Insulation vermiculite features and application
Vermiculite composition and processing
Vermiculite contains several components linked by one chemical formula. Most of all it contains silicon - about 35%, there is also 10% magnesium, iron, potassium, calcium, etc.
Natural vermiculite is a large, flaky crystal. From exposure to high temperature, they are transformed into twisted twisted filaments-columns, increasing in volume up to 10 times.
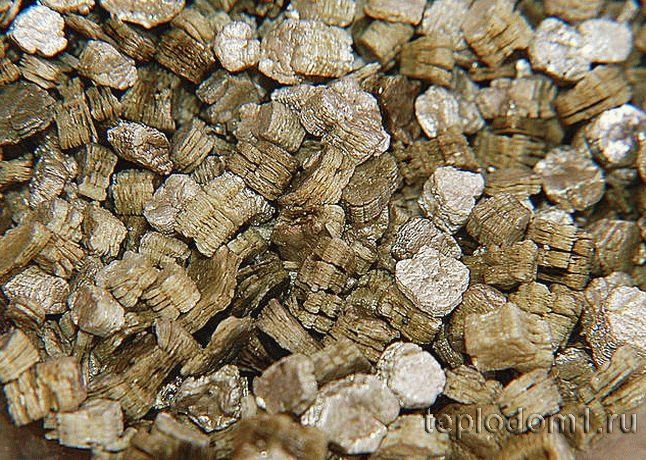

When the material is heated over 1000 degrees, expanded vermiculite is obtained - a light free-flowing material, brownish, golden in color.
Hygroscopicity
The main distinguishing feature of expanded vermiculite (hereinafter referred to as vermiculite) is its high hygroscopicity. 100 grams of material can absorb up to 500 ml of water. But vermiculite is just as easy with water and parting.


In fact, it is a natural hydraulic accumulator. Therefore, it is mainly used in plant growing, as an additive to the soil.
Thermal insulation
Another feature of the material is its high thermal insulation qualities. The thermal conductivity coefficient of bulk vermiculite is in the range of 0.05 - 0.07 W / (m * K), depending on the size of the fractions and the density of the rammer. That makes it possible to use the material as an effective insulation.
1 mm, 120 kg / cubic meter - 0.059
2 mm, 110 kg / cubic meter - 0.057
4 mm, 95 kg / cubic meter - 0.054
8 mm, 65 kg / cubic meter - 0.052
The use of vermiculite as insulation
It is effective to use vermiculite as a bulk insulation for thermal insulation of floors and ceilings. And also for filling various cavities in walls, partitions, pipe boxes ....


