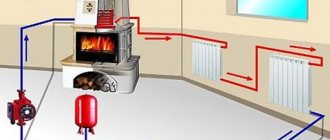
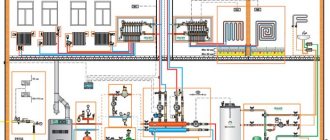
The "nightmare" of any owner of an autonomous heating system (CO) at home is the boiling or freezing of the coolant. Everyone is well aware that both the first and the second can lead to depressurization of the circuits or destruction of the water jacket of the heat generator, which is fraught with huge financial costs. And if the boiling of the liquid, as a rule, is prevented by the automation, then only the constant operation of the boiler plant can save the CO from freezing, which is not always possible (power outage, failure of the boiler unit). This publication will focus on liquids with a low freezing point, used as a coolant in autonomous heating systems.
[contents]
What is antifreeze and why should it be used in a heating system
It is customary to call antifreeze liquids with a low freezing point. On the modern market of climatic technology, there are antifreezes for the heating system of a country house, made in the form of concentrates, which, before filling with CO, are diluted with distillate until the desired concentration and specified parameters are obtained.
In fact, water is the ideal heat transfer medium. It has ideal (for CO) viscosity, fluidity and heat capacity (4.169 kJ / kg). Water has two significant disadvantages:
- transition from a liquid to a solid state already at a temperature of 0 ° C;
- an increase in volume by 10-12% when freezing.
So what should the owner of suburban real estate, which is not supposed for permanent residence, do to use an almost ideal, but freezing coolant or "non-freeze"? Drain the system is not an option, and insulation will not help. There is only one way out: to use antifreezes as a coolant for the heating system of a country house, despite the fact that distilled water is better for its physicochemical characteristics than any antifreeze.
Application rules
Also, antifreeze, unlike water, is more "scrupulous" in relation to the rules of use - the possibility of its use significantly depends on their observance.
- The pumps required to circulate the coolant must be very powerful, otherwise it will be difficult for the antifreeze to move through the pipes. In some cases, it may be necessary to install an external blower.
- Large diameter pipes should be used and the radiators should also be large.
- Air removal devices should not be automatic.
- The gaskets and seals used in the system can be made only of dense and resistant to chemical compounds rubber or made of teflon and paronite.
- When the boiler is turned on, the heating temperature should be increased gradually. In this case, the temperature of the coolant should not exceed 70 degrees.
The power of the heating boiler should be increased gradually after starting.
Antifreeze should never be used in the following cases:
- if the heating system in the house is an open type system;
- if the heating system is galvanized;
- if the heating boiler is capable of heating the antifreeze to more than 70 degrees;
- if oil paint was used as a sealant for the joints in the system, linen winding;
- if ion boilers are used.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Why the washing machine growls when draining water
Types of antifreeze
Today, in the Russian market, non-freezing fluids for heating systems are widely represented, made on the basis of the following components:
- Propylene glycol.
- Ethylene glycol.
- Glycerin.
- Pickles.
- Alcohol.
Each of the above components has advantages and disadvantages. There are also common problems inherent in all antifreezes for a home heating system.
- Lower (than water) heat capacity. The difference is 20-30%
- High viscosity due to increased density.
In addition, the components of these "non-freezing" elements quite aggressively affect the CO elements, including the seals.
Important! Antifreeze must not be brought to the boiling point, which for some solutions is more than 100 ° C. The main components decompose and lose their performance properties.
To eliminate these negative factors, most manufacturers of anti-freezing fluids introduce various additives and inhibitors into their composition, which increase the boiling point of the solution, the effect on metals and seals, which reduce the foaming of the composition.
Today, the most common antifreezes are those based on propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. Further, we will focus on them.
Ethylene glycol: what keeps its popularity

This substance is a polyhydric alcohol, tasteless, colorless and odorless. In its pure form, it loses its properties even at -13 ° C. That is why only aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol in various concentrations are used. The maximum temperature at which the composition freezes (-50) is reached when the concentration of the active substance with water is 6: 4.
