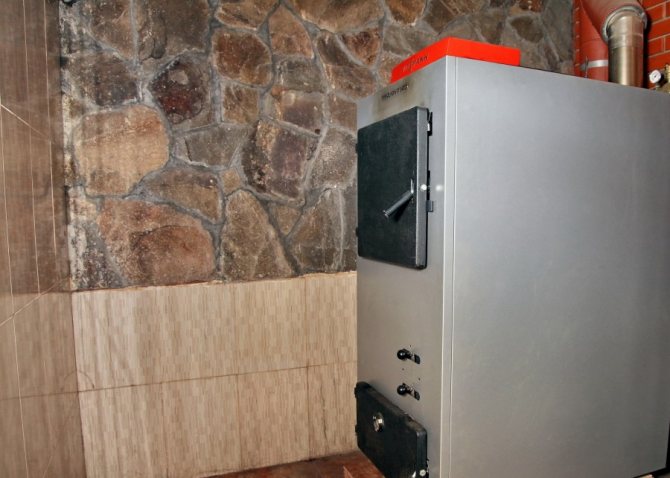
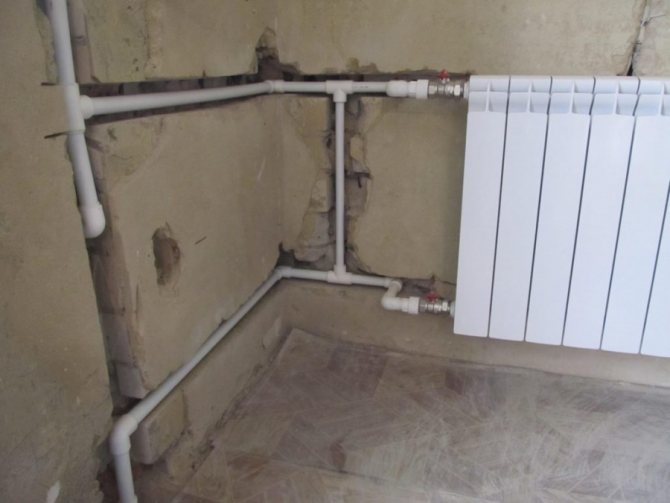
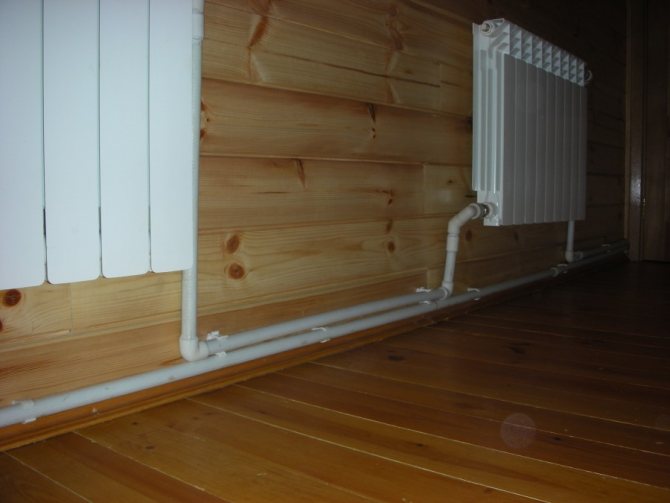
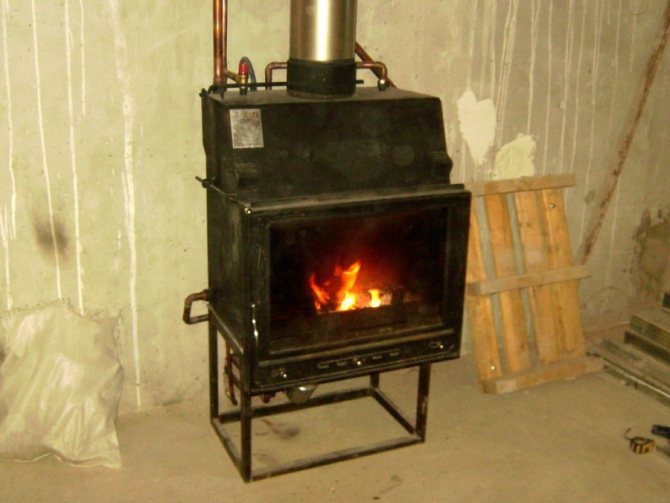
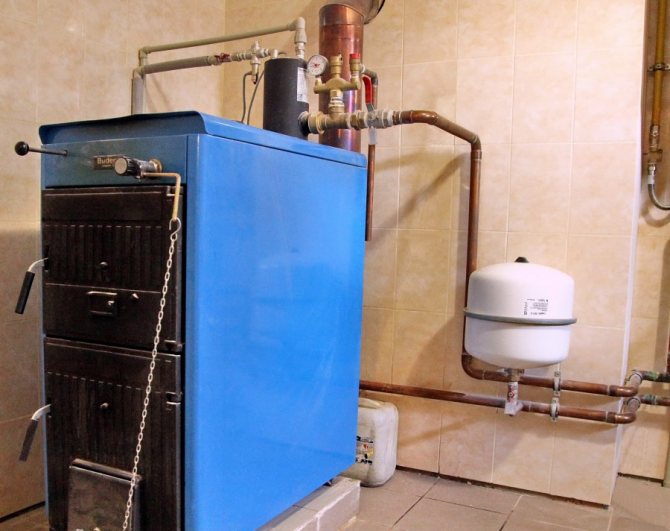
How the natural circulation heating system works
The main task of the water heating system - this is to make the coolant circulate through the pipes. In order for the house to warm up, hot water from the boiler must flow into pipes and radiators. The natural circulation heating system works on the principle of gravity. The liquid moves through the pipes in a gravity way without using a pump. The density and weight of the liquid becomes less when heated, and after cooling it returns to its original state.
In such a device, there is virtually no pressure. According to calculations, you can see that with a pressure of a 10-meter water column, there is a pressure of 1 atmosphere. It turns out that in the heating device of a one-story house the pressure will be from 0.5 to 0.7 atm., and in a two-story house - no more than 1 atm.
Advantages and disadvantages of natural circulation heating
As with any device, water heating with natural circulation has its advantages, but also disadvantages. Why is the system good?
- Simple installation and maintenance, easy system start-up. All installation can be done by yourself.
- No need to buy expensive equipment.
- The system works stably. The heat carrier gives the greatest heat output and maintains the required temperature in the room.
- No dependence on electricity. The device will continue to work if the power is cut off.
- If the house is well insulated, then with such a system you can save a lot.
- No pump that makes a lot of noise.
- If maintenance is carried out on time, the heating device can work for over 35 years.
Cons of the system:
- Despite the fact that the heating system requires few materials, the costs will become much higher when the local resistance of the pipeline decreases. Because you will have to install larger pipes.
