Key Features
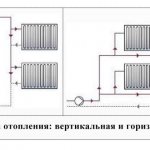
The vertical scheme differs from the horizontal analogue, first of all, by insignificant heat losses. This feature is due to the carefully thought-out layout of the main pipes, which function as risers.
Interestingly, this technique owes its appearance to new building standards in the country. Initially, it was not widespread due to certain nuances of the installation. The matter radically changed when five-story Khrushchev buildings began to be actively built in the USSR, the area of apartments in which was not large, and therefore there was no need for horizontal wiring. In order to save money, a vertical method was created, characterized by a number of nuances:
- Several risers with a circulating coolant run vertically, to which radiators are connected;
- Each of the radiators can be adjusted separately;
- The coolant enters the premises through a separate circuit.
What should you prepare for?
If we talk about private cottages, then such a heating layout can be used there, but the owners need to prepare for a meeting with some difficulties. An example of such a problem is that most batteries on the modern market are focused on connecting to horizontal systems, have an appropriate arrangement of nozzles, technological holes and sections. Thus, the circuit, ideally, needs special radiators oriented specifically towards vertical mounting.
Another problem follows from this feature. As you know, it is better to mount radiators closer to the floor, this will allow you to establish effective air exchange without unnecessary effort. Cold air, according to the laws of physics, will go down, and heated air will rise up. It is extremely difficult to install a vertical radiator in this way, as a result of which heating is insufficient.
However, the downsides do not end there. The described problem can still be solved by slightly increasing the length of the pipes leading to the radiator. If we adhere to the classical implementation of the scheme, then another drawback appears. It consists in the fact that vertical tubular radiators are clearly tied to the laid risers. If the room does not differ in a large area, then the tenants will not feel any discomfort. If the area of the room is about 40 squares with 2 external walls, then it will not do without installing two risers at once, otherwise it will be quite cold. So, vertical wiring of the heating system of a modern apartment building is beneficial in the following cases:
- The number of floors is greater than or equal to five;
- Each separate room has a small area;
- Adequate wall insulation.
If we talk about metering heat energy, it is recommended to install the meter directly on the riser.
Read in more detail: Diagram and installation of a two-pipe heating system.
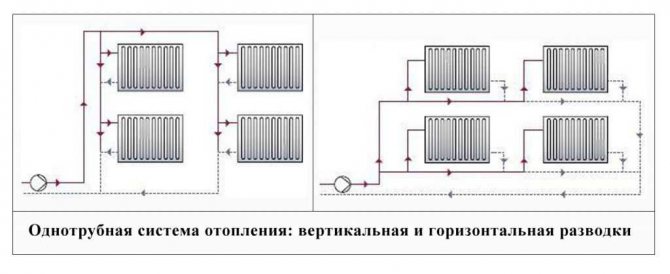
General diagram of a one-pipe heating system (Leningrad)
The figure shows a diagram of a one-pipe wiring system:
The following diagram also shows a one-pipe system, but with two circuits, each of which bypasses on two sides of the room:
Why are two contours made? Apparently, the room is large, and in order not to "plant" many radiators on one circuit, they were divided into two. If it's not entirely clear, then just read the article to the end and pay attention to the disadvantages of one-pipe heating systems.
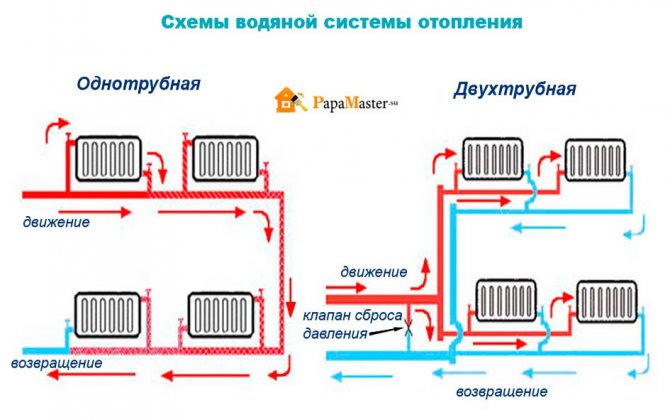
In a one-pipe heating system, there is no division of the pipeline into supply and return.The radiators are connected in series here. And the coolant moves in an annular loop.
