Hello dear readers! How are you feeling? Are you ready for the cold? Have you insulated yourself?
Today I came across an article that puzzled me, to put it mildly. It said that this winter will be very vigorous. That is, frosty and snowy. Well, what can I say? There are advantages and disadvantages to this. On the positive side - perky entertainment - sledges, skates, skis, snowballs. And negative - heating the house will cost a pretty penny. In order not to be speechless, looking at the amount in the receipt, it is recommended to insulate the "nest". Fortunately, there are a lot of materials for warming the room.
I decided to see what the manufacturing organizations offer today. My attention was drawn to the "old new" raw material - foam glass. Why "old new"? Well, how can I explain to you? The old one is 86 years old, and the new one is improved. However, let's study the material in more detail. So, here's a topic for you - foam glass: disadvantages, advantages, production, cost and much more. Let's start? Go!
Cellular glass: product features
A bit of history
The foam glass was invented by the honored worker of technology and science Isaak Ilyich Kitaygorodsky. The professor specialized in glass production technology, since he considered it the material of the future. The professor's invention was improved by US specialists in the 40s. Initially, foam glass was used as a floating material. But it soon became clear that it demonstrates excellent heat and sound insulating properties, easily glued, and easily processed. Therefore, it was decided to use it in construction.
Thus, in Canada, there was a building created from concrete slabs with a layer made of aerated glass. This event happened back in 1946. The experiment was very successful. The material received well-deserved recognition. But, to the great regret of the inventor, in the Soviet countries he did not gain popularity, since the cost was high, and the production technology was not worked out. It was made in the USSR, but the quality of the products left much to be desired, which led to the closure of factories.
But at the present time the manufacture of this product is in full swing!
Concept
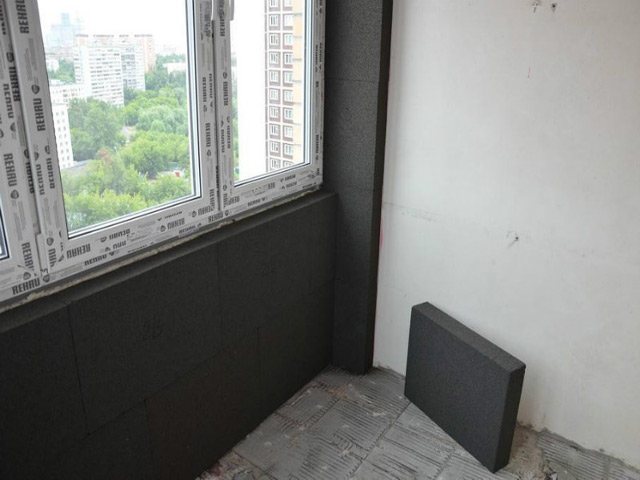


Thermal insulation of the balcony
Foam glass is a heat-insulating material made of silicate glass and raw materials that contribute to the formation of gas. Insulation is often called foamed or honeycomb glass because it has a honeycomb structure. Due to which it can boast of the most unique properties.
Production
Heat-insulating raw material - foam glass is made using powder technology. The process is quite simple but time consuming. It consists of the following steps:
- broken silicate glass is crushed;
- the crumb is thoroughly mixed with substances that form gas;
- charge (homogeneous mass) is placed on a conveyor belt or in molds and sent to the oven;
- glass softens, turning into a liquid but viscous mixture;
- under the influence of gases, the gruel foams;
- the mixture cools slowly;
- blocks, plates (sheets) or granules are formed from the product;
- the product is processed according to the requirements;
- plates, granules or blocks of foam glass are packed.
We can say that ordinary glass, which is used in everyday life, and the cellular product are twins, since they are identical in composition, the only difference is the pores filled with gas in the foamed product.
Only high quality materials and innovative equipment are used for the production of blocks, granules or slabs. In addition, the products are checked by experts in accordance with European quality standards.
Description and types of foam glass
Foam glass combines the advantages of two materials at once. It combines silicate glass, which is strong and brittle, and foam, an incredibly lightweight material. The production of foam glass consists in heating the silicate mass with the addition of a substance that forms a gas. The high temperature leads to the melting of the substance, as well as the formation of small bubbles. This technology makes it possible to obtain a lightweight and durable material that has a high heat resistance.
In the field of thermal insulation, two main types are used:
- Slab foam glass. The insulation is in the form of a slab, which has a structure with closed cells. Ideal for insulating basements, façades, ceilings, ceilings and foundations. The thickness is 6-12 cm, and the size of the slab is 45 * 60 cm. They can withstand even significant operational loads, do not shrink and are resistant to deformation under mechanical stress.


