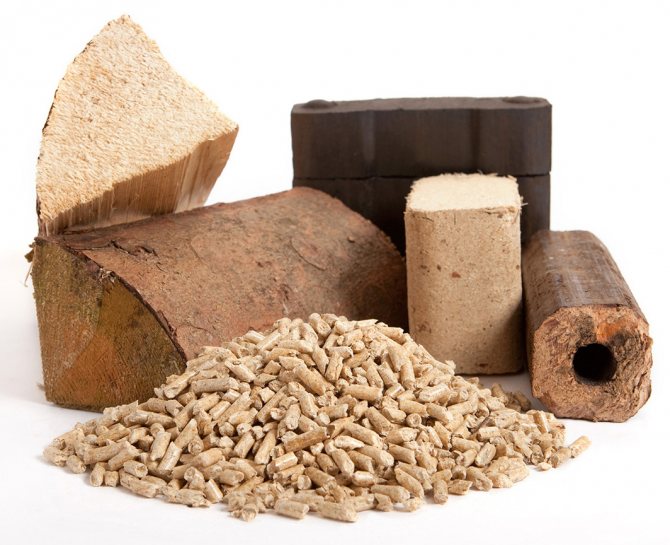
When choosing a stove or fireplace, you need to build on not only the design of the heat source, but also the type of fuel. Solid fuel for different types of furnaces is usually used when heating a relatively small area. There are several types of energy sources and a lot of subspecies. Consider the features, advantages and disadvantages of the main options.
Figure 1. As fuel - the usual firewood
Heating with classics - wood
Firewood is a traditional option that literally everyone has come across. The classic logs are gradually being replaced by the modern alternative. But the drovish do not intend to completely give up their positions - they still have many advantages over new products.
Advantages of firewood:
- characteristics that are familiar to everyone - you know what to expect from wood blanks;
- aesthetic component; firewood is used in fireplaces not only for practical purposes - the characteristic crackling sound in the hearth is still important for many consumers; soundtrack - the result of the impact of high temperature on the moisture remaining in the logs; modern solutions do not indulge in such aesthetics;
- relatively constant parameters; firewood can become damp and moldy, but they do not tend to crumble even after long-term storage;
- wood ash hardly smells.

Figure 2. Firewood in the firebox
Disadvantages of firewood:
- the need for a dry storage place - logs do not tolerate high levels of moisture;
- different shapes and sizes (even if they are close in this regard) do not contribute to the convenience of storage;
- shorter combustion time than wood alternatives;
- less heat transfer;
- different intensity of combustion; usually the logs flare up for a certain time, followed by the culminating heat emission and attenuation;
- a large amount of ash - at least 15%;
- smoke;
- potential threat to health; firewood is safe, but damp logs can contain mold and mildew, and when burned, they can emit toxic smoke.
Firewood can be chopped and sawn. But the nature of the wood, on which its calorific value depends, is much more important. The approximate indicators of various tree species are in the table.
| Breed | Calorific potential, kW / h / kg |
| Larch | 4,3 |
| Spruce | 4,3 |
| Pine | 4,3 |
| Oak | 4,2 |
| Beech | 4,2 |
| Hornbeam | 4,2 |
| Ash | 4,2 |
| Birch | 4,2 |
Main characteristics of heating oil
Fractional composition:
- 10% - distillation at a temperature not lower than 160 ° С;
- 90% - distillation at a temperature not exceeding 360 ° С.
Mass fraction of sulfur in fuel:
- in low-sulfur grades up to 0.5%;
- in sulfurous - up to 1.1%.
Other characteristics:
- kinematic viscosity no more than 8 mm2 / s at 20 ° С;
- acidity not higher than 5 mg KOH / 100 cm3;
- flash point in a closed crucible is not lower than 45 ° С;
- coking capacity no more than 0.35% of 10% residue;
- ash content is not higher than 0.02%;
- trace water content;
- shade from light brown to black;
- density is not standardized, determination is obligatory at 20 ° С.
Briquettes (euro wood)


Figure 3. Euro wood in the oven
Briquettes are furnace fuel formed by pressing wood waste. During production, shavings, wood dust, chips, etc. are used. Due to the vegetable binder - lignin - Eurowood under normal conditions keep its shape reliably and do not crumble.
There are 3 types of Euro briquettes.
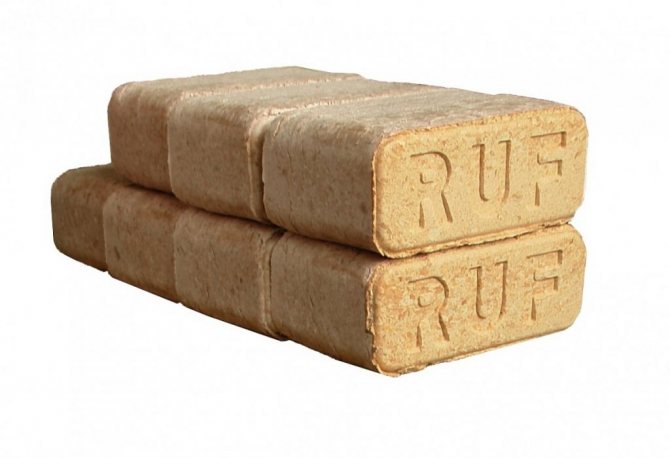
Ruf


