The most used heat sources for heating homes are electricity, gas, coal or wood. Despite the technical availability of each of them, the use of one or another is due to some factors, such as: economic feasibility, place and frequency of use, safety. Nowadays, the first two types of energy listed are the most popular. Consider the aspects of the use of electricity, as well as the types of electric heating devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Electricity for Heating Purposes
It should be noted right away that the use of electric heating devices for heating is not the cheapest option, since the cost of the equipment itself, as well as operating costs, are too high. Therefore, it is most often considered as an alternative, in case of gas supply interruptions or, if there is no gasification at all. At the same time, heating a house with electrical appliances has some obvious advantages:
- Almost ubiquitous availability.
- Very quick and easy installation.
- Convenient management.
- Compact device device.
- Complete absence of any combustion products.
Thus, with all its shortcomings, mainly associated with the economic component of the issue, electrical appliances have a lot of useful qualities that heating devices based on fuel combustion cannot boast.
Heating methods and heating devices
Flame and non-oxidizing heating methods are often used.
Flame heating. Flame furnaces are more often used to heat ingots and large billets. In flame heating, furnaces are used, in the working space of which fuel is burned and the exhaust gases heat the workpiece. Forges, wells can also be used. Forges differ from heating furnaces in small size, they are fired with coal or coke, the metal is heated in them by direct contact. Horns are of limited use, since they are ineffective. It is difficult to create uniform heating in them and they are used to heat small parts. Flame furnaces run on fuel oil and gas. Thus, according to the type of fuel used, furnaces are divided into fuel oil and gas. During flame heating, scale is formed on the surface of the workpiece as a result of metal oxidation with atmospheric oxygen. The loss of metal as a result of oxidation is called waste and reaches up to 3% in one heating.
Non-oxidizing heating.The following non-oxidative heating methods are used.
1. Heating in baths with molten salt mixture. Used for small workpieces up to 1050 ° C.
2. Heating with the formation of protective films on the surface of the workpieces. used up to 980 ° C when covered with a film of lithium oxide.
3. Heating in molten glass. Applicable up to 1300 ° C.
4. Heating in muffle furnaces filled with protective gas.
Furnaces and heating units are used as heating devices.
Heating devices. By the nature of the temperature distribution and the method of loading the metal, the furnaces are divided into chamber and methodical ones.
AT chamber
furnaces (Fig. 3.8), the metal is loaded periodically and all of its amount is heated at the same time. These furnaces are used in small-scale production because of their versatility and for heating very large workpieces weighing up to 300 tons. Chamber furnaces are uneconomical, since they are not economical.a very large amount of heat is lost with exhaust gases, the temperature of which is not lower than the metal heating temperature and reaches 1150 ... 1200 ° C.
Much more economical methodical
furnaces (Fig. 3.9). They are used in large-scale stamping and rolling production. The working space of the furnace has several zones: for example, heating zone I, zone with maximum temperature II, holding zone III. The workpiece 2 is pushed by the pusher 5 through the loading window. Further, the workpieces themselves push each other along the hearth 1 of the furnace and, after a full heating cycle, are unloaded through the unloading window 4.
