Choosing a profile pipe for supporting structures on their own, the customer understands the importance of accurate calculations of parameters and loads. In this article we will try to figure out whether it is worth saving on calculations.
With the arrival of summer, the construction season begins for companies, owners of cottages, summer cottages. Someone builds a gazebo, greenhouse or fence, other people block the roof or build a bathhouse. And when a question arises before the customer about the supporting structures, the choice is more often settled on a profile pipe because of the low cost and bending strength with low weight.
What is the load on the profile pipe
Another question is how to calculate the dimensions of a profile pipe so as to get by with "little blood", to buy a pipe that is suitable for the load. For the manufacture of railings, fences, greenhouses, you can do without calculations. But if you are building a canopy, roof, visor, you cannot do without serious load calculations.
Important! Every material resists external stress, and steel is no exception. When the load on the profile pipe does not exceed the permissible values, the structure will bend, but withstand the load. If the weight of the load is removed, the profile will return to its original position. If the permissible load values are exceeded, the pipe is deformed and remains so forever, or it breaks at the bend.
To eliminate negative consequences, when calculating a profile pipe, consider:
- dimensions and section (square or rectangular);
- structural stress;
- strength of steel;
- types of possible loads.
Classification of loads on a profile pipe
According to SP 20.13330.2011, the following types of loads are distinguished by the time of action:
- constants, the weight and pressure of which does not change over time (the weight of parts of a building, soil, etc.);
- temporary long-term (weight of stairs, boilers in the cottage, plasterboard partitions);
- short-term (snow and wind, weight of people, furniture, transport, etc.);
- special (earthquakes, explosions, car blows, etc.).
On a note!
For example, you are building a canopy in the yard of a plot and using a profile pipe as a supporting structure. Then, when calculating the pipe, take into account the possible loads:
- canopy material;
- snow weight;
- strong wind;
- possible collision of the car with the support during unsuccessful parking in the yard.
To do this, use SP 20.13330.2011 “Loads and Impacts”. It contains the maps and rules necessary for the correct calculation of the profile load.
Design schemes of loading on a profile pipe
In addition to the types and types of load on the profiles, the types of supports and the nature of the load distribution are taken into account when calculating the pipe. The calculator calculates using only 6 types of calculation schemes.
Maximum loads on the profile pipe
Some readers ask the question: "Why do such complex calculations if I need to weld the railing for the porch." In such cases, there is no need for complex calculations, taking into account the nuances, since you can resort to ready-made solutions (tab. 1, 2).
| Table 1. Load for a square shaped tube | ||||||
| Pipe dimensions, mm | ||||||
| 1 meter | 2 meters | 3 meters | 4 meters | 5 meters | 6 meters | |
| 40x40x2 | 709 | 173 | 72 | 35 | 16 | 5 |
| 40x40x3 | 949 | 231 | 96 | 46 | 21 | 6 |
| 50x50x2 | 1165 | 286 | 120 | 61 | 31 | 14 |
| 50x50x3 | 1615 | 396 | 167 | 84 | 43 | 19 |
| 60x60x2 | 1714 | 422 | 180 | 93 | 50 | 26 |
| 60x60x3 | 2393 | 589 | 250 | 129 | 69 | 35 |
| 80x80x3 | 4492 | 1110 | 478 | 252 | 144 | 82 |
| 100x100x3 | 7473 | 1851 | 803 | 430 | 253 | 152 |
| 100x100x4 | 9217 | 2283 | 990 | 529 | 310 | 185 |
| 120x120x4 | 13726 | 3339 | 1484 | 801 | 478 | 296 |
| 140x140x4 | 19062 | 4736 | 2069 | 1125 | 679 | 429 |
| Table 2. Load for rectangular shaped pipe (calculated for the larger side) | ||||||
| Pipe dimensions, mm | ||||||
| 1 meter | 2 meters | 3 meters | 4 meters | 5 meters | 6 meters | |
| 50x25x2 | 684 | 167 | 69 | 34 | 16 | 6 |
| 60x40x3 | 1255 | 308 | 130 | 66 | 35 | 17 |
| 80x40x2 | 1911 | 471 | 202 | 105 | 58 | 31 |
| 80x40x3 | 2672 | 658 | 281 | 146 | 81 | 43 |
| 80x60x3 | 3583 | 884 | 380 | 199 | 112 | 62 |
| 100x50x4 | 5489 | 1357 | 585 | 309 | 176 | 101 |
| 120x80x3 | 7854 | 1947 | 846 | 455 | 269 | 164 |

It is interesting!
Using ready-made calculations, remember that tables 2 and 3 indicate the maximum load, from which the pipe will bend, but not break. With the elimination of the load (the termination of the strong wind), the profile will regain its original state. Exceeding the maximum load even by 1 kg leads to deformation or destruction of the structure, therefore, buy a pipe with a safety margin that is 2 to 3 times higher than the limit value.
