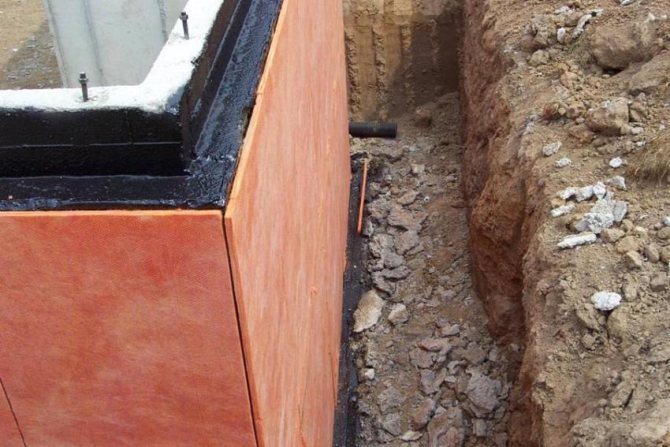
Until recently, the issue of heat loss was not raised acutely in construction, they were compensated for by powerful heating, without particularly thinking about thermal insulation. But in view of the emergence of the need to launch a policy of saving energy resources, the approach to this problem has also changed. And, as it turned out, thermal insulation, firstly, makes it possible to avoid up to 20% of heat loss, and secondly, it provides comfortable conditions inside the structure and prolongs its operational life.
Practice has shown: insulated, waterproofed structures are much less susceptible to destruction and, therefore, will last much longer. The problem of thermal insulation is now, in the era of a breakthrough in the field of construction technologies, solved with the use of an innovative material - extruded polystyrene foam.
Extruded polystyrene foam Penoplex
Extruded polystyrene foam is a whole line of building materialsmade of expanded polystyrene by foaming at high temperatures. Extrusion is provided by adding a mixture of carbon dioxide and freon. As a result, a high-strength material is obtained, the dense uniform structure of which contains granules of 0.1-0.2 mm in size.
One of the popular brands of insulation in Russia is Penoplex. Extruded polystyrene foam of this brand is produced in a wide range and for various tasks - insulation of facades, roofs, road surfaces, pipes, etc., and, accordingly, each of its types has a number of unique properties. For example, Penoplex Foundation slabs are specially designed for thermal insulation of the foundation.
Thermal insulation technology
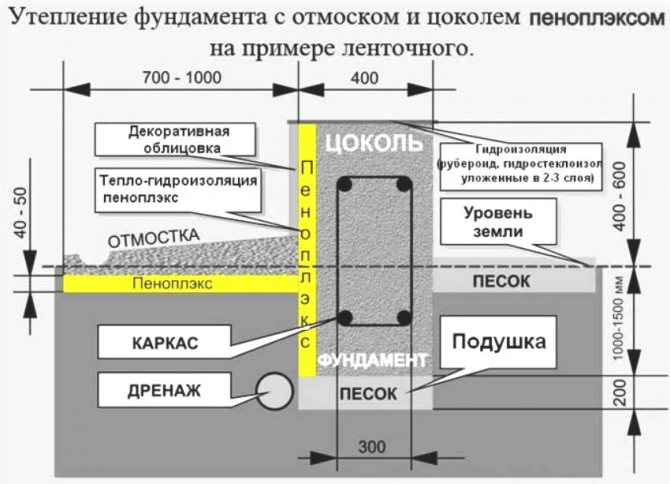
When insulating the foundation with penoplex, the technology must be strictly observed, taking into account the cost of the material. - a very technological material. If the foundation tape is insulated from the inside out, then the installation sequence will be as follows:
- Foundation;
- Waterproofing layer;
- A layer of foam boards;
- A layer of cement-based plaster;
- Ground pillow;
- Again a layer of foam boards - under the blind area;
- The blind area itself.
The scheme of insulation of a concrete foundation with penoplex
When insulating from bottom to top, the following sequence is used:
- Sand pillow;
- A layer of foam boards;
- Foundation;
- Waterproofing layer;
- Sub-floor concrete screed;
- A layer of waterproofing material along the end of the foundation wall;
- A layer of foam boards at the end of a part of the foundation slab. The slabs are laid from the beginning of the sand cushion and above the level of the soil surface by 0.4-0.5 m;
- A layer of foam boards under the blind area;
- The blind area itself.
Penoplex characteristics and benefits
- resistance to aggressive substances, mold, decay, decomposition
- high strength and resistance to deformation
- wide temperature range
- light weight
- high moisture resistance
- easy installation
- low thermal conductivity
- durability.
