Modern private houses are most often built taking into account the fact that even at the design stage, they provide for a warm floor as the main or additional source of heating. In any case, the advantage of houses with underfloor heating is obvious - they are more comfortable and warm. It is important to understand that the underfloor heating system must first be calculated - especially for the water system. The project of a warm floor allows you to foresee the power of the system, correctly arrange all the components, and calculate the amount of material. A lot of nuances will be taken into account when developing a project: the area of the room and the calculated heat loss in it, the type of pipes, the material of the finish coating and the method of installation of the system itself, as well as much more, without which a high-quality installation is impossible.

A properly designed underfloor heating project guarantees the durability and high-quality operation of the heating system
Where to begin
Among all the variety of technologies for underfloor heating (electric, infrared and others), the water system is especially popular. It is durable and reliable, but without preliminary correct calculation, there is a possibility of increased costs during installation and a decrease in the operational properties of the system.


Water heat-insulated floor
The project of a water heating system can be developed as one of the items in the design documentation for a house. You can also order it separately or do it yourself. Some companies specializing in the installation of a water heated floor independently carry out a preliminary design of the system.
The project will be required even with an independent installation of a water-heated floor. This will allow you to purchase material and fittings in the required quantity, and perform the installation itself in a short time, without being distracted by calculations and alterations.


Layout and connection diagram in a private house
To draw up a project, you will need to have and record the following data:
- Floor plan of the building.
- Material of external walls and windows with doors.
- Desired indoor temperature.
- Information about where the risers and bends are located inside the building.
- Furniture layout plan.
Knowing the listed nuances of the room, they first perform a thermal calculation, and then proceed to drawing up an installation diagram.
Now on the construction market there are several types of "warm floors". They differ in the type of coolant and work efficiency. How to choose a warm floor? Let's tell in our article.
Underfloor heating project price
The cost of design is determined individually and depends on various parameters, it is natural that with the integrated design of not only the warm floor, but also the entire heating system, the price will be lower, with the design of the furnace it will be even lower, and with the integrated design of not only heating, but also ventilation and air conditioning below. To get the cost, you just need to contact us and our managers will prepare an individual commercial proposal for design, and, if necessary, for installation and commissioning.


Documentation
Before proceeding with the installation of the system, it is necessary to have a plan of the heating system and a list of necessary materials and equipment.


Warm floor plan
The plan structure includes the following data:
- On the location of heating devices.
- A diagram showing the location of the pipes, the distance between them, their diameter and the length of each straight section.
- Information about the required power of each radiator and their locations.
- Thermal calculation of the water floor heating system.
Stages of the project
The first step in any heating project is always heat calculation. It determines the amount of heat loss that must be compensated for by the heating system.
The algorithm for the development of the project given in the article will be considered fair for premises with an average rate of thermal insulation of building structures, where the amount of heat loss does not exceed 80 - 100 W per 1 m2 of heated area.
The construction of underfloor heating in rooms with a greater amount of heat loss is not recommended; they should only be used as a local additional heating. You also need to know that underfloor heating is absolutely volatile - in the absence of electricity, the circulation of the coolant is impossible.
The design process of water-heated floors consists of the following stages:
- Selection of pipe material;
- The choice of the method of laying pipelines;
- Drawing up a circuit diagram;
- Calculation and selection of elements of the control unit (circulation).
The choice of pipe material is discussed in detail in the article "Pipes for a water-heated floor". Consider the following stages of project development.
Materials (edit)
In the process of designing a water underfloor heating system, a list of materials is drawn up. Conditionally, they can be divided into components of the system itself and raw materials for creating a screed.
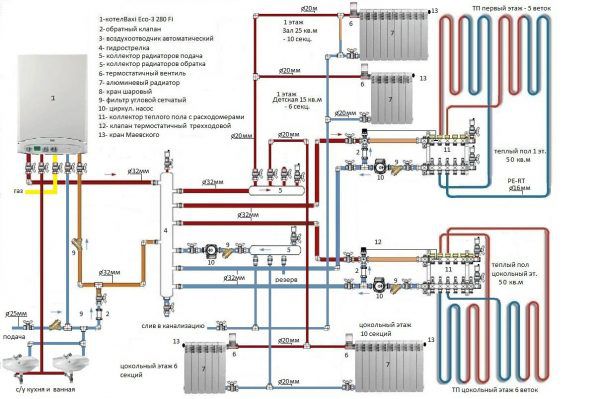

The main elements in a heating system with an additional heat source in the form of a warm floor
Components of a warm water floor are:
- A heat boiler that heats the heating medium in the absence of a central heating system.
- Built-in boiler or separately located pump for pumping water into the system.
- Pipes for the movement of the coolant.
- A collector is installed to distribute water through the pipes.
- The collector is placed in a special cabinet, and you will also need to purchase splitters for distributing cold and hot, valves, fittings, ball. You will also need to provide for an emergency drainage of water and air removal from the pipes.


Pipe fastening methods
The list of materials depends on the method of installation of the system - wet (screed) or dry (using mats with bosses, eg).


The principle of connecting a warm floor
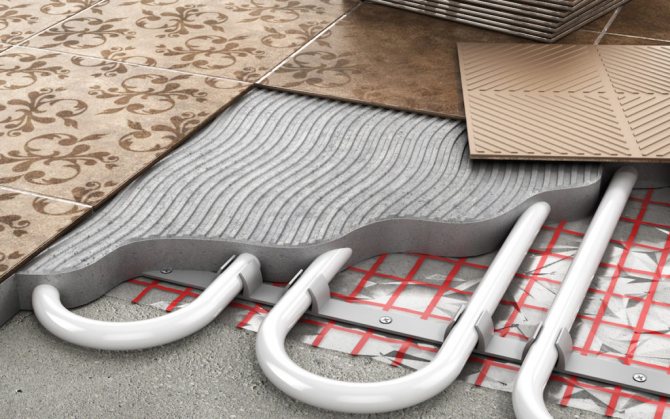
In the first case, a reflective layer is laid along a rough screed, reinforced mesh and pipes are fixed. After that, a finishing screed is poured onto which the finishing flooring will subsequently be laid.


Pipes can be laid with boss mats and thermoplastics that effectively reflect heat
In the second case, the pipes are fixed in a given position using special mats with bosses and thermoplates with a groove, where the pipe is laid. This method is relevant for rooms with old or weak floors.
How to choose the length of the pipe
One loop (loop) can have a certain maximum length depending on the diameter of the pipe used. With a pipe diameter of 16 mm, the maximum loop length is from 70 to 90 m, with a 17 mm diameter, the loop length varies from 90 to 100 m, if the pipe diameter is 20 mm, then one loop can have a length of up to 120 m.
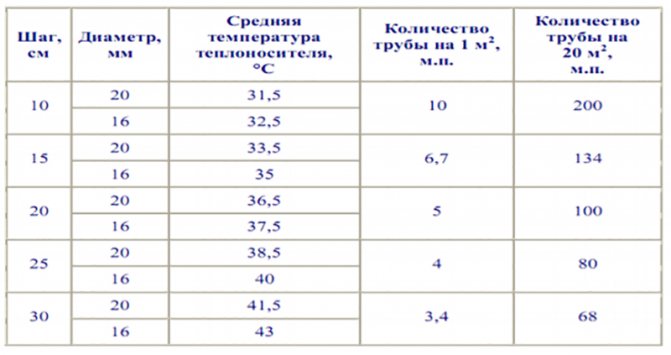

Calculation of the number of pipes, taking into account the main criteria
The dependence of the loop length on the diameter is due to the fact that pipes of different diameters have different hydraulic resistance and heat load. Less hydraulic resistance is observed in pipes with a large diameter.


