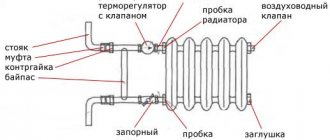
In what cases is the volume of the coolant calculated?
The liquid in the water circuit of the heating system performs the most important function - it is the carrier of heat. Many elements of the heating system are selected in relation to the volume of the coolant to be distilled. Therefore, preliminary calculations will make it possible to complete the heat supply most efficiently. It is easy to calculate the total volume of the coolant, given that the amount of liquid in the radiators is 10-12 percent of the total amount of liquid to be distilled.

The calculation of water in the heating system must be done in the following cases:
- before installing the heating, determine the amount of coolant that will be distilled by a boiler of a certain power;
- when an anti-freezing liquid is poured into the system, it is necessary to maintain a certain proportion in relation to the entire distilled liquid;
- the size of the expansion tank depends on the amount of coolant;
- you need to know the required volume of water in the heating system of country or private houses, where the water supply is not centralized.
In addition, in order to properly mount the batteries on the wall, you need to know their weight. For example, just one section of a cast-iron radiator, already heavy, holds 1.5 liters of fluid. That is, the seven-section cast-iron battery becomes over ten kilograms heavier when the system starts up.
Why you need to know the amount of water in the battery
Usually, they pay attention to radiators at the beginning or end of the heating season or during general cleaning. Meanwhile, inside it, vital processes for a person take place, for which the coolant is responsible - most often water. Is it valuable to know how much of this liquid fits in one battery, section?


The volume of water inside this "web" can be easily recognized
It turns out that there is more than one reason for this:
- do not "weigh down" the heater, because the volume of water in a cast-iron heating radiator increases its already considerable weight;
- installation of a heating system with a certain boiler power requires calculating the total amount of heat carrier, including in radiators;
- knowing that the amount of coolant in the battery is 10-12% of the heating system - all batteries, pipes and the boiler, you can drain the water "dry";
- when choosing an expansion tank;


The volume of the expansion tank must correspond to the amount of coolant in the system
- so as not to overdo it with concentrated antifreeze, which is poured in a certain proportion with water;
- for natural / forced circulation type, the optimal battery size is selected - large in the first case and no difference in the second.
What situations can be avoided if the volume of the coolant is correctly calculated
Many people do the installation of the heat of the system, relying on the advice of craftsmen, friends, or their own intuition. The boiler is chosen more powerful, the number of radiator sections is increased "just in case". As a result, the opposite picture is obtained: instead of the expected heat, the batteries do not warm up evenly, the boiler “shakes” the fuel with no load.


The following unpleasant situations can be avoided if you know how to calculate the amount of water in the heating system:
- uneven heating of the water circuit in the rooms;
- increased fuel consumption;
- emergency situations (breaks in connections, leaks in radiators).
All these "surprises" are quite predictable in case of incorrect calculation of the volume of the coolant.
Attention! Antifreeze must not be used for heating systems that use galvanized pipes or other elements.
Summarizing
It is better to underfill the principle than the opposite is not applicable in heating systems, since airing the system will mean cold batteries. By calculating the volume of each structural element of the heating system using tables or empirically, heat consumption will become more meaningful and enjoyable. And the repair or replacement of a separate fragment will no longer be a secret behind seven seals.
The video in this article shows the process of pouring the coolant into the heating system.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our channel Yandex.Zen
What can be taken from the documentation
Technical data sheets for devices, if any, will help you find out how much water in the heating battery and boiler will circulate during the operation of the heat supply system.
If you need to choose a radiator by the volume of the coolant, you can compare different options:
- aluminum and bimetallic with a height of 300 and 500 mm, respectively, accommodate 0.3 and 0.39 l / m;
- cast iron MS-140 with a height of 300 and 500 mm. holds respectively 3 and 4 l / m;
- an imported cast-iron radiator with a height of 300 and 500 mm will include 0.5 and 0.6 l / m.
Thus, the volume of a bimetallic radiator is the same as that of an aluminum one.