When used on attic floors, a reliable waterproofing is required on the roof side, as well as covering the material layer with a vapor-permeable membrane (paper layer). On the side of the room under the material there must be a vapor barrier-film
During installation, special attention is paid to ensuring continuity
Special use
Rigid slabs are made from vermiculite. They are more expensive, but can be used instead of mineral wool, as they have similar characteristics.
Perlite and vermiculite - what's the difference?
Despite the lightness, flowability of these two materials differ in appearance: perlite is white, dusty, vermiculite is dark in color. There are no nutrients in perlite, and vermiculite contains aluminum, calcium, magnesium, iron, silicon, potassium (in bound form).
Vermiculite, unlike perlite, can absorb beneficial compounds from the soil, and then gradually release them. It is also very water-absorbing compared to perlite.
Perlite is an excellent conductor of moisture, but a poor retainer, while vermiculite, on the contrary, retains it very effectively. Vermiculite has an elastic structure, and perlite collapses and becomes dust with active physical influence.
Perlite or vermiculite - which is better for plants? This question cannot be answered unequivocally, it cannot be said which material is better, since everything depends on the plant itself, its needs. For example, for some flowers (the same indoor violets or gloxinia), wick watering is sometimes used.In this case, perlite is ideal, which is used to dilute the substrate in the pot - it contributes to an even distribution of moisture over the soil, and the soil itself dries faster. Vermiculite, on the other hand, will be more appropriate with the usual method of irrigation - the soil will stay moist longer due to its moisture-accumulating properties.
It is impossible to determine which is better than perlite or vermiculite, since one or another additive is equally suitable for each type of plant. These two materials are equally good, have similar qualities, but still slightly differ in "technical" characteristics.
They complement each other perfectly, improve the soil. To get the optimal soil mixture, growers take 15% of each material, mix them, while the total additives (relative to the rest of the soil mixture) should be 30%. A mixture of peat, perlite and vermiculite is most commonly used for cultivation. Vermiculite is suitable for delicate, capricious representatives with a vulnerable root system, perlite is more suitable for powerful plants, cacti or succulents.
New opportunities for growing plants are constantly appearing on the market - care products, all kinds of additives. Almost any product can be purchased today. If you are not yet familiar with these materials, pay attention to them. Vermiculite or perlite for plants will save you time in caring for them, eliminate many problems (fungi, mold), improve the composition of the soil, and help keep the planting material in good condition.
Starting our passion for violets, we are faced with advice to make a looser substrate by adding various leavening agents. The main ones are vermiculite and perlite. What is it? And which one is better? Let's consider each of them in more detail and make a comparative description.
Vermiculite
Vermiculite (from Latin vermiculus - worm) is a mineral from the hydromica group, which is obtained by secondary transformation (hydrolysis and subsequent weathering) of dark biotite mica.
During firing in vermiculite kilns, the water crystallized between the mica layers evaporates, and the mica flakes delaminate and swell. Expanded vermiculite is a free-flowing, granular material with a flaky structure. In this case, vermiculite increases in volume by 7-10 times. The resulting product is the lightest material that floats freely on the surface of the water.
Expanded vermiculite has all the unique properties of natural mica: low thermal conductivity, fire resistance, chemical inertness, harmlessness. Due to swelling, vermiculite has a low bulk density - only 30-100kg / m3. Has a high coefficient of water absorption (100 g of vermiculite absorbs 400-530 ml of water). It easily absorbs moisture and also easily gives it to the plant, creating an optimally moist environment for root nutrition. Biologically stable: it is not subject to decomposition and rotting under the influence of microorganisms, it is not a favorable environment for insects and rodents. Vermiculite is a chemically inert material (neutral to the action of alkalis and acids). Possesses unique ion-exchange properties. Due to the content of oxides of such trace elements as calcium, magnesium, potassium, aluminum, iron, silicon - vermiculite is an effective biostimulator of plant growth. Vermiculite is a highly porous mineral with air between the flakes. Its structure makes it possible to achieve the necessary aeration properties from the substrate, in which the earth does not cake, does not form a crust on its surface, it remains loose. Vermiculite can be used neat for rooting cuttings. Due to the fact that the mineral is not subject to rotting and decomposition, various microorganisms and fungi do not live in it. This has a beneficial effect on rooting. Vermiculite prevents the appearance of various rot and mold.
Perlite
Perlite (fr perlite, from perle - pearl) is a rock of volcanic origin.
At the edge of the lava flow, in the places of primary contact of magmatic melts and the earth's surface, as a result of rapid cooling (quenching) of the lava, volcanic glass - obsidian is formed. Subsequently, groundwater penetrates through obsidian, it is hydrated and the formation of obsidian hydroxide - perlite.
Water in the original perlite is in two main forms: free (on the surface of the rock) and bound. The presence of constitutional water gives perlite the ability to swell when heated. Water lowers the softening point of the rock and acts as a means of expanding it when molten. Swelling of pearlite is carried out in furnaces by thermal shock at 900-1100 ° C. In this case, pearlite passes into a pyroplastic state. The release of gases, mainly H2O, has the character of an explosion, and the glass foams, forming expanded perlite with a high viscosity. The bound water evaporates and creates countless tiny bubbles in the softened mass. The rock decomposes into spherical grains with an increase in volume of 4-20 times and a porosity of up to 70-90%. In appearance, perlite is sand or crushed stone (depending on the degree of preliminary grinding), color from snow-white to gray-white, odorless. Perlite is fire resistant, has heat and sound insulating properties, high absorbency (up to 400% of its own weight). Perlite is able to first absorb water intensively, and then gradually give it to plant roots and other perlite particles. Due to this ability, the perlite in the upper layers of the soil, when dry, will draw water from the lower layers, providing moisture to the roots of plants. Due to the fact that moisture is evenly redistributed in the soil, this averages the temperature well in the root area. It is known that the thermal conductivity of the soil directly depends on the density. The lower the density, the worse the energy moves through such an environment: the soil cools more slowly and heats up more slowly. This protects the roots from both freezing and overheating. Perlite is not subject to decomposition and rotting under the influence of microorganisms, it is not a favorable environment for insects and rodents. Chemically inert: neutral to alkalis and weak acids.
Let's sum up
Perlite and vermiculite are materials of different origins and have one common purpose: to make the substrate looser and more breathable.
1. The advantage of perlite is a more even distribution of moisture inside the earthen clod, it dries out faster between waterings, which allows it to be used for wick watering. On the contrary, vermiculite is good for traditional watering, as it allows you to increase the time between waterings.
2. In addition, perlite has a positive electric charge, and therefore cannot retain the positive ions of fertilizers, does not participate in the process of ion exchange.
3. In the composition of perlite, all substances are in a bound state, inaccessible to plants. At that time, vermiculite contains potassium and magnesium in an accessible form.
4. Vermiculite has a more elastic structure, which gives it advantages over perlite, in which the structure is destroyed at the slightest physical impact, turning it into fine dust. Perlite is essentially expanded glass and dust is not removed from the lungs when inhaled, therefore the use of protective equipment when working with it is mandatory.
As a rule, I use expanded clay as drainage for my indoor flowers, and if it runs out, I go to the basement in search of a box from under the TV - there will always be a piece of foam in it, which can be quickly cut into small pieces.
But when a friend gave a stalk of a new flowerpot, she strictly ordered: you will root it in a mixture of perlite and peat. I obeyed, went to the store, they sold a bag. Having brought it home, I examined it - and was upset: there was an inscription "Vermiculite" on the package.
Really cheated? She returned, began to question the saleswoman with maximum passion. And it turned out that these are almost the same materials. Although, of course, there are differences between them too ...
This word is consonant with the French "pearl" - "pearl". Indeed, before us are small white stones.
It is a natural rock. It is formed through several chemical processes.
- Magma touches the upper balls of the earth's crust and cools. This is how obsidian is made from it.
- Water molecules "stick" to obsidian (the so-called hydration), and now we have obsidian hydroxide. This is perlite.
- This material can be black, green, brown. After the obsidian hydroxide undergoes heat treatment, it becomes whitish pebbles that are well known to us from shops (as in the photo above).
Taking a handful of perlite, you can see that it resembles sand, but larger, lighter and more porous. Also, the stones can have sharp edges, so be careful not to squeeze this substance in your fist.
It is a homogeneous material, without admixtures of other rocks.
His dignity
- With its help, moisture in the soil is distributed capillary.
- The material does not retain water for a long time, quickly giving it back to the roots.
- Perlite dries quickly, so you are less likely to flood the plant with frequent watering.
Nomenclature