Fig. 3.9 Scheme of the methodical furnace: 1-hearth; 2-blank; 3-burner;
4-window for unloading; 5- pusher; I. Heating zone (600-800 ° C); II.
Maximum temperature zone (1200-1350 ° C); III. Exposure zone.
In the holding zone Ш, the temperature is equalized over the cross section of the workpiece.
Hot gases entering the heating zone through the burners 3 move towards the moving workpieces, which ensures high heating efficiency.
Electric heating.A distinction is made between indirect heating, direct (contact) electric heating and induction heating devices.
Chamber electric resistance furnaces (indirect heating) are used in industry for heating small workpieces. The metal in electric furnaces is heated due to the heat released when the electric current passes through the spirals of heat-resistant metals with high resistance. Electrical heating produces negligible dross. Their design is similar to fired chamber furnaces, but instead of nozzles or burners, metal or ceramic heaters are used. To heat up to 1150 ° C, an alloy of nichrome grade Kh20N80 is used as a heater material.
Contact heating
(Figure 3.10) is based on (Joule-Lenz's law) the property of an electric current to generate heat when a current of up to 10,000 A passes through a conductor (workpiece). Advantages: low consumption of electrical energy, speed, good quality. In this way, workpieces up to 75 mm can be heated.
Induction heating
(Figure 3.11). With induction heating, the workpiece is placed inside the coil 1 (an inductor made of a copper tube through which cold water flows for cooling). A current is passed through the coil, which creates an electromagnetic field and the eddy currents that appear in the workpiece 2 heat it up.
Advantages: high speed and uniformity, no scale, heating of workpieces of any shape. Disadvantage: the complexity and high cost of equipment, high power consumption.
The processes of metal processing by pressure with preheating, in which the recrystallization process fully manages to occur and there are no signs of hardening, are usually called "hot".
Initial blanks processed by forging and stamping
Various metallic materials are used for forging and forging: steels (carbon, alloyed, high-alloyed), heat-resistant alloys, as well as non-ferrous alloys. They are widely used for forging and forging of steel.
The initial steel billets for forging and forging are ingots (Fig. 3.12), crimped ingots (blooms) and bar stock. The ingot is a billet for large forgings, can be used for one or more forgings. Ingots are obtained by casting steel into molds from converters or open-hearth and electric furnaces.
The ingot weighs from 135 kg to 350 tons. The configuration of the ingots can be different depending on the remelting method and the manufacturer's plant.
The shape of the ingots can be different and depends on the metallurgical enterprise producing the ingots. The most common form of an ingot is in the form of a multifaceted truncated pyramid. The cross-section of the middle part of the ingots can be 4-, 6-, 8- and 12-sided. The top (profitable) part of the ingot (l
1) contains a shrinkage cavity and cannot be used in a forging. The lower (bottom) part [
L
– (
l
1 +
l
2)] is also an ingot waste. The ingot waste is 18 ... 30% for the profitable part, and 3 ... 8% for the bottom part of the total mass of the ingot.
Fig. 3.12. Steel ingot of Novokramotorsk metallurgical plant