Thermal insulation of the foundation using Penoplex will provide durability of the foundation, and thereby extend the life and structure of the entire building as a whole.
Thermal insulation Penoplex for foundations
High-strength panels Penoplex Foundation are used for thermal insulation of loaded structures - bases, basements, floors. They are able to withstand significant compression loads for a long period of time, and their high resistance to heat transfer has made this product one of the most effective thermal insulation materials.
We offer to buy at an affordable price Penoplex Foundation, which is in demand in low-rise construction and performs the functions of protecting shallow foundations from frost heaving, moisture, destruction.
Subtleties of thermal insulation
In the task of thermal insulation of the foundation, it is not only the question of how to insulate it, but also how it matters. And there is a certain nuance here. Based on the fact that the foundation of a house is usually made of a material that is not highly resistant to freezing, moisture absorption and low thermal conductivity, in the absence of external thermal insulation it remains unprotected and susceptible to all negative impacts of the environment, with which it contacts directly, and its insulation from the inside is the thermal insulation of only the room that will be located directly above it, but not the foundation itself.
Therefore, the insulation of the foundation must be carried out without fail from the outside, which will help to avoid its deformation and the formation of cracks in it for much longer. And this must be done directly at the stage of building a house. Thus, the advantages of external thermal insulation of the foundation include the following:
- frost protection
- protection of concrete from moisture and many cycles of its freezing and defrosting
- protection against seasonal temperature changes
- dew point shift and the presence of a reliable barrier that protects against storm and groundwater
- optimal microclimate of the lower floor.
Types of insulation used
Among the thermal insulation materials that meet the above requirements and have an affordable cost, you can name:
- sprayed polyurethane foam;
- sheet expanded polystyrene;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- expanded clay.
Each of the listed types of thermal insulation has its own characteristics associated with the installation technology, the efficiency of the insulation layer and the cost of purchasing the material.
Polyurethane foam (PPU)
Of all the insulation materials listed, sprayed polyurethane foam is the most expensive material that requires the use of special equipment to apply it to the surface. However, it is also the most effective insulation of all existing polymeric materials.
Its main feature is that the polyurethane foam coating does not have connecting seams, being a single continuous layer. This material for insulating the foundation of a house from the outside:
- has excellent adhesion and adheres perfectly even to dirty surfaces;
- has one of the lowest thermal conductivity coefficients;
- after complete curing, it becomes waterproof;
- has good hardness combined with high ductility;
- absolutely unattractive to rodents and insects.
The waterproofness of polyurethane foam allows you to abandon the installation of a waterproofing layer This significantly reduces the time required to insulate the foundation of the house from the outside, reducing the overall cost.
Conventional Styrofoam Boards
This material is made by heating the raw material, poured into a mold, with hot steam. Under the influence of temperature, expanded polystyrene granules expand, forming a porous mass that occupies the entire volume of the mold. This technology is used for the manufacture of most soft foams.


PPP is supplied to the market in the form of flat slabs with a locking recess at all ends. This shape allows for partial overlapping of the joints at the junction of adjacent slabs and avoids the formation of cold bridges.
The material is cheaper than polyurethane foam, but the presence of connecting joints cannot guarantee the surface against moisture. Therefore, before installing the thermal insulation layer, a mandatory waterproofing device is required.
Extruded polystyrene foam
This material differs from the previous version in the manufacturing technology and quality of the plates. Forming of plates provides for the supply of ready-made molten polymer mixture through a special extrusion machine. In this case, the foaming of the composition occurs by filling it with neutral or carbon dioxide. Regular air is not used for this, because this will affect the fire hazard.


Extruded polystyrene foam is somewhat more expensive than usual, but, thanks to this method of molding, it does not have a single open pore on a smooth and even surface. This means a longer service life and improved thermal insulation properties.


Expanded clay
The main advantage of expanded clay granules is the lowest cost among all heaters used for foundations. In terms of other technical indicators, expanded clay, frankly, loses to foamed polymers. The use of new modern technologies for the insulation of building structures has made this material poorly in demand, its use is now rare.


The ability of expanded clay to partially absorb water over time increases its thermal conductivity by 25-30%. Therefore, ensuring the effectiveness of the bulk heat-insulating layer requires a large thickness, and, therefore, a significant consumption of material. This, in turn, leads to an increase in costs and, as a consequence, a complete leveling of the previously mentioned main advantage of expanded clay.
