Floor quality
The main function of the floor is to provide a solid structure that meets the standards of sound insulation, heating technology and hygiene. As a rule, materials of different strengths are used in the construction of the floor for optimal efficiency. Usually they are located in structures from more durable to less durable from the bottom up, or an option is adopted in which materials with different strengths alternate.
An example of alternating materials in a floor structure can be the use of a dense concrete screed, laid on less dense sound and heat insulating materials (mineral wool, expanded polystyrene). In some floors, sturdy parquet boards are laid on logs, which in turn are laid on a sand cushion. A perfect example of alternating layers is a laminate floor construction, where a durable laminated board is laid on a soft backing laid on a concrete screed. The most durable material in any floor structure is a reinforced concrete slab.
Recommendations
The choice of the type of underfloor heating is based on:
- on the type of room in which the installation will be carried out;
- for the purpose of installing the heating system (whether it will be additional heating or the main one);
- on your financial capabilities, since each system costs differently;
- on installation skills (installation of infrared film does not require special skills, while installation of a water system requires more effort and skill).
In any case, each system has the right to be installed, since the choice depends only on you. Just do not forget to take into account the principle of operation of underfloor heating and the type of room in which they will be installed.
- Similar posts
- Can laminate flooring be laid on a warm floor?
- What should be the height of the warm floor?
- How to choose a wire for a warm floor?
- How to connect a warm water floor in a house from a gas boiler?
- How to repair a warm floor?
- How to install Devi underfloor heating?
Constructive floor "pie" depending on the face layer
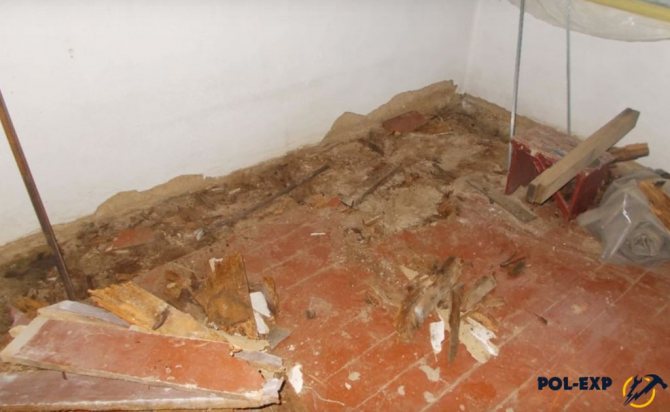
Depending on the type of existing topcoat, conclusions can be drawn about the presence of certain layers in the construction of your floor. This will help you when carrying out repairs. So, under the face layer of parquet boards or boards, there is a high probability of a screed made of a cement-sand mixture or a prefabricated-board screed made of hard fiberboard grades. By the way, if you have a solid monolithic base, it is enough to make minor repairs to it, and you will get an ideal base for laying any floor covering. If a prefabricated screed is found under the front layer, then it is enough to inspect all the shields and replace or repair the damaged elements.
If you are replacing a ceramic tile flooring in a bathroom or toilet, then try not to damage the screed layer, since there is a waterproofing carpet under it, damage to which will cost you dearly. If the waterproofing layer in these rooms is violated, you will have to tear off the entire layer of the screed and restore the damaged coating from the waterproofing material, after which you will have to perform a new screed.
Under the linoleum on an insulated basis, as a rule, a lightweight expanded clay screed was made. Tearing off this layer is not recommended as it is an ideal base for any kind of flooring.
The base device for non-insulated linoleum is made of fiberboard or chipboard boards on a cement screed.When repairing the bases of such floors, you need to pay attention to the condition of the base of the slabs, especially in the places where they are adjacent to the walls. In case of damage to the plates, they must be replaced with new ones. Slabs that have rotted from the edges need to be cut down or replaced completely.
If your house has floors made of parquet piece elements or boards, then the front layer was laid using lag - beams made of wood of a significant section. The bars, in turn, were laid on a substrate made of rolled materials or fiberboard.
