Natural resources are not unlimited: sooner or later they will run out. Therefore, humanity is increasingly using renewable resources for its needs. And it doesn't matter if it is energy, construction or other areas of industrial production.
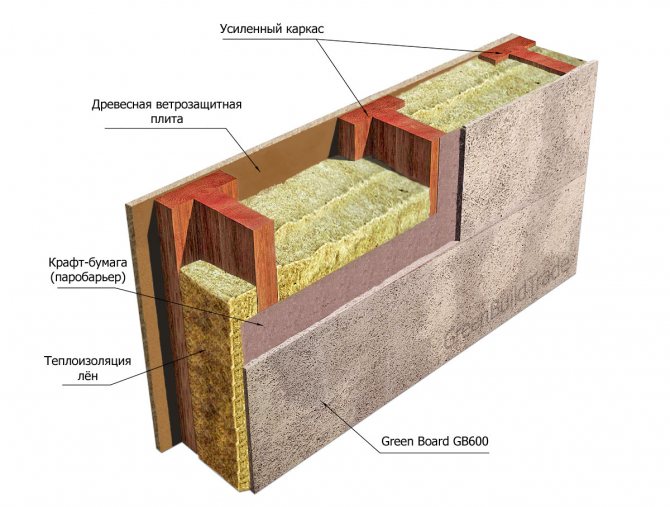
Natural linen insulation also fully belongs to the category of renewable building materials. At the same time, its use began so long ago that even in fairy tales for children, foam plastic and basalt wool, which are currently popular, were not even allegorically mentioned.

The editorial staff of the StroyGuru portal decided to figure out how relevant linen insulation is in the XXI century, where are the advertising moves of manufacturers, and where are the real advantages of thermal insulation material.
Features of linen insulation
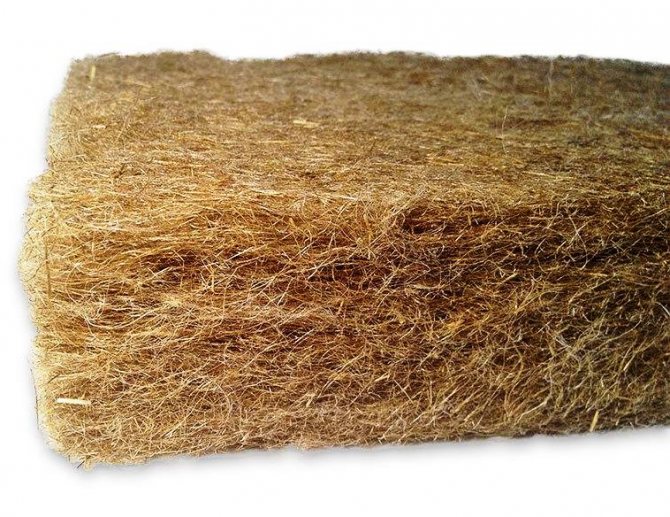
Flax belongs to annual bast crops with thin fibers (20-50 pieces per stem). In turn, the fibers consist of porous, up to 150 cm long, separate "hairs" (10-40 each), enclosed in a flexible sheath. Thus, a flax stem can be fluffed into 200-2000 simple cellular structures that perfectly keep heat and absorb sound waves propagating in the air.
In its pure form, flax cannot be used for insulation - it quickly cakes, due to the presence of a solid trunk and is subject to decay. Therefore, primary processing is needed in the form of crushing and scutching to free the fibers from the fire.
