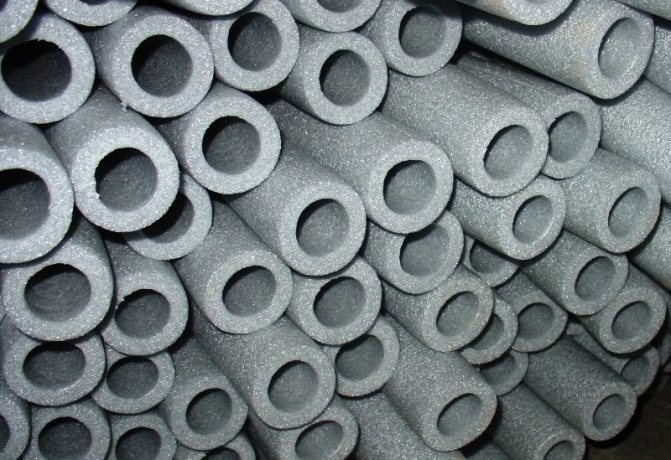
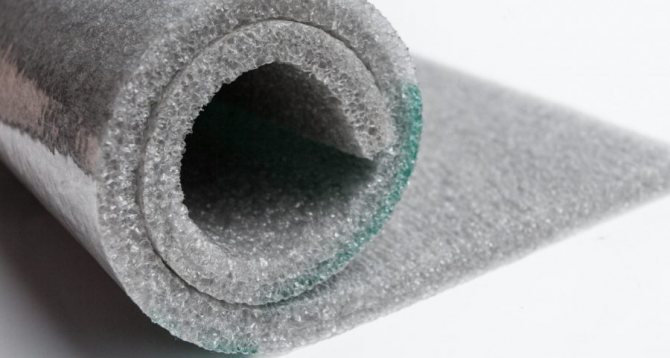
Foamed polyethylene is a unique heat, noise and moisture insulator, which is now enviable popularity. The combination of polyethylene and air, simple to the point of genius, ultimately gives a heat saving of 70% in terms of construction, although its scope is far from being limited to this. <. P>
It is this material that successfully combines low cost and great efficiency. Moreover, without prejudice to human health and life. The same characteristics have expanded the scope of application of foamed polyethylene from construction, mechanical engineering, medicine, footwear and leather goods industries to packaging.
Types by production method

For simplicity of explanation, polyethylene foam is divided into "cross-linked" and "non-cross-linked" according to the production method, although the technologies used for each type may be different. The main difference between the obtained materials is that during production, the molecular structure of the "uncrosslinked" polyethylene foam does not change, in contrast to the "crosslinked" one, although both materials are called foamed.
Each of the obtained types of material has a number of distinctive features and, as a result, a slightly different field of application. The technology of "stitching" means the process of cross-linking of molecular units into a three-dimensional region with wide cells.
Selection of polyethylene foam backing
Floor covering type
When choosing a polyethylene foam backing, it is necessary to take into account what kind of floor covering you will use it under.
The polyethylene foam backing is selected according to the following criteria:
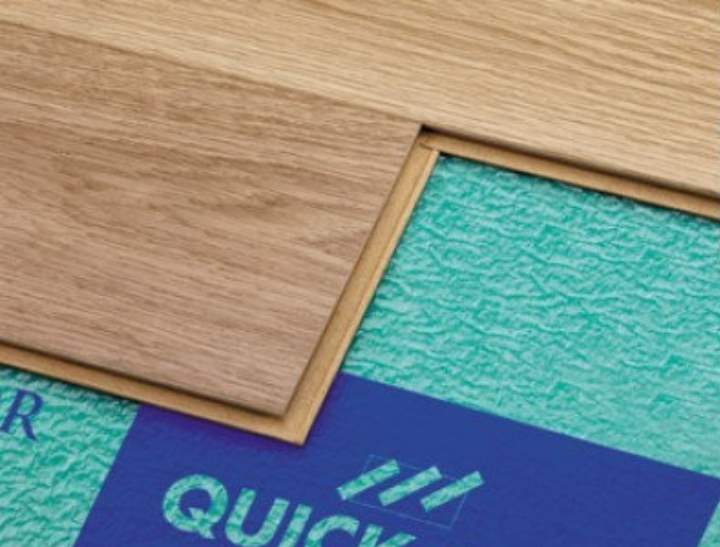