Figure 4. Eurobriquettes Roof
This is the most popular option, which has been used by Europeans for several years. After the work of the press, cute practical bricks remain.They bear little resemblance to firewood, but are characterized by an optimal ratio of quality and cost.
Pini kay
This look is in many ways similar to Roof, but briquette firing has been added to the production cycle. This allows you to increase the operational life and resistance of eurodrops to environmental aggression. Due to firing, a protective shell is formed on the outside of the products.
Nestro
Combined view. Unlike the first two, it has a shape similar to ordinary logs. There is a through hole inside the elements. No external firing.
Pros of briquettes:
- long burning time - up to 4 times longer than that of the traditional version; the advantage is due to the higher density of eurodrops;
- high heat transfer - approximately twice as high as that of logs;
- the same intensity of combustion; unlike firewood, pressed blocks burn evenly; moreover, even coals are capable of giving off the same amount of heat as a “fresh” briquette;
- almost complete wastelessness - after the combustion of the blocks, 1-3% of ash remains;
- the usefulness of ash; the previous plus can be considered a disadvantage, since waste serves as a very good fertilizer, in which there is a lot of potassium;
- environmental friendliness; briquettes do not contain any harmful substances; moreover, eurowood almost does not smoke, and the smoke that is there does not smell;
- saving;
- ease of storage and operation; the blocks are easy to store, they require less than firewood, there is no garbage left after them - secondary, but also important advantages.


Figure 5. Euro wood with a hole
Cons of eurodrops:
- with a higher heat transfer, heat blocks give less than the "classic"; this means that they are not suitable as fuel for a sauna stove;
- under unimportant storage conditions, they can crumble; the reason is excellent moisture resistance; but in this case dignity becomes a disadvantage;
- variable characteristics depending on manufacturers; you need to try various options to understand your needs and preferences; briquettes differ somewhat in density and strength;
- the remains of the blocks have a not very pleasant smell;
- exceptional practicality - to the detriment of the aesthetic component.
Main properties and features
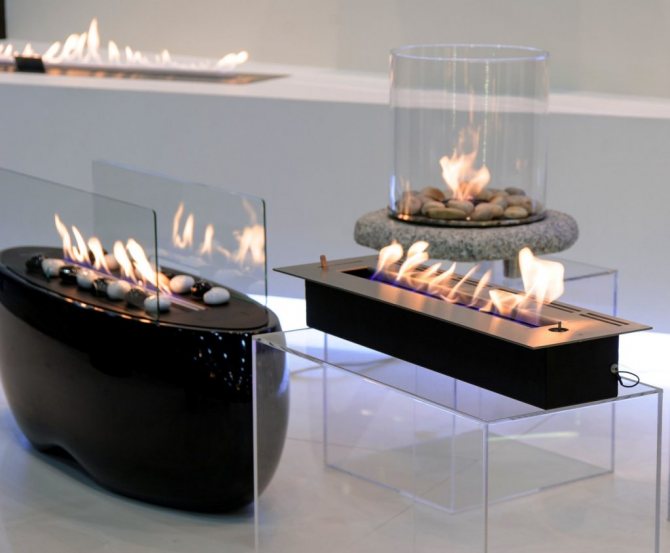
In the process of biofuel production, ethanol is denatured, making it neutral and safe for the human body, animals and other organisms. It decomposes easily during combustion, producing carbon monoxide, some steam and, of course, heat.
At the same time, the outlines of the fire are quite colorful, the tongues of flame are even, bright, saturated with color. The color of the flame, of course, is slightly different from the usual one, it is not so orange, since burning ethanol gives off carbon dioxide and water. To get a more natural fire, natural, environmentally friendly additives are added to the liquid fuel for fireplaces that color the fire in the desired orange color.
During combustion, environmentally friendly biofuel on bioethanol does not emit smoke or soot, the process is odorless and does not annoy us with any unpleasant aroma. It is for this reason that a fireplace with biofuel does not need a chimney and an exhaust hood.
Better yet, the heat generated by the combustion is not lost, but completely enters the room. Thus, the efficiency of such an installation reaches 95-100%. At the same time, by the type of flame, ecofuel for fireplaces is not much different from ordinary firewood, which allows you to contemplate a real fire. Fireplace gel, created on the basis of ethanol with the addition of sea salt, allows you to create a complete illusion of burning real firewood, since in addition to a similar fire, a characteristic sound design will appear in the form of crackling.
Good to know: How to make a biofireplace with your own hands, step by step instructions