Calculation of the thickness of Penoplex insulation
In order for, as a result of the work on thermal insulation, the level of heat saving approaches the maximum value, and the price of materials does not bite, it is necessary to determine what thickness of insulation should be chosen for the task at hand. It will help to solve this a number of calculations... Since the choice of the thickness of Penoplex directly depends on the climatic conditions of the area in which the future house will be located, the manufacturers, of course, made approximate recommendations on the minimum thickness of Penoplex for different regions of the country, but for greater reliability it is better to do the corresponding calculations yourself.
The formula by which you can calculate the thickness of Penoplex is as follows:
h2 = λ2 * (R-h1 / λ1),
Where:
h2 is the desired thickness of Penoplex insulation;
h1 is the thickness of the foundation;
R is the resistance to heat transfer (this indicator is different for each specific region);
λ1 is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material from which the foundation is made;
λ2 - coefficient of thermal conductivity of Penoplex insulation.
For example, it is necessary to insulate a 400 mm thick reinforced concrete foundation in the Moscow region. By simple calculations, the desired thickness of the general Penoplex layer it turns out about 95 mm... Since in the process of insulation there is also the task of overlapping all joints and cracks and maximizing the reduction of cold bridges, it is usually recommended to lay the insulation in two layers, shifting one relative to the other (i.e., in a checkerboard pattern).
Since in this case the total thickness of the insulating layer is 95 mm, and Penoplex slabs, as you know, will be stacked in two layers, then by dividing 95/2 the thickness of one slab is obtained - about 47.5 mm. In this case, the resulting number is rounded up and, thus, the final optimal thickness of the insulation plate becomes known - Penoplex Foundation 50 mm is suitable for insulation of the foundation given in the example.
What are the advantages of UWB?
[1] High speed of construction in 2-3 weeks. The duration of the work depends on the area and geometry of the slab: the larger in size and more complex in shape the foundation, the longer it will take to build. Weather conditions also play a role: it is better not to pour concrete during heavy rain. [2] The possibility of the device on almost any soil, including with a high level of groundwater and heaving - clays, loams. Thanks to the insulation, the earth does not freeze, which means that the foundation is protected from deformations due to frost heaving of the soil. However, UWB cannot be done on soils with very low bearing capacity, for example, peat bogs. In this case, foundation settlement is possible. [3] No deep excavation required: savings in excavation costs. [4] The readiness of all communications at the stage of foundation construction. This significantly speeds up the construction of a house. [5] High energy efficiency thanks to thermal insulation layer. This means that the cost of heating the building is low. USB with 200 mm thick insulation has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.17 W / (m • ° С). For comparison: the coefficient of thermal conductivity of a conventional monolithic concrete slab, as a rule, exceeds 0.40 W / (m • ° C)
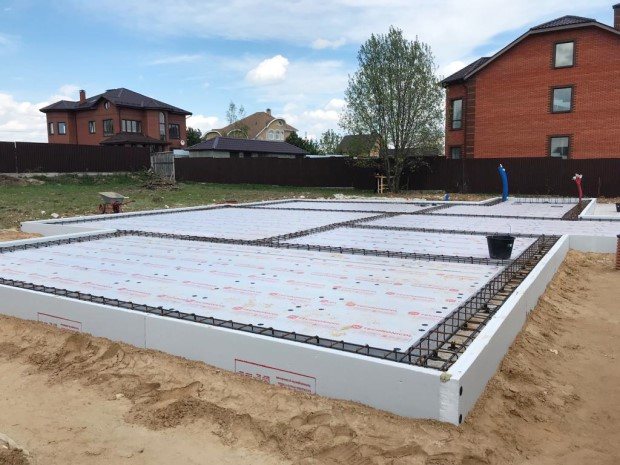


[6] There are no cold bridges in the structure of the slab and freezing of the lower corners of the building due to the continuous layer of thermal insulation under the foundation and the insulated blind area. [7] Heating with a hot water floor is 20-30% more economical than radiator heating, since the heat carrier is supplied to the radiators with a temperature of about 70 ° C, and into the underfloor heating - with a temperature of about 40 ° C. In addition, the warm floor warms up the room evenly, creating very comfortable temperature conditions for the inhabitants of the house. Finally, the absence of radiators improves the appearance of the premises. [8] There is no need to put a screed on top of the slab: the surface of the foundation is leveled and sanded, it serves as a ready-made base for laying the floor covering. This means that when finishing the premises, you can refuse additional wet work.


[9] There are no seams in the slab (expansion gaps are required in the screed), which simplifies the installation of the floor covering.
What is the thickness of the foam on the foundation slab under the screed?
