Description of steel pipes
The main advantages due to which galvanized steel pipes are preferred for heating:
- resistant to high temperatures and pressure (especially this variety - seamless thick-walled);
- mechanically strong, resistant to stress;
- a wide range of applications: even for the transfer of heated steam, the polymer pipe would not withstand;
- allows the ability to carry out any kind of processing: welding, cutting, drill, lathe.
Unfortunately, galvanized steel pipes for heating have negative properties:
- corrosion - although there are methods to reduce the susceptibility to corrosion of steel products, they are one hundred percent unable to protect the heating system;
- inside, foreign substances are deposited on the walls, especially with centralized heating - long-term operation is not possible (only 15-20 years, then the pipes are changed);

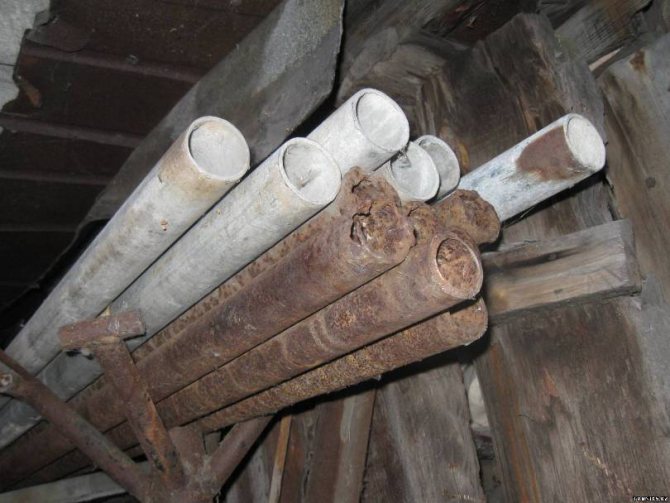
Galvanized steel pipes
Features of steel pipes
Classic
Conventional ferrous metal pipes have been used in the construction of various buildings and structures for a very long time. Their popularity is due to their ability to withstand increased loads, and also not to collapse under the influence of negative external factors.
Price also has a significant impact on popularity. Carbon steel pipes, with their high technical characteristics, are quite affordable.
The materials in question are simply created for the design of heating networks:
- they can be used to transport a coolant heated to a temperature above + 100 degrees Celsius;
- if the liquid freezes in the cold season (for example, in the event of a boiler failure), pipelines can be warmed up with an open flame.
Steel is strong and reliable, but corrosive
But one cannot fail to mention the significant disadvantages:
- The process of constructing a heating network from steel pipes is quite laborious and requires special skills and the use of sophisticated equipment.
- Steel pipes are hard to shape, especially when they need to be bent in several places at different angles.
- Metal conducts heat well, therefore, when installing a heating network (especially with open areas), steel pipes must be carefully protected with heat-insulating shells, glass wool or mineral fiber.
- Metal products are highly susceptible to corrosion, so their average service life does not exceed 10-15 years.
As already mentioned, it is the last factor that limits the use of the described materials for the construction of pipelines.
There are two ways to deal with the problem:
- Use polymer parts... There are pipes made of various types of plastic, many of which are successfully used in the design of heating systems for houses and apartments. However, they are not able to withstand more internal pressure and very high temperature of the coolant.


Plastic pipes do not corrode, but have little strength
Another disadvantage of plastic pipes is their low strength, especially to impact.
- Cover the steel pipe with a protective zinc layer... In this case, corrosion can be avoided, but only if water is used as the heat transfer fluid. Antifreeze, being chemically active, will reduce all the advantages of zinc plating to zero.
Nevertheless, a heating system made of galvanized pipes is more reliable, so it makes sense to dwell on the description of these parts in more detail.
Galvanized
Galvanizing the pipe helps to reliably protect it from corrosion foci and extend its service life by several years.
Note! Not only steel products are coated with a protective zinc layer. It can be cast iron pipes, as well as other products intended for the transportation of liquids.
Instructions for the manufacture of galvanized pipes provide for two main methods of applying a protective layer:
- Hot. The finished steel part is immersed in a container filled with liquid zinc at a temperature of + 450 degrees Celsius.


In the photo - the process of hot-dip galvanizing of steel parts
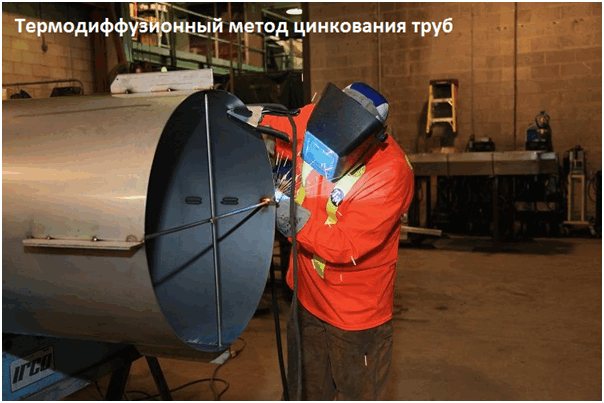
- Diffusion In this case, zinc does more than just create a protective layer. Thanks to a special technology, the atoms of the two materials mutually penetrate each other, forming a strong coating that resists oxidation.
For diffusion processing, powder zinc is used instead of liquid. The pipes are placed in special containers, where special reactions take place, which give the pipe not only mechanical, but also electrochemical strength.
Note! The diffusion coating is only applied to the steel pipe, since other materials are not able to interact with zinc in this way.
Diffusion galvanizing covers pipes with a more reliable protective layer
Prevention measures
In connection with all of the above, it is worth moving on to the issue of preventing corrosion, freezing, and damage. The technology of creating heating systems has been improved and today we know many ways to reduce the shortcomings of steel pipes and increase the efficiency of the system, and extend its service life.
- To prevent deposits from forming in the pipes, they are impregnated with an energy carrier fluid. They are also cleaned with chemicals that are delivered inside with water.
- Insulation lining allows you to solve the problem of freezing and heat loss. Heating cable, special materials (polyethylene) - anything can be used. These preventive measures also eliminate corrosion, i.e. reduce the exposure of steel to it.
- It is possible to avoid the appearance of rust with the help of synthetic coatings, processing with metals that are not so susceptible to corrosion - for this they began to apply a layer of zinc. Pipes with such a coating very quickly became in the highest demand due to their low cost. Compared to other anti-rust methods: stainless steel or steel pipes coated with polyethylene. Very quickly, the method spread to other areas of production (in metal profiles, in tiles, zinc began to be used in other alloys, for example, cast iron). In addition, the service life has increased by 10, or even 15 years. Although more expensive methods extend the life of the pipes up to 25 years.