Plate insulation
- Granular material. Represents microporous spherical granules. It is produced in granules of various sizes from 1-5 mm to 7-20 mm. Can be used as insulation for interior walls, ceilings and floors.


Granulated foam glass
The technical characteristics of the two types of material are similar, therefore, when choosing it, one should rely only on the convenience and expediency of using a heater of one form or another.
Views
Today there are two types of foam glass - granular and block.
In addition, there are three types of granular insulation:
- foam glass gravel;
- foam glass crushed stone;
- foam glass sand.
And there are also three types of block insulation:


- plates (sheet foam glass);
- blocks;
- shells (shaped foam glass).
If we compare the thermal properties of granular and block glass, of course, gravel, crushed stone and sand are inferior to slabs, shells and blocks. But, nevertheless, granular insulation is more popular due to its relatively low price.
Features of the production of plates
Foam glass is produced in two forms - blocks and granules. The main raw materials are obtained by breaking bottle and window glass. This allows the use of technology for recycling raw materials, since glass decomposes for a long time.
After cleaning and sorting, the broken glass is crushed to a powder state. For foaming, carbon is added to the fraction and the mixture is heated to a thousand degrees. At this temperature, the gas evaporates and the molten glass foams.


Heated molten glass is a viscous mixture, which, after being removed from the furnace, solidifies and is fired.
Thus, the technological scheme from raw material to finished product contains:
- Glass cleaning;
- Sorting of raw materials;
- Glass melting;
- Gas transmission;
- Cooling;
- Firing the finished slab.


[ads-pc-3]
Scope of application
Foam glass, due to its properties, is used for insulation:


