02.12.2014
Many people associate electric heating at home with the installation of appropriate water boilers with heating elements, convectors or the installation of warm film floors. However, there are many more options. In modern private houses, electrode or ion boilers are installed, in which a pair of primitive electrodes transfer energy to the coolant without any intermediaries.
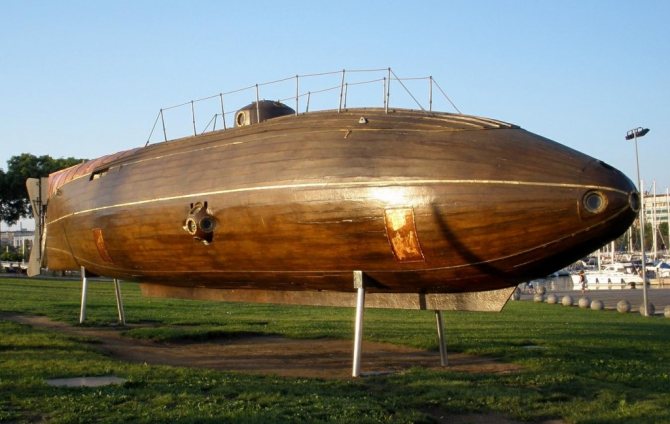
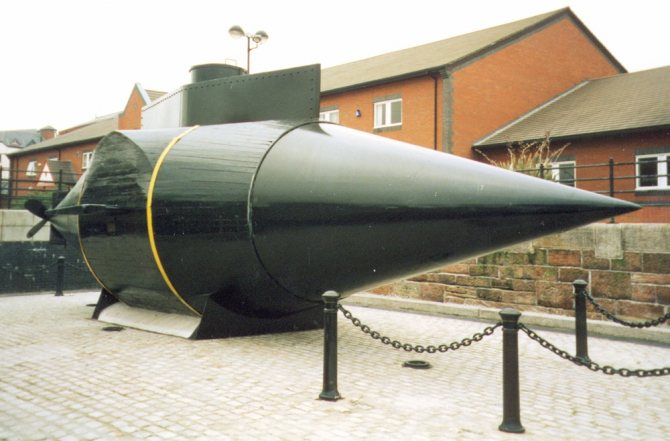
For the first time, ion-type heating boilers were developed and implemented in the Soviet Union to heat submarine compartments. The units did not cause additional noise, had compact dimensions, there was no need for them to design exhaust systems and effectively heated seawater, which was used as the main heat carrier.
The heat carrier that circulates through the pipes and enters the working tank of the boiler is in direct contact with the electric current. Ions charged with different signs begin to move chaotically and colliding. Due to the resulting resistance, the coolant heats up.

- 1 History of appearance and principle of operation
- 2 Features: advantages and disadvantages
- 3 Design and specifications
- 4 Video tutorial
- 5 Simple DIY ion boiler
- 6 Features of installation of ionic boilers
- 7 Manufacturers and average cost
History of appearance and principle of operation
During just 1 second, each of the electrodes collides with the others up to 50 times, changing their sign. Due to the action of alternating current, the liquid does not divide into oxygen and hydrogen, retaining its structure. An increase in temperature leads to an increase in pressure, which forces the coolant to circulate.
To achieve the maximum efficiency of the electrode boiler, you will have to constantly monitor the ohmic resistance of the liquid. At a classic room temperature (20-25 degrees), it should not exceed 3 thousand ohms.


Distilled water must not be poured into the heating system. It does not contain any salts in the form of impurities, which means that you should not expect it to be heated in this way - there will be no medium between the electrodes for the formation of an electrical circuit.
For additional instructions on how to make an electrode boiler yourself, read here
Making an electrode boiler on your own is simple and effective
The study of the thermal heating circuit makes it possible to make electrode heating boilers with your own hands.
Here you need to consider the principle of operation and properties of the elements involved, namely:
- electrode;
- water;
- control and automation devices.
When heated, water loses resistance and releases energy due to the splitting of a water molecule under the influence of an electric current, increases in volume and works to heat the volume of the room.
This phenomenon and its consequences are well studied, therefore, at present, the boilers use not the usual composition of water, but a specially designed distilled one, to increase the duration of operation.