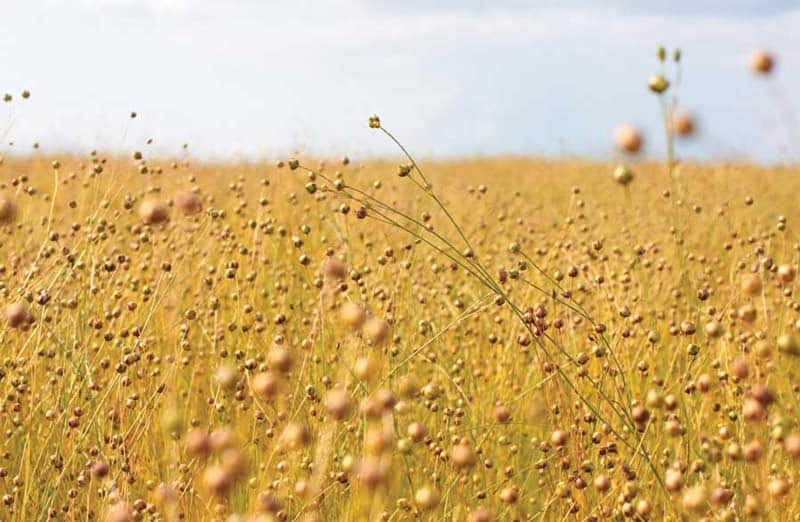


However, even in this form, the fibers are quickly caked. Therefore, synthetic substances (synthetic winterizer) are added to them, which are responsible for the elasticity of the canvas and its volume. To combat the putrefactive microflora, the method of heat treatment is used, as a result of which all microorganisms die - the material becomes biologically pure. But this does not mean that over time, flax will not begin to deteriorate. This is facilitated by two factors:
- starch (an excellent base for the development of pathogenic microorganisms) - added to mats for gluing fibers;
- constant dampness in a room with a linen insulation.
In addition, one should not forget about the high degree of flammability of flax fiber, which requires the treatment of belts, cloths and mats with fire retardants. These points need to be considered when buying linen insulation.
Is it really as environmentally friendly as they say
The cost of linen insulation is very high. Therefore, to promote a product on the market, chips are needed that should stimulate sales growth. Among them is the absolute ecological purity of the product.
This advertising ploy is confirmed by the quality mark awarded by the EU Commission to environmental building materials. In this regard, we note that for the most part, all construction products from flax of Western firms have this sign. How is it in Russia? After all, we buy mainly a domestic product.


Let's try to find out if linen insulation is really eco-friendly. For the analysis, you need to know the composition of the insulation. And here questions arise. If boron salt was used as fire retardants, and starch is a binder, then there is no doubt about the ecological purity of linen insulation.
But to improve consumer characteristics, chemical binders are increasingly used instead of starch (in some brands, up to 30% of them). In this case, it is not necessary to say that the products are natural, although manufacturers claim the opposite.
Specifications
Information on the technical and operational characteristics of linen fiber insulation is still controversial. There are a number of objective reasons for this.Therefore, we will not refer to different sources to explain our choice, but we will give the lower and upper boundaries of each indicator:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.03-0.04 W / (m * K);
- density - 15-38 kg / m3;
- sound absorption coefficient - 0.98;
- operating temperature - from -70oС to + 169oС;
- service life - more than 50 years;
- flammability class - G1;
- vapor permeability - MU1 (yes, equal to 0.4 mg / m * h * Pa);
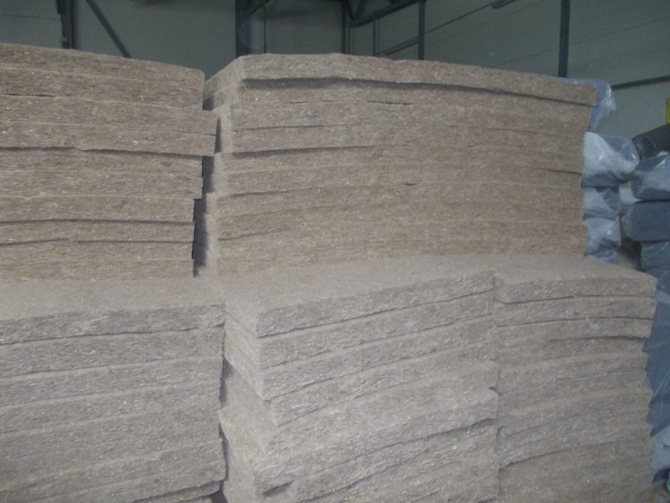
- sizes of mats: length - 100-120 cm; width - up to 60 cm; thickness - 5 and 10 cm.
Rolls can be up to 160 cm wide, and cuts from 20 to 400 mm.
Material characteristic
Linen insulation is made from natural raw materials - properly processed technical flax fibers. It is characterized by the following main parameters:
- Thermal conductivity, determines the ability of a material to retain heat. The lower the score, the better the material. The thermal conductivity coefficient of linen heaters is about 0.038 W / mK. This is an analogue of mineral wool.
- Soundproofing. The ability to absorb sound. Flax surpasses mineral wool by one third.