- private houses;
- outbuildings;
- sports complexes;
- underground structures;
- industrial buildings;
- medical institutions;
- educational institutions;
- office objects;
- recreational facilities - (for example, for baths, water parks, etc.).
The scope of application of the material is very wide, since the heat-insulating material is flawless:
- for ceiling insulation: the floor of the attic is filled with cement-sand mortar, and then the plates are laid, after which a reinforcing screed is made;
- for walls: the surface is prepared, special glue is applied, the product is applied, pressed tightly and covered with plaster;
- for the floor: a layer of sand (3-5 cm) is poured, thermal insulation is laid or filled in, joints are closed, a screed is made, a covering is mounted;
Yes, the material is popular due to its good technical characteristics.
Fields of application of foam glass
As already mentioned, this material can be used widely, due to its properties.
Of course, its main use is for sound and thermal insulation... As a heat insulator, it can be used in the construction of residential buildings in housing and communal services, in the agricultural industry (in cowsheds, chicken coops), in the construction of individual projects. An important role in all this is played by its ecological purity.
Despite the large selection of thermal insulation materials, foam glass blocks are much more effective in some areas:
- during the construction of high-rise buildings, since the material is high-strength and fire-resistant;
- irreplaceable if you need thermal insulation of large areas, for example, stadiums (non-standard roofs, floors, walls);
- in structures related to the aquatic environment (water parks, swimming pools, baths);
- can be used when restoring some old buildings;
- very important for various underground structures and basements (not only thermal insulation, but also environmental protection);
- acts as a heater and, due to sanitary safety, an important component in the construction of buildings associated with the food, medical and pharmaceutical industries;
- having the ability to withstand any temperature changes, it is used for thermal insulation of pipelines;
- due to the absence of the effects of the acid-alkaline environment, plus the insulating properties of the material and fire resistance - all this makes it possible to use it in the chemical and oil industries, which in our country are mainly associated with the north;
- according to the fire safety classification it is used in the nuclear industry.
Each type of foam glass products has found its application exactly where it is needed.
Blocks are used to insulate walls outside buildings, insulate foundations and pipes, as heat protection for stoves.
Granules are also used for insulation, but in the form of backfill for attic floors, in wall cavities, floor insulation. It even occurs as a filler for free-flowing building mixtures. In some countries, namely due to frost resistance, it is used to insulate the roadway.
The modern development of technologies makes it possible to produce foam glass of different colors and use it as facing.
Prospects for the use of foam glass in individual construction
Comparing all the pros and cons, the conclusion suggests itself: this material is still ahead. The material is versatile both in terms of its characteristics and areas of application.
Today road material for individual construction. If we talk about the prospect of its use in the future in this area, then this is indicated by Western developments and the use of foam glass.
In Germany, the production of prefabricated houses from monolithic sections has already been established. The thickness of the walls of such a house is 30 centimeters. This thickness is sufficient for use in any climatic zone. The manufacturer claims that at home easy to assemble... The relative lightness of the blocks will allow them to be assembled quickly and not involve heavy cranes. Such a technology of houses in places of disasters and natural disasters will come in handy.
And what is also important - these houses are not "temporary houses", but quite permanent housing with all the conveniences.
Features of the use of foam glass in building insulation
Let's consider the features of insulation with some examples.
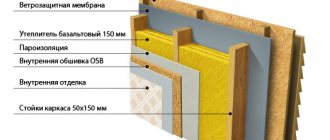
- Wall insulation... It is possible to insulate with such material, both outside and inside the building.There is nothing complicated in working with foam glass blocks. Old cladding material, dirt and dust are removed from the walls. After that, a layer of special glue or cement mortar is applied to the wall (as when working with tiles). We put a block on the layer of adhesive and press it down. You can, of course, additionally strengthen it with dowels, but this can damage the material. The top is covered with a layer of plaster. No additional vapor barrier or waterproofing is required.
- Warming of floors... Blocks, chips or foam glass granules are used to insulate floors. Blocks are the best option. First, the base is covered with sand five centimeters thick. Slabs (blocks) can already be laid on the sand. The joints can then be sealed with polyurethane foam. On top of our heat-shielding coating, we need to make a reinforced screed. And finally, a wooden floor is made.
- Roof insulation... The roof is one of the most moisture-prone elements of a home. In this case, the optimal insulation is foam glass. If the attic is not residential, then it is enough to insulate the attic floor following the example described above.
- Insulation of the foundation... Insulation of the foundation is the main point in building a house. Flooding is a major problem in many wetlands or lowland areas. In this case, the foundation begins to damp, and from it the walls are already. All this begins to rot, mold and decay over time. You can, of course, make permanent repairs, but this is not only a failure to get out of the situation, but it will still not cancel the destruction that has begun. Therefore, at the stage of building the foundation, it is necessary to veneer the foundation both from the side of the street and from the inside of the basement. We already know how to cover the wall.
- Bath insulation... A bathhouse in a personal summer cottage is an invariable and important attribute of relaxation. The bath can be a source of dilution of an aggressive environment due to high humidity and temperature changes. Foam glass plates can be ideal for such premises. The very process of insulating the walls of such structures as a bathhouse is no different from the insulation of walls in ordinary rooms.
To really understand how foam glass differs from other heaters, you just need to compare their characteristics.
Comparative characteristics of heat-shielding materials
Expanded polystyrene advantages - low price, low thermal conductivity. Disadvantages - low (less than that of mineral wool) vapor permeability, increased labor intensity in terms of fitting the material, high flammability. The only place where it can be applied is wet, even wet places when insulating the facades of stone buildings. Not suitable for wooden buildings.
Mineral stone wool advantages - withstands temperatures up to 1000 degrees Celsius, does not absorb moisture, High degree of resistance to mechanical stress.
Extruded polystyrene foam advantages - low thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength, no capillarity, no water absorption, resistance to temperature changes, durability. Disadvantages - lack of vapor permeability.
Foam concrete and aerated concrete advantages - they are not afraid of dampness, regulation of air humidity in the room due to the return and absorption of moisture (creating a microclimate), high sound insulation, good thermal insulation (3–3.5 times higher than that of bricks), low labor intensity when working with them , incombustibility of materials, easy handling, durability.
Fiberglass (glass wool) advantages - fire safety, convenience when working with them, low thermal conductivity, does not rot, is not afraid of moisture (the ability to absorb and give up moisture). Disadvantages - a necessity making gaps during installation to remove moisture, aging and destruction of the structure of the material.
Advantages of cork materials - environmental friendliness, the ability to use for decoration, insulation for floors and interior walls. Disadvantages - high cost.
Foamed material advantages - low weight, low thermal conductivity, ease of use. Disadvantages - vapor and gas tightness (walls "do not breathe").
Properties
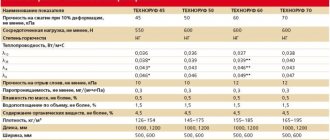
Cellular glass is famous for the following properties:
- noise absorption - 56 dB;
- water absorption - 0–5%;
- vapor permeability - 0–0.005 mg / m * h * PA;
- thermal conductivity - 0.04–0.08 W / (m * K);
- humidity (sorption) - 0.2–0.5%;
- bending strength - 0.4–0.6 MPa;
- compressive strength - 0.7–4 MPA;
- effective operating temperature - –260 - + 400 ° С;
- real operating temperature - –260 - + 230 ° С;
- deformation temperature - + 450 ° С.
Based on this data, recognized advantages and disadvantages can be identified.
Heaters
141 votes
+
Voice for!
—
Against!
One of the best heat and sound insulation materials is foam glass. This insulation was created by Soviet scientists in the 30s, but due to its high cost and imperfect manufacturing technology, it was not widely used. Three decades later, the Canadians found practical use for it, where foam glass was used as thermal insulation for a building. This material entered mass construction relatively recently, when all the shortcomings were taken into account and the production costs were reduced. The article will focus on how to insulate with foam glass.
- Foam glass stacking technology
What is foam glass
- This inorganic thermal insulation material has a porous structure. During the production process, the molten glass is heated under high temperatures, the added gas-forming substance forms bubbles with a diameter from a millimeter to a centimeter. The porosity ranges from 80-95%.
Foam glass photo