When repairing wooden floors, special attention should be paid to the condition of the front layer. If the parquet boards or boards do not creak, rot or crack, then the new facing layer can be laid directly over the existing flooring without dismantling it. Small irregularities can be eliminated with a grinder, and the cracks can be putty.
If the old floor along the logs is not suitable for further use due to the fact that some of the boards have rotted, then the floor can either be dismantled completely, or the rotted elements can be replaced. When completely dismantled, the new floor covering is placed over the cement screed.
Types of pipes for a water-heated floor
Most of the usual metal structures are not suitable for the floor, since any welded seams are prohibited. An exception can be made only by copper structures. But here it is worth noting their cost and weight. Not every home can afford such pleasure. Installation involves laying pipes under the screed, which makes it almost impossible to repair and assess their condition during operation.
To date, there are several options for material for pipes for a warm water floor. It:
- polypropylene

- metalloplast


- corrugated stainless steel
- cross-linked polyethylene
Each variety has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
Polypropylene is known as a rather flexible material, which in this case allows the pipes to expand and return to their original position. Temperature fluctuations are easily tolerated by such pipes. Polypropylene pipe fittings are inexpensive, resulting in a significant reduction in the final cost of the structure. Inside the polypropylene pipes there is an aluminum layer protected by a polymer. It increases the strength of the pipe and guarantees its durability.
Metalloplast similar to polypropylene. Pipes made of it are durable and flexible. They are corrosion resistant and environmentally friendly. The structures are reinforced with a layer of aluminum, protected on both sides by polymer. The disadvantages of metal-plastic pipes are that they expand strongly at high temperatures, and pipe fittings should be chosen very carefully. Press fittings are more compatible with them. And this inevitably leaves an imprint on the cost of the project.
Corrugated stainless steel it has good flexibility and is quite robust. It minimizes connections to reduce the risk of leakage. The material does not rust and has a long service life. Heat transfer is one of the main advantages of corrugation.
XLPE is distinguished by an affordable cost, corrosion resistance. They are recognized as one of the durable options. The laying of such pipes is quick and does not require the participation of specialized equipment. The downside of the material is that it has low thermal conductivity, and this increases energy consumption. Mechanical stress is also detrimental to this material.
When choosing pipes, you need to focus on their diameter. The following indicators were adopted:
- 16 mm
- 20 mm
- 25 mm
When choosing a diameter, it should be borne in mind that it affects the heat transfer, the operation of heating devices, the peculiarity of the screed. The most commonly used pipes are 16 and 20 mm.
Repair of squeaky floors
Separately, I would like to say about the repair of wooden creaking floors, since here the situation is solved somewhat differently.The first thing to do to eliminate the squeak is to determine the cause. Usually there can be several reasons:
- the top layer of the wooden floor has crumbled;
- the fastening of the floor slat to the log bar is weakened;
- the log beams have rotted;
- creaking lags, which have lost their former horizontal position.
With a weak fastening of the floor slats, everything is simple: just screw the floorboard with a self-tapping screw to the joists. Moreover, the head of the self-tapping screw must be recessed into the body of the floorboard.
With lag creeps due to their uneven position, the situation is more complicated. There can be many reasons why they began to lie unevenly, and most of them are associated with violations during the construction of the building (lining under the logs of wedges, laying on a brick or several layers of loose fiberboard and roofing material). To eliminate such a squeak, you need to restore the evenness of the lag. To do this, you need to remove the front layer and align the bars or change them to others. By the way, you need to know that it is impossible to rigidly fasten the logs to the reinforced concrete slabs using bolted connections, since in this case any blows are easily transmitted through the floor slab.
All ceilings, except for attic floors, include floors. The floor construction consists of a series of layers. In accordance with P1-03 to SNiP 2.03.13-88 floor design the following terms are used:
Gender - a building structure, on which the entire production process and human activity is carried out and on the state of which the quality of products or human health depends.