- Water vapor permeability. The ability of the insulation to remove water vapor and not accumulate moisture in its volume. This reduces the risk of mold and the development of harmful microorganisms. Breathable insulation contributes to the creation of comfortable climatic conditions in the protected area.
- Refractoriness. Flax itself is easily flammable. As part of the insulation, it is impregnated with substances that stop combustion. Smoke emitted during smoldering does not contain toxic substances.
- Specific gravity. Based on the insulation model, it varies in the range of 15-85 kg / m3
The environmental friendliness of the material should be noted separately. It is made from natural raw materials; a minimum of harmful substances is used in its production. The design service life of the insulation is set at 75 years. Its reuse is possible.
Advantages and disadvantages
All building materials have their own advantages and disadvantages. Linen is no exception. According to reviews on the forums to pluses this type of insulation includes:
- high thermal insulation properties - the thermal conductivity coefficient is only 0.03-0.040 W / (m * K), which is only slightly inferior to polyurethane foam, is on the same level with foam and surpasses mineral wool;
- durability, confirmed by practice - the service life is 50-100 years (manufacturers indicate the number 50, but in practice, when dismantling wooden buildings, linen insulation was in working order for 75-100 years);
- vapor permeability, allowing the walls to "breathe", removing excess moisture from the room to the street;
- increased hygroscopicity, which on the one hand is a negative property - it quickly gets wet, on the other hand, linen-based insulation, like wood, regulates the humidity regime in the room: with an excess, it absorbs vapor molecules, with a deficiency, it gives off, and dries very quickly. A big plus in this property is that no vapor barrier is required. Consumers do not need to be afraid of frequent, but short-term wetting of flax, because after drying, all characteristics are restored in full. The only thing that can happen is darkening of the fibers;
- Possibility of installing a raspor, without using glue and dowels. Such installation became possible after manufacturers began to make mats in width and length slightly larger (by 2.5 cm) than the standard dimensions of the lathing cells or the distance between the lags (beams);
- environmental safety, while not only in relation to homeowners (not an allergen, does not emit harmful and toxic substances when heated and burning), but in general, flax absorbs CO2 during cultivation, completely decomposes, can be reused, belongs to renewable resources;
- good sound insulation performance, but only airborne sound waves are absorbed. Flax is practically useless against structure and impact noise;
- simple and safe installation - all work can be done with your own hands without the use of overalls. The problem arises only if the mats need to be adjusted to the size - the flax fiber is poorly cut.
Among the many advantages of a heat insulator, one should not forget about disadvantages... And they are critical in many ways. Among the cons:
- high price. The material is available at a cost only to wealthy property owners;
- increased flammability. It is not for nothing that the powder contains flax components. Therefore, processing with fire retardants is required. And not just sprinkle with boron salts, but add up to 13% of this substance to the mat. After processing, the flammability class decreases from G3 to G1 (does not support combustion);
Attention: studies by Finnish scientists have shown that with a mass fraction of flame retardants of less than 12%, flaxseed products burn well. And the lower the percentage of boron salts, the more difficult it is to extinguish the flame.
- susceptibility to complete decomposition, whatever the manufacturers' brochures say. However, there is one thing: putrefactive microflora reproduces only in an environment with constant humidity or the presence of a base in the form of starch. This must be taken into account during construction and repair;
- damaged by rodents, which again conflicts with advertising, albeit with a proviso. Mice and rats do not digest flax fiber, so advertising seems to be right - the product is not included in the rodent food chain. But the fact that this natural insulation is the favorite habitat of these pests is modestly silent;
- loss of operational properties (heat and sound insulation), under mechanical stress (squeezing);
- needs to be treated with moisture-proof compounds when used in rooms with high humidity, which further increases the cost of thermal insulation.
Scope of application
Modern insulation based on linen fibers can be used to insulate almost any units and structures of residential and commercial buildings. Their use is especially relevant in the so-called. green homes with low or no environmental impact. They allow you to build a residential building entirely from environmentally friendly raw materials, without using synthetic materials.
In addition, the use of linen insulation can improve the climate and increase comfort in buildings built of stone, brick and wood.
The use of flax is especially useful in families whose members are prone to allergic reactions.