It's not a secret for anyone that the concrete floor in the premises of the first floor becomes hellishly cold in winter, and if you do not take care of normal thermal insulation, then over time, dampness and microbes will simply destroy the expensive parquet or laminate. But it's not even about the flooring, the ice floor in the house is the shortest way to the disease of the joints of the legs, therefore, before finishing, it is imperative to insulate the floor with penoplex under a screed on concrete mortar.


Why is penoplex used
For specialists, the answer is obvious - it is no more difficult to lay penoplex under a screed on a concrete floor than any other material, the technique is proven and reliable. In addition, even people with minimal experience with this kind of material can technically manage the technology of installing an insulated floor by laying foam.
In fact, penoplex is the only material that simultaneously combines several unique qualities:
- High strength of the foam for bending and contact pressure. You can safely step on a sheet of penoplex in shoes, with practically no consequences for the material;
- Extruded polystyrene foam, from which the insulation is made, does not generate dust, does not emit gases or volatile substances, you can work with it practically without SDOD, in this sense, penoplex compares favorably with mineral wool or basalt mats;
- Penoplex can be laid under a screed even on a floor slab above a wet basement, the laid layer of thermal insulation will not absorb moisture and will not lose its insulating properties even after 30 years of operation.
If we compare penoplex with its closest relative - polystyrene, it can be noted that with almost equal thermal insulation characteristics, EPSP compares favorably with the fact that it does not crumble or collapse under uneven load. Extrusion technology allows to obtain closed pores in the foam, inaccessible to moisture and water vapor.


Important! The only significant drawback of penoplex is its sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and various organic solvents.
The first drawback is compensated by a protective layer of concrete floor screed on foam. The second just needs to be remembered. If you decide to paint a layer of insulation with some kind of paint on an organic solvent, or treat a concrete screed on foam with a primer, as a result, instead of a thick layer of insulation, you will get a thin layer of molten polystyrene.
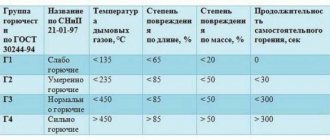
Sellers of mineral thermal insulation materials like to scare developers with the combustibility of expanded polystyrene, but at the same time they forget that foam flooring is laid under a concrete screed, which means that in the absence of air oxygen, in order for the expanded polystyrene to begin to decompose with the release of carbon monoxide, it is necessary to heat the concrete floor at least than up to 200 ° C.
EPPS insulation technology
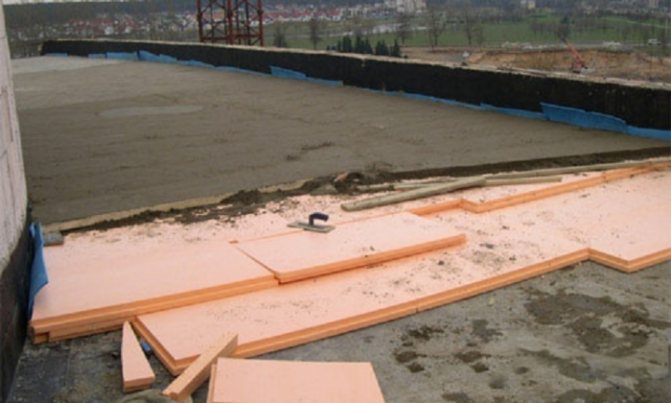
Theoretically, penoplex under the floor screed can be laid on almost any surface, without even removing the remnants of debris and gravel. In many cases, penoplex is laid on a floor of soil or a cushion of gravel, but in such conditions, a layer of expanded polystyrene presses to the floor and fixes a thick concrete screed or reinforced foundation slab. In our case, the thickness of the screed does not exceed 4-5 cm of reinforced concrete, and it depends on how carefully the foam layer is fixed on the floor whether cracks appear in the screed from the vibrations of the insulation.
Preparation of the base for laying the foam under the screed
At the preparation stage, you need to do the following:
- Measure the floor area and calculate the required amount of foam in square meters. For laying, we buy insulation for 10% more than the received footage for trimming and scrap;
- Using a chisel, an angle grinder, we level the concrete floor, knock down and remove all bumps, humps and growths more than 7 mm high;
- We carefully remove dust and dirt from the concrete surface;
- Any traces of oil, kerosene, organic solvents, which are always abundant on the floor in garages and utility rooms, are neutralized with a solution of caustic soda and washed out with plenty of water;
- We carefully prime the cement floor with a deep penetration primer, no matter what brand, most importantly, high-quality, and dry it for at least another day.


For your information! All the procedures performed were aimed at ensuring that no air pockets form between the concrete floor and the foam layer, in which, as a rule, condensate accumulates under the thermal insulation, and often cracks form in the screed.
