Choosing a heater
The main reason for pipelines freezing is insufficient circulation rate of the energy carrier. In this case, at sub-zero air temperatures, the process of liquid crystallization may begin. So high-quality thermal insulation of pipes is vital.
Fortunately, our generation is incredibly lucky. In the recent past, pipelines were insulated using only one technology, since there was only one insulation - glass wool. Modern manufacturers of heat-insulating materials offer simply the widest selection of heaters for pipes, differing in composition, characteristics and method of application.
It is not entirely correct to compare them with each other, and even more so to claim that one of them is the best. So let's just look at the types of pipe insulation materials.
By scope:
- for pipelines of cold and hot water supply, steam pipelines of central heating systems, various technical equipment;
- for sewerage systems and drainage systems;
- for pipes of ventilation systems and freezing equipment.
In appearance, which, in principle, immediately explains the technology of using heaters:
- roll;
- leafy;
- shroud;
- filling;
- combined (this rather already refers to the method of pipeline insulation).
The main requirements for the materials from which heaters for pipes are made are low thermal conductivity and good fire resistance.
The following materials fit these important criteria:
Mineral wool. Most often sold in rolls. Suitable for thermal insulation of pipelines with high temperature heat carrier. However, if you use mineral wool to insulate pipes in large volumes, then this option will not be very profitable from the point of view of savings. Thermal insulation with mineral wool is produced by winding, followed by its fixing with synthetic twine or stainless wire.

In the photo there is a pipeline insulated with mineral wool

It can be used at both low and high temperatures. Suitable for steel, metal-plastic and other plastic pipes. Another positive feature is that expanded polystyrene has a cylindrical shape, and its inner diameter can be adjusted to the size of any pipe.
Penoizol. According to its characteristics, it is closely related to the previous material. However, the method of installing penoizol is completely different - a special spray installation is required for its application, since it is a component liquid mixture. After curing of penoizol, an airtight shell is formed around the pipe, which almost does not allow heat to pass through. The pluses here also include the lack of additional fastening.
Penoizol in action


Foil penofol. The latest development in the field of insulation materials, but has already won its fans among Russian citizens. Penofol consists of polished aluminum foil and a layer of polyethylene foam.
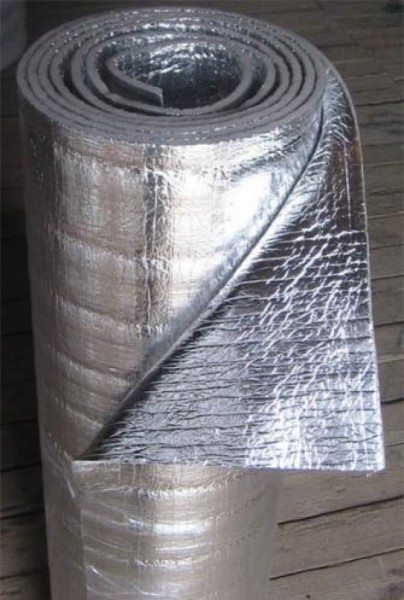