Expanded vermiculite is produced in accordance with TU 5712-091-00281915-2007 and is subdivided into grades depending on the bulk density and grain size of the main fraction.
VVF means Expanded Fractionated Vermiculite. Grade 100 means that the bulk density of vermiculite is not more than 100 kg / m³.
St. Petersburg Mica Factory offers expanded vermiculite:
Most heat insulators have one or more flaws - they are either fire hazardous, expensive, or not environmentally friendly. In search of the best option, developers are often interested in the idea of using vermiculite in this role - a layered mineral that changes its structure at high temperatures and acquires new properties that, at first glance, are quite suitable for insulating a building. How versatile is such a heater, does it have any drawbacks, and how to use it correctly?
Vermiculite - what is it
This mineral was first discovered in 1824 in Massachusetts, but for almost 150 years no one knew about the usefulness of this stone. It took a century and a half of research to learn how to use the material. Large vermiculite deposits have been explored on all continents, its richest deposits are being developed in Russia - on the Kola Peninsula, in the Chelyabinsk and Irkutsk regions.
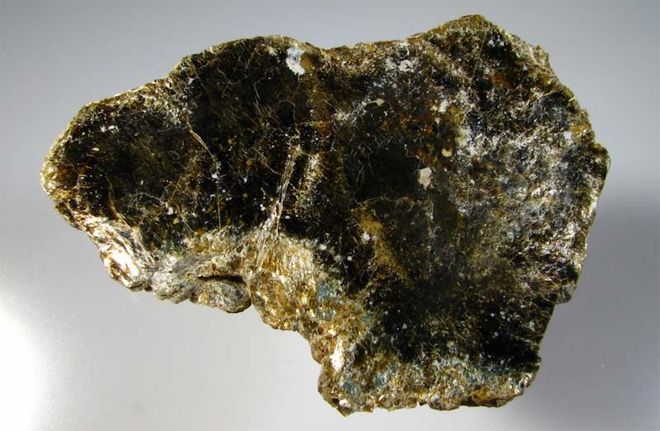


Vermiculite is a natural golden-brown mineral of a layered structure, included in the group of hydromica. The mineral owes its Latin name - "vermiculus" (worm or worm-like) to its appearance: when the mica deposit is heated to 900-1000 ° C, water evaporates and dehydrates, the stone changes, increasing 6-15 times, and forming worm-like threads or columns. The mineral contains zeolite water, oxides of potassium, magnesium, lithium, iron, chromium, manganese, aluminum, etc.
At enrichment plants, sorting, separation into fractions and heating of the feedstock takes place, as a result of which the expanded vermiculite is obtained.


During the firing process, the chemical composition of the stone does not change. Depending on the size of the fraction, the expanded material is divided into 6 grades:
- No. 1 up to 0.5 mm - 0 (Super Micron);
- # 2-0.5 mm (Micron);
- No. 3-1 mm (Super fine);
- No. 4–2 mm (Fine);
- No. 5-4 mm (Medium);
- No. 6-8 mm (Large).
Vermiculite of all grades is used in construction, aircraft construction, energy, agriculture. The expanded mineral of large fractions is used in agronomy under the name "agrovermiculite" in accordance with GOST 12865–67.


