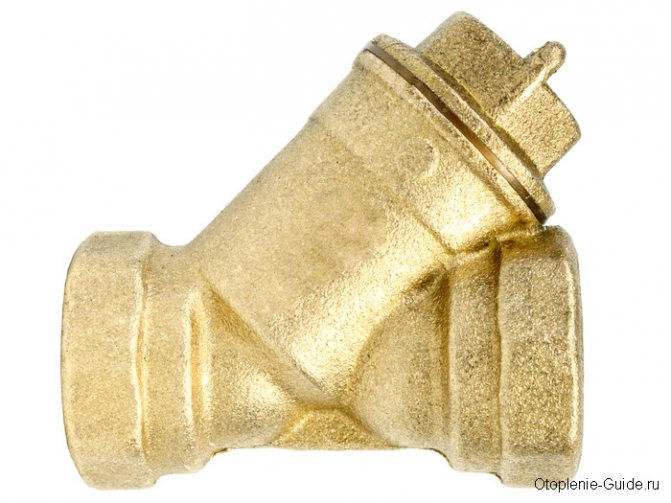

Filter for water purification from mechanical impurities.
What does the installation of mud collectors for the heating system give?
There are no questions about the need to install mud filters for water in centralized heating systems. Where the coolant is periodically drained and the system is refilled, it is impossible to argue with the obligation of this element in the system - there will always be dirt and impurities.
Disregard for mud collectors begins with the independent design of small autonomous systems. For example, heating systems in a private house. It only seems that in a closed circuit of small dimensions, there is nowhere for foreign impurities in the coolant to come from.
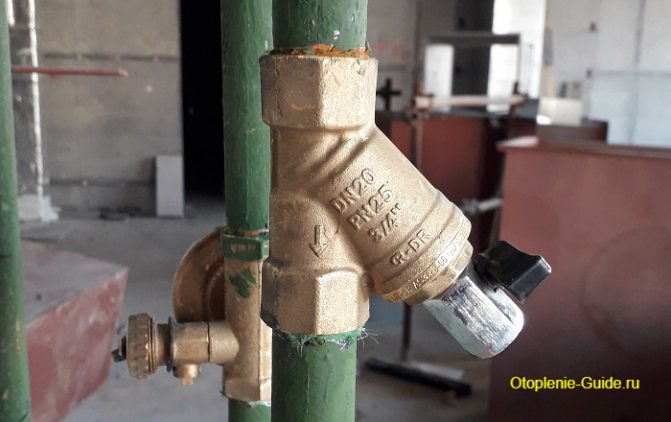


Mud filter with a tap.
Whatever type of coolant is used, and whatever initial cleaning it is subjected to, it will still be based on water. Water, which begins to interact with the metal nodes of the system, and there is metal in any system. As a result of this interaction, rust particles are formed, circulating in the system. In some parts of the system (irregularities inside the pipes, weld beads, sharp turns, narrowed passages, etc.), these particles accumulate, which impedes the movement of the coolant.


Mechanical filter for coarse water purification.
Since the rate of circulation of the coolant decreases, in order to achieve the required temperature parameters in the room, it is necessary to increase its temperature. This increases the load on the boiler and all other elements of the system, which does not add to their reliability, economy and efficiency. Competent installation of mud collectors in the system eliminates most of these problems, or at least postpones the time of their occurrence.
Additional benefits
The sump contributes to fuel economy. Using this water filter (photo below), you thereby protect the convective elements of the boilers - this, in turn, maintains their high efficiency and does not increase the volume of fuel. Accordingly, there is no excessive consumption of fuel, which leads to impressive financial costs.
In addition, the mud filter allows you to change or pump water in the heating system much less often, which also contributes to savings, since there is no need to consume reagents and unnecessary electrical energy. The volume of the coolant, which is discharged into the sewage system, also decreases.
The cost of these devices may vary depending on their type and size. The most common is for water (photo below). On such equipment, the filtration mesh is built into its housing.
Classification of mud collectors
The principle of operation consists in passing the coolant through a special mesh or magnetic filter, screening out mud fractions and depositing them at the bottom of the glass. The main condition for proper operation is the installation of the sump in the direction of the heat carrier flow.


Mud filter partially covered with primer.
The classification of mud collectors for heating systems is made according to several criteria.According to the degree of cleaning, devices for fine and coarse cleaning are distinguished. By mounting options: threaded, flanged and welded. By service method:
- self-cleaning - the sediment from the sump and from the surface of the mesh is washed off by a stream of water when the tap on the sump is opened;
- washing - the glass is washed without dismantling the filter, but manually;
- non-flushing - for cleaning it is required to dismantle and disassemble the unit.