Metal pipes for heating system
Galvanized pipe: its main advantages
Everything is learned by comparison, and galvanized steel pipe is no exception in this respect. The most important thing is to know what to compare with - we will do this both in relation to modern polymer pipes and in relation to other types of metal products of this type. Let's start in order.
- Very high strength - naturally compared to plastic pipes. Here they are out of competition - if the plastic is easy enough to cut with an ax or even cut with a knife, then such a number will not work with a galvanized metal pipe. These pipes practically do not need protection from mechanical damage.
- Dimensional stability. Galvanized pipes, like, in general, any other metal products of this type, in comparison with plastic, have a lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
- Huge operating temperature range - any metal pipe can withstand exposure to even superheated steam.
- High working pressure of the liquid transported through the pipes.


Galvanized steel pipe photo
And there are quite a few such advantages - in what they are not able to surpass modern plastic, it is in cheapness, ease of operation and resistance to corrosion. That is why plastic began to displace metal, but, you see, these reasons are quite significant. As for the advantages that a galvanized water pipe can boast over its metal counterparts, there are not so many of them - just a couple can be distinguished.
- Slightly better corrosion resistance - not only the outer part of the pipe is coated with zinc, but also its inner bore diameter.
- Antiseptic. Zinc is a fairly serious antiseptic that kills almost all pathogens found in tap water.
This completes with the advantages of galvanized iron pipes. It is thanks to this parity situation that they remain afloat.
Varieties of metal pipes
The classification of pipes was based on several criteria for dividing into types:
- by scope of application;
- by material;
- according to the main characteristics of the model: additional coating and production method (welded, cast, seamless).
Since we are talking about a specific area of application - the heating system of a house, we are more interested in the last classification criterion. Pipes are:
- galvanized;
- seamless or welded (with a longitudinal or spiral seam), or cast;
- water and gas pipelines.
Also, manufacturers began to combine metals to improve properties. This is how:
- massive ribbed cast iron with a zinc layer. Ideal for heating, as a heat exchanger (take heat);
- to increase heat transfer, transverse plates of black steel are applied to the finished pipes;
- stainless steel with thin corrugated walls is capable of bending, strong, resistant to a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
All of them are used in the heating system. For heating residential premises, galvanized steel pipes of different diameters and lengths are more suitable. The main thing is that they comply with GOST: 3262-75; 10704-91; 10705-80. Such a model costs 35 thousand rubles per ton, 58 per kilogram.
Installation of corrugated stainless steel pipes
We will talk in more detail about the penultimate item from the list and their installation, that is, about the installation of corrugated stainless steel pipes. This is the material that we have recently, so, perhaps, many do not know how to install them. In principle, there is nothing supernatural, although there is one nuance in the connection of parts with each other.


Corrugated stainless steel in the heating system
To make one part "converge" with another, you should use special pipe fittings. Attention: they must be without a fitting. Outside, it is still necessary to make a special silicone gasket that can withstand high temperatures.
How galvanized products are made
There are only two main technologies that allow zinc coating to be applied to steel.
- The steel product is immersed in a zinc solution heated to a temperature of 400-450 C.
- A more expensive way is diffusion coating. It happens at the atomic level. When atoms interact, and for this special conditions are created (placed in a powder container), they penetrate from a substance into another substance, a crystal lattice is formed. This creates a stronger, more durable zinc coating. Protection against chemical and electrical influences is increased.
Features of production
Zinc coating can be applied to a metal surface in several ways:
- hot when the material is dipped into a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of 450 ° C;
- diffuse, if the connection of zinc crystals occurs by their penetration into the crystal structure of the metal surface;
- thermal diffuse, when the penetration of zinc powder into the metal surface occurs under the influence of a temperature of 290-450 ° C.
Each type of coating has its own advantages. Hot - technologically simpler and cheaper, but the paint applied to the pipe surface is faster chipping and rubbing off. The diffuse method provides a strong bond between zinc and the metal surface. This coating lasts a long time and does not peel off during use. The thermal diffusion method provides electrochemical protection of the material. Black steel becomes the cathode, and the zinc coating becomes the anode, which takes over all corrosion processes. Accordingly, this method is the most expensive, but it provides maximum protection of the material.
Installation
Experts say that it is possible to lay steel pipes in the heating system with your own hands.
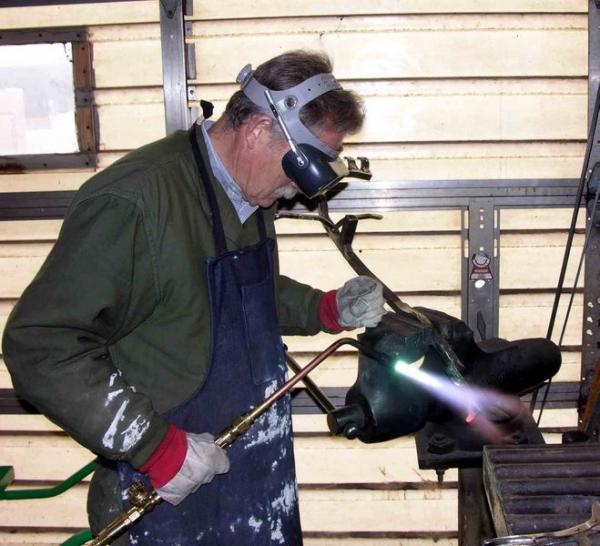
The first feature that the craftsmen draw our attention to is threaded connections. Thermal stresses arising from welding lead to burnout of zinc. Even the sparing regime does not help to solve the problem. Therefore, instead of welding, these joints are used. They are reliable, they are threaded couplings, coals. On the pipe itself, you need to cut the same thread yourself. It is difficult, but possible. However, there is a simpler method - gas welding, it is safe for zinc and gives a high-quality connection of system elements, especially when using thick-walled products (trunk systems). The use of an inverter device will simplify the work.