- The house warms up much more slowly.
- If pipes pass through unheated rooms, then these areas should be insulated. Otherwise, there is a risk that the liquid will freeze.
- Such a heating system is only suitable for private houses with an area of no more than 100 sq. m., since it operates within a radius of up to 30 meters. This is due to the fact that the system has a small circular head.
- The main condition is an attic in the house. It is there that the expansion tank is installed.
Installation and slope calculation
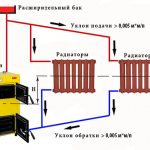
To prevent the movement of the coolant from being hampered by friction, slopes are created in the horizontal sections of the pipes. Thanks to this, the gravity heating system of a house like "Leningradka" has no places where air can accumulate. To calculate the slope, you need to remember that the difference in the height of each meter of the pipeline should be about 10 mm. But this rule does not always have to be followed with precision. If the number of branches and turns is less, then the slope may be less. In this case, the difference between the heights of the pipes over 1 m can be 5 mm. Thanks to the knowledge of these data, a calculation is made, on the basis of which all elements are installed and connected.
Installation is carried out in a certain sequence:
- When creating a two-pipe heating scheme with your own hands, you first connect a gas boiler, from which the main line is diverted upward, connected to an expansion tank. The latter is set at the highest point;
- After that, work is carried out to install a pipe from the bottom of the tank, which will be connected to the radiators.Its height is one third of the distance to the ceiling.
- Next, the radiators are connected, from the bottom of which pipes for the cooled coolant are diverted. Then the pipes are connected to a common line. To do this, you first need to draw up a diagram in which the two-pipe system will be fully displayed.