Application area
In terms of sales volume of 0.5% in physical terms (in m3), linen insulation in slabs (together with tapes for warming between joints) occupies a modest last place in the market of thermal insulation materials. There are two reasons: the high price and a special niche in thermal insulation tied to wooden houses. It is rarely used in buildings made of other types of building materials, although flax can be used for thermal insulation:
- floor, but only along the logs (not used under the screed due to the loss of performance under pressure);
- walls, both inside and outside. But there are also limitations here: you cannot use the “wet method” of insulation;
- interior partitions, but mainly as a sound-absorbing material;
- ceiling, but outside. For internal insulation, the height of an apartment or house decreases too sharply (to the thickness of the mat of 10 cm, you also need to add a cladding or a suspended (suspended) ceiling);
- roofs, but only pitched;
- door and window blocks - serves as a seal.
In addition, fiber tapes are used to insulate the interconnection of log cabins, and tow is used to seal various cracks and gaps. If we consider in the context of the types of buildings, then flax can be effectively used in frame and wooden houses, apartments.
Frame house. Difficult climatic conditions in Russia did not allow finding the best insulation option for frame houses.Negative nuances always appear. With the advent of linen mats for insulation, it turned out that they are almost ideal for this type of buildings: they perfectly protect against noise, heat loss in winter and overheating of rooms in the house in summer. The ability of the insulation to regulate the indoor microclimate all year round turns flax into the main type of heat insulator for frame buildings.
Wooden house. Initially, linen and wooden houses were inseparable. Their collaboration goes back several millennia. Therefore, with the advent of new qualities in linen insulation, the use of flax fiber thermal insulating materials for insulating various structural elements of a wooden house is most organically seen.
Apartment. Linen mats do their job well in an apartment when insulating the floor and walls. Limitations exist for the bathroom and kitchen due to the high hygroscopicity of the fibers.
Benefits of linen insulation
As always, with the appearance of something new, a kind of psychosis arises, of course, not on level ground. Manufacturers push their product, and marketers make every effort to make you believe that you don't need anything else, just linen insulation. Reviews of the results of its use on the network are rare, since this material received a new breath not so long ago, and in fact it is not very much in demand.
Perhaps somewhere in Europe or other parts of the world people are more gullible and naively believe what advertisements are presented to them, but our person is prone to analysis.
Based on the results of their conclusions, the buyer comes to the conclusion that the only plus of linen insulation is its controversial environmental friendliness.
Why controversial? Take, for example, thermolen linen insulation: it does not burn - it means that it is treated with fire retardants, and this is chemistry. Chemistry cannot be eco, well, no way
Another alleged advantage is that it is not necessary to lay a vapor barrier during installation, although it will not interfere. So, for that matter, stone wool also does not need a vapor barrier, since it does not absorb water at all and also belongs to the “eco” category. In fact, there are simply no real advantages that one could catch on to. And talking about environmental friendliness, usefulness and age-old traditions is not constructive. When choosing linen insulation in slabs or mineral wool, one must proceed from the banal ratio of characteristics-price-quality, and according to these criteria, linen is clearly inferior.
The classical method of heating your home with gas or wood can be replaced with an alternative heating of your home. In this case, free energy is used, available to everyone.
By installing infrared heating in a wooden house, you can save money due to the speed of heating with infrared radiation. More information here.
Insulation types
The construction industry offers consumers several types of linen insulation:
- tow;
- felt (linen);
- batting (linen);
- mats (plates).
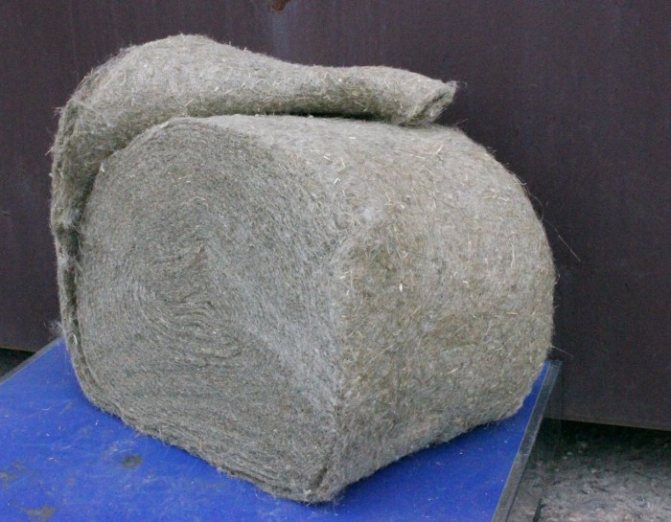
Tow. Oakum is waste from the processing of flax and other bast crops (hemp, jute, etc.), arising in the process of scutching. Consists of coarse, short, tangled fibers heavily contaminated with fire. It has been used in construction since the beginning of the cultivation of flax for the production of textiles.