In addition to bulk vermiculite, expanded vermiculite is produced in the form of plates with a gradation of thickness from 20 to 60 mm and in the form of a paste.
Expanded clay properties
- high strength
- fireproof
- frost resistant
- does not contain harmful impurities;
- does not absorb water;
- durable
- does not lose its properties and does not collapse when frozen
- not subject to decay
Absolutely safe for humans and the environment.
Expanded clay is a product of fast firing of low-melting clays. From Greek, the word "expanded clay" is translated as "burnt clay", which is absolutely true. Despite the heat treatment, it not only does not lose the properties inherent in the clay itself, but also acquires additional, becoming porous.


Photo: Properties of expanded clay material. Application area
On their basis, kermzite-concrete blocks are made, the thermal insulation and mechanical properties of which make it possible to use them for the thermal insulation construction of floors, walls, ceilings, foundations and basements. Thanks to the expanded clay filler, these blocks also acquire its properties. They are lightweight, strong, fireproof, acid resistant, etc.
Applications
Discovered relatively recently, a mineral such as vermiculite and its derivatives have found many different fields of application today:
- Ecology, oil and chemical industries. Few people will be able to answer when asked about vermiculite, that it is an excellent sorbent capable of binding alkalis and acids. This property allows it to be used to neutralize a variety of chemicals in production, as well as to limit oil spills.
- Nuclear industry and power engineering. It is used as an absorber for radioactive elements such as cobalt-58, strontium-90 and cesium-137, as well as a reflector of gamma radiation.
- Automotive and aviation industry. Various sound-absorbing and heat-insulating materials and products are made from vermiculite.
- In industrial and civil construction, vermiculite is used as follows:
insulation, as well as sound and heat insulator for roofs and floors;
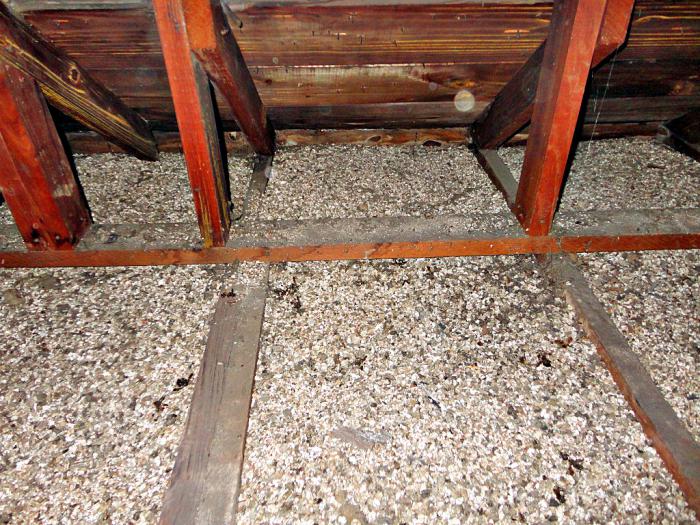


- for filling as an insulating material into hollow panels;
- as an integral component of various plasters, lightweight concrete and dry building mixtures;
- in the manufacture of concrete and cement blocks, as well as heat-insulating mastics as a filler;
- in the production of fire retardant and heat-resistant plates, panels and other wall materials;
- when arranging self-leveling floors.
5. In industrial and private plant growing and horticulture. Let's take a closer look at how vermiculite is used for plants.
Technologies for stacking vermiculite building materials
Work with mineral insulation is not difficult or harmful - according to the degree of impact on the human body, the vermiculite coating, according to GOST 12.1.007-76, belongs to class IV (low-hazard substances). To prevent dust from entering the eyes and respiratory system, before using vermiculite, the worker should protect them with glasses and a respirator. Provided that the building material is stored in dry, closed rooms, its shelf life is unlimited.
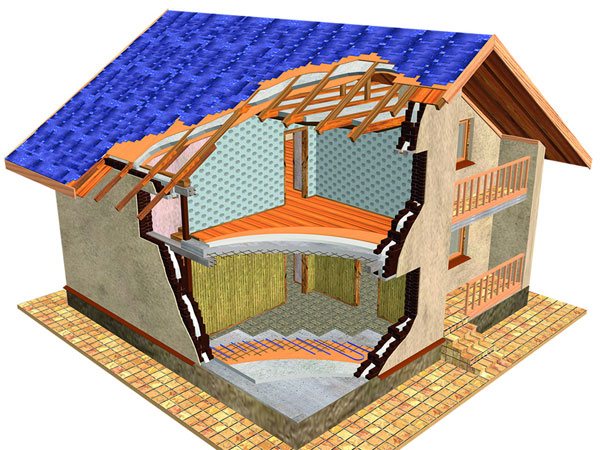


