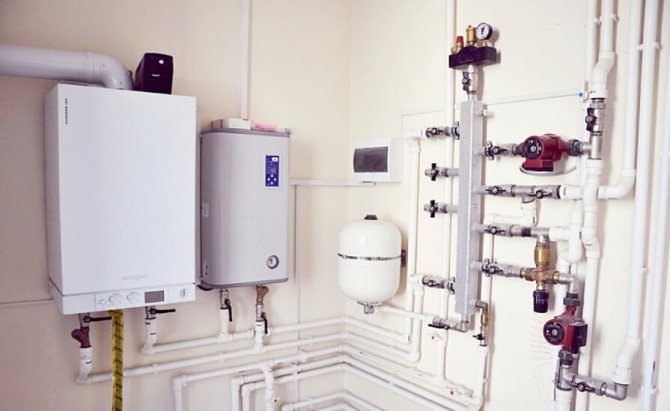
Natural circulation heating systems
The natural circulation heating system became widespread in the pre-war period due to its efficiency, simplicity and reliability. Most often, this type of heating system is used in summer cottages, as well as in country houses due to frequent power outages at such facilities. Such systems are conventionally divided into two types - with bottom and top water supply. To determine with the choice of the type of heating system, it is necessary to consider their differences, characteristics and scope.
Schematic diagram of heating with natural circulation of the coolant
Natural circulation heating systems
Heating systems with top water supply
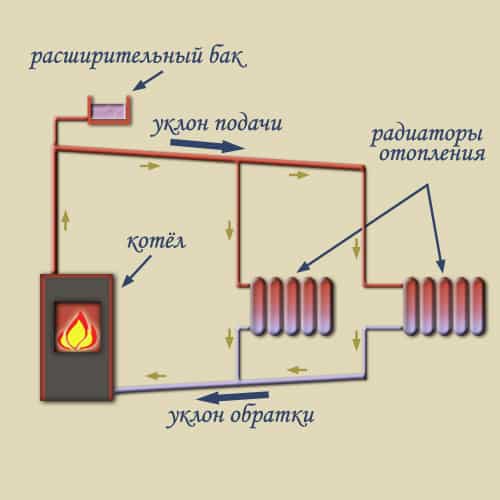
The heating medium - in this case water - must be heated and supplied to the upper part of the heating system through a pipeline. The pipe used to supply water must have a large diameter compared to the pipes that are responsible for supplying water to the radiator. This is necessary to achieve the greatest resistance to heat exchange. Horizontal pipes should be installed with a minimum slope of one centimeter per fitting meter.
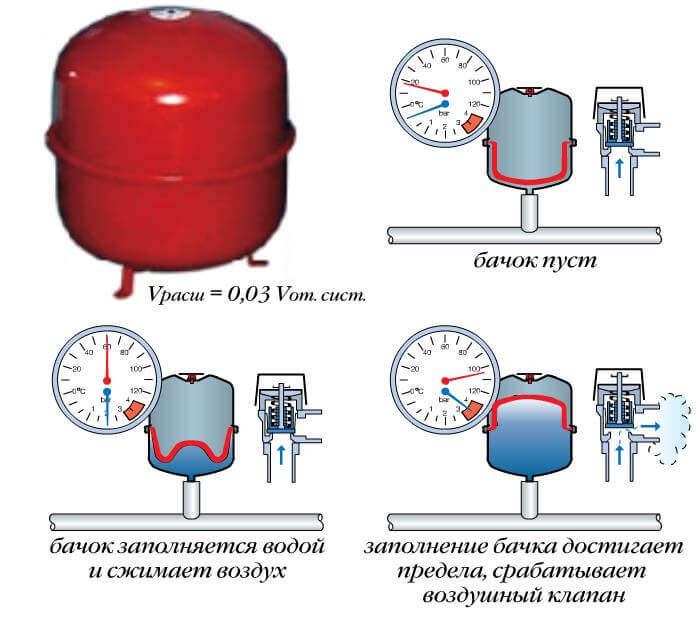
The expansion tank must be installed in the upper part of the system: it will perform the function of receiving steam and excess heat - this is necessary due to the property of water to expand when heated and go into a steam state. The tank must have a drain cock and a cap or valve at the top. After the water is heated, it is distributed through the supply pipe to the risers and radiators.
Advice: if you are going to use a heating system with natural water circulation, remember that radiators must be connected using a diagonal method
After direct heating of the room, the water flows into the boiler through a specialized pipe - the return line. Here it is reheated and the cycle of water movement is repeated. The boiler for heating is located in the lowest part of the system, under the radiators. Usually, these elements are installed in boiler rooms, for which basements are allocated.