Such a two-layer construction not only retains heat, but even serves as a kind of heater! As you know, foil has heat-reflecting properties, which allows it to accumulate and reflect heat to the insulated surface (in our case, it is a pipeline).
In addition, foil-clad penofol is environmentally friendly, slightly flammable, resistant to temperature extremes and high humidity.
As you can see, there are plenty of materials! There is plenty to choose how to insulate pipes.But when choosing, do not forget to take into account the peculiarities of the environment, the characteristics of the insulation and its ease of installation. Well, it would not hurt to calculate the thermal insulation of pipes in order to do everything correctly and reliably.
DIRECTORY
Selection table for the ratio of pipe diameters (copper pipes, steel pipes, polyethylene pipes) with standard sizes of thermal insulation (foam rubber insulation, polyethylene foam insulation, mineral wool cylinders).
This thermal insulation selection table for pipes will help not to make mistakes in the selection of insulation.
Basically, three types of pipes are used for thermal insulation: steel, copper and plastic. To designate the diameter of steel and copper pipes, three methods are used: in millimeters, inches and nominal diameters - Du *. DN is a "conditional passage" that is used when calculating various parameters of pipeline systems. For example, such parameters as head, flow rate, consumption, drain, etc. inner pipe diameter.
Very often, the use of high pressure in the pipeline system is not required, therefore, the pipe wall thickness is reduced in order to save on metal consumption during production, and vice versa, if a high pressure is required in the pipeline or for threaded connections, the pipe wall thickness is increased.
The diameter of the pipes is called conditional, because there are pipes with a square, not a circular cross section. In this case, for pipes with a square cross-section, the nominal passage is calculated through the cross-sectional area of a particular pipe, the calculation should be reduced to the formula for the area of a round pipe and is taken for further calculations as if the pipe is round and has such and such a nominal diameter. In pipes with a circular cross-section Nominal size - Du completely coincides with the inner diameter of the pipe.
As a rule, nominal diameters (DN) of steel pipes are indicated up to size 50, after which it is customary to indicate the outer diameters of the pipes. But for plastic pipes, usually only the outer diameters are indicated.
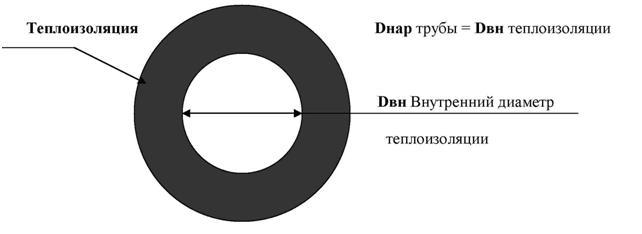
Technical insulation for pipes, which is supplied in the form of heat-insulating pipes (tubular elements), is represented by standard sizes that take into account Dnap - the outer diameters of the pipes (not to be confused with Dу -conditional diameters) of pipes.
Example:
Suppose your technical specification indicates a steel pipe with a diameter of DN 20 and a heat-insulating layer with a thickness of 13 mm. Take your time to order pipe thermal insulation with internal diameters - 20 mm or the closest to it 22 mm (respectively, insulation standard sizes 20x13 and 22x13).
Be sure to pay attention to the factor that if you have a steel pipe with DN 20, then taking into account the thickness of the pipe wall, its outer diameter will be approximately 28 mm, therefore the required size of thermal insulation is 28x13, and if a copper pipe with DN 20 is used, then its outer diameter will be about 22 mm, and the size of the thermal insulation will be 22x13 (where 13 mm is the thickness of the thermal insulation layer).
Insulation laying
The insulation calculation depends on the type of installation used. It can be outside or inside.


External insulation is recommended for the protection of heating systems. It is applied along the outer diameter, provides protection against heat loss, the appearance of traces of corrosion. To determine the volumes of material, it is sufficient to calculate the surface area of the pipe.
Thermal insulation maintains the temperature in the pipeline regardless of the effect of environmental conditions on it.
Internal laying is used for plumbing.

It perfectly protects against chemical corrosion, prevents heat loss from routes with hot water. Usually it is a coating material in the form of varnishes, special cement-sand mortars.The choice of material can also be carried out depending on which gasket will be used.
Duct laying is in demand most often. For this, special channels are preliminarily arranged, in which the tracks are placed. Less often, the channelless method of laying is used, since special equipment and experience are required to carry out the work. The method is used in the case when it is not possible to carry out work on the installation of trenches.
Insulation installation
The calculation of the amount of insulation largely depends on the method of its application. It depends on the place of application - for the inner or outer insulating layer.
You can do it yourself or use a calculator program to calculate the thermal insulation of pipelines. The outer surface coating is used for hot water pipelines at high temperatures in order to protect it from corrosion. The calculation with this method is reduced to determining the area of the outer surface of the water supply system, to determine the need per running meter of the pipe.


Internal insulation is used for pipes for water mains. Its main purpose is to protect metal from corrosion. It is used in the form of special varnishes or a cement-sand composition with a layer of several mm thick.
The choice of material depends on the installation method - channel or channelless. In the first case, concrete trays are placed at the bottom of an open trench for placement. The resulting gutters are closed with concrete covers, after which the channel is filled with previously removed soil.
Channelless laying is used when digging a heating main is not possible.