We prime the floor, then we mark the laying of the foam sheets. The main condition for fitting the material is that the seams between the sheets must be the same along the entire length of the joint.
Laying foam on the floor under the screed
It is best to use special glue for installing foam and mineral based insulation to stick foam on a concrete floor. Apply the adhesive mass on the floor and on the working surface of the sheet along the perimeter and in the center of the slab. When laying under a screed, it is important to roll the insulation tightly to the floor and fix the laid layer with mushroom dowels. After a day, the seams between the plates are cleaned of glue residues and foamed with ordinary polyurethane foam.
Experts recommend to make an expansion gap 4-5 mm thick along the perimeter of the laid foam field, along the walls. The gap is filled with polyethylene foam tape. After pouring the concrete under load, the insulation layer will settle and expand in width.
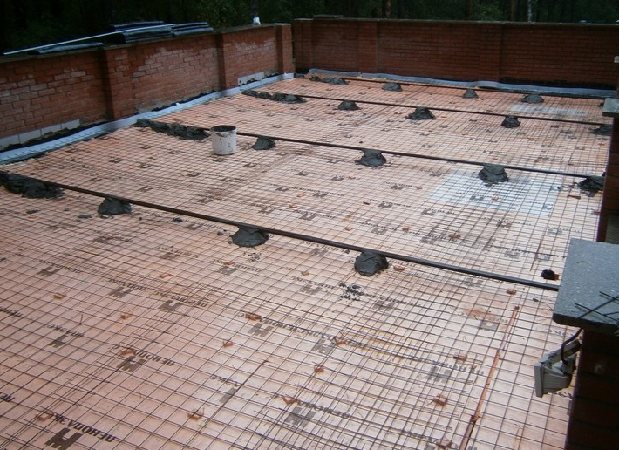


The seams and joints between the foam slabs are sealed with construction tape so that the concrete milk from the screed material does not seep inside and does not form a bridge of cold and moisture on the floor.
Pouring foam concrete
Before pouring the screed, the surface of the laid foam is covered with a vapor barrier membrane, the panel is glued along the perimeter of the laid insulation, and the edges are laid out on the walls. The membrane must be leveled without folds or looseness over the entire surface of the floor.
If the screed is supposed to be reinforced with fiberglass or steel mesh, then you must first lay the mesh on the "cups" of wire scraps so that the plane of the reinforcement is at a height of at least 2 cm from the membrane. In this case, the concrete screed works for deflection, so we deliberately shift the reinforcement plane closer to the floor, in the area of tensile stresses.
At the next stage, we expose beacons; for home screed, you can use wooden, aluminum or galvanized profiles. Due to the laid mesh, beacons must be installed on supports, screw supports resting on a layer of insulation. After pouring the concrete, such supports are usually unscrewed from the floor screed.
The width between the slats should not exceed ¾ of the rule length. We check the position of each rail with a one and a half meter building level.
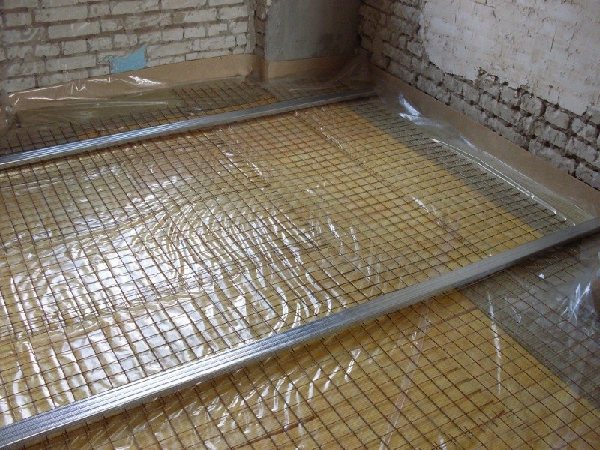


To prepare the concrete mass, you can independently make a batch of M400 cement, washed sand and a small amount of fine 1-3 mm gravel. To obtain the most smooth surface, the plane of the poured concrete screed, after leveling, is smoothed with a plaster float moistened with a PVA water emulsion.
The room with a filled-in foam screed must be closed from sunlight, and the ventilation must be opened to the smallest airflow. If the room is hot enough, then once a day the floor can be sprayed with water for 5 days. After two weeks, you can start cleaning the floor, but it is recommended that further operations be carried out no earlier than three weeks after the screed has been exposed.
