Is water heating of a wooden floor possible?
In fact, no matter what skeptics say, arranging a warm water floor in a wooden house from a bar is not only a possible, but also a reasonable solution to the heating issue. Of course, you will have to take into account certain nuances associated with the peculiarity of the operation of a wooden house.
So, for example, it is forbidden to heat floors over 30 degrees. A wooden surface under the influence of high temperatures is easily deformed, turns into dust. Therefore, a warm water floor on a wooden base should not be connected to the central heating circuit, but to use a separate heat source for this purpose.
A warm water floor cake in a wooden country house severely limits the use of a concrete screed. The heating system will have to be laid dry, which also creates certain inconveniences.
When choosing a floor covering, it should be borne in mind that some popular finishing materials: laminate, parquet board - when heated above 25 ° C, they begin to emit toxic fumes of formaldehyde.
Most manufacturers of heating equipment take into account the need for the simultaneous use of two heating circuits with different heating intensities, providing customers with boilers with the ability to connect heating radiators and underfloor heating.
Warm floor on a wooden base
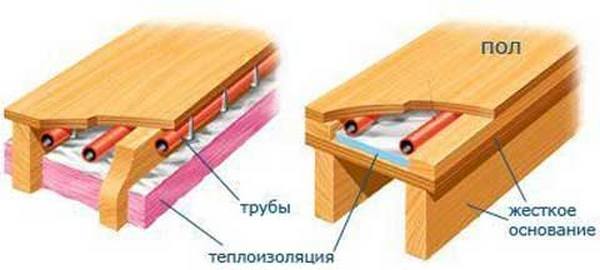
A more affordable way to install a floor with water heating on a wooden base is to install it on the floor. The main advantage of this option is that the base for installing the system does not need to be disassembled: the warm floor is laid out on a worn-out basis.
Related article: How to repair a dimmer with your own hands?
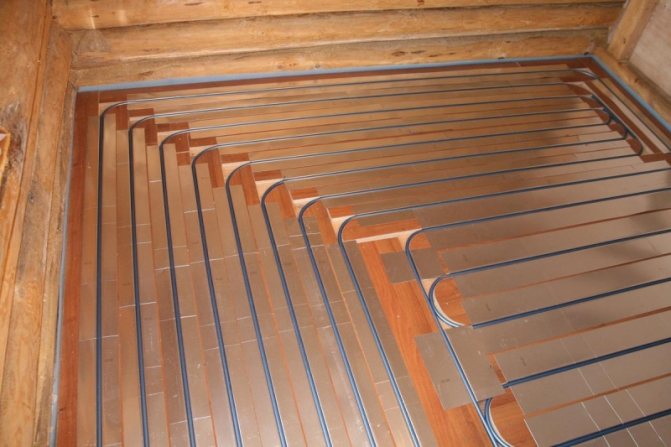

To lay a warm water floor on a wooden base, you should purchase special metal products into which pipes are inserted
The floor is advised to disassemble only if it makes squeaks when walking, bends.
Before laying, it is necessary to calculate the required length and pitch of the pipes. To do this, you can use either the services of a specialist or an online calculator.
The optimal pipe spacing for our climate is 150-200 mm. It is better to choose pipes for the system with a diameter of 1.6-1.7 cm, corrugated.
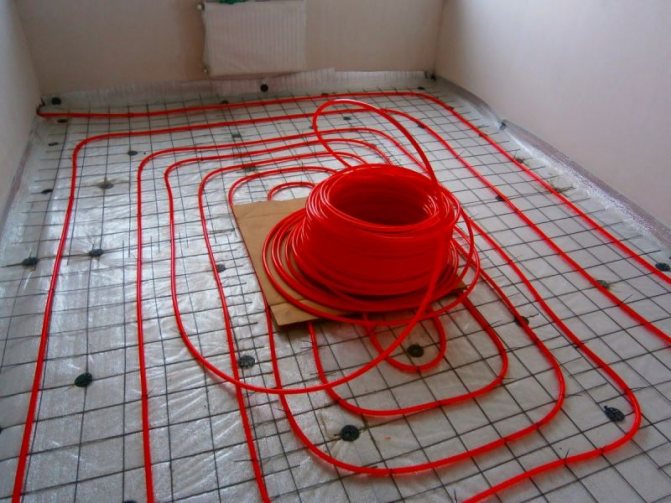
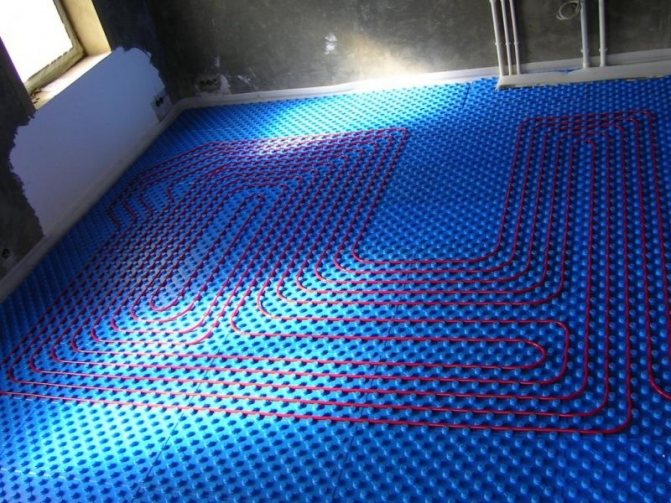
The easiest way to lay it is a snake. After the calculation has been carried out, it will be necessary to mark the floor, starting from the walls and moving towards the center of the room. According to the outline, heating pipes and chipboard guides will be laid.
The guides should be laid so that there is space between them for pipes plus 1 cm.
The guides can be attached to the subfloor using self-tapping screws or nails. In this case, as in the previous case, the guides must have rounded ends for turning the pipes. To increase heat transfer, you can wrap heating pipes with foil.
Before placing the plywood and topcoat, start the heating and check the circuit for leaks.
As a floor covering, builders are advised to choose materials that do not contain formaldehyde.
Water heat-insulated floor under tiles on the first floor
A water-heated floor without a layer of concrete is installed in rooms where pouring a concrete screed is difficult or impossible, for example:
- in houses with wooden beams;
- in low rooms;
- indoors, delivery of concrete wherever possible.
The advantages of underfloor heating without screed are:
- Lightweight construction.
- The small thickness of the structure does not significantly change the height of the used room.
- The possibility of fixing the floor covering immediately after the installation of the warm floor, since there is no need to wait for the complete hardening of the concrete.
- Minimum sub-floor requirements. It can be either a concrete or a wooden base.