Smaller waste values correspond to carbon steel ingots, while larger ones correspond to alloy steel ingots. The bottom and bottom parts are separated from the ingot by forging at the beginning of forging (after billetting) or from the ends of the forging at the final stage and sent to remelting. The bottom and bottom parts are defective and are remelted. The middle part, suitable for forging, is a pyramid expanding towards the top with an angle of inclination of the edges from 30o - 1o. The pyramid has 4-12 sides. The edges are concave with a large radius.
Ingots of the production association "Izhora plant" them. A.A. Zhdanov. They look like a truncated cone.
Cutting with crank shears
.
In addition to these ingots, the industry uses elongated, hollow, low-profit ingots, ingots with increased taper, shortened with double taper, three-taper, etc.
Ingots are usually used to produce large forged forgings, the mass of which is calculated in tons, and the minimum section exceeds 1200 cm2 (Ø> 100 mm, ٱ> 350 mm). Ingots are rarely used for die forging.
The crimped ingot (blooms) is a blank for medium forged forging with a cross-sectional area of 130 ... 1200 cm2 or Ø 130 ... 400 mm. Blooms are also used for large forgings. Blooms in cross-section have the form shown in the figure, the sides of the square are concave, the corners are rounded. Size A = 140 ... 450 mm, length 1 ... 6 m. GOST 4692-71.
Long products
is a blank for most stamped forgings. Small forged forgings with a section of 20 ... 130 cm2 are also made from it. The cross section is usually round or square. The circular section has dimensions 5 ... 250 mm (GOST 2590-71), square also from 5 to 250 mm (GOST 2591-71). The length of long products is 2 ... 6 m.
In addition to crimped blanks and rolled sections, profile rolled products are used for die forging:
rolling of a periodic profile:
and strip blank:
Long products used for most stamped and small forged forgings. The length of the rods is 2 ... 6 m. The cross-section of hot-rolled steel can be square (GOST 2591-88) or round (GOST 2590-88). The cross-sectional dimensions (diameter, side of the square) are established by these standards and according to the assortment are: 5; 6; 8; ten; 12; 15; 18; twenty; 22; 24; 25; 26; 28; thirty; 32; 34; 36; 38; 40; 42; 45; 48; fifty; 56; 60; 65 70; 75; 80; 85 90; 95; 100; 105 110; 120; 125; 130; 140; 150; 160; 170; 180; 190; 200; 210; 220; 240; 250 mm.
An example of the designation of a rolled square section made of Steel 45 with a square side of 60 mm and a circle with a diameter of 60 mm from St 3:
⇐ Previous4Next ⇒
What are the principles for the classification of electric heating devices
All modern electric heating devices are classified as follows.
By the way the device is mounted:
- Portable or mobile, which include oil coolers and various convectors.
- Installed in one place or stationary, including boilers, air conditioners, electric boilers and fireplaces, infrared heaters.
By the type of coolant that heats up in the device:
- Air - heating of the surrounding space is carried out by heating the air. These include convectors, radiators, electric fireplaces and many other devices.
- Liquid - the coolant in them is any liquid that has a good heat capacity: water, oil, antifreeze. The most famous devices with this principle of operation are electric boilers and boilers.
- Solid-state or radiative - heat in these devices is transferred from a source to some solid surface, which then heats the air in the surrounding room. These include radiant and infrared heaters.
By type of heating element (heating element):
- Standard tubular elements are successfully used in many types of heating devices that run on electricity. They can have a very wide range of technical characteristics, both in terms of performance and power. They are made from steel and titanium.
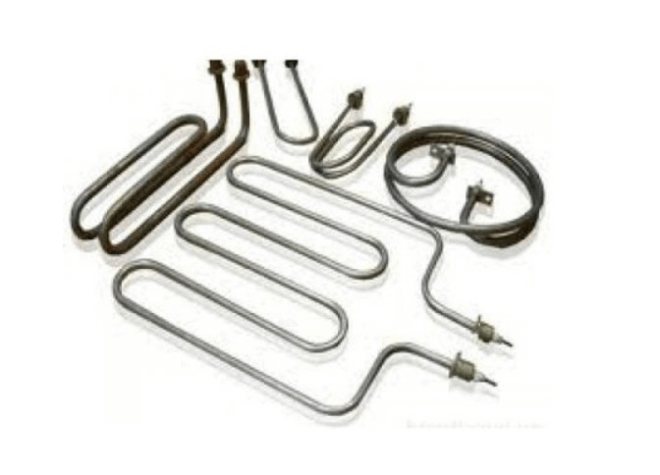