This requires special engineering equipment. Calculating the volume of thermal insulation of pipelines in online calculators is a fairly accurate tool that allows you to calculate the amount of materials without fiddling with complex formulas. Consumption rates of materials are given in the corresponding SNiP.
Posted on: December 29, 2017
(4 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5) Loading ...
- Date: 15-04-2015Comments: Rating: 26
Correctly performed calculation of the thermal insulation of the pipeline can significantly increase the service life of pipes and reduce their heat loss
However, in order not to be mistaken in the calculations, it is important to take into account even minor nuances.
Thermal insulation of pipelines prevents the formation of condensate, reduces heat exchange between pipes and the environment, and ensures the operability of communications.
Overview
Thermal insulation calculation is one of the most time consuming design tasks. Modern requirements for timing and project execution make manual insulation calculation for large projects almost impossible! Even the use of standard design albums does not allow to fully provide the required work efficiency.
The program developed in NTP Truboprovod allows you to calculate and select thermal insulation, saving up to 90% of the time that you usually spend on this task. The program in automatic mode completely forms the thermal insulation structure, calculates and generates a general data sheet (list of reference and attached documents), a technical installation sheet, a bill of quantities (for the estimate department) and a specification in accordance with GOST 21.405-93, GOST 21.110-2013 and GOST R 21.1101 -2013.
The program is recommended for use in design bureaus and departments in the design and reconstruction of main and technological pipelines and heating networks, equipment in oil refining, chemical, petrochemical, gas, oil, heat power and other industries that calculate and select thermal insulation for pipelines and equipment.
Pipeline insulation options
Finally, we will consider three effective methods for thermal insulation of pipelines.
Perhaps some of them will appeal to you:
- Thermal insulation using a heating cable.In addition to traditional isolation methods, there is also such an alternative method. The use of the cable is very convenient and productive, considering that it takes only six months to protect the pipeline from freezing. In the case of heating pipes with a cable, there is a significant saving of effort and money that would have to be spent on earthwork, insulation material and other points. The operating instructions allow for the cable to be found both outside the pipes and inside them.
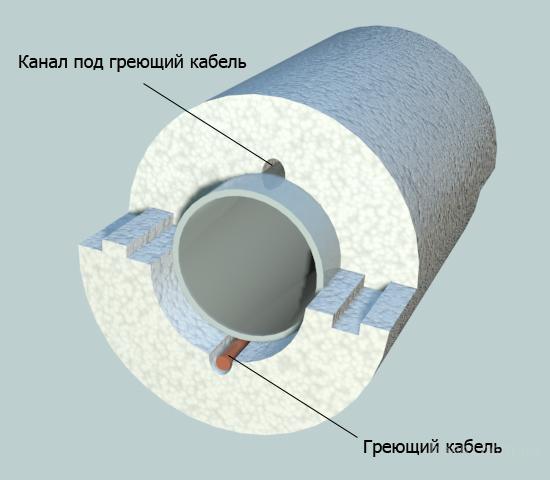

Additional thermal insulation with heating cable
- Warming with air. The mistake of modern thermal insulation systems is this: it is often not taken into account that soil freezing occurs according to the principle "from top to bottom". The heat flux emanating from the depths of the earth tends to meet the freezing process. But since the insulation is carried out on all sides of the pipeline, it turns out that I also isolate it from the rising heat. Therefore, it is more rational to mount a heater in the form of an umbrella over the pipes. In this case, the air gap will be a kind of heat accumulator.
- "A pipe in a pipe". Here, more pipes are laid in polypropylene pipes. What are the advantages of this method? First of all, the pluses include the fact that the pipeline can be warmed up in any case. In addition, heating is possible with a warm air suction device. And in emergency situations, you can quickly stretch the emergency hose, thereby preventing all negative moments.