Heating radiator installation
Galvanizing technology
Zinc coating is applied to pipes using various methods:
- electrogalvanized galvanizing,
- hot-dip galvanized,
- applying thermal diffusion zinc coating.
Electroplated zinc plating
As a result of the electrolysis process, during which zinc electrodes are placed in a solution of salts capable of conducting electric current, the substance decomposes, and zinc settles on the surface of the pipe. Thus, an even coating is obtained. However, the adhesive properties of such a pipe are insufficient for strong adhesion; the porous surface limits the pipe's service life to a five-year period.


Hot dipped galvanized
The method is expensive, but it achieves the most durable coating, although not even enough, therefore additional mechanical processing is required.
Hot-dip galvanizing is the process of applying zinc to a pipe by placing it in molten zinc mass.
Note! Not all steel grades can be subjected to this treatment: if the carbon content exceeds 0.24%, this galvanizing method is not suitable.
Thermal diffusion coating
In sealed containers, zinc vapor is applied to the pipe surface. At the same time, the protective layer formed during the thermal diffusion process is very strong and even, regardless of the complexity of the pipe configuration, it is practically impossible to damage it during welding. A galvanized pipe has a service life of up to 15 years, is more expensive and differs in that the surface does not have a characteristic zinc sheen.


Cold galvanized
This method is used for already existing communications and is a conventional painting of pipes with a composition containing zinc, manually or by gas-thermal method. Such a coating is sometimes in no way inferior to hot galvanizing, while it does not require dismantling the pipes being processed, although the resistance to mechanical stress is slightly lower: in the first case, the pipe will last no more than 5-6 years, in the second case, the use time increases to 7-8 years term.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Types and advantages of seamless steel pipes
Installing the radiator
Consider the features of installing galvanized pipes when assembling a radiator at home.
- Prepare the tool: an electric carving tool is welcome (in his absence, use either a grinder for steel or a hacksaw for metal); file; die; vice; gas wrench No. 1 (for assembling connections) and 2 (for threads and for radiator plugs).
- Buy materials: galvanized pipes, steel DU 20 and fittings of the required amount for inserting the device. For example, modern ball valves, not screw-type - this is the last century. They will be installed on the piping to the radiator, on the jumper. Do not forget about the sealant - traditional plumbing flax. Buy for him and impregnation - paint, drying oil or silicone.
- We cut the threads at the riser and the liner, taking into account the length of the pipes with a margin. It recedes from the floor, walls 8-10 cm. This should be enough to freely cut.
Carving instruction:
- Remove the burrs from the end, from the outside, be sure to make an approach at an angle, into which the die will fit. Use a file or other suitable tool. You can squeeze the end with a gas wrench for lack of a better one.


It will be enough 5 threads for the pipe and angle, and for driving into the radiator - 7-8.
- We carry out the assembly of threaded connections. The threads of both elements must match. If we press with force, a new one can form, and we do not need this, since it will lead to damage to the connection. Also, do not "drive" the valve all the way. Even if the handle remains in an uncomfortable position for you, further efforts will lead to a crack in the body. It is better to stop before reaching the end of one revolution. And in general, be extremely careful, as you are dealing with fragile brass.
Drive the locknut to 5 mm between the coupling until you feel resistance. Wind the winding along the thread, into the gap. After assembling the threads, paint. Since during the work we have broken the zinc layer, and some joints require additional protection (cast iron is stronger than brass).
- Connect the device from below. It will not need to be rinsed. And the brass elements will not break if you suddenly fall on them. You will have to put a tap in the upper plugs.
Despite the disadvantages known to everyone, galvanized pipes for heating will be used for many decades to come. And even if they only seem to be more reliable than modern plastic ones, their use in centralized systems is more justified if preventive measures are taken. Firstly, the heating schedule always gets lost, the pressure in the pipes constantly jumps, like the temperature. It is unlikely that in such conditions plastic will show itself as strong as steel. Secondly, it makes no sense to connect powerful radiators to such pipes.
However, arranging an autonomous system, you can calculate the "ceiling" of pressure and temperatures, display your own schedule and adjust all structural elements to your calculations. If you do not need a powerful radiator, your house is already warm, especially in summer - the only season that you spend in the country, then there is no point in spending money on galvanized pipes. You can give preference to reinforced polypropylene or metal-plastic with fittings. By the way, they are well suited for the installation of an autonomous system with controlled parameters in a year-round living environment. In this case, the installation of pipes will be easier than in the case of steel products.
Types of galvanized pipe products
Pipes with a protective zinc layer are used for pipelines for various purposes:
| View | Application | Dimensions (edit) |
| Water and gas pipeline | for indoor highways | length - 4-12 m |
| Electric welded pipe | agricultural engineering and construction | diameter - 110- 480 mm |
| Square or rectangular profile | industrial and domestic construction | section size - 10 -150 mm |
| Seamless pipe made of carbon or alloy steel | mechanical engineering | wide size range |


The diameter of tubular products with a galvanized surface is from 17 to 150 mm. The size of the nominal diameter is 10-155 mm.
Distinguish by weight:
| Pipe type | Wall size (thickness) in mm |
| light galvanized | 2 — 4 |
| galvanized conventional | 2.2 — 4.4 |
| galvanized reinforced | 4.5 — 5.0 |
Note! Generally accepted state standards for steel pipes are applied to galvanized pipes, they do not have special standardization.
Is it possible to use galvanized pipes for heating systems and hot water supply.
Very often you can hear a question from a customer, is it possible to use galvanized pipes for heating and hot water supply systems? Sometimes this question is even pronounced with a reproach, why are you putting "rusty" pipes to us? Save on us! And really why? Why put a "rusty" pipe or plastic that melts from high temperatures, because everyone has long known galvanized pipes that do not rot and serve for more than 50 years.