The underfloor heating system without pouring concrete involves laying heating pipes on a polystyrene or wooden base with special grooves. Under them, a waterproofing film and a layer of insulation - penoplex - are spread on the rough floor.
Metal heat-distribution plates are placed in the grooves, and pipes are placed in them. On top of the pipes, they are covered with a moisture-insulating substrate and a floor covering is laid: parquet, laminate, tiles or special carpet. In conclusion, we can say that a water-heated floor is an effective and fire-safe heating system for a wooden house.
When installing a water underfloor heating system, maximum protection against moisture ingress on wood surfaces must be created. It is impossible to connect such a system to the central heating pipe, for its operation it is necessary to have an autonomous heat generator.
Waterproofing layer. The material depends on the method of installation of the system: if the installation is carried out on the ground floor and the screed is supposed to be poured, you can use dense polyethylene or roofing material. If the screed is dry, it is better to use a special waterproofing membrane.
- Insulation. As it can be used polystyrene or expanded polystyrene.
- Metal heat distribution plates with pipe channels.
- Underfloor heating pipes.
- Solid base for tiles. Usually these are sheets of moisture-resistant plywood or drywall, a better option is GVL-plates.
The thickness of a warm water floor under a tile in a wooden house can be different and depends on the insulation layer, base, pipe diameter and type of screed. The height of the dry screed can start from 35 mm, which makes it a better choice for rooms with low ceilings, while the minimum is 80 mm for concrete.
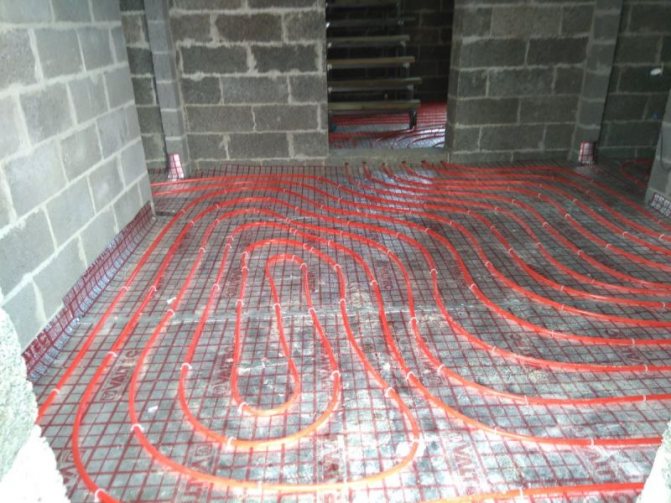
A water-heated floor in a wooden house under a tile on the ground floor can be made with a concrete screed. When properly filled, it does not bond to the base and does not have a negative effect with seasonal changes in the wood. Many experts do not support this idea and are inclined to believe that it is better to use a dry screed, but, nevertheless, this technology continues to exist and is often used.
Even in a wooden house, a concrete floor has several advantages. It is more durable, does not deform and does not creak over time, and withstands a greater load. You can easily lay any decorative coating on it, in particular, tiles. A concrete screed transmits heat much better than a dry one, so it is not necessary to warm the water to a high temperature: already at a temperature of 40 degrees, you can feel a pleasant warmth.
Water heat-insulated floor under tiles with a screed for the first floor
A water heat-insulated floor in a wooden house under a tile with a concrete screed is mounted according to the following scheme:
- Preparatory stage. Old floors are removed, the base is prepared (cleaning and smoothing).
- Waterproofing is laid on the surface. The outer edges are laid on the walls, and the inner ones are overlapped and fastened with mounting tape.
- A damper tape is mounted along the perimeter at a height of two centimeters from the screed surface, which compensates for expansion during heating.
- Foam or polystyrene mats are placed on the waterproofing. On the upper floors of buildings, where there is a heated room below, a layer of insulation 4 mm thick will be sufficient, on the first it should be made thicker - 8-10 cm.
- Heat-distributing plates are laid over the entire surface of the insulation, which are attached to the channels of the mats. Underfloor heating pipes are laid in their grooves.
- The ends of the pipes are connected to the heating system and checked for operability and tightness.
- If the warm floor is ready for use, a concrete screed is poured, the thickness of which should be 3-7 cm.
- At the end of the work, you must wait for complete drying, which occurs by 25-28 days.
- When the screed is dry, the tiles are laid.
If the base of the floor is wooden logs, or the installation is carried out on the second or third floor, the use of a concrete screed is impossible, since it will put an unacceptable load on the structure. In this case, the laying method is used.
A dry screed is less effective, as it conducts heat much worse. To increase its efficiency, a minimum step is made between the pipes, and therefore cold and warm spots will not form on the tile. Another more complex and expensive solution to the problem is the installation of deflectors, which will help raise heat upward.
Water heat-insulated floor without screed.
One of the main advantages of a dry screed is a high installation speed and almost complete absence of dirt. If, when using concrete, it is necessary to wait up to a month until the coating is completely dry, then in this case you can start finishing work immediately after the underfloor heating structure is ready. The duration of work in a medium-sized room usually does not exceed two days.
Before proceeding with the installation of a warm floor and dry screed, it is necessary to assess the quality of the base.
- If there are gaps between the floor boards, it is necessary to eliminate them with heat insulating materials.
- If the floors are not insulated, this issue also needs to be addressed. Alternatively, you can carry out the installation of a raised floor with a layer of mineral wool, protected by a waterproofing film.
- The floor on wooden logs assumes that the distance between them does not exceed 60 cm, so if they are located at a farther distance, this point must be corrected.
A water-heated floor in a wooden house without a screed for tiles can be made using several different technologies:
- Polystyrene system.
- Finnish technology.
- Wooden system.
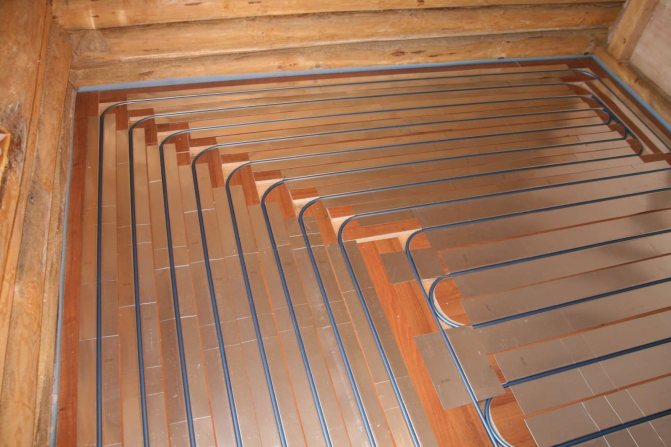