- The color of the products can be different: cream, green or black. This property depends on the raw material, because crushed quartz, sodium sulfate, sedimentary rocks, and irrecoverable cullet are used in production.
- Insulation is offered in the form of granules, slabs and fittings (pipe shells). Blocks of foam glass are popular, which can be of the following sizes: length - 200, 250, 400, 475 mm;
- width - 125, 200, 250, 400 mm;
- thickness - 80,100, 120 mm.
Foam glass characteristics
- It is a lightweight material with a density of 120-200 kg / m. cub.
- As for the ultimate compressive strength, this indicator is very high and varies from 0.5 to 1.2 MPa.
- Thermal conductivity is even better than that of wood - 0.06 W / m * s versus 0.09 W / m * s, respectively.
- The absorption index of sound waves for a 100 mm thick slab is 50 dB, which provides increased comfort.


- The amount of sorption is negligible and does not exceed 4% of the volume.
- The temperature range for the use of the material is very wide - from -200 to + 500C. At a higher temperature (from + 540C), the plates begin to deform, but do not emit toxic gases or vapors. Heat resistance makes it possible to use foam glass at facilities that are subject to increased fire safety requirements.
- Chemical inertness is high. The material does not interact with acids, alkalis, oil products and other aggressive media.
Benefits of using foam glass
- In addition to high physical and technical characteristics, among the advantages can be noted the absolute ecological purity. The material is recommended for use in buildings with increased requirements for sanitary and hygienic conditions.
- The mats do not change their size during the entire period of service. Glass cells do not deform under operational loads and seasonal temperature changes.Thus, the formation of cold bridges due to compression, sagging, swelling or shrinkage is not allowed.


- Foam glass is not subject to decay and the development of corrosion processes. Also, it is not attractive to microorganisms, molds, fungi and rodents, which indicates biological resistance. Due to the above advantages, the service life of the units is at least 100 years.
- The thermal insulation material is easy to process. It can be cut, drilled and sawed without crumbs or cracks. It can be combined with almost all types of building materials: cement, brick, iron surfaces, holds finishing compounds well.
Disadvantages of foam glass insulation
- The main disadvantage is the high cost, because the manufacturing process itself is a complex technological task. For the production of insulation in the form of a shell, additional equipment is required, which entails an increase in the cost of the finished product.
- One more drawback can be noted - low resistance to shock loads. But this indicator is not critical, since the insulation is not subjected to such tests.
Attention! "Analogs"
- A cheaper analogue is presented on the market, which is made of liquid glass. The finished product does not differ in strength and moisture resistance. At its core, it is a porous glue.
- The only plus of such a material is its low cost, which can be 2 or even 3 times less than that of foam glass products made from solid raw materials.
Foam glass application
Due to its heat-insulating properties, the material is used:
- in civil engineering. It is widely used for thermal insulation of engineering communications. This material is used to equip "warm floors", exploited roofs, attics, basements, foundations. They also insulate the inner and outer walls;