One-pipe and two-pipe heating schemes
When developing a heating scheme for a house with natural water circulation, it is possible to design one or several separate circuits. They can differ significantly from each other. Regardless of the length, the number of radiators and other parameters, they are performed according to a one-pipe or two-pipe scheme.
Single line circuit
A heating system using the same pipe for sequential supply of water to radiators is called a single pipe. The simplest one-pipe option is heating with metal pipes without the use of radiators.
This is the cheapest and least problematic way to solve the heating of the house when choosing in favor of the natural circulation of the coolant. The only significant disadvantage is the appearance of bulky pipes.
At the most economical with heating radiators, hot water flows sequentially through each device. Here, a minimum number of pipes and valves are required.
As it passes, it cools down, so subsequent radiators receive colder water, which must be taken into account when calculating the number of sections.
A simple one-pipe system (above) requires a minimum amount of installation work and investment.A more complex and costly option at the bottom allows you to turn off the radiators without stopping the entire system
The most effective way to connect heating devices to a single-pipe network is considered to be a diagonal option.
According to this scheme of heating circuits with a natural type of circulation, hot water enters the radiator from above, after cooling it is discharged through the branch pipe located at the bottom. When passing through in this way, heated water gives off the maximum amount of heat.
With the lower connection to the battery of both the inlet and outlet, the heat transfer is significantly reduced, because the heated coolant must travel the longest possible path. Due to significant cooling in such circuits, batteries with a large number of sections are not used.
"Leningradka" is characterized by impressive heat losses, which must be taken into account when calculating the system. Its plus is that when using shut-off valves at the inlet and outlet nozzles, the devices can be selectively turned off for repairs without stopping the heating cycle (+)
Heating circuits with a similar connection of radiators are called "". Despite the noted heat losses, they are preferred in the arrangement of apartment heating systems, which is due to the more aesthetic type of pipeline laying.
A significant disadvantage of one-pipe networks is the inability to turn off one of the heating sections without stopping the circulation of water throughout the circuit.
Therefore, a modernization of the classic scheme with the installation of "" is usually used to bypass the radiator using a branch with two ball valves or a three-way valve. This allows you to regulate the water supply to the radiator, up to its complete shutdown.
For two or more storey buildings, variants of a one-pipe scheme with vertical risers are used. In this case, the distribution of hot water is more even than with horizontal risers. In addition, vertical risers are less extended and fit better into the interior of the house.
A single-pipe scheme with vertical wiring is successfully used when heating two-story rooms using natural circulation. An option is presented with the ability to turn off the upper radiators
Return pipe option
When one pipe is used to supply hot water to radiators, and the second is used to divert cooled water to a boiler or furnace, such a heating scheme is called a two-pipe heating scheme. A similar system in the presence of heating radiators is used more often than a one-pipe one.
It is more expensive, as it requires the installation of an additional pipe, but it has a number of significant advantages:
- more even temperature distribution
coolant supplied to the radiators; - easier to calculate
dependence of radiator parameters on the area of the heated room and the required temperature values; - more efficient regulation of heat supply
to each radiator.
Depending on the direction of movement of cooled water relatively hot, it is subdivided into associated and dead-end. In associated circuits, the movement of chilled water occurs in the same direction as hot water, so the cycle length for the entire circuit is the same.
In dead-end schemes, cooled water moves towards hot water, therefore, the lengths of the coolant turnover cycles differ for different radiators. Since the speed in the system is low, the heating time can differ significantly. Radiators with a shorter water cycle will heat up faster.
When choosing a dead-end and associated heating schemes, they primarily proceed from the convenience of conducting a return pipe
There are two types of positioning of the inlet in relation to the heating radiators: upper and lower.With the upper connection, the hot water supply pipe is located above the heating radiators, and with the lower connection, it is lower.
With a bottom connection, air can be removed through the radiators and there is no need to run pipes on top, which is good from the standpoint of the design of the room.
However, without a runaway manifold, the pressure drop will be much less than when using the top line. Therefore, the lower connection is practically not used when heating premises according to the principle of natural circulation.
Heating systems with bottom water supply
A system in which the heating medium is supplied from below is usually used to heat houses where there is no attic space or access to it is closed. The main difference between the presented heating system is that the pipes are laid under the radiators. There is also an expansion tank, which is installed in the upper level of the system; usually utility rooms are used for this. If, at the same time, there is no circulation of water in the heating system, which should occur naturally, then it is created by force.