Thermal insulation of building envelopes with backfill vermiculite
To protect the attic ceiling and the pitched roof surface from heat leaks, you must follow a simple algorithm:
- Cover the inner lining with an overlap with a vapor-tight film, which will prevent moisture from entering the vermiculite from the inside.
- Pour dry vermiculite into the formed cavities in the roof frame.
- On top of it, lay a windproof superdiffusion membrane, the task of which is to prevent the material from weathering and at the same time allow vapors to circulate freely.
- Install the counter-batten and lay the roofing.
The insulation scheme for attic floors is, in principle, the same:
- Reliable waterproofing is placed on the filing between the beams.
- A lag system is mounted, with a layer of 100–150 mm.
- A bulk insulation for the floor is introduced, which must be immediately covered with a vapor-permeable film.
- After installing the plank or plywood flooring, the floor is ready for finishing.
- To reduce material costs, vermiculite can be mixed with sawdust in a 1: 1 or 3: 2 ratio.


The layout of the insulation of frame wooden walls
Filling vermiculite into the walls is possible at the stage of their construction using frame or well technology, or in the process of external insulation. To do this, as the load-bearing wall and facing layer are being erected, the space between them is filled with vermiculite granules with light tamping. The approximate layer thickness is 100 mm (for Moscow). Additional vapor and waterproofing is not required, ventilation gaps in the outer wall are also not required.
Another way to create an insulated wall is to fill the cavities of the building blocks with vermiculite. The thermal insulation effect of such a structure increases dramatically, and the free steam exchange in the wall is not disturbed, and it remains light and breathable. If necessary, the outer wall can be further insulated if it is erected from concrete panels based on fast-setting cement with the addition of bulk insulation for the walls.
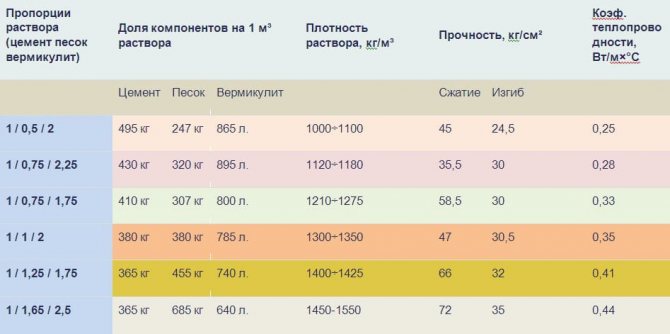

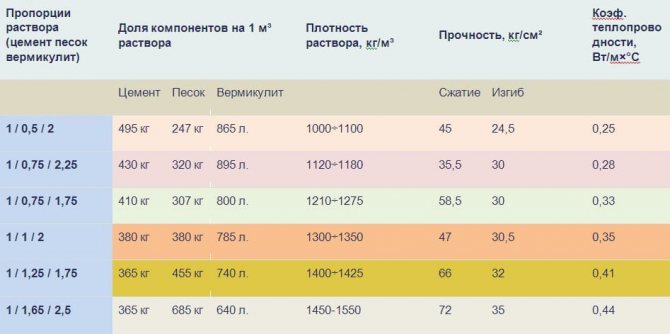
Proportions of mortars for screeds
Warming with dry vermiculite is a rather expensive solution, therefore in private construction they prefer to add this material to the composition of building and finishing mixtures. To prepare a solution for a thermally insulated screed, you need to stock up on standard M400 Portland cement, sand and fine or medium-fraction vermiculite. Due to its high water absorption, the solution must be consumed within 30 minutes after mixing.
For reliable insulation of a floor over an unheated space, 100 mm of a screed is usually enough, and for interfloor floors, 30 mm is enough. It must be remembered that the flooded ceiling, due to the small mass fraction of cement, does not have frost resistance, therefore, such screeds are recommended only for heated rooms.
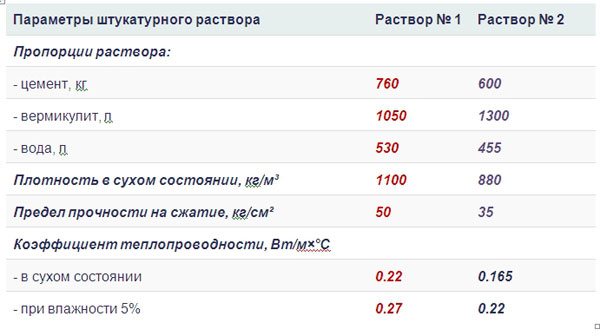