- in sports facilities. Block and granular material is widely used in the construction of ice arenas, swimming pools, playgrounds and other facilities to which special requirements are imposed;
- in industrial facilities. Foamed glass melt works to reduce operating costs due to its high thermal resistance. Therefore, its application is relevant not only for ground, but also underground structures, such as: buried reservoirs and other containers;
- in the national economy. Crushed stone from foam glass makes it possible to erect buildings on clay and waterlogged soils. It provides reliable thermal insulation for farms intended for breeding poultry, cattle, etc.
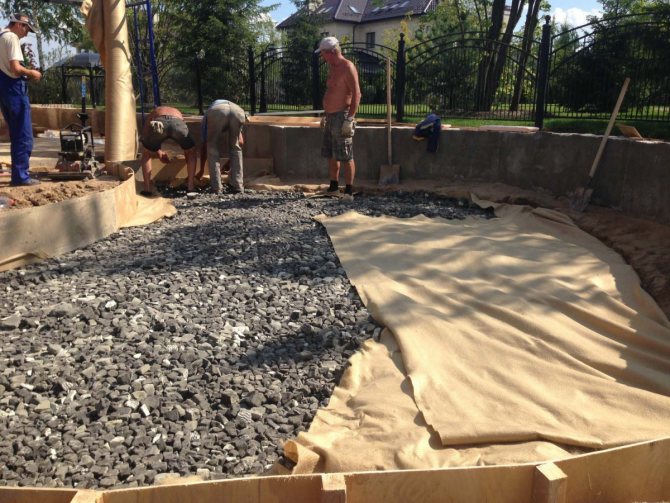


- in the improvement of home gardens. Foam glass bulk material has found its application in the arrangement of greenhouses and hotbeds. The operational characteristics make it possible to form the relief on the site, equip pedestrian paths, create gabions, and use them in drainage systems and groundwater diversions. They also insulate buried containers.
Improving efficiency
- When choosing the thickness of the slabs, it is necessary to take into account the thermal insulation properties of the material used to build the house. So for external insulation of brick, concrete and silicate walls, foam glass plates with a thickness of 120 mm are used.
- For buildings made of wood, foam and expanded clay concrete blocks, this heat-insulating material with a thickness of 80-100 mm is suitable.
- Internal insulation works are carried out by means of 60 mm thick foamed glass melt. Plates are fixed with adhesives, thin dowels and steel L-shaped brackets.


- For the "warm floor" system, foundation and interfloor (attic) floors, granular material is used. It will fill all voids and provide the necessary thermal insulation. The calculation of the layer thickness is based on the temperature conditions of the region of residence.
Installation of foam glass
- For fixing the mats, a special foam glass glue is used. It is applied to the back and 2 side walls. Cement-containing mortars and bitumen-based compounds are evenly distributed around the perimeter.
- If there are slight bulges or depressions on the surface, then it is recommended to apply the adhesive mixture to the foam glass with “slaps” (at least 5 pieces per plate). With this method, the consumption of glue will increase, but the base will become as even as possible.
- For wooden surfaces, use special dowels. This is because wood is subject to thermal expansion. In this connection, the plates must be fixed mechanically, which will allow the foam glass blocks to "move" after the tree.
- Before installing the boards on vertical surfaces, a horizontal strip is installed at the level of the basement under the level. It can be a bar or a metal profile, if necessary, wedges are placed between the base and the rail. The empty space is filled with foam.
- The first row of insulation is installed on a profile that acts as a support. After the adhesive has hardened, the support is dismantled. For reliability, it is better to remove the horizontal bar upon completion of all work.