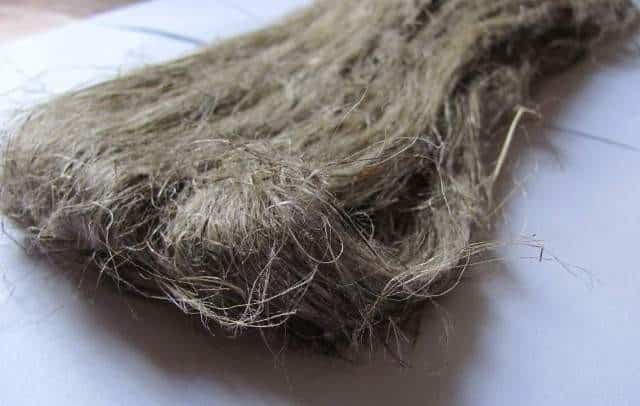


It is mainly used for insulating log cabins. But it can be found in the openings of doors and windows (instead of polyurethane foam), as well as in the joints of the plates of the main insulation, for example, foam.
Felt. The definition of "felt" has nothing to do with linen insulation, because the word originated to define a dense nonwoven fabric made of wool. But manufacturers of a similar material made from flax fibers could not come up with an independent name for dense nonwoven ribbons. So they began to call their products linen felt.
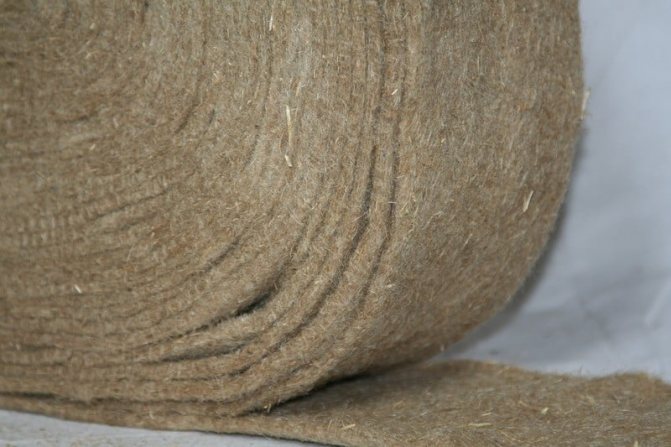


A product is made from long fibers using needle-punched technology - this is when special needles with barbs form a canvas, fastening it with their own fibers. It is used as an inter-crown linen insulation.
Batting. Batting is another type of nonwoven fabric. It differs from felt in that a nylon or cotton thread is used to fasten the flax fiber layer. It is used in the same way as felt, but with one difference: it fits in two layers. This requirement is explained by the production technology - the insulation tape has a low density. Only about 500 g / m2.


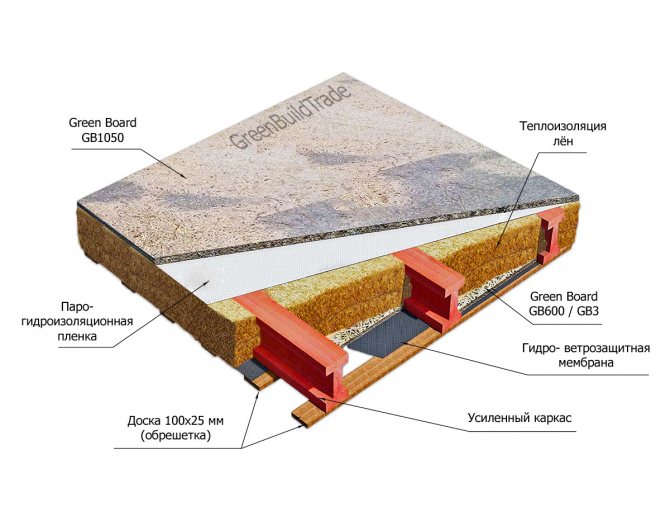
Mats. Flax fiber insulation mats are produced using starch, which serves as a binder between the fibers. In many industries, mats are additionally stitched with silk or cotton threads. Thermal insulation material is produced in the form of rolls and plates with a thickness of 5 and 10 cm. It is used for thermal insulation of various building structures.