Almost non-freezing coolant compositions based on ethylene glycol became popular all over the world already in the middle of the last century. The basis of the popularity of ethylene glycol-based antifreezes is its cheapness.
Ethylene glycol is toxic. According to the international classification, this substance is assigned a hazard class 3. His vapors are dangerous to humans and pets. That is why it is used only in closed COs. Ethylene glycol based antifreezes attack elements of heating systems, especially metals coated with zinc and its alloys. There is one more drawback - the decomposition of ethylene glycol in solution at a temperature of + 70 ° C. To detect leaks, the data "non-freezing" is colored red.
Important! It is forbidden to use antifreeze in double-circuit heating systems due to the risk of the active substance entering the hot water supply system.
Propylene glycol: what you need to know


This substance is a colorless liquid with a slight specific odor and sweet taste. It is widely used in the food industry and in the manufacture of e-liquids. This completely safe and environmentally friendly substance became available to the Russian consumer only at the end of the last century, but immediately gained universal recognition and well-deserved popularity.
Propylene glycol-based solutions are not aggressive and have excellent performance as a CO coolant. Freezing point and density vary depending on the concentration of the active substance.


Ready mixes based on propylene glycol have a significant disadvantage - high cost. You have to pay for quality! Non-freezing liquids based on propylene glycol are painted green by manufacturers.
Many of our compatriots ask the question of how to make a high-quality and safe non-freezing coolant for the heating system with your own hands? There is nothing simpler: a solution of ethyl alcohol (technical) in water in a percentage ratio of 7: 1 will not freeze at 10 ° C, it will be completely safe for humans and CO.
Instructions for the use of the coolant "Energos Lux -30C"
Instructions for the use of the coolant "Energos Lux -30C"
Application.
Designed for use as a low-freezing heat and coolant in autonomous heating systems of industrial and residential buildings, especially where a high level of environmental safety is required; in double-circuit heating systems; as a coolant in cooling systems of industrial equipment in food and pharmaceutical industries; in ventilation and air conditioning systems in contact with life, ventilation and air conditioning for residential and industrial buildings, for cooling systems of industrial equipment, chillers, refrigeration units, etc., operating in severe climatic conditions, where steel, cast iron are used as structural materials , aluminum alloys, copper and its alloys in the range of operating temperatures from -30 ° C to 106 ° C.
It can work with any type of heating devices - gas, diesel, electric boilers, not suitable for use with boilers of electrolysis type (Galan type),
in which heating occurs due to the passage of an electric current through the coolant.
Preparation for use.
Heat carrier "Energos Lux -30C" (hereinafter referred to as EL-30) with a crystallization onset temperature of -30 can be diluted with water. Undiluted coolant is worse than water in terms of its thermophysical properties. Dilution with water, in addition to saving for the consumer, allows you to increase its heat capacity (heat transfer) and reduce the viscosity (density), that is, improve the circulation (fluidity) through the system. The likelihood of soot EU-65 on the heating element or in the burner zone and the formation of tarry deposits, burnout of the heating element, etc., also decreases, since the penetrating ability of antifreeze is significantly higher than that of water.
The optimal dilution for the Central region is considered to be the dilution of EU-65 to a temperature of -30 ° C, for electric boilers up to -20-25 ° C. It should be borne in mind that at the indicated temperatures the crystallization process is just beginning, and the thickening of the working fluid occurs with a decrease by about 5-7C. The destruction of the system is excluded, since even if the ambient temperature drops below the specified parameters, since the heat pump will not expand. It will turn into a jelly-like mass, which becomes liquid again as the temperature rises.
But remember, the choice of dilution proportions is primarily determined by the temperature conditions of your region and the tasks solved by the coolant.
Considerations when designing a system.
It should be noted that TH has a lower surface tension coefficient than that of water, therefore it more easily penetrates into small pores and cracks. In addition, the swelling of rubber in HP is less than in water, therefore, in systems that have been operating on water for a long time, replacing water with HP can lead to leaks due to the fact that the rubber gaskets take on the initial volume. We recommend that the first days after pouring the heat pump to monitor the condition of the system fittings and, if necessary, tighten them or change the seals. The best protection against leaks is good new gaskets and a well-built system.
