Selection recommendations
And it seems to me that aluminum and bimetallic heating radiators will gradually replace cast-iron radiators. They began to be used not so long ago, so there is still a wary attitude towards them. But they have already proven themselves well and more and more people prefer them. I installed aluminum radiators in my apartment 3 years ago. They look very beautiful, no need to paint and the house has become warmer.
Considering that in the old days there was no particular choice among radiators (as a rule, most had classic cast-iron radiators), then at present there is a wide range of products on the radiator market. In my case, when choosing a radiator, there was "where to turn around", since the heating system is closed and created in my own house
On the advice of familiar installers, I drew attention to bimetallic radiators and made the right decision. For several years I have not bothered with the painting process, as is the case with cast iron, radiators do an excellent job with their functions and the house is always cozy and comfortable, regardless of the outside temperature
The only thing that had to be done additionally to protect the radiators from deposits was to install a system for deeper cleaning of the coolant.
I would not be at home and I do not advise anyone to install an aluminum or bimetallic radiator in their apartment. Bimetal in those regions where there are serious problems with water treatment - such a battery will have to be changed after one heating season. Aluminum and bimetal are assembled by hand by a craftsman and the quality of assembly depends on the professionalism of the person. Steel, for example, is assembled in fully robotic factories. Austrian radiators, among other things, have insurance against damage for 1 million and a guarantee for the entire device, and not a section like bimetal and aluminum happens. With its help, you can block the entire window opening, providing an even flow of heated air to the window. This eliminates the formation of cold air currents on frosty days.
I completely agree with you, Sergey. Bimetal and aluminum in an apartment is a risky undertaking, it is not possible to avoid contact of the coolant with the metal and there is a threat of explosion. The quality of a steel radiator is much easier to determine, here are the signs of a quality device: the uniformity of welds, gaps, painting and the availability of guarantees, insurance. And do not be lazy to consult with your master or HOA!
Bimetal has higher operating pressure characteristics - they can be safely installed in high-rise buildings (in them, the pressure usually does not exceed 6 atm). The working pressure of bimetallic radiators is 10 atm, and some can withstand 16 atm in general. It is advisable to take a little promoted brand - the plant always does the first order well.
From the section of the article on steel radiators: "Steel radiators do not withstand water hammer and pressure increased to 25 atmospheres, so it is better not to use them in heating systems of city apartments." From the section of the article on bimetallic radiators: “It turns out that the bimetallic radiator has combined the best properties of steel and aluminum heating devices. From the steel he took. resistance to pressure drops (withstands up to 40-50 atmospheres) ". Where is the truth?
The steel radiator according to the "German" technology has served a little more than 10 years. At one point, a needle-thick trickle appeared at the spot welded. For a battery, this is not a period.Soviet cast-iron batteries last half a century or longer. Now I am racking my head which one to buy. The quality of modern technology is deliberately damaged. You buy a pig in a poke.
Radiator compatibility with heating system
The modern assortment of batteries is diverse - cast iron, aluminum, steel, copper, bimetallic devices - it is only important to understand which heating radiators will best "fit" into the specific heating system of your home. What does this mean? This means how much the technical parameters of the heater - the permissible temperature of the coolant, its pressure and composition, as well as heat transfer and inertness correspond to the indicators of your heating system

A heating radiator not only heats the room, but also carries an aesthetic load in the interior design
When buying a radiator, its appearance, durability, and, of course, the price are also important. It should be borne in mind that there are nuances in the selection of heating batteries for open systems (apartment buildings) and closed systems (individual houses). In the event that the indicators declared by the manufacturer do not correspond to the characteristics of your heating system, then rapid wear and even failure are possible.
Technical specifications
Paying attention first of all to the appearance and cost of the radiator, nevertheless, do not forget that the technical and operational characteristics of the device should be in the foreground. Not every heating battery, both imported and domestic, will withstand the working conditions in existing domestic heating networks.
The centralized heating system, inherited from the Soviet Union, is characterized by fluctuations in pressure and temperature, as well as poor quality of the coolant (water). The design temperature for a single-pipe open domestic system in high-rise buildings is 105 degrees Celsius, the pressure is 10 atmospheres. However, these parameters sometimes go off scale when starting the heating system after the summer period, which leads to water hammer, which some heating devices from foreign manufacturers are not designed for.
Not every heating battery, both imported and domestic, will withstand the working conditions in existing domestic heating networks. The centralized heating system, inherited from the Soviet Union, is characterized by fluctuations in pressure and temperature, as well as poor quality of the coolant (water). The design temperature for a single-pipe open domestic system in high-rise buildings is 105 degrees Celsius, the pressure is 10 atmospheres. However, these parameters sometimes go off scale when starting the heating system after the summer period, which leads to water hammer, which some heating devices from foreign manufacturers are not designed for.
It is imperative to pay attention to the permissible temperature and pressure of the coolant in the heating system, which are indicated in the passport of the heater. Anodized aluminum panel radiators allow operation in pressurized systems and do not require paintwork


Anodized aluminum panel radiators allow operation in pressurized systems and do not require paintwork
Another fundamental parameter for a heating battery is its heat transfer. This characteristic affects the efficiency of heating the air in the room and depends on the material incorporated in the structure. It is well known that the heat transfer of steel is lower than that of aluminum, and copper is better than cast iron in terms of this indicator. But, based on any one technical parameter, it will not be entirely correct.It is necessary to comprehensively evaluate all the pros and cons of each type of heating device in order to opt for the best option.
What are flat heating radiators
It is necessary to start talking about flat heating batteries from their depth size. There is no exact indicator that would indicate the fineness of the device. This is mostly determined by eye. For example, a cast-iron radiator can be taken as a standard - this is a common design. Anything that is two times less than its depth, and can be attributed to flat heating radiators.
If you make an overview of all existing models, then only steel panel batteries are suitable for this standard. We will consider them. Why is it that panel structures are thin? It's all about the technology of their manufacture.
How can you flush the heating battery
These are devices made from stamped steel sheets. The form is based on a solid sheet with a sufficiently large embedment area. That is, it is not a sectional design, but flat over the entire area of the heater itself. This is precisely what is achieved by increasing the heat output. But at the same time, the depth of each panel is not very large, and accordingly the volume of the coolant used in the heating system in the flattest radiator will be small. This ratio has a definite plus - a small fuel consumption for heating the coolant. That is, these two values are in direct proportion.