Connecting a single-phase boiler with automatic control
The instruction given by one of the authors who patented their version of such an electrode boiler will tell you how the calculation of the required amount of heat and heating power of the coolant leads to the choice of a thermal heating scheme. It is shown in the video.
The design of the electrode boiler is very simple. Breakdowns of internal parts are practically excluded, therefore, the durability of work for many years exceeds TEN boilers, whose resource is exhausted, firstly, regularly, and secondly, it is quite unpredictable.
The price of an electrode boiler made according to the author's method is several times lower than the same factory-made version.
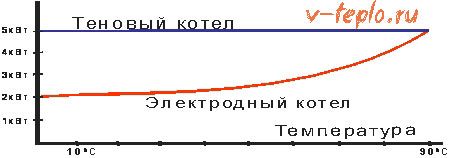
However, a factory electrode boiler is also very economical in operation due to the use of low-calorie fuel and a good work automation system. At the same time, maintenance is not required, there are no operating costs.
Depending on the specific needs, there are various schemes for connecting the boiler to the overall system:
- in parallel with other boilers;
- single-phase;
- three-phase boiler;
- connection of blocks of regulation and automatic control.
The electrode boiler can be used both for heating and for heating water in bathrooms and kitchens for domestic needs. Here are the connection diagrams for different applications.


Connecting an electrode boiler as an instantaneous water heater
Stages
The sequence of work in the manufacture of an electrode boiler with your own hands is as follows:
- planning the scheme of the heating system. A single-circuit scheme is possible, used for heating, or a double-circuit one - for providing hot water and heating;
- installation and grounding of the boiler to neutralize static electricity;
- ensuring the circulation of water by increasing the temperature of its heating;
- the use of effective battery materials that interact well with the coolant;
- the level of automation of the heat supply is regulated by the room temperature measuring device.


Connecting the boiler without forced recirculation
Advice. When using this boiler connection diagram, pay attention to the indicated angles of inclination and diameters of the water pipes, as this will ensure correct circulation.
Features: advantages and disadvantages
The ionic type electrode boiler is characterized not only by all the advantages of electric heating equipment, but also by its own characteristics. In an extensive list, the most significant ones can be distinguished:
- The efficiency of installations tends to the absolute maximum - not less than 95%
- No pollutants or ionic radiation harmful to humans are released into the environment
- High power in a body relatively small in size compared to other boilers
- It is possible to install several units at once to increase productivity, a separate installation of an ion-type boiler as an additional or backup heat source
- Small inertness makes it possible to quickly respond to changes in ambient temperature and fully automate the heating process through programmable automation
- No need for a chimney
- The equipment is not harmed by the insufficient amount of coolant inside the working tank
- Voltage surges do not affect heating performance and stability

You can find out how to choose an electric boiler for heating here
Of course, ion boilers have numerous and very significant advantages. If you do not take into account the negative aspects that arise more often during the operation of the equipment, all benefits are lost.
Among the negative aspects, it is worth noting:
- For the operation of ionic heating equipment, do not use direct current power sources that will cause electrolysis of the liquid
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the electrical conductivity of the liquid and take measures to regulate it
- You need to take care of reliable grounding. If it breaks down, the risks of being electrocuted increase significantly.
- It is prohibited to use heated water in a single-circuit system for other needs.
- It is very difficult to organize effective heating with natural circulation, the installation of a pump is required
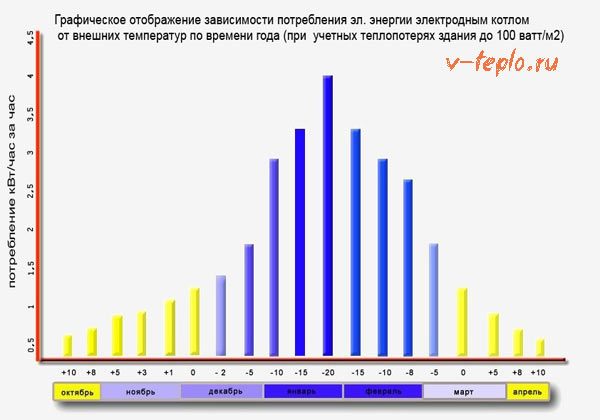
- The temperature of the liquid should not exceed 75 degrees, otherwise the consumption of electrical energy will sharply increase
- Electrodes wear out quickly and need to be replaced every 2-4 years
- It is impossible to carry out repair and commissioning work without the involvement of an experienced master

Read about other methods of electric heating at home here.
Submarine power systems
Since the beginning of the 20th century, electric motors, which were powered by batteries, have been used for underwater submarines. The batteries were charged on the surface by electric generators powered by diesel engines.
The emergence of nuclear submarines (nuclear submarines) after World War II did not stop the construction of diesel-electric submarines. Quieter, cheaper, non-nuclear submarines capable of operating in shallow water are still in service with most of the world's fleets.
GENERAL DEVICE
The electric power system of diesel-electric submarines (diesel-electric submarines), in the classical scheme, consists of storage batteries, a diesel generator, a propulsion motor, auxiliary engines and other electricity consumers.