Pipe-in-pipe insulation
Calculation of the volume of pipe insulation and laying of material
- Types of insulating materials Laying of insulation Calculation of insulating materials for pipelines Elimination of insulation defects
Insulation of pipelines is necessary in order to significantly reduce heat loss.
First, you need to calculate the volume of pipe insulation. This will allow not only to optimize costs, but also to ensure the competent performance of work, maintaining the pipes in proper condition. Correctly selected material prevents corrosion and improves thermal insulation.
Pipe insulation diagram.
Today, different types of coatings can be used to protect tracks. But it is necessary to take into account exactly how and where the communications will take place.
For water pipes, you can use two types of protection at once - internal coating and external. It is recommended to use mineral wool or glass wool for heating routes, and PPU for industrial ones. Calculations are performed by different methods, it all depends on the selected type of coverage.
Network Layout Characteristics and Regulatory Computing
Performing calculations to determine the thickness of the heat-insulating layer of cylindrical surfaces is a rather laborious and complex process
If you are not ready to entrust it to specialists, you should stock up on attention and patience to get the right result. The most common way of calculating pipe insulation is to calculate it using standardized heat loss indicators.
The fact is that SNiPom established the values of heat loss by pipelines of different diameters and with different methods of their laying:
Pipe insulation scheme.
- in an open way on the street;
- open in a room or tunnel;
- channelless method;
- in impassable channels.
The essence of the calculation is in the selection of heat-insulating material and its thickness in such a way that the value of heat losses does not exceed the values prescribed in SNiP. The calculation technique is also regulated by regulatory documents, namely, by the relevant Code of Rules. The latter offers a slightly more simplified methodology than most of the existing technical reference books. Simplifications are contained in the following points:
Heat losses during heating of the pipe walls by the medium transported in it are negligible compared to the losses that are lost in the outer insulation layer. For this reason, they are allowed to be ignored. The vast majority of all process and network piping is made of steel, its resistance to heat transfer is extremely low. Especially when compared with the same indicator of insulation
Therefore, it is recommended not to take into account the resistance to heat transfer of the metal pipe wall.
Process features
What determines the thickness of the thermal insulation of pipelines? What factors should be taken into account in the calculations?
Network characteristics
Why does the thermal insulation of process pipelines differ? First of all, this process depends on the location and data of the system itself.
There are the following ways of laying routes:
- outdoor installation - on the street;
- in room;
- by channelless technology;
- through the tunnel;
- in impassable channels.
According to the SNiP standards, for each of the installation options, different indicators of permissible heat losses are provided. Many people think that a pipeline insulation calculator based on such input data is the most practical and correct tool. Of course, other parameters are taken into account, which you will learn about later.
The main rule of the technique is that the amount of heat loss of the route being laid should not exceed the level prescribed by SNiP.
There is also an alternative methodology (according to novice homeowners - a simpler one), based on the standards set out in documents called the Code of Rules. This guide is considered the most accessible for understanding, and, therefore, a "magic wand" for beginners in the field of laying trails. What are the simplifications?
- It is allowed not to take into account the opposition of the metal walls of the elements to the heat transfer process. The reason for such a relaxation is the following: almost all network and technological pipelines are made of steel, which is distinguished by extremely low resistance to heat transfer.
- If we compare the heat losses in the layer of heat-insulating material and inside the structure itself (due to the transfer of heat from the contents of the system to the walls), then the latter are so scanty that they can be ignored when calculating the installation of thermal insulation of pipelines.
Only after carrying out detailed calculations, it will become clear what materials for thermal insulation of pipelines you need to purchase, what thickness of this raw material is applicable for a particular option, how everything should happen.
It is worth paying attention! Neglecting calculations, which seemingly aims to save time and money, can lead you to the opposite result. For example, the choice of the thickness of the material according to the "by eye" method will entail unjustified expenses if the indicator exceeds the established norms.
Before installing the system, you need to calculate everything in detail: what kind of insulation you need, what is its thickness applicable to cover a particular structure
Influencing factors
On what points does the choice of the thickness of the material and the type of thermal insulation of pipelines depend?
Remember the list of these important factors:
- system content temperature;
- type and characteristics of insulation;
- temperature changes outside the network - in the environment surrounding the track;
- the limit of the mechanical load on the structure;
- the tendency of the thermal insulation material to deformation;
- in the case of underground placement of the system - the load from the ground.
This is important to know! For routes with a content temperature not exceeding 12 degrees, there is not enough thermal insulation of pipelines with mineral wool. In such cases, foil-clad material should also be used, which successfully copes with the mission of the vapor barrier.
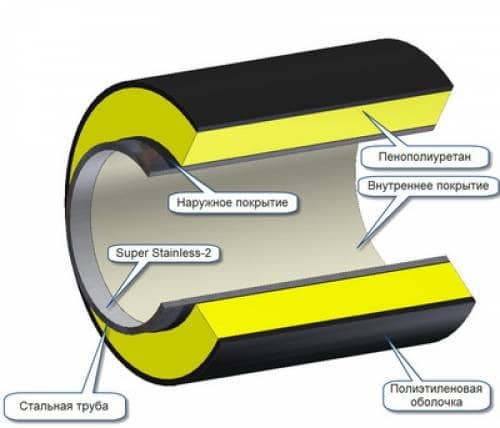