Manufacturers have gone further. They did not get hung up on devices with a purely panel form, because, as mentioned above, this form has a reduced power. To increase this indicator, additions were made to the structure itself in the form of a finning system, the so-called convection ribs. They are welded over the entire area of the battery by spot welding. The main shape of the ribs is trapezoidal.
Types of flat radiators
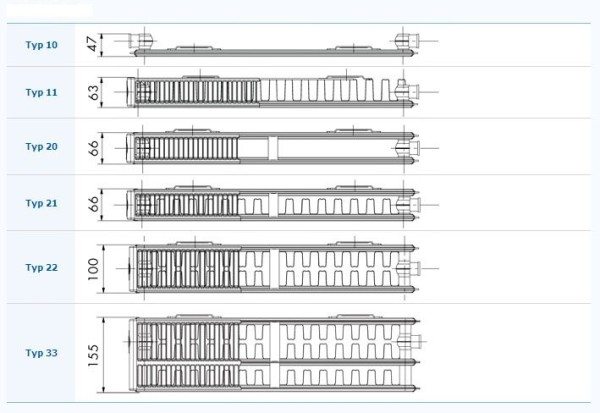
The classification of flat radiators is the same for all manufacturers. There are five types in total: 10, 11, 12, 22 and 33. How do they differ from each other?
- Type 10 is just a no-nonsense stamped panel. If we talk about the category "the thinnest heating radiators", then this type is the basis of this category. You will not find it thinner on the market. Let's look at the type using the example of Kermi radiators. So type 10 has a depth of 46 mm.
- Type 11 is one panel with one layer of finning system. The depth of this model is 59 mm. Quiet and it can be categorized as "flat".
- Type 12 consists of two panels with convection ribs installed between them. Its thickness is 64 mm.
- Type 22 is a structure consisting of two panels and two finning systems, which are located between the panel planes. Depth - 102 mm.
- Type 33 consists of three panels. Between the first two, two layers of ribs are installed, between the second and the third one layer. Depth 157 mm.
For other manufacturers, the depth size can vary in the same range with small deviations in one direction or another. The deviations are insignificant, so the dimensions of Kermi heating radiators can be taken as the basis for our analysis.
Attention! All types of steel panel radiators, except for type 10, are equipped with protective side walls and an upper grill. This improves the appearance of the device, but increases its cost.
And one more thing, convection fins are a real dust collector, which is very difficult to clean.
But now let's choose from this type those heating devices that can enter the category of "flat". To begin with, the depth of the ChM-140 cast-iron radiator is 140 mm. We will build on this.
You can immediately determine that the first three types, which are 10, 11 and 12, are subtle.But 22 and 33 are not included in this category. That is, it turns out that not all steel panel heating radiators can be considered flat.


Varieties of panel thin batteries
All manufacturers use the same classification for thin flat heating radiators.
We are talking about five types of heating devices:
- Type 10. The simplest panel (stamped), without any decorative frills. It belongs to the popular products from the series "maximally flat panel radiators for heating": the depth of this structure is 46 mm. The most popular of this product line is the Kermi model.
- Type 11. Appliances of this type are characterized by the presence of one layer of convection ribs. The depth of the product was increased to 59 mm.
- Type 12. This design was somewhat complicated by dividing two flat panels by a ribbing system. The thickness of the device is 64 mm.
- Type 22. An even more complex scheme is used here: in addition to two panels, there are two finning systems located between the planes. The depth of such a battery is 102 mm.
- Type 33. The most complex model, which includes three planes. The first pair of panels is divided by two ribbed sections at once. Another section is installed between the second and third panels. Due to the increased complexity, the depth of the device also increases: it reaches 157 mm.