Profile pipes: sizes and prices, purpose and functionality
Square pipes are used in various industries, including the production and installation of metal structures for outdoor and indoor use. There are no special requirements for them in terms of surface quality. A general-purpose profile is produced on the basis of hot-rolled steel strips, the thickness varies in the range of 1.5-5 mm. By functional features or conditions of use, products are classified into the following types:
- metal profiles for general and special purposes;
- products for oil production, gas transportation and geological exploration;
- drilling and casing equipment;
- compressor and pumping equipment;
- water pipes;
- heat-resistant steel products for boiler rooms;
- chemical equipment;
- large highways;
- steel supports with stiffeners for construction;
- durable products for multipurpose purposes.
The use of rolled products is widespread in mechanical engineering and construction, agriculture, communication systems and oil refining. All parameters, including pipe length and wall thickness, are regulated by GOST 13663-86.


Sectional views of profiled pipes
Methods for calculating loads on a profile pipe
To calculate the loads on the profiles, the following methods are used:
- load calculation using reference tables;
- use of the bending stress formula;
- determination of the load using a special calculator.
How to Calculate Load Using Reference Tables
This method is accurate and takes into account the types of supports, the fastening of the profile to the supports and the nature of the load. To calculate the deflection of a profile pipe using look-up tables, the following data is required:
- the value of the moment of inertia of the pipe (I) from the tables GOST 8639-82 (for square pipes) and GOST 8645-68 (for rectangular pipes);
- span length value (L);
- pipe load value (Q);
- the value of the modulus of elasticity from the current SNiP.
These values are substituted into the desired formula, which depends on the anchoring on the supports and the distribution of the load. For each design model of the load, the deflection formulas are changed.
Calculation according to the formula for the maximum bending stress of a profile pipe
The bending stress calculation is calculated using the formula:
where M is the bending moment of the force, and W is the resistance.
According to Hooke's law, the elastic force is directly proportional to the amount of deformation. Now the values for the desired profile are substituted. Further, the formula is refined and supplemented, based on the characteristics of the steel for the profile pipe, load, etc.
You will be interested in:
- manufactures metal structures: Hangars and pre-fabricated structures Canopies made of polycarbonate and corrugated board Classical and forged gratings, sliding gratings such as ...
- A fur coat for a summer residence Eco-friendly thermal insulation Arrangement The old stone house did not keep heat very well and needed insulation. The owners decided ...
- manufactures sliding grilles ...
- The well-being of the building erected on it depends on the correct choice and quality of the foundation. The foundation must be stable, durable, which is achieved ...
Profiled pipes are becoming an increasingly popular building material. It is used for the construction of such building elements as floor, supporting frame, beam.
Such widespread use is associated primarily with the simplicity of construction, operation, maintenance of structures, as well as the low weight of the products themselves. However, it is important to remember that the profile pipe must have increased bending strength, and how to calculate it will be discussed later in the article.
Profile pipes are pipes that have a cross-section different from a circular cross-section. The most common options are rectangular and square products. As already mentioned, the particular popularity of this type is associated with one of its key advantages - the design will have a low weight.
Moreover, the specific shape greatly simplifies fastening to each other and to other surfaces. This type of building products, according to GOST, is made from a wide range of metals and alloys. However, the most commonly used are carbon steel and low alloy steel profiled pipes.
Each metal has an important natural quality - a point of resistance. It can be either minimum or maximum. The latter, for example, is the cause of the deformation of the erected structures, leads to bends and, as a result, to fractures.
When performing a bend, it is important to evaluate characteristics such as size, section, type of product, its density, as well as the rigidity of the material and its flexibility. Knowing all these general properties of metal, one can understand how the structure will behave during operation.
It is important to remember that when you bend the product, the internal parts of the structure are compressed, their density increases, and they themselves decrease in size. The outer layer, accordingly, becomes longer, less dense, but more stretched.
At the same time, the middle sections retain their original characteristics even after the completion of the process. Hence, it should always be remembered that in during bending, tension will necessarily arise even in areas as far as possible from the neutral zone
... The maximum pressure will be in those layers that are very close to this very neutral axis.
Electromechanical pipe benders
These devices are used when pipes have different cross sections. They differ from their counterparts in the very high accuracy of the bend radius and the unnecessary use of human physical strength. These devices are also distinguished by a very high cost, which indicates their professional purpose.
Electromechanical pipe benders can bend products of large diameters, and this indicator is limited only by the size of the device itself, the force that is created during bending. The bending radius of steel pipes must fully comply with the standards. They can be observed using special templates that can be easily replaced during the bending process.
Permissible bending radii based on material strength
GOSTs regulate in great detail both the properties and characteristics of the elements, and the procedure for transformation. This includes the minimum bend radius of the profile pipe. It is determined depending on the conditions under which the bend is carried out. When bending using sand with which it is packed, or through heating, the outer diameter should start from 3.5DN.
If the master has the ability to apply, which allows the necessary operations to be carried out without heating or other additional actions, then in this case the diameter should be at least 4DN.