Calculation depending on the laying step
Note! In a small room, it is enough to mount one circuit that does not go beyond the maximum permissible length values.But if the room is large, then it is better to mount two circuits than to exceed the recommended optimal pipe length.
It is also worth considering that in fact, when installing the system, it is necessary to use pipes of the diameter for which the calculation was made in the project. You can make calculations for pipes of different diameters and choose the right option at this stage, and not later, choosing the right material empirically.


Calculation of the length of the contours for various rooms
When laying several contours, it is necessary that their lengths coincide as much as possible. The length of the contour is the length of the entire pipe, that is, it starts from the collector. It is clear that in the course of work it is not always possible to achieve the same length of the contours, but it is necessary to strive to ensure that the difference between the lengths does not exceed 10 m.


Specialist recommendations
The area of the room affects the way the contours of the same length are laid. Where it is less, when laying pipes between the turns, a smaller step is provided. Alternatively, to heat a small room with minimal heat loss (hallway, bathroom), you can use the return pipe of the adjacent loop.
How to choose a pipe laying step
The distance between adjacent pipe coils (pitch) is 15-30 cm. In this range, the values are multiples of 5, i.e. 15, 20, 25.30. For large rooms such as gyms, the pitch can be 30 - 45 cm. Near a large window or outside wall, the pitch is 10 cm. These areas are called edge zones.


Laying pipes in the edge zone (by the window)
Various factors influence the choice of the pipe laying step: heat load, the purpose of the room, the length of the circuit, the material of the finished floor and other nuances. Concerning:
- For edge zones, the optimal number of rows is 6, the laying step is 10-15 cm.
- For central areas: 20 - 30 cm.
- For bathrooms, the step is 10 - 15 cm, but you should be prepared for the fact that due to the need to bypass the plumbing equipment, the step may not be the same.
- If the finishing coating has high thermal conductivity (tile or marble tiles, porcelain stoneware), then the distance between the turns is 20 cm.


Calculations of the main parameters for contours of different lengths
Note! In practice, it is not always possible to adhere to these recommendations. According to experienced craftsmen, the best option is a step in the marginal zone - 10 cm, in the center - 15 cm. These are the values at which the system will work.
How to choose a pipe diameter
For residential premises, the area of which starts from 50 m², the best option would be pipes with a diameter of 16 mm. The height of the screed from the top of the tube is 5 cm.


Pipe diameter specifications
It is this diameter that allows you to comply with the conditions for laying pipes with a step of 15 - 20 cm.This applies even to houses with good thermal insulation, where the pipe laying step should not exceed 15 cm.For private houses, these parameters are optimal in terms of ease of installation, cost of materials and volume of coolant.


Performance properties of pipes for underfloor heating
Pipes with a diameter of 18 mm, due to their larger volume, lead to unnecessary costs, including for related materials (fittings, etc.).


The advantages of pipes specially designed for underfloor heating are obvious
Accordingly, for pipes with a diameter of 20 mm, even more energy will be required to heat the coolant. In addition, laying with a snake with a step of 15 cm is not realistic, due to the impossibility of bending a pipe of this diameter to the required radius. As a result, the laying step will be larger, the heat in the room will be less, and this is at a significantly increased cost of the heat carrier. Pipes of this diameter are used in public premises with a thick screed.


