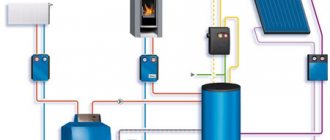
Connection options
Currently, there are two main connection schemes:
- dependent - it is considered the simplest, therefore it is most often used;
- independent - has gained popularity relatively recently, it is widely used in the construction of new residential areas.
Below we will take a closer look at each method in order to find out which solution will be the most effective for providing comfort and coziness to your premises.
Dependent connection method
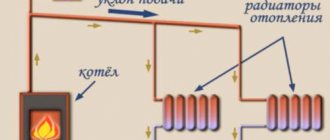
This connection option usually requires the creation of in-house heating points, often equipped with elevators. In their mixing unit, overheated water from the external main network is mixed with the return flow, which makes it possible to reduce its temperature to the required one, as a rule, below 100 ° C. Thanks to this, the heating system inside the house is completely dependent on external heat supply.

| Dignity | The main feature of the scheme is that water is supplied to the heating and water supply system directly from the heating main, so the costs in this case are paid off in a short time:
|
| disadvantages | As in any scheme, here you can find not only positive aspects, but also negative ones, among which it should be noted:
|
Connection methods:
- direct connection
; - with elevator
; - with on the jumper
; - with installation of the pump on the supply or return
; - combined version - elevator and pump
.

Independent connection method
Experts say that this option for heat supply makes it possible to reduce resource costs by almost 40%.
In today's situation, with their constant rise in price, this will significantly save the family budget.
- The principle of operation is as follows:
- connection of the heating system of subscribers is carried out using an additional heat exchanger;
- heating occurs due to two hydraulic isolated circuits - the main heating main heats the coolant of the closed internal heating network;
- in this case, no mixing of water takes place.
- The circulation of the coolant takes place in the heating mechanism due to the circulation pump, which regularly supplies it through the heating elements. In an independent connection diagram, an expansion vessel can be provided with a supply of water in case of leaks. In this case, it is possible to maintain the circulation of the coolant with a certain amount of heat even in case of accidents in the heating main. In fact, this suggests that if the supply of hot water along the heating main stops, the temperature in the heated rooms will not drop sharply for a long time.
- The scope of this connection method is quite wide, for example, it is used:
There is one condition - the pressure in the return line must be more than 0.6 MPa.
- Advantages of the method:
- the instruction allows temperature adjustment;
- great energy saving effect.
- Disadvantages:
- high price;
- the complexity of repair and maintenance work.
Comparison of schemes
- The dependent option has one, but an important advantage - the low cost of implementation.An elevator assembly in a small country house is easily assembled with your own hands from valves, which can be purchased in a store or on the market. The only expensive part will be only the nozzle, on which the power of the elevator depends.
- An independent scheme makes it possible to:
- adjust the temperature of the coolant;
- to increase the efficiency of use, bringing this level to 40%;
- The heating system does not receive a large amount of contaminants such as scale, sand and mineral salts. The heat carrier can be purified water or non-freezing liquids.
- you can easily heat clean drinking water for hot water needs.


Dependent
Such a connection scheme, as a rule, provides for the presence of in-house heating points, often equipped with elevators. In the mixing unit of the heating station, overheated water from the main external network is mixed with the return one, while acquiring a sufficient temperature (about 100 ° C). Thus, the internal heating system of the house is completely dependent on the external heating supply.


Dignity
The main feature of such a scheme is that it provides for the flow of water into the heating and water supply systems directly from the heating main, while the price pays off quite quickly.
- subscriber input equipment is simple and inexpensive;
- heating systems can withstand large temperature differences;
- the size of the pipeline is smaller in diameter;
- the scheme reduces the consumption of the coolant;
- low operating costs.