It is important to know that the term "flat water heating radiator" is not used to refer to the last two models. Some manufacturers allow a change in thickness in both directions within 10 mm. All versions of panel heaters (except for the 10th type) use a protective top grill and side walls. Thus, the decorativeness of the product increases (this affects its price).
Characteristics of sectional types of heating batteries and their comparison
- Cast iron sectional radiators
... Considering the types of heating batteries, it should be noted that it is cast iron devices that have been known to consumers for a long time, since the times of the Soviet Union. In those years, they were installed everywhere - in residential, industrial and public premises.
The design solution of cast-iron sectional radiators allows them to be heated to high temperatures. Due to the peculiarities of cast iron as a material for making batteries, they give off heat for a long time and therefore in those years they were assigned leading positions among heating devices, the heat transfer of cast iron radiators is quite good.
True, cast-iron radiators need to be warmed up to the desired temperature for a longer time, and this requires a larger amount of fuel or energy carrier. In order to save money, not all consumers choose cast iron products for installation.
The appearance of modern cast iron radiators has undergone minor changes with the same technical characteristics. One section is capable of heating about two "squares" of the area. You can even find designer models on sale that can decorate a room.
Since a large amount of fuel is needed to heat cast iron appliances, they are not installed if they plan to use expensive energy sources, for example, electricity. They choose more economical heating radiators, including aluminum batteries.
Aluminum sectional radiators
... These devices are considered a modern alternative to cast iron devices, since they are lighter and less heat-consuming. Aluminum sectional products give off heat no worse than cast iron and quickly warm up to the desired temperature (for more details: "How to choose aluminum radiators: technical characteristics"). Thanks to their aesthetic and neat appearance, they fit perfectly into a modern interior. One aluminum section heats one "square" of the room.If you install such batteries yourself, you can handle the installation without any problems on your own, since they are much lighter than cast iron products. According to experts, if we compare heating batteries for a private house, then aluminum sectional radiators have now become the clear leaders.
Bimetallic radiators
... Outwardly, such heating batteries are similar to aluminum appliances. Sectional bimetallic heating radiators can be seen in the photo. They are joined by elements made of steel and aluminum. Due to the manufacture of two alloys, these devices are called bimetallic.
When you look at a cross-sectional view of a bimetallic heating radiator, you can see a stainless steel heat-conducting channel inside it. Thanks to this design, the durability of the devices has increased significantly. And the thermal conductivity of bimetallic radiators is greater than that of aluminum. These heating products can be installed with an economy class coolant. One section of such a radiator supplies heat to 1.4 "squares" of the area. Bimetallic radiators are lightweight, and their installation is similar to the installation of aluminum batteries.
For different types of modern heating devices, sections may differ in size. Therefore, when choosing radiators, the section power should be specified. Based on this parameter, you can calculate the number of sections, taking into account the area of the room.
We disassemble flat heating radiators
Anyone who has visited a specialized store selling heating equipment at least once can appreciate the whole variety of heating appliances offered on the market. In fact, this is a huge assortment that allows you to make a choice according to the taste of the consumer. No wonder they say that demand creates supply. So this postulate is directly related to modern heating radiators. But the topic of our article is flat radiators. Why are they called that, and why are they needed at all? We will answer these and other questions.
Let's start with the second question, which defines the purpose of the flat structure. There are several positions here:
- Reducing the size of the heater - increasing the free space of the room. This is especially true for the windowsill. With flat radiators, its width decreases dramatically. Good or bad, everyone decides for himself, but the designers are delighted with it. There is an opportunity to experiment.
- The heating battery itself is a kind of dust collection. By reducing the width of the device, we reduce the plane on which the dust settles.
- Let's add that flat batteries have a presentable appearance. In any case, they differ significantly from the sectional models.
And now the most important question related to the heat transfer of this type of radiators. How much is this indicator decreasing? It's no secret that the size of the heating battery affects the amount of heat output. To thoroughly understand this issue, you need to understand what flat heating devices are.
Installation
Flat radiators are most suitable for rooms with a closed heating system. The presence of an expansion tank is a prerequisite.
The heating process consists of the following steps:
- The pump acts on the coolant, which, in turn, begins to circulate through the pipeline.
- Then it goes through the valve.
- At the next stage, it ends up in the radiator.
- Then he moves along the air carrier.
- It moves to the return pipe until it reaches the expansion tank with a membrane.
If you decide to install flat radiators for an open heating system, then remember that in this case they will not last long, because will not be able to withstand corrosive processes.
Do not purchase thin radiators for installation in rooms with high humidity.
The device and principle of operation of flat batteries
For the manufacture of steel flat heating radiators, stamped metal sheets connected to each other are used. High-tech welding contributes to the formation of reliable, durable joints.
Two connected planes-panels exhibit a high degree of heat transfer, a small internal cavity is formed in them, through which the coolant circulates. To use the equipment as efficiently as possible, you need to adhere to the recommended temperature regime. To optimize fuel consumption, ribs were added to the planes, resulting in a new class of technology - convection finned batteries. Additional elements are attached to the surface using spot welding; in cross-section, the equipment has the shape of a trapezoid.
Flat batteries in the upper part are equipped with perforations - these are the hot air outlet zones. The casing contains metal pipes with radiator plates. The working fluid, circulating through the tubes, releases part of the heated air; the flow path also passes through the upper zone with metal perforations. As the face heats up, some more heat energy is released.
Flat radiators are optimal for closed-type heating systems; it is not advisable to install them in centralized networks. These devices work with heat transfer fluids showing a low pressure level.
Overview of flat products
Features of production
If we are talking about flat models, then most often we mean not the surface relief, but the depth of the radiator. In this case, the term "flat" can be interpreted in different ways, because this category very often includes all batteries, the depth of which is less than that of a standard cast iron product.


Shallow depth aluminum products
Almost all devices of this type are steel panel heaters. No, in principle, you can find both a flat oil cooler and an aluminum structure, but the main niche in this market segment is occupied by steel.
The following mixed technology radiators are produced:
- The basis of the product is a stamped steel sheet, which is machined and forms the inner contour of the heater.
- Due to stamping, a profile is formed, which provides an increase in the heat transfer area.
- Trapezoidal convection fins are sometimes welded to the main sheet to increase efficiency. As it passes through the fins, the air is heated and then distributed throughout the room. (See also the article Repairing heating pipes: features.)


Appearance of a flat panel model
As a result of all these operations, a flat steel radiator is obtained, which combines compact dimensions with a fairly good heat transfer. Of course, in this parameter it will be inferior to full-size models, however, if it is the shape that is important for us, then we will have to put up with some heat losses.
Types of panel radiators
Most panel radiator manufacturers use the same product classification. Once you understand it, you will be able to determine the depth of the model and its structure at a glance - even if you are not in front of the battery itself, but only the instructions with markings.
Note! Typically, the first number indicates the number of panels, the second the number of rows of convection fins.

Design features of different types
How the legend is deciphered, we will tell in the table below:
Main varieties
Flat heaters are easy to distinguish from traditional sectional counterparts in appearance. The front side of the devices is a solid panel, sometimes smooth, more often a corrugated panel with or without perforation.


Smooth surface model
Conventionally, all heating devices belonging to the flat category can be subdivided into the following types:
- wall panel batteries with heated water as a heat carrier;
- oil-fired electric heaters with the possibility of mounting on a wall or with a floor arrangement;
- electric convectors with wall and floor arrangement.
All these heating devices, despite the obvious differences, are characterized by a small thickness, which greatly simplifies their installation on the wall. Consider the features of the device and operation of each of the listed modifications.
Panel batteries
The photo shows an example of a compact installation of a flat heater
This category of equipment, first of all, should include a flat steel radiator, which today can be purchased in most specialized stores.
Outwardly, such devices are a rectangular plate, in the upper part of which there is a perforation necessary for the release of heated air. Metal tubes with radiator fins are located inside the casing.
Due to the circulation of the coolant through the tubes, warm air is partially released, passing through the upper perforation, and partially heats the front metal surface, which, in turn, also releases heat into the room.
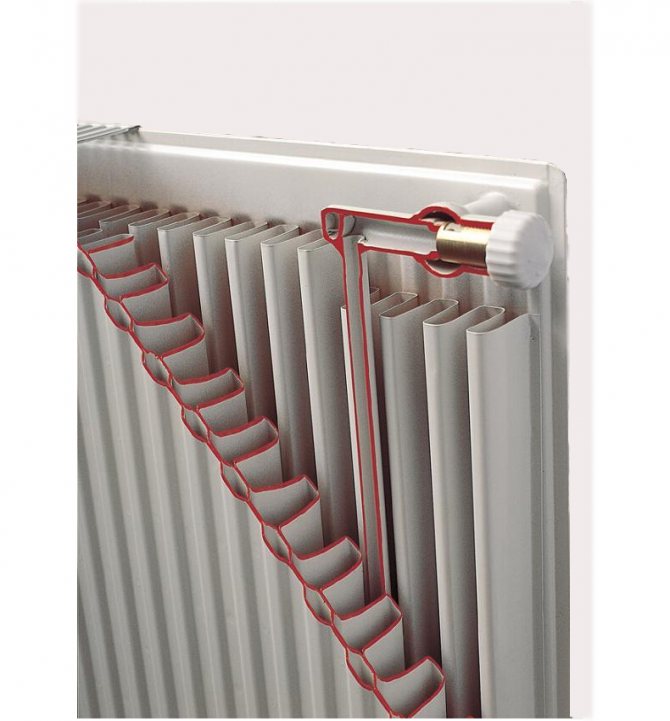