Properties affecting styling quality
Pipe material
Different pipe materials have a direct impact on the correct operation of the system.
Table 1. Varieties of material
| Type of material | Positive traits | disadvantages |
Copper | 1. The material conducts heat well. 2. Copper is highly resistant to corrosion. 3. The material has a long service life. 4. Copper possesses a unique ductility that allows pipes to bend along a rather small radius. 5. The walls are characterized by high mechanical strength and high resistance to temperature extremes. 6. The outer polymer coating protects the copper from negative external influences. | 1. Laying copper pipes requires skill in working with such a material. 2. The need to use special equipment. 3. High material cost. |
Stainless steel (corrugated pipes) | 1. Excellent flexibility. 2. Resistance to fracture. 3. High mechanical resistance. 4. High resistance to temperature changes. 5. A wide range of high quality fittings that allow joining pipes in a long circuit. | High price. |
Polypropylene | 1. Simple installation. 2. Low cost. 3. Suitable for supplying heating medium from the boiler to the collector. | 1. Low plasticity. 2. Short length. 3. Forming the contour produces many welds that are potential leaks. 4. Low thermal conductivity. 5. High level of thermal expansion. |
XLPE | 1. High strength of the material 2. Tight connection of the circuits. 3. Ability to create a contour of any length. | Large bending radius. |
Independent psychological tests show that the most acceptable indoor climate is established with a floor surface temperature between 22 ° C and 25 ° C and an air temperature at head level between 19 ° C and 20 ° C. Underfloor heating gives architects a high degree of freedom. It is invisible and thus suitable for any interior, it is protected from damage, makes cleaning the house easier and prevents injuries to people such as burns. The temperature of the floor surface is especially important as it is a contact surface, which is essential for the thermal balance of the human foot. Limits have been established for medical indicators that must be taken into account when designing and installing underfloor heating systems. The following values for floor surface temperature are maximum limit values:
- for living quarters and work rooms in which people mainly stand - 21 ° С - 27 ° С
- for living rooms and offices - 29 ° С
- for lobbies, hallways and corridors - 30 ° С
- for baths and pools - 33 ° С
In this case, the warm floor can be of two types: electric or water, powered by a boiler.
An electric underfloor heating is installed by laying shielded wires on pre-laid insulation (foamed polystyrene foam, cork sheet). Further, these wires (of a strictly defined length) are connected to a wall thermostat, to which the supply buses are connected. The thermostat switches on the underfloor heating by means of a temperature sensor inserted into the concrete floor screed. Next, the laid wires are poured with a concrete screed with a thickness of 30-100 mm, depending on the load on the floor and its heat intensity.
By design, the cables are single-core and two-core, in turn, the heating cores can be all-metal and from several wires. In the construction of cables, insulation is important, which protects the live part from the external environment and from mechanical damage. The level of electromagnetic radiation of a two-core cable is two times lower than that of a single-core cable, however, this radiation can also affect the operation of computers and other microprocessor equipment.
It is advisable to make an electric "warm floor" when it is not possible to connect to the main heating system, for example, this situation is possible when creating a floor heating system in an apartment or office, as well as in small areas in houses and cottages.
Let's take a look at the electric "warm floor" scheme in layers.
In country houses, cottages and other facilities that have an individual boiler room, it recommends the creation of only water "warm floors" systems.
Specialists carry out design, supply of equipment, installation, integration and maintenance of systems of water "warm floors" for houses, cottages, apartments, offices and restaurants. Our company has extensive experience in creating water underfloor heating systems at facilities with an area ranging from 200 to 2500 sq. M. The surface of the water "warm floor" is, in fact, a low-temperature radiator, which provides comfortable horizontal heat radiation and a slow convection flow.
Let's take a closer look at this system.
Water underfloor heating system
The water underfloor heating system can be used as a main or additional heating system. We would like to note that in our climatic zone - we are talking about Moscow and the Moscow region - the underfloor heating system is used in combination with a radiator heating system.
A hot water underfloor heating system has a number of advantages for two related reasons.
First, water can be heated by various energy sources (gas, diesel, coal, electricity, etc.)
Secondly, water has a high heat content per unit volume.
The construction of a water "warm floor" can be "self-leveling". In this case, the pipes of the "warm floor" are filled with concrete. Ultimately, the concrete slab becomes a heat-emitting element.
Another option is a dry underfloor heating design. In this design, the pipes of the "warm floor" system are placed in special metal plates. In this design, they are a heat-emitting element. Then the pipes in these plates are closed with plywood or drywall, and a finishing material is placed on top.
The underfloor heating system works according to the principle of flow and return collectors, each loop is controlled at both ends.
The valve on the supply manifold can be equipped with an actuator, which is controlled from a room thermostat or manually. The return manifold is equipped with a control valve that regulates the flow of water through all loops of the underfloor heating, thus equalizing any pressure drops. The system operates normally with a temperature drop of 5 ° C in the loops. A sharper drop in temperature will be perceived by the human foot as an uneven floor temperature.
Design
We would like to point out right away that without a project of water "warm floors" systems, reliable underfloor heating cannot be created. You do not need to think that a foreman with installers will come to you and quickly and correctly install "warm floors" for you.
In our projects for underfloor heating systems, we use solutions that allow you to make the most of the capabilities of the underfloor heating system.
The underfloor heating system must be designed in strict accordance with the applicable rules and regulations. To understand the significance of our work, below we propose to consider the list of works that our specialists perform when designing a water "warm floor".
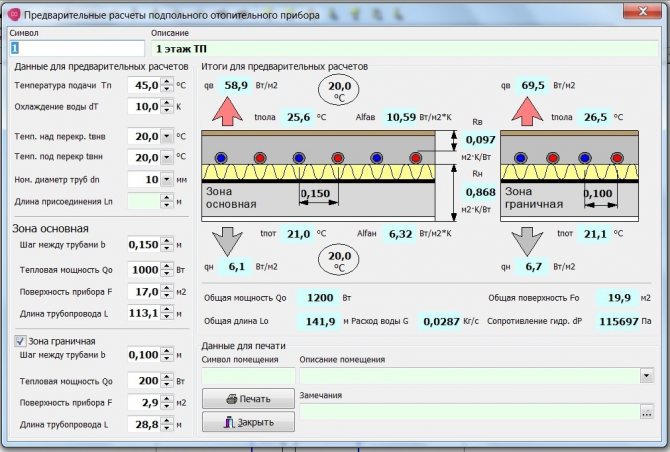
Employees of our design department choose the design of the "warm floor", the installation scheme, the thickness of the floor screed, the diameter and type of pipes for underfloor heating.
In addition, the calculation of the required flow rates of the coolant on the contours of the "warm floor". This calculation affects the floor and room temperature.Further, a hydraulic calculation (calculation of pressure losses) and selection of pumping equipment are performed.
Laying and wiring diagram
When designing systems for water "warm floors", we use pipe layouts that provide the most even distribution of heat over the floor surface.
In the design of this heating system, the indents from the walls are taken into account, as well as the indents from the planned places of furniture installation. Those. When designing water-heated floor heating systems, we try to take into account designers' projects or customer plans in order to create the most efficient and reliable underfloor heating system.
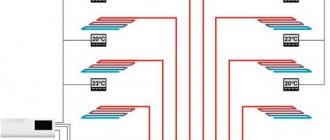
In our projects, we use a collector-beam layout of water "warm floors". The arrangement of the collectors of the water "underfloor heating" is designed in such a way that the length of the laid pipes between the collectors and the underfloor heating zones is minimal. This will help balance the underfloor heating system and improve temperature control in individual rooms.
Regulation of water temperature in underfloor heating systems
One of the simplest control principles is to keep the flow temperature from the boiler to the system at a constant level using a three-way motorized mixer. In this case, with an increase in heat demand, the average temperature in the loop decreases. This can be avoided by applying an internal temperature correction. According to this principle, a faster compensation of temperatures that occur inside the building is achieved.
An increase in indoor temperature due to, for example, sunlight or an increase in the number of people means that the air will soon be as warm as the floor. Once this point of equality is reached, the laws of physics dictate that no heat should rise from the floor. The effect is as if the system is closed. This process is fast and accurate. At an air temperature of 20 ° C and a floor temperature of 23 ° C, the heat input from the floor will decrease by one third per each degree of temperature by which the air temperature has increased. Thus, an increase in air temperature of 3 degrees will be enough to completely neutralize the system. In theory, such a built-in self-regulation system makes it possible to design and install underfloor heating without using other types of room temperature controllers (thermostats or valves). Underfloor heating can be combined with other heating systems such as air conditioning, radiators and floor convectors. These additional heating systems must be installed in such a way that they do not interfere with the temperature control of the underfloor heating system. This means, for example, that the air conditioning system must operate at a temperature 2-3 ° C below the room temperature reading of the underfloor heating system. At the same time, the response time to a disturbance in air temperature near a warm floor will be longer than that of radiators and convectors.
Floor screed thickness
Below is a diagram of a water "warm floor" in layers, which we use when laying floor heating using metal-plastic or polymer pipes. The thickness of such a water "warm floor" can be from 70 to 110 mm. The diagram shows the thickness of each layer of the water "warm floor".
Coating of a water "warm floor"
Of great importance in the construction of a warm floor is its covering, because different materials conduct heat differently. Floor covering materials with increased thermal conductivity are ceramic tiles or monolithic concrete. Thick wall-to-wall carpet acts as an insulator and therefore requires a higher heating medium temperature to achieve the desired surface temperature.With wood floors, special heat spreaders must be used to achieve an even floor temperature (since wood floors do not conduct heat as efficiently as concrete). You should also check how dry the wood is (the maximum moisture content is 10%). It should be noted that the relative humidity decreases with increasing temperature (Moliere diagram). In a warm floor, the relative humidity will increase with decreasing temperature. An underfloor heating installation must be designed to operate over the entire floor area in such a way as to avoid “damp spots”. Pay particular attention to the above point if you are using coating materials that react to moisture, such as parquet. The relative humidity of the floor structure must not exceed 80%. To do this, it is necessary to maintain the temperature difference between the tile and the underlying material from і 3 to 4 ° C.