The answer here is simple and unambiguous, galvanized pipes for heating and hot water supply systems with temperatures above 55 degrees cannot be installed, and that's why. When the coolant in the heating system or hot water supply is heated above 55 degrees, and especially strongly at 70 ° C, a chemical reaction occurs in the coolant with active flaking of zinc, while filters and thin sections of pipes are clogged first, then fistulas will appear on the pipes and the heating system naturally leaks ... If you use water as a heat carrier, and we use it in 99 percent of the heating systems of garden and country houses and 100% of apartment buildings, in the water over 70 degrees, and especially after 82 degrees, oxygen is actively released. As you know, oxygen is an active catalyst that accelerates any chemical processes. Consequently, the corrosion process will go even faster.
The situation is not the best with cold water supply, if your water runs on schedule, or it very often does not exist. The alternating contact of galvanized pipes with water, and then with air, is very bad for their integrity, galvanized containers and pipes in such conditions give a leak after two to three years. And only galvanized pipes that work without temperature extremes and interruptions in water serve thirty years or more. By the way, too, provided that they are isolated from moisture and outside.
Permissible limit deviations
On the walls, GOST generally allows deviations of up to 15%, and for diameters in the range of 17-48 mm - 0.4-0.5 mm, with diameters from 60 to 159 - 0.8-1%.
The weight of a pipe directly depends on its size and density. It ranges from 1 kg of a meter product to 35. Weight is commonly used for structural design. But pipes are bought by meter.
It should also be noted that the galvanized pipe does not have a certain single standard. Therefore, they are manufactured to the standard of common steel pipes. Even though this is not entirely correct, GOST is taken alone, for the 91st year.
Why galvanized pipes?
By and large, today there are a lot of pipe materials for communications. However, galvanized steel not only does not leave the market, but also occupies a confident position there. Largely due to its qualities. In addition, galvanized pipes, depending on the type, are used in various industries and construction.


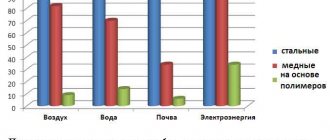
The difference between steel and galvanized pipes after 10 years
Galvanized products are often used for ventilation and chimneys. This is due to the fact that the material does not accumulate sediment, even in the case of a chimney.
In addition, the great advantage of galvanized pipes is the ease of installation. Naturally, when it comes to household scale. For example, ventilation pipes are connected quite simply without the use of welding, while the connections are tight and practical.And in the case of a chimney, these products give good traction, that is, they have excellent aerodynamic properties, which is necessary for the correct removal of combustion products.
Is there an alternative to galvanized pipes.


Glass fiber reinforced pipe
So what alternative to galvanized pipes exists, do we really have to drink water flowing through rusty pipes. Of course not. For many years, low and high pressure polyethylene has been produced and is used everywhere for water, and for hot water the so-called PPRS pipes (polypropylene reinforced pipes) or as they say now everywhere in advertising - this is "kalde". Such pipes can withstand temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius, although their service life at such a temperature is no more than 6 months, but how many days a year does this temperature occur in our heating plants? But the owners of private houses using polypropylene pipes in their heating systems should not forget about this. The temperature in an improperly designed or installed heating system can be kept at the temperature limit of using polypropylene pipes for a very long time, as a result of which they can become covered with deflectors and collapse.
This defect is typical for heating systems with automatic regulators on heating devices. When the boiler is 85 degrees constantly, and the heat is controlled by radiator regulators. This is also bad, like the temperature in the heating system is below 55 degrees, when condensation forms on the pipes, and especially on the outer surfaces of the boiler and its chimney. They say that the boiler cries, and naturally its surfaces, especially the chimney, even if it is made of stainless steel, are actively corroded.
the answer to the question - is it possible to use galvanized pipes for heating systems and hot water supply and what is better to use a "rusty" pipe or PPRS pipes received.
If anyone else has questions or you need heating system project for a private house and competent professionals for its implementation are welcome to contact us. The company has been operating in this service market since 1985, has self-regulatory organizations and certified specialists. Designs and builds roof and conventional boiler houses, conducts installation of heating systems for residential apartment buildings and private houses. Examples of our work, address and phone numbers on the next page.
Advantages of galvanized pipes
The characteristics of the pipe with a protective zinc coating allow it to be used in various pipelines. It has important advantages over other types of tubular products. And although today plastic displaces metal everywhere, galvanized pipes are not yet threatened with this fate, they still remain in demand, due to a number of advantages:
- The smooth surface of the pipe does not allow various impurities to settle on its surface, even when it comes to chimneys.
- Galvanized products are easy to assemble.
- They have excellent aerodynamic properties - the pipe provides good traction, does not impede the free movement of air and the release of combustion products to the outside.
- Pipes with a protective galvanized coating are out of competition in terms of strength in comparison with plastic products. They are not easily damaged and do not need additional protection against mechanical stress.
- Technical characteristics: low coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal stability (the ability to work at high temperatures), resistant to resistance even to very high operating pressure.
- In addition, galvanized pipes are more resistant to corrosion, and therefore can compete with plastic in this seemingly indisputable advantage.
- The ability to kill almost all microorganisms in tap water is another significant advantage of zinc pipes. Zinc is a natural antiseptic; therefore, galvanized pipe products are in demand especially in plumbing systems.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Where are stainless steel profile pipes used and what is their advantage
How to choose galvanized pipes for heating and water supply
Despite the saturation of the market with many varieties of high-tech polymer pipes, metal for the installation of heating systems, hot and cold water supply is widely used today. Metal pipes for these purposes are mainly made from steel and copper, less often from aluminum. Each type of such pipes, depending on the material of manufacture, has a set of individual characteristics that provide the consumer with enough room for maneuver when choosing.
One of the most common types of pipes is zinc-coated steel products - a material that has many positive characteristics, but is specific in application. Consider what kind of material it is, and how to properly use galvanized pipes for heating.