Washing filter for mechanical water purification.
Filter types
The most common type of filter is a strainer. It serves to trap mechanical impurities and filter the medium. Cleaning here takes place with a filtered mesh, which is inserted into the filter housing.
Mesh filters are of the following subspecies:
- By the degree of purification: coarse cleaning (mesh up to 300 microns-microns) (mud collectors) and fine cleaning (up to 5 microns-microns).
- By the way of washing: self-washing, washing, non-washing.
- By the method of connection with the pipeline: threaded and flanged.
The angle strainer for the heating system (sump) belongs to coarse filters. Such filters are used to purify water from large and medium suspended fractions present in pipelines of water and heating networks.
Filtration classification
Strainers... The most common and familiar type of water sump filter used in everyday life. In the simplest design, the dirt is retained by the mesh and deposited in the accumulation zone. Periodically, the bottom of the glass is turned away and the dirt is removed. The design can be supplemented with a drain valve installed instead of the bottom, and then the sump turns from a flushing into a self-flushing one.
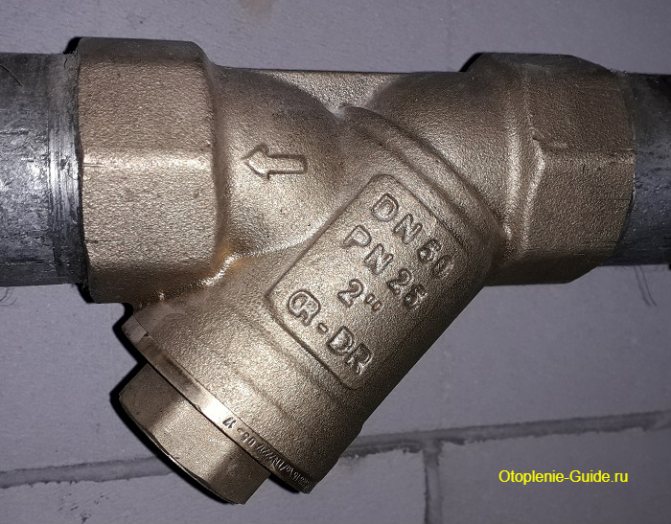


Danfoss FVR strainer, DN50.
The installation of an additional mesh that removes air from the coolant, a float and a needle valve adds a gas protection function to the mud collector. The efficiency of the mesh sump depends on the pressure in the line before and after it. With a significant difference in these values, solid particles can be forced through the mesh.
Magnetic filter removes metal particles from the coolant flow. During the operation of such a filter, no inhibitory effect on the fluid flow occurs, which is important when operating powerful pumps.
There are also inertial-gravitational and subscriber mud collectors. The principle of operation of the first is clear from their name and they are used in large enterprises. Subscriber devices clean the coolant at the entrance to metering units.
Classification of filters for heating systems


If a filter for the heating system of a private house is selected to cleanse the coolant from solid particles, then you should choose from the following varieties:
- The work of conventional sedimentation tanks is based on the use of earth's gravity. Under the influence of gravity, heavy particles settle to the bottom of the container. When the direction of flow of the coolant changes, centrifugal and turbulent forces wash away the particles to the edge. From the periphery, they easily fall into the sump.
- Mesh structures have cells of different diameters. It is important to choose the correct size of the cells so that the mesh filter does not quickly clog up or, conversely, does not allow large particles of debris to pass through.
- Magnetic filtering devices attract scale and metal particles. Thanks to the use of these elements, the likelihood of scale formation on the walls of pipelines and devices is reduced.
Also on sale you can find combined designs that contain a magnetic element and a mesh filter.
Features of the use of mud collectors
All mud filters for heating systems can also be divided into those intended for vertical or horizontal installation. Vertical structures are more often used in large heating systems.It should also be remembered that vertically installed mud collectors need to be serviced more often. The choice according to the size and parameters of cleaning is carried out based on the diameters of the pipelines, the power of the pumps and the places of installation.


Dirt trap with drain cock.
During installation, there are several rules that must be followed.
- Arrow on the case. As a rule, the filter has an arrow indicating the direction of movement of the coolant.
- The best location is a horizontal pipe run.
- Spatial orientation. The branch with mesh and nut or drain valve must point downwards.
- The presence of shut-off valves before and after the mud filter for water, as well as a pressure reducer after it.
- Convenience of service.


Strainers DN25, 1 ”.
Maintenance of mud filters
Any type of filter requires periodic maintenance, as debris constantly accumulates inside the device.