Thermal insulation diagram
Thermal calculation of the heating network
For the thermal calculation, we will accept the following data:
· Water temperature in the supply pipeline 85 ° C;
· Water temperature in the return pipeline 65 ° C;
· The average air temperature for the heating period of the Republic of Moldova is +0.6 oC;
Let's calculate the losses of uninsulated pipelines. An approximate determination of heat losses per 1 m of an uninsulated pipeline, depending on the temperature difference between the pipeline wall and the ambient air, can be made according to the nomogram. The heat loss value determined from the nomogram is multiplied by the correction factors:
Where: a
- a correction factor that takes into account the temperature difference,
but
=0,91;
b
- correction for radiation, for
d
= 45 mm and
d
= 76 mm
b
= 1.07, and for
d
= 133 mm
b
=1,08;
l
- pipeline length, m.
Heat losses of 1 m of uninsulated pipeline, determined from the nomogram:
for d
= 133 mm
Qnom
= 500 W / m; for
d
= 76 mm
Qnom
= 350 W / m; for
d
= 45 mm
Qnom
= 250 W / m.
Considering that the heat loss will be both on the supply and on the return pipelines, the heat loss must be multiplied by 2:
kW.
Heat loss of suspension supports, etc. 10% is added to the heat loss of the uninsulated pipeline itself.
kW.
Standard values of average annual heat losses for a heating network during above-ground laying are determined by the following formulas:
where:, - standard average annual heat losses, respectively, of the supply and return pipelines of the above-ground laying sections, W;
, - standard values of specific heat losses of two-pipe water heating networks, respectively, supply and return pipelines for each diameter of pipes for aboveground laying, W / m, determined by;
l
- length of a section of a heating network, characterized by the same diameter of pipelines and type of laying, m;
- coefficient of local heat losses, taking into account heat losses of fittings, supports and compensators. The value of the coefficient in accordance with is taken for an overground installation of 1.25.
Calculation of heat loss of insulated water pipelines is summarized in Table 3.4.
Table 3.4 - Calculation of heat loss of insulated water pipelines
| dн, mm | , W / m | , W / m | l, m | , W | , W |
| 133 | 59 | 49 | 92 | 6,79 | 5,64 |
| 76 | 41 | 32 | 326 | 16,71 | 13,04 |
| 49 | 32 | 23 | 101 | 4,04 | 2,9 |
The average annual heat loss of an insulated heating network will be 49.12 kW / an.
To assess the effectiveness of an insulating structure, an indicator is often used, called the coefficient of insulation efficiency:
Where Qr
, Qand
- heat losses of uninsulated and insulated pipes, W.
Insulation efficiency ratio:
Thermal insulation of pipelines to ensure the required surface temperature
The pursuit of such goals is usually associated with the fact that safety requirements prescribe the need to reduce heat generation in the room to protect the operating personnel from burns, and heat losses at the enterprise are not regulated. By law, in accordance with the norms and requirements of SNiP, at a coolant temperature below 100 ° C in the room, the temperature on the surface of the pipe insulation should not exceed 35 °. At a coolant temperature above 100 ° C, the surface temperature should not exceed 45 °. In the open air, the temperature bar rises, but is still limited to 55 ° C when using a metal protective coating and 60 ° when using other types of pipe insulation coatings.
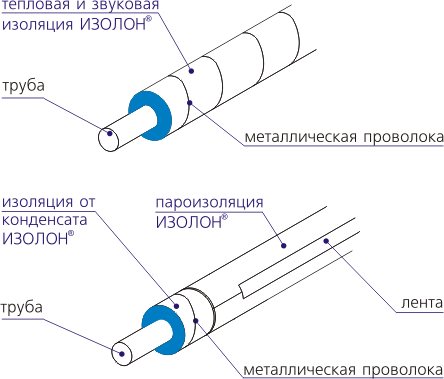