Types of galvanized pipes and their features
Studying the varieties of galvanized pipes, one should immediately note the fact that they are practically the same as the types of conventional "black" pipes - the difference between them is due solely to the presence of zinc coating. In general, there are four main types of galvanized pipes.
- Galvanized water and gas pipes. This high-quality pipe is manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262 and is used for the manufacture of both water supply systems and gas pipelines. It is intended for indoor use only. Galvanized steel water and gas pipes are manufactured in lengths from 4m to 12m.
- Electrowelded galvanized pipe. This type of pipes is made from ordinary steel in accordance with GOST 10704. They are used exclusively in mechanical engineering, agriculture and construction for non-critical structures. As in the case of a water and gas pipe, the length of these products can vary from 4 to 12 m, and the diameter can be in the range from 110 to 480 mm.
- Profile galvanized pipe - differs from all other types of galvanized pipes in the shape of its section. As a rule, it is a square or rectangular pipe with a range of side sizes from 10mm to 150mm.
- Seamless galvanized pipe - it can be called universal, and it is used in almost all sectors of the national economy. A seamless pipe is made either from high carbon steel, or from alloy steel, which in itself raises it to the category of high-quality, and most importantly, durable products.


Galvanized water pipe photo
All these types of pipes have fairly high performance characteristics - their outer diameter can vary from 17mm to 159mm, and the bore diameter of galvanized pipes is from 10 to 150mm.
Among other things, all types of galvanized pipes can be divided into three groups depending on their weight.
- Light pipes with a wall thickness of 2-4mm.
- Standard pipes - the thickness of their walls, depending on the diameter, can vary from 2.2 mm to 4.4 mm.
- Reinforced pipes with a wall thickness of 4.5-5 mm.
Basically, that's all. There are no more varieties of galvanized pipes. Unless, of course, we do not consider ventilation, but this is already another area of construction.
Production methods and varieties of galvanized pipes
The main enemy of steel pipes is corrosion. One of the ways to protect against it is to apply a protective zinc layer to the surface of the steel pipe, after which the material is classified as a separate subgroup - galvanized pipe for water supply and heating systems.
The method is moderately costly, so the cost of a steel pipe after galvanizing remains affordable - an approximate price ratio can be found according to the table:
| GWP pipe size (gas pipeline) | Price (rub / m) | |
| black steel | galvanized | |
| 15x2.8 st1-3sp / ps | 33 | 50 |
| 20x2.8 st1-3sp / ps | 42 | 66 |
| 25x2.8 st1-3sp / ps | 59 | 95 |
| 32x2.8 st1-3sp / ps | 81 | 127 |
| 40x2.8 st1-3sp / ps | 90 | 155 |
| 50x2.8 st1-3sp / ps | 117 | 194 |
There is no independent standard for galvanized products. Zinc-protected steel pipes are manufactured in accordance with regulatory documents for electric-welded products with a straight seam (GOST 10704) and material for gas pipelines (GOST 3262-75).
Zinc coating methods
Zinc coating, depending on the operating conditions of the pipe, can be performed both on its outer surface and on its inner surface.
There are 4 methods of galvanizing pipes, each of which is used depending on the size of the products and the requirements for the thickness and strength of the zinc coating:
- hot - the prepared part is immersed in molten zinc, which ensures high quality and durability of the coating, but the energy consumption of the process is high;
- cold - products are painted by one of the painting methods with substances containing zinc, which does not provide high strength of the zinc layer (used to protect already mounted structures against corrosion);
- electro-galvanic - the coating is carried out by the method of electrolysis, that is, the deposition of zinc dissolved in the electrolyte (cathode) on the part (anode), when an electric current passes;


- thermal gas - a device for a protective coating by gas-flame spraying on the surface of a zinc powder part, a disadvantage is porosity and low strength of the layer;
- thermal diffusion - parts are covered with a layer of zinc, which is after heating to 2500 degrees. in a vapor state, it is used for processing small parts in large quantities - screws, bolts, nuts, washers, requiring high adhesion of zinc to metal.


Production of galvanized pipes: technology and types
When using a material such as steel, it must be borne in mind that it oxidizes when interacting with air and various liquids. To reduce this negative quality, galvanizing is performed. Zinc oxidation is faster, which protects the steel from corrosion. In the production of galvanized pipes, high-quality carbon steel grades are used:
- 10;
- 15;
- 20;
- 35;
- 45
The most common production methods for this type of product include hot and diffusion galvanizing. In hot-dip galvanizing, a steel billet is dipped in molten zinc at a temperature of about 450 ° C. Diffuse zinc plating is based on the penetration of zinc atoms into the intercrystalline lattice of iron. This method provides high mechanical strength of the coating, resistance to flaking and chips. For thermal diffusion galvanizing, a ferrous metal structure is placed in a container with zinc powder. Zinc saturation of the surface occurs at a temperature of 290-450 ° C. As a result, the galvanized pipe, in addition to anti-corrosion properties, has electrochemical protection. Ferrous metal becomes a cathode, and zinc anode is gradually destroyed by corrosion.
Modern manufacturers offer an extensive range of galvanized steel products. Along with the classic round, you can buy a product with a square or rectangular section. Besides shape, pipes also vary in length and wall thickness. The outer diameter can be from 17 mm to 159 mm, and the bore diameter of galvanized pipes varies from 10 to 150 mm. This diversity leads to a variety of applications.


