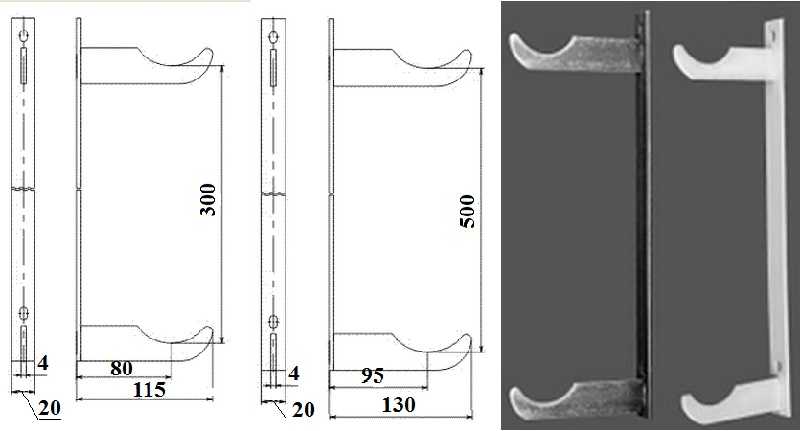
Structural differences and appearance
Cast iron
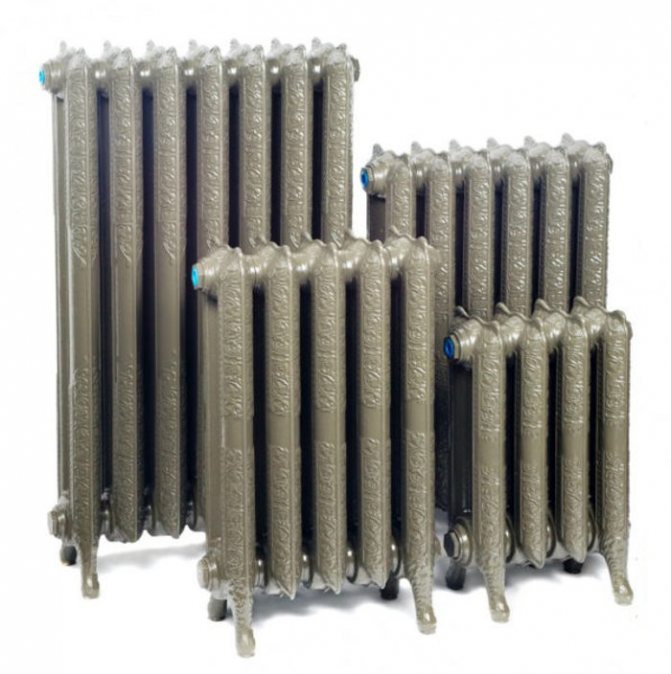
Let's start with cast iron radiators, which today have changed their design, but, as before, have wide water channels and are made up of several cast sections. Heat-resistant gaskets made of rubber or paronite, which are placed between the sections, provide the required tightness. The length of the finished radiator is determined by the number of sections, the height varies from 0.35 to 1.5 meters, and the depth can be 0.5 meters or several centimeters. In accordance with the volume of the room, you can select the desired size of the radiator, while there is a possibility of its modification (for example, remove an extra section or add several new ones).

Varieties of cast iron heating radiators.
It is worth mentioning the models of radiators, artistically cast from cast iron. They will not only perfectly heat the room, but are also able to give it charm and charm. Such radiators with molding patterns skillfully executed on their surface are produced mainly by foreign manufacturers. Like any piece of art, such devices cost a lot of money.
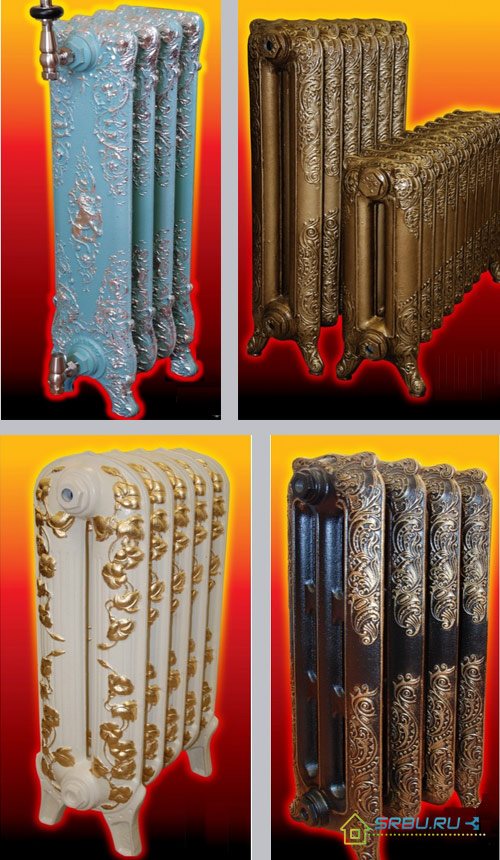