Before pouring liquid into the heating system, we recommend testing the operation of the system on water, pressure testing the system to make sure that there are no leaks, as well as that there are no impurities. As tests have shown, gaskets made of rubber, paranite, teflon, as well as flax seals and sealants withstand contact with the coolant well. You can use sealants resistant to glycol mixtures (eg Hermesil, LOCTITE and ABRO) or silky linen, but not oiled.
Elements containing zinc, in particular galvanized inside the pipe, must not be used in the heating system.At temperatures exceeding + 70C, the zinc coating will peel off and settle on the heating elements of the boiler, and if HP is poured into the system, then zinc will weaken its anticorrosive properties.
In the operating temperature range (from + 20C to + 90C), the coolant has a viscosity that is 2-3 times higher than the viscosity of water, and the heat capacity is also 10-15% lower than that of water. This must be taken into account when calculating the power of the circulation pump and other characteristics of the system.
Since glycol-based heat transfer fluids are more viscous, it is necessary to install circulation pumps more powerful than when operating on water (by 10% in performance, 50-60% in pressure).
When choosing an expansion tank, it should be taken into account that the coefficient of volumetric expansion of the EU-65 (as well as other heat carriers) is 15 - 20% higher than on water.
Thus, the expansion tank should not be less than 15% of the system volume.
The maximum thermal power of the boiler when operating on the EU-65 will be approximately 80% of its nominal value.
Water quality when diluted.
To obtain a working fluid, EU-65 should be diluted with water (distilled or prepared tap water) with a total hardness of no more than 5 mg-eq / l (5 hardness units).
Ideally, it is better to dilute the coolant with distilled water, in which there are no calcium and magnesium salts, since it is they that crystallize when heated and form scale. EU-65 has a special additive that ensures normal operation when diluted with ordinary tap water no more than 5 units. rigidity.
Get full text
Tutors
Unified State Exam
Diploma
If water from wells, wells, etc. is used to dilute the coolant, where an increased content of salts and metals is possible (hardness 15-20 units and more), and a softening system is not provided, then this can lead to precipitation.
If you do not know the hardness of your water, in this case, as in the case of tap water, it is recommended to pre-mix a small amount of antifreeze with water in the proportion you need in a transparent container and make sure there is no sediment (let the mixture settle for 2 days ).
The proportions for the preparation of the working mixture.
To obtain a working fluid, EU-65 should be diluted with prepared or distilled water in accordance with the following proportions.
| Working temperature | EU -65 | Water |
| - 20 ° C | 77% | 23% |
| - 30 ° C | 65% | 35% |
| - 25 ° C | 60% | 40% |
| - 20 ° C | 54% | 46% |
So, for example, with a total liter of the heating circuit of 100 liters, at the required temperature of -30C, the proportions are: 65 liters of EU-65, 35 liters of water. For other contour volumes - multiples, in accordance with the percentage from the table of the total contour volume.
It should be borne in mind that at the indicated temperatures the crystallization process is just beginning, and its thickening occurs with a decrease by about 5 -7 C. The destruction of the system is excluded, since the heat pump does not expand.
Important: dilution of TH by more than 50%, in addition to an increase in the freezing point, will lead to a deterioration of its anti-corrosion properties, since simultaneous dilution of additives will occur above the possible norm, which will entail the precipitation of hardness salts dissolved in water.
The mixing of the coolant with water can be carried out immediately before filling the system (especially for systems with natural circulation) or by filling it alternately in small portions.
ATTENTION: it is not recommended to mix different heat transfer fluids without first checking for compatibility. If the chemical bases of the coolant additive packages are different, this can lead to their partial destruction and, as a consequence, to a decrease in anticorrosive properties, precipitation.
Danger of overheating.