Standard tubular type heating elements
- Ribbed tubular - similar to the previous ones, but have a ribbed surface that increases heat transfer. They are used only in devices where the heating medium is a gaseous medium (air curtains and convectors). Such elements are made of stainless or structural steel.


This is how finned heating elements look
- Block electric heaters are several heating elements connected into one structural unit. Such devices are installed in devices where there is a possibility of power adjustment. Heat carriers in them can be liquid or free-flowing solids.


Block of electric heaters, assembled in one unit
- Equipped with a thermostat - they are the most common type of household electric heaters for heating with a liquid heat carrier. They are made from copper, steel, or nickel-chromium alloy.


Equipped with a heating element thermostat
All considered heating elements are only the main details of the devices, about the features of which read below.
Chamber, tunnel, bell and bogie hearth furnaces
Chamber, tunnel, bell-type and bogie-hearth furnaces are used to heat large ingots, blooms and billets, thick and thin sheets, bags, pipes, rolls, stoves.
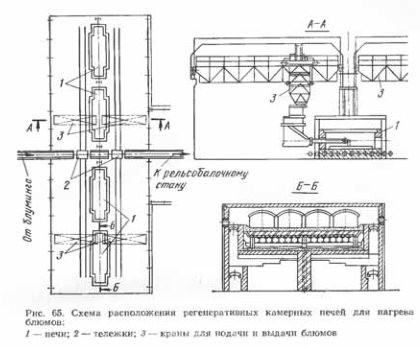
Regenerative chamber furnaces are used to heat blooms on rail and steel mills, shown in Fig. 65. Furnaces are located on both sides of the mill feed roller table. Blooms are fed to the ovens with a trolley. Heated blooms from the ovens are fed to the mill with the same cart. Blooms are planted in the oven and dispensed from them using special crane-type planting machines, called caricatures. The fuel for the furnaces is a mixture of blast furnace and coke oven gases with a calorific value of 5250 kJ / m3, and gas and air are heated in the regenerators.

Annealing of sheets is carried out in boxes. Piles of sheets are placed on a pallet and covered with a box. Depending on the size of the sheets, the designs of pallets and boxes are different. Sheets in boxes are heated in tunnel ovens and bogie hearth ovens.
Tunnel oven is a long tunnel (over 90 m) with a horizontal vault. The furnace consists of three zones: heating, milling and cooling zones. Boxes with sheet metal are installed on trolleys, which move one after another in the furnace. When a new trolley is pushed into the oven from the inlet side, the other is simultaneously pushed out from the outlet side.
For heat treatment of steel is also used bell furnaces (fig. 66), which consist of pallets, a box and a hood with vertical tubular heaters. The furnace is heated with gas, which, through the burners, enters the heating tubular elements located vertically or horizontally and radiating heat. For annealing rolls, bell-type furnaces of circular cross-section are used, more often with electric heating. For a more uniform heating of the bales, the hoods have a neutral core with electrical resistance wires, which goes inside the bale.
To heat large sheet ingots, use bogie hearth furnaces (fig. 67). The ingots are placed on a platform 1 moving along the rails. With the help of stationary blocks 2 and 3, a rope and a winch or a crane hook, the platform with ingots is pushed into and out of the furnace chamber.Gas flows through pipes through valve 4, channel 5, vertical channels 6 to burners 11, where it mixes with heated air supplied through valves 8, 14, channels 9, 13 and regenerator nozzles 10, 12.
The same furnaces are used for heat treatment of long products, but without regenerators. The platforms move on wheels or roller chains to reduce the furnace height and increase the load on the platform.
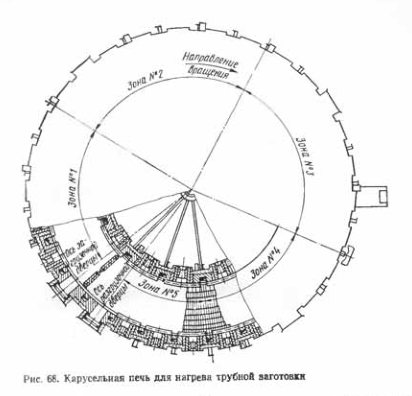
Rotary ovens (Fig. 68) are used in modern tube rolling mills, as well as for heating billets during piece rolling of thin sheets. The burners are located around the circumference of the furnace from the inner and outer sides. The walls of the furnace rest on the foundation, and under the furnace it has rollers, which, when the hearth rotates, move along rails closed in a circle. The loading of the metal is carried out through the loading window of the furnace. The heating duration is determined by the length of the furnace (circumferential) and the speed of the hearth movement.

Air convectors
These devices are made in the form of compact portable devices equipped with legs or wheels for installation on the floor or wall. The working element in them is ribbed heating elements, closed with a decorative metal case with slots for air circulation. They are used in apartments or private houses, mainly as additional sources of heat.