One-pipe heating system: diagram for connecting radiators and the movement of the coolant through the pipeline
In large buildings, most often the wiring to the apartment is done using a two-pipe system, and the wiring across the floor is done using a single-pipe system:
Coolant distribution in large buildings
In a one-pipe system, as in a two-pipe system, top and bottom routing can be used.
Choosing the number of pipes
The scheme may assume the presence of one or two pipes:
- The option with one pipe implies that the circulation of the coolant occurs in a closed loop, and the radiators are connected in series. This design feature leads to the fact that the temperature of the last battery will be lower than that of the first devices. Nevertheless, with a small length of the contour, this drawback is naturally corrected. As an additional way of adjustment, you can use the taps between the radiator pipes. The minimum volume of materials for the formation of the system, no need for a circulation pump, a small volume of circulating coolant - these properties can be attributed to the advantages of the technology.
- The two-pipe scheme is based on the installation of two circuits. The first is used to supply the coolant to the radiators, while the second sends the cooled water to the boiler for new heating. When laying, it must be remembered that the pipes must go next to each other, because the radiators are connected in parallel. An additional pipe increases the total volume of the coolant used, often its flow by gravity is impossible, and therefore it is necessary to install a circulation pump. However, with some inconveniences of installation, the system is more reliable than the first option, since the formation of an air lock is excluded.
Horizontal option


For the sake of completeness, it is worth considering the horizontal wiring technique. Its advantages are as follows:
- In the event of an emergency, it is possible to disconnect only the damaged battery. The method is also convenient when changing heating devices in a separate apartment, there is no need to overlap a whole riser.
- It is possible to install energy meters in each apartment, thanks to which residents will be able to adjust the operation of the batteries so that it is both economical and contributes to the formation of an optimal microclimate. For example, during a long business trip or vacation, the room temperature is artificially lowered.
- The technique is independent of the rest of the apartments in the house, and therefore the owner equips the heating in full accordance with personal requirements. There are no risers in the apartment, and individual pipes can be laid in niches, which is valuable in the formation of designer interiors.
- This technology is believed to be more durable.
- Pipes are not laid in walls, but in special niches and corrugations. This approach is optimal from the point of view of maintainability, the lightweight structure can be easily disassembled to get to the emergency area.
Thus, a residential building can be supplied with heat according to any of the described schemes. In order to make the best choice, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances, positive and negative aspects of decisions. Even the vertical version, which, as it may seem, is inferior to the horizontal analogue, in a multi-storey building guarantees effective heating with a small financial investment at the installation stages.
Horizontal and vertical distribution of heating in an apartment building in 2020
The level of heat supply directly depends on the type of wiring of the heating system in an apartment or house.The most common schemes are one-pipe and two-pipe horizontal heating systems.


Heating system device
In any apartment, all elements of the heating system are connected in one way or another. The pipeline can be routed vertically or horizontally.
In the first case, the main lounger is in the basement. Risers of smaller diameter depart from it, to which pipes and radiators in the apartment are connected. The main advantage of vertical wiring is its cheapness and simplicity.
A single pipe vertical system can be top or bottom wired. Both types have their own technical features. When installing a single-pipe vertical system with top piping, the supply pipeline is laid in the attic or on the technical floor. From the lounger, the coolant is supplied to the apartments through the series-connected risers.
Such a system is static. Scaling it by changing the number of radiators and installing regulators will not work. It is capable of saving pipes during installation, but requires the installation of a large number of heating devices. Single-pipe vertical systems are well suited for projects with natural circulation of the heating medium.
The two-pipe system with bottom piping has a supply pipe and a return pipe. They are laid on the floor surface or in the floor, for example, in a screed. When implementing such a system, the coolant enters each battery independently. Such a scheme is not devoid of nuances. Each radiator must have a tap through which air can be deflated.
Unlike one-pipe systems, two-pipe systems are controlled schemes. Communications built in a similar way allow you to turn off any heating device in the network. Excessive consumption of radiators is not typical for them, but the total length of the pipeline will be much greater in comparison with the one-pipe scheme. In apartment buildings, the two-pipe system has another nuance. It is almost impossible to install an individual heat meter here. And the use of general house heat meters is beneficial mainly for residents of the first floors.