The thickness of the "warm floor" must be taken into account by builders, designers, architects, and the customer when designing the premises in which the installation of the underfloor heating system is planned.
Selection of pipes for underfloor heating
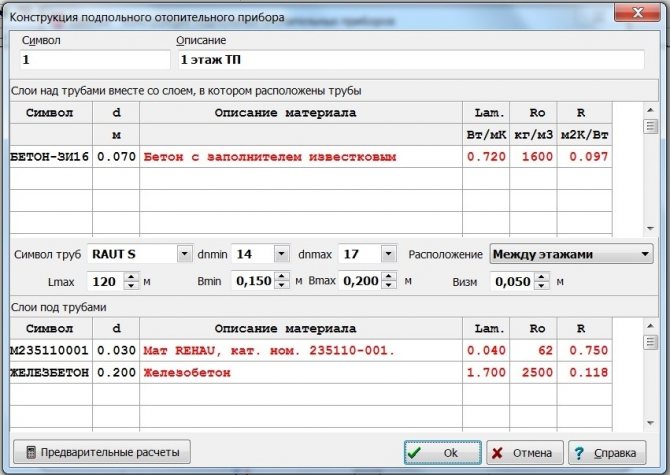
When designing systems of water "warm floors", special attention should be paid to the material and diameter of the pipe, which is installed underfloor heating. Currently, underfloor heating is installed with pipes made of various materials, such as:
- pipes made of multilayer polyethylene, cross-linked according to one of the technologies - PE-Xa, PE-Xb and PE-Xc
- metal-plastic pipes
- copper pipes
When choosing a pipe material, attention should be paid to the following aspects:
reliability of the resulting connections,
resistance of the pipe to oxygen diffusion,
coefficient of linear expansion of the pipe or the resulting system as a whole,
thermal conductivity of the pipe,
maintainability of the pipeline in the event of an abnormal situation (for example, a pipe was drilled when installing furniture).
When designing systems of "warm floors", the diameter of pipes for laying a water "warm floor" is also selected.
Installation
Installation of systems of water "warm floors" is carried out by the assembly teams of our company. This ensures maximum conformity of installation work to design solutions, since there is no inconsistency in the work of various subcontractors.
The installers of our company strictly adhere to the technology and the main stages of the installation work when laying the system of water "warm floors".
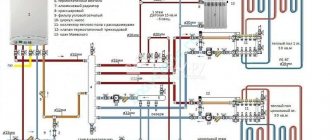
The system of water "warm floors" is built according to the collector scheme using metal-plastic, polymer and copper pipes and modern shut-off and control valves.
When installing collectors of the underfloor heating system, our company uses balancing valves equipped with indicators (rotameters) of the coolant. The use of such fittings allows you to more accurately balance the underfloor heating system, because the indicator of the passing volume of the coolant shows the state of each heating line of this system.
The final stage
At the final stage of installation work, our specialists carry out the hydraulic connection of the underfloor heating system, start-up, adjustment and regulation of the heating system parameters in accordance with the project documentation. In the collectors on the flow meters, the values of the coolant flow rates are set in accordance with the design documentation.
Below is an example of an underfloor heating system installed by our company in country houses. All "underfloor heating" collectors are equipped with rotameters for proper balancing of the heating system.
The collectors of the underfloor heating system are equipped with flow meters and thermostatic valves that allow room-by-room adjustment of the coolant temperature.
| Like |
| Share this |
| Comments (1) (+) [Read / Add] |
All about the country house Water supply Training course.Automatic water supply with your own hands. For Dummies. Malfunctions of the downhole automatic water supply system. Water supply wells Well repair? Find out if you need it! Where to drill a well - outside or inside? In what cases well cleaning does not make sense Why pumps get stuck in the wells and how to prevent it Laying the pipeline from the well to the house 100% Protection of the pump from dry running Heating Training course. Do-it-yourself water-heating floor. For Dummies. Warm water floor under a laminate Educational video course: On HYDRAULIC AND HEAT CALCULATIONS Water heating Types of heating Heating systems Heating equipment, heating batteries System of underfloor heating Personal article of underfloor heating Principle of operation and scheme of operation of underfloor heating Design and installation of underfloor heating materials for underfloor heating Water underfloor heating installation technology Underfloor heating system Installation step and methods of underfloor heating Types of water underfloor heating All about heat carriers Antifreeze or water? Types of heat carriers (antifreeze for heating) Antifreeze for heating How to properly dilute antifreeze for a heating system? Detection and consequences of coolant leaks How to choose the right heating boiler Heat pump Features of a heat pump Heat pump operating principle About heating radiators Ways of connecting radiators. Properties and parameters. How to calculate the number of radiator sections? Calculation of heat power and the number of radiators Types of radiators and their features Autonomous water supply Autonomous water supply scheme Well device Do-it-yourself well cleaning Plumber's experience Connecting a washing machine Useful materials Water pressure reducer Hydroaccumulator. Principle of operation, purpose and setting. Automatic air release valve Balancing valve Bypass valve Three-way valve Three-way valve with ESBE servo drive Radiator thermostat Servo drive is collector. Choice and rules of connection. Types of water filters. How to choose a water filter for water. Reverse osmosis Sump filter Check valve Safety valve Mixing unit. Principle of operation. Purpose and calculations. Calculation of the mixing unit CombiMix Hydrostrelka. Principle of operation, purpose and calculations. Accumulative indirect heating boiler. Principle of operation. Calculation of a plate heat exchanger Recommendations for the selection of PHE in the design of heat supply objects Contamination of heat exchangers Indirect water heater Magnetic filter - protection against scale Infrared heaters Radiators. Properties and types of heating devices. Types of pipes and their properties Indispensable plumbing tools Interesting stories A terrible tale about a black installer Water purification technologies How to choose a filter for water purification Thinking about sewage Sewage treatment facilities of a rural house Tips for plumbing How to evaluate the quality of your heating and plumbing system? Professional recommendations How to choose a pump for a well How to properly equip a well Water supply to a vegetable garden How to choose a water heater Example of equipment installation for a well Recommendations for a complete set and installation of submersible pumps What type of water supply accumulator to choose? The water cycle in the apartment, the drain pipe Bleeding air from the heating system Hydraulics and heating technology Introduction What is hydraulic calculation? Physical properties of liquids Hydrostatic pressure Let's talk about resistances to the passage of liquid in pipes Modes of fluid movement (laminar and turbulent) Hydraulic calculation for pressure loss or how to calculate pressure loss in a pipe Local hydraulic resistance Professional calculation of pipe diameter using formulas for water supply How to choose a pump according to technical parametersProfessional calculation of hot water heating systems. Calculation of heat loss in the water circuit. Hydraulic losses in a corrugated pipe Heat engineering. Author's speech. Introduction Heat transfer processes T conductivity of materials and heat loss through the wall How do we lose heat with ordinary air? Heat radiation laws. Radiant warmth. Heat radiation laws. Page 2. Heat loss through the window Factors of heat loss at home Start your own business in the field of water supply and heating systems Question on the calculation of hydraulics Water heating constructor Diameter of pipelines, flow rate and flow rate of the coolant. We calculate the diameter of the pipe for heating Calculation of heat loss through the radiator Heating radiator power Calculation of the radiator power. Standards EN 442 and DIN 4704 Calculation of heat loss through enclosing structures Find heat loss through the attic and find out the temperature in the attic Select a circulation pump for heating Transfer of heat energy through pipes Calculation of hydraulic resistance in the heating system Distribution of flow and heat through pipes. Absolute circuits. Calculation of a complex associated heating system Calculation of heating. Popular myth Calculation of heating of one branch along the length and CCM Calculation of heating. Selection of pump and diameters Calculation of heating. Two-pipe dead-end Heating calculation. One-pipe sequential Heating calculation. Double-pipe passing Calculation of natural circulation. Gravitational pressure Water hammer calculation How much heat is generated by pipes? We assemble a boiler room from A to Z ... Heating system calculation Online calculator Program for calculating Heat loss of a room Hydraulic calculation of pipelines History and capabilities of the program - introduction How to calculate one branch in the program Calculation of the CCM angle of the outlet Calculation of CCM of heating and water supply systems Branching of the pipeline - calculation How to calculate in the program one-pipe heating system How to calculate a two-pipe heating system in the program How to calculate the flow rate of a radiator in a heating system in the program Recalculating the power of radiators How to calculate a two-pipe associated heating system in the program. Tichelman loop Calculation of a hydraulic separator (hydraulic arrow) in the program Calculation of a combined circuit of heating and water supply systems Calculation of heat loss through enclosing structures Hydraulic losses in a corrugated pipe Hydraulic calculation in three-dimensional space Interface and control in the program Three laws / factors for the selection of diameters and pumps Calculation of water supply with self-priming pump Calculation of diameters from central water supply Calculation of water supply of a private house Calculation of a hydraulic arrow and a collector Calculation of a hydraulic arrow with many connections Calculation of two boilers in a heating system Calculation of a one-pipe heating system Calculation of a two-pipe heating system Calculation of a Tichelman loop Calculation of a two-pipe radial wiring Calculation of a two-pipe vertical heating system Calculation of a single-pipe vertical heating system Calculation of a warm water floor and mixing units Recirculation of hot water supply Balancing adjustment of radiators Calculation of heating with natural circulation Radial wiring of the heating system Tichelman loop - two-pipe associated Hydraulic calculation of two boilers with a hydraulic arrow Heating system (not Standard) - Another piping scheme Hydraulic calculation of multi-pipe hydraulic arrows Radiator mixed heating system - passing from dead ends Thermoregulation of heating systems Pipeline branching - calculation of a hydraulic pipeline branching Calculation of the pump for water supply Calculation of the contours of a warm water floor Hydraulic calculation of heating. One-pipe system Hydraulic calculation of heating.Two-pipe dead-end Budgetary version of a one-pipe heating system of a private house Calculation of a throttle washer What is a CCM? Calculation of the gravitational heating system Constructor of technical problems Pipe extension SNiP GOST requirements Boiler room requirements Question to the plumber Useful links plumber - Plumber - ANSWERS !!! Housing and communal problems Installation works: Projects, diagrams, drawings, photos, descriptions. If you are tired of reading, you can watch a useful video collection on water supply and heating systems
What else needs to be taken into account in the process of designing a warm floor
In the process of developing a project for a warm floor system, it is recommended to perform a schematic drawing with a designation of pipe laying, basic dimensions, distances and indents, furniture placement.