Conclusion
When filling the floor, you can use ready-made sand-cement mixtures, but due to the large number of low-quality fakes, craftsmen, as a rule, prefer to prepare the filling mass on their own from the ratio of 1 scoop of cement to 4 scraps of clean sand. 100 ml of the polyvinyl acetate composition and 20 g of liquid soap are added to a bucket of solution. Such a screed adheres perfectly to the vapor barrier membrane and penoplex, and practically does not give bubbles or cracks on the floor surface.
- Parquet floors creak
- Laying parquet boards on plywood
- Laying foam on the floor
- Solid larch parquet board
What is slab foundation technology?
The slab type of foundation has another name - floating, since the slab can be erected on bulk, eroded, weak soils and with a high rise of groundwater. The slab foundation acts as a raft on which the house "floats".
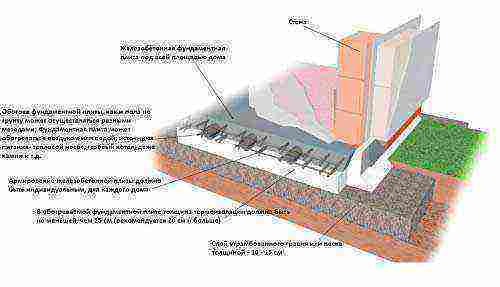

Scheme of thermal insulation of a slab foundation.
This type of foundation is ideal for small buildings. Its functions are similar to those of other types of foundations: thanks to the slabs (their rigidity) located under the entire area of the building being erected, it is a deterrent to the movement of soil and protects the house from destruction.
Slab foundation refers to one of the types of shallow strip foundation. Its main difference is that it uses a solid slab made of reinforced concrete and rigidly reinforced over the entire bearing surface of the slab.
Shallow foundation slab:
- makes it possible to reduce concrete consumption by 30%;
- labor costs for installation up to 40%;
- the cost of the foundation as a whole is up to 50%;
- applicable for almost all types of soil;
- short construction time.
Back to the table of contents
Slab foundation construction technology
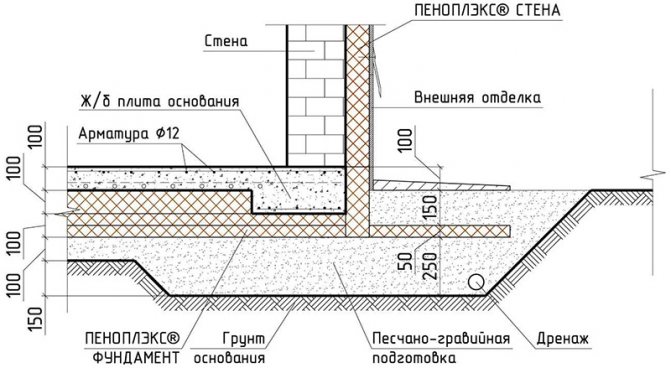
To build a slab foundation, they begin with the fact that only a fertile soil layer is removed in a previously prepared and marked area.At the bottom of the dug pit, a sand cushion is laid with the addition of sand, which is well tamped. A layer of waterproofing material is placed on the pillow, then a layer of insulation. After that, the slab foundation is carefully reinforced. For slabs, reinforcement d = 12 mm is applicable. And the last stage is the construction of the formwork and pouring concrete into it.
Back to the table of contents
Foundation slab: insulation
Diagrams of the device of unburied monolithic and precast-monolithic foundation slabs.
It will help to reduce heat loss through the slab, and, accordingly, prevent soil subsidence under the slab by warming the slab. For this, a 10- or 15-centimeter layer of heat-insulating material is laid. The slab foundation will be protected from freezing by insulating it between the slab and the ground.
Is it so necessary to insulate the foundation?
The issue of thermal insulation of the foundation should be given special attention to residents of regions with harsh climatic conditions and deep freezing soil.
The zone of heaving soils makes up about 80% of the entire territory of Russia. When freezing, heaving soils increase in volume and rise, which causes the destruction of the foundation structure.
Back to the table of contents
Benefits of base plate thermal insulation
- relieves (or significantly reduces) the influence of frost heaving forces on the foundation;
- reduces heat loss through the foundation and reduces heating costs;
- creates the necessary conditions for the establishment of a constant required temperature inside the room;
- protects against the appearance of condensation on surfaces inside the building;
- serves as protection for waterproofing from mechanical damage;
- prolongs the life of the waterproofing material.
Back to the table of contents
How can you insulate a slab foundation?
Installation diagram of a monolithic slab foundation.
Thermal insulation materials for external insulation of the foundation should not absorb moisture, as well as shrink under soil pressure. High rates of water absorption and compressibility when backfilled with soil make mineral wool not quite a suitable material as a heater. Only foam glass and expanded polystyrene meet these requirements. The first option will cost several times more.