Installation of pipes for cold water is carried out in parallel with those through which the coolant enters the radiators. Do-it-yourself installation of a one-pipe system for a private house differs only in the layout of radiators and pipes.
Installation features
If the installation of a "Leningradka" type circuit is carried out, then the minimum number of pipes is used, because all radiators are connected in series at the same level. There are several ways to create such a system. For example, installation according to this scheme can be carried out without shut-off valves, due to which the coolant partially bypasses the radiator system. An option is possible in which taps are installed under all batteries. In this case, water begins to pass only through the radiators.
Bypasses (bypass sections of the pipe) are installed to adjust the heating level of the radiator, that is, when part of the coolant passes along the bypass path, the heat transfer of the radiator decreases.
The one-pipe system of the Leningradka type is installed in many houses due to the simplicity of the work performed. But it also has disadvantages, which include the lack of the ability to control the temperature in the room. Its installation can be carried out in a house with one or two floors. The two-pipe system is installed in cottages with many rooms and is more efficient.
Before starting work, it is necessary to make a hydraulic calculation.
Hydraulic calculation is the act of determining the optimal pipe diameter and calculating the liquid head drop to ensure efficient system operation. In some cases, the calculation is needed to determine the throughput of the highways.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the system operation, it is possible to determine:
- Possible pressure loss;
- Required pipe diameter;
- Number of radiators;
- Required slope.
The calculation is necessary to draw up a diagram according to which the boiler will be installed and other elements connected.
Before starting the installation of a heating system, the owner is faced with the choice of a way to circulate water in the system. This will be natural or forced circulation. Natural circulation in the heating system is the most common these days. What is a natural circulation heating system? It is a heating system in which water circulates naturally according to the laws of physics. Moreover, such a system does not need electricity or any additional devices.
The main feature of such a system is that water circulates through the system without the help of a pump, by gravity.
Natural circulation of heating
Types of natural circulation systems
Before creating a circuit for heating a private house, first calculate the amount of heat required for the premises. The calculation includes data on the boiler, placement and diameter of pipes, as well as the level of thermal insulation of the outer walls. Even the smallest errors in calculations can affect the quality of home heating. Therefore, it is better if all the calculations are carried out by specialists. Heating systems are of several types:
- Open and closed type (differ by expansion tanks).
- One-pipe and two-pipe type (heating radiators are connected in different ways).
Open system
The open device includes a reservoir (open tank), which is equipped with a pipe (emergency overflow). The pipe is connected to the sewer system or taken out into the street. The tank is installed under the ceiling, sometimes in the attic.An open-type tank can be made of any size with your own hands, which is its main advantage. Has an affordable price... Disadvantages of the device:
- You constantly need to add water to an open-type tank, as it evaporates quickly. In order not to constantly add water manually, a water pipe can be brought to the tank.
- Often, corrosion forms on the metal elements of the circuit. Due to the fact that oxygen is constantly flowing into the open tank.
- Air enters the pipeline. By fixing the radiators at a slight slope, and installing automatic air vents, you can get rid of the problem.
Closed system
Natural circulation system a closed-type coolant is well suited for both one-story and two-story houses. A membrane tank is installed in the heating circuit. Thanks to the tank, the metal parts of the device are less susceptible to corrosion. A closed device works as follows:
- The closed flexible diaphragm tank is a diaphragm expansion tank. The membrane creates two sections in the tank. The first section is for the coolant, the other contains air or nitrogen. During the expansion of the coolant, excess water from the heating circuit goes into the tank.
- The membrane begins to stretch due to hot water, and the gas in the second part starts to shrink.
- When the water cools down, the gas increases again and pushes the coolant back into the system. Thus, there is a continuous filling of the water circuit with the coolant.
If you choose between an open system and a closed one, it is cheaper to purchase or create an open tank with your own hands. Diaphragm tank costs several times more, so it is rarely used.
One pipe system
For single-storey houses with a small area, one-pipe heating is suitable. In a two-story house, this type of heating will be ineffective. The advantages of the system are cheap installation, simple design, pipes are not installed under the ceiling, which means that the overall interior of the room will not deteriorate. One-pipe type of heating works according to the following principle:
- The liquid rises along the vertical section of the pipe.