Each of them has its own characteristics and advantages. Let's consider them in more detail.
The technology of laying a warm floor with polystyrene allows you to create the lightest dry screed, which is important if the structure of the house does not imply serious loads on the floors. This material has a number of advantages:
- Has zero water absorption, does not allow steam and water to pass through.
- It is characterized by high sound-absorbing properties.
- Has a long service life and affordable cost.
- Easy to assemble.
Warm water floor on polystyrene
In this technology, polystyrene plates are the basis on which heat-distributing plates and floor heating pipes are laid. If the installation is carried out on the ground floor, the layer of material must be at least 8 cm, on the upper floors there will be enough thickness of 5 cm. A rigid substrate is mounted on top of the structure, on which the tiles are subsequently laid.
Tip: It is best to use polystyrene mats with projections (bosses) into which it is convenient to insert metal plates. If you use ordinary sheets, you will first have to prepare special grooves in them.
Finnish technology
Warm water floors in a wooden house without a screed are often installed using Finnish technology, which involves the use of gypsum fiber sheets.This material is more durable, resistant to damage and deformation than conventional drywall, and at the same time is characterized by increased thermal conductivity.
Underfloor heating according to Finnish technology with GVL modules
The simplest and most convenient way to make a dry screed from gypsum fiber board is as follows: the surface is prepared for work, waterproofing and insulation are laid on it. The slabs are attached to the logs, and the path of the pipes with water is applied to their surface. Then the material is sawn along the drawn contours and fixed on the base.
Wood system
In the modular method, ready-made modules from wood-based panels are used, in which grooves are prepared for laying pipes. They are mounted directly on the logs with a pitch of 60 cm, between which a waterproofing layer and insulation were previously laid. The gap between the modules, which compensates for thermal expansion, should be 2 cm. They are fastened to each other using a conventional snap lock.
The rack system assumes the use of ordinary boards or slats, it requires preliminary preparation of the subfloor. Installation is carried out at a distance sufficient to leave a little free space when laying the pipes.
Wooden floor heating.


Metal plates are laid on the prepared system, into the grooves of which the pipes of the underfloor heating are inserted. On top of the system, a solid substrate of plasterboard, chipboard or plywood is installed, which are carefully fixed, and the joints between them are putty. Only after that they start laying the tiles.
Options for the device system underfloor heating on wooden logs
The installation of a water-heated system in wooden houses is carried out either on logs or on a rough base. Often, underfloor heating is laid on wooden floors using Finnish technology. We call this method the dry screed method: instead of the solution in which the system is placed, GVL plates are used here.
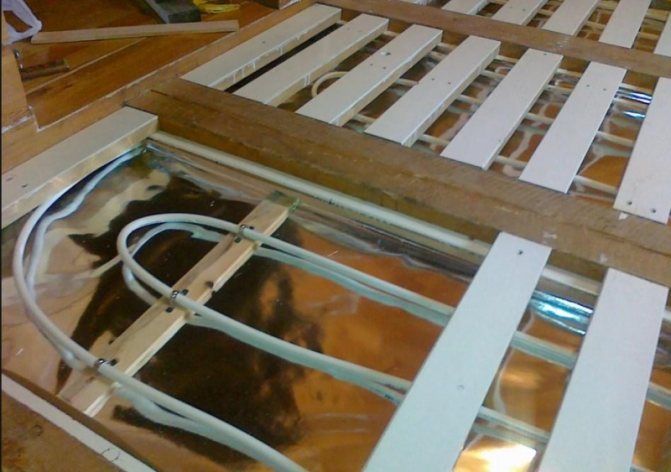