disadvantages
Along with the advantages, this connection also has some disadvantages:
- inefficiency;
- regulation of the temperature regime is significantly difficult during weather extremes;
- overexpenditure of energy resources.
Connection methods
Connection can be made in several ways:
- through direct attachment;
- with an elevator;
- with a pump on the lintel;
- with a pump on the return or supply lines;
- mixed method (pump and elevator).
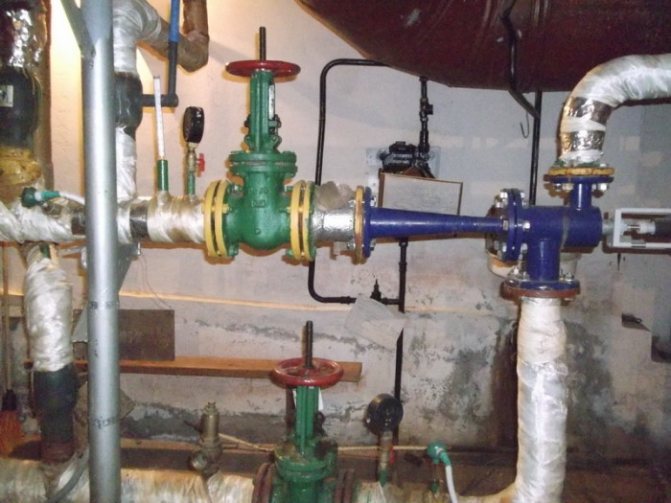


Connection with an elevator.
Comparison of reliability and durability
The practice of operating technically complex and multi-level systems shows that they are less maintainable and more often have to undergo preventive inspections with maintenance measures. It cannot be said that the independent connection of the heating system reduces the overall level of reliability and safety (in some cases even increases), but the tactics of carrying out repair and restoration measures should be at a different and more responsible level.


At a minimum, an increase in labor and time resources will be required when inspecting the heat exchanger and the adjacent piping. Possible uncontrolled accidents at this node can damage the pipeline. Therefore, experts recommend installing several sensors with pressure, temperature and tightness control. The newest collector cabinets also provide for the use of self-diagnostic complexes for continuous monitoring of the system state. As for the closed heating infrastructure, such instrumentation will not be superfluous for it either, but in this case its need is not so high.
Pros of independent systems


Already on the way to the main consumers of the home water supply network, a whole set of preparatory measures is provided to ensure the distribution, filtration and adjustment of the coolant pressure. All loads fall not on the end equipment, but on a heat exchanger with a hydraulic tank, which directly take resources from the main source. Such resource preparation is practically impossible in private when operating dependent heating systems.The connection of an independent circuit also makes it possible to rationally use water for drinking needs of optimal purification. The streams are divided according to their intended purpose and on each line they can provide for a separate level of preparation corresponding to the technological requirements.
Independent heating system
The principal feature of this system is the presence of an intermediate collection point. In residential private houses, it can be implemented as a control station (including for pressure reduction), but the integration of a heat exchanger makes this scheme independent. It performs the functions of a rational and balanced redistribution of hot streams, also maintaining, if necessary, the optimal temperature regime. That is, with an independent connection of the heating system, the heating network as such does not act as a direct source of supply, but only directs the flows to an intermediate technological point. Further, from it, in accordance with the settings made in a more point version, the supply of drinking water and hot water supply with heating and other household needs can be made.
Independent heat supply scheme
An independent heating scheme looks like this:
- from the supply pipeline, the liquid enters the return line, while simultaneously giving off thermal energy to the heat exchanger. In this case, water is not used for hot water supply and space heating;
- the same heat exchanger, but its other circuit receives drinking water from the water supply. After heating, it is supplied to the heating system and for household use.
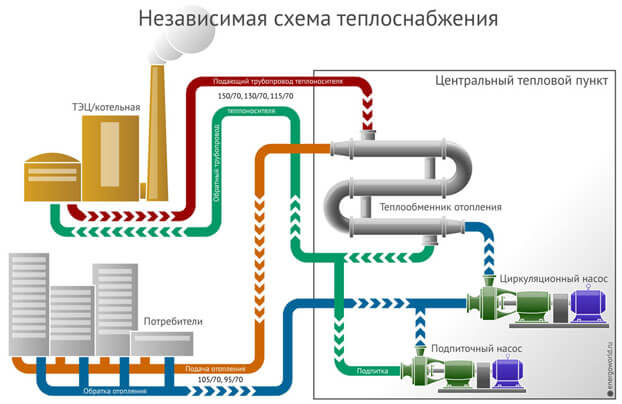

This is what an independent heating system connection looks like.
Which heat supply scheme is better