Sectional steel flat heating radiator
The steel panel radiator is mainly intended for installation in autonomous heating systems and is not recommended for use in centralized systems.
The fact is that the device is designed to operate with a low pressure of the coolant, no more than 10 atmospheres at a temperature of no more than + 100 ° C. Nevertheless, the statistics of the operation of panel steel batteries show that such devices are successfully operated in apartment buildings.
Important: A serious threat to steel batteries is the specific composition of the coolant in the centralized heating system. The presence of reagents in the circulating water can accelerate the course of corrosive processes.
Oil fired electric heaters


Flat oil cooler, wall-mounted and floor-mounted
There are two types of oil heaters on the market: sectional and panel heaters. We are interested in a flat panel version with the possibility of wall or floor installation.
This heater differs from other batteries in that not water, but mineral oil is used as a heat carrier. This solution has the characteristic advantage that oil cools longer than water and, as a result, releases heat longer.
Oil panel radiators have the following advantages:
- Low energy consumption compared to spiral electric heaters.
- Does not dry the air and, as a result, comfortable living conditions in the room.
- Low temperature of the heated surface and, as a result, there is no danger of getting burned with careless touch.
- A wide range of heaters on sale and, as a result, the ability to choose a device with suitable dimensions.
- Affordable price.
- Relatively low weight and, as a result, the ability to mount on any walls.
- Simple installation instructions, and therefore it is possible to do the installation yourself.
Important: Due to their independence from heating systems, such heaters can be installed not only in apartments used for permanent residence, but also in seasonal suburban houses.
Wall mounted electric convector


Electric convector in the interior of the cottage
When listing flat thin heating radiators, one cannot fail to note electric heating convectors.These devices are also available for sale in a wide range of modifications, which are distinguished by price, standard sizes, power consumption, design of heating elements, etc.
Unlike a traditional radiator, in which one or another coolant circulates, this device uses heating elements that transfer heat to metal plates, which, in turn, release this heat through slots in the upper part of the protective casing.


Electric convector in the interior of a modern apartment
In the process of air convection, the device can quickly warm up the room. This category of heating devices is universal in terms of operation, but, nevertheless, it is the best choice for cottages, in which residence is of an episodic nature.
So, we have decided on the main types of flat heating devices that can be used in an apartment or a country house. In conclusion, we will consider in more detail the features of the selection of panel heating radiators in relation to a particular living space.
Features of the selection of steel panel batteries
When choosing steel radiators, you should pay attention to the marking.
The following letter designations can be found in the marking:
- kv - lower connection type;
- k - lateral connection type.
In addition to letter designations, there are numerical values in the marking:
- 11 - type of batteries with one external heating surface.
- 21 - type with two heating panels and one heat exchanger through which the heat carrier circulates.
- 22 is a type with two panels and two heat exchangers between them.
- 33 is a type with three panels and three heat exchangers.
So, we have decided on the marking, but which one to choose?
For use in standard-layout apartments, the twenty-first type of radiator will be the best choice. This choice is explained by the small thickness, acceptable heat transfer and low cost.
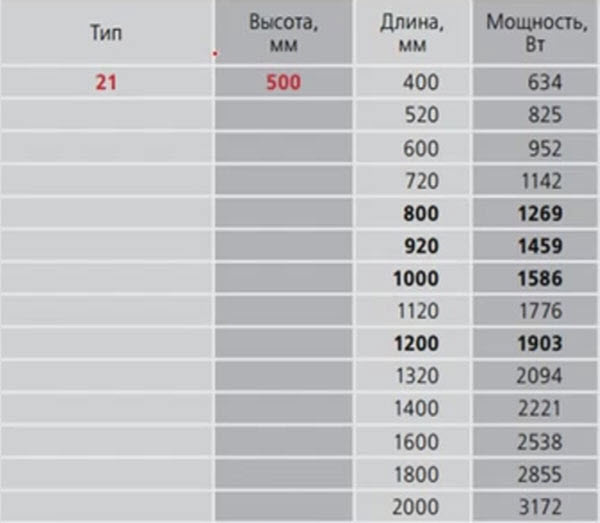

The ratio of the height and length of panel radiators of 21 types with power parameters
Let's try to calculate the heat dissipation of a device with a length of 1 m.
As we can see in the table, this parameter is approximately 1.5 kW. At the same time, you need to understand that this value is possible only if the coolant is heated to + 90 ° C.
In fact, the temperature of the coolant in a centralized system is much lower, and therefore the real heat transfer will be 1.5 kW not indicated in the table, and not more than 1 kW. Thus, if for normal heating of the room there is enough battery power of 1.5 kW, we do not limit ourselves to the installation of one radiator, in the passport of which the power we need is spelled out.
In order not to freeze in winter, it is better to install not one, but two such radiators. Or, if the configuration of the room allows, we install a single panel 1600 mm long and this will be enough to create comfortable climatic conditions.
Popular types of heating batteries
If we compare heating radiators, then first of all it is clear that they all differ in design. Based on the fact that they look differently, batteries are divided into sectional and panel products.
Sectional radiators. Such devices are divided into three main groups:
- cast iron batteries;
- radiators made of aluminum alloy;
- bimetallic products.
From the name it is already clear that the heating device consists of sections assembled into a single structure. For example, many consumers are familiar with cast iron batteries used for more than one decade, which are a set of a specific number of sections. New aluminum appliances also consist of several sections, but if you look at these heating radiators, the comparison will be in favor of modern products, since they look more aesthetically pleasing (for more details: "Aluminum radiators - technical characteristics, installation").
Panel batteries
... They are made only of steel. Outwardly, they are a flat product with bulges. Flat batteries were widely used in the 80s of the last century. They were mainly installed in panel houses.Modern panel radiators have been modified and their appearance has changed slightly. After that, their heat transfer increased, and they are once used for heating living quarters. Comparing sectional and panel heating radiators, it can be noted that the former are widely used in heating systems and consumers respond positively to them.