Several types of artistic cast iron heating radiators.
Bimetal
The case of bimetallic radiators is aluminum, its shape is ribbed-shaped. This is how it is designed for better heat dissipation. A strong steel core is hidden under the body - this refers to "real" bimetallic radiators. However, there are also semi-bimetallic (or pseudo-bimetallic) radiators - their difference is that only the vertical radiator channels are reinforced with steel.
The rest of it is made of aluminum. Such a device costs 20 percent less than a completely bimetallic one, and gives more heat. But it is less reliable and durable, and it is highly undesirable to use it in a centralized network.
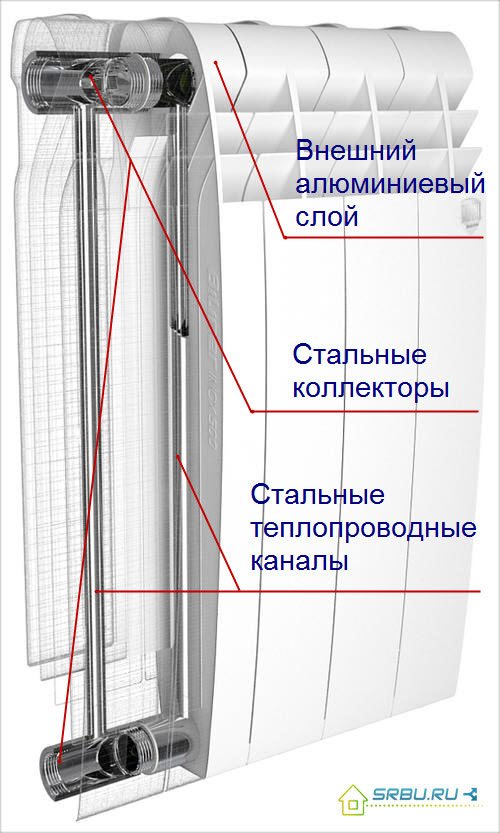