- Foam glass mats are mounted on walls and sloped roofs from the bottom up, on horizontal surfaces (for example, on interfloor ceilings, foundations) in the direction - "towards you", that is, from the far corner.
- Laying of foam glass products is carried out close to each other with the obligatory displacement of one row relative to the other (with bandaging of the seams). If, in addition to glue, it is planned to additionally use dowels, then their fasteners are made after the binder mixture has completely dried.
- Thermal insulation boards around window or door openings, chimneys and other elements are mounted in solid pieces. Docking of foamed molten glass blocks on corner lines is not allowed.
Foam glass stacking technology
Knowing the method of fastening this material, you can quickly and easily perform the insulation of any objects under construction. Proper placement of all layers will help improve the effectiveness of thermal insulation.
Unique physical and technical properties make it possible to reduce the thickness of the "cake" and to abandon the use of wind and moisture protection membranes. Below is the most common use of foam glass slabs.
- Heavy cladding wall... Products made of foamed glass melt are glued to a reinforced concrete or brick surface. Additional fixing is done mechanically (4-5 dowels per plate). After the entire perimeter has been laid, they switch to the installation of a metal profile intended for a facing stone. This option is also applicable for arranging the basement.


- Plaster wall... Foam glass mats are attached to brickwork or walls erected from foam or aerated concrete blocks using an adhesive composition. Before applying the finishing material, the boards are covered with an overlap mesh (at least 100 mm). It is fixed with disc dowels with pressure washers. The thickness of the plaster layer can be up to 30 mm.
- Wall with facing bricks... The brick base is pasted over with foam glass plates. It is more convenient to insert flexible connections after the insulation is laid, and not before its installation. Next, a facing brick masonry is erected. Here you can also use granular material, which is poured between the main and the facing wall as the latter is being erected (the distance between the masonry is at least 250 mm).
- Wall for profiled sheet... Wall surfaces are covered with foam glass mats. On top of them, a crate made of wooden slats or a metal profile is arranged. Fasteners are selected depending on the material from which the walls are erected.Profiled sheets are installed according to the appropriate technology (from bottom to top and from left to right, with an overlap along the horizontal and vertical level).


- Internal walls (partitions)... Indoor work is not much different from outdoor installation of the presented insulation. Insulation is also attached to the surface, which is covered with a layer of plaster (you can mount the profile under gypsum plasterboards).
- Roof for roll materials... The reinforced concrete slab, if necessary, is covered with a bitumen-polymer primer, which provides a high level of moisture protection. Next, a hot bitumen-based mastic or glue solution is applied to the foam glass block and fixed on the surface with slight pressure. The finished fabric is treated with hot bitumen. With the help of a torch, an EPP waterproofing layer is fused, and then a roll material of the EKP type.


- Roof with a slight slope for sheet coverings... Foam glass blocks are glued to the reinforced concrete floor. You can use special adhesives or bituminous mastics. Upon completion of the work, the foam glass surface is covered with a hot bitumen-polymer mass. To increase the waterproofing of the roof, fused roll materials are used. After hardening, a lathing is performed that corresponds to one or another roofing material.
- Wooden roof... The rafters are equipped with a continuous flooring. On top of it, a layer of waterproofing materials on a bitumen basis is spread, the fastening of which is carried out mechanically. Next, the foam glass is mounted, then the waterproofing material. Now the surface is completely ready for laying any roofing material.
- Insulation of floors with foam glass... Foam glass slabs are laid out tightly on top of a concrete base or a compacted layer of sand or cement. Here, the thickness of the slab will depend on the expected loads. Next, polyethylene is laid in 2 layers, and then the whole cake is poured with a sand-cement mixture. This base is completely ready for arrangement with various finishing materials: linoleum, parquet, ceramic tiles, etc.
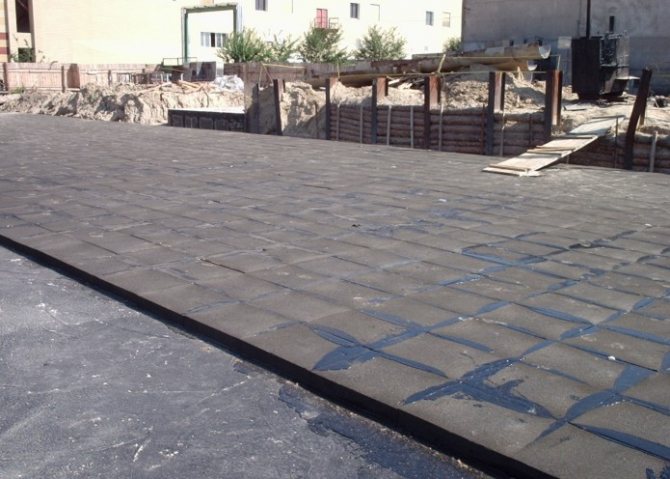