The basis of the horizontal distribution is the supply riser that runs through all floors. Sun loungers are connected to the riser, supplying heat to individual apartments. The use of horizontal wiring requires careful insulation of the riser, since significant heat loss occurs here. To reduce heat losses as much as possible, risers are often installed in specially equipped mines.
Single-pipe schemes have a narrow scope - heating large-area rooms. Therefore, they are almost never installed in residential buildings. Horizontal two-pipe system
well suited for providing heat to apartment buildings.
The installation of a two-pipe heating system, in general terms, is as follows:
- From the main supply riser, a supply pipe and a return pipe are laid on each floor, as well as radiators are connected.
- All radiators, without exception, are fitted with shut-off valves.
An important advantage of the scheme is the ability to connect / disconnect heat by floor. Loungers can be laid in the floor screed. This arrangement allows the use of radiators with bottom connections. All this has a good effect not only on heat supply, but also on the aesthetic appeal of apartments. It should be noted another important fact - the possibility of installing individual heat meters.
For all its undeniable merits, the system is not perfect. The difficulty lies in the need to install expansion joints with a significant length of the main line. The operation of the system as a whole is also becoming more complicated, since the installation of shut-off valves and air valves is required on each radiator, without exception.
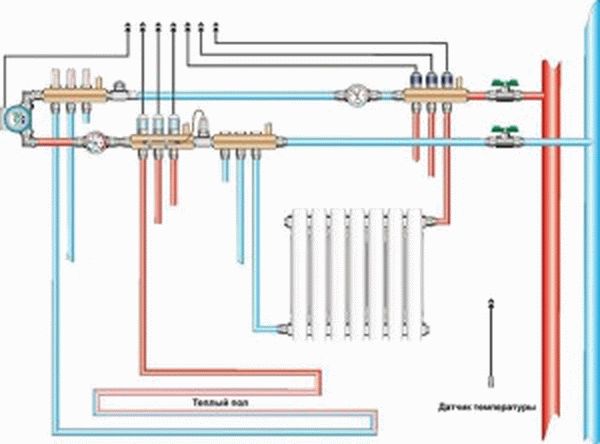

Heating wiring diagram in a private house
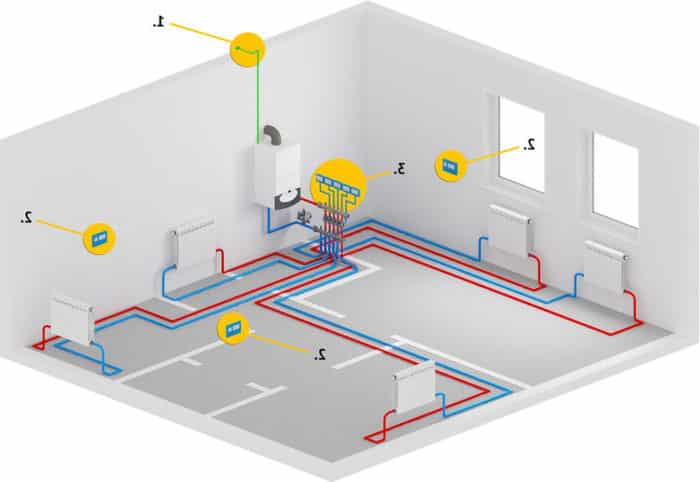
Separately, it is worth talking about another popular wiring scheme - this is a two-pipe collector floor system. Its peculiarity lies in the installation of supply and return collectors on each floor. As in the case of the already described variant, the heart of the system is the common supply riser. With a large number of consumers in the house, it is allowed to install several risers. On each floor, two collectors are mounted - supply and return, and from them there are pipelines that supply the coolant to the radiators.
Unlike traditional options, the collector floor scheme has a significant length of the pipeline. Considering that metal-plastic pipes are used for the installation of the circuit, the implementation of such a project turns out to be more expensive than conventional options.
Important! Despite this drawback, collector circuits from the point of view of operational features are much more efficient and simpler than other options. This makes them more and more popular not only in multi-storey, but also in individual construction.
The two-pipe collector system guarantees an even supply of heat to all rooms. For comparison, it is worth remembering the principle of operation of one-pipe circuits. In them, the supply and removal of heat is carried out through one pipe, and the radiators are connected in parallel. As it moves through the pipeline, the coolant cools down. As a result, the farther the radiators are from the supply pipe, the colder the water in them, and, as a consequence, the lower the air temperature in the room. It is impossible to install regulators in such connection schemes. Therefore, even within the same apartment, it is impossible to achieve uniform heat.