The device of a bimetallic heating radiator.
Like cast iron radiators, their bimetallic counterparts are usually sectional, which allows them to be modified. Models are usually sold with an even number of sections. A small segment of the market is occupied by monolithic models, which cannot be disassembled, assembled and improved. The design of all bimetal radiators is very attractive.
Appearance: Cast iron + — | Bimetallic +
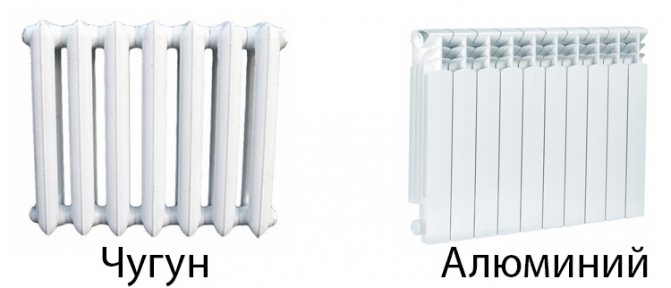
What is the Difference Between Cast Iron and Aluminum Radiators
Cast iron batteries have been in high demand since the times of the USSR, now they are less common, but they are also installed. Initially, such products were in short supply, and new settlers who received housing stood in lines to buy a cast-iron radiator.
Panel steel - an option of the basic configuration - were valued much lower due to the worst operational parameters.
Important! Cast iron batteries are the most durable option, despite the abundance of other systems on the market, it is more popular.
Compared to steel, cast iron has a number of advantages. The first is that such products do not flow, the second is that the material is practically not prone to corrosion. Cast iron radiators are almost eternal, they will easily last 50 years or more. There are drawbacks - this is a low thermal efficiency in comparison with other types of batteries. The internal volume is significant (approximately 3 liters per edge), and the total weight of the system, accordingly, is also.
Correctly selected high-quality radiators are a guarantee of comfort and warmth in the house
Due to the significant volume of the internal space, heating a cast iron battery takes a long time. It will therefore be difficult to quickly adjust the temperature in a living space. And still, cast iron radiators are one of the most demanded on the modern market.The myth that cast iron is a relic of the past, an irrelevant, ugly option, remains a myth.
Aluminum radiators are a more modern and progressive solution. They are beautiful, lightweight, have a high thermal efficiency, about 4 times more than cast iron. That is, it heats aluminum much better and faster with the section size equal to that of cast iron. There are also disadvantages, the main one is corrosion. Destructive processes associated with the design and other features of the system are often unnoticed inside aluminum radiators. Poor water quality plays a role in the centralized water supply system. Such models heat up the premises quickly, 20 minutes is enough to achieve comfortable conditions.
Important! Never leave aluminum batteries with closed taps for a long time. If you do this, corrosion will "eat" at least 0.1 mm of material in a year.
Due to the tendency to corrosion, aluminum radiators need to be replaced quite often; the average service interval is 15-20 years.
Aluminum is a more modern option, but in a number of parameters it is inferior to cast iron
The models of aluminum radiators presented for sale differ in terms of performance parameters, appearance. Therefore, it is very important to make the right choice, it will determine the design of the product, the comfort of use, and the efficiency indicators.
Let's compare the heat dissipation of radiators
Cast iron. Let's start again with traditional cast iron radiators. They are so slow that you can sometimes freeze while waiting for a cold room to warm up. But on the other hand, such radiators cool down for a long time - and this is a completely different matter. After all, it is not uncommon for the heating to be turned off once. Because of an accident or repair, for example. And near the cast-iron battery you can still warm up for a long time.
A great advantage of cast iron products is that they heat up the room not only by convection, but also by radiation. That is, when they are turned on, in addition to air, objects close to the batteries also become warm. As for the thermal power, it is usually given for one section and ranges from 100 to 160 watts. These are average values and may vary from model to model.
Bimetal. The good thing about these radiators is that they just heat up instantly. However, they cool down just as quickly, alas. Heating in them is carried out mainly according to the principle of convection - the radial component is much smaller. This is some disadvantage. The thermal power of sectional models is comparable to cast iron products. This figure ranges from 150 to 180 watts (on average). If we compare the heating rate of the room, then they certainly outperform the cast iron ones.
Heat dissipation: Cast iron + — | Bimetallic +
So what should you choose?
In their own way, these two types of heating batteries are good. They will find their supporters and use for many years, but there are times when it is still preferable to install batteries of a certain type.
- In the case when the additional load on the wall is undesirable or it is not capital, then due to relatively light weight, it is better to mount an aluminum radiator.
- If the apartment is located in mapartment building with central heating, especially when it comes to the first five floors, then in this case there is nothing better than good old cast iron.
- If the battery is supposed to be hung next to the bed or in the children's room, then it is better to hang a cast-iron radiator, since it does not have an unbearably hot surface, gives off heat gradually, evenly distributing it throughout the room, which is why the air does not dry out so much and does not cause any particular discomfort.
- Aluminum radiators are not suitable for heating systems using alternative fuel to gas, for example, on coal.
- Cast iron radiators slightly susceptible to corrosion and can do without flushing for years.Therefore, if the plans are to "hang and forget", then this is definitely about them.
- In dacha-type houses, in which they live from time to time, it would be better to install aluminum radiators. This choice is dictated by the need to quickly warm up a stagnant room, as well as because of the danger of rupture of a cast-iron battery in case of freezing, when they did not have time to arrive and turn on the heating.
- When it comes to a large house with many diverse premises, it is better, from the point of view of the convenience of temperature control, to install aluminum radiators. Each family member will be able to adjust the temperature in their bedroom to their liking. In the bathroom, you can make it warmer, but in the kitchen you just need coolness, there is already a lot of warm air formed during the cooking process.

As you can see from the above, each of the considered types of radiator has its own functional pros and cons. It's really hard to choose. It is good if some aspect plays a decisive role and makes the choice of the consumer as easy as possible.
Ability to hold pressure
In a traditional central heating system, typical of multi-storey buildings, the pressure is by no means stable. Sometimes even water hammer occurs. After all, the cranes of circulation pumps, according to the rules, should turn on smoothly, but often workers do not follow these rules. And with a sharp shutdown of hot water, its pressure in the entire system jumps so that many batteries burst. Therefore, apartment residents should definitely choose radiators with a good pressure margin.
Cast iron radiators can withstand 9-12 atmospheres of pressure. This may be enough until a strong water hammer occurs. If it does happen, then brittle cast iron, unfortunately, can burst. Therefore, if you look from this point of view, that it is better to cast iron or bimetallic radiators, then it is better, of course, to insure yourself and take bimetal.
After all, a bimetallic radiator is not afraid of any pressure surges - in the passport it has declared indicators for this parameter up to 20-50 atmospheres (depending on the model). So even powerful water hammers are not capable of breaking a quality bimetal product. And we will also mention the models with a monolithic steel core - they can easily withstand up to 100 atmospheres. An example of such radiators can be Russian-made radiators Rifar Monolit, you can see its technical features in the photo below.