Foam glass products have the characteristics necessary for effective thermal insulation of buildings for any purpose. They combine: low heat transfer rates, ease of installation, long service life, fire and biological resistance, environmental safety for both humans and structures.
Foam glass video
Despite the high cost of this material, laying foam glass will pay off all costs due to the absence of additional layers of cake and due to the minimum amounts in heating bills.
Dignity
The material has many advantages. Let's consider the main ones.
- Security. Does not contain substances harmful to the human body.
- Environmental friendliness. Produced from environmentally friendly raw materials.
- Hygiene. It has antiseptic properties.
- Durability. Service life - over 100 years.
- Versatility. It is used for insulation of any buildings.
- High adhesion. Combines with a lot of building materials.
- Biological passivity. He is not afraid of rodents, insects and microorganisms.
- Resistance to the negative effects of climatic factors. He is not afraid of temperature drops, precipitation, UV, etc.
- Resisting mechanical factors. It does not deform and does not lose its properties, since it can withstand impacts and high loads.
- Not susceptible to chemical influences. Does not react to acid.
- Resistant to thermal factors. Foam glass is absolutely non-combustible insulation.
- Ease of processing. Perfectly cut with a regular hacksaw.
The material is worthwhile, but there are drawbacks and there are many of them, unfortunately.


roof insulation with foam glass
Advantages of foam glass
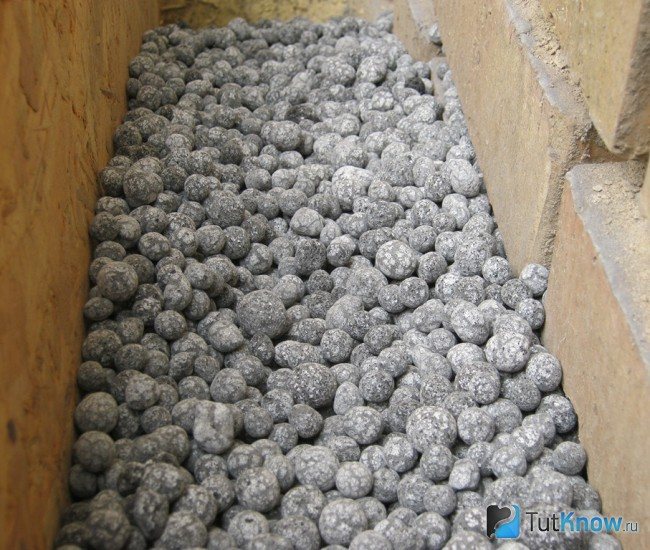