Electric heating battery
Such radiators are used in cases where it is impossible to use a centralized or autonomous gas heating system. The operating cost of such devices is quite high, however, they have some undeniable advantages. Electric batteries are distinguished by a simple installation process, high fire safety and programmability. Electric heating batteries can be oil, water and infrared; they are extremely convenient in self-contained rooms.
What are the heating radiators
Heating batteries, they are also radiators that are installed in residential premises, are mainly water or electric.
Water types of heating batteries heat housing with water, which is used as a heat carrier (in more detail: "Water heating radiators - types and types"). After the liquid is heated to a certain temperature, it begins to circulate through pipes and batteries, giving off thermal energy to the surrounding air.
Electric heating radiators are only outwardly similar to conventional appliances, but their principle of operation is different. They are usually used as an additional source of heat, since high electricity prices make the operation of such heaters economically unprofitable.
True, if there is no opportunity to equip water heating, there is nothing else to do but to use electrical appliances for heating. Suppose that the family goes to the country house outside the city only on weekends - in this case, the electric convector will be enough, because it will not freeze.


Type classification
The main criterion for dividing into types is the standard size, it is indicated on the product labeling:
- type 10. Standard panel models without additional options, they are simple, have a minimum depth of 46 mm;
- type 11. Slightly thicker than the previous version due to the fact that convection ribs were added to one side. Here the depth is 59 mm;
- type 12. A complex product formed by two panels and ribbing between them, the thickness of the device is 64 mm;
- type 22. Two panels equipped with two finning systems, depth 102 mm;
- type 33. The thickest panels at 157 mm are three panels with three ribbed parts.


Flat radiators, type 33
Sectional and panel oil heaters can be floor-mounted and wall-mounted; here mineral oil is used as a heat carrier. Liquid cools longer than water, which enhances the performance benefits of the model. Oil-type flat radiators have the following advantages:
- simple installation that you can do on your own;
- low dead weight, expanding the possibilities of application on any walls;
- loyal prices and a wide range of technical solutions, dimensions;
- low-temperature mode of use, excluding burns;
- the device does not dry the air, provides a healthy microclimate;
- moderate power consumption.
In wall-mounted flat convectors, there is a heating element inside, it directs heat energy to the metal plates. The heated air enters the room through the slots provided in the upper segment of the casing. The principle of convection of air flows ensures fast and uniform heating of the room. Such universal devices are often used in country cottages with year-round living.
The battery connection can be side or bottom: the letter "K" on the marking for the first option, "Kv" - for the second.
What are the types of heating batteries review and comparison
With the onset of the heating season, many residents complain about cold batteries in the apartment. But utilities are not always to blame for the problem of poor heating. Often the reason lies in the fact that the heating radiators are clogged or have already become unusable and need to be replaced with modern types of heating batteries. Before proceeding with the reconstruction of the heating system, it does not hurt to ask what kind of heating batteries are and what advantages and disadvantages they have.


This topic is devoted to this article, which tells about modern heating devices for apartments and private households. It talks about what kind of heating radiators are.
Radiators and convectors
The types of heating devices used in the water heating system are distinguished not only by the material from which they were made, but also by the principle of operation. Since the days of the Soviet Union, radiators and convectors have been used in heating systems. Radiators have higher heat transfer rates than convectors. They radiate heat from their surface and provide constant heating of the room, and convectors move air flows from bottom to top, thus forming a draft.
Externally, convectors are also very different from radiators, just look at the photo of these devices, and you can accurately determine which device is a convector and which is a radiator.
The basis of the convector's design is the pipe through which the heat carrier passes. The pipe has thin, sharp steel plates.
The advantages of convectors include small dimensions, reliability, and low cost. These devices can be built into the floor, into the wall and placed where there is simply not enough space to install a radiator.
The disadvantages of convectors include a low heat transfer coefficient. Therefore, it is unlikely that it will be possible to warm up a large room with the help of these devices; they can only be used as additional sources of heat.
The convection method of heating a room can hardly be called an advantage. Since the convection of air, or the movement of air is simpler, this is nothing more than a draft, and you will hardly be delighted with such a phenomenon in your home. Convectors are often used in office buildings where a large glazing area makes it impossible to install conventional radiators.
What are the possible types of connection of radiators
The efficiency of the heating devices is influenced by the chosen scheme of their installation.
There are different types of connecting heating radiators:
- Diagonal connection. This method of installing heaters is suitable for long batteries that can heat up evenly. The pipe supplying the coolant is fed on one side to the branch pipe at the top, and at the bottom to the branch pipe is supplied to the branch pipe. If hot water is supplied from below, the battery efficiency will decrease by 10%.
- One-way side connection. This is the most common way to install radiators. This method of connection, in which the supply pipe is connected to the upper branch pipe, and the outlet pipe to the lower one, provides the greatest heat transfer.
- Bottom connection. This method of wiring batteries is used only if the heating system is located in the floor.
The service life of the heating system, as well as its functionality, efficiency and reliability, depend on how correctly the type of connection is chosen and how well the installation of radiators in the heating system will be made.
Types of water radiators
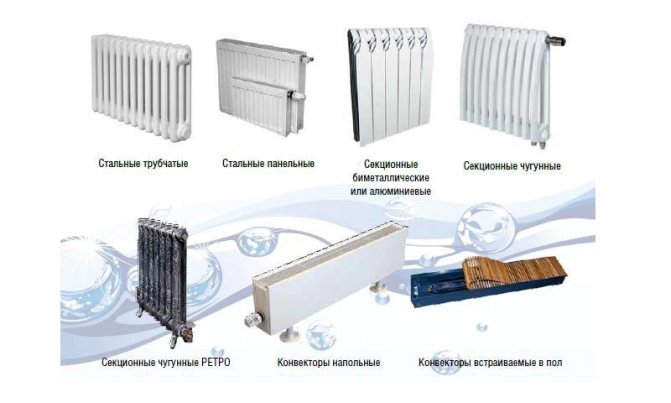