Can regular foam be used? Can. Only it must be placed on a waterproof layer (waterproofing), which serves as protection for structural elements from soil moisture. Otherwise, within a few years from the moment of installation, the foam can be expected to turn into a shapeless pile of balls. The accumulated moisture in the insulation during freezing will increase the foam in volume, while destroying its structure.
Extruded polystyrene foam is considered the most optimal heat-insulating material for conditions of increased loads and humidity.
Due to the characteristics of the feedstock and the closed cellular structure that prevents water penetration into it, expanded polystyrene plates have excellent technical characteristics, a long service life, which makes it possible to use it in the insulation of foundation slabs.
Foundation insulation scheme.
Extruded polystyrene foam has water absorption close to zero (no more than 0.5% by volume for 672 hours and for the entire next period of operation). This prevents soil moisture from accumulating in the thickness of the insulation, expanding in volume under the influence of temperature changes and destroying the structure of the material during the entire period of service.
To insulate the slab foundation for vertical thermal insulation of civil and industrial facilities, polystyrene is used with a compressive strength of at least 250 kPa (linear deformation - 10%).For private low-rise construction, slabs with a strength of at least 200 kPa can be used, since in this case the depth of the foundation will be less, and the pressure of underground and groundwater on the insulation is lower. For structures that require increased strength indicators (loaded floors), plates with a compressive strength of 500 kPa should be selected.
Advantages of expanded polystyrene:
- stability of thermal insulation properties during the entire service life;
- validity period - 40 years;
- compressive strength indicator - 20-50 t / m²;
- is not a nutrient medium for rodents.
Back to the table of contents
How to insulate a slab foundation with expanded polystyrene?
Scheme of a slab foundation with stiffeners.
Insulating the vertical part of the foundation, expanded polystyrene is installed at the depth of soil freezing, which is determined individually for each region. If you install the insulation deeper, the effectiveness of this will sharply decrease.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer in the corners should be increased by one and a half times with an indent in both directions of at least 1.5 m.
To insulate the slab foundation from the outside is a more rational way, since this way the level of heat loss will be lower.
Thermal insulation boards are placed on the waterproofing layer. If you plan to use knitted reinforcement for reinforcing a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slab or load-bearing floor, then for expanded polystyrene slabs it is necessary to arrange protection from liquid concrete components. To do this, use a polyethylene film (150-200 microns), which is laid in one layer. If the reinforcement work involves the use of welding, then a screed of low-grade concrete or cement mortar must be made over the film to protect it. Polyethylene is laid with an overlap of 100-150 mm on double-sided tape.
Back to the table of contents
External insulation of the foundation
Pile foundation diagram.
To reduce the depth of freezing of walls and the base of the foundation, to keep the border of freezing in the thickness of non-porous soil - a sand and gravel cushion and backfilling will help warming the soil around the entire perimeter of the house under the construction of the blind area.
When laying polystyrene foam, it is important to take into account the given slope of the blind area - about 2% from the house. The width of the extruded polystyrene foam insulation along the perimeter should be no less than the depth of seasonal soil freezing.
The horizontal thickness of the insulation must be no less than the vertical thickness of the foundation insulation.
Back to the table of contents
Internal insulation of the foundation
If it is impossible to insulate the slab foundation from the outside, it is allowed to install thermal insulation from the inside of the walls of the foundation.
Laying of thermal insulation from the side of the walls of the room is carried out either by gluing extruded polystyrene foam to the surface of the walls with solvent-free compositions (it is possible on a cement basis), or by mechanically fixing the insulation plates with a subsequent finishing device.
Back to the table of contents
How to fix expanded polystyrene sheets to the foundation?
Reinforcement scheme for the slab foundation.
The insulation is placed on the leveled surface of the walls outside the insulated structure with waterproofing already made on it.
It is not allowed to mechanically fix the polystyrene foam plates from the outside when insulating the foundation plates. Since in this case, the integrity of the continuous waterproofing coating can be violated.
To the surface on which there is already a waterproofing layer, polystyrene foam plates can be attached in two ways:
- glue;
- method of melting bitumen on waterproofing.
The adhesive is applied at 5-6 points, then the boards are firmly pressed to the surface.
The gluing of the slabs must be carried out from below, laying the slabs in a horizontal row. The second and next rows of slabs are attached end-to-end to the previous row already glued.Reinstallation of the glued boards is not allowed, as well as changing the position of the boards after a few minutes after gluing.
Strip foundation waterproofing scheme.