Collector group
You should also choose the material of the finishing (top) coating. To do this, you can see our article... In it, we will consider the most suitable topcoats.
At the design stage, the type of coolant is determined: in 70% of cases, water is used, since it is the most accessible and cheapest substance. Its only drawback is its reaction to temperature changes, as a result of which there is a change in the physical properties of water.


Floor cake with pipes in a screed
Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol with special additives that reduce the chemical and physical activity of fluids is often used as a heat carrier for underfloor heating. In any case, the type of coolant must be taken into account precisely at the design stage, since its properties form the basis for hydraulic calculations.


Antifreeze as a coolant
You will also need to take into account the following nuances:
- One contour fits into one room.
- To place the collector, the center of the house is chosen. If this is not possible, then to adjust the uniformity of the coolant flow through the circuits of different lengths, flow meters are used, which are installed on the manifold.
- The number of circuits connected to one collector depends on their length. So, with a circuit length of 90 m or more, no more than 9 circuits can be connected to one collector, and with a circuit length of 60 - 80 m - up to 11 loops.
- If there are several collectors, each has its own pump.
- When choosing a mixing unit (mixing module), it is important to take into account the length of the circuit pipe.
- A more accurate calculation will be based not only on data on heat loss in the room, but also on information about the flow of heat from household equipment and appliances, from the ceiling, if a heated floor is also installed on the upper floor. This is relevant when calculating for a multi-storey building, which is conducted from the upper floors to the lower ones.
- For the first and basement floors, the thickness of the insulation is taken at least 5 cm, for higher floors - at least 3 cm. The insulation on the second floor is used to exclude heat loss through the concrete base.
- If the pressure loss in the circuit exceeds 15 kPa, and the optimal value is 13 kPa, it is necessary to change the flow rate of the coolant downward. You can fit several smaller contours in the room.
- The minimum allowable flow rate of the heating agent in one loop is 28-30 l / h. If this value is higher, then the loops are combined. The low flow rate of the coolant leads to the fact that it cools down without having passed the entire length of the circuit, which indicates the inoperability of the system. To fix the minimum value of the coolant flow rate in each loop, a flow meter (control valve) installed on the manifold is used.


Connecting pipes to the manifold
Warm floor and topcoat
After installing a warm floor, the question arises - which coating to choose? Different materials have a different thermal conductivity coefficient. Topcoat options:
- Laminate.Choose a special laminate designed for laying on a warm floor - it will definitely not deteriorate from heat, and it conducts heat well.


If an ordinary laminate is laid, its class must be at least 32, and for installation you need to use a special substrate. Typically, a polyethylene foam backing is used. - Wood. This natural material is only suitable for a system that does not heat the surface above 27 ° C.
- Parquet board. It is better to choose parquet covered with oil, the thickness of which is no more than 16 mm.


Porcelain stoneware is a durable coating that can withstand multiple heating cycles. Special glue is used for laying, and heating the floors is allowed only after the glue solution has completely dried. - Self-leveling floors.
It is not recommended to use ordinary linoleum, bamboo and classic parquet.
The role of a water floor as a main or additional source of heat
A warm floor in a room as a heating system can perform an additional or main function. As an additional system, underfloor heating affects the surface comfort of the floor covering. In this case, the main source of heat is traditional heating radiators. The thermostatic principle of regulation is used to maintain the temperature of the coolant.


Combined heating system
To compensate for heat losses in the room and protect it from temperature changes outside, when the water floor is the main source of heat, it is possible to control the level of heating of the coolant. The warmer it is outside, the lower the temperature of the coolant should be and vice versa.
In fact, a warm floor is a low-temperature type of heating system and, theoretically, the required temperature of the coolant can be obtained by setting the boiler to minimum heating. However, a conventional boiler, tuned to a low-temperature range, is characterized by a sharp decrease in efficiency and from the economic point of view, such a system becomes unprofitable.


Mixing unit
In this regard, there are other ways. For example, the use of a modern heat generator supplying a heat carrier heated to +30 - 50 degrees. When such a boiler is equipped with a circulation pump, each circuit has a heat carrier of the same temperature, due to which the most economically efficient process of heating a house with a "warm floor" system is carried out.
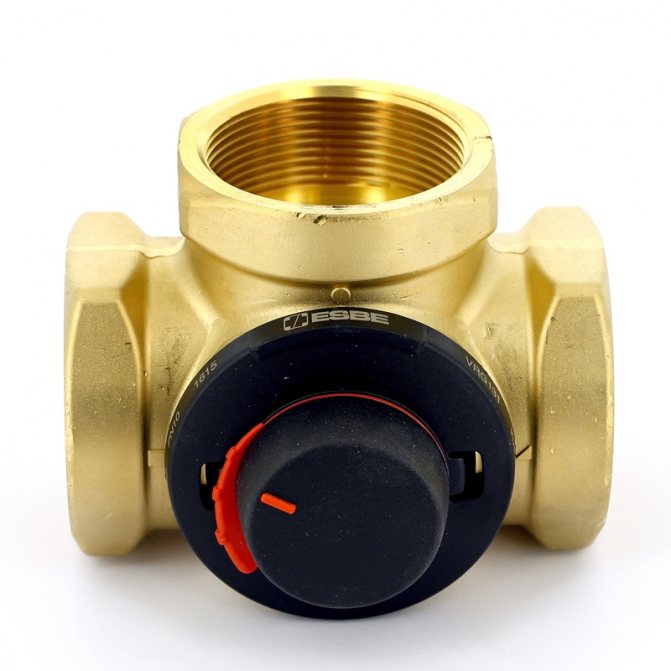


Three-way mixing valve
If the boiler is not equipped with the function of low-temperature operation, then a three-way mixing valve can be used, and the required temperature can be obtained by equipping the mixing unit with a thermostat.
Note! When installing a combined floor covering, for example, made of wood and ceramic tiles, a separate contour is laid under each material, since each of the materials differs in terms of thermal conductivity. The water in the circuits will have different temperatures to create an even heating of a room with such a floor.
It should also be borne in mind that some types of finishing materials are not suitable for a water floor and can be mounted in tandem with film or cable electrical heating systems.