Scheme of thermal insulation of pipelines to ensure the required surface temperature.
When choosing a protective coating for thermal insulation of pipes located in a room, it is necessary to take into account the radiation properties of its surface. So, to reduce the thickness of the thermal insulation layer of pipelines, a non-metallic protective coating with a high emissivity should be used, since under the same calculation conditions, the thickness of the non-metallic coating of the thermal insulation of pipes will be significantly lower than with a metal coating.The dimensions of the insulating layer, determined by the calculation for a given temperature on its surface, will depend on such factors as:
- ambient temperature;
- location of the structure (can be indoors or outdoors);
- outer diameter of the pipe;
- the temperature of the coolant itself;
- coefficient of heat transfer from the surface of the thermal insulation of the pipeline to the ambient air.
The method of calculating a single-layer thermal insulation structure
The basic formula for calculating the thermal insulation of pipelines shows the relationship between the magnitude of the heat flux from the operating pipe, covered with a layer of insulation, and its thickness. The formula is applied if the pipe diameter is less than 2 m:
The formula for calculating the thermal insulation of pipes.
ln B = 2πλ [K (tt - to) / qL - Rn]
In this formula:
- λ is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation, W / (m ⁰C);
- K - dimensionless coefficient of additional heat losses through fasteners or supports, some K values can be taken from Table 1;
- tт - temperature in degrees of the transported medium or heat carrier;
- tо - outdoor air temperature, ⁰C;
- qL is the heat flux, W / m2;
- Rн - resistance to heat transfer on the outer surface of the insulation, (m2 ⁰C) / W.
Table 1
| Pipe laying conditions | The value of the coefficient K |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, along canals, tunnels, open indoors on sliding supports with a nominal diameter of up to 150 mm. | 1.2 |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through canals, tunnels, open indoors on sliding supports with a nominal diameter of 150 mm and more. | 1.15 |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, along canals, tunnels, open indoors on suspended supports. | 1.05 |
| Non-metallic piping laid on overhead or sliding supports. | 1.7 |
| Channelless way of laying. | 1.15 |
The value of the thermal conductivity λ of the insulation is a reference, depending on the selected thermal insulation material. It is recommended to take the temperature of the transported medium tt as the average temperature throughout the year, and of the outside air tо as the average annual temperature. If the insulated pipeline passes through the room, then the ambient temperature is set by the technical design assignment, and in its absence it is assumed to be + 20 ° C. The indicator of resistance to heat transfer on the surface of a heat-insulating structure Rн for outdoor installation conditions can be taken from Table 2.
table 2
| Rн, (m2 ⁰C) / W | DN32 | DN40 | DN50 | DN100 | DN125 | DN150 | DN200 | DN250 | DN300 | DN350 | DN400 | DN500 | DN600 | DN700 |
| tт = 100 ⁰C | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.017 | 0.015 |
| tт = 300 ⁰C | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.015 | 0.013 |
| tт = 500 ⁰C | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.012 |
Note: the value of Rn at intermediate values of the coolant temperature is calculated by interpolation. If the temperature indicator is below 100 ⁰C, the Rn value is taken as for 100 ⁰C.
Indicator B should be calculated separately:
Heat loss table for different pipe thicknesses and thermal insulation.
B = (dfrom + 2δ) / dtr, here:
- diz - outer diameter of the heat-insulating structure, m;
- dtr - outer diameter of the protected pipe, m;
- δ is the thickness of the heat-insulating structure, m.