- Then the coolant moves into a horizontal pipe. This pipe connects the heating radiators.
- The cooled liquid returns back to the boiler from the outer radiator.
This system has its drawbacks. The further the supply riser, the lower the temperature of the radiators. Bypasses will help increase productivity. To establish uniform heating of the house, jumpers are placed in the places where radiators are connected. Even after making accurate calculations, a one-pipe type of system will be ineffective if a one-story house has more than three rooms. The problem can be solved by upgrading the system with a circular pump.
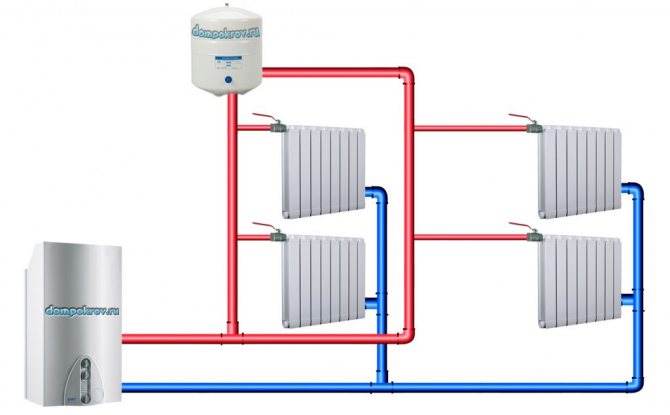
Scheme of two-pipe water heating for a private house with natural circulation
The two-pipe heating type is suitable for heating a two-story house. If we compare a one-pipe and two-pipe system, then in the second - the liquid is supplied to all radiators hot. The two-pipe circuit has a special design consisting of two pipes. One for supply, the other for return. A supply pipe is connected to each heating device. The connection is made through a separate input tap. And the return pipe is connected separately. The advantages of a heating system with upper and lower wiring are that its installation is very simple, and the operating characteristics are effective. With a system like this:
- It is possible not to add additional sections to the radiator in order to improve heating.
- Unlike a single-pipe circuit, pipes of a smaller diameter are used for laying the pipeline in this system.
- Easy system adjustment.
- The heat is evenly distributed.
Currently, it is possible to create with your own hands a two-pipe type of heating with natural circulation... For its manufacture, steel or polymer pipes are used..
Scheme for calculating a heating system with natural circulation
The most difficult thing in designing a heating system is the correct calculation. How well a device will perform depends on the length and angle of the pipes, as well as the number of turns on it. You need to know this because there is no pressure in the circuit. What you need to consider when drawing up a diagram and calculation:
- What is the diameter of the pipes and the material from which they are made.
- Angle of inclination of pipes.
- Types of coolants.
- Coolant supply methods.
Features of two-pipe heating

The two-pipe scheme differs in that a pipe with a slope departs from each radiator, along which water is removed. This means that after heating has been created, the temperature in all rooms will be the same. Also, the temperature can be adjusted in a specific room without affecting the water passing through the rest of the rooms. This is one of the advantages of such systems.
Another advantage is the ability to install more radiators. This means that such heating with natural circulation is suitable for heating large areas or several rooms more than single-pipe heating of the Leningradka type.
The main disadvantage is the significant amount of work during installation. To create two-pipe heating, you need to not only spend more time, but also buy more materials than one-pipe. The calculation of pipes according to the "Leningradka" scheme, with a slope, should be done especially carefully.
Comparison of the advantages of open and closed heating
In the open heating system "Leningradka", in contrast to the forced circulation design, in addition to the gas boiler, an expansion tank is installed that takes over the excess coolant and ensures its return after the liquid in the system cools down. Its principle of operation is based on the fact that some of the water evaporates, so its level must be checked periodically.
An open system of the "Leningradka" type differs in that the coolant circulates more slowly, therefore, when the gas boiler warms up, the temperature should be raised very gradually. In closed systems, a circulation pump is used, which contributes to the forced circulation of water. Their peculiarity lies in the automatic intake of excess coolant, which occurs thanks to an expansion tank with a valve. After the water cools down in it, it returns to the pipes again. This means that its level in a closed-type forced circulation system does not need to be monitored.
The advantage of heating without an expansion tank is the ability to use antifreeze instead of water. Thanks to this, forced circulation systems can be used in winter after a long break without preliminary preparation and slow heating of the boiler.