The underlay should not be very thin, because it may not give the desired effect, but if the underlay is too thick, then it will spring when walking.- For a seven millimeter laminate, the backing thickness should be approximately two millimeters.
- For thick coatings (up to about eight or nine or even more millimeters), a substrate of at least three millimeters must be selected.
Features of mounting a polyethylene foam substrate
Laying a polyethylene foam backing is not at all difficult, but several rules must be followed:
- Before laying the underlay, it is necessary to level and dry the subfloor well;
- If the floor is leveled with cement - concrete screed, then first you need to check the percentage of its moisture.
- The foil substrate must be laid with the foil side up and insulated from electrical wiring that may be laid nearby;
To prevent displacement of the polyethylene foam backing sheets and to ensure good waterproofing, it is laid end-to-end and not overlapped. And also all joints (seams) must be glued with adhesive tape, that is, tape.
Well, we told you about such a material as expanded polyethylene, (more precisely, about a substrate made of this material) about the nuances of its installation and technical qualities, and we hope that this article will be useful to you. We wish you good luck in your endeavors and patience!
"Uncrosslinked" polyethylene foam (NPE)


It is obtained using a physical blowing agent, by the extrusion method, or, more simply, by the method of foaming a polymer material with a gas mixture, which is subsequently replaced by ordinary air.
Its production is one of the most environmentally friendly due to the fact that the freon gas banned in all European countries and in most domestic environmental organizations has been successfully replaced with butane, propane-butane and isobutane.Although, in fairness, it must be said that it is freon, due to its high heat of vaporization, that is ideal for this production, but for the sake of health it has to be abandoned.
The result is a translucent, large-pore material. But its tensile strength is inferior to "cross-linked" polyethylene foam. This is due to the fact that there is no strong bond between polymer molecules. This indicator determines the area of application of the IPE.
Classification
Polyethylene based foam classified according to the following characteristics:
- type of feedstock;
- foaming method;
- stitching method.
For the manufacture of PPE, LDPE and HDPE granules are used, as well as various compositions based on them. The molecular structure of any type of polyethylene makes it possible to obtain materials with predictable properties.


In the production of polyethylene foam
two methods of creating a gaseous phase are applied:
- Physical. This direct injection of gas (butane or other light saturated hydrocarbons) into the feedstock melt is the cheapest method of foaming. However, it requires the use of specialized equipment and compliance with increased preventive fire safety measures.
- Chemical. Reagents that decompose with the release of gases are introduced into the feedstock. Chemical foaming can be performed on standard foundry and extrusion equipment. The composition of the additives is determined by the requirements for density and cell size.
Modern production technologies make it possible to obtain various molecular structures gas-filled polyethylene:
- Unstitched (NPE). It is obtained by the technology of physical foaming. At the same time, polyethylene retains the original structure given during the synthesis. NPE is distinguished by relatively low strength characteristics and its use is justified under conditions of insignificant mechanical loads.
- Chemically crosslinked (HS-PPE). The technology includes the following stages: mixing of raw materials with foaming and crosslinking reagents, formation of the initial matrix blank, stepwise heating in a furnace. Heat treatment leads to the fact that cross-linking occurs between the polymer threads (crosslinking occurs), and then gassing occurs. Products made of KhS-PPE have a fine-pored structure, a matte surface and higher mechanical indicators in comparison with products made of PPE: strength, tear resistance, elasticity, i.e. the ability to return to the previous thickness after squeezing.
- Physically cross-linked (FS-PPE). The material does not contain crosslinking additives, and instead of the first stage of heat treatment, the matrix blank is treated with an electron flow, which initiates the crosslinking process. The ability to control the number of crosslinks allows you to vary the characteristics of the material and the size of the cells.


Unlike most construction materials, polyethylene foam is marked not by strength indicators, but by average density, that is, the ratio of weight per unit volume (kg / m 3): 15, 25, 35, 50, 75, 100, ... 500, as shown in the photo above for example.
"Cross-linked" polyethylene foam (PPE)
There are two types of this material, depending on the technology used:
- chemically "cross-linked";
- physically "stitched".


Both types are foamed in the oven, but the way of forming stable internal bonds at the molecular level is different. The so-called chemical "crosslinking" uses a chemical reagent, and the physical - a pulse-beam accelerator, which regulates the molecular structure of the material due to the flow of electrons.
As a result, in both cases, a material with rather small, closed cells is obtained, which is distinguished by excellent resistance to stress.
Production stages
The PE foam production line consists of:
- extruder;
- compressor for gas supply;
- cooling lines;
- packaging.
Depending on the type of the final product, the equipment can be called bag making, pipe stitching, etc.