If you want to make a bend that would be steep enough, for example, to make a bent sewer or pipeline, then the diameter should be at least 1DN, since bending will be in other ways, mainly using high temperatures.
Of course, the values provided for by state standards can be slightly reduced, then you need to very carefully calculate the bending strength of the pipe. If the method of bending makes it possible to be sure that the wall thickness decreases by 15% from the initial one, then in this case deviations from GOST are possible, and the bending itself can be carried out less than the indicated values, which will not have a significant effect on the strength in the future.
Material resistance
Every material has a point of resistance. This is taught in technical educational institutions. Upon reaching the specified point, the material may burst, and the structure, accordingly, crumble.Thus, when the reliability of any building structure is calculated, it is taken into account not only what are the dimensions of the structural elements, but also what material they are made of, what are the features of this material, what kind of bending load it can withstand. The environmental conditions in which the structure will be located are also taken into account.
Strength calculation is carried out according to normal stress. This is due to the fact that stress spreads unevenly over the surface of a rectangular pipe.
It will be different at the point of pressure and at the edges of the pipe. This must be understood and taken into account.
It should be added that profile pipes can be tested for bending and in practice. There is special equipment for this. In it, the pipe bends, its stress is recorded. The stress at which the pipe breaks is noted.
The need for practical experimentation is related to the following:
- in practice, there may be deviations from GOSTs. If the building is large-scale, then you should not trust the numbers. Everything needs to be checked empirically;
- if the pipes are not manufactured at the factory, for example, welded from a metal corner, then, based on theoretical calculations, it is impossible to understand what bending stress the pipe will withstand.
Applied formulas and tables
In order to successfully, without unforeseen complications, perform the calculation of the pipe for deflection, you need to calculate the size of the part in length. This value is calculated using a simple formula that looks like:
L = 0.0175 × r × α + I
In this expression, the main indicators are represented by the following letter expressions:
- r is the bending radius of the profile pipe (mm);
- α - corresponds to the angle that you ultimately want to get;
- I is a distance of 100/300 used when working with special equipment to hold the workpiece.
When calculating a pipe for deflection, an important stage in the work is the calculation of the bendable element.
Watch the video
When making an assessment, we must estimate the size of the area that needs to be bent. The formula for this is extremely simple, it looks like this:
U = π × α / 180 (r + DH / 2)
Here, the elements included in the formula can be represented as follows:
- π in this case is taken equal to 3.14;
- α - is the bend angle, expressed in degrees;
- r - bending radius (mm);
- DH is the outer diameter.
For the convenience of the master and for the greatest safety during work, as well as during the operation of erected structures made of copper and brass, GOSTs contain the lowest indicators for the main characteristics used to calculate the bending strength of a profile pipe. This information is contained in GOSTs No. 494/90, No. 617/90.
For your convenience, the main characteristics required to determine the bending strength of a profile pipe are in the table.
Table 1.
Whereas the previous table mainly contained fixed values for copper and brass elements, the next one will contain data for steel elements. This table allows you to estimate the bending load of a shaped pipe (GOST No. 3262/75).
Table 2.
As already mentioned, wall thickness plays an important role in calculating the bending strength of a square pipe (as well as a round one). That is why the following table makes it possible to simultaneously take into account both the wall thickness and the diameter in the calculations.
Table 3.
Bending Technological Process
As already rightly noted, any deformation of the metal structure causes additional stress on the walls of the structure. On the inner layer, this is due to an increase in the density of the metal due to compression, and not on the outer section, the cause, on the contrary, becomes tension, which reduces the density of the metal.
During bending, the section shape changes as expected. This is true for round, rectangular and square pipes.For the latter two, these changes are not very pronounced, which cannot be said about round ones.
This is how the ring profile becomes oval. It is noteworthy that the greatest change in shape can be observed directly at the place of the fold, and the farther from it, the closer the section will remain to the original shape.
Watch the video
However, it is important to correctly assess the force of impact, the degree of deformation of the pipe in order to avoid unnecessary breaks and bends. For a part with a diameter of up to 20 mm, the degree of oval deformation should not exceed 15%.
With an increase in the profile, the value decreases even more and is only 12.5%. Another important element is the presence of folds (products with thin walls are especially susceptible to this). This factor is very important if the bending structure will serve as a pipeline.
The formed folds reduce the permeability, increase the resistance of the passing fluid, and increase the degree of clogging. So when using a bent pipe precisely for these purposes, it is necessary to carefully approach the choice of the wall thickness of the product.
What is the load on the profile pipe
Calculation of the bending strength of a pipe is reduced to a simple determination of the maximum stress at a particular point in the structure. It is important to understand what material the profile is made of, since each of them has its own stress indicator.
For correct calculations, you need to apply the correct formula. In this case, the provisions of Hooke's law are applied, which state that the elastic force is directly proportional to the deformation. The expression for calculations is as follows:
VOLTAGE = M / W, where:
- M is the value of the degree of bending along the axis along which the force acts;
- W is the bending resistance value taken along the same axis.