Infrared film for underfloor heating
The choice of pipes for underfloor heating
To create warm floors, you can use pipes made of various materials. Which ones are optimal and not troublesome, and which ones have too many disadvantages? Let's take a look at the most common options:
- Copper - heats up well and quickly gives off heat, warming up the surface of the warm floor, in addition, copper is resistant to corrosion and has a long service life. The disadvantages of copper pipes include the high cost and complexity of installation.
- Polypropylene - such pipes are widely used in plumbing works, but are rarely used in warm floors due to complex installation.They practically do not bend, and it is impractical to use fittings in a screed, because they significantly increase the risk of leakage.
- Metal-plastic - flexible and reliable, such pipes have a long service life and are widely used in the arrangement of warm floors. The disadvantage can be that the properties (including flexibility and elasticity) of such pipes change over time, which can lead to rupture due to pressure surges.
- XLPE - flexible, easy to install, durable and affordable - such pipes were created for underfloor heating and are gaining more and more popularity.
What affects the operation of a warm water floor
How to ensure that the warm floor really was and creates a comfortable temperature for the floor covering. Often, due to the long circuit length, a high pressure drop value is observed.
For the system to work correctly in a house with several floors, a separate low-power pump is installed at each level, or one high-power pump is connected to the collector.


Pump group
When choosing a pump, take into account the calculated data, the volume of the coolant and the pressure. However, it is worth remembering that to determine the level of hydraulic resistance, it is not enough to know the length of the pipe. You will need to take into account the diameter of the pipes, valves, splitters, the laying pattern and main bends. More accurate calculations are obtained using a special computer program into which the main indicators are entered.
Alternatively, it is possible to use standard equipment with already known technical characteristics. The hydraulics of the system is adjusted to the characteristics of the pump by maneuvering its parameters.


Collector with installed pump
Recommendations for the use of warm floors
For long-term operation of the heating system, follow a few simple rules:
- Unplug the system when you are away from home for a long time.
- Monitor the working pressure level.
- Monitor the operation of the pump and valves, eliminating problems in a timely manner.
- Do not allow the heating temperature to exceed 45C.
- Start up the system gradually, especially during the cold season. Every day, the operating time of the system should be increased by half an hour.
Heat distribution: features
Since the area of the premises in the house is different, the circuits also have different lengths, therefore it is necessary to ensure the same hydraulic pressure in all parts of the system. It should be borne in mind that the pump is a constant.


Distribution of heat from different sources
The supply of the same volume of water to the circuits of each length leads to the fact that in the longer one the coolant cools faster and at the outlet its temperature will differ from the coolant of the shorter profile. As a result, the floor surface will warm up unevenly - somewhere overheating will be observed, but somewhere on the contrary, the coating will be cold.


The advantage of using underfloor heating
Due to the high hydraulic resistance, the coolant may not enter at all into a long circuit, since it will move into shorter circuits with less resistance. To prevent this from happening, the system is equipped with a distribution manifold, which allows you to maintain a balance of supply and uniform heating of the coolant in each loop.
What you should pay attention to when designing a water heated floor
Thermal insulation of the base of the floor must be at least 0.38 W / m2;
Be sure to lay a damper tape (thermal seam) around the perimeter of the room, if several contours are laid in the same room in a warm floor, then the contours should also be separated with a depfer tape.
If the finishing floor covering is a tile, then the contour should be marked based on the size of the tile. Because the tile lays down from the thermal seam. The center of the tile should not fall on the thermo-joints, otherwise it may crack.
In places where pipes pass, such as through walls, doorways, a peshel (corrugated tube) should be inserted 15-20 centimeters to the sides of the wall or opening, in a word, this is a sleeve through which the pipe will pass;
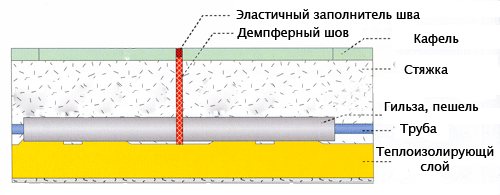

According to the recommendations of valtec, the minimum thickness of the finishing screed for a water-heated floor is 3 centimeters, and that of herz is 4.5 centimeters. These dimensions are taken from the top of the pipe;
Thin finishing screed of a water-heated floor does not give a complete feeling of comfort. Yes, it warms up faster, but if you have a large pipe-laying step, you will feel uneven heating of the floor, the so-called zebra effect - black, white - cold, warm. Let's look at a small example with ideal conditions that there is no heat loss to the floor at all and we give off heat only to the room. The pipe lies at the very bottom under the stitch and the heat from it tends upward. But what it looks like.
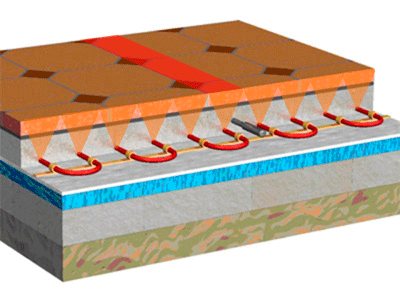

The pipe is the top of the triangle, and its base will be formed on the tile. Accordingly, the lower the height of the triangle, the narrower its base and one turn. Accordingly, the thicker the layer of the finishing screed, the floor surface becomes more evenly heated. The whole task is to optimally select the pipe pitch and there were no cold, unheated zones.
With a thicker screed, another advantage appears - the floor cools down longer.
In the finishing screed of the warm floor, be sure to add fiber to prevent cracks in the screed, and add a plasticizer for screeds on a water-heated floor. The plasticizer improves the properties of the solution, when it is used, the amount of water added to it decreases. When the solution dries up, the water evaporates from it and there are voids, tiny air shells. And since air makes the solution porous (the density becomes less), then the transfer of heat from us decreases due to the air in the solution, and we shake watts from each square of the warm floor not a lot, but still we would not want to.
If the underfloor heating collector is installed with a pump (the pump can be located in the boiler room, and the cabinet with the collector is on the floor), try to position it so that it is far from the bedrooms, since at night the noise from the pump, even the quietest one, will be heard by you, and if correct adjustment of the underfloor heating loops, you can even hear the circulation of the coolant in the pipes;
How to calculate the number of pipes
At the design stage, after all the calculations have been made, it is possible to understand how many pipes in running meters may be required. This will allow you to estimate the cost of the material.