Another "cheat sheet" will help with the selection of cast iron radiators of different models (the amount of coolant per section is indicated):
- MS 140 - 1.11-1.45 l
- World Cup 1 - 0.66-0.9 l s;
- World Cup 2 - 0.7-0.95 l;
- World Cup 3 - 0.155-0.246 liters;
As for the pipes, the calculations are as follows.
Based on the internal diameter of the pipes, in the documentation you can find out the amount of liquid that they hold per running meter:
- 13.2 mm - 0.137 L;
- 16.4 mm - 0.216 L;
- 21.2 mm - 0.353 L;
- 26.6 mm - 0.556 l;
- 42 mm - 0.139 l;
- 50 mm - 0.876 l.
The calculations are simple. So, for example, 4.4 liters of water will fit in a 5-meter pipe with an inner diameter of 50 mm: 5x0.876 = 4.4

Attention! If you compare how many liters of water are in heating radiators of different models, you can choose the appropriate option corresponding to the boiler power.
We calculate the volume of the radiator
So, it remains only to determine the volume of water in the heating radiator. What is the easiest way to do this? Again, we advise you to use the tables. Please note that manufacturers offer various models of heating devices on the market. The model line may include radiators not only of different designs, but also of different sizes. In terms of the size range, the basis is the center-to-center distance, that is, this is the distance between the axes of two collectors (upper and lower). In addition, manufacturers now offer custom-made devices that use individual sketches and drawings. Determining the capacity of these batteries is much more complicated.
But let's return to this indicator and show the average values for heating appliances. We take models of the form 500 (center distance).
- The old-style ChM-140 cast iron radiator - 1.7 liters the volume of one section.
- The same is only a new sample - 1 liter.
- Steel panel appliance type 11 (i.e. one panel) - 0.25 l for every 10 cm of appliance length. Measuring the type in a quantitative ratio increases the volume of the heating medium by 0.25 liters. That is, type 22 - 0.5 l, type 33 - 0.75 l.
- Aluminum battery - 0.45 l for each section.
- Bimetallic - 0.25 liters.
There are no steel tubular radiators in this list. Even the approximate volume of this model will be difficult to determine. The point is that manufacturers use pipes of various diameters for their manufacture, hence the impossibility of choosing at least an average version. Therefore, we recommend that you pay attention to the passport data, where the volume indicator should be indicated.


Type ratio
Calculating the volume empirically
And if there is no such indicator, what to do? Then we recommend finding the volume of the heating battery in a practical way. How can I do that:
- Install three caps on the radiator.
- Place it on the end so that the open nipple is on top.
- Take a measuring container, for example, a bucket or a ladle (that is, you must know the volume of this container, even an approximate one).
- Now you manually pour ordinary water into the battery, while counting how many buckets went into the heater. By multiplying the quantity by the volume of the bucket, you get the volume of the coolant in the device.
Please note that this method of determining the volume of a heating appliance can be used for all types and models. If the capacity of the device is not indicated in the passport data, and you did not find the definition table, then you can empirically determine this indicator quite accurately with your own hands.
Now I would like to touch on the topic of how the capacity of the heating battery affects the total heat transfer of the heating system. Here the dependence is not direct, but indirect. Let us explain the essence of the matter. Much will depend on how the coolant itself will move along the contours: under the action of physical laws (that is, with natural circulation) or under artificial pressure (under the action of a circulation pump).
If the first option is chosen, then the optimal solution is radiators with a large volume. If the second, then there is no difference. The pressure will create conditions under which the coolant will be distributed evenly throughout the entire network, and, therefore, the temperature will be evenly distributed.
How to calculate the amount of coolant in radiators yourself
Sometimes you have to deal with the situation that it is impossible to determine the belonging of the radiators to a certain model. Radiator documents may be lost, model name is not visible. There is an easy way to find out how many liters are in a heating radiator without resorting to documentation or tables from the Internet.
Proceed as follows:
- close one side of the radiator with a plug;
- pour the liquid to the top;
- pour the liquid into a measuring container.
Attention! There are two options for calculating the volume of water in a heating radiator: immediately note the amount of liquid poured in, or after draining it.