How do you know if the calculations are correct?
As stated, each metal or alloy has its own normal stress values. It is the determination of these values that is one of the main tasks that you face when you decide to build a building from a profile.
In order to be sure of the correctness of the results, you need to know several important rules and, of course, follow them.
- Perform all calculations accurately, accurately, without haste. At each stage, one should be guided by the appropriate formulas, not trying to adjust the values to suit those that are convenient for oneself.
- Having calculated the bending strength of the profile pipe, you should ensure that the obtained indicators do not exceed the specified maximum values.
- Take into account the material from which the profile is made, the thickness of the walls, in order to prevent its destruction or deformation, which impedes the functioning of the structure in the future.
- Before performing calculations, it is necessary to schematically depict the future element. Based on this technical drawing, more accurate calculations can be made, which will be insured against errors associated with a misunderstanding of the shape of the structure.
Watch the video
By following all the necessary rules, as well as safety precautions, even a non-professional can be sure that all his results in calculating the pipe bending strength will be correct and the result will be successful. Constant checking of your calculations and control at every stage of the work is the key to the successful completion of the case.
Add to bookmarks
Roman Gennadievich, Omsk asks the question:
Good day! The following question arose: how to calculate the deflection of a profile pipe? That is, I would like to know what maximum load a profile pipe of one size or another can withstand, in order to determine this size. I don't understand this myself, so I ask you to speak in understandable expressions and explain all the designations in the formulas.The bottom line is that I have some ideas for arranging a summer shed, I would like to make it from a steel profile, so you need to know exactly what size to buy it so that you don't have to redo it later. Thanks in advance for your answers.
The expert answers:
Good day! Calculation of profile pipes for deflection is carried out using a simple formula: M / W, where M is the bending moment of the force, and W is the resistance. The essence of its implementation is simple. In this case, Hooke's law applies: the elastic force has a direct proportional dependence on deformation. Therefore, knowing the degree of deformation and the maximum stress value for a given material, you can choose the parameter you need.
Figure 1. Design resistances of the base metal of building structures.
So, M = FL, where F is the deformation, expressed in kilograms, and L is the shoulder of the force, expressed in centimeters. The shoulder is the distance from the attachment point to the point where the force is applied.
It is also necessary to determine the maximum strength (R), for example, for St3 steel it is equal to 2100 kg / square centimeter.
Now, for further calculation, we transform the expression and get: R = FL / W, transform again and get: FL = RW, whence F = RW / L. Since we know the parameters, except for W, then only it remains to be found. This requires the parameters of the profile pipe, that is, a is the outer width, a1 is the inner, b is the outer height, b1 is the inner, and also correctly substitute them in the equalities to find the unknown value for different axes: Wx = (wa ^ 3 - b1 (a1) ^ 3) / 6a, Wy = (ab ^ 3- a1 (b1) ^ 3) / 6b.
If the product has a square section, then the formula becomes even simpler, since now the W index in both directions (horizontal and vertical) will be the same, and the equality itself will be simplified, since the length and width of the profile are also the same.
For these equalities, calculations can be done using a regular calculator. The values for maximum loads are a reference, so it is not difficult to find them on the Internet. In fig. 1 shows a small such table. In it you will find the necessary numbers for different types of steel for deflection, tension and compression - it may come in handy.
22 July, 2020 Specialization: facade decoration, interior decoration, construction of summer cottages, garages. The experience of an amateur gardener and gardener. He also has experience in repairing cars and motorcycles. Hobbies: playing guitar and much more, for which there is not enough time :)
To perform the turn of the pipeline, special fittings are used - angles and tees. However, sometimes there are situations when it is necessary to bend the pipe. As a rule, if a beginner takes on this work, the pipe crumples or even breaks at the bend, so further I will introduce you to some of the secrets of folk craftsmen that will allow you to successfully cope with this task at home.
Benefits of Using Heat Resistant Finned Tubes
To create a heat-resistant layer, the surfaces are coated with magnesium oxide. After annealing, they get:
- increase in heat transfer coefficient;
- high resistance to corrosion;
- long service life;
- increased resistance to temperature drops;
- no need for special care, they can work in any conditions;
- the possibility of using in aggressive environments.
Due to the acquired advantages, heat-resistant finned types have the following advantages:
- High manufacturability of production. The used resistance welding consumes little energy; it does not require special consumables and expensive equipment.
- Turbulent air vortices appear in the spaces between the ribs, which increases the intensity of heat transfer in all areas.
- Through the use of resistance welding, a connection is created between the petals and the base with a low temperature resistance.
- Reducing the thickness of the condensate film. This is due to the use of a heat-resistant coating.As a result, the level of condensation of the carrier vapors decreases.