Electric convectors
The principle of operation of such devices is based on the fact that cold air freely or forcibly enters the device and passes through all heating elements (heating elements). Then, as befits heated gases, it rises up and passes through a special grate. Convectors can be equipped with built-in fans for forced air circulation. These devices do not have any restrictions for their use.
Oil-cooled radiators
The appearance and principle of operation of such devices is completely similar to ordinary heating batteries. Only they are filled with mineral oil, and electric heating elements installed directly inside the inner cavity of the device heat it. They are successfully used in offices and residential premises. There are oil coolers open and closed. The ribs of the latter are protected by a metal casing. The main advantage of these devices is that they do not burn out oxygen in the room and do not heat up to temperatures that are dangerous for small children. Especially the latter property applies to closed radiators.


Open and closed oil coolers
Classification of storage devices
According to the method of installing storage tanks, vertical and horizontal devices can be distinguished, which are mounted on the wall in the appropriate way. Recently, universal heaters have also begun to appear in the assortment, which can be placed both vertically and horizontally. Storage devices with a capacity exceeding 200 liters are usually installed on the floor.
On our website there is a detailed instruction on how to install an accumulative model of a water heater with your own hands.
In addition, there are a number of other features that can be used to classify storage devices for heating a liquid.
By the principle of functioning
By the way of work, products can be distinguished open and closed type... The first option includes models that can be used in water supply with a weak pressure or even for autonomous use without a water supply system.
Such devices are indispensable in summer cottages or in private houses where there is no connection to the central water supply line. They can serve only one point of water intake, for example, a tap in the kitchen.
A more complex option is closed-type products that are mounted in a common system with a dedicated cold water supply line. Once connected, they heat the liquid to the desired temperature - usually up to 60-85 ° C.


Among the main advantages of open-type water heaters are fast water heating, ease of installation and low energy consumption
By volume of the working tank
Various types of electric boilers for heating water differ in capacity, which varies from 10 to 500 liters.
Conventionally, all models can be divided into three categories:
- up to 30 liters;
- with a capacity of 30-100 liters;
- with a tank exceeding 100 liters.
Devices with mini-reservoirs, which do not require pressure in the water supply system to fill, are usually installed to provide water to one point, for example, a washbasin. As a rule, such models are equipped with copper heating elements. The assembly of such structures is not difficult and can be performed by the owner in strict accordance with the attached instructions.
Medium-sized water heaters can serve one or several points located close to each other. Boilers of this type can have a more complex design with additional functions. When assembling them, it is better to involve specialists.
The maximum volume units can hold up to 400-500 liters of water. Such devices, which, as a rule, are used in public buildings or in production, supply hot water to several points distant from each other at once. They can also be connected to boilers and district heating. The installation of such devices should be carried out by professionals.


Water heaters with a capacity of 10-30 liters, which are used for domestic purposes, are usually installed in the kitchen - under or above the sink
By design features
Different types of electric storage water heaters may also differ in their internal structure, namely:
- by the location and power of the heating element;
- by the method of adjusting the heating temperature;
- according to the provided possibilities.
The heating element can be conventional or "dry", that is, located in an isolated space. The latter option provides a longer service life, but these models are somewhat more expensive.
You should pay attention to the power of heating elements, which varies from 1.2 to 3 or more kilowatts.
The required temperature can be set directly on the thermostat of the unit, which is less convenient, since it requires disassembling the electric heater. In modern models, a more convenient temperature control device is usually carried out - on a remote panel.
In many modern units, additional functions can be provided, such as the ability to self-diagnose the device, monitor the tank filling level, and an increased degree of protection against overheating.