In such a simple way, you can calculate the amount of liquid that enters a radiator of any complexity or model.
Average data


If, for some reason, the user cannot determine the exact volume of water or antifreeze in heating radiators, then averaged data can be used that are applicable to certain types of heating radiators. If, say, we take a 22 or 11 type panel radiator, then for every 10 cm of this heating device there will be 0.5-0.25 liters of coolant.
If you need to determine "by eye" the volume of a section of a cast-iron radiator, then for Soviet samples the volume will range from 1.11 to 1.45 liters of water or antifreeze. If imported cast iron sections are used in the heating system, then such a section has a capacity from 0.12 to 0.15 liters of water or antifreeze.
There is another way to determine the internal volume of the radiator section - to close the lower necks, and pour water or antifreeze into the section through the upper ones - to the top. But this does not always work, since aluminum alloy radiators have a rather complex internal structure. In such a design, it is not so easy to remove air from all internal cavities, therefore this method of measuring the internal volume for aluminum radiators cannot be considered accurate.
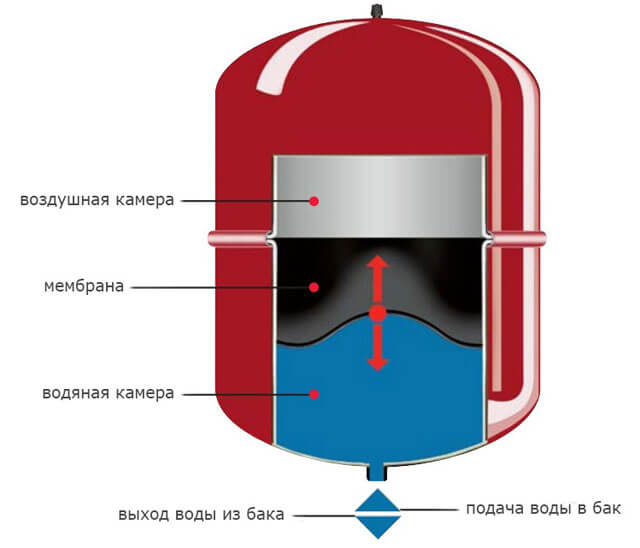
The critical stage: calculating the capacity of the expansion tank
In order to have a clear idea of the displacement of the entire heat system, you need to know how much water is placed in the boiler heat exchanger.
You can take the average. So, an average of 3-6 liters of water is included in a wall-mounted heating boiler, and 10-30 liters in a floor or parapet boiler.
Now you can calculate the capacity of the expansion tank, which performs an important function. It compensates for the excess pressure that occurs when the heat carrier expands during heating.


Depending on the type of heating system, tanks are:
- closed;
- open.
For small rooms, the open type is suitable, but in large two-story cottages, closed expansion joints (membrane) are increasingly being installed.
If the capacity of the tank is less than required, the valve will release pressure too often. In this case, you have to change it, or put an additional tank in parallel.


For the formula for calculating the capacity of the expansion tank, the following indicators are needed:
- V (c) is the volume of the coolant in the system;
- K is the coefficient of expansion of water (a value of 1.04 is taken, in terms of the expansion of water at 4%);
- D is the expansion efficiency of the reservoir, which is calculated by the formula: (Pmax - Pb) / (Pmax + 1) = D, where Pmax is the maximum allowable pressure in the system, and Pb is the pre-pumping pressure of the expansion joint air chamber (parameters are specified in the documentation for the reservoir );
- V (b) - capacity of the expansion tank.
So, (V (c) x K) / D = V (b)