Notit is recommended to bring EU-65 to a boiling state (the boiling point at atmospheric pressure is +106 - + 112C, depending on the degree of its concentration)
... With prolonged overheating, in particular to temperatures exceeding 170C, thermal decomposition of the additives and the glycol itself begins. The coolant becomes dark brown, an unpleasant odor appears, and a precipitate is formed. Often, carbon deposits form on the heating elements, which becomes the reason for their failure. In order to prevent soot, it is necessary: when diluting the coolant, take into account that the optimally prepared solutions should be at -25 -30C; maximum -40C; install a more powerful circulation pump; limit the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the boiler - 90C, and for wall-mounted -70C; in the cold season, heat the coolant gradually, without immediately turning on the boiler at full capacity.
During operation, the liquid can weaken or lose its color, which is associated with the thermal decomposition of the dye, and this does not affect the properties of the TN.
Get full text
Life time.
Attention! The service life of the coolant depends on the mode of its operation. The anti-corrosion properties of the coolant are designed for 5 years of continuous operation or for 10 heating seasons. After this period, the coolant will remain a low-freezing liquid, but will lose or weaken the protective properties of the additives. If this period is exceeded, the manufacturer does not guarantee the safety of your heating system. It must be drained and disposed of. Before pouring new coolant into the heating system, it must be flushed with water.
TH is intended exclusively for technical use (ethylene glycol is toxic), therefore do not let it get into food and drinking water to avoid poisoning!
In case of accidental contact with hands or clothing, wash off immediately with soap and water. The coolant should be stored out of the reach of children, in an airtight container, away from food, keep out of direct sunlight.
Safe household antifreeze - heat carrier "Teply Dom - Eco" is produced on the basis of imported pharmacological propylene glycol (green with the addition of fluorescent). It is intended for various heating and air conditioning systems as a working fluid that ensures operation in the range from -30 ° C to 106 ° C (in accordance with the instructions for the rules for the operation of equipment), and, first of all, for double-circuit boilers and in facilities with increased environmental requirements. security.
A specially selected package of coolant additives reliably protects against scale, foaming and corrosion. As an exception, it is undesirable to use it in systems with galvanized pipes, since precipitation is possible. The coolant does not have an aggressive effect on plastic and metal-plastic, rubber, paranite and flax, that is, the possibility of leaks is excluded. However, you should know that it has a slightly higher fluidity than water, therefore, it is necessary to carefully assemble all the docking assemblies and it is imperative to carry out a preliminary pressure test of the system. "Warm House - Eco" cannot be used for electrolysis boilers ("Galan" type). The coolant for electrolysis boilers must have a certain electrical resistance, for which it is saturated with salts. But this worsens all other parameters for protection against corrosion and scale, so the developers of "Teply Dom" refused to create a joint universal recipe.
If necessary, the joints in the systems can be treated with sealants resistant to glycol mixtures (Hermesil, ABRO, LOCTITE), as well as use silky linen without lubrication with oil paint.
The heat carrier is highly stable and provides continuous operation for 5 years.To obtain a working mixture of the required crystallization start temperature, the "Warm House - Eco" coolant is diluted with distilled or ordinary tap water: when 10% water is added, the crystallization start temperature rises to - 25 ° C, with the addition of 20% water - to -20 ° C. The destruction of the system is excluded, since the coolant does not expand in volume when freezing, it becomes jelly-like.
Get full text
Dilution of the coolant with water increases the heat capacity and decreases the viscosity, i.e., improves its circulation. It is considered optimal to dilute the coolant by -25 ° С, for electric and gas boilers - by -20 ° С. The use of a mixture with a lower crystallization start temperature can lead to the burning of glycol on heating elements or in the burner zone, which will lead to the formation of tarry deposits, burnout of heating elements, etc.
If water from wells, wells, etc. is used to dilute the coolant, where there may be an increased content of salts and metals, it is recommended to pre-mix the coolant with water in the required proportion in a transparent container and make sure that there is no sediment. The mixing of the coolant with water can be carried out immediately before filling the system (especially for systems with natural circulation) or by filling it alternately in small portions.
ATTENTION: mixing with other coolants and antifreezes without preliminary checking is UNWANTED, since this can lead to the destruction of the additives and deterioration of anti-corrosion properties.