Pipe bending methods
The need for pipe bending may arise in a number of cases, for example, during the installation of a pipeline, if you need to "bypass" any obstacle. Also, it is often necessary to resort to this operation in the process of manufacturing various metal structures, such as sheds, greenhouses, gazebos, etc.
It should be noted that when it comes to bending pipes, we mean the following types:
Round metal
The bending process of metal workpieces with a circular cross-section is rather complicated, since they are easily deformed, and sometimes even torn. Therefore, when bending is done in an industrial environment, especially if a small radius is required, a pipe bending design is performed before performing this operation.
At home, of course, you will not need an exact formula for calculating a pipe for bending. The only thing you need to determine is the minimum allowable radius. Its meaning largely depends on the way this operation is performed:
- when heating a part packed with sand
- R = 3.5xDH; - using a pipe bending machine
(cold bending) - R = 4xDH; - bending to obtain corrugated folds
(hot bending) - R = 2.5хDH.
You can get a minimum radius equal to two diameters by hot drawing or stamping. However, it is impossible to make such a bend at home.
These formulas use the following values:
I must say that there is a more universal calculation - the radius must be at least five pipe diameters.
So, we figured out the theory a little, now let's move on to practice. As mentioned above, there are several ways to solve this problem. The simplest of them is the use of a special machine - a pipe bender.
True, the price of such a tool is quite high - the cost of a hydraulic machine, which allows bending workpieces up to four inches in diameter, starts at 15,000-16,000 rubles. The cost of a manual pipe bender, which allows you to work with parts with a diameter of up to one inch, is 4,700-5,000 rubles.
If you often have to deal with such an operation, but you do not want to pay big money for a pipe bender, you can do it yourself. On our portal you can find detailed information on how to make a machine for bending profile pipes with your own hands.
However, the pipe bender is not always at hand, moreover, if you need to perform this operation once, then it certainly does not make sense to purchase a tool for this. In this case, you can make a bend with pegs.
This is done as follows:
- first of all, you need to draw a bend radius on a suitable site;
- then metal rods are dug in along the contour. It is desirable to place them as close to each other as possible. For reliability, the rods can be concreted.
Next to the extreme rod, you need to insert another one so that the bent part can fit between them. This is necessary to fix it;
- then you need to pour salt or sand into the bent pipe. In this case, plugs should be hammered into the holes on both sides;
- after that, the part is fixed between the first two rods and then bent around the remaining rods, as shown in the diagram above.
An alternative to this option is to use hooks that are attached to a piece of plywood and form the required radius, as in the photo above. If you want to get a smaller diameter, a wide disc or roller should be used as a template.
I must say that both methods are suitable for parts with a diameter of no more than 16-20 mm. If you want to bend a workpiece with a larger diameter, the bend should be well heated.
If you need to shape non-ferrous metal blanks that have significantly less flexural strength than steel counterparts, you can use a spring. The latter must strictly correspond to the inner diameter, as it is inserted into the tube. Of course, you can put the spring on the outside, but in this case it is inconvenient to make a bend.
Having protected the tube with a spring, it bends with its own hands. The work should be done carefully to achieve the desired radius without damaging the part.
Profile
Profile pipes are much more difficult to bend, as due to their shape they have increased strength. Small-section products can be bent using the methods described above.
There is also another way to bend a profile pipe, which allows you to work with workpieces of a sufficiently large section. Its principle is as follows:
- sand or salt must be poured into the workpiece, and then reliably plug the ends with plugs;
- further, the part must be securely clamped in a vice;
- then the fold area should be warmed up red-hot;
- after that, the workpiece must be trimmed with a mallet until the desired radius is obtained.
If you have a welding machine and a grinder, then you can bend workpieces of even the largest diameter without much effort. This is done as follows:
- first of all, the bend radius is marked on the workpiece;
- further along the entire radius, you need to mark the strips on three sides of the profile blank. The smaller the radius, the smaller the step between the stripes should be;
- then the grinder makes cuts on three sides of the part according to the markings made;
- now the workpiece is bent without any problems;
- after obtaining the desired angle, the cuts should be welded;
- at the end of the work, you need to clean the seams and grind.
In this way, parts of even complex shapes can be produced, while the bending accuracy is very high. However, experience with a grinder and a welding machine is required.
Reinforced plastic
On the one hand, metal-plastic pipes bend very easily, but on the other, they break easily. Therefore, the work must be done very carefully. It should be remembered that the minimum bending radius of a metal-plastic pipe is similar to the radius of metal blanks, i.e. must be at least five diameters.
If the pipe diameter is 16 mm, then it can be bent without any special devices. This is done as follows:
- take the part with both hands from above. In this case, place your thumbs under the pipe, parallel to it, and close together, as shown in the photo above;
- then bend the pipe with both hands and be sure to provide support with your thumbs;
- bending the pipe to the required radius, move it in the palms to the left or right, and then repeat the procedure;
- in this way, bend the workpiece and move it until you get the desired angle.
To "fill your hand", practice performing this procedure on pipes, since it is likely that at first the workpieces will break.