Two-pipe schemes make it possible to minimize this disadvantage. The cooled coolant is discharged from the system via the return line. Water does not cool down when moving from radiator to radiator, which means that all rooms will have approximately the same temperature. Such thermal indicators provide the most comfortable microclimate in the apartment. We must not forget that temperature controllers can be installed in such systems. This provides not only comfort, but also savings and efficient use of funds. In general, the installation of an expensive collector circuit pays off within 2-3 heating seasons.


Installation of heating systems
Important differences between two-tube beam (collector) systems are:
- Flexibility and scalability of the scheme.
- Possibility of installing thermostats on each radiator.
- The need to ensure forced circulation of the coolant using circulation pumps.
- Each circuit is a separate system with additional equipment and automation.
- Installation of air vents on radiators is not required.
- High system reliability, reducing the number of accidents and leaks.
- High resistance to water hammer.
- Aesthetic issues
This is interesting: The schedule of cleaning the entrances in an apartment building in 2020
We can talk about the economic and operational advantages of horizontal two-pipe collector systems for a very long time, but one cannot fail to note their one more advantage - aesthetics. The modern person values comfort. Even inexpensive repairs are done, if not with the involvement of a designer, then at least using the latest design trends. The presence of risers throughout the apartment does not coexist well with modern design. In old houses, the issue of risers is aggravated by another significant problem - constant smudges, leaks that can kill any, even the best and most expensive repairs.
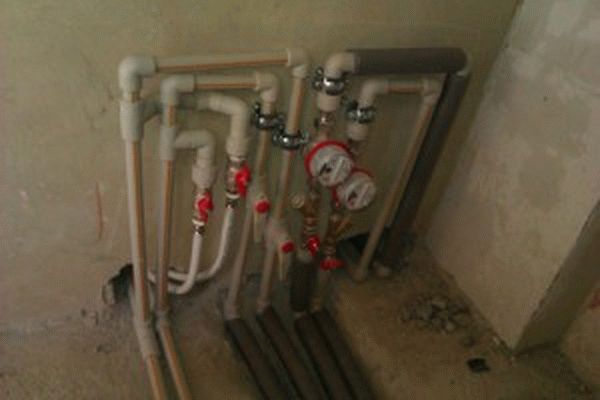


In two-pipe manifold schemes, all pipelines are laid in the floor screed. They not only do not spoil the apartment - they are absolutely invisible.Laying pipes in a screed is possible thanks to the use of modern materials - plastic and metal-plastic. They are not subject to corrosion, are not afraid of low temperatures and even freezing of the coolant.
Horizontal beam patterns also allow you to provide really high comfort in every room due to the possibility of installing heat regulators. The temperature of the house is regulated depending on the weather outside the window. The result is a highly energy efficient system.
Among all existing schemes for installing heating networks, the horizontal beam two-pipe system remains the best option. Despite the higher cost of installation, it is becoming more and more popular not only in multi-storey, but also in private housing construction. Such popularity of collector circuits is due to the unique combination of excellent technical, operational, economic and aesthetic performance.
Homes can use horizontal and vertical heating systems. In modern high-rise construction, horizontal wiring is increasingly used, which demonstrates good technical, aesthetic and operational characteristics. This article will consider the horizontal layout of the heating system.
Horizontal heating distribution has a number of advantages:
- High degree of heat transfer control... In such a scheme, the heat consumption is very easy to monitor due to the automatic remote control.
- The ability to individually configure each site... On any part of the circuit, you can adjust the temperature separately, depending on the specific needs of the room.
- Concealed gasket option... The horizontal heating system is perfect for hidden installation, which allows you to visually relieve the room and thereby improve its interior.
- Reliability... With the use of good components and correct installation, a horizontal system can work without problems for several decades.
Of the shortcomings, only the following points can be highlighted:
- Sometimes it becomes necessary to manually configure the system;
- In the event of mechanical damage, serious problems arise with the system.
Horizontal and vertical heating systems have a lot of differences, so you need to study them in detail to choose the right design. Further we will focus only on the horizontal system.