Before laying a warm floor on wooden logs, it is worth checking them for damage.
There are several options for installing a warm floor on wood:
- Pipes are laid in factory plates (for example, reflective, with grooves for the pipeline), which are mounted on top of the log. Insulation and topcoat are laid on top.
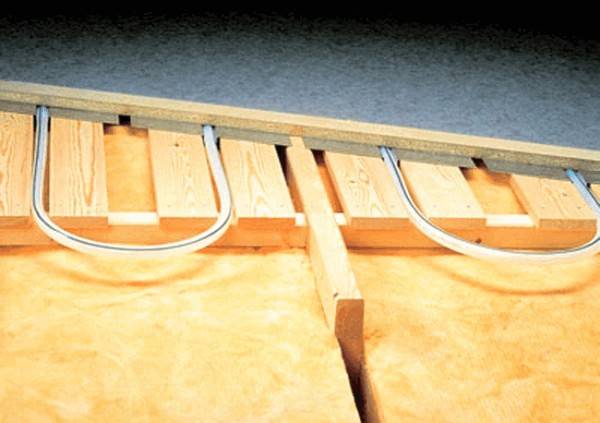
- Pipes are laid directly on the logs in the cuts arranged according to the laying pattern. The gaps between the lags are filled with insulation, plywood and a topcoat are placed on top. The disadvantage of this technology is an air gap between plywood and pipes, which impairs thermal conductivity.
- Pipes are placed on insulation (polystyrene) between the logs. The space between the elements is filled with either dry sand or gypsum.
- The pipes are laid on slabs with bosses, which are laid flush with the joists on the raised floor. In the logs, slots are made for laying the system along the entire perimeter without interruption. A reflective hard material (such as metal sheets) and a topcoat are laid on top.
- Insulation is placed between the logs, and plywood is placed on it. Slats with rounded corners are cut from chipboard sheets, which are stacked on plywood. The pipes are laid in the grooves between the plywood slats.
- This method is similar to the previous version, only instead of plywood slats, a board 5 cm thick and width equal to the pipe pitch is used. Foil is placed in the groove under the pipe to retain heat.
Based on the proposed options, you can create your own way of laying a water-heated system on wooden beams, which will meet your wishes, financial capabilities and skills. The main thing is that the principle of the floor remains unchanged.
Mounting options
There are several options for arranging underfloor heating in a wooden house. The choice of installation method is chosen depending on the technical characteristics of the building.
Common installation methods are:
- Mats represent ready-made structures with grooves for laying the water circuit. The mats can be laid on a flat base of the floor. For this, the surface is preliminarily trimmed using plywood or QSB - plates. The modular floor does not require the use of cement mixes. On top of the polypropylene pipes, the DSP is closed, the floor covering is laid.
- Installation of warm concrete water floors on top of wooden structures. Before installation, ensure maximum insulation of wooden elements from moisture. All work is carried out exclusively with ready-made compounds with a short drying period.
- Milling a wooden floor for pipes of the underfloor heating system. With the help of machine cutters, recesses are cut out for the passage of the pipeline. The wooden base begins to function as mats. As a result, the cost of flooring components is reduced. The disadvantage of milling is the laboriousness of the process. But with a specialized tool, installation time can be minimized.
Other methods can be used to lay water-heated floors on a wooden floor. There is the following way. In a wooden frame, a pipeline is simply laid under the logs. The plank floor is disassembled, the water circuit is laid, after which the flooring is laid back.
To protect the tree as much as possible from moisture ingress, the water circuit is laid in a special corrugation. The corrugation protects against the effects of water even in the event of leaks.
Wooden water floors are often used in the construction of panel houses or timber houses. They are mounted directly on the joists or on the subfloor, which rests on them.
These systems have significant design differences. In the first, ready-made modules are used, in which there are channels for plates and pipes.
The second option involves the placement of system elements between boards or fragments of chipboards.
Most often, tile or porcelain stoneware acts as a finishing coating when installing a warm floor. These building materials are durable and long-lasting, and do not emit harmful substances when heated. Less often, the installation of the system is carried out under a special laminate, linoleum and some types of carpet, which have a corresponding mark from the manufacturer.
For the construction of a warm water floor, 3 types of pipes can be used:
- Cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX and PERT). Highest quality materials. PEX pipes have a high crosslinking density and have the best "memory effect". This means that after stretching, the pipe gradually returns to its original position. They are not afraid of liquid freezing and are suitable for repair.
- Metal-plastic pipes are considered the best option. They have a budget price, are easy to install and perfectly keep their shape.
- Copper is the most expensive option; when used in a screed, they must be covered with a protective layer to avoid alkaline attack.
For the underfloor heating system, 3 main pipe sizes are used - 16 x 2, 17 x 2 and 20 x 2 mm. The most famous pipe manufacturers are Rehau, Tece, KAN and Valtek.
The length of the pipe contour of 16 mm should not be more than 100 m. The optimal spacing of the pipes should be 15 cm when using good thermal insulation. At this step, the consumption of pipes will be about 6.7 m per 1 m² of the room. For an accurate design of a water floor system, it is necessary to contact a heating engineer.
The first stage is heat calculation and drawing up a floor diagram. You can calculate heat loss and hydraulics using a network calculator. As a result, you will have a recommended pipe cross-section and a laying step.
The second stage is the dismantling of the coating. If necessary, dismantle the log.
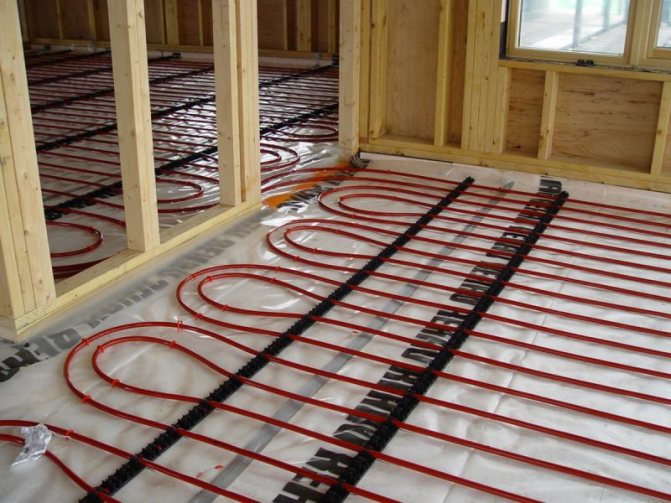
In general, there are two installation options: a water underfloor heating on a wooden floor over the flooring and with pipes laying between the joists.
- Level the subfloor: fill up the cracks, check the horizontal alignment of the plane. The slope should be no more than 0.2 percent, i.e. a drop of 4 meters is not more than 8 millimeters.
- Lay in waterproofing. The layer must be airtight - either a continuous film, or the joints of the strips are glued with a waterproofing tape.
- Lay wooden logs.
- Place insulation between them. The recommended layer is at least 10 centimeters, but this depends on the thermal conductivity of the material and the heat calculation data.
- Lay pipes on the insulation. The pitch between the turns depends on the width of the intervals between the lags. Optimally - 20 centimeters. In the places where the pipes turn in the logs, slots are made.
This is the simplest scheme for a warm water floor under a wooden floor, but not the most effective.
Second way
- Waterproofing, insulation.
- Aluminum foil reflective surface to the room. The joints of adjacent areas are glued with heat-insulating tape.
- Reinforcement mesh to strengthen the structure.
- Lags and pipes.
- A temperature sensor in a corrugated casing is placed under the floor covering. The signal from it will go to the thermostat.
- The thermostat is installed at a low height from the floor, placed in a strobe or mounted overhead in a plastic box.
Most often, logs are placed on the edge. When using reflective plates, horizontal laying of the beams is preferable.
The plate is shaped like the Greek letter Ω. It is placed with its wings on adjacent logs with the convex part down, in the space between the logs. A pipe is located in the resulting channel.
The plates perform a heat-reflecting function, provide convenient laying and fixation of the pipe.
Fourth way
- Dismantle the floor boards.
- To trim, adjust in thickness so that the base is even.
- Turn around the edge: cut one centimeter on both sides so that there is a gap of 2 centimeters between the adjacent ones (pipe laying channel).
- In places where pipes turn, it is recommended to round off the boards. If you do not have the ability and desire to tinker with boards, you can purchase chipboard boards with already milled grooves.
- Lay a waterproofing film on the logs. The film is laid with sagging: a place for insulation is left between the lags.
- Install insulation plates in the intervals between the lags, tightly against the back.
- Install the vapor barrier.
- Lay moisture resistant plywood and treated boards.
- Place a 50 µm reflective foil. You can use aluminum stainless steel boxes instead of foil (pipes are removed from them). The foil is attached to the flooring with a stapler.
- Lay pipes. At all bends and in a straight line after one meter, they are fixed with metal plates: the plate overlaps the pipe and is attached to adjacent boards.
- Connect the floor to a common pipeline and test for a couple of days. If there are flaws in the installation, it is better to identify them immediately, so that later you do not have to dismantle the coating.
- Lay the covering in accordance with the instructions for it.
Information for those who are interested in electric underfloor heating under the laminate.
Do you want to know everything about the support - columnar foundation, its pros and cons?
The whole process of installing a warm wooden floor can be conditionally divided into the following stages:
- Drafting a project.
- Preparatory work.
- Assembly and subsequent testing of the heating pipeline.
- Finishing works (laying of fine floor coverings).
Project
Before starting any work, you need to draw up a detailed project and perform all the necessary calculations. It is possible to do this on your own, having studied significant amounts of information, you can order an individual project or choose a suitable one from those developed earlier.
The project includes:
- Detailed drawing (diagram).
- Calculation of heat losses for each room.
- Calculation of the amount of heat that should be supplied to each room.
- Resistance of the heating system pipeline.
- Calculation of the step of laying the pipeline, depending on the heat loss of each room.
- The number of consumables that may be needed in the course of work.
After the project has been drawn up and all the necessary calculations have been completed, you can proceed to the next stage.
Wood floor cake
Includes all the necessary work up to pipe laying. You should start with the placement of the lag. The distance between them should not exceed 60 cm.
Before mounting, wooden logs must be treated with antifungal and antiseptic solutions. To exclude the possibility of the appearance of a wood bug, it is unacceptable to leave fragments of bark on any wooden products.
Between the lags, an insulating material (mineral wool, polystyrene, foam insulation, etc.) must be laid on the vapor barrier film. The thickness of the insulation depends on the height of the log, but, in general, does not exceed 100 mm.
The next step is the laying of the subfloor, the function of which, on the one hand, is to ensure an even distribution of the load on the logs, to reduce their deformation (if they are used as overlapping). On the other hand, it will eliminate possible deformation of the finished floor, providing the necessary rigidity.
The subfloor is usually made from some kind of sheet material or from planed boards. The thickness of this floor depends on the distance between the joists, the installation methods and the material used for subsequent layers.
Further actions completely depend on which type of warm floor is chosen.
Modular option
- Modules are mounted on the subfloor, this is usually done with screws or nails, sometimes glue is additionally used.
- Metal plates are inserted into the slots of the modules for heat reflection, if this is provided for by the design of the module (instead of plates, special foil is sometimes used).
- When everything is ready, the heat-conducting water circuit is laid.
- According to the project, slats of the required width and thickness are prepared. The thickness of the lath depends on the pipes to be used. The most suitable outer pipe thickness for residential premises is 16 mm. The slats should be several millimeters thicker than the pipe, so that there are no unnecessary difficulties during installation. The width of the board ranges from 100 to 200 mm and depends on the amount of heat required in each particular room, or its area.
- The slats prepared accordingly are screwed to the subfloor, guided by a pre-developed project.
- Heat-reflecting plates or foil are placed in the grooves obtained after mounting the rails.
- Next, you can do the wiring of the thermal circuits.
Installation