The diesel-electric submarine's underwater engine has always been an electric motor powered by rechargeable batteries. It does not require oxygen to operate, is safe and has acceptable weight and dimensions. But a serious limitation of its use is the small capacity of the batteries. For this reason, the continuous underwater travel margin of diesel-electric submarines is limited and depends on the mode of movement. When driving at economy speed, the batteries need to be recharged every 300-350 miles. And when driving at full speed - every 20-30 miles. In other words, the submarine can move in a submerged position without recharging at a speed of 2-4 knots for three or more days or an hour and a half at a speed of more than 20 knots.
Read: Power plants of the first submarines
Since the size and weight of submarines are severely limited, electric motors and diesels combine different functions. The electric motor can work as a reversible machine. It consumes electricity when driving or generates it to charge batteries. Diesel can be a motor that drives a propeller or an electric generator, and can be a reciprocating compressor if it is driven by an electric motor.
After the 1950s diesel-electric submarines practically disappeared, in which the diesel engine would work directly on the propeller. The propeller is now driven exclusively by an electric motor. (This does not apply to nuclear submarines whose propellers are driven by a steam turbine). Diesel only rotates the generator. This scheme makes it possible to operate a diesel engine in a constant, optimal operating mode and makes it possible to separate propulsion electric motors (PRM) and generators. The use of these devices in an individual mode increases the efficiency of both, and therefore increases the underwater power reserve. The disadvantages include the double conversion of energy - first mechanical into electrical, then back - and the associated losses. But we have to put up with this, since the main one is the mode of charging the batteries, and not the mode of consumption for the GED.
CURRENT STATE OF DEPL
As indicated, all modern diesel-electric submarines use full electric propulsion. Most boats with full electric propulsion have previously used two engines: main and economic. In modern projects, their role is played by one motor with two operating modes. Recharging of batteries is carried out on the surface or at periscope depth using a snorkel - a device for engine operation under water (RDP). A new stage in the development of diesel-electric submarines was the use of fuel cells based on various chemical compounds. This made it possible, in particular, to increase the range of continuous underwater navigation by economic speed by five to ten times and reduce the noise of the submarine.Nevertheless, fuel cell installations do not yet provide the required operational and tactical characteristics of submarines, primarily in terms of performing high-speed maneuvers when pursuing a target or evading an enemy attack. Therefore, modern submarines are equipped with a combined propulsion system. For movement at high speeds under water, batteries or fuel cells are used, and for sailing on the surface, the traditional pair "diesel generator - electric motor" is used.
Read: Operation "KAMA"
ANAEROBIC POWER PLANTS
Further development of non-nuclear submarines is associated with the use of anaerobic (air-independent) power plants. There are four main types of anaerobic EIs: a closed-cycle diesel engine (CCD), a Stirling engine (DS), a fuel cell or electrochemical generator (ECG), and a closed-cycle steam turbine. The most promising direction is the use of Stirling engines. The use of this engine significantly increases the time the boat remains in a submerged position without serious losses in other indicators.
The development of submarines with auxiliary air-independent propulsion units began more than 30 years ago, but a little more than a dozen of such boats were built - these are the Swedish project "Gotland", the French "Saga", the Japanese "Soryu".
At present, all submarines of the Swedish Navy are equipped with DS, and Swedish shipbuilders have already worked out well the technology of equipping submarines with these engines. The use of DS allows these submarines to stay under water continuously for up to 20 days.
Ha ha
Wow
Satisfied
Sad
Angry
Voted Thanks!
You may be interested in:
- Diesel-electric installations on submarines
- Submarines of project 636 "Varshavyanka"
- Colombian navy strengthens its submarine fleet
- Power plants of non-nuclear submarines
- Diesel-electric submarines (DPL or DPL)
- Submarines type 209
- Submarine Stirling engines
- Diesel-electric submarines type S
- Steam generator anaerobic power plant MESMA
- Type D mini-submarines
- Electric propulsion systems on ships
- Submarines of project 641
Subscribe to
our channel in Yandex.Zen
Device and technical characteristics
At first glance, the construction of an ion boiler is complicated, but it is simple and not compulsory. Externally, it is a steel seamless pipe, which is covered with a polyamide electrical insulating layer. Manufacturers have tried to protect people as much as possible from electric shock and expensive energy leaks.
In addition to the tubular body, the electrode boiler contains:
- The working electrode, which is made of special alloys and is held by protected polyamide nuts (in models operating from a 3-phase network, three electrodes are provided at once)
- Coolant inlet and outlet nozzles
- Grounding terminals
- Terminals supplying power to the chassis
- Rubber insulating gaskets
The shape of the outer casing of ionic heating boilers is cylindrical. Most common household models meet the following characteristics:
- Length - up to 60 cm
- Diameter - up to 32 cm
- Weight - about 10-12 kg
- Equipment power - from 2 to 50 kW