The main stages of installation
So, with a room area of 12 m², the air temperature should correspond to + 20 degrees. The width of the edge sections along the walls with furniture should be 30 cm.If one wall has a length of 6 m, and the other two are 2, then the working area of the system can be calculated using the following formula: 12 - 0.3 * (6 + 2 + 2) = 9 m².
Note! The pitch and diameter of the pipes depends on the level of heat loss. The smaller they are, the larger or smaller the pipe diameter is.
When determining heat loss in a room, the glazing area, the characteristics of the insulation used in the enclosing structures, and the height of the room are taken into account. The value obtained varies in the range from 20 to 300 W / m², depending on the thermal efficiency of the structures and the glass units used, the thickness of the walls and the number of openings.
Underfloor heating is a serious cost item for renovation, so it is important to calculate exactly how much and what materials will be needed. To ease your labor costs, we have prepared a special instruction telling you how to calculate the warm floor - water or electric. Online calculators are included. And in the article "What is needed for a warm floor?" you will find a complete list of everything you may need during installation.
Order turnkey warm floor
A turnkey underfloor heating arrangement can be carried out at any time, both after the completion of the installation of an electric heating boiler or the installation of gas heating in a private house, and before the start of any work on the arrangement of such a system. It is very simple to order a turnkey underfloor heating at Mosvodostroy - just call or fill out the form and answer the questions of our specialist - then we will do everything ourselves. You do not have to worry about the progress of work, the delay in the deadline, the quality of performance or the materials that you need to buy for the warm floor - we will do everything ourselves and on time, and we also guarantee the quality not only in words, but also in the contract.
To receive a standard contract or estimate an estimate, fill out the application form and our specialists will call you back.
Popular pipe laying schemes and their features
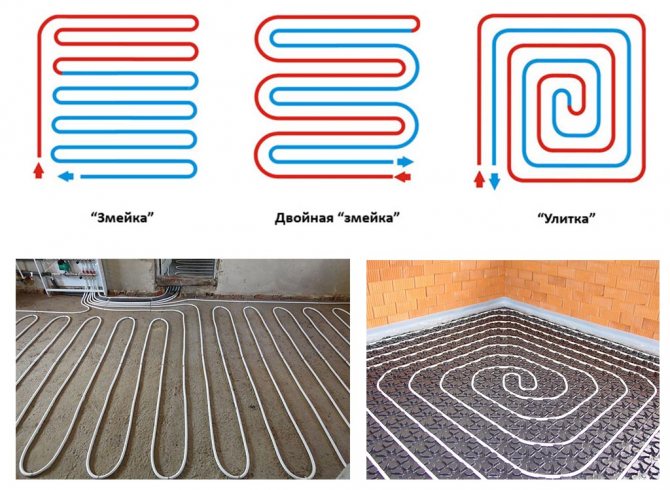
The main schemes for laying pipes with a coolant include "snake" and "spiral", and other types of laying based on them are often used, for example, a "snake" without edge zones.


Common styling methods
"Snake" is a convenient option, which can be easily fitted in a small area, but the pipes are heated unevenly in this case. Therefore, along the wall, characterized by large heat losses, pipes are laid that are located closer to the collector (at the beginning) and warm up better.


The pipe-laying step according to this scheme should not be more than 30 cm, otherwise the flooring will have an uneven temperature - the heat will be felt over the pipes, and the cold between them. The distance between the extreme pipes is made 20 cm or less.

"Snake" and "spiral" - the best ways to form a contour
Note! So that when laying pipes according to the "snake" scheme, the heating of the floor surface is still uniform, a second (reverse) snake is laid.
The "spiral" scheme is characterized by such a laying method in which the supply and return pipes are placed parallel to each other. Due to this, the issue of uneven floor heating is solved, and the temperature above both pipes is approximately equal.


Styling options
The spiral type of installation is most relevant for large rooms, with the distance between the pipes being 20 cm.
Development of a pipeline laying scheme
The next stage of project development is drawing up a pipe laying scheme. To do this, you need to know a number of basic requirements for the construction of water underfloor heating complexes.
When choosing a laying step, the following requirements should be observed:
- In the marginal zones, the laying step is taken in 100 - 150 mm;
- In other areas - from 200 to 250 mm;
- In rooms requiring an elevated floor temperature (bathroom, pool, toilet), a constant step of no more than 150 mm is used.
In the edge zones, pipes are laid with a step of 100 - 150 mm to create a heat flow in the place of maximum heat loss. The number of pipes in the wall area is usually taken at least 6.
When choosing a step, it should be taken into account - when using metal-plastic pipes, a step of 100 mm cannot be observed. This is prevented by the value of the maximum bending radius - the pipe may break or damage the inner aluminum layer.
In the main areas of the contour laying, the step is taken in the range of 200 - 250 mm. When using a pipe with a diameter of 16 mm, the laying interval should not exceed 200 mm. When laying with a center-to-center distance of more than 250 mm (300, 400, 500), heat flow stratification and uneven heating of the floor monolith are possible. A pitch of more than 250 mm is most often used in industrial and other large-area facilities, where only the total value of the heat flux and space saving are important.
For the installation of underfloor heating, pipes with an outer diameter of 16 and 20 mm are usually used. There is a recommended maximum length for each diameter. For circuits made of a pipe with a diameter of 16 mm, it is 80 meters (recommended 60 - 70 m), for pipes with a diameter of 20 mm - no more than 100 meters (recommended from 80 to 90 m).
The length of all contours must be calculated approximately of the same length, the recommended maximum difference in length is no more than 10-15 meters. Also, the best option is to use pipelines of the same diameter for all circuits. The fulfillment of these two conditions greatly simplifies the balancing of the system as a whole and of each circuit separately.
Heating a separate room is best done with one circuit. This makes it easy to adjust the temperature in each room, depending on the requirements and its purpose. In the case of a large area of the heated room, a larger number of circuits (preferably of the same length) are laid in the project. Short circuits (for bath and toilet) should be combined into one.
The scheme must be applied to the floor plan, preferably on graph paper (for greater accuracy). According to the completed scheme, the amount of required material (pipe) is calculated. An enlarged amount of material can be determined at the rate of 4 - 5 meters of pipeline per 1 m2 of heated area, but this method has an increased error.
Also, according to the scheme, the amount of heat-insulating and waterproofing material, reinforcing lattice (over the area of the premises) is calculated, the length of the damper tape - along the length of the perimeter of the heated premises. According to the total length of the pipeline, the number of fasteners is calculated, the frequency of fasteners is usually 2 fasteners per 1 meter of length, fasteners are installed at turns after 20-30 cm.
When developing the scheme, the pumping and mixing unit must be located in the center of the underfloor heating complex to equalize the average length of each circuit.
Installation of underfloor heating: features
One of the design stages includes the creation of an installation scheme, which will subsequently need to be adhered to when performing work directly on the site.


Floor cake with pipes inside the screed - optimal thickness
The following points should be reflected in the installation diagram:
- Plan for dividing the base surface into several sections. This stage cannot be ignored when pouring a screed over a large area, since thermal expansion in this case leads to its destruction. The division into separate sections allows the formation of expansion joints between them. In this case, one section should not exceed 40 m², and the rooms of the L and U-shaped configuration are divided into sections, regardless of their area.


Principle of laying on mats
- In the installation diagram, there should be a reference to the presence of expansion joints, which are filled with a damper tape, elements from extruded polystyrene foam or expanded polyethylene. Inside the seam, the pipes are placed in a casing, for example in a corrugation.
- The project specifies the way in which the pipes will be laid - this will allow purchasing the necessary material in a certain amount. They also reflect the way the screed is installed - wet, semi-dry or dry.
- They calculate the temperature of the pipes - this will help to determine the final floor material, the manufacturer of which indicates the compatibility of the material with the "warm floor" system and its permissible heating. So, the parquet can be heated up to 25 degrees - no more.