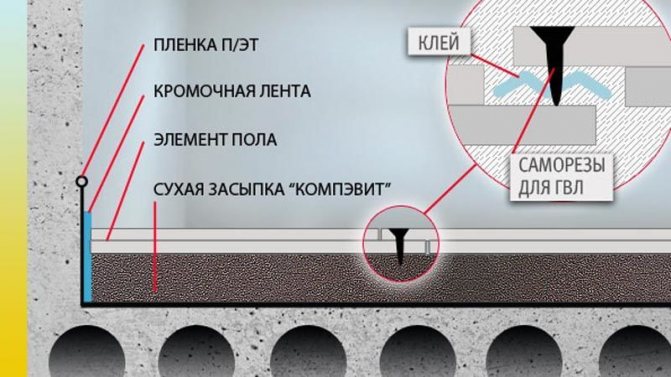
When installing GVL, steam and thermal insulation is also used.
There are several ways in which floors are laid without screed. One of the most demanded and popular is the use of gypsum fiber sheets. In any case, the work should begin with drawing a route, in accordance with which the pipe contour will be laid.
This scheme is applied to the bottom layer of the dry screed. To create such a foundation, you will need to lay materials such as:
- vapor barrier;
- insulation;
- thermal insulation.
Having noted all the places of installation of furniture and household appliances, the angles and points of installation of the thermostat and temperature sensor, you can start creating a support system.
Heat has to rise upwards, so it is important to pay special attention to insulating materials. It is advisable to use only foil-coated roll materials during installation, which guarantee effective heat reflection in the desired direction.


Between the lags, it is necessary to lay a vapor barrier, on top of it a heater and again a layer of vapor barrier that can protect both the wood and the heater from condensation.Gypsum fiber sheets are attached to the lags, the distance between which does not exceed 60 cm, using self-tapping screws.
On the resulting surface, a route for laying the pipe contour is drawn, accurately repeating all the turns and bends. Now you can start cutting the sheets into small strips and attach them to the base of the structure with self-tapping screws. The distance between the GVL strips should slightly exceed the diameter of the pipes used for the underfloor heating.


The surface under the water circuit can be covered with foil
If necessary, such strips are attached in two rows, making sure that the height of the structure slightly exceeds the diameter of the pipe. At the request of the consumer, the entire surface of the future floor is lined with aluminum foil so that it penetrates into the recesses created for laying pipes. This contributes to more efficient heat reflection from the surface.
Between the GVL strips, in accordance with the drawn route, the contour of the pipes is laid and fixed with plastic tape and self-tapping screws. After completing the layout, you can start filling the remaining voids with gypsum mixture or tile glue.