It is much more difficult to bend a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm around the fingers. Therefore, any other suitable surface can be used as a stop. However, it is most convenient to carry out this work using a spring conductor, which can be both external and internal, i.e. which is inserted inside the workpiece.
To make a bend with an inner jig in the middle of a long workpiece, tie it to a rope and then push it to the desired depth. After completing the bend, draw out the spring by pulling on the rope.
Manual pipe benders
The manual pipe bender is used when bending materials of small diameter. This device can easily be made of non-ferrous metals and stainless steel. The principle of operation of this device is that by inserting one end into a special clamp, you need to start turning the handle. Through this procedure, the pipe will pass between the rollers, and thus the desired turn is created.When carrying out this procedure, it is recommended to adhere to GOST, which indicates that the minimum radii of pure non-ferrous metals and stainless steel must be:
- if the diameter is less than 20mm - not less than 2.5D;
- if the diameter is more than 20mm - 3.5D and more.
D is an indicator of outdoor.
Output
As we found out, there are quite a few popular ways to bend pipes. With a little practice, you can achieve good results. However, it should be remembered that the quality of the bend performed on professional equipment will always be higher.
The video in this article provides additional information on how to bend reinforced plastic pipes. If in the process of performing this operation you have any difficulties, ask questions in the comments, and I will definitely try to help you.
July 22, 2020
If you want to express gratitude, add clarification or objection, ask the author something - add a comment or say thank you!
In industrial and private construction, shaped pipes are common. They are used to construct outbuildings, garages, greenhouses, gazebos. Designs are both classically rectangular and ornate. Therefore, it is important to correctly calculate the pipe bending. This will keep the shape and provide the structure with strength and durability.
Calculation of beams for deflection. Work algorithm
In fact, the algorithm by which such a calculation is made is quite simple. As an example, consider a somewhat simplified calculation scheme, while omitting some specific terms and formulas. In order to calculate the deflection of beams, it is necessary to perform a number of actions in a specific order. The calculation algorithm is as follows:
- A calculation scheme is drawn up.
- The geometric characteristics of the beam are determined.
- The maximum load on this element is calculated.
- If necessary, the bending moment strength of the beam is checked.
- The maximum deflection is calculated.
As you can see, all actions are quite simple and quite doable.
Bendable metal properties
Metal has its own point of resistance, both maximum and minimum.
The maximum load on the structure leads to deformations, unnecessary bends and even kinks. When calculating, we pay attention to the type of pipe, section, dimensions, density, general characteristics. Thanks to this data, it is known how the material will behave under the influence of environmental factors.
We take into account that under pressure on the transverse part of the pipe, stress arises even at points remote from the neutral axis. The zone of the most tangential stress will be the one located near the neutral axis.
During bending, the inner layers in the bent corners contract, decrease in size, and the outer layers stretch, lengthen, but the middle layers retain their original dimensions after the end of the process.
Bend pipes are widely used in everyday life
What is a rectangular tube?
A rectangular metal pipe is a metal product several meters long. The rectangular pipe has a corresponding cross-section. Its area can be very different. All parameters of such pipes are regulated by special GOSTs - documents emanating from the state. The requirement that all dimensions comply with GOST is associated with the following:
- a pipe manufactured in accordance with GOST will meet safety requirements. If the pipe is made in artisanal conditions, then there is a possibility that the proportions do not meet safety requirements. There is a danger that the product will not withstand the loads and will cause the structure to collapse;
- When calculating pipe loads, it is not required to measure each specific product. Its parameters are set by GOST, therefore, you can take data from this document.
Products are made from various types of steel.Some steel grades do not require additional processing. This is, for example, the so-called stainless steel. Steel, which is afraid of corrosion, must be treated with special solutions or paint.
How to make correct calculations
Calculation of a profile pipe for deflection is the determination of the degree of maximum stress at a specific point in the pipe.
Each material has a normal stress rating. They do not affect the product itself. To make the calculations correctly, a special formula should be applied. It is necessary to ensure that the indicators do not exceed the maximum permissible values. According to Hooke's law, the resulting elastic force is directly proportional to the deformation.
When calculating the bending, it is also necessary to apply the stress formula, which looks like M / W, where M is the bending indicator along the axis, on which the force falls, but W is the bending resistance indicator along the same axis.
The pipe bend must be correct and accurate
Features of the production of shaped metal pipe
According to the method of production, profile pipes are hot and cold deformed. Due to the ductility of metals, profiling of any steel blank is available under the influence of high temperatures. On the cut (in section), the pipes have the form:
- square;
- rectangle;
- oval.
The flat-oval arched profile (or oval pipes) is no less in demand, and its production is growing. The technology of their forming practically does not differ from the rolling of standard professional pipes. This is, as it were, an intermediate option between round and rectangular structures, and their quality and endurance indicators are an order of magnitude higher than those of these products. The technology for the production of a standard pipe size assumes:


In cross-section, the pipes have the shape of an oval, square or rectangle.