Floor layer - an integral part of the floor, interconnected with the rest of the parts and performing certain functions.
The main layers in the floor structure:
- covering (clean floor) - the upper part of the floor structure, consisting of a single or multi-layer system, directly exposed to operational influences;
- interlayer - an intermediate connecting (adhesive) floor layer, which connects the coating with the underlying floor layer (screed) or serves to cover with an elastic bed;
- screed - a floor layer used to level the surface of the underlying floor or floor layer, impart a given slope to the floor covering on the floor, and distribute loads over the non-rigid underlying floor layers on the floor. The screed material is usually a cement-sand mortar. A screed made of asphalt, lightweight concrete and other materials can be used;
– base - the structure of the floor (with floors on floors) or a layer of soil (with floors on the ground).
Depending on the operating conditions, the following additional layers are introduced into the floor structure:
- underlying layer (preparation) - a floor layer that distributes loads on the ground can be lime - crushed stone, slag, gravel, adobe, 80 ... 100 mm thick. At increased loads, concrete preparation is used and, if necessary, reinforce it;
- waterproofing - the layer (s) of the floor, preventing the penetration of sewage and other liquids through the floor, as well as protecting the entire floor structure from the penetration of underground waters of various origins;
- soundproofing - a floor layer that prevents the penetration of impact noise into or out of the room. Calcined sand, lightweight concrete and other porous materials are used, which sometimes simultaneously perform a heat-shielding function.
- thermal insulation - a layer of the floor that reduces its overall thermal conductivity. Applied in floors along the overlap, when the overlap separates the heated and unheated rooms. The heat-insulating layer is made of wood-fiber boards, from lightweight and cellular boards and other porous materials, sometimes in the form of loose insulation (slag, expanded clay). Thermal insulation is also arranged in floors on the ground from lightweight concrete slabs, slag, expanded clay, placing it on the underlying layer.For thermal insulation, a leveling screed with a thickness of 15 ... 20 mm is arranged. A tie for loose and soft insulation (for example, glass wool) must be sufficiently rigid and strong to prevent it from being pushed under load. In this case, the screed is made reinforced with a thickness of 30 ... 40 mm;
The following applies to the sexes Requirements:
- general technical - the floor must have adequate strength and durability to resist tensile, compression and bending forces, impacts and abrasion. The floor must withstand physical and chemical aggressors;
- technological - the floor should be smooth, but not slippery, and ensure safe and comfortable movement of people and vehicles;
- sanitary and hygienic - the floor during operation should not have a harmful effect on human health, that is, it should not emit dust, hazardous gases, harmful chemicals, odor, and in some cases - provide comfortable thermal and sound insulating conditions;
- operational - the floor structure should provide for the possibility of quick and convenient repair; floors should be easy to clean.
The general name of the floor should be taken by the name of its covering.
Depending on the purpose, the following types of floors should be distinguished:
- industrial buildings; - residential buildings; - public buildings;
- livestock buildings.
Floor classification:
- by the nature of the material: piece; roll; solid (monolithic).
- by the nature of heat assimilation: warm floors; cold floors.
- at the place of the device: on the medzhdu-floor overlap; over basements and technical undergrounds; on the ground.
By design, the floors of residential buildings are divided into the following three main groups:
a) single-layer - the covering material of such floors is designed to absorb shock acoustic effects and meets the standardized requirements for heat assimilation;
b) separate - they consist of a continuous sound-insulating layer of loose or elastic-soft materials, screeds and coverings made of piece, plate or roll materials;
c) hollow - they consist of a coating, a log and soundproofing gaskets under them.
All three floor groups must provide (together with load-bearing floor slabs) impact sound insulation.
The design and material of the floor depend on the purpose of the room.
The floors are made of piece materials. These include plank floors, parquet floors, ceramic tile floors..