A layer of zinc is applied to finished steel pipes - welded or seamless
Parameters of zinc coated steel pipes
The main technical parameters of zinc coated steel pipes are:
- outer diameter (10.2 - 165 mm);
- weight of 1 m of pipe (0.4 - 22 kg);
- nominal bore (6 - 150 mm);
- wall thickness (1.8 - 5.5 m);
- length (4 - 12 m).
As with ordinary pipes, the walls of galvanized products can be light, reinforced or standard, the accuracy of execution is assigned ordinary or increased.
Important! Protective zinc coating should be applied to the entire surface of the product and have a thickness of 30 microns or more. Peeling of the protective layer, peeling and swelling on it are not allowed ("Steel water and gas pipes", Technical conditions, GOST 3262-75, rev. No. 4.6).
Types of galvanized pipes
The standard sizes of galvanized round pipes are the same as those of the "black" counterparts, the difference is a protective zinc coating.
- Galvanized water and gas pipes are high-quality products manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262-75 (relevant for 2020). They are used for the installation of gas and water pipelines inside the premises. Nominal bore - 6-150 mm, length - 4-12 m. Products are made of ordinary quality steels (GOST 380-2005) and high-quality steels (GOST 1050-88).
- Galvanized electric-welded pipes are manufactured in accordance with GOST 10704-91 in a wide range of outer diameters - 10-1420 mm. These products are in demand in construction for the creation of irresponsible structures, in agriculture and mechanical engineering.
- Seamless galvanized pipes are high performance products. Produced in accordance with GOST 8732-78 - hot-deformed, in accordance with GOST 8734-75 - cold-deformed.
- Profile products have a rectangular (special case - square) section.
Advantages and disadvantages
Most of the characteristics of galvanized VGP pipes, both positive and negative, coincide with the parameters of products made of black steel, but there are also individual qualities.
Dignity
- Strength (especially tensile strength).
- Fire resistance.
- Low coefficient of thermal elongation.
- Absolute tightness.
- Shock resistance.
- Durability.
- Can be used as a heat exchanger.
- The possibility of installation, including maintenance, do it yourself.
- Two assembly methods (welding, threaded connection).
- Ease of disposal.
In favor of steel GWP pipes is the fact that the external laying of the gas pipeline from the main to consumers is allowed only from steel material.
disadvantages
- Significant share.
- Electrical conductivity.
- High thermal conductivity (the need to insulate pipes in heating and hot water systems).
- Corrosion susceptibility when zinc protection is damaged.
Installation and assembly methods
Galvanized pipes that form a heating or hot water system are mounted in three ways:
- welding;
- flange connection;
- threaded connection;
- soldering.
Each of these methods has its pros and cons. Consider these installation methods and the nuances associated with them.
Welding galvanized pipes
Zinc-coated water and gas pipes can be connected by electric or gas welding - both types of installation are convenient because they take little time. But there is one negative factor, the effect of which must be minimized, since it will not be possible to completely eliminate it.
The fact is that the temperature of the weld seam reaches 1200 degrees, and zinc boils at 906 degrees and begins to evaporate from heating during the welding process. In this case, the following happens:
- the harmful effects of zinc vapors on the welder, up to the onset of suffocation, as they are poisonous;
- Evaporating zinc exposes steel and makes it vulnerable to corrosion;
- zinc vapors contribute to the formation of pores and cracks in the weld, which reduce the strength of the joint.
For maximum localization of these processes, before starting welding, apart from the mandatory device for efficient ventilation of the room, the following actions must be performed.
- prepare the edges of the joint, that is, make an external chamfer on them and remove the zinc coating by 25-30 mm on both sides of the joint;
- to weld the joint, followed by cleaning the weld seam from slag and coating the bare pipe section with zinc-containing paint (zinc dust content - 94%, binder - 6%) - cold galvanizing.
To prevent the zinc layer from boiling, you can treat the junction with hydrochloric acid 5 cm in both directions, but in this case, acid fumes will form during welding.
Important! According to clause 4.6 of the joint venture (Building Regulations) 73.13330.2012, the device of welded joints on galvanized steel pipelines is not allowed, since zinc is not removed from the inner surface of the pipe before welding, and zinc vapors, the formation of which cannot be avoided, cause the formation in the seam pores and shells. But this document is voluntary, and if there is no reference to the mandatory use of this item in the project, then the installation of galvanized pipes by welding is permissible.
- perform welding at a low speed, but avoiding pipe burn-through, and with an increased current strength;
- use rutile coated electrodes (the electrode contains titanium oxide).


Electric welding of zinc-coated pipes requires certain skills from the welder. In addition to the composition of the outer coating of the electrode, the quality of the weld is affected by the thickness of its rod, which determines the power of the arc - an excessively thick electrode will burn through the wall, and a thin one will not provide the necessary strength of the welded joint. For welding galvanized pipes with a wall thickness of 1.5 - 5 mm, electrodes with a diameter of 2-3 mm are used.
Flange connection for galvanized pipes
This method is based on bolting together fragments of pipes, at the ends of which flanges are welded - steel rings with an inner diameter equal to the outer diameter of the pipe, and holes along the perimeter for mounting bolts. Two flanges of different fragments are applied to each other using an intermediate gasket and tightened with bolt-nuts or studs.