- method of cold forming of rounded products by a press;
- welding of rectangular steel sheets.
Important! The cost of rolled products with a welded seam is lower than the price of solid pipes. There is no need to doubt their quality: the joint is checked with a flaw detector before receiving a certificate and acceptance certificate.
In accordance with GOST, pipes of any size (in inches and mm) are formed using two technologies that differ significantly from each other:
- By welding a sheet or strip profile (a seam can reduce product quality only under significant loads, and the product has a lower price).
- Rounded rods pass the pressing of workpieces of the same shape on a rolling mill (the technology is more expensive, seamless products endure the maximum load in vertical frames).


Pipes are produced by cold forming of rounded products using a press and welding of rectangular sheets
Bending Technological Process
Bending creates a certain degree of stress in the metal walls. Tensile stress is obtained on the outer section, and compressive stress on the inner section. Thanks to these influences, the tilt of the axis changes.
In the process of bending at the bent place, the shape of the cross section changes. As a result, the annular profile becomes oval. A clearer oval shape is seen in the middle of the deflection, but towards the end and towards the beginning the deformation decreases.
For pipes with a cross section of up to 20 mm, the ovality in the deformed place should not exceed 15%. For pipes with a cross section of 20 and more - 12.5%.
Pay attention to the fact that folds may occur in the concave area of thin-walled products. They, in turn, negatively affect the functioning of the system (reduce the permeability of the working medium, increase the level of hydraulic resistance, the degree of clogging).
Curved pipes are used in industry and private construction
Allowable bending radii of the pipe
Pipes have a minimum bend radius according to government standards.
If bending is carried out by heating and sanding, the outer diameter of the pipe is at least 3.5DN.
Forming a pipe on a pipe bending machine (without heating) - at least 4DN.
Bending when heated with a gas burner or in an oven to obtain half-corrugated folds is possible with an index of 2.5DN.
If the bend is provided for a steep (for bent sewer bends made by hot broaching or by stamping) - not less than 1DN.
The pipe bend may be less than the specified values. However, this is possible if the manufacturing method guarantees that the pipe walls are thinned by 15% of the total thickness.
We carry out the calculation of the bending strength of the pipe responsibly.
Bending of pipes of different diameters
Formulas and tables
To calculate the deflection of the pipe, we determine the length of the part. It is calculated using this formula:
L = 0.0175 ∙ R ∙ α + l
R is the bending radius in mm;
α is the value of the angle;
I - straight section of 100/300, necessary to grip the product (when working with the tool).
When calculating the bending of a profile pipe, we take into account the size of the bent element. It is determined by the following formula:
A = π ∙ α / 180 (R + DH / 2)
The value of the number π = 3.14;
α is the bending angle in degrees;
R - the value of the radius (the value is taken into account in mm);
DH is the diameter on the outside of the pipe.
Minimum bending radii for copper and brass products are given in the table. The data correspond to GOSTs No. 494/90 and No. 617/90. In addition, the values for the outside diameter, the minimum length of the static free part, are also given here.
The bending of shaped pipes can be performed on special machines
Pipe bend diagram
The following table will help to calculate a round pipe for bending. It includes data related to steel analogs (indicators correspond to GOST No. 3262/75).
| Pipe dimensions | Minimum bend radius | Minimum free length | ||
| Conditional pass | External | Hot | Cold | |
| 8 | 13,5 | 40 | 80 | 40 |
| 10 | 17 | 50 | 100 | 45 |
| 15 | 21.3 | 65 | 130 | 50 |
| 20 | 26.8 | 80 | 160 | 55 |
| 25 | 33.5 | 100 | 200 | 70 |
| 32 | 42.3 | 130 | 250 | 85 |
| 40 | 48 | 150 | 290 | 100 |
| 50 | 60 | 180 | 360 | 120 |
| 65 | 75.5 | 225 | 450 | 150 |
| 80 | 88.5 | 265 | 530 | 170 |
| 100 | 114 | 340 | 680 | 230 |
In order not to make a mistake in the calculations, one should also take into account the diameter and wall thickness of the pipes.
Manual hydraulic pipe bender
Bending the pipe with your own hands
If you do it yourself, the calculation of the pipe for bending will help, the formula of which is simple and universal (these are 5 pipe diameters).
We calculate the bend on parts with a cross section of 1.6 cm.
1st step: you need to clearly understand what kind of circle will be the result (for correct bending, one-fourth of the circle is needed).
2nd step: define the radius - 16 multiplied by 5. Result - 80 mm.
3rd step: calculate the starting points for the bend. To do this, use the formula C = 2π ∙ R: 4. The C value is the length of the pipe that will be used in the work. Two pi numbers are used, as well as an indicator of the outer radius of the pipe.
4th step: values are replaced with known data: 2 ∙ 14 ∙ 80: 4. As a result, we get 125 mm. This will be the length of the section where the minimum bending radius is 80 mm.