What is the best pipe material?
The method of installing the circuit, protection against corrosion and hydraulic resistance, all these indicators will depend on the material from which the pipeline is made. For the heating system, you can use polypropylene, steel, metal-plastic and copper pipes.
- Polypropylene material. Polypropylene pipes withstand high temperatures well, have a long service life (over 25 years), and are smooth inside. Installation requires special tools and is expensive.
- Steel. Despite the fact that such pipes are quite durable and have an affordable price, they are prone to corrosion and overgrowth. In addition, the installation requires welding or multiple fittings.
- Metal-plastic. Lightweight pipes have a perfectly smooth inner surface. As a result, they are free of corrosion and deposits.But after installation, you will have to constantly pull on the threaded fittings, which is a big drawback. Their service life is about 15 years, and for pipes this is very short. They have a high cost.
- Copper pipes. Copper pipes have a beautiful appearance and a service life of over 100 years. Soldering is used for installation, very expensive in cost.
To determine what pipe diameter suitable for warming up your home, you need to know that:
- The diameter of the pipe is selected according to the material from which the pipes are made and from the heat engineering calculations made.
- Calculate the amount of heat required for the room and add 20% to the result.
- Using the values indicated in the SNiP tables, the cross-section of the pipeline is calculated. For the calculation, readings of the heat capacity and the size of the pipe (internal section) are taken.
If, after each branching, install the supply pipe 1 size smaller than the previous one, then the circulation of the heat exchanger will become several times more intense. The return pipe is mounted with an extension. This calculates the minimum diameter of two pipes. Adhering to the obtained values, for each pipe section, its own size is established.
What it is
A one-pipe heating system scheme implies the absence of separate supply and return pipes. The coolant leaves the elevator unit or boiler and returns there along one ring that encircles the room or several rooms around the perimeter.
In contrast to it, there is a two-pipe system, in which each radiator is a jumper between two heating lines.
What kind of one-pipe system can be?
Closed and open
What is it and what is the difference between the schemes?
- A closed one-pipe heating system does not communicate with the ambient air and, accordingly, can have a rather large excess pressure in the circuit. If it is necessary to bleed air, this is done manually; the volume of water in the system is constant.
Useful: now automatic air valves have become widespread, which, without human intervention, release air and block the path of the coolant. Thanks to them, a one-pipe closed heating system is started by simply turning the valves and turning on (or kindling) the boiler.
- Open, in contrast to it, has a leaky expansion tank, into which air is displaced. It is clear that such a scheme leaves an imprint on the heating wiring. In particular, the ring passing along the perimeter of the house should be located above the heating devices - otherwise the air will collect in them.
The slope of an open heating system is needed for the same purpose - so that all the air is forced out into the expansion tank.
Horizontal and vertical
- A single-pipe horizontal heating system is most typical for a cottage or a private house. In general, the name is intuitive: the ring layout is located in the horizontal plane.
- A single-pipe vertical heating system is typical for two- or three-storey houses with a small floor area. The ring through which the coolant is pumped simply unfolds in a vertical plane. This scheme does not have any other fundamental differences.
Vertical one-pipe systems may include several parallel rings that connect at the bottom to form a common pipeline, which is why such a system is sometimes not quite correctly referred to as a single-pipe vertical heating system with a bottom wiring.
Flow-through and with by-passes
In a flow-through one-pipe system, the ENTIRE volume of the coolant passes only and exclusively through radiators or other heating devices. In the author's humble opinion, such a system is meaningful only if the ring surrounds ONE small room and supplies two or three batteries with heat.
Why is it so?
The disadvantages of such a scheme are too great, which are often described in a comparative analysis of heating systems as characteristic of all one-pipe systems:
- It is not possible to control individual heaters. It is worth pressing the throttle on one, and all the others will also stop heating.
- Dismantling one radiator requires a complete stop and reset of the heating system.
- The temperature difference between the first and the last heatsink is very large.
The bypass system uses the constant circulation of the bulk of the water through the weirs. More precisely, the MAIN ring is a thick pipe, parallel to which heating devices are cut in without breaking it.
The one-pipe heating scheme implemented in this way has a mass merits
:
- The circulation of water will be fast, and the temperature difference will be small.