Forced circulation heating systems
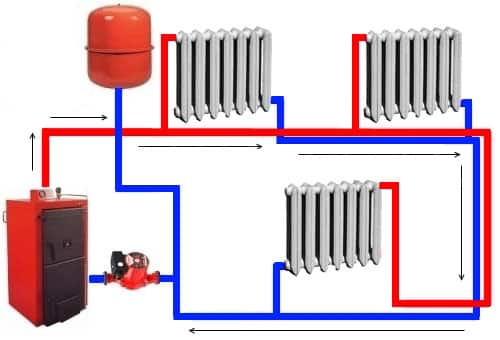
A standard forced circulation heating system operates using the same connection methods. The difference is that due to the long length of this system or the absence of natural conditions, it is necessary to include a pump in the system to create a slope of the pipes. The circulation pump is mounted to the main pipe - this helps to increase the life of the heating system. The use of a pump helps not only to increase the heating efficiency, but also to reduce the number of lines. A forced circulation system has the ability to heat not just several rooms, but even a house with several floors.

Forced circulation heating systems
In order to produce high-quality work of this type of system, you need a continuous power supply. Installation of a pump for circulation in the heating system is required in order to create forced circulation of water in a closed loop. In this type of system, the pump is the central component among the equipment. It should be noted that the circulation pump may not differ in significant performance: its power is only needed to direct the liquid into the supply pipe. The same pressure pushes the water in the opposite direction, since the system is closed.
The circulation pump is necessary to ensure the smooth operation of the heating system, therefore, it must fully correspond to the system in which the installation is carried out. Due to its functionality, this type of pump can be used everywhere in a wide variety of pipelines.
Swimming pool water circulation and purification systems
However, just a few days after filling the bowl, disappointment sets in. This is because the pool, especially outdoors, is prone to contamination. Determined that the water in the swimming pool is biologically active, and every day organic and inorganic substances inevitably enter it, coming from the environment (for example, fallen leaves or insects); or brought in by bathers (hair, creams, lotions, etc.). The first thing that comes to mind for an inexperienced owner is simply to drain the water (and water the garden at the same time) and refill the pool. Believe that, having done this procedure 2-3 times, even for a small children's pool, you will fully realize the futility and tediousness of this approach. Therefore, manufacturers develop and implement whole complexes of physical and chemical measures for water treatment.Carrying out simple operations will ensure that for a long time the water in the pool is in perfect condition, remains crystal clear and fresh.
Pool water circulation schemes
To keep the pool clean, circulation systems (water intake and return) are required.
There are two schemes for circulating water in a stationary pool: skimmer and overflow.
What is a skimmer? Translated from English skimmer - "sliding on the surface of the water." Beautiful, is not it? Almost surfing. In real life, the skimmer is a distant relative of the bath overflow. It is a metal or plastic box with a width of 15 to 50 cm with a water intake window and a collector of floating waste. It is placed on the wall of the bowl a few centimeters below the edge of the pool. The top, most polluted layer of water is removed from the pool through the skimmer. Water is drawn into the skimmer by means of the pump of the filtering unit and passes through a sieve that retains floating debris. To clean not only the upper layers of water, but also the lower ones, the skimmer is connected to the bottom drain. Skimmers differ in capacity, the maximum value of which is 12 m3 / h. The number of skimmers depends on the size of the pool: 1 skimmer should fall on 30–40 m2 of water surface.
Then the water enters the filtration, heating and disinfection and returns to the pool through the nozzles. The number of return nozzles depends on both the surface of the water surface and the depth of the pool. For depths less than 1.35 m, one nozzle per 6 m2 is required, for deeper depths one nozzle per 8-10 m2.
The movement of water in pools with a skimmer occurs from one wall to another, which limits the use of this scheme when the pool has a complex shape (for example, eights, stars) or large sizes. In this case, warm water cannot be evenly distributed throughout the pool. Therefore, the skimmer method is more often used in private swimming pools. In large and curved pools, it is more convenient to use an overflow method of taking water for cleaning.
In the overflow system, water flows through troughs located around the pool perimeter into the expansion tank. Water from the tank flows by gravity into the filter unit, is purified and poured into the pool through return nozzles, which are usually located at the bottom. Thus, the filtered and heated water is distributed evenly throughout the pool. Such a scheme is more complicated and costs about 30% more than a skimmer one, but it allows water to circulate in pools of any shape and size.
Water treatment methods
For the normal functioning of the pool, in addition to the circulation system, two more systems are definitely needed. The first is the "heart" of the pool - the filtration system. It is provided by an installation, the filtering element of which is quartz sand or a cartridge. Filtration units can be hinged. To clean the filter, there is a backwash mode, which is activated either manually (at least once a week or as indicated by a pressure gauge), or automatically. Backwash takes only 3-4 minutes.
The second mandatory element of any pool is a disinfection system.