Attention: in the materials about linen insulation, another type is called: flax-jute. However, the use of the term "flax-jute" to define insulation as an independent type, consisting of a combination of linen and jute fibers, is incorrect. It would be more correct to say that other types of bast crops can be added to flax fibers. After all, the so-called “linen-jute” insulation is produced in the form of felt, batting and mats. Therefore, it is impossible to say that this is an independent type of heat insulator.
Classification and release forms
The following forms of production of insulating materials from flax fiber are presented on the modern market:
- Ribbon felt. Long shredded fibers are heaped into a dense felt-like material. The orientation of the fibers in it is random, this ensures the uniformity of the heat-insulating properties in the directions. Air pockets between adjacent matted fibers provide reliable heat retention. Impregnations provide its fire resistance and reduced hygroscopicity.
- Linen tow. The traditional form of use for flax is in bunches of shredded plant stems. It is used as a linen mezhventsovy insulation of houses made of logs and beams, for caulking window and doorways. It is attractive to birds and rots when moistened, so the insulation needs to be covered with decorative strips.
- A mixture of flax and jute fibers in equal proportions. Used as a cord seal, jute gives it elasticity and strength.
- Linen batting. Several layers of brushed linen fabric are stitched with a strong thread, thus forming a low-density material, similar to batting. To obtain the required thickness of thermal insulation, it is mounted in several layers.
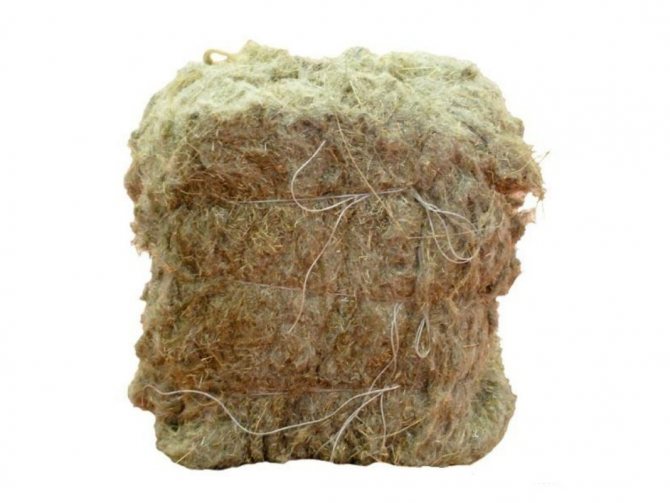


Linseed tow
Recently, board material molded from flax fiber has become more and more widely used. It is glued to thick cardboard, comparable in strength to mineral wool and is used for thermal insulation of frame houses and other pre-fabricated buildings. Its breathable structure especially attracts buyers.
Popular brands and prices
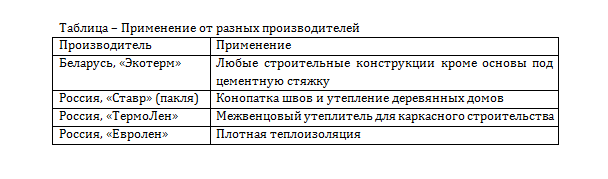
In the Russian trade network, linen insulation can be found under many brands: Thermo-Hanf, Val-Flax, TermoLen, Flaxan, Ecoteplin, Ecoterm, Ekolen, etc., as Russian production and manufacturers from Europe.
"TermoLen". The products under the TermoLen brand are manufactured by the Novosibirsk Flax-Jute Company. She was the first in Russia to master the latest AirLay and thermal bonding technologies for the production of environmentally friendly natural insulation materials from flax.
The use of modern equipment in the processing line made it possible to abandon starch as a binder (a bicomponent synthetic winterizer fiber is used), which provided the mat with additional elasticity, durability and volume recovery after removing mechanical loads.All this together allows you to install the insulation in the cells of the lathing raspor, without additional fastening.
You can buy insulation at a price of 5,760 rubles / m3 and above (depending on the density).


Ecoteplin. One of the leaders in the production of various types of flax products is the Russian concern "Khors". It includes not only processing enterprises, but also agricultural production. Therefore, the TermoDom enterprise, which specializes in the production of heaters from bast crops, uses its own raw materials.