- Adjusting a separate heater with a thermal head or throttle is no problem and will not affect the rest of the system in any way.
- Any radiator with shut-off valves can be turned off and removed without stopping the heating.
Correctly configured, such a system is extremely fault-tolerant and even in the most severe frosts, without any balancing, it will not stop and will not be defrosted. In addition, the price of materials is minimal, and all installation work can be done easily and in the shortest possible time with your own hands.
Forced and natural circulation
Forced circulation is not necessarily a circulation pump.
The single-pipe system of a private house, powered by an elevator unit connected to the heating main, is also forcibly circulating: the coolant sets in motion a pressure drop created from the outside.
It is customary to call natural circulation due to the natural thermal expansion of water. Having heated up, it rushes upward, for which the so-called booster collector is made as a constructive part of the boiler itself or the loop after it; and then it returns by gravity to the repeated heating cycle.
What needs to be considered when designing a one-pipe connection diagram for heating radiators in a system with natural circulation?
- The main ring must be large in diameter. A reasonable minimum would be DU32 for a house with an area about 100 m2
... More is better.
The reason is that the pressure difference between the points at the outlet from the boiler and at the inlet to it will be minimal. The smaller the diameter of the pipe, the more resistance it has to the flow of liquid in it.
Attention: do not confuse the outer diameter of the pipe and its DN, which is approximately equal to the inner clearance. The clearance of a pipe with an OUTER diameter of 32 mm, made of polypropylene, is only 20.1 mm, which is clearly not enough.
- After the booster manifold, the ring should go to the boiler with a constant slope of 5-7 degrees, thanks to which the cooling water can be transported by gravity.
- Plastic and multilayer pipes have a much less rough surface than steel pipes. More importantly, this surface does not overgrow over time with deposits that impede the flow of water in the pipe.
That is why for heating systems where the temperature of the coolant is not planned to be too high, any instructions for self-installation strongly recommend using polypropylene, metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene.
Coolant supply methods
The heating medium can circulate from the boiler to the heating device in two ways. Through the bottom or top filling.
- Bottom filling. This filling method is only used for one-pipe systems. The pipeline is laid at floor level, while vertical pipes can be omitted. Bottom filling is ineffective without a circular pump.
- Top filling. They are used for both one-pipe and two-pipe systems.Due to the fact that the distribution pipe is installed under the ceiling, the hot coolant is actively supplied to each radiator. Further, cooling down, the water goes into a return pipe mounted along the floor.
How to install a one-pipe system in a cottage
The general scheme has already been described. Let's repeat the main points again so that there are no ambiguities:
- Even if it is planned to use a circulation pump, it is better to ensure the normal operation of heating through natural circulation. The light is sometimes turned off, the wires are often torn by falling trees in a blizzard, and sitting without heating at -30 is at least unpleasant.
The way to do this is simple: after the boiler, the wiring pipe goes up sharply and then descends to the boiler along the perimeter of the house with a 5-degree slope. The pipe must be thick enough -DU32 - DU40 mm.
From the author: a more accurate hydraulic calculation of a one-pipe heating system operates with a huge number of variables, including pipe material, radius and number of turns, pressure drop, number and type of valves, and so on. In addition, take the word - the formulas used in the calculation are very complicated: Bernoulli's law describes only the simplest case of flow movement through a DIRECT pipe without taking into account the roughness of its walls.
The good news for us is that in the real world, the calculation of hydraulic heating — one pipe system or any other — is needed when designing an apartment building to save money. The difference in costs in the scale of state construction with a decrease in the diameter of the pipe by one step will amount to millions of rubles.
In the case of a small private house, we can afford to trust someone else's practice and simply put a pipe with a deliberate margin of diameter.
- The radiators cut parallel to the main ring.
A pipe DN20 mm is usually used for insertion. No narrowing of the main line between the points of the radiator tie-in is made: water will circulate through it anyway. - Each heater is supplied with a throttle or thermal head for regulation.
A valve is placed on the second inset, which allows it to be completely cut off and, if necessary, removed and replaced. - Radiators cut in from below on both sides.