Gypsum fiber sheets are laid on top of this structure. They will serve as the basis for the final floor covering.
The length of the purchased pipe will depend on:
- room area;
- features of the coolant;
- heat loss;
- the power of the equipment that will heat the heat carrier.
Air way of laying pipes for underfloor heating
Possible pipe contours
There are three most common pipe laying methods, of which the optimal one is selected depending on the size and design features of the premises. It:
- "Spiral".
- "Snake".
- "Double snake".
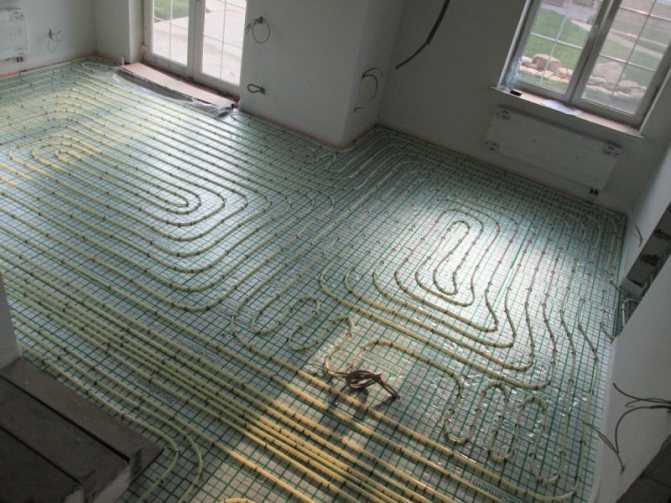
"Snake" is popular due to the fact that it is the most economical in terms of material consumption. However, it has a drawback: when using a circuit of this type in different areas of the room, the temperature may differ due to the cooling of the water. Therefore, it is recommended to use it only in rooms with a small area, where the coolant will not have time to cool down during its movement. This installation has another drawback - the complexity of installation, during which it is necessary to bend by 180 degrees.
The "double snake" assumes a smaller temperature difference in different zones, but at the same time, the difficulties with laying due to the angle of rotation of the pipes remain the same.
For rooms with a large area, it is recommended to choose a spiral contour. Pipes are laid out with a description of the perimeter of the room, starting from the walls and gradually approaching the center, and then in the opposite direction. In such a circuit, heat is distributed evenly and there are no cold zones on the floor. Due to the slight bending of the pipes, this installation method is the least labor-intensive.
“Recently we made repairs in a wooden house. We decided to install a water floor heating system. The height of the ceilings is 3 meters, the pipe was taken 16, in a step of 15 cm. The contour was mounted with a snail with a concrete screed.
Insulated with penoplex base. A month later, the tiles were laid. Radiators were not installed. It's winter now, and we walk barefoot on the floor. The tiles are at a pleasant temperature for the feet, the room is generally warmer than it used to be. "
“I have 75 square meters of timber floors in my house. Insulation cake: beams 100x200, board 40, waterproofing, a layer of foam with grooves, polyethylene pipes, dry screed with reinforcing mesh. We made the floors without pouring concrete, since the house has wooden floors and low ceilings.
The pipes were laid in the grooves of the foam boards. The flooring is 40 squares of laminate, the rest is tiles (kitchen, bath). Already 4 years without problems and cracks. The temperature suits me, I didn't regret the choice.
The selection of material for the finishing coat depends on the method of laying the previous layers and should be carried out at the design stage.
Traditional types of flooring:
- Wooden plank.Can be attached directly to the surface in which the pipes are laid. The thickness of the board should not exceed 22 mm. There is an opinion that a foam polyethylene backing can be placed under the board to compensate for possible unevenness of the base, but it should be remembered that the heat transfer of the floor will decrease.
- Floor tiles. These materials must be settled on an intermediate layer of sheet metal panels (QSB, DSP). This is necessary to evenly distribute heat and pressure over these coatings. The advantages of these coatings are good heat dissipation.
- Linoleum, carpet. The laying process is similar to that of tiles, the difference in temperature conditions, which should not exceed 25˚.
- Laminate floors, parquet. The installation of these coatings is the same as for laying a wooden board. The difference is that these materials cannot be heated more than 25˚.
A solution adequate in simplicity and cost, based on the available materials available in response to the inventions of Western "firms", could appear only in Russia.
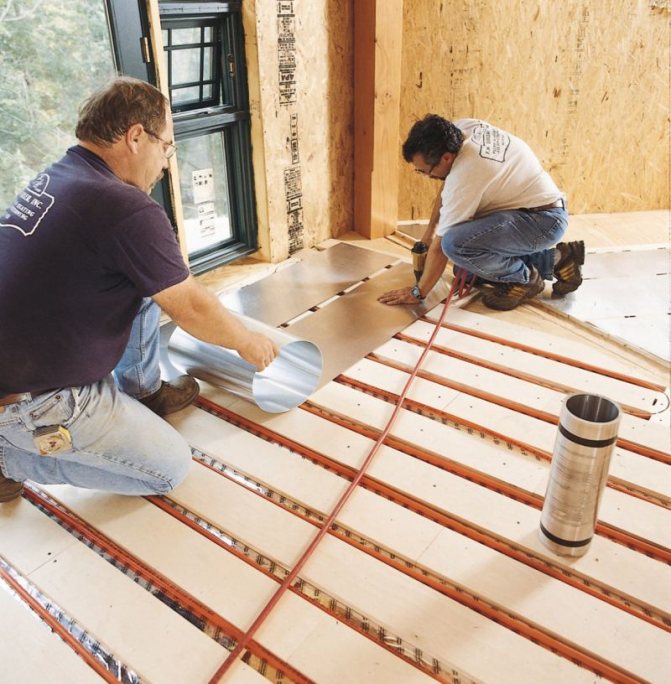
Unlike reinforced concrete slabs, prefabricated wooden floors with heat and sound insulation filling (4) between the load-bearing beams (3) are themselves a good heat insulator, which means that the problem of heat leakage downward is completely eliminated. Either plywood (6) or the popular OSB board (OSB) can be laid directly on the floor beams. No special discoveries are expected here. But then it gets more interesting.
The role of the main heat sink and at the same time heat distribution element of the floor will be played by ordinary aluminum foil (8), which is used in baths and saunas. And since such a serious task is entrusted to her, it is worth looking for thicker foil. Vapor barrier (2) and waterproofing (5).
As the main element of the underfloor heating, it is best to take a corrugated stainless steel pipe (9). It has the best thermal conductivity of all pipes used in such water heating systems. In addition, the corrugated pipe is not afraid of either local overheating, which is possible with not very accurate laying, or movements of the floor structure itself.
The pipe is laid with a predetermined spacing between the inserts (7) made of plywood or the same OSB. It is important to ensure full adherence of the foil (8) to the pipe, for which it is squeezed by hand right on the spot. The height of the plywood inserts, in order to prevent lateral squeezing of the pipe, can be equal to or slightly more than its thickness.
In this case, a standard corrugated stainless steel pipe is used, used in water floor heating systems. Necessarily without a polyethylene cover. A pipe with a diameter of 16 millimeters is 50 meters long in a bay, and a 20 millimeter one is 30 meters long. Based on the condition that 3.8-4 linear meters of pipe are required per 1 m2 of underfloor heating, one can calculate the area that one circuit can occupy.
The speed of installation of the described system is an advantage of this method. The finished floor (10) can be laid and the system can be put into operation immediately after the installation of the pipe. Laminate, linoleum or carpet can be used as flooring. If you plan to use a laminate as a flooring, it is laid directly on top of the resulting structure.
For this, foil is also used, which is laid under the screed in a continuous layer with an overlap of strips, gluing the joints with special tape. To give the monolithic structure additional strength, a welded reinforcing mesh is used, which will also help to distribute heat.
Before pouring the screed, the pipes must be filled with water so that they assume their natural position. It will not be possible to start laying the flooring and start up the system earlier than in a month. Small areas of the floor can be tiled, however, the choice of glue must be approached more carefully, since the overlap will "walk" under the influence of temperature changes.
Varieties of dry floor heating
Depending on the type of backing material, you can choose the most suitable option. This allows you to find the right system for your coverage.
How to make water floors in a wooden house
The device of a warm water floor on a wooden floor with your own hands is practically no different from the structures used in other buildings. The exception is the special safety measures required to protect wooden surfaces from moisture ingress.
Practice has shown that the best option would be to use polypropylene pipes.
Installation work is carried out as follows:
- Floor design - laying the heating system begins with drawing up a diagram. A hydraulic calculation is performed, the efficiency of the water circuit is calculated, and a decision is made to ensure an increase in the efficiency of heat transfer. Floor projects are developed individually, or ready-made solutions are selected.
- The base is being prepared - the floor is leveled with plywood. Soft insulation can be placed under the layer on the rough ground. Correctly make reliable waterproofing. Traditionally, roll fusing materials are used for this, but for best results, you can also apply a special waterproofing mastic in several layers.
- Further actions depend on the choice of the heating system cake. If you plan to pour a concrete screed, then a reinforcing layer must be laid. A water circuit is attached to the mesh from above with clamps. The entire structure is filled with mortar. Pouring of laid pipes is carried out exclusively with solutions intended for work with warm floors.
- In the case of choosing special mats, installation on a wooden floor is carried out as follows. Polystyrene systems are laid on the leveled surface. The mats have ready-made recesses and latches for pipe mounting, or grooves into which heat-reflecting plates are inserted. A water contour spreads over it.
- Floor covering - the effectiveness of floor heating largely depends on the correct choice of finishing material. A sheet of DSP or plywood is laid on the mats. The rest of the work is carried out depending on the choice of flooring.
The maximum length of the water circuit should not exceed 70 m. If this is not enough for the heated area, so-called zones for laying water floors are created. To ensure an even supply to each heating circuit, a water collector is installed.
↑ What is a screed for a warm floor for?
A screed on a warm floor is used when installing a heating system to level the floor surface. A layer of concrete covers the cable, penetrating into all voids and filling the spaces between the turns. Thus, the heating system is inside the concrete screed, which reliably isolates it from the external environment, reducing heat loss during its operation.