A biofuel fireplace in the process of its work, as we have already said, practically does not emit soot and soot.Experts compare its emissions into the atmosphere of a room with the combustion of one ordinary candle. At the same time, the liquid for the biofireplace does not emit carbon monoxide during combustion, which in large volumes can be dangerous.
Bioethanol used for fireplaces can also be poured into a regular kerosene lamp. In this case, during combustion, soot and odor will not be released, as during the combustion of kerosene, and the device will perform its initial functionality perfectly, illuminating the room.
Pellets


Figure 6. Pressed pellets for stoves
Pellets are small fuel pellets that are also produced by pressing waste from the woodworking industry and other types of economic activities. First, the source code is turned into wood dust, then thoroughly dried and granulated in special forms. Pellets are mainly used in furnaces that are designed for this particular type of fuel.
Depending on the raw material, pellets are divided into the following types:
- wood - from woodworking waste;
- straw;
- granules made from sunflower husks;
- peat.


Figure 7. Burning pellets
The advantages of fuel pellets are similar to those of Euro briquettes. But pellets also have an original plus - their small dimensions allow them to be used in boilers with autoloading fuel.
The downside is that in most cases, pellets are only suitable for equipment that was originally designed for pellets. Although the use of pressed miniblocks is also possible in conventional ovens. But this requires a certain modernization of the units.
Biofuels
Conventionally, all produced biofuel for fireplaces can be divided into three groups:
- Bioethanol, denatured alcohol with some additives for realistic fire.
- Biodiesel based on vegetable oils.
- Biogas fuel produced from human waste and is considered an analogue of natural gas. It is mainly used for industrial purposes.
Biofuels are produced all over the world: in Europe, America, Asia and even Africa. Currently, Brazil is the main supplier of such products. Let's look at the fuel for a bio fireplace in more detail:
- Bioethanol, which looks like a colorless, odorless liquid, is created on the basis of alcohol. Alcohol for creating fuel is obtained from carbohydrates that are found in sugar, which is the key to the naturalness of the product. Sugar is extracted from reeds, potatoes, beets, and corn. Ethanol can be produced from wood raw materials in which cellulose is present.
- Biodiesel fuel, like bioethanol, is a safe and clean product; when it gets into water, it does not harm other organisms and the environment. This fuel is created from vegetable and animal fats, which can be obtained from coconut, soy, palm oils. Almost every liquid fuel fireplace in Europe uses biodiesel.


Biofuels made in Switzerland
When choosing a biofuel for use in a fireplace, pay attention to the certification documentation, and then to the level of thermal performance of the fuel, a description of the color of the flame, its sharpness and sound. After all, you have chosen a biofireplace for yourself in order to be able to contemplate a real fire at home, which is safe for you and the environment.
Good to know: Biofireplace production: device, manufacturing technology, business
Is it better to say which is better: a hydrolysis boiler or a pyrolysis oven?
As you know, hydrolysis heating boilers are devices that run on solid fuels. They use firewood, straw, wood waste, coal, pellets and much more for their work.These boilers, operating on wood and coal, are widely used in heating systems for industrial and domestic premises. The advantages of such boilers include efficiency, ease of use, high environmental friendliness, and affordability. Hydrolysis boilers can be used even where there are power outages, or there is none at all.
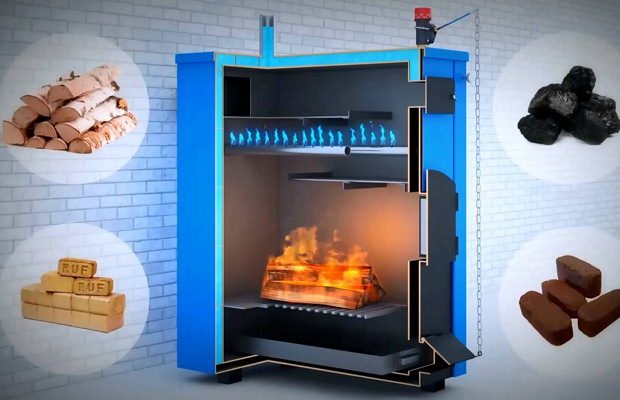


The combustion process of pyrolysis gases can be easily controlled and regulated, which makes it possible to automate the operation of such a boiler to approximately the same extent as the operation of gas or liquid fuel boilers.
Long-term searches for new energy-saving technologies have found it possible to qualitatively use the knowledge of organic chemistry.
Scientists have noticed that:
- In a high-temperature environment, in conditions of limited oxygen access, the combustion process of some solid natural substances is accompanied by the constant release of combustible gas;
- The resulting gas is suitable for further combustion;
- A lot of heat is generated during combustion.
In other words, the hydrolysis boiler can be called the progenitor of the new pyrolysis boiler. But it is irreplaceable where installation or maintenance of a modern model is impossible.