Recipe for plastering solutions for outdoor use
To plaster the walls from the inside, you can use the same composition, and for their external treatment, the proportions of the solution must be slightly changed. Both external and internal plasters have high vapor permeability, contributing to the normal self-regulation of the internal microclimate. Warm vermiculite-based plasters have a natural golden or silvery sheen, but if desired, you can add pigment of the desired shade to their composition.
Interior plaster: C - cement, I - lime, G - clay, V - vermiculite
When laying walls, it is advisable to use modern thermal insulation materials (gas, foam blocks, vermiculite concrete), and the joints between them should be made of masonry mortar with a low coefficient of thermal conductivity. You can knead it using all the same vermiculite, having previously determined the optimal composition.
Thus, the demand for vermiculite in construction is obvious: excellent manufacturability and a unique combination of properties bring vermiculite backfills and slabs to the fore among fire-resistant insulation materials. The only significant obstacle to expanding the scope of their application is the high price, but the increase in production gives hope that it will soon be eliminated.
Vermiculite in mortars and mixtures
On the basis of a fine fraction of vermiculite, masonry and plaster mixtures are prepared. They can be purchased ready-made or you can mix cement, sand and vermiculite on your own in a ratio from 1: 0.5: 2 to 1: 1.25: 1.75. The thermal conductivity coefficient of such a plaster mixture will be from 0.24 to 0.4 W / m * K.
On the floor from reinforced concrete. instead of backfill, slabs are made of lightweight mortar with vermiculite filler. Such a screed, in addition to insulation, perfectly dampens noise. The technology for making the screed is no different from the rules for arranging screeds for beacons made of other materials.
Vermiculite plaster or slabs are an excellent fire retardant material, a layer 20–40 mm thick will provide fire protection for metal structures from 30 minutes to 2.5 hours.


PLEASE NOTE: Due to the high hygroscopicity of the material, it is not recommended for use in underground, moisture-saturated parts of buildings - basements, foundations, ceilings above cold undergrounds.
Insulation properties vermiculite
Insulation vermiculite is a material that is widely used in construction and finishing works in the construction of new buildings, in carrying out major and current repairs of old buildings. It is used in the form of compressed slabs, as a filler and as an additive to plaster mixes. It is used to insulate walls, floors, attics and ceilings. Vermiculite insulation is carried out during the construction of pipeline systems and highways for various purposes, which significantly extends their service life. This has a positive effect on the operation of the equipment and pipeline fittings installed for the smooth functioning of the entire system.
Technological features


Vermiculite in the form of slabs and in bulk.
Vermiculite is an environmentally friendly material created by nature. Refers to the minerals of the hydromica group. Has a crystalline form of golden brown, yellowish or bronze color. It was found that when the vermiculite plates are heated, they are transformed into threads or worm-like columns. Actually, this property made it possible to give the material such a name, tk. vermiculite translated from Latin means a worm. After examining its physical and chemical properties obtained after heating, the vermiculite insulation began to be used in various industries, agriculture and construction. Also read: "Choosing the best insulation for the roof."
The main advantages of the material include:
- fire resistance (1350 0 С);
- density (not higher than 150 kg / cubic meter);
- low thermal conductivity (no more than 0.12 W / m * K);
- resistance to aggressive environments, bacteria and does not form mold on the surface;
- hygroscopicity;
- the ability to absorb sound (sound absorption coefficient up to 0.8);
- environmental friendliness;
- service life (60 years).
Before pouring antifreeze into the heating system of the house, you need to clean the pipes and batteries from all kinds of contaminants.
Here you can read what equipment is needed for pumping the heating system with antifreeze (non-freezing liquid).
Ways to insulate walls with vermiculite


View of a wall plastered with a solution with the addition of vermiculite.
Vermiculite warming of walls is carried out in the process of erecting new buildings and objects of old buildings, erected from different materials. Bulk thermal insulation can serve as a filler in the manufacture of heat-resistant concrete and is used for plastering surfaces. It is produced in different fractions (from 0.5 to 12 mm) and is sold in the retail network in paper bags, most often weighing 25 kg.
Granular vermiculite can be poured into inter-wall cavities. The pressed plates are fixed with special fasteners; they can be cut before assembly.Slabs can serve as good insulation when cladding fireplaces, stoves, chimneys and pipes. Vermiculite for ceiling insulation additionally performs soundproofing functions in multi-storey buildings.
Vermiculite insulation, the properties of which remain unchanged regardless of its type, is also used for plastering vertical surfaces. To do this, in certain proportions, it is added to concrete mixtures. You can make them yourself or buy ready-made ones. Comprehensive insulation of the house with vermiculite (walls, floors, attic) will save on heating bills.
The method of how to install an electric heating boiler consists of two parts: an insert with a circuit and a connection to the network.
Insulation with vermiculite of the floor, attic
The technology of vermiculite insulation of the floor and the attic is the same. In this case, the thermal insulation is protected with special films. From the side of a warm room, a vapor barrier should be installed, and from the side of a street or an unheated attic - waterproofing.
When performing thermal insulation with vermiculite, the presence of waterproofing and vapor barrier is mandatory
In doing so, it is extremely important to correctly place these protective layers.
Insulation of a pitched roof