Additionally, flying shears and punching presses of various designs, molding machines are used.
LDPE, HDPE granules or compositions based on them are loaded into the receiving hopper.
Trimmings - the main type of waste from the production of polyethylene foam - are returned to the production cycle after minimal processing.
Many businesses mix primary raw materials with regranulate.
The main requirements for secondary raw materials for the production of foamed polyethylene are the absence of mechanical impurities, uniformity in color and average molecular weight with primary PE.
If the requirements are met, the quality, performance and mechanical properties of the finished product are not affected.
Comparative characteristics
| Main characteristics | "Cross-linked" polyethylene foam | "Wired" polyethylene foam |
| Thickness, mm | from 0.5 to 15 | from 0.5 to 20 |
| Density, kg / m3 | 33(± 5) | 25(± 5) |
| Working temperature, ° С | from -60 to +105 | from -60 to +75 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W / (m • ° С) | 0.031 | 0.045-0.055 |
| Heat absorption coefficient, W / (m • ° С) | 0,34 | — |
| Water vapor permeability, mg / (m.h.Pa) | 0.001 — 0.0015 | 0.003 |
| Impact noise reduction index, dB, not less | 18 | — |
| Compressive strength at 25% linear deformation, MPa | 0,035 | |
| Water absorption by volume at full immersion 96 h,% | >1 |
A common disadvantage is that in the absence of extinguishing additives (fire retardants), they are flammable.
General positive characteristics:
- high moisture resistance;
- resistance to aggressive media - acids, oils, alkalis, etc .;
- excellent interaction with other materials;
- ease of installation;
- light weight;
- complete absence of a specific smell;
- resistance to microbiological effects;
- environmental safety and a small amount of waste in production.
However, the technologies for the production of "cross-linked" polyethylene foam are more complex, therefore it has a number of advantages over "non-cross-linked":
- by almost 30% it has a denser structure, which puts it in a much more advantageous position in matters of sound insulation;
- due to increased strength and higher resistance to UV radiation than that of NPE, it has a longer service life;
- its thermal conductivity is 20% lower than that of NPE;


- higher microbiological resistance of the material;
- resistance to temperature and mechanical stress;
- insensitivity to organic solvents;
- vibration resistance;
- high deformation strength.

Nevertheless, NPE has an undeniable advantage - a low price, which often leads to a great temptation for sellers to artificially inflate its characteristics, passing it off as a full-fledged sound-proof material used in construction. It is worth noting that today you can find a rather original use of polyethylene foam.
Due to the fact that the characteristics of the types of polyethylene foam sometimes differ very significantly, it would be more expedient to consider their areas of application separately.
Basic properties
The technical characteristics of foamed PE are a synthesis of the properties of polyethylenes, soft elastic materials with a low melting point, and foams with their light weight and low thermal conductivity:
- Like ordinary polyethylene, foamed PE is a combustible material, the maximum operating temperature of which should not exceed + 102 ° C. At higher rates, it will melt.
- At low temperatures, even when lowered to -60 ° C, polyethylene foam will retain all its properties, including strength and elasticity.
- The thermal conductivity of this product is very low, it is 0.038-0.039 W / m * K, which gives products from it a particularly high thermal insulation coefficient.
- In direct contact with water, foamed PE absorbs it no more than 1-3.5% of its volume per month.
- Foamed polyethylene is very resistant to chemically active media, in particular to oil and petrol products.
- Does not break down in a biologically active environment (does not rot, does not lend itself to the action of bacteria and fungi).
- Perfectly absorbs sounds, so that PPE can be used for noise isolation.
- Absolutely non-toxic, even while burning.
- Easy to transport and install,
- Wear-resistant and durable up to 80 - 100 years of service.
INTERESTING! In terms of thermal conductivity and, accordingly, the possibilities of thermal insulation, foamed polyethylene can become an excellent alternative to many popular thermal insulators: PPE 1 cm thick can replace 5 cm of mineral wool or 15 cm of brickwork.
disadvantages
A negative property of foamed PE is its intolerance to ultraviolet rays. Direct exposure to sunlight has a destructive effect on it, therefore, both storage and use of polyethylene foam should take place in a place protected from light. Otherwise, the material itself must contain protection, at least in the form of an opaque film.