1. Plank and parquet floors. They are installed on any base - floor slab, on the ground.
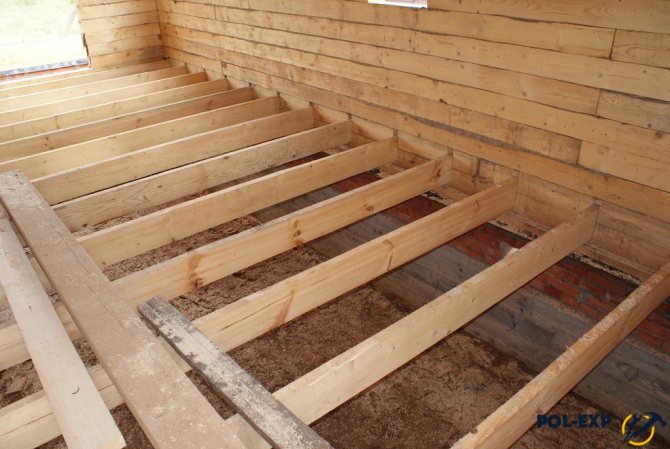
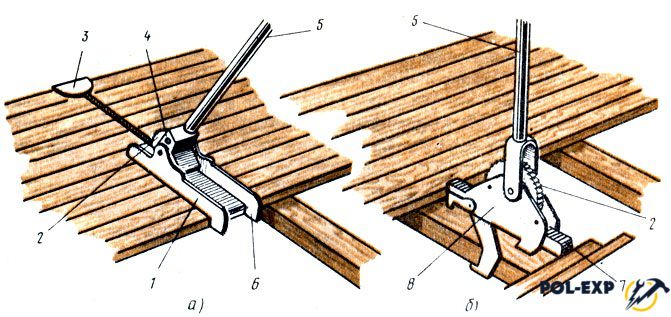
By design, plank floors are divided into one- and two-layer. Single-layer floors are laid on logs made of planed grooved boards with a thickness of 29 mm, nailed to wooden beams (logs), and when arranging the floors of the first floor on the ground, the logs are laid on brick posts measuring 250 × 250 mm in plan, two rows of masonry, t i.e. 150 mm.
The distance between the lags L (Figure 5.1) is taken for coatings from:
- parquet boards with a thickness of 25 mm or sheet piling boards with a thickness of 28 mm - from 400 to 500 mm;
- parquet boards - from 300 to 400 mm;
- boards with a thickness of 21-23 mm - from 350 to 400 mm
The distance between the first one from the wall and the next log should be no more than 300 mm, the distance between the log and the wall (partition) - 20 ... 30 mm.
At large distances between the joists, the floor will bend under load. Between the lags and the posts, a centering pad made of an antiseptic board is provided, isolated from the brickwork with a layer of roofing tar paper or roofing material. The distance between the posts depends on the height of the log. Usually logs are taken with a height of 80 mm - from beams 60 × 80 or from half a log with a diameter of 160 mm. In this case, the distance between the posts along the log should be no more than 1500 mm.Plank floors are putty and painted with oil paint.
Brick posts are installed on leveled and compacted soil (Figure 5.1).
| 1 - outer wall; 2 - brick or concrete column; 3 - lag; 4 - plank floor along the logs; 5 - floor from parquet boards or boards; 6 - inner wall; 7 - quarter boards (subfloor), if necessary; 8 - waterproofing layer; 9 - plinth or fillet; 10 - antiseptic pad; 11 - two layers of roofing roofing; 12 - lime-crushed stone preparation; 13 - bedding; 14 - compacted soil. |
| Figure 5.1 - Constructions of the floors of the first floors on the lags |
| 20 ... 30 mm |
Double-layer floors consist of a sub-floor in the form of a 25 mm thick diagonal unplaned plank flooring and a clean floor of 22 mm thick planed and grooved planks. In the case of flooring from insufficiently dry wood, the boards are partially nailed, and a year after the boards have dried, they are rallied, puttyed again and painted with oil paint.