Screed laying principle
Prices for warm floors Caleo
warm floors Caleo
Video - 5 key rules for installing a water heated floor
Heating system and underfloor heating project
Underfloor heating is usually designed in conjunction with a heating system, since it is the furnace that usually acts as a heat source. At the same time, even in the most well-insulated cottage and with the highest thermal conductivity coefficients of flooring materials, one underfloor heating system does not always manage to cover all the heat losses of the room and there is a need for additional heating devices. Moreover, usually the customer wants to equip not all rooms with warm floors, but only some, mainly toilets and bathrooms, bedrooms and living rooms, and staircases, corridors, storerooms and other auxiliary rooms are heated with radiators. Therefore, the specialists of our design institute for heating in Kharkov and Ukraine recommend considering the project of a warm floor together with the project of the main heating system.In the case of a cottage, this is the most optimal solution, because the heating project includes a furnace project, in which various complex energy-saving solutions can be envisaged.
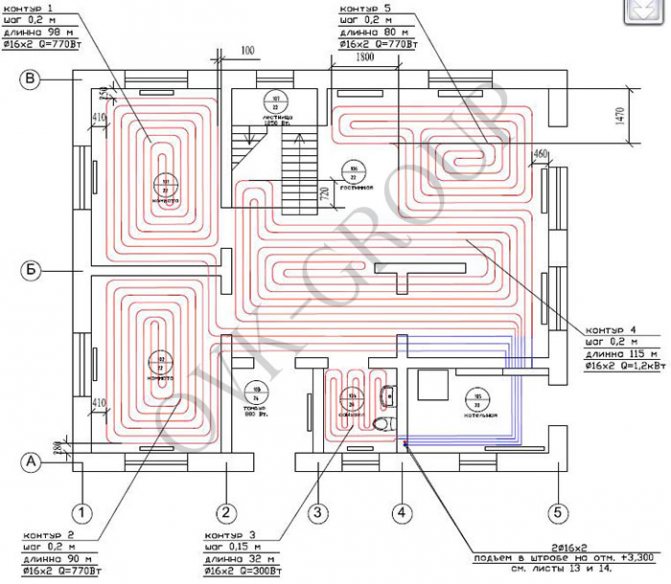

Underfloor heating water: instruction
First you need to finish all the plastering work in the room. In addition, it does not hurt to also remove the skirting boards and all traces of the old floor covering in order to ensure the most even and clean surface.
The design of warm water floors can be carried out exclusively on a leveled surface, with a maximum permissible height difference of up to 5 mm. If this result cannot be achieved, it is recommended to put an additional leveling layer of concrete or under the concrete screed. Then you can start laying the waterproofing layer. As a material, you can purchase a polyethylene film with a thickness of more than 25 cm. The waterproofing sheets are superimposed on each other with a minimum overlap of about 12 cm, the sheets are also connected with construction tape.
It should also be noted that it is also recommended to leave certain allowances for waterproofing on the walls, and before calculating the water-heated floors, it will be necessary to remove all excess parts of the waterproofing.
In order to prevent the so-called cold bridge from forming between the wall and the unit, it is recommended to cover all walls around the perimeter with damper tape. It will also compensate for the stretching of the screed layer, as a result of constant temperature changes.


After that, we proceed to the installation of thermal insulation materials. If the room in which the heating system will be installed is on the ground floor, it is possible to allow the installation of a thick layer of thermal insulation (about 5 cm), but on the upper floors this indicator should not be more than 2 cm.
Penofol is best suited as a material for making a layer of thermal insulation. It is a foamed polystyrene sheet or rolls, which are also covered with a layer of aluminum foil.
As a simpler alternative, you can also use a profiled thermal insulation board, which is made from high density polymeric materials. They can also withstand a lot of pressure without the risk of deforming the entire system. These plates can also serve as a fixation for the pipe system, due to the special type of coating, this is also facilitated by the laminate principle of fixing.
Design and calculation of the underfloor heating system
To the question - where to start, how to make a water-heated floor with your own hands, the answer is unequivocal. You need to start with thermal calculations and the creation of a detailed pipeline layout for using the underfloor heating system as the main heating. First, the calculations of the heat losses of the premises and the required power of the water heating of the floors are carried out. In the absence of experience and knowledge, it is strongly recommended to entrust this difficult work to professionals in order to avoid disappointment and significant material losses in the future.
To carry out thermal calculations, you can use specialized computer programs or use a calculator for calculating a warm water floor. The practice of using underfloor heating, the obtained statistics and experience made it possible to systematize recommendations on how to make underfloor heating from water heating in the house.
When making thermal calculations, it is necessary to consider first of all:
- comfortable temperature conditions for each room;
- heat loss in rooms and in individual areas;
- hydraulic resistance of the circuits;
- diameter of pipes for the underfloor heating circuit (10 - 20 mm);
- the temperature of the coolant after the collector, usually its average value is 45 - 55 degrees;
- accurate calculations of the parameters of the supply and control units.
Having the initial data, you can easily draw a general diagram on which to mark the main highways and the location of the collector unit.A special (three-way or two-way) valve is usually installed in the collector for a warm water floor to regulate the temperature of the coolant by mixing. The circuits have a considerable length (up to 80 meters), therefore the system is supplied with circulation pumps. For large areas of premises, the system should not be simplified; it is better to make several heating circuits with a pipe length of no more than 100 meters.
Designers and specialists in heating systems give a number of recommendations, in particular, before making a water heated floor yourself, you need to follow certain rules for installing the circuit as the main method of heating your home.
The essence of these rules is as follows:
- of the two pipe-laying methods (serpentine and cochlea), snail is preferable;
- for reliability, each circuit must consist of a solid pipe;
- the maximum length of the contour is up to 100 meters, and the optimal one is 50 - 80 meters;
- the difference in the length of the pipes of the circuits due to a possible imbalance in the heating system should not exceed 10 - 15 meters;
- the distance between the pipes of the circuit for temperatures up to - 22 degrees - 150 mm;
- the distance between the pipes of the circuit for temperatures below - 22 degrees - 100 mm;
- pipe consumption at a step of 100 mm per 1 m2 = 8 meters, at a step of 150 mm per 1 m2 - about 7 meters.
These recommendations must be accurately followed and taken into account when creating a draft design, which on a sheet of paper will reflect the device of a water-heated floor with your own hands and prevent possible errors during the installation of the circuit.
The recommended sequence is as follows:
- a plan of the apartment is drawn on a sheet of paper in the desired scale;
- the sketch indicates the places of installation of furniture, it is believed that in these places the contour of the warm floor should not be drawn;
- the rest of the area to be heated is divided into equal parts of 15 m2 each with a pipeline pitch of 100 mm;
- it is necessary to find a place on one of the walls in order to install a collector for a warm water floor with your own hands, which would be equidistant from each heating circuit;
- all outlets of pipes for underfloor heating are connected to the collector;
- in the drawing, the length of the heating circuit is measured, the result is multiplied by the scale and the size of the pipe footage required to create the system is determined.
What else should be considered when designing a warm floor?
Warm floors are divided into three categories according to their purpose:
1 - a comfortable warm floor (the floor is made a little warm, and the main load for heating the house is borne by radiators), it can be a floor heating system or a wooden one, along the logs,
2 - main heating (the most common option when a warm floor is the main and only heating system), such a warm floor should be with a concrete screed,
3 - heat accumulation (such a system is suitable if there are double tariffs in your region, for example, for electricity: it is cheaper at night; then at night you heat the underfloor heating to the maximum, in the daytime it gives off the accumulated heat); this is also a warm floor with a concrete screed.
Attention! The smaller the area of the warm floor, the more expensive it costs (no matter how paradoxical it may sound), because, despite the small area, you need to buy the same equipment as if the warm floor was on the entire floor. So, if it is possible to make a warm floor for the entire floor, do so.
What should be the temperature of the underfloor heating surface?
Actually, I already wrote about this in a separate article, but it will not be superfluous to repeat it. Listed below maximum limiting temperatures of the floor surface for premises for various purposes:
In the marginal areas up to 35 degrees.
What pipes are needed for water floors?
The most commonly used polymer tubes are PERT or PEX. They are made of polyethylene, which is sewn together in production, forming a cylinder. The seam density reaches a record 85%, which allows them to be placed in the screed without consequences and defects.
There is the so-called “memory effect” of the material. The stretched tube tries to shrink back, which is very convenient for repairing damage, etc.
As for the PERT lines: they have no "memory" and should not be bricked up (due to the use of collet fittings).