There is one more drawback in gas non-volatile heating boilers - they do not have the ability to control the weather and control the unit by an external thermostat, which determines the temperature regime, for example, in the most remote room. Accordingly, it is not possible to program the temperature for a long period, for example, for two weeks.
About the types of heating systems in detail on the video:
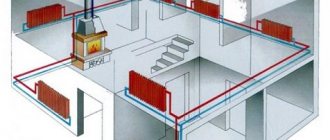
In apartment buildings, the overwhelming majority of them use the central heating system for heating. However, the quality of such services depends on many factors, including the condition of the heating main and equipment. The scheme of connecting the house to the heating network is also important. In this case, you will learn about dependent and independent connection methods, as well as how to make heating in an apartment non-volatile.
Heating system volatility
Volatility is understood as the ability of heating to work in the absence of power supply. Energy independence may be needed when there is a danger of frequent and prolonged power outages. You can, of course, install an emergency power supply at home: an electric generator or batteries with an inverter. The automatics will start emergency power supply immediately after power failure in the network. But the equipment costs money and not everyone is willing to go to the expense. How to ensure non-volatility of heating?
First, to provide non-volatile heat generation. Finding a solid fuel boiler that does not require an electrical connection is not a problem. But the vast majority of pellet, liquid fuel and especially gas boilers are equipped with automation that does not work without power supply. Nevertheless, you can find models with simpler controls. But you need to understand that you should not expect special efficiency and high comfort from a non-volatile gas boiler.


Gas non-volatile heating boilers are equipped with the simplest control. Piezoelectric ignition, the set level of the coolant temperature is maintained
Secondly, to ensure effective circulation of the coolant. The movement of liquid through pipes and heating devices can be carried out naturally (gravitationally) and forced (circulation). Let's briefly explain these concepts:
Gravitational (non-volatile) heating
The movement of a liquid in a gravitational system occurs due to the difference in the densities of a heated and already cooled liquid. The hot coolant, leaving the boiler, has a lower density and volumetric weight than the one that has already passed through the pipes and batteries, cooled down. Accordingly, heated water constantly rises, cooled water descends. As long as there is a sufficient temperature difference, the coolant circulates. For normal operation of the gravitational system, a number of stringent conditions must be met:
- The boiler must be installed at the lowest part of the system. It is desirable in a pit if heating devices are located on the same floor.
- All horizontal pipes must have a slope in the direction of movement of the coolant.
- The diameter of the pipes must be large enough to reduce the flow resistance. For an individual residential building, this is approximately 35-50 mm.
The advantages of gravitational heating include simplicity of design and energy independence. The "gravitational" system has a lot of disadvantages:
- Difficulty of adjustment, low efficiency.
- The natural pressure of the liquid is low, therefore the rate of passage of the coolant in the pipes is low, which is why the heating is very "thoughtful", reluctantly warms up and does not quickly respond to changes in the boiler operating mode.
- The longer the pipelines, the weaker the circulation and the worse the heating of the remote radiators. Horizontal branches over 30 m in length will not work normally at all.
- The low flow rate of the liquid corresponds to a low heat transfer, the dimensions of the heating devices have to be increased.
- In a non-volatile gravitational system, it is impossible to arrange underfloor heating, the choice of heating devices is limited to standard radiators.
- Thick pipes, which are difficult to hide, do not look aesthetically pleasing.


Gravitational heating is relatively simple, but it is necessary to strictly observe the necessary slopes in the direction of movement of the coolant
Circulating (volatile) heating
In a circulation system, the movement of the coolant is controlled by a circulation pump. The pump creates a pressure sufficient to eliminate all the limitations associated with overcoming hydraulic resistance, characteristic of gravitational heating. The circulation system is completely devoid of the drawbacks of the gravitational one. In it, without taking into account the slopes, pipes of small diameter are used, which is why they are easy to hide in grooves or screeds. There are no restrictions on the height of the boiler, the expansion tank can be placed in the boiler room. In addition to wall-mounted radiators, underfloor heating, floor convectors are available, you can additionally heat the air for supply and exhaust ventilation, pool water. The forced movement of the coolant makes it possible, with proper design and adjustment, to constantly maintain the set temperature in all rooms. Heating quickly warms up, sensitively reacts to changes in the heating mode.
The circulation system is more economical, more comfortable and more aesthetically pleasing than the gravitational one. Its only significant drawback is its volatility. In our opinion, the numerous advantages of "circulation" clearly outweigh its only drawback, and when choosing a heating system for a modern comfortable house, it is worth giving preference to it. And you can insure against power outages by installing a generator or battery.