If it is not possible to work with the formulas, we calculate the deflection of the profile pipe using a calculator (it is easy to find a special program on the Internet).
There are several types of such a tool. The segment bending device provides for work on the bases of special templates. Their shape is already calculated for a certain diameter and shape of the fold. The tool helps to reshape pipes up to 180˚.
Backing equipment has a segment that moves inside the future product. This prevents deformation, opens access to several areas at once.
Whichever type of tool is used, we remember that accurate, repeatedly verified calculations are the key to successful installation.
Bending of pipes in stationary conditions: drawings and fixtures
In industrial enterprises and in private shops, where only two or three people work, a pipe bender with a mandrel is used. Despite the fact that industrial machines and pipe benders in shops differ in size and functionality, the principle of operation is similar. The work of the pipe bender is as follows: the pipe is inserted into the groove of the machine, fastened with a clamp to the straight part, the second clamp presses it against the bending roller.When the machine is turned on, the roller carries the inserted part behind it, it slides off the mandrel, forming a bent piece of pipe of the required size. The spoon-shaped mandrel for pipe bending has become widespread. It is designed for bending thin-walled pipes up to 75 mm in diameter. Due to its high cost, mandrel bending of pipes is not available to every owner, therefore, amateurs use pipe benders assembled by themselves in the garage or carpentry.
Classes of operation of PEX pipes, service life and temperature modes of operation.
When speaking about the characteristics of PEX pipes, we always mean the service classes of pipes made of a given polymer material. In addition to the strength characteristics, which vary from the type of pipe production. There are also classes of pipe operation described in the ISO 10508 standard. Almost all manufacturers have the same materials, but due to the wide range of applications of PEX and PERT materials and catalysts used, the classes of pipe operation are divided into 6 subspecies. All these classes do not affect the quality of the pipe, but only indicate the modes of operation of the pipe and its operating temperature conditions relative to the service life of the material. You can see these classes in the table below.
Table of operating classes for PEX and PERT polymer pipelines:
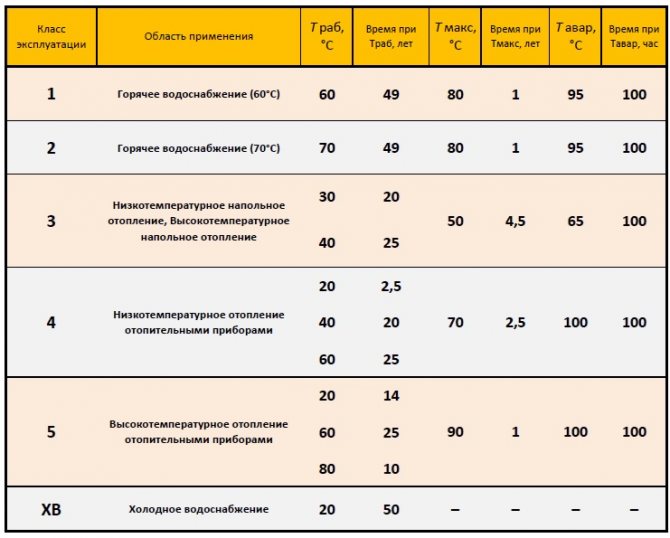



In short, in the ISO 10508 standard, the areas of application of pipes of various classes are defined as follows:
· Class 1 [A] *
(DHW distribution systems 60 ° C, service life 50 years)
· Class 2 [B] *
(DHW distribution systems 70 ° C, service life 50 years)
· Class 3 [C] *
(underfloor heating only 35 ° C, service life 22 years)
· Class 4 [D] *
(underfloor heating with temperatures up to 20 ° C - 2.5 years and low-temperature radiators [KERMI] 50 ° C, service life 22 years) Operation of the class assumes that at an average daily temperature of 40 ° C [20 to 60] of the heating system, the pipe will serve minimum 15 years.
· Class 5 [E] *
(high temperature radiators and heating systems 53 ° C, service life 16 years)
* All temperatures of the classes are considered based on the average daily temperature of the coolant in the pipe.
For each material and for each S series, the maximum working pressure (4, 6, 8, 10 bar) is calculated for a specific service class.
for instance
, for PP-RCT-S3,2 pipe, the information on the pipe will be presented as follows:
Class 1 / 10bar, 2 / 10bar, 4 / 10bar, 5 / 8bar - this means that the pipe can be used:
for hot water distribution systems with a temperature of 60 ° C, an operating pressure of 10 bar and a service life of up to 50 years (class 1/10); for hot water distribution systems with a temperature of 70 ° C, an operating pressure of 10 bar and a service life of up to 50 years (class 2/10); for underfloor heating and low-temperature radiators with an operating pressure of 10 bar and a service life of up to 15 years (class 4/10); for high-temperature radiators with an operating pressure of 8 bar and a service life of up to 16 years (class 5/8)
