There are several types of horizontal routing:
- One-pipe;
- Two-pipe;
- Two-pipe collector.
Each scheme needs to be considered in more detail.
In such a system, there are several heat sources through which the heating pipes pass. The coolant moves through such a system and gives off heat to devices located in certain sections of the circuit. Single-pipe horizontal heating in an apartment building has good efficiency and is relatively low cost.
The advantages of such a system are as follows:
- Minimum cost;
- Ease of installation;
- Wear resistance and long service life;
- The ability to fully warm up a building of any area.
- The ability to adjust the temperature on each individual device is limited;
- Weak resistance to mechanical damage.
A key feature of single-pipe wiring is the need to gradually increase the size of the radiators in order of their distance from the heat generator - this rule allows you to balance the heat transfer. In the case of a long system, heating collectors will have to be installed more often so that the coolant does not have time to lose temperature.
Such a horizontal distribution of heating in an apartment building, as the name implies, includes two main highways, along one of which the coolant moves forward, and along the second it returns to the heat generator. Heat transfer is carried out by radiators, which are installed under windows or near walls facing the north side, because the most noticeable flows of cold emanate from them.
The two-pipe system must be completed with shut-off valves. These elements allow, if necessary, to disconnect individual parts of the system without stopping the entire heating circuit. In addition, expansion joints are needed that neutralize the negative effects of pressure. A properly assembled system can normally withstand maximum pressure and water hammer, and will not freeze even at negative temperatures.
Of the advantages of such a system, it can be noted:
- No temperature difference between inlet and outlet;
- Can be used in buildings of any configuration;
- The ability to turn off a separate section of the circuit without completely stopping the system
The main and most noticeable drawback is the difficulty of fine tuning the temperature in the event that the system has a large number of branches - the vertical wiring of the heating system in this regard is somewhat simpler, but not as effective.
This horizontal distribution scheme has a closed structure, consisting of several branches, each of which is supplied to its own devices. As a rule, for such a wiring, polymer or polyethylene pipes are used - their strength and performance characteristics are quite enough for the normal operation of the system, and they are cheap.
In such a system, the connection goes directly to the collector, thereby ensuring an even distribution of heat energy throughout the entire heated area. With this scheme, the supply and return circuits work independently of each other. The heating medium passes through the radiators and is sent back for the next heating cycle. The result is a closed system, the operation of which is automatically regulated.
The horizontal layout of the parallel type is quite suitable for the arrangement of any projects, since the design includes several simple elements that are easy to customize. What is important, when using such a scheme, the radiators do not need to be equipped with valves for air exhaust.
The system must have a good circulation pump - heating operation in the considered variant of horizontal wiring is possible only with a pump. The distribution board, in which all the equipment is located, is usually placed in corridors or bathrooms, and for multi-storey buildings, the option with placing the shield in the basement is quite satisfactory.
It's interesting: Certificate of title to land 2020
The list of advantages of such a layout is as follows:
- Low cost of arrangement;
- Possibility of hidden laying;
- Possibility of combining several separate elements into one system;
- Possibility of full heating of large areas;
- Lack of water hammer.
There are also disadvantages, and among them the most prominent is:
- Complexity of installation;
- The need to use pipes of the same diameter.
During installation, it is imperative to pay attention to the quality of the thermal insulation of the heating system, especially the riser. It will not be superfluous to equip an insulated box intended for installing a riser. In any case, it is better to entrust the design and installation of a two-pipe collector circuit to specialists who have experience in carrying out such work.
The horizontal layout of the heating system has a number of positive qualities and is well suited for a wide variety of conditions.The arrangement of such a wiring in a complex configuration cannot be called simple, so it is worth hiring specialists for this work.
Heating distribution - This is a diagram of the location of heating devices and pipes connecting them. The type of wiring significantly affects the efficiency of the heating system, its efficiency and aesthetics. The main types of heating wiring:
- One-pipe and two-pipe
- Horizontal and vertical
- Dead-end and with oncoming movement of the coolant
- Heating with top and bottom piping
A specific heating system must have one of two characteristics from all four groups of characteristics. For example, the wiring can be single-pipe horizontal with upper heating wiring and dead-end movement of the coolant, or it can be two-pipe horizontal with lower wiring and counter movement of the coolant, etc. Consider these schemes based on the possibility of installing a heat meter for apartment heat metering.