An example of circulating heating, pipe slopes do not really matter
The gravity system also has the right to live in a country house or in a country house, in which high requirements are not imposed on the aesthetics of the interior, comfort and efficiency of heating. It is more logical to combine natural circulation with a solid fuel boiler. A rational solution is to install a circulation pump in parallel on the supply pipe of the gravity system. This will allow the heating to be operated in two modes: in the presence of electricity, it will work as a circulation one, more economically and comfortably. No electricity - it operates in gravity mode. Less efficient, but works.


A circulation pump is built into the gravity circuit, where all the requirements for slopes and pipe diameters are met, so that the coolant can circulate both by gravity and forcibly
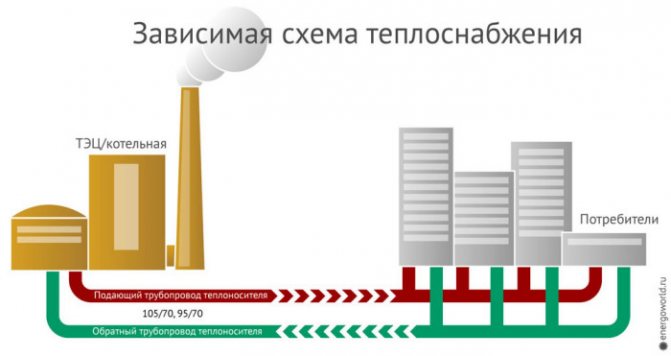
Dependent heating system
The central link of such communications is the elevator unit, through which the tasks of regulating the coolant are performed. From the heating main to the distribution unit of a residential building, water is supplied through a pipeline, and mechanical control is carried out by a system of inlet valves and valves - typical plumbing fixtures. On the next level, there are locking mechanisms that regulate the supply of hot water to the return and inlet circuits. Moreover, the heating system in a private country house can provide for two tie-ins - on the return line and the supply channel. Further, after the home inserts, there is a chamber in which the coolants are mixed. Hot streams can indirectly contact water in the return loop, transferring part of the heat to it. Summarizing this part, we can conclude that water is directed to the DHW system directly from the central heating main.
Terminology
Let's get rid of the confusion first.
Energy independence
Is the ability of heating equipment to work in the absence of electricity. The ability is undoubtedly pleasant, but we are not talking about it now. However, we will also touch on this topic.
What is the difference between an independent and dependent heating system? Connection diagram to the heating main.
Dependent schema
Imagine an ordinary residential building. How does it work?
- Entrance valves cut off the elevator from the line.
- Behind them, on the supply and return, valves or valves are embedded through which hot water supply can be fed from the supply or return pipeline.
- After the hot water connections, we see the actual elevator - a nozzle with a mixing chamber. A jet of hotter water with high pressure from a direct pipe heats up part of the return water and draws it into re-circulation.
- Finally, house valves cut off the heating system. They are closed in summer and open in winter.
A key feature that a dependent heating scheme has is that water enters the heating and water supply systems directly from the heating main.


Independent scheme
Now let's imagine another scheme:
- Water from the supply pipeline goes into the return, giving energy to the heat exchanger along the way. Again, water is not used for heating and hot water supply.
- In the same heat exchanger, but in its other circuit, drinking water is supplied from the water supply. It heats up and enters the heating system. It can also be used for economic purposes.
Actually, we have exhaustively described an independent heating system connection diagram.
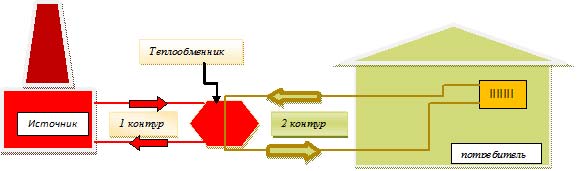

Dependent heat supply scheme
If we imagine the elevator unit of a residential building (you can see how it looks in the photo), then it is arranged as follows:
- the elevator is separated from the heating main by the inlet valves;
- behind them, in the place of supply and return, valves or valves are located. Through them, hot water supply is connected from the supply or return pipelines. Often in modern elevators there are two tie-ins on the supply line and return line, which are separated by a retaining washer.Their purpose is to ensure constant circulation of hot water;
- after inserting the elements for providing DHW, there is a nozzle with a chamber where mixing is carried out. A stream of hotter liquid coming from a direct pipeline under high pressure heats up some of the water in the return and is sent for re-circulation;
- house valves shut off the heating system of the building - they are open in winter and closed in the warm season.