When insulating the floor, waterproofing is placed under the vermiculite.
With such insulation, it is important to choose the correct thickness of the poured vermiculite. It depends on temperature conditions and ranges from 10 to 20 cm
The technology for insulating a pitched roof is as follows:
- a vapor barrier film is laid on the rafters;
- granulated vermiculite is poured;
- covered with a layer of waterproofing and a counter-lattice is stuffed;
- the roof spreads;
- internal lining with any material is performed.
Insulation vermiculite, the properties of which are well studied, is a modern material that has a wide range of applications.
Heat and thermal insulation from expanded vermiculite ↑
The first thing for which vermiculite is used is to insulate the walls of the building. Heat-insulating backfill 20 cm thick in terms of thermal conductivity is equal to a two-meter concrete or one and a half meter brick wall. It is especially effective to insulate a facade made with a well masonry, since a 5-cm layer of vermiculite backfill can reduce heat loss by 75% (data are given for the Krasnodar Territory).
In addition, vermiculite is quite suitable for solving other construction problems:
- thermal insulation of attics, floors and roofs;
- thermal protection of chimneys, pipelines, industrial equipment;
- arrangement of heat-resistant casings and partitions, for example, for facing fireplaces.
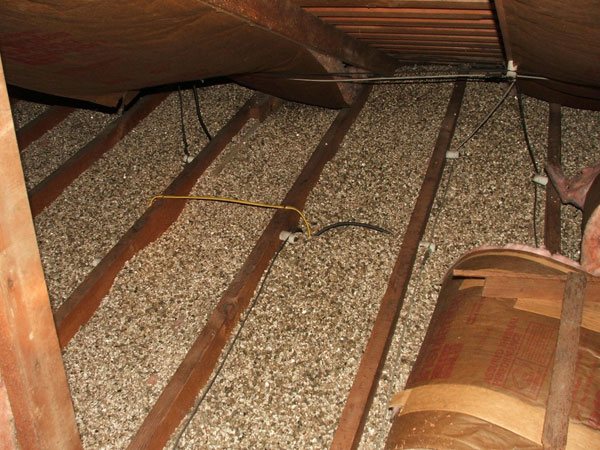


Backfilling of vermiculite on the attic floor
Plastering the walls with a cement-vermiculite compound from the outside protects them from bad weather and sudden temperature changes, prevents mold and insect damage. Insulating plaster mixes are also relevant for interior decoration: their layers are applied with familiar tools, easily rubbed off and acquire an aesthetic appearance. It makes sense to add vermiculite to masonry concrete mixes, so that it prevents heat loss through the joints.
Expanded vermiculite can be fully used for the floor: it is recommended to include it in the composition of the concrete solution for pouring the screed, as well as for laying warm and self-leveling floors. Thus, a significant reduction in volumetric weight is achieved, an increase in the reliability of the coating and a reduction in material consumption. At the same time, vermiculite is not suitable for insulating underground and basement floors, since it does not have the proper level of hydrophobicity.