Scope of "uncrosslinked" polyethylene foam (NPE)


- This type cannot boast of a wide range of applications directly in construction. However, its properties make it absolutely indispensable in product packaging, which indicates the absence of toxicity.
- Despite the fact that, due to air-filled cells, the use of an IPE under a point load is fraught with ruptures, it is widely used for packaging any electronic equipment, glass products, packaging furniture, dishes, and so on.
- As a packing material, NPE is very convenient. It dampens even multiple shock loads well. Moreover, it does not deteriorate at all. This is the most valuable quality when transporting all kinds of items. It is used both as a cushioning material and as a wrapping material. It quickly replaced corrugated board and bubble wrap, accounting for 90% of the packaging market today.
- Another advantage is that due to its fine-bubble structure and softness, it is able to pick up some technical debris that settles on the surface of the material during loading and unloading operations, excluding the subsequent possibility of debris contact with the surface;
- NPE is even used as insulation against water, steam, condensate and structure-borne noise. But, it should be noted that this is only in those cases where there are no powerful bearing loads and high temperatures;
- Also, with low quality requirements, it is used in mechanical engineering and even construction as a heat-insulating material;
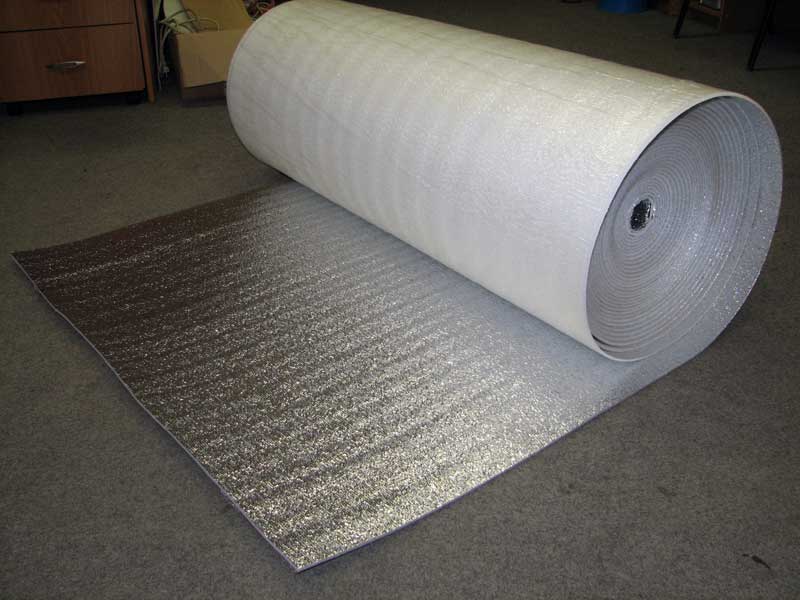
- It is used as reflective insulation to retain heat in the house and, as a result, reduce energy costs;
- It is used as a substrate for laminated parquet to level the surface;
- NPE is produced in different thicknesses (see table) and in different formats - in rolls, sheets, in the form of polyethylene foam mesh. There is also foil and laminated EPS. Therefore, there is a choice depending on the task at hand;
- Its low cost allows it to be used for the production of disposable products.
In the EU countries, the scope of its application is strictly limited only to packaging.
Technical and consumer characteristics
Polyethylene foam - what is it, and what properties does it have? To answer this question, you need to remember the main property of any material with a foamed structure - the ability to retain heat inside itself and prevent its loss.
Thermal insulation is considered the main consumer characteristic of this material, which made it possible, first of all, to use it in the construction industry.
In addition, the polymer has a number of characteristics:
- light weight. Due to this property, the material is widely used in all areas where a small mass does not give a significant load on the supporting elements and does not increase the weight of the finished product or structure;
- not subject to decay. An important quality that allows the polymer to be used in the external insulation of pipelines and buildings, as well as in places with a tropical climate and an aggressive microbiological environment;
- a wide range of operating temperatures makes it possible to use foam in different climatic zones;
- ecological purity and chemical inertness guarantees that during operation the material will not release toxins and carcinogens.
In addition to the above properties, polyethylene foam has a low water absorption coefficient (less than 2%), good noise insulation properties and ease of processing.


Foamed polyethylene and aspects of its safety
Polyethylene foam has found active use in the production of a wide range of different products. Its use at the household level is completely safe. It is only important not to go beyond the limit temperatures. Heating up to +110 degrees or more can lead to serious consequences. Combustion of polyethylene foam is accompanied by the release of hazardous substances, and the process of decomposition of this material takes about 200 years. This directly indicates its longevity, but is negatively perceived from the standpoint of the impact on the earth's ecology.