Do not worry about the circulation in the sections: practice shows that any heating devices with such a connection ALWAYS heat throughout the entire volume and do not need to be flushed. - With the lower wiring (when it is located below the heating devices), each of them is supplied with an automatic air valve or manual air vent: a Mayevsky tap, a valve or a conventional water tap. A single-pipe heating system with top wiring does not need this: all the air will be forced upward into the expansion tank.
- Sometimes a slightly modified scheme of a one-pipe heating system of a flow-through type is used.
: A large diameter steel pipe (100-150 mm) is laid or suspended along the walls without any heating devices being cut in.
It can be masked with a decorative box that does not obstruct ventilation. The scheme is extremely simple, inexpensive to implement and VERY efficient in terms of heating.
Two-pipe system diagram
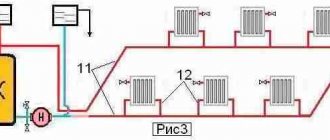
Here, heat is transferred to the radiators through one pipe, and the cooled water returns through the other. This allows for efficient operation of more batteries connected to one horizontal branch. In a one-story house, the supply collector is placed in the attic or under the ceiling, the return collector is above the floor. Overclocking is not required here, the pipe is already raised to a sufficient height, which is shown in the image:
As you can see from the diagram, the optimal solution for good natural circulation is a two-pipe heating system, divided into 2 branches with the same number of radiators on each.Otherwise, due to slopes over a long length, the installation of pipelines will be difficult. As for a two-story house, here again, vertical wiring is appropriate, but with a division into supply and return lines. How to do this correctly is reflected in the diagram:
With a two-pipe system, all batteries receive a coolant with the same temperature, this is an important plus. It also becomes easier to carry out automatic regulation, since the devices are independent of each other. The disadvantage is the higher consumption of materials for horizontal routing options, for example, in a two-story building:
For reference.
Most homeowners still install a circulation pump on the return manifold to improve system performance. But they put it on the bypass, so that in the event of a power outage, you can always go to gravity by opening the corresponding tap.
The principle of operation and features of gravity systems
As the name implies, in our case, the coolant moves through the pipelines independently, without any external influence using a pump. This type of circulation was originally used in all hot water heating systems. At the present time, when circulation pumps have appeared, the owners of private houses are interested in gravity schemes with one goal: to be independent from external sources of electricity.
The independent movement of the coolant is based on the phenomenon of convection. One and the same medium (in this case, water), which has different temperatures, also differs in specific gravity. In simple words, a cube of cold water weighs more than 1 m3 of hot water due to its different density. Inside the closed space of pipes, this will lead to the fact that the cooling medium will constantly push up the lighter hot water. A typical diagram of such a system is shown in the figure:
Due to the difference in the densities and masses of water inside the gravity heating system, a slight excess pressure arises that overcomes gravity and frictional forces, as a result of which a natural circulation of the coolant occurs. Hence the second name - gravitational.
Since the magnitude of the resulting excess pressure is small, favorable conditions must be created for the natural circulation of water in the heating system. This is facilitated by the following activities:
- the use of pipes of increased diameters, designed for a slow flow of water (0.1-0.3 m / s);
- compliance with the slopes of horizontal highways. The slope is at least 3 mm per 1 m of the pipeline;
- a significant difference in the temperatures of the coolant in the supply and return lines (at least 25 ° C);
- installation at the highest point of the network of an open-type expansion tank in communication with the atmosphere;
- installation of the boiler in such a way that its return pipe is as low as possible to the level of the heaters on the first floor.
For reference.
In practice, when arranging gravity systems with your own hands, main pipelines are laid from pipes with a diameter of at least 50 mm (2 inches), and the connections to the radiators are 20 mm (3/4 inches).
Often homeowners ask the question - is it possible to make the natural circulation system closed by installing a membrane-type expansion tank? The answer is obvious: when expanding, the liquid will have to overcome the resistance of the tank membrane, and the excess pressure in the network is already small. The speed of movement of the coolant will decrease to a minimum, or even to zero. Therefore, circuits using the gravitational principle of operation are always made open.
An important advantage that a gravity heating system gives is independence from electricity, which is very important in areas with unreliable power supply. But you have to pay for this with more expensive installation and large pipes going through all the premises.The scheme cannot be implemented in private houses of large area and number of storeys due to low efficiency and economic inexpediency. In such cottages, a closed-type system with a pump and uninterruptible power supplies is used.