Types of water radiators
In modern specialized stores there is a large selection of models of heating batteries. Floor radiators differ from each other in the following parameters:
- dimensions;
- the weight;
- power;
- the amount of heat loss;
- design;
- material.
Therefore, when choosing a new heater, it is important to take into account the individual parameters of your home and what is of the highest priority in these conditions.
Important: the established standard for heating a dwelling is 100 W per 1 m2 (the value is correct for a room with one window and one outer wall).
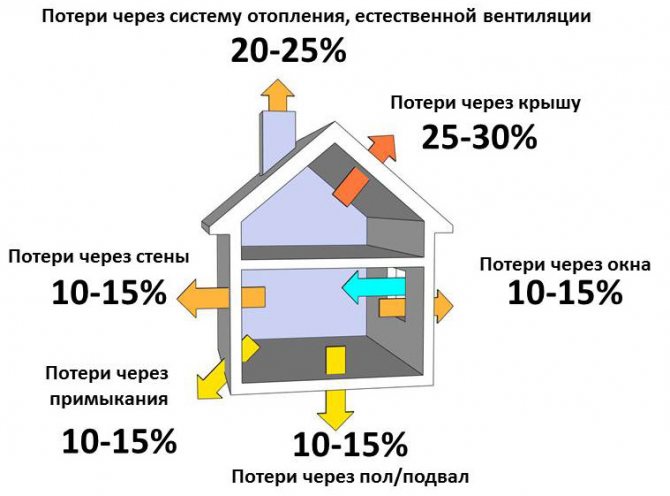

Heat loss
If the room has two windows and two outer walls, then a radiator should be purchased one third more powerful than the classical value. Throw in another 15% if you plan to cover the structure with decorative screens, as they do not transmit heat well. Another 5-10% of additional power is needed if the room is on the north side. If there are several factors, the percentages are summed up.


Cast iron heating radiators
Types of materials from which water heating batteries are made:
- cast iron;
- steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetal.
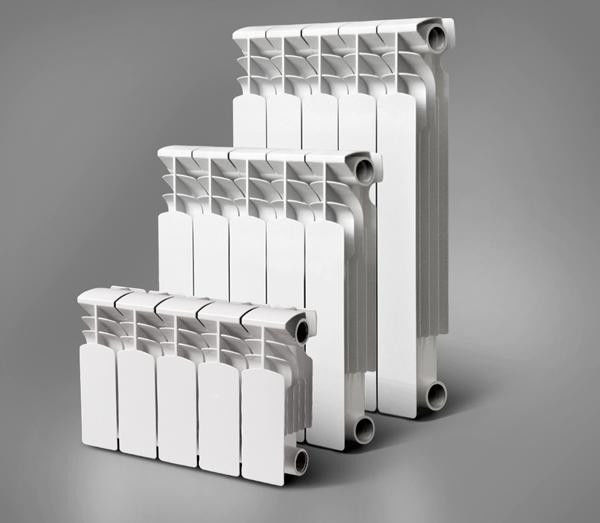


Sectional bimetallic radiators
Radiators are divided by design type:
- sectional (cast iron, aluminum, bimetal);
- panel (steel).
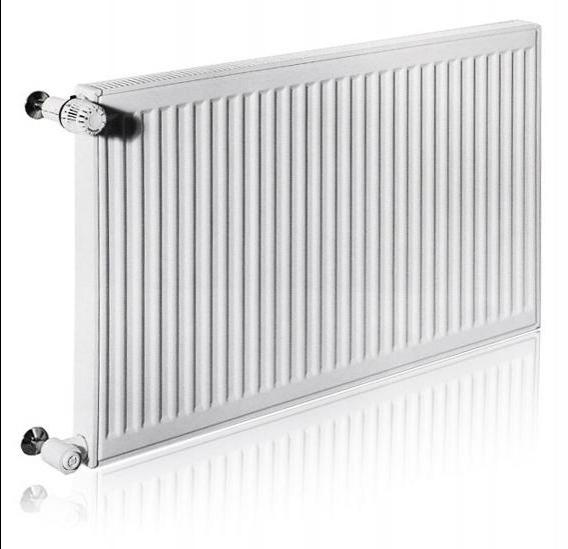


Steel panel radiators Korado
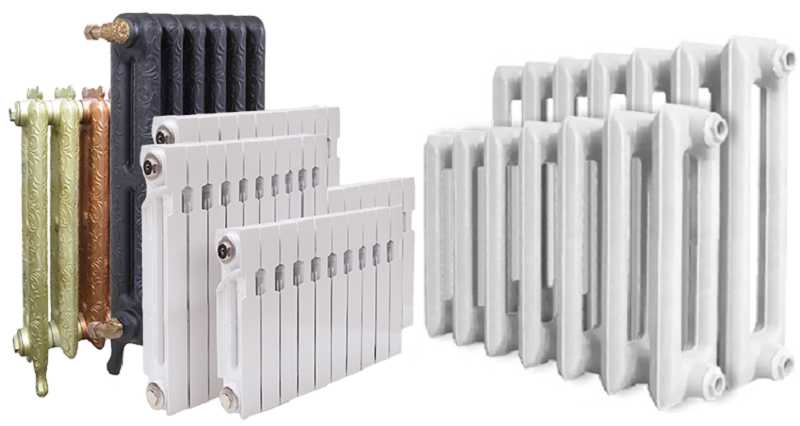
Cast iron
Cast iron outdoor batteries are familiar to everyone from childhood. This is a classic of Soviet apartments. Such devices are popular now, but modern radiators have a more elegant appearance, and some can be of the most unimaginable shapes.
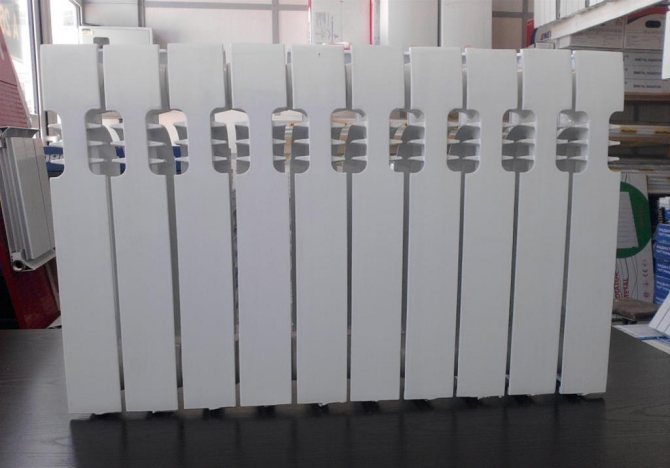