A feature of the product is the complete absence of synthetic materials. Starch is used as an adhesive. This is both an advantage and a disadvantage. The plus is that the product is categorized as absolutely environmentally friendly. Therefore, it can be used without restrictions in living quarters with children or allergy sufferers.
Minus in fast caking and a service life of 40-50 years (starch is to blame - it serves as a basis for the reproduction of putrefactive bacteria), which is almost half the size of analogues with synthetics in the composition.
The cost of 1 m3 starts from 5500 rubles.
Ecoterm. Insulation "Ecoterm" gets into the trade networks of Russia from Belarus (CJSC "Politeks"). It is produced in the form of mats with a thickness of 5 and 10 cm. It is used for sound and heat insulation of private houses and apartments.
Mounted by a polyester fiber binder. It has high density and elasticity, resistance to deformation and shrinkage (does not cake for a long time). However, such properties still do not allow the use of insulation under the screed.
In addition, the lack of impregnation from fire retardants should be attributed to a serious drawback, which really affects the price - it is lower: insulation can be bought from 5,000 rubles / m3.
Val-Flax. Products with an unusual name "Val-Flax" are manufactured by LLC "Artemida" (Novgorod). Newcomer to the construction market. However, the high quality of the product that meets all EU requirements and the price (from 5400 rubles / m3) paint its prospects in a rainbow color.
EcoLen. Smolenskaya specializes in the production of linen felt using needle-punched technology. Dense tapes "EcoLen" are used for sealing connecting joints between the crowns of a log house and in the form of seals when installing window and door blocks.
On the recommendation of the manufacturer, this material can also be used to insulate the walls of wooden houses from the inside of the room, which raises a number of questions: why is it necessary at all and what fastening technology to use for a thin canvas. The downside is the lack of fire protection.
The company's products cost from 4900 rubles / m3.
Selection features
When choosing linen insulation, you need to pay attention to the following parameters:
- the material should not have foreign impurities in the form of a fire, which not only impairs the appearance, but also reduces the technical and operational characteristics;
- the density of the tape or web must be uniform. Otherwise, cold bridges form over time;
- when choosing between tow, batting, felt and mats, you need to focus on the place of use. Here the role is played by the width and thickness of the insulation, its density and purpose. So, for profiled beams, felt up to 3 mm thick and up to 300 g / m2 density is suitable. The joints of rounded timber crowns must be sealed with felt 5 mm thick and 500 g / m2 density or 15 mm thick batting (it will settle when the log is laid). Between the timber you need a linen felt 10 mm wide and 8 kg / m2;
- the binder must still be polyester fibers. There will be no harm to the health of family members, and the service life is almost doubled.
Criterias of choice
The choice between linen and tow should be based on several indicators. Both heaters are 100% linen, but there are differences between them.So, tow is produced in only one width (the equipment gives only 15 cm). At the same time, its plus is that it is loose and flexible - it can be squeezed, stretched manually as needed. This material costs 2 times cheaper than flax. Flax, although more expensive, is more versatile - the tape can be of different widths, so it can be used for all types of wooden houses.


Linen insulation meets all the requirements for the construction of small houses for pitched roofs, attics, walls (external and internal), floors, ceilings, ceilings and interior partitions. Oakum is used for insulating joints between logs, beams, for assembling log cabins, caulking or filling voids between door and window frames. The use of tow is optimal for houses made of ordinary timber, and linen felt is optimal for houses made of profiled timber and calibrated logs.

Insulation technology
A feature of the technology of insulation with linen mats is that the insulation cannot be fixed with glue or dowels. Only setting by surprise. Therefore, using the example of wall insulation inside a house with linen insulation, we will consider all the nuances of thermal insulation work. They are executed in the following sequence:
- the wall is cleared of everything unnecessary: switches, sockets, fixtures, etc.;
- an audit of the condition of the wall surface is carried out. Repair work is carried out if necessary;
- the crate is stuffed with cells 1-2 cm smaller in width and height so that the mats become a surprise;
- the rolled insulation is cut to size, while you should not forget about an overlap of 1-2 cm;
- mats are installed in cells;
- counter-lattice is stuffed;
- the insulation layer is closed with a finishing material, for example, PVC panels or clapboard or sheets of drywall for painting or wallpaper.
Important: vapor barrier works under flax are not carried out.