TO mud collectors
How the device is cleaned:
- The taps located on the sides of the device overlap, in this case it is not necessary to drain the coolant from the system.
- Before disassembling, a container must be installed to drain the remaining water.
- There is a plug on the filter that needs to be removed.
- The mesh is washed and reinstalled.
- A muffler is mounted.
- Couplings are twisted.
- The taps are opening.
Periodic filter cleaning extends the operating life of the entire system.
Maintenance of mud collectors in the heating system
The mud collectors are cleaned at least twice a year - before and at the end of the heating season. The frequency largely depends on the size of the system, the intensity of the coolant replenishment and the degree of its preliminary cleaning.
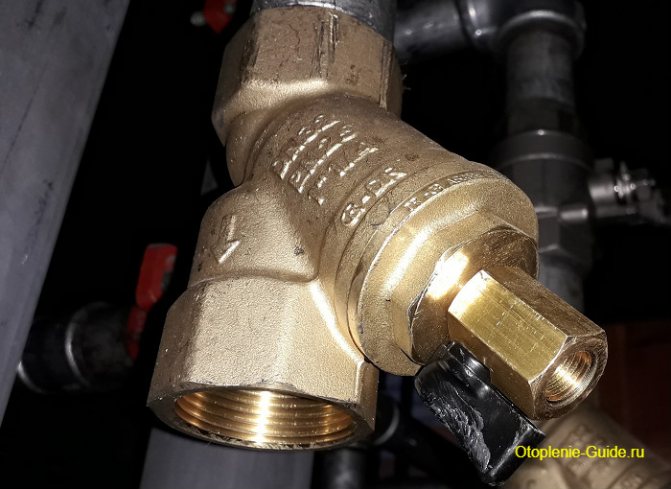


Danfoss FVR-D DN32, PN25, 1 ”¼ with drain cock.
In most cases, maintenance of household mud filters can be done by yourself. It is enough to shut off the lines, unscrew the glass cap, remove and rinse the filter mesh.
Equipping heating systems with mud filters allows you to protect expensive system components, reduce the frequency of flushing and replacement of the coolant, and, consequently, operating costs.
The purpose of the expansion tank
To maintain a certain pressure in the circuit, an expansion tank of the heating system is installed. This container is needed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the heat transfer fluid. If the tank was not there, then when the water was heated, it would greatly expand and cause a critical increase in pressure in the pipeline, which could lead to an emergency.
Due to the presence of the tank, the surplus of the expanded liquid enters the container and the pressure in the system is maintained within normal limits. When the coolant cools down, the lack of liquid is compensated for by water flowing back from the expansion tank into the system.
Expansion tank design


There are two types of tanks - open and closed. The first is a metal barrel with a lid. Below there is a branch pipe for tapping into the heating system. The open tank is mounted at the highest point in the system. Also, this container has an emergency drain pipe, through which the excess coolant is drained into the sewer to protect against overflow.
The closed-type expansion tank has two chambers - air and water. At the bottom there is a branch pipe for connecting to the heating circuit. In the upper part there is a nipple for filling the air chamber and a pressure gauge for pressure control. The closed design is necessarily equipped with an automatic air vent and a safety valve.
Both chambers are separated by an elastic membrane.When the coolant enters the water chamber, the membrane is pushed into the air compartment, which causes an increase in pressure in it. When the temperature of the coolant drops, the liquid is squeezed out of the chamber back into the system due to the increased pressure in the air compartment.
How to calculate the volume of the expansion tank?
The volume of the expansion tank should be 10% more than the volume of the heated coolant circulating in the heating system.
For the calculation, you can use the formula Vb = Vc x k / D, where:
- Vb - the volume of the expansion tank;
- Vс - the amount of coolant in the circuit;
- K is the coefficient of expansion of the heat carrier fluid when heated;
- D is an indicator of the efficiency of the compensation capacity
To calculate the total amount of cold coolant, it is worth adding up the data from the characteristics of all components for heating (heating boiler and radiators). The internal volume of pipelines is calculated separately, based on the cross-section of the pipes.
The expansion coefficient of the coolant when it is heated to 95 ° C is 4% (0.04). But there are corrections taking into account the concentration of impurities in water. If their concentration is within 10%, then the correction factor is 1.1, that is, 4 percent must be multiplied by this number. When the concentration of impurities is within 30%, the correction factor is 1.3. Typically, the efficiency of the expansion vessel is 0.375. After carrying out all the calculations, the resulting value is increased by 10%.