New generation cast iron batteries
The gray cast iron from which the structure is made functions well. But this metal is quite fragile. Such heating systems can break from a strong impact from the outside or from a powerful water hammer from the inside due to a sharp pressure surge (in case the metal is too thin). Most of the products are capable of withstanding a maximum pressure of 10-13 atmospheres. The disadvantages of cast-iron radiators include the fact that sections and pipes are quickly silted up. They must be rinsed every 2-3 years of use. Silting can be avoided by using some connection methods.
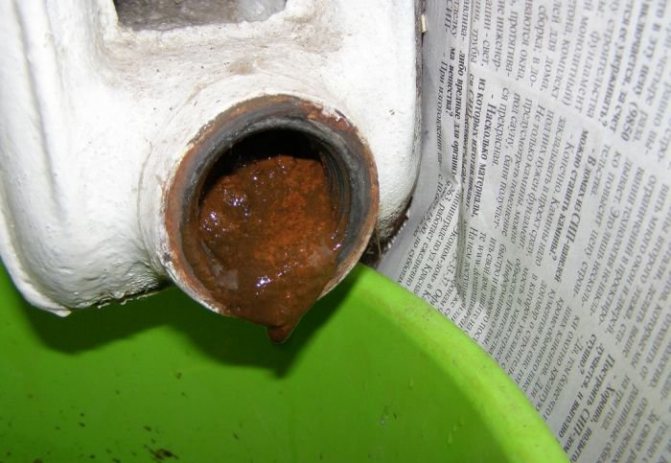


Garbage and dirt in the radiator
Another disadvantage of cast iron is the frequent leakage of the gasket between the sections. Paronite is almost not elastic, and after a few years it completely loses this quality. The cooled heating batteries begin to leak. Ugly streaks of rusty color appear on their surface. To fix it, you have to completely sort out the heater and replace all the gaskets with rubber ones (with resistance to high temperatures).
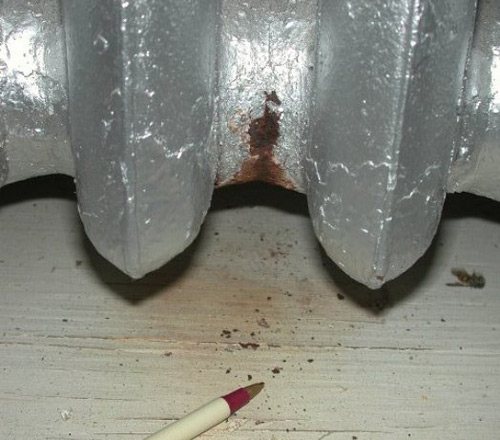


Leakage between sections of cast iron batteries
Steel
In terms of thermal conductivity, steel floor radiators differ little from cast iron, but steel is a stronger metal. But its strength is not always a reliable quality. The most vulnerable steel batteries are plate batteries. The weak point of such batteries is the welding seam along the contour of the plates.


Steel plate radiators
Domestic plates serve little - only seven years. Their strength is lower than cast iron (they can withstand a maximum load of 6 atmospheres). Together with low heat transfer, such floor-standing radiators cannot be called a good purchase. Imported plate type heating heaters have an attractive design and can withstand 10 atmospheres. Their service life is from 10 years.
Heat transfer directly depends on the surface area of the radiator, but with equal parameters, steel is inferior to aluminum in terms of efficiency.

Steel tubular radiators
The design of tubular steel batteries differs from their plate counterparts. The design is clear from the name. The coolant circulates through pipes of a straight or curly shape. Such radiators are beautiful and durable, you can often find models with a very unusual design without compromising heat transfer.
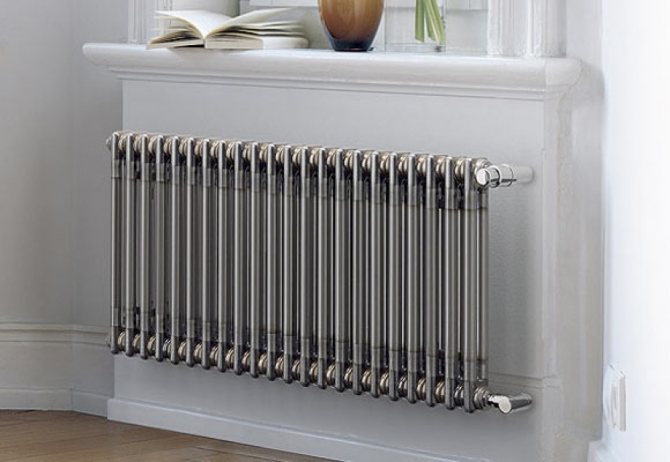