Parquet floors are made of small prefabricated rectangular planks (rivets) with a thickness of 12 ... 17 mm - inlaid parquet. Wood is used of hard species (oak, beech, etc.). Such floors are laid on a concrete or plank (subfloor) base (made of planks 35-40 mm thick). To eliminate the squeak of parquet floors when walking and better sound insulation, thick paper is usually placed between the parquet and the wooden base.
Figure 5.2 - Plank (painted), parquet boards and boards on the floor slab
The factories produce four types of parquet riveting (Figure 5.3).
| 3 - bituminous mastic |
| 2 - asphalt |
| - paper |
| - paper |
| d) - with an oblique edge |
| c) - with a fold |
| b) - with grooves |
| a) - with grooves and a ridge |
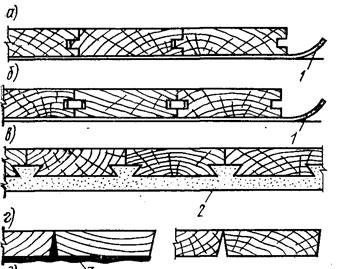

Figure 5.3 - Types of parquet riveting
The floors are made of panelboard parquet (Figure 5.4, a). The panels measuring 400 x 400 mm have a slatted base with glued parquet rivets. Shields are laid on the logs, nailing them. When laying on a concrete base (floor), the method of gluing to the base is mainly used.
Inlaid (mosaic) parquet is made of rivets with straight edges, which are assembled into squares with a gap of 5 mm and glued to the front surface on kraft paper with dextrin glue (Figure 5.4, b). Such cards of 400x400, 480x480 and 600x600 mm in size are glued to the base with bitumen mastic, then the paper base is removed from its front side.
| 1– interfloor overlap; 2 - screed made of porous mortar; 3 - bituminous mastic; 4 - lag; 5 - parquet boards; 6 - linings at the joints of the boards; 7 - rack base of the shield; 8 - map of mosaic parquet; 9 - paper on the surface of the card |
| Figure 5.4 - Panelboard (a) and mosaic (b) parquet floors |
Parquet flooring (Figure 5.5). The boards consist of a slatted board, on top of which parquet riveting made of hardwood wood is glued on with waterproof glue. Parquet boards are laid on logs, tightly rallying the grooved edges and hammering nails into the edge of the groove of the slatted shield. Such boards are made with a length of 1800 and 3000 mm and a width of 150 mm.
1 - lag; 2 - soundproofing pad; 3 - parquet boards; 4 - longitudinal cuts on the back of the rack base
Figure 5.5 - Floors from parquet boards
Floors made of parquet boards with a thickness of 25 ... 27 mm are suitable only in rooms with a dry mode of operation, since frequent and abundant moistening of the floor leads to warping of the boards and peeling off the strips of the front covering. When laying parquet boards on a concrete base (floor), the method of gluing to the base is mainly used.
Ceramic tile floors (Figure 5.6) are arranged in wet rooms (showers, bathrooms, restrooms), lobbies, and stairwells. The floors are durable, waterproof, decorative, but cool
1 - ceramic tiles; 2 - cement-sand mortar; 3 - bituminous mastic; 4 - concrete or crushed stone base; 5 - soil compacted with rubble; 6 - lightweight concrete; 7 - floor slab
Figure 5.6 - Ceramic tile floors
The floors are made of rolled materials. Floors made of linoleum, Relin, PVC tiles are characterized by high resistance to abrasion, bursting, high elasticity and low water absorption.Lay linoleum, relin, PVC tiles on a layer of cold mastic on waterproof binders on a screed made of lightweight concrete 20 mm thick or on a screed made of cement-sand mortar.