Ability to hold pressure: Cast iron — | Bimetallic +
What criteria should be considered when choosing radiators?
Why are only bimetal and cast iron considered? Products made from them meet more user requirements. To determine which of them will work better and last longer, you will have to compare their qualities.
- Cost. For some, this moment is unimportant. Unfortunately, for most of the population of our country, it is one of the most important. Many, coming to the store to make a long-awaited purchase, first of all pay attention to the price, and only then to the technical characteristics and appearance of the products.
- Lifetime. Since radiators are stationary elements, I want them to stand for a long time and work flawlessly. And after a couple of seasons, there was no need to dismantle, buy new products, and install batteries from scratch, while performing all the dirty and difficult processes.
- Heat transfer. In order for the battery to perform its functions as well as possible, it must give the maximum amount of energy it receives from the coolant. Products with better heat transfer rates heat the room faster to the desired temperature.


Heat transfer from cast iron and bimetallic radiators.
- Strength, ability to withstand high pressure and withstand its drops. To prevent the radiator from starting to leak, it must be able to withstand water hammer and be resistant to various mechanical influences.
- Complexity of installation. The harder it is to complete the installation, the greater the risk of doing it incorrectly and harming the battery itself and other elements of the heating system.
- Reaction to poor heat transfer fluid. The water supplied to the pipes can be of very poor quality. This moment will negatively affect the heating radiators. Products that are less resistant to the effects of a low-quality coolant will last much less.
- Maximum coolant temperature. The water circulating in domestic heating systems is not characterized by temperature stability. Therefore, it is very important that the radiator is able to withstand fluctuations.


Battery selection criteria
Resistance to poor quality of the heating medium
Another disadvantage of central heating is the dubious quality of the coolant. The hot water going from the pipes to the radiators is neither clean nor chemically neutral. And it also contains a considerable amount of the smallest grains of sand and pebbles that can affect the inner walls of the battery, like an abrasive.
Cast iron is chemically absolutely "calm", so a high level of alkalis or acids in hot water will not harm it. And in the summer, when there is a general drainage of water from the system, it will not rust. But she does not like small abrasive stones - they wear out gradually. However, if the radiator walls are rather thick, this is not so critical.
Bimetal is also resistant to chemically active water during the heating season. However, in summer, when water is drained from the system for repair and maintenance work, air appears in the radiators, the steel core can be attacked by corrosion. So the bimetal is a little less durable than cast iron.
Low-quality heat carrier: Cast iron + | Bimetallic + —
How to make the right choice
Cast iron products are suitable for private and residential buildings up to five floors. In high-rise buildings, very high pressure can occur, which can lead to rupture, therefore bimetallic models are chosen.
Aesthetically, classic cast-iron models look ugly, but when designing a room, decorative grilles are often used to hide the appearance of radiators.
When buying, experts recommend paying attention to the following characteristics:
- heat transfer quality;
- the frequency of performing the necessary preventive work to extend the service life of heating devices;
- lifetime;
- pressure retention;
- aesthetics.
The maximum temperature of the coolant and its fluctuations
And the temperature of the coolant in our heating systems does not shine with stability. Now the pipes are barely warm, then hot, like fire. It is important for us how the radiators will behave in the latter case, whether they can withstand too hot water. For this parameter, the indicators are as follows. For a cast iron radiator, the coolant can be heated up to 110 degrees. Hot water flowing through the pipes of the core of a bimetallic radiator can have a temperature of up to 130 degrees. But in general, both types of radiators tolerate temperature changes well. The only thing is that due to the difference in the expansion of steel and aluminum, with a sharp change in temperature, small crackles can be heard at the bimetallic radiator.
Maximum coolant temperature: Cast iron + | Bimetallic +
Output
We tried to give as much information as possible about which of the options presented is most suitable for a living space. But do not be confused that the advantages of a certain type become disadvantages in a variety of situations, it is important to take into account many nuances, up to the size of the heated area.
In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our channel Yandex.Zen
Which radiators are easier to install
There is nothing to argue about - naturally, there will be more problems with cast iron during installation and transportation. And it is beyond the power to lift such a battery alone, and special brackets are needed for it - especially strong, and the plasterboard wall will not withstand it.
And one more thing: when purchasing cheap domestic radiators, one must be prepared for the fact that they will additionally need painting and broaching.
But working with bimetallic radiators is, one might say, a pleasure. They are so light and neat that hanging them (and on any surface) is not difficult. And if in the first place you have ease of installation, then the answer to the question of which is better - bimetallic or cast iron radiators, is unambiguous. Of course, bimetal.
Ease of installation: Cast iron — | Bimetallic +
Complexity of installation
Trying to understand which is better, cast iron or bimetal for central heating, depending on the complexity of installation, one can come to the following conclusion: according to this parameter, bimetallic radiators win unconditional victory - with the same dimensions as cast iron, they weigh several times less. They are much easier to transport, carry and install, therefore, if ease of installation is critical, then bimetallic products will be the obvious choice.
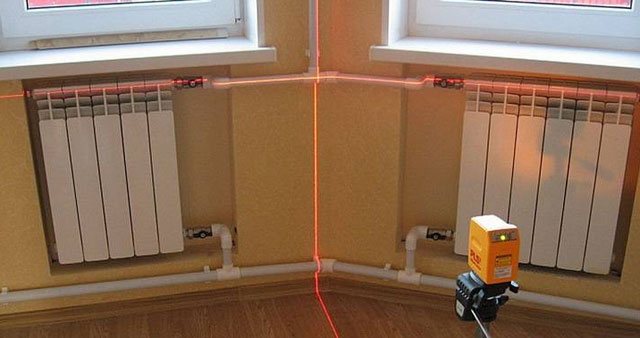