The calculation of the insulation thickness of pipelines begins with determining the indicator ln B, substituting the values of the outer diameters of the pipe and the thermal insulation structure, as well as the layer thickness, into the formula, after which the parameter ln B is found from the table of natural logarithms. It is substituted into the basic formula together with the indicator of the normalized heat flux qL and calculate. That is, the thickness of the pipeline insulation must be such that the right and left sides of the equation become identical. This thickness value should be taken for further development.
The considered calculation method applied to pipelines with a diameter of less than 2 m.For pipes with a larger diameter, the calculation of insulation is somewhat simpler and is performed both for a flat surface and according to a different formula:
δ = [K (tt - to) / qF - Rn]
In this formula:
- δ is the thickness of the heat-insulating structure, m;
- qF is the value of the normalized heat flux, W / m2;
- other parameters - as in the calculation formula for a cylindrical surface.
Calculation of screen thermal insulation of pipelines of heat supply systems
(I.G.Belyakov, A.Yu. Vytchikov, L.D. Evseev)
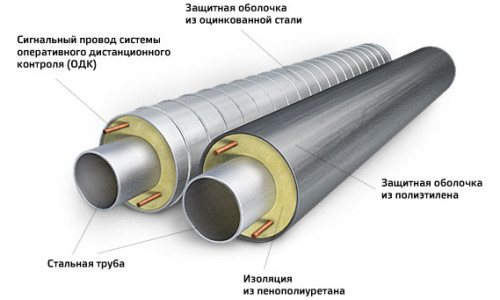
In heat supply systems for the insulation of pipelines, polyurethane foam is widely used as a heater, which has a low value of the thermal conductivity coefficient. The maximum operating temperature for various brands of polyurethane foam is in the range from 80 to 200 ° C, therefore, it becomes necessary to protect it from overheating by applying aluminum foil to the inner surface of the shell.
An air gap is created between the shell and the pipeline, the size of which significantly affects the temperature difference between the outer surface of the pipeline and the polyurethane foam. A schematization of the heat transfer process in an insulated pipeline is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Heat transfer in an insulated pipeline
The calculation of the thickness of the thermal insulation layer was carried out for pipelines located in the open air with a coolant temperature from 100 to 150 ° C.
The mathematical formulation of the problem under consideration will take the following form:
Where:
q1 - the density of the heat flux passing through the structure, W / m; t - coolant temperature, ° C; t0 - ambient temperature, taken equal to the average temperature of the heating period (t0 = -5.2 ° C, Samara); dy - nominal diameter of the pipeline, m; dн - outer diameter of the pipeline, m; dfrom1, dfrom2 - inner and outer diameter of a polyurethane foam shell, m; - coefficient of heat transfer from the outer surface of the insulation, taken equal to 29 W / (m2 ° C) in accordance with Appendix 9, SNiP 2.04.14-88 "Thermal insulation of pipeline equipment". M., 1999; λ, λ out of 1, λ out of 2 - coefficient of thermal conductivity of the pipeline material, air gap and polyurethane foam, respectively, W / (m ° C). The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the air gap is determined taking into account convection and heat transfer by radiation:
Where: λm - value of the coefficient of thermal conductivity of air, W / (m ° C); - coefficient of convection, taking into account the effect of natural convection> = 1 - coefficient of heat transfer by radiation, W / (m2 ° C); - thickness of the air gap, m;
To find the convection coefficient, it is recommended to use the criterion equation obtained by M.A. Mikheev at 103
In the above equation, the thickness of the interlayer should be taken as the defining size, and the average air temperature should be taken as the defining temperature.
Where: g - acceleration of gravity, m2 / s; - coefficient of kinematic viscosity of air, m2 / s;
- coefficient of volumetric expansion of air, 1 / ° K;
- average air temperature in the interlayer, ° C;
- the difference between the temperatures of the surfaces of the layers, ° C; Pr - Prandtl criterion.
where: - reduced emissivity for a system of parallel plates having emissivity degrees
Is the emissivity of an absolute black body;
- temperatures of the surfaces of the plates, ° K;
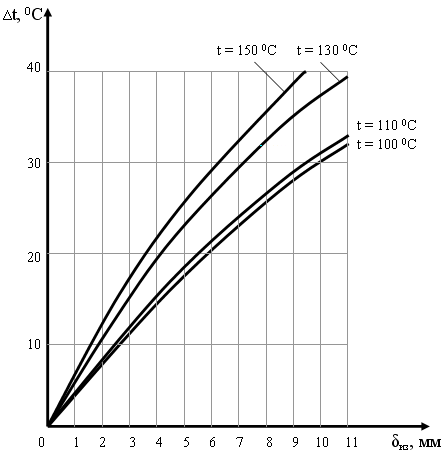

Fig. 2. Dependence of the temperature difference delta t on the size of the air gap
Figure 2 shows the dependence of the temperature difference between the outer surface of the pipeline and the inner surface of the shell delta t on the size of the air gap at du = 0.82 m.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer made of polyurethane foam grade PPU-110 is 16 mm.