The insulation boards must be of the same thickness and touch each other and the base tightly. In this case, you need to arrange them by shifting the joints (in a checkerboard pattern). If the distance between the joints between the boards is more than 5 mm, they must be filled with polyurethane foam. It is better to use the plate with a stepped edge. The slab is laid close to the adjacent one so that their adjacent parts of the edges overlap each other. With this installation, cold bridges do not appear. Arranging a two-layer (or from more layers) thermal insulation, the seams between the plates are spaced apart.
The choice of glue will depend on the waterproofing used. If you use roll or mastic waterproofing on a bituminous basis, use a special adhesive composition with bituminous mastics. When choosing glue, you need to make sure that it does not contain solvents, which, when applied, can dissolve the expanded polystyrene board.
The glue layer is applied in several points on the sheet along its perimeter and in the center, if the foundation is glued over to the one that is located below the surface of the earth. This technique is needed in order to enable the unhindered drainage of moisture that collects between the building base and the surface of the slab.
It is impossible to install insulation on not yet dried out bituminous waterproofing. There are several reasons for this:
- Elements of waterproofing during installation can simply "disperse", and there will be no full guarantee of the tightness of the waterproofing.
- Solvent particles may contain waterproofing agents with cold bitumen. They can damage the insulation material. Therefore, using cold bitumen waterproofing, it is recommended to install a plate of extruded polystyrene foam after the surface has dried. For which it will take at least 7 days.
Watertightness and resistance to increased loads makes extruded polystyrene foam the optimal insulation for the foundation slab.
| 7 years ago | tanya (Builderclub expert) This construction of the foundation is called "Swedish plate". Insulation is laid at the base, but not foam (it absorbs moisture and has insufficient density for this design), but extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) with a density of 38-50 kg / m³. Such insulation can withstand about 40 tons of distributed load per 1 m2. This is quite enough for this design. For example, insulation of this density is laid under the road surface on Khreshchatyk Street in Kiev. And epps with a density of 100 kg / m3 does not exist, 50 kg / m3 is the maximum. Under the epps, depending on the type of soil and the level of groundwater, either simply compacted sand (15-20 cm), or 10-15 cm of sand + 10-15 cm of crushed stone, or about 20-30 cm of crushed stone in a cage from a filtering geotextile cloth (drainage ). The foundation is "insulated Swedish plate". Drainage device. Then the insulation is laid. The foundation is "insulated Swedish plate". Insulation laying. Next, pre-connected (or welded) reinforcing cages are installed. And if a warm floor is planned, then the pipes of the warm floor are laid. The foundation is "insulated Swedish plate". Laying reinforcing bars. Concrete is poured - about 30 cm, but it can be more, depending on the type of soil and loads on the foundation. Therefore, together with the sand and gravel cushion, the depth of such a foundation will be at least 50 cm. The foundation is "insulated Swedish plate". Concreting. That's all. Finished foundation "insulated Swedish plate". Is it possible to make such a foundation for a frame house? - yes, you can. This is a very good, but far from the cheapest foundation, as Svarog rightly noted.The consumption of materials for it is higher than, for example, for tape, pile or columnar. Otherwise I also agree with Svarog. Ask if you have any more questions or clarifications. to answer |
I am slowly planning to build a workshop. Probably it makes sense to insulate the floor - while it is not planned to heat, but you never know what else, even at current energy prices ... It seems like extruded polystyrene should be used for these purposes. Which is better (brand and thickness) - or any extruded from the supermarket will go ? I talked with several people - opinions differed about how to lay it under the concrete. Most say that it is laid on rammed sand, and concrete is poured directly onto it. I have a reinforcing mesh made of pieces (about 1200/1200 mm) will be cooked, so it won't work, the foam will melt and ignite from metal splashes. Is it possible to put (pour) 40-50 mm of sand on top of the foam, and only then pour concrete on it? Or what is better?
And won't the concrete mix all the sand when pouring and will the foam damage it?
Similar:
Foundation insulation methods
The horizontal insulation method is used for the base of the slab and strip foundations of the house. In this case, do-it-yourself penoplex slabs are placed under the foundation base. This method protects the base well from freezing.
The vertical method of warming the foundation involves gluing foam boards on the outer walls of the base and basement. Plates are mounted using polymer glue, and in the area of the basement they are also reinforced with dowels.


Insulation options for various types of foundations
Insulation of the blind area around the house with foam-plastic slabs. This method is resorted to when the soil on which the building stands is heavily heaving, which leads to deformation. In this case, the foam slabs are laid on a pre-filled special pillow, and a concrete blind area is installed on top of them.