For domestic needs, compact single-phase models with a power of no more than 6 kW are used. There are enough of them to fully provide heat for a cottage with an area of 80-150 sq. M. For large industrial areas, 3-phase equipment is used. An installation with a capacity of 50 kW is capable of heating a room up to 1600 sq. M.
However, the electrode boiler works most efficiently in conjunction with the control automation, which includes the following elements:
- Starter block
- Surge protection
- Control controller
Additionally, control GSM modules can be installed for remote activation or deactivation. Low inertness allows a quick response to temperature fluctuations in the environment.
Due attention should be paid to the quality and temperature of the coolant. The optimal liquid in a heating system with an ionic boiler is considered to be heated to 75 degrees. In this case, the power consumption will correspond to that specified in the documents. Otherwise, two situations are possible:
- Temperature below 75 degrees - electricity consumption decreases along with the efficiency of the installation
- Temperatures above 75 degrees - electricity consumption will increase, however, the already high efficiency rates will remain the same
A simple ionic boiler with your own hands
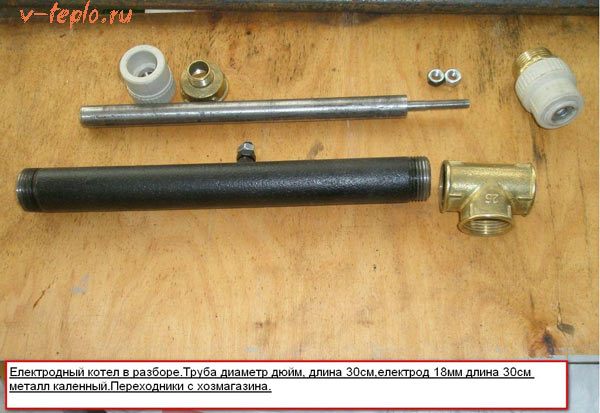
Having familiarized yourself with the features and principle by which ionic heating boilers function, it is time to ask the question: how to assemble such equipment with your own hands? First you need to prepare the tool and materials:
- Steel pipe with a diameter of 5-10 cm
- Ground and neutral terminals
- Electrodes
- Wires
- Metal tee and coupling
- Tenacity and desire


Before you start putting everything together, there are three very important safety rules to remember:
- Only phase is applied to the electrode
- Only the neutral wire is fed to the body
- Reliable grounding must be provided
To assemble the ion electrode boiler, just follow the instructions below:
- First, a pipe with a length of 25-30 cm is prepared, which will act as a body
- The surfaces must be smooth and free of corrosion, the notches from the ends are cleaned
- On the one hand, electrodes are installed by means of a tee
- A tee is also required to organize the outlet and inlet of the coolant.
- On the second side, make a connection to the heating main
- Install an insulating gasket between the electrode and the tee (heat-resistant plastic is suitable)
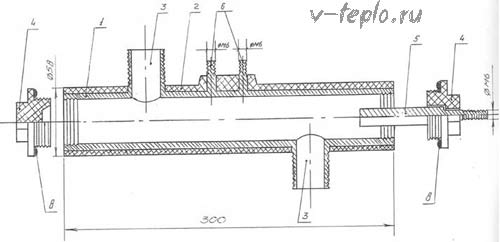