Linoleum floors are durable, elastic, wear-resistant, hygienic. In rooms with a long stay of people, they arrange "warm" linoleum floors with a heat and sound insulating underlay (Figure 5.7, a). Overlappings made of baseless linoleum or on a fabric base must have a heat-insulating layer at the base (Figure 5.7, b).
a) b)
a) - "warm" with a heat and sound insulating substrate (on the floor)
b) - "cold" on a fabric base (on the ground)
c) d)
c) and d) - "warm" baseless and fabric-based
1 - linoleum with heat and sound insulating base; 2 - a layer of glue; 3 - screed made of porous mortar; 4 - floor slab; 5 - baseless linoleum; 6 - adhesive mastic; 7 - heat-insulating layer; 8 - linoleum on a fabric basis; 9 - cement mortar screed; 10 - concrete preparation
Figure 5.7 - Linoleum floors
They are laid on a flat and dry base of planks, hard fibreboard and chipboard or on cement screeds. Linoleum is glued to the base with a special glue based on synthetic, casein or bituminous resins.
Tapiflex is delivered to construction sites folded into room-sized carpets, since the floor covering made of this material should not contain joints into which water can get into when cleaning the floors. Due to its elasticity, such a floor has good sound insulation against impact and airborne noise, it is quiet, hygienic, strong and durable.
In recent years, in addition to those discussed above, other constructive solutions for floors have found application, such as carpets (carpet) and laminated floors (laminate).
The advantages of carpets include: additional sound and heat insulation, a feeling of softness and comfort, as well as the preservation of linear dimensions during wet cleaning.
The disadvantages are that the carpet is laid on the entire floor surface, from skirting board to skirting board, since rubber tends to stick to the floor surface, and therefore the probability of moving the covering without damaging the base is very small.
Laminated flooring (laminate). This coating results from a manufacturing process in which different materials are pressed together under high pressure to form a new material.
The structure of the laminate is as follows - it is, first of all, carrier the foundation (plate), on top of which there is decorative layer with various patterns, which in turn is protected from external influences protective layer... From below, the base is covered with the so-called stabilizing layer (anti-deformation). The protective layer is mainly made of melamine resins with various additives.
As a basis, wood fiber boards (fiberboard) are used, as well as (but less often) particle boards (chipboard). The stabilizing layer is waxed paper impregnated with melamine resin.
Before laying the laminate on a cement floor or a floor made of ceramic tiles, a vapor-moisture-proof layer should be placed and only then a sound-absorbing underlay. Laying of the laminate is carried out in a "floating" way (without gluing or adhesion to the base of the floor).
Solid (monolithic) seamless floors - these are mastic, cement, concrete, asphalt concrete, cement, mosaic, asphalt, xylolite, etc.
Mastic floors - polyvinyl acetate and polymer-cement - are arranged over a screed made of cement-sand mortar or light concrete with a thickness of 20 mm (Figure 5.8, a) or 40 ... 50 mm, if the coating is arranged over a heat or sound insulating layer (Figure 5.8, c).The color of the floors can be any. The thickness of the layer of the polyvinyl acetate coating is 3 ... 4 mm; polymer-cement - 8 mm.
| 1 - mastic floor; 2 - cement-sand mortar screed; 3 - heat or sound insulating layer; 4 - floor slab; 5 - floor slab with a flat surface; 6 - underlying layer or floor slab; |
| Figure 5.8 - Continuous seamless mastic floors |
Concrete and cement floors are most widely used in industrial buildings (Figure 5.9, a). Fine fractions of stone materials from granite and gravel are used as filler for concrete floors. Cement floors are a layer of greasy cement-sand mortar. Concrete or cement coatings have a thickness of 20 ... 50 mm, which depends on the mechanical effects on the floors. The floors are laid on a concrete base layer, a floor slab or on a 40 mm thick cement mortar screed, if a heat or sound insulation layer is located along the floor slab.
Metal-cement floors are made of concrete with the addition of steel or cast iron sawdust and shavings with a grain size of not more than 5 mm, which are degreased by calcining before use.
Mosaic floors (terrazzo) are made of Portland cement filled with grinded and polished stone, for example, marble, limestone.