The concrete screed reliably isolates the heating system from the external environment, reducing heat loss
The addition of a special plasticizer helps to remove air bubbles from concrete, thereby increasing the density of the screed and improving its thermal insulation properties. The outer layer of the screed is the basis for the decorative floor covering.


The outer layer of the screed is the basis for the decorative floor covering
Important! A screed under a warm floor water performs not only the function of protecting pipelines from damage, but also evenly distributing heat over the floor surface. In addition, it maintains heat and sound insulation of the lower floors.
Laying the floor covering

The choice of material is limited both by subsequent operation and by the method of manufacturing the heating system.
Traditionally, the following types of flooring are used:
- Ceramic tiles - the advantage of ceramics is the rapid heating of the surface and high heat transfer. The use is limited to the hallway, bathroom, kitchen and non-residential areas. When choosing ceramic tiles, heated floors must be screed or covered with cement-bonded particleboards.
- Laminate and parquet boards - there are two types of installation of hot water heating on wooden floors: on mats or prepared grooves. Laminate or parquet can be laid regardless of the installation method. The only drawback of the floor covering is the impossibility of heating the surface above 25 ° C.
- Ordinary board - you can also lay a water-heated floor on wooden beams with your own hands, laying the boards over the water contour. The solution does not require serious material investments. This method is chosen if it is not possible to reduce the distance to the ceiling. Subsequently, it is possible to additionally cover linoleum or laminate.
Subject to the step-by-step installation plan, there are no problems with laying on wooden joists. To avoid further difficulties during operation, it is extremely important to make high-quality floor insulation and waterproofing of the room.
USHP - Insulated Swedish Plate
A little bragging first :). Many people know that information about USB was brought to Russia by a user of the Forumhouse known as Vladimir “Tallinn”. But at the same time, not many people know that the very name “Insulated Swedish Plate” was invented by me :).
And it happened as follows.
For the first time, a friend from Germany hinted about such a foundation, who wrote on the forumhaus that the construction of this type of foundation would be ideal for a frame house. It was then that what later became known as USP was first demonstrated to the Russian Internet public. It was in June 2008.
Unfortunately, at the suggestion of a builder popular at that time on the Forumhouse, the author of a shYdev called Russian Power Frame (he is RSK, he later - Rushen Strasen Karkashen) - a comrade from Germany was hounded, and his ideas were declared heretical and for the mysterious Russian soul - unsuitable (by the way, this ingenious builder subsequently received a term for fraud).
The second coming of the USP took place in 2009. Then a new participant appeared at the forum, now widely known - Vladimir “Tallinn”. In one of the forumhouse topics, he spoke about the foundation of his house in Estonia, which he either designed or built by a builder from Sweden (the homeland of the domestic USP is the Swedish company Dorocell).
It just so happened that your immodest servant stumbled upon this topic. That is, I :). And since at that time I absorbed all the available knowledge on frame house building like a sponge and, along the way, was a moderator at Forumhouse, then assessing the potential of the idea, I separated the messages of Vladimir “Tallinn” into a separate branch and after a little thought, called it “Insulated Swedish Plate”. And then he protected Vladimir in every possible way at the initial stages, from attempts at persecution by domestic amateurs to fill in slabs 40 cm thick.
The name stuck to the foundation, and Vladimir became the “guru” to whom everyone turned for advice. Vladimir Tallinn himself recently reminded me of this story, at the same Forumhouse
Therefore, I can quite honestly say that there is a certain personal merit in the fact that UWB has become so widespread. But let's get down to business
The general principle of construction of the USP can be described as follows: it is a kind of huge "trough" of foam plastic of "foundation" grades (capable of withstanding heavy loads with a small relative deformation). The trough, which is a permanent formwork, is assembled on a prepared crushed sand cushion that provides drainage. Then, in this trough, a reinforcing cage and a mesh are laid, to which, according to the layout of the premises, a pipe for water heated floors is fixed and other communications are scattered - water supply, sewerage and sometimes an electrician. Then all this is poured with concrete and, for good reason, is rubbed with “helicopters” to obtain the slab surface as ready as possible for finishing.It is also important to note that the slab is not simple, but with stiffeners under the load-bearing walls. That is, the thickness of the slab differs under the load-bearing walls from the rest of the surface.
It was a rough, rough description of what UWB is like. Below you can see a typical design diagram:
The original scheme of the Swedish company Dorocell
Interpretation from Knauf
Benefits of USB construction
- We receive an insulated foundation slab with a base / plinth finish suitable for most soils
- With a high-quality performance, we get a floor covering of the first floor ready for finishing
- Communications integrated into the plate - plumbing, sewerage, electrical parts, etc.
- Drainage and drainage system around the house
- Almost ready-made comfortable, low-temperature heating system with water-heated floors - to which it is enough just to connect the boiler equipment
- Insulation of the slab itself and the blind area around the house removes the phenomena of frost heaving, which can become a big problem for more traditional tapes and slabs.
- Energy efficiency. This is one of the most energy efficient foundations - saving on heating costs
- UWB is a highly efficient heat accumulator, eliminating one of the often mentioned disadvantages of frame houses - low heat capacity.
In other words, the construction of UWB is that it is a complex solution. All the same can be obtained separately. But doing everything separately and adding up the costs in the aggregate, with a 90% probability, you will get a more expensive solution.
Disadvantages of UWB
Of course, UWB has some drawbacks that are worth mentioning. True, some of them also apply to other slab foundations.
- The UWB is ideal for flat areas. On sites with a slope, the construction of a USB, like any other slab foundation, can result in "a pretty penny"
- UWB is suitable for many types of soil, but not all. For example, it is necessary to approach the construction of UWB on peatlands and other soils with very low bearing capacity with great care.
- Demanding qualifications of performers. Since the slab includes a lot of communications that require competent wiring, then not all "builders with experience" will be able to take up such a foundation and not screw up
- Low plinth. The disadvantage is conditional, but nevertheless, many are annoyed by the fact that the floor level in the house is practically the same as the ground level behind the wall. The Russian mentality is accustomed to high plinths, while in the USP the entire thickness of the structure is 30 cm. of which, God forbid, usually 20 sticks out above the ground.
- Material consumption. This is especially true now (autumn 2014) - when, due to the rise in exchange rates and sanctions, many materials based on imported raw materials (the same foam) are sharply more expensive.
- Despite the enthusiasm and examples of the construction of even rather heavy stone houses on the USHP, all the same, this is a foundation designed primarily for lighter ones - frame and wooden houses
- Tangible one-time financial injections at the initial stage. The minus is conditional, since doing everything separately will ultimately be more expensive. But you can stretch the cost over time.
- Maintainability of communications. The minus is conditional, since most of the materials used in modern systems of engineering communications are designed for periods that clearly exceed our lives. There are solutions for the maintainability of the main communications (sewerage, water supply), but they require additional costs. So you need to think carefully about how much it is needed
How much does it cost to build a UWB?
Again, a common question is how much all this pleasure is worth. In prices of the summer of 2014, the average cost of USB construction in St. Petersburg was about 6-6.5tr per m2. In Moscow, prices were more expensive, on average 7.5-8tr per m2, depending on the degree of "promotion" and the qualifications of the performers. I have no information on other regions.Unfortunately, given the sharp drop in the ruble exchange rate and the large number of "import-dependent" materials in the USP, the price for it will increase significantly next year.
That is, the construction of a 100m2 USP would cost the customer 600-800tr on average, depending on the region and the contractor's appetites. The amount is not small. But go back to the advantages of USHP and estimate how much it will cost separately - a slab, insulation of the foundation, a screed with a warm floor, drainage, communications, etc. Perhaps, when you add up all the costs, the price of UWB does not seem so huge. The heating system alone in the assessment of "specialized specialists" can pull 300-400tr.
USHP before pouring with concrete, with divorced floor heating pipes
After pouring. Outside, only the communication exits and the underfloor heating collector remained
What tool is required for installation
To install the water circuit you will need:
- Roulette.
- Plastic pipes and fittings.
- A set of locksmith and construction tools.
- Screwdriver.
- Milling machine.
Installation of a concrete water underfloor heating on wooden floors will additionally require:
- Perforator.
- Rules.
- Angle grinder for cutting reinforcement.
- Construction level.
A set of cutters and drills and a powerful drill are useful for working with wooden surfaces.
Advantages and disadvantages
This foundation has its pros and cons of using, like any other type of foundation.
There are the following advantages of the Finnish slab:
- the possibility of creating a high base;
- a small amount of earthwork is required, since a deep pit is not needed under the Finnish slab;
- high energy efficiency;
- no subfloor arrangement is required;
- the ability to install a system of underfloor heating;
- can be installed on difficult terrain;
- suitable for installations with high groundwater levels;
- the possibility of finishing after the completion of the installation.
The foundation of this type is excellent for the construction of buildings on difficult types of soil. It can be land with deep soil freezing, sandy, swampy and heaving soils.
Main disadvantages:
- relatively expensive construction;
- the installation of a Finnish slab can take up to 2 weeks, depending on the characteristics of the soil and the speed of the main work.
What mistakes should be avoided during installation
The design features on a wooden base are that any violations and changes in the phased installation of heating will lead to operational problems. Condensation and leaks are critical.
The pipe-laying system prevents the following violations:
- Exceeding the maximum length of the circuit - the pipe should not be more than 70 m in length. The circuit should be located below the boiler, so that the natural circulation of the coolant is ensured, in the absence of a circulation pump.
- Lack of waterproofing - organizing wooden floors with water heating on their own often leads to the desire to save on consumables. It should be remembered that good insulation of wooden surfaces from moisture is essential in a wooden house. It is best not to limit yourself to simple measures, but to use additional means of protection: impregnations and a protective corrugation for the pipe.
- The choice of finishing material - even before choosing a method for installing underfloor heating, you should consider what kind of material the surface will be faced with. The maximum heating temperature and the stages of work depend on this.
Underfloor heating for a wooden house is a smart solution. Provided that the recommendations for installation are followed, possible difficulties in the process of future operation can be avoided.
Polystyrene
Lightweight and inexpensive material, due to its ease of use, and low cash costs in case of error or damage, you can lay dry warm floors with your own hands.