- To achieve tightness, threaded connections must be precisely matched to each other.
- To fix the zero terminal and grounding, 1-2 bolts are welded to the body
Putting everything together, you can embed the boiler into the heating system. Such home-made equipment is unlikely to be able to heat a private house, but for small utility areas or a garage it will be an ideal solution. You can close the unit with a decorative cover, while trying not to restrict free access to it.
Electric ion boilers
Such boilers operate on the principle of heating water (heat carrier) by the ionization method. This process takes place as follows:
When the boiler is turned on to the network, water molecules are separated into positive and negative ions, which vibrate between two electrodes (anode and cathode). During this process, heat energy is generated. It is immediately transferred to the coolant, which distributes it throughout the heating system.
Such units are used as an autonomous heating system. They differ from boilers with heating elements in small sizes, as well as in a block of electrodes, which has high performance and efficiency. Table salt is additionally added to the water, which plays the role of a heat carrier. This is necessary to increase the electrical resistance of the water. To avoid metal corrosion or scale formation, instead of water, antifreeze, developed specifically for ion boilers, is poured into the system.
Electrode boilers were originally used only for military purposes to heat submarines or warships. After that, having slightly changed the design, the developers began to produce boilers for domestic or industrial use.
For example, the Galan boiler is manufactured in accordance with all the established standards of military equipment, since the manufacturers specialize in the manufacture of instruments for submarines and ships.
Features of installation of ion boilers
A prerequisite for installing ionic heating boilers is the presence of a safety valve, a pressure gauge and an automatic air vent. The equipment must be positioned in a vertical position (horizontal or at an angle is unacceptable). At the same time, about 1.5 m of the supply pipes are not galvanized steel.
The zero terminal is usually located at the bottom of the boiler. A ground wire with a resistance of up to 4 ohms and a cross section of over 4 mm is connected to it. Do not rely solely on RAM - it cannot help with leakage currents. The resistance must also comply with the rules of the PUE.
If the heating system is completely new, there is no need to prepare the pipes - they must be clean inside. When the boiler crashes into an already operating line, it is necessary to flush with inhibitors. There is a wide range of descaling, scale and descaling products on the markets. However, each manufacturer of electrode boilers indicates those that they consider to be the best for their equipment. Their opinion should be adhered to. Neglecting flushing will fail to establish an accurate ohmic resistance.
It is very important to select heating radiators for the ion boiler. Models with a large internal volume will not work, since more than 10 liters of coolant will be required for 1 kW of power. The boiler will constantly run, wasting part of the electricity in vain. The ideal ratio of the boiler output to the total volume of the heating system is 8 liters per 1 kW.


If we talk about materials, it is better to install modern aluminum and bimetallic radiators with minimal inertia. Choosing aluminum models, preference is given to the material of the primary type (not remelted). In comparison with the secondary, it contains less impurities, reducing the ohmic resistance.
Cast iron radiators are least compatible with the ion boiler, since they are most susceptible to contamination. If there is no way to replace them, experts recommend observing several important conditions:
- The documents must indicate compliance with the European standard
- Mandatory installation of coarse filters and sludge catchers
- Once again, the total volume of the coolant is produced and equipment suitable for power is selected
Ion boiler "Galan"
For domestic use, Galan boilers are manufactured in the Ochag series, which has several models:
«Hearth2»- designed for heating a room not more than 80 m3. The power consumption of the unit is 2 kW. The boiler operates from 220 V. With normal thermal insulation of the room, the electricity consumption fluctuates within 0.5 kW / h. The recommended amount of coolant fluid varies between 20-40 liters.
«Hearth 3»- Can heat up a room with a volume of 120 m3. The boiler power is 3 kW. Energy is consumed within 0.75 kW / h. Fluids for heating the system need from 25 to 50 liters.
«Hearth 5»- used in rooms with a volume of no more than 180 m3. The boiler has a power of 5 kW. Consumes about 1.25 kWh. The volume of the coolant varies between 30-60 liters. "Hearth 6" - capable of heating 200m3. The power consumption is 6 kW, and the consumption is 1.5 kW / h. Recommended from 35 to 70 liters. coolant.
Only the specially developed Potok liquid, which prevents pipe corrosion, can be poured into the Galan boiler system.





