Vermiculite boards
Vermiculite scope, pros and cons, installation features
Solving the topical issue of thermal insulation of a home, one has to face the problem of choosing a thermal insulation material.
The range on the market is wide enough, but almost every option has significant drawbacks.In one case, flammability is discouraged, in the other - a high rate of hygroscopicity.
The article discusses the characteristics and benefits of vermiculite, which is the golden mean of price and quality.
Description and scope of vermiculite
Vermiculite is a natural crystalline mineral with a layered structure. Belongs to the hydromica group. It contains: silicon, iron, magnesium, calcium and other mineral components.
The main advantages due to which the material is used in construction are resistance to aggressive influences, high acidity, retains its integrity for a long time, does not decompose.
Many gardeners are familiar with vermiculite, it is often used as a mulching material, a component of a substrate, an aerator. In construction work, it is not used so often, although properties and physical indicators are of great interest for this field of activity. Among the mastered areas:
• production of paints and varnishes, soft roofing;
• when arranging a "warm floor" system;
• as a filler for heat-insulating and decorative plaster mixes;
• for insulation of individual zones in the house (chimney, floor, roof, etc.);
• as a component of a screed mixture.
Vermiculite has good insulating characteristics, so it is used in regions with a warm climate as a backfill in three-layer walls to prevent overheating of the house, and in the northern regions - for thermal protection of housing.
The land in the regions of the middle zone and the Urals freezes over in winter, which often causes cracks in the concrete bowls of the pools. Vermiculite helps to correct the situation. It is poured to the bottom, as well as into the cavity between the bowl and the edge of the trench during construction.
Insulation is produced in the form of backfill, pressed plates, blocks, pipe segments, liners.
Pros and cons of vermiculite
To appreciate the material, you need to familiarize yourself with its advantages and disadvantages.
Among the main advantages of vermiculite:
• environmental friendliness, no toxic substances are emitted during operation when heated;
• low thermal conductivity (0.055–0.098 W / m • ° C);
• fire resistance (operating temperature range from minus 260 ° to plus 1200 °);
• does not shrink over time;
• has good vapor permeability, which excludes the formation of condensation in the room;
• resistance to microbiological processes, rodents and insects show no interest in the material;
Application of expanded clay gravel
| Indicators | Fractions of expanded clay gravel, mm | ||
| 8/20 | 4/10 | 0/4 | |
| Pitched roof insulation | + | ||
| Thermal insulation and the creation of a slope of flat roofs, lawns on terraces | + | ||
| Production of ultra-lightweight concrete and lightweight ceramic-concrete blocks | + | + | + |
| Thermal insulation and sound insulation of floors and ceilings | + | + | |
| Thermal insulation and reduction of the depth of laying of foundations | + | + | |
| Thermal insulation of soil | + | + | |
| Thermal insulation and drainage in earth embankments of roads laid in water-saturated soils | + | + | |
| Hydroponics, creating an optimal microclimate for the root system of plants | + | + | |
| As a dry backfill for GVL floors in order to improve the heat and sound insulation capacity of the floor | + | ||
| Warm solution production | + | ||
| Production of facade and paving slabs | + |
Expanded clay will also be useful to those who lay heating networks near their homes. First, you will be sure that your pipes are heating you, and not the cold earth. Secondly, in the event of an accident, you will not have to dig long and tediously in search of a leak. Thirdly, after a successful repair, nothing prevents you from using the material again, while it will not lose its properties.
Expanded clay can be used not only in construction. With its help, the paths at the summer cottage are landscaped and even the yield of fruit trees is increased, creating a kind of drainage system for their roots.The same applies to indoor flowers and plants. For these purposes, expanded clay is used smaller in size.
The use of expanded clay when pouring the foundation as a concrete filler is not recommended. In this case, it is better to use any crushed stone, even crushed stone, even granite. Expanded clay is bad in this quality in that it has smooth rounded edges, and this does not prevent the occurrence of work on shear (shear-break) of the concrete mass. And the foundation should precisely exclude cracks (shifts) of the tape in the cross section.
Vermiculite and its uses
Initially, the material is mica flakes. When heated to 800 ° C, the particle swells and takes the form of a worm. After that, the granules are crushed to a certain size. Vermiculite cavities are open and active. It absorbs moisture, increasing in volume up to 5 times. Centers of activity are created on the surface, the composition is used as a catalyst for chemical processes. This is the main difference between vermiculite and perlite. The material has different shades, since not only mica is used during melting, but also the accompanying rocks in the deposit. Vermiculite is neutral. In construction, sand is used to create lightweight concrete mixes, structures and as an insulating material.
Perlite and vermiculite belong to the group of inorganic soil improvers. Their main advantage is that they are now very easy to purchase in any garden center. And therefore, with their help, you can quickly improve your affairs, that is, quickly improve the performance of soil intended for transplanting plants or sowing seedlings.
Scope of expanded clay
In addition, expanded clay is also used as an insulation, but it must be a highly porous material, and before using it as a backfill insulation, calculations that are not very complicated, but accessible only to specialists, should be made. Regarding its capabilities in the field of heat saving, we can only say that as a filling option, it loses to other heaters. The estimated thickness of the expanded clay backfill with a density of 600 kg / m3 is approximately 40 cm. This is not entirely effective.
At the same time, used in the manufacture of expanded clay concrete blocks, it significantly increases their heat-saving characteristics.
Expanded clay is actively used in the construction of a dry screed. Now this method is very popular, as it allows you to get a solid base for laminate, linoleum, cork in the shortest possible time, literally back.
Also, due to its unique properties, including resistance to moisture and frost, it is actively used for filling the foundation during the construction of various buildings and structures. This makes it possible to reduce the depth of the foundation by almost 2 times - from 1.5 m to 0.8 m, which leads not only to savings in building materials, but also to prevent freezing of the soil near the foundation of the building. The latter is fraught with distortion of the doors and window frames of the building.