The service life of the coolant depends on the conditions of its operation. It is not recommended to bring the coolant to a boiling state, since when overheated to 170 ° C, the thermal decomposition of propylene glycol and additives will begin. Therefore, a good circulation of the heating medium must be ensured in heating boilers. To do this, it is necessary to dilute it, as previously recommended, and have a more powerful circulation pump than when operating on water (by 10% in performance, by 60% in pressure), and also to gradually heat the coolant at negative temperatures, not including the boiler at full capacity.
It should also be borne in mind that the coolant has a higher coefficient of volumetric expansion than water, therefore the expansion tank in the systems must be at least 15% of their volume.
"Warm House - Eco" is harmless to people and animals, it is approved for use as a refrigerant in the food industry. However, this does not mean that it can be eaten (its fumes are also harmless to humans).
Heat carrier "Teply Dom - Eco" is fire and explosion-proof, has a certificate of conformity and a sanitary-epidemiological conclusion, has been tested at the Scientific Research Institute of Plumbing and is approved for widespread use.
After 5 years of operation, the HP will remain a low-freezing liquid, however, it will exhaust the service life of anti-corrosion additives. It must be drained and disposed of. Before filling in a new VT, carefully check all the joints and flush the system.
The use of a masterbatch allows to increase the crystallization temperature and additives in already operating heating and air conditioning systems.
Deliveries of masterbatch to the regions provide tangible savings on transport costs. Safety rules should be strictly observed, since "Warm House-K" is fire and explosive. Non-flammable after dilution.
Supercon deliveries are carried out in 216-liter metal euro drums
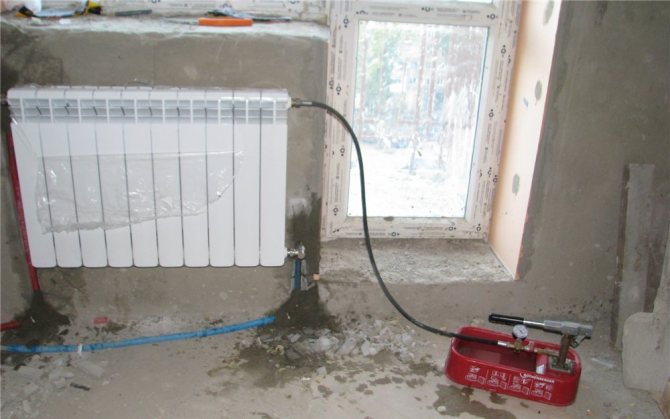
How to fill the heating system with antifreeze


Filling CO with antifreeze can be conditionally divided into three stages: system preparation; dilution of the concentrate in the required proportion; directly filling.
The first stage is preparation.
- Check the tightness of the CO connections.If required by the manufacturer, replace gaskets and materials incompatible with this active substance.
- Check CO for leaks, limescale on heat exchangers and lime deposits in piping and radiators.
- Calculate the required volume of coolant.
This is quite simple to do: fill your CO with water, then drain it and measure the amount using a measuring container.
Water requirements and recommended proportions
Concentrated ethylene glycol can only be diluted with demineralized or softened water (hardness should not exceed 5 mg per equivalent). This is done so that dissolved salts do not lead to the formation of sediment, clogging the climate system and impairing the heat transfer of equipment.
Manufacturers do not recommend pouring a coolant with a glycol concentration of more than 70%, because it has an increased viscosity and creates an additional load on the pumping equipment. Concentrated glycol also has a reduced thermal conductivity, which negatively affects the efficiency of the climate system.
In addition, to obtain a workable solution, it is necessary to take into account the climatic conditions in which the equipment will be used. If we are talking about a purchased glycol solution with a volume fraction above 40%, then the freezing point of such antifreeze will be 65 degrees below zero.
In temperate latitudes, this is practically impossible, therefore, in order to save money, you can dilute the solution with water, increasing the freezing point to the following indicators:
- Dilution in a ratio of 1 to 1 allows you to achieve a freezing temperature of - 35-40 degrees;
- Dilution in the proportion of two liters of concentrated glycol to three liters of water -30 degrees below zero;
- The ratio is 1 to 2 - 20 degrees below zero.