It should be noted that the currently widespread purification scheme based on mechanical filtration and chlorination ensures the production of clear water of satisfactory quality. At the same time, the reverse side of using the chlorination method is well known - the formation of toxic compounds in water. At the same time, one should take into account the fact that when using such systems, complete disinfection cannot be achieved and microorganisms that retain viability may remain in the water.Therefore, experts recommend more effective disinfection methods to obtain high-quality water.
These include an ultraviolet disinfection unit. It consists of a disinfection chamber, a remote control panel and a flushing unit. Gas-discharge mercury lamps are located inside the steel chamber, which are a source of bactericidal ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Using the control panel, set the automatic or manual mode of the system. The flushing block is designed to clean the disinfection chamber. Water passing through the disinfection chamber is continuously irradiated with ultraviolet light, which kills almost all microorganisms in the water. UV rays, acting only on living microorganisms, do not affect the chemical composition and physical properties of water. This cleaning method does not require complex equipment and can easily be used in household water treatment complexes in private houses.
Ozonation systems are considered to be the most high-tech method of water treatment today.
The bactericidal effect of ozone is associated with the active penetration of this chemically active form of oxygen through the cell membranes and the subsequent oxidation of organic substances, which causes the death of the bacterial cell. Along with disinfection, ozonation fights algae, improves taste and eliminates water odors. Ozone has the following advantages in comparison with chlorine: ozone reacts to pollution 15–20 times faster than chlorine, while it is needed 2.5 times less; does not irritate the skin, lungs and eyes, does not disturb the pH balance, is safe for the environment. Ozonation increases the content of oxygen dissolved in the water, which contributes to the return of the freshness, characteristic of pure natural sources, to the water purified by ozone. Manufacturers offer both complete ozone systems and partial ozone water treatment.
In general, the process of water treatment of the pool consists of several stages: filtration with coagulation to remove mechanical impurities; disinfection with ozone, ultraviolet radiation or other methods; heating water to the required temperature; dosing of chemicals to regulate the pH level; dispensing disinfectants before feeding water into the bowl to ensure the neutralization of bacteria introduced by bathers. The cost of equipment for water purification can be conditionally divided into three price classes: economy - from 1.5 thousand. That is, the standard is about 4 thousand. e. and premium - from 7 thousand. e.
Choosing a circulation pump for a heating system
In order to select a circulation pump for a heating system, it is necessary to make appropriate calculations. Please note that during an hour, this element will run three times more water than its total volume in the system. Thus, the total volume of a suitable amount of liquid is on average 10 liters per 1 kilowatt of heating boiler output. The required pump model for the heating system and its power are determined by the pressure-flow parameters. The head must be equal to the hydraulic resistance of the heating system.


Circulation pump
Typically, the head velocity of the liquid in systems with forced circulation is quite low, which gives the right to judge the low loss of hydraulic resistance, which usually does not exceed 2 meters. The exact resistance is not easy to calculate, so the performance of the circulation pump is determined at the midpoint. In order to calculate the productivity, the dimensions of the area of the heating object and the power that the source of electricity possesses are also taken into account. It should be remembered that a pump is only needed in a forced circulation system; a natural circulation system does not need it.
Circulation pump installation: what should you pay attention to?
To install the circulation pump yourself, use the following recommendations:
- to extend the operating life of the entire system, install a filter in front of the circulation pump to purify the liquid. the filter must be installed on the suction pipe;
- do not choose a circulation pump for the heating system with a higher power and capacity than required. Otherwise, there is a risk of encountering additional unpleasant noise during its operation;
- Never turn on the pump before filling the heating main with water and removing air from it, this can lead to equipment failure;
- install the pump in an area as close as possible to the expansion tank;
- when installing a pump in a closed heating system, if possible, install a pump on the return. This is due to the fact that this section of the line has the lowest temperature.


Installation of a circulation pump
Advice: before starting the heating system, flush it with water to remove various foreign particles. Do not forget that even a short-term idle operation of the circulation pump in the absence of liquid in the system may result in the failure of the pump itself and other elements of the system.
Almost all circulating pumps on the modern market are equipped with communication with automatic control of boilers for heating. This function provides owners with the ability to regulate the air temperature in the heated facility by changing the speed of water movement in the heating system. In order to take into account the level of heat consumption in the premises, special meters are installed, thanks to which the heat losses arising from the wear of the mains are controlled. The heating circuit itself is not subject to any changes.
You can get acquainted with the method of installing the circulation pump yourself by watching the video:
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Organization of a one-pipe circuit based on an electric boiler for a small house:
The operation of a two-pipe system for a one-story wooden house based on a long-burning solid fuel boiler:
The use of natural circulation during the movement of water in the heating circuit requires accurate calculations and technically competent installation work. When these conditions are met, the heating system will qualitatively heat the premises of a private house and relieve the owners of the pump noise and dependence on electricity.