Cast iron radiators, in turn, cause a lot of problems during installation:
- Firstly, they weigh a lot, so it is very difficult to lift and hang them;
- Secondly, due to the weight, even delivering radiators to the apartment will be problematic;
- Thirdly, the same large weight does not allow hanging such radiators on plasterboard walls, and special brackets will be required for fastening to brick walls.
In addition, when buying cheap domestic-made radiators, there is a high probability that they will additionally have to be painted and stretched.
Let's talk about the difference in the price of radiators
Pig iron is undoubtedly cheaper, especially domestically produced. So, the cheapest section of the MC model, for example, costs only about 300 rubles. However, only classic models will have such a "tasty" price. But radiators in the "retro" style, made by the method of artistic casting, are several times more expensive. Such models of the Konner brand cost from 2000 rubles (for one section).
Sectional models of bimetallic radiators will be somewhat more expensive than similar cast iron ones. For example, one section of a radiator from the Rifar company (Russia) will cost at least 500 rubles. The price of a section of the same Italian radiator starts from 600-700 rubles.
Price: Cast iron + | Bimetallic —
Options for calculating and installing a bimetallic radiator
The most commonly used method for calculating radiators by the area of the heated room. On average, about 100 watts of radiator thermal power is required per 1 square meter of the room.
To do this, we calculate the area of the room (the most accurate assignments are indicated in the technical passport for an apartment or house) and find out the capacity of one section. The manufacturer always indicates it in the documentation.
In premises in new buildings with facade insulation, good thermal insulation, multi-chamber double-glazed windows, the power value per square meter can be reduced. In new buildings, bimetallic radiators are often installed according to the scheme of 75 - 80 W per square meter.
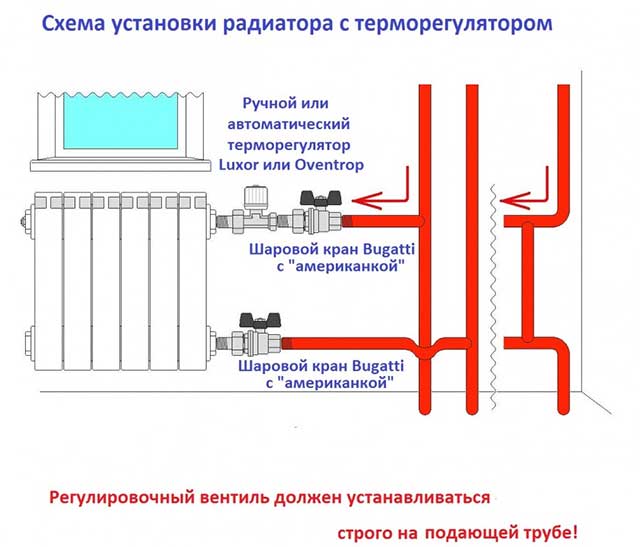

Due to the lower weight, bimetallic radiators are very easy to install. Work begins with laying a parallel line on the wall. Then the following installation steps are carried out:
- pipe trimming, threading;
- installation of a Mayevsky crane in front of each radiator;
- installation of anchors or dowels;
- hanging a radiator;
- connecting the radiator to the pipelines.
The brackets provide a distance from the wall of at least 5-7 cm. This ensures that even at a maximum operating temperature of 90 ° C, the wall covering will not be damaged.The distance from the floor should be at least 15 cm, which will provide the necessary space for cleaning.