Control can be carried out mechanically or electronically, the latter option assumes extended functionality
By material and shape of the tank
The most important part of the capacitive device is the internal tank, since it is he who has to withstand changes in temperature, pressure, exposure to chemicals and impurities contained in the water. When choosing a water heater, you should pay special attention to this structural element.
The tanks are usually made of stainless steel, which is often covered with an additional layer of protective material. In the cheapest models, glass porcelain is used for this. It resists corrosion well, but it is quite fragile when exposed to high temperatures.
Over time, constantly deepening cracks can appear on the surface, which leads to the failure of the tank.
Enamel coatings are a more reliable option. They are flexible and less susceptible to cracking, due to which tanks with such a surface have a longer service life.


If an internal tank breaks down in a capacitive heating device, it is no longer possible to repair it, this important part will need to be replaced
Of particular note is titanium enamel, which has high corrosion resistance, low weight and good ductility. In addition, titanium forms a very smooth surface of the container, which increases the hygiene of the device, since micropores often serve as a harbor for microorganisms.
The capacity and shape of the tanks also largely determines the configuration of the heater. A standard storage device looks like an oblong cylinder with a diameter of about 45 centimeters. There are also models of smaller diameter, the so-called "slimy", which can be installed in a secluded corner or in an inaccessible place.


Recently, manufacturers have begun producing appliances with a spectacular design, for example, boilers with a square or other original shape. Such functional products can serve as a real decoration of the kitchen or bathroom.
Electric fireplaces
These electric heaters have a great design, so they can be used not only as heaters, but also as a decorative element. These devices can be found in luxury apartments or country houses due to their prohibitive cost.
Modern electric fireplaces are made floor-standing, imitating classic wood-burning options and wall-mounted, which look like thin panels hung on the wall. The principle of operation of fireplaces is similar to that of convectors.


Wall and floor electric fireplaces
Electric boilers
Unlike previous appliances, these devices are used to create a permanent heating system in the home. They are used in conjunction with a liquid heat carrier circulating in a closed loop that ties all rooms in the house.
By the type of the main heating element, electric boilers are divided into:
- Heating elements - work with any kind of liquid and have the simplest design. They allow you to smoothly change the power, stepwise change the heating intensity by switching on a different number of devices.
- Electrode, which are compact in size and are used exclusively for water systems. In this case, the coolant must strictly comply with the requirements of GOST 2874-82 "Drinking water". This circumstance greatly affects the cost of equipment. Thermal energy arises according to the principle of electrolytic dissociation, due to which a potential difference arises on the electrodes due to dissolved salts. This heats the water up nicely. Such a device is much more economical than the previous one.
- Induction boilers are the most innovative and expensive devices. They are very reliable and durable. Any coolant can heat such boilers due to the principle of electromagnetic induction. Such a device consumes the maximum amount of electricity, but it is easy to install, does not require a separate room and has maximum efficiency at the smallest dimensions.
All electric boilers must be grounded very reliably.
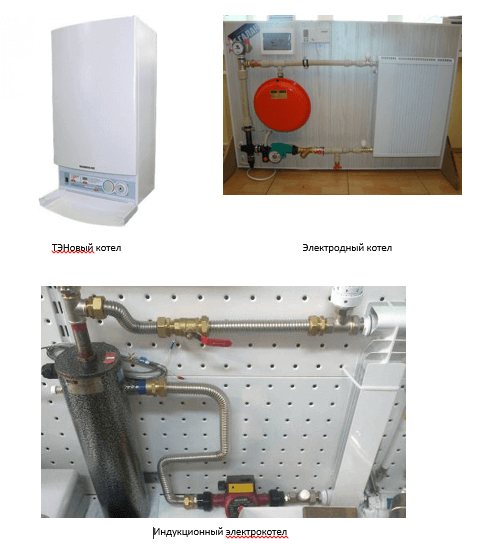


All types of electric boilers
Electric heating devices
All electrical appliances used in case of impossibility to install a water heating system have different features and characteristics - from power to the principles of heat generation. At the same time, the main disadvantages of any such equipment are the high cost of operation and the need for a power grid capable of withstanding heavy loads (with a total power of electric heaters of more than 9-12 kW, a 380 V power grid is required). The advantages of each variety are different.
Convection appliances
The design, which have electric heating devices of this type, allows you to quickly heat up the room with the help of air currents moving through them.