It was most widespread in the Soviet Union in the period from 1960 to 1999 due to the cheapness and ease of laying engineering communications. The engineers of that time did not think too much about the problems associated with its applications.
Such a wiring system is common mainly in old houses before the beginning of 2000. In such houses, the supply line runs along the technical floor or in the basement of the house, and the coolant enters each battery sequentially (gradually cooling down) along vertical risers.
Advantages: low pipe consumption. Because of it, some unscrupulous developers continue to create houses with this layout to this day. Disadvantages: the impossibility of turning off individual heating devices, and the impossibility of adjusting them, excessive consumption of heating devices, and large heat loss of the coolant. What does it mean impossibility of installing apartment heat meters.
If, with a single-pipe wiring, the coolant moves along one integral circuit through all radiators, then with a two-pipe system there are two risers: from one the coolant enters the radiator, and leaves the other.
With a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring, the supply and return main pipelines pass in the floor of the lower floor of the building or in the basement, and the coolant flows independently into each radiator.
Benefits: good regulation of the heating system, the possibility of a separate shutdown of each heating device, no overspending of heating devices.
Disadvantages: the length of the pipelines increases in comparison with the one-pipe scheme, the practical impossibility of installing apartment heat meters.
- Metrological problem... The heat meter is considered to be working correctly when the temperature difference of the coolant between the inlet and outlet (supply and return) is more than 3 ° C. The heat consumption of 1 radiator, depending on the size, finning coefficient and heating area, is from 0.5 ° C to 2 ° C.
- The need to install heat meters for each riser, which is expensive and very troublesome. In the future, the user will have to manually take readings from each of the meters, add them up and submit them to the heat supply organization. Risk of mathematical error and human error. High verification costs, which partially offsets installation savings and increases return on investment.
- The scope of application of the device is written in the passport of the heat meter... For example, for Ultraheat T-230 - “The meter is used to meter the energy consumption in apartments, cottages, apartment buildings and small business facilities ... the temperature is measured in the supply and return pipelines .... etc.". Nowhere is there a word about the battery, and there is no supply and return pipelines on the battery.
All of the above reasons are arguments for heat supply organizations not to take into commercial accounting heat meters installed in houses with a vertical distribution of the heating system.
The only way to organize heat metering in a vertical heating layout is with heat distributors.
In this case, the main pipeline goes through all the floors, on each floor there are heating niches, in which, through the outlets from the risers, each of the rooms on the floor has its own connection (through horizontal pipes located in the floor) to the general heating system.
Horizontal single-pipe schemes they are rarely used, they have a rather narrow field of application and they are not used for heating apartment buildings, so here we will consider the options for two-pipe wiring.
Looking at the figure, you can see that pipelines are laid from the main supply and return risers along the perimeter of the room in the floor to each heating device. Each apartment has its own heating system input. A heating niche with main risers can be located both in the apartment itself and in public corridors (on the floor of the location of the apartment or 1 floor below the location of the apartment), depending on the design of the indoor heating distribution.
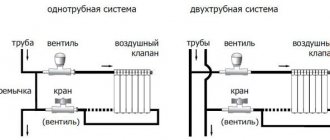
Each radiator is equipped with Mayevsky taps for air release and often automatic air collectors are installed on each of the floor heating outlets.
This wiring scheme is the most common in multi-storey residential buildings due to the ease of execution and affordability for developers.
Benefits: similar to a two-pipe vertical system, plus there are no risers on each heating device (except for main risers). It is possible to turn off the heating system by floor and use radiators with bottom connection, which, along with the laying of main pipelines in the floor structure or in the baseboard, allows you to minimize the number of open pipes and improve the aesthetics of the interior of the premises.
This is interesting: Intra-building engineering systems are 2020
In such heating systems, apartment heat meters can be used.
Disadvantages: the need to use pressure compensators with high number of storeys of buildings, complication of operation due to the presence of air valves on each heating device, high heat loss in the floor and through the enclosing structures.
In the heating niches at the outlets from the main pipeline (riser) on each floor there are collectors - supply and return. From the collectors, the supply and return pipelines under the floor are fed individually to each radiator in the apartment.
Benefits: are similar to two-pipe horizontal heating systems with a higher reliability of the system as a whole, a high level of energy efficiency and lower energy consumption for heating.