It can be installed in private wooden houses.Due to its low weight, even old wood can be used as a base.


The polystyrene plates are placed directly on the floor. They represent a surface with bumps arranged in rows. They contain aluminum or steel plates, necessarily galvanized.


The plates have a recess for heating pipes. On top are sheets of gypsum fiber board to give the system stability and strength.
Why is a warm floor without a screed suitable for installation on joists?
The advantages of underfloor heating, where the pipes are laid in a cement screed, are obvious:
- The heating temperature of the coolant is small, no higher than 55 degrees, so you can save money on energy.
- The cement screed, inside which the pipes are laid, provides uniform heating of the entire floor surface.
- Since the heat spreads over the entire floor area, a comfortable temperature and a favorable microclimate are established in the room.
There are still many advantages of the traditional technology of installing water heating under the floor screed. The catch is different: how to make the water floor heating system have the same advantages, but at the same time it was possible not to use a heavy screed. After all, floor beams made of wood are already exposed to loads:
- They are affected by static loads from partitions that are located in the room and pieces of furniture.
- Wooden beams without deflection compensate for the weight of the subfloor, subfloor and installed thermal insulation.
- They are constantly exposed to dynamic influences from the movement of people living in the house.
So, imagine what will happen if a concrete monolith is added to all of the above loads, which has a heavy weight - several tons for each room.


Underfloor water heating device in screed
In order for the beam device to withstand the weight of such a structure, the cross-section of the beams will need to be doubled, and this will directly affect the cost of construction. However, the Finns helped to solve this problem, who developed a technology for installing a warm floor on logs by a dry method, that is, there is no need to create a screed.


Installation of a warm water floor without screed
This technology is suitable if you want to arrange a structure that will heat the floor on a wooden base. In this case, the loads will be only 20 kg per 1 sq. m of the room area. And now compare the difference in weight between the installation of a warm water floor in a screed and without a screed, the result is stunning!
Water heating circuits in wooden houses can be removed in a screed in several cases:
- If in a wooden house, the covering of the first floor rests on a slab or strip-type foundation or on solid ground.
- In houses built from SIP panels 200 mm thick, if they are supported on a tape-type foundation or on a screw-pile foundation.
- If a frame or log house has a base made of very powerful beams that can freely support the large weight of the screed.
Attention! Before installing the underfloor heating on wooden logs, you need to choose the right installation technology and calculate the pressure force that will create a pie of the heating system on the beams. If a wooden house stands on a high-quality foundation, and the beams are thick and powerful, then a screed can be made, otherwise such installation is unacceptable. If you are not sure that the ceiling will support the weight of the warm floor, consult a professional.
Now you know why the screed-free installation technology has become the optimal solution for installing a floor heating system. This technology provides high-quality heating of the floor and premises, while the load on the wooden base is insignificant. However, before proceeding with the installation, you will need to properly prepare the base, we will talk about this below.