Air gets inside the devices through the holes in the lower part, it is heated using a heating element, and the exit is provided by the presence of upper slots. Today there are electric convectors with a capacity of 0.25 to 2.5 kW.
Oil devices
Oil fired electric heaters also use the convection heating method. Inside the body there is a special oil, which is heated by a heating element. In this case, heating can be controlled using a thermostat that turns off the device when the air reaches the set temperature.
The peculiarities of the heaters are their high inertia. Due to this, the heating devices heat up very slowly, however, even after the power supply is turned off, their surface continues to emit heat for a long period of time.


In addition, the surface of oil equipment heats up to 110-150 degrees, which is much higher than the parameters of other devices and requires special handling - for example, installation away from objects that can ignite.
The use of such radiators makes it possible to conveniently regulate the heating intensity - almost all of them have 2-4 operating modes. In addition, taking into account the productivity of one section of 150–250 kW, it is quite easy to select a device for a specific room. And the range of most manufacturers includes models up to 4.5 kW.
Infrared electric heaters
This is the most modern type of electrical devices for space heating. Its work is based on the emission of electromagnetic waves in the infrared spectrum. In this case, thermal energy is transferred from the device to those objects that are located nearby. The radiant energy reflected from them effectively heats the air in the room. This is probably the most economical type of electric heaters. In addition, such devices do not dry out the air. Some of them have a very nice decoration.

Ceiling infrared electric heater
Despite the high cost of electricity, the popularity of electric heaters is not decreasing. This is due to their convenience and, in many cases, to mobility, which is not available for gas equipment.
Various heating device
Various heating devices (heating, production) must be kept in good working order, and after the end of the work they must be brought into such a state that they cannot cause a fire. Especially carefully it is necessary to monitor the serviceability of electrical wiring and the prevention of short circuits, which often cause fires.
Various heating devices are used. Coil-closed hotplates are designed for direct heating of round-bottom flasks.
The pressure of the various heating devices in the system is not the same. This head is the less (formula IV, 17), the lower the heating device is located.
Various heating devices are used in the laboratory. Closed spiral hotplates are designed for direct heating of round bottom flasks.
| Burner Teklu | Bunsen burner. |
Various heating devices are used in the laboratory: gas burners, electric stoves, baths, drying cabinets. The most commonly used gas burners are Teklu and Bunsen.
Various heating devices are used in the laboratory: gas burners, electric stoves, drying ovens, baths, muffle and tube furnaces, as well as spirit lamps.
Various heating devices are used in the laboratory: electric stoves, baths, drying cabinets, electric ovens, desktop and portable gas burners.
Various heating devices are used in the laboratory: gas burners, stoves, baths, drying cabinets.
| Bunsen burners. |
In chemical laboratories, gas is very important as a fuel for various heating devices. Nowadays it is rare to find a chemical laboratory without a gas supply.
The conversion of electrical energy into heat, which is effectively used in various heating devices, in electrical networks, starting devices and machines, causes their premature wear, and under certain conditions leads to accidents, explosions and fires.
Converting electrical energy into thermal energy is of great practical importance and is widely used in various heating devices both in industry and in everyday life. However, heat losses are often undesirable because they cause waste of energy, for example in electrical machines, transformers and other devices, which reduces their efficiency.
Must know: the device and the electrical circuit of the continuous hot tinning unit within the scope of the work performed and various heating devices.
Should know: the device and the electrical circuit of the continuous hot tinning unit within the limits of the work performed and various heating devices used for tinning, the rules for working with them; hot tinning process; basic properties of metals and alloys used in tinning, production of various alloys and powders for tinning; device, purpose and conditions for the use of complex instrumentation and instruments for determining the thickness of the coating.