In this method of installation, the same negative factor is present as in the welded joint - in the process of welding the flanges to the pipes, zinc boils and the protective layer is destroyed in the area of the weld. Therefore, it is also necessary to take measures to localize the temperature effect on the zinc layer, and after the end of welding, clean the seam and apply an anti-corrosion zinc-containing coating on it (cold galvanizing).
The flange connection is not compact, therefore it is used in most cases when laying pipelines in utility rooms or outside. On the abutting side of the flange, there is an annular area called a mirror. A paronite gasket with a hole, the diameter of which must coincide with the inner diameter of the pipe, is installed between the two mirrors of the abutting flanges before they are pulled together. The outer diameter of the gasket is made equal to the distance between the opposing fastening bolts.
Threaded connection
This installation method eliminates the need for thermal connection methods and is performed using fittings of various types, designed to connect individual fragments of the pipeline after threading them.


Threaded assembly also has its drawbacks:
- the threading process is laborious and time-consuming;
- a cutting tool (die) removes a layer of steel of a certain thickness along with a protective zinc coating when cutting a thread.
- the tightness of the threaded connection is ensured by winding the thread with FUM tape, sealing paste or tow with paint, which eventually lose their properties and require replacement.


Soldering galvanized pipes
To mount a heating system or hot water supply from galvanized pipes without damaging the zinc layer, brazing is used, which is performed in the following sequence:
- the pipe ends to be connected are butted and, if the wall thickness is more than 3 mm, chamfer is performed on the outer edges;
- the joints are degreased by heating, after which the flux (composition HLS-B) heated to plasticity is also applied in a thick layer to the surface adjacent to the planned joint;
- the ends are positioned with a gap of 2-3 m;
- the burner flame is exposed to excess oxygen.
The size of the burner is selected depending on the diameter and wall thickness of the galvanized pipe:
For high-quality brazing of a galvanized pipe, it is necessary to adhere to the rule: the size of the burner must be one unit smaller than when welding a pipe of the same dimensions without a zinc coating. During the brazing process, the flame should be concentrated on the edges to be joined and the joint gap in order to exclude heating and evaporation of zinc from under the flux layer.


Joint seams of high-quality brazing of galvanized pipes do not need additional anti-corrosion protection, but applying on zinc-containing paint as a safety operation will not be superfluous.
Galvanized pipes
Galvanized pipeswhich differ from other rolled pipes in higher strength, resistance to the negative effects of corrosion and other destructive factors.
The main disadvantage of steel is its poor corrosion resistance. To prevent rust from corroding steel, the metal is covered with a layer of zinc. After going through all these procedures, the product lasts much longer. If the service life of an ordinary pipe is 4-5 years, then for a galvanized pipe it is 5-6 times more (25-30 years). This is the main value of galvanized products.
In addition to unusually high strength and better performance characteristics, galvanized pipes have other differences from their uncoated counterparts - they have electrochemical protection and (due to the coating) are on average 2-3% heavier. That is why their shipment is carried out not according to the actual, but according to the theoretical weight in full accordance with the certificates from the manufacturing plant.
Of course, galvanized steel pipe is no exception in this regard. When comparing galvanized pipes with other pipes, the following points can be highlighted:
1. Very high strength - naturally compared to plastic pipes. In this comparison, galvanized pipe has a huge advantage over plastic pipe, because it is quite easy to cut the plastic with an ax, but this cannot be done with a galvanized metal pipe. These pipes practically do not need protection from mechanical damage.
2. Dimensional stability. Galvanized pipes, like, in general, and any other metal products of this type, in comparison with plastic, have a lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
3. Huge operating temperature range - any metal pipe can withstand exposure to even superheated steam.
4. Large working pressure of the liquid transported through the pipes.
Often, a galvanized pipe is hot-dip galvanized, due to which a protective layer is formed both outside and inside the pipe. This method involves bonding the coating to the base metal at the molecular level, which ensures good corrosion resistance of metal products. The method is highly efficient and economical to apply.
Depending on the manufacturing method, galvanized pipes are divided into seamless and electrowelded.
Seamless products are made either by hot or cold deformation. Galvanized seamless pipe is widely used in main pipelines because it can withstand high pressure of the working medium.
Galvanized pipes are of different types:
1. The pipe is electro-welded galvanized. This high-quality pipe is manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262 and is used for the manufacture of both water supply systems and gas pipelines.It is intended for indoor use only. Galvanized steel water and gas pipes are produced in lengths from 4 m to 12 meters.
2. Profile galvanized pipe differs from all other types of galvanized pipes in the shape of its section. It is a square or rectangular tube with a range of side sizes from 10 mm to 150 mm.
3. Seamless galvanized pipe is used in almost all sectors of the national economy. A seamless pipe is made either from high carbon steel or alloy steel, which makes it a high-quality, and most importantly durable product with a long service life.
All these types of pipes have fairly high performance characteristics, since their outer diameter can vary from 17 mm to 159 mm, and the bore diameter of galvanized pipes is from 10 mm to 150 mm.
All types of galvanized pipes can be divided into three groups depending on their weight.
- Light pipes with a wall thickness of 2-4mm.
- Standard pipes - the thickness of their walls, depending on the diameter, can vary from 2.2mm to 4.4mm.
- Reinforced pipes with a wall thickness of 4.5-5 mm.
The scope of application of galvanized pipes is very wide, for example, from the arrangement of ventilation systems to the manufacture of road signs. Due to their strength and long service life, these products are widely used in industry, in particular, in oil and gas production, which contributes to a fair cost savings in such industries. In addition, galvanized pipes are often used in the construction of residential / non-residential buildings, namely in their gas and water supply systems. galvanized pipe in modern construction is used not only to create water supply lines - its scope is much wider. It is great for buried or underfloor electrical cables and many other communication systems.
The length of galvanized pipes ranges from 4 to 12 m. The diameter is measured according to generally accepted standards. But often in gas pipelines, these pipes are of small diameter.
Approaching the issue of studying the technology of assembling systems from galvanized pipes, the first thing to note is the fact that this type of material is connected exclusively using threaded connections. Welding galvanized pipes is a gross violation of technology, especially when it comes to assembling plumbing systems. The fact is that welding works involve heating the material to a high temperature, which simply burns out the zinc, as a result of which the pipe becomes vulnerable to corrosion. In addition, zinc vapor is a significant hazard to the person who inhales it.
- 57x3.5
- 76x3.5
- 89x3.5
- 108x3.5
- 133x4
- 133x4.5
- 159x4.5
- 219x6
Specificity of using galvanized pipes in heating and hot water systems
Zinc coated pipes in heating systems and water supply systems are used taking into account the operating conditions.
If the temperature of the coolant does not exceed 65 degrees, then the zinc coating successfully performs its functions. In the northern regions, where this parameter is much higher, the inner zinc layer reacts with water under the influence of high temperature:
Zn + H2O = ZnO + H2.
Both substances resulting from this interaction are negative factors:
- ZnO is flakes that precipitate and clog the lumen of small-diameter pipelines;
- H2 is hydrogen, which, when mixed with air in a certain proportion, is explosive or, at least, forms blockages in the system.
Therefore, in hot water and heating systems with a coolant temperature above 60 degrees, it is allowed to use pipes that have only an outer protective zinc coating, which will protect the pipeline from corrosion during periods of inactivity.However, when water gets on the surface of the hot pipe, the zinc sheath begins to peel off from the base, therefore, to avoid this, it is necessary to paint such pipelines on top of the zinc, which will lead to an even greater rise in the cost of the system.
Output: the use of pipes galvanized from the outside in hot water and heating systems with a coolant temperature above 60 degrees is unreasonably expensive, and galvanized pipes from the inside are harmful and dangerous.
Independent design of the heating system
In the manufacture of a climatic network from galvanized steel pipes, two types of connections can be used:
- electric or gas-welded;
- using threaded fittings.
It should be noted that both the first and second methods require the master to have certain building skills. If you doubt your abilities, it is better to entrust the installation procedure to experienced plumbers.
Welding
The process of manufacturing heating using the welding method consists of the following stages:
- Vertical main risers (supply and return) are mounted, and then horizontal wiring is made from them to each central heating radiator.
Advice! If you are modernizing an old heating system, it is advisable to install pipes according to the old scheme, performing their successive replacement. Such engineering networks are very carefully designed and tested, so there is no need to make major changes unnecessarily.