Asphalt floors are economical and waterproof. Their disadvantages include high deformability under prolonged load and insufficient hygiene. They are used mainly in garages, parking lots, as well as in basements, where they can serve as a waterproofing layer that protects the premises from groundwater. The abutment of the floors is arranged so that it is possible to ensure the possibility of floor settling regardless of the walls, for which gaskets are arranged in these places. Floors located on intermediate floors must also be separated from walls, columns and partitions. For this, a gap of 10 ... 12 mm wide is left along the edges of the floor, closed by a plinth, which is fixed on the wall, and not to the floor.
Some features of floors using lag
If your room is located on the 1st floor of the house, then wood floors using log beams should be made using insulation. In most cases, sheets of glass wool are used, which are laid between the logs on a reinforced concrete slab. By the way, in constructive "pies" of floors with insulation, a vapor barrier must be used. A layer of glassine is used as it. The glassine carpet is laid on the logs without tension, that is, it can sag freely on the insulation. This is necessary to provide an air gap in order to ventilate the underfloor space.
Quite often, log floors are made using a sub-floor. For the device of such a floor, ordinary non-grooved boards are used. Subfloors are a kind of basis for laying the front layer of parquet boards and boards. By the way, in subfloors, you can use plywood or particle boards instead of boards. These subfloors are an excellent base for any kind of topcoat. As a rule, subfloors are arranged where the height of the screed, according to calculations, should exceed 15 cm. In this case, it is more logical to make a subfloor using a lag on the posts. Since subfloors are made of wood, all the problems inherent in wood structures are inherent in them.
In connection with the above, the following conclusions can be drawn. If you are planning to repair the floor in the room, then you can draw conclusions about the degree of costs and the work required only after inspecting the base of the existing floor. So, it is possible that it will be enough for you to replace the face layer or overhaul the entire floor.By the way, when changing the constructive "pie" of the floor to a more massive and heavy one, you will need to obtain permission from the appropriate authorities.
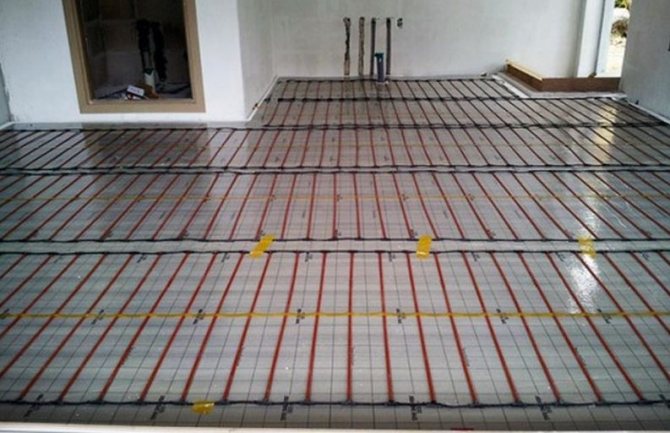
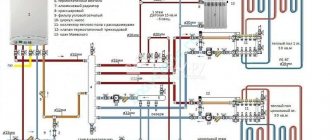
Ways of laying pipes for underfloor heating
Efficiency, relevance for a particular room is largely determined by the method chosen for laying pipes for a warm water floor. He also sets the pace for the fastening tools. The method is applied:
- snake
- double snake
- evidence


When choosing, it is worth considering that the water moves through the pipes from the source of water supply, that is, from one side. Therefore, you need to pay attention to its location in order to avoid uneven and inappropriate heating of the surface.
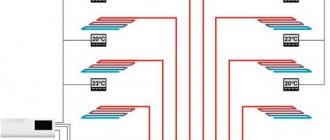
In conclusion, it should be noted that the room temperature and the energy efficiency of a warm water floor depend on the selected temperature controller. It is designed to control and maintain a given degree of floor and room heating.
Highlighted digital and mechanical thermostats. The first ones are practical in that they show all the work of the floor, including its heating at a particular moment. They are easy to operate and can be programmed for a number of actions.
Mechanical ones do not have such modern capabilities, but they are easily diagnosed in case of breakdown and repaired.