Disadvantages: long length of supply pipelines, high cost.
The beam layout is innovative for our country. Today such a system is gaining more and more popularity in construction.
In such heating systems, apartment heat meters can be used.
When distributing heating pipes, various schemes are used that determine the features of the functioning of the system, material costs, and methods for connecting radiators. The heating wiring diagram in a modern apartment building, as a rule, is carried out according to a vertical technology that most fully meets the requirements of non-standard layouts.
The vertical scheme differs from the horizontal analogue, first of all, by insignificant heat losses. This feature is due to the carefully thought-out layout of the main pipes, which function as risers.
Interestingly, this technique owes its appearance to new building standards in the country. Initially, it was not widespread due to certain nuances of the installation. The matter changed dramatically when five-story Khrushchev buildings began to be actively built in the USSR, the area of apartments in which was small, and therefore there was no need for horizontal wiring. In order to save money, a vertical method was created, characterized by a number of nuances:
- Several risers with a circulating coolant run vertically, to which radiators are connected;
- Each of the radiators can be adjusted separately;
- The coolant enters the premises through a separate circuit.
If we talk about private cottages, then such a heating layout can be used there, but the owners need to prepare for a meeting with some difficulties. An example of such a problem is that most batteries on the modern market are focused on connecting to horizontal systems, have an appropriate arrangement of nozzles, technological holes and sections. Thus, the circuit, ideally, needs special radiators oriented specifically towards vertical mounting.
Another problem follows from this feature. As you know, it is better to mount radiators closer to the floor, this will allow you to establish effective air exchange without unnecessary effort. Cold air, according to the laws of physics, will go down, and heated air will rise up. It is extremely difficult to install a vertical radiator in this way, as a result of which the heating is insufficient.
- The number of floors is greater than or equal to five;
- Each separate room has a small area;
- Adequate wall insulation.
If we talk about metering heat energy, it is recommended to install the meter directly on the riser.


Read in more detail: Diagram and installation of a two-pipe heating system.
The scheme may assume the presence of one or two pipes:
- The option with one pipe implies that the circulation of the coolant occurs in a closed loop, and the radiators are connected in series. This design feature leads to the fact that the temperature of the last battery is lower than that of the first devices. Nevertheless, with a small length of the contour, this drawback is naturally corrected. As an additional way of adjustment, you can use the taps between the radiator pipes. The minimum amount of materials for the formation of the system, no need for a circulation pump, a small volume of circulating coolant - these properties can be attributed to the advantages of the technology.
- The two-pipe scheme is based on the installation of two circuits. The first is used to supply the coolant to the radiators, while the second sends the cooled water to the boiler for new heating. When laying, it must be remembered that the pipes must go next to each other, because the radiators are connected in parallel. An additional pipe increases the total volume of the coolant used, often its flow by gravity is impossible, and therefore it is necessary to install a circulation pump. However, with some installation inconveniences, the system is more reliable than the first option, since the formation of an air lock is excluded.
For the sake of completeness, it is worth considering the horizontal wiring technique. Its advantages are as follows:
- In the event of an emergency, it is possible to disconnect only the damaged battery. The method is also convenient when changing heating devices in a separate apartment, there is no need to overlap the entire riser.
- It is possible to install energy meters in each apartment, thanks to which residents will be able to adjust the operation of the batteries so that it is also economical,and contributed to the formation of an optimal microclimate. For example, during a long business trip or vacation, the room temperature is artificially lowered.
- The technique is independent of the rest of the apartments in the house, and therefore the owner equips the heating in full accordance with personal requirements. There are no risers in the apartment, and individual pipes can be laid in niches, which is valuable in the formation of designer interiors.
- This technology is believed to be more durable.
- Pipes are not laid in walls, but in special niches and corrugations. This approach is optimal from the point of view of maintainability, the lightweight structure can be easily disassembled to get to the emergency area.
Thus, a residential building can be supplied with heat according to any of the described schemes. In order to make the best choice, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances, positive and negative aspects of decisions. Even the vertical version, which, as it may seem, is inferior to the horizontal analogue, in a multi-storey building guarantees effective heating with a small financial investment at the installation stages.
»
Other
How to get the register of owners of MKD for free in 2020
Read more
Excellent article 0