Foam glass "inherited" many of its advantages from silicate glass.Others received due to the presence of gas microcapsules.
The main advantages of this insulation are:
- Excellent thermal insulation performance
... This almost universal material insulates walls, foundations, roofs and pipes well. It is actively used to isolate objects with increased fire hazard and where there are high temperatures. - Durability
... Most manufacturers of this material indicate at least a hundred years of operation without loss of insulating qualities. Temperature changes will not cause destruction of the foam glass. Its operating ranges are from +650 to -250 degrees. Also, the insulation is not subject to deformation, shrinkage and other changes in dimensions during operation. - Good sound insulation
... A block or layer of foam glass granules 100 millimeters thick can drown out the rumble of a tractor under the house. With such insulation, you can not be afraid of the penetration of extraneous sounds from the outside. - Incombustibility
... This material is practically incapable of burning. At high temperatures, the foam glass will only melt without emitting any harmful compounds and smoke. - Ease of installation
... The installation of blocks or slabs of foam glass is similar to the installation of foam concrete. This material is cut with an ordinary hacksaw. It is also easy to work with due to its low weight. A cubic meter of insulation weighs about 160 kilograms. - Sanitary safety
... Foam glass will not become a place of concentration of pests, and also does not produce any harmful volatile compounds. It can be used in public buildings, child care facilities and hospitals.
disadvantages
Of course, every raw material has negative points. Foam glass is no exception. Before purchasing material, it is necessary to scrupulously study the negative points.
- High price. For the production of raw materials, innovative high-tech equipment is required, which leads to its rise in price. And also the manufacture of foamed glass requires high energy costs.
- Fragility. Raw materials, despite their strength, are very fragile, which leads to cracking if you ignore the installation recommendations.
- Lack of steam permeability. Foam glass, as it was said, is not exposed to the destructive effects of biological factors, but the surface under it is easy.
- Fear of alkalis and hydrofluoric acid. Cellular glass, like an aspen leaf, trembles at the "sight" of alkalis and hydrofluoric acid, as they are capable of destroying it.
- Severity. The raw materials are relatively heavy, which negatively affects the building structure.
- Durability. Of course, a long service life is a plus. But the materials used to build the facility are unlikely to last more than 100 years. This means that the structure needs to be repaired periodically, and the cellular glass is not intended to be reused. Which exit? Replacement of insulation.
- Low impact resistance. Cellular glass does not withstand even light blows. Mechanical influence is the “death” of the material. Of course, if the insulation is in the structure, it is not afraid of blows. He is afraid of them when transporting, unloading and installing.
- Impossibility of "resuscitation". If the glass is damaged, it can be taken to landfill. It is impossible to glue or cover up the cracks.
The properties have played a cruel joke with honeycomb glass, turning a huge number of advantages into disadvantages.
Main disadvantages
Despite the obvious advantages of foam glass, when choosing it as a heater, disadvantages should also be taken into account. These include:
- High price. In the building materials market, foam glass is one of the most expensive insulation materials. This is due to the high energy consumption during production. In addition, expensive equipment is required for manufacturing.
- Low impact strength.The material has a high compressive strength, but it is quite brittle material. Therefore, with strong impacts, the foam glass can crack, and such cracked slabs can no longer be used as insulation.
- Low steam permeability. This material property is both its advantage and disadvantage. Despite the fact that fungi and mold cannot form in the foam glass, the surface it covers does not exchange air, therefore, foci of infection may appear.
Foam glass is a high-quality and modern insulation for various types of surface, but when choosing it, disadvantages should also be taken into account.
Details of home insulation with foam glass can be found in the video:
Price
The cost of foam glass bites. Prices, of course, vary, since they depend on many factors, but on average, you can buy blocks for $ 120-400 per cubic meter. You can buy plates and shells by paying $ 110–350, and you can get a granular version by spending $ 35–100 per cubic meter.
What can you say? Foam glass insulation is a very dubious and costly undertaking, since the material has a lot of serious drawbacks, and, moreover, is incredibly expensive. But, as they say, the owner is a master. Maybe it's not for nothing that they call it the raw material of the future. To buy or not to buy? That's the question! The choice is yours, dear readers.
Warmth and comfort to your home, dear friends! See you on other blog pages!
Quote of Wisdom: Reading is the best teaching (A.S. Pushkin).
Application
A feature of the material is its excellent thermal insulation properties combined with high strength. Therefore, it can be used to insulate the basement, foundation, load-bearing walls and pipelines. The low rate of water absorption allows it to be used for thermal insulation of the basement, foundation and basement. Granular material can be used as an insulating additive for concrete. For thermal insulation of walls, it is enough to fill it in their cavities.


Thermal insulation with granular foam glass
Foam glass is well cut and drilled, so it is easy to make pieces of the desired size from the plates. In addition, the boards hold plaster, putty, glue and other surface finishing compounds well.
The material can be used not only for residential and public spaces. It is used for housings of various technological and industrial equipment that operate at high temperatures.


Insulation with foam glass
Disadvantages of foam glass
There are very few disadvantages:
- The weight. Having a high density, this material turns out to be heavier than all other heat insulators.
- High price. The foam glass production process is quite laborious and complex, and this increases its cost. In addition, it is possible to produce molded products from foam glass only on special equipment, which also has a negative effect on the cost of the material.
- Brittleness and low resistance to mechanical stress. Glass, as you know, is a brittle material and breaks on impact. Damaged blocks lose some of their positive properties, for example, they begin to leak water or cold.