Welding is a responsible and complex process
- Gas welding is carried out using a special solder with a thickness of 0.8 to 1.2 mm. If electric welding is used, it is necessary to use electrodes with calcium fluoride or rutile coating with a diameter of up to 3 mm. Otherwise, it will not be possible to achieve a tight connection.
- Galvanized pipes, unlike conventional steel pipes, are overlapped welded. To do this, one of the parts is flared a little.
When welding pipes with a protective coating, special attention should be paid to the quality of the seam. The joint should not have sagging, chips, cracks and other defects.
With the same care, it is necessary to make holes for pipes and fittings. You can use a drill, a milling machine, or punch out the hole with a press.


You need to carefully monitor the quality of the seams.
If you have initial skills in working with a welding machine and decide to mount galvanized pipes yourself, you must adhere to the following tips during operations:
- the seam must be started from the central part of the part, starting from the floor and gradually moving up;
- the electrode should be placed strictly perpendicular to the surface of the product (otherwise it will be impossible to make a high-quality joint);
- if welding is carried out on a vertical surface, the electrode must be positioned at an angle, directing it from top to bottom;
- spot welding technology can be used to achieve the best quality.
Note! Welding of galvanized pipes is practically not used. Under the influence of high temperature, the protective layer completely evaporates, as a result of which the joints will corrode, and you will lose all the benefits of using expensive galvanizing. It is better to dwell on the connection technology involving the use of threaded fittings.


The welding arc evaporates the protective zinc layer from the pipe surface
Fitting connections
To install the heating system using the twisting method, you need to stock up on the required amount of fittings: elbows, adapters, valves and so on.


Galvanized Threaded Pipe Fittings
Tools of various diameters are also required for threading. You can use dies, but it is better to purchase a die cutter: this device allows you to cut more efficiently, avoiding distortions.
In addition, you will need:
- grinder for cutting steel pipes into pieces of the required length;
- a file with which the end chamfer is removed;
- a vice that will help to securely hold the workpieces while working with them;
- gas wrenches for twisting fittings and pipes (preferably torque wrenches - they will not damage the fitting thread by dosing force).
The cutting process usually does not cause difficulties even for a novice master, but here you need to take into account several features:
- when measuring pipes, do not forget to take into account the distance at which the pipe will enter the fitting when twisting;


It is better to use special equipment for cutting galvanized pipes.
- during installation, pay attention to the fact that placing the pipe too close to the wall will not make it possible to cut threads (this requires at least 8-10 cm of free space).
Assembly is not particularly laborious.
Here, novice masters make only two common mistakes:
- Misalignment of products along the longitudinal axis. If the pipe and fittings are inaccurately aligned, the threads may be broken. Because of this, it will be impossible to achieve the desired tightness, and the damaged parts will have to be replaced with new ones.
- Tightening fitting or shut-off valve too tight. It often happens when screwing on taps, when the master wants to tighten the nut a little more so that the crane handle moves more freely. Most often this leads to breakdown.
Complete disassembly and rewinding of additional layers of polymer tape or tow will help to cope with the situation.
Docking with radiators
Another crucial stage of installation is the connection of pipes with heating radiators. For this, a special type of fittings is used - bends.
The operation is performed according to the following scheme:
- the squeegee is screwed onto the pipe until the distance between its cut and the inlet of the battery reaches 5 mm;
- tow is wound on the inlet pipe of the radiator (along the thread);


Flanges for connecting pipes to radiators
- the squeegee is screwed onto the thread until the force becomes noticeable, but not excessive;
- joints can be painted to avoid corrosion.