Steel tubular radiator
Aluminum
Aluminum floor heating radiators began to conquer the domestic market in the distant nineties. Previously, such heating systems were presented only by foreign manufacturers, but by now Russian companies have begun to produce good models.China is not lagging behind either. As a result, aluminum radiators have a beautiful design, excellent heat transfer and, at the same time, a fairly low price. But over 20 years of operation of such heating devices, some of the disadvantages of aluminum have been identified.
Large pressure surges in heating systems are difficult to predict. The cause of sudden surges can be human error. Heating systems should start up smoothly, slowly, filling with water from the return pipe. Only then is the supply opened and the air released. A sharp supply of coolant to the network provokes a water hammer - a pressure jump of up to 25 atmospheres. Sometimes water hammer occurs due to malfunctioning of valves.
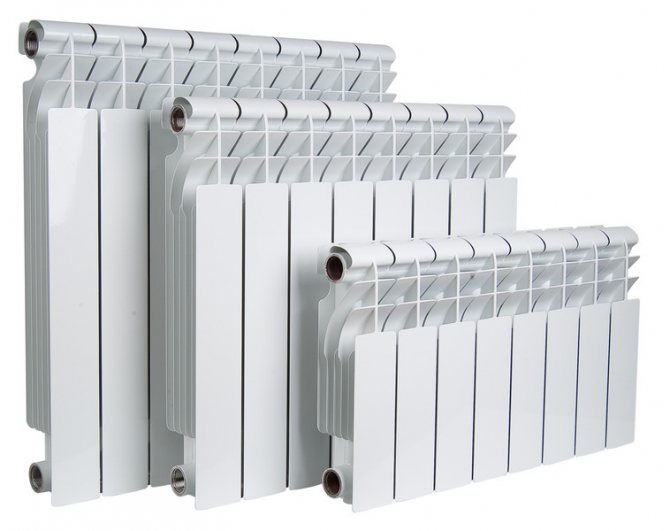


Aluminum radiators
Aluminum is able to withstand normal operation. It is strong enough, but water hammer is the actual "death" of the radiator. In the best case, disconnection from the liner will occur, in the worst case, the destruction of the structure.
The second major drawback of aluminum as a material for a heating radiator is the ability to form galvanic vapors with some other metals. For example, with copper. Considering that copper pipes are often used for piping, the radiator will be constantly exposed to the influence of a weak current, which, as a result, will significantly reduce the service life.
Bimetal
Aluminum structures paired with another metal combine the advantages of both materials and at the same time solve the above problems. Everything is extremely simple. A corrosion-resistant steel core is hidden under the aluminum radiator shell. At the same time, heat transfer losses are minimal.
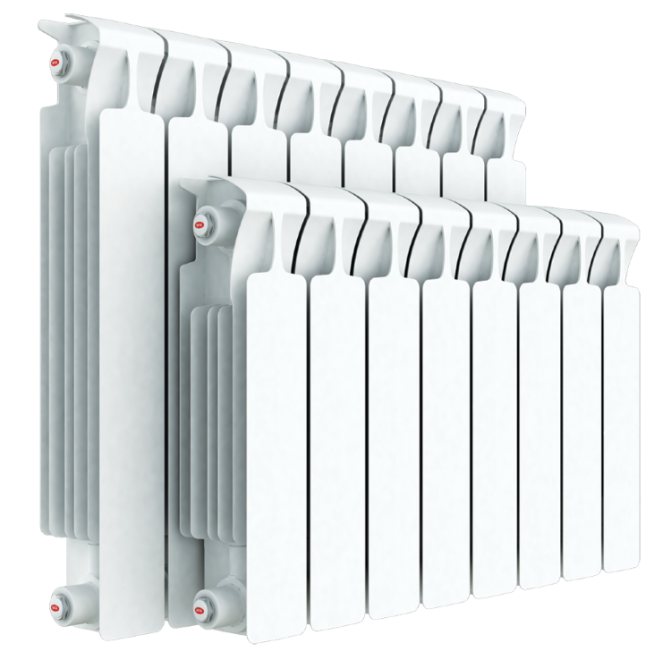


Bimetallic monolithic radiator
Since the steel core does not allow aluminum to come into contact with the coolant, electrochemical processes are excluded. At the same time, the resistance of such structures to water hammer increases significantly - 25 atmospheres are taken as the norm.
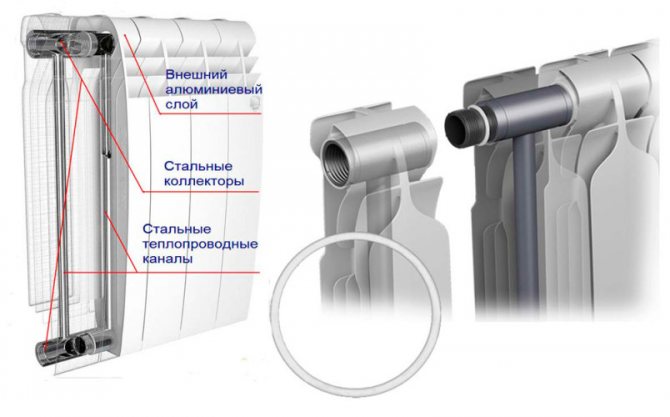

The device of bimetallic heating devices
Bimetallic floor radiators can be not only based on aluminum and steel. There are models made of copper with aluminum spraying. The design of such heaters is very compact. The design is based on a thick-walled copper pipe with aluminum silvering applied by pressing. From the outside, the heater is protected by a steel casing, which reliably protects it from mechanical damage.
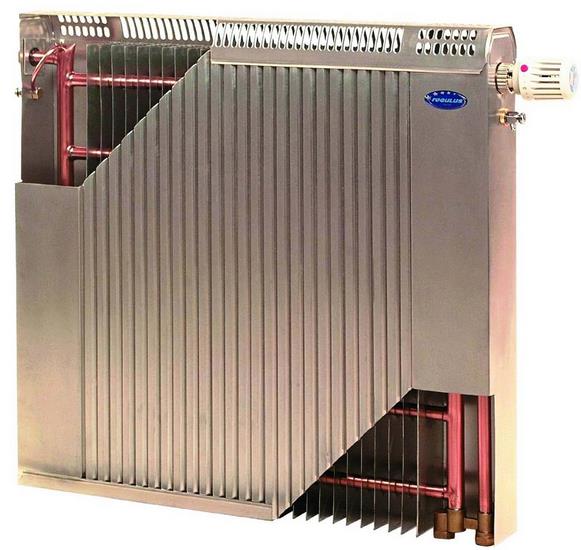


Bimetallic (copper-aluminum) heating radiator
The thermal conductivity of such devices is higher than that of pure aluminum or aluminum-steel. Copper conducts heat twice as well as aluminum. As a result, such floor structures give off an enormous amount of heat to the environment in a fairly compact size.