Dependent and independent heating systems differ in that in the first version, water enters the hot water and heat supply systems directly from the heating main.
Comparison of solutions
The dependent circuit for connecting heating has, in essence, only one advantage, but very important - the low cost of implementation. An elevator unit for a small cottage can be assembled with your own hands from consumer-grade shut-off valves
Noticeable against the background of the wiring of batteries around the house will be only the price of making the nozzle - the only exclusive one made, the diameter of which determines the thermal power of the elevator.
What is the asset of an independent scheme?
Incomparably more flexible temperature control. It is enough just to reduce the flow of the coolant through the heat exchanger - and the house will become colder.
- The practical consequence of flexible adjustment of heating to the needs of the house is economy.
In relation to the dependent system, it is estimated at 10-40 percent. - Finally, the main thing: in a dependent system, we are forced to use water with a lot of pollution.
It carries sand, scale and a lot of mineral salts.
We are not talking about the use of water as drinking water, moreover, in some regions it is undesirable to even wash with hot tap water. An independent scheme makes it possible to use purified water or non-freezing coolants as a coolant.
For the needs of hot water supply, it is not a problem to heat drinking water.
Dependent and independent heating system - comparison
The advantage of a dependent heating connection scheme is that the cost of its implementation is inexpensive. The fact is that with a small area of \ u200b \ u200bthe house, the elevator unit of the heating system for it can be mounted independently, using ordinary shut-off valves for this. The most expensive is the manufacture of the nozzle, the thermal power of the elevator depends on its diameter.
Advantages that an independent heat supply scheme has:
- it allows you to more flexibly regulate the temperature of the heating medium for heating. To do this, it will be enough to reduce the flow of coolant through the heat exchanger, and as a result, the air temperature in the house will drop. It is also possible to press the valves in the elevator unit and thereby remove the differential. Such a scheme of an elevator heating unit will avoid many problems. But for these elements, such a situation is considered abnormal, since the cheeks may fall and the circulation may stop. If the system is independent, the capacity is regulated simply - using a circulation pump;
- efficiency is a consequence of the availability of flexible heating settings depending on the needs of residents. In the dependent system, this indicator is at the level of no more than 40%;
- an independent heat supply system allows the use of water purified from impurities or non-freezing liquids as a heat carrier (for more details: “Non-freezing liquid for heating systems - we make the right choice”). It is not difficult to heat drinking water for hot water supply. In turn, in the presence of a dependent system, consumers are forced to use water with large pollution - sand, scale and mineral salts.


Dependence on electricity
Now let's get back to volatility. When is electricity needed for the heating system to function, and when can you do without it?
Solid fuel boilers
The canonical solution is a conventional steel or cast iron boiler with a water jacket in the firebox and mechanical adjustment of the blower by means of a thermostat. This unit is completely non-volatile.


The photo shows a classic solid fuel boiler.
However, this design has an important disadvantage: the boiler requires frequent fuel loading. Three technical solutions allow making heating as independent of a person as possible:
- Hopper and conveyor belt,
as the fuel burns out, feeding new portions of sawdust or pellets. Electricity is necessary at least for the operation of the conveyor. - separates combustion into two stages: firewood pyrolysis with a limited oxygen supply and combustion of the resulting gas. In this case, the gas combustion chamber is located below the pyrolysis chamber. The movement of combustion products against the natural thrust vector requires the operation of an electric fan.
- Top combustion boiler
able to work on one coal fill for up to five days. Only the top layer of fuel smolders; air is supplied to it from top to bottom, and ash is carried away by a stream of hot combustion products. Air circulation is provided ... correctly, by an electric fan.
Gas
Non-volatile gas heating boilers use manual ignition with a piezoelectric element and flame regulation with a mechanical thermostat. When the main burner is extinguished at a high temperature of the coolant, the pilot continues to work.


Boilers with electronic ignition stop the gas supply completely during standstill. As soon as the coolant cools down below the critical temperature, the discharge ignites the main burner, and heating resumes. In addition, a forced draft fan is often driven by electricity to supply air to the burner.
Which circuit is better? If you have frequent power outages, a non-volatile gas heating boiler would be more appropriate. Precisely because he is able to do without electricity in principle. On the other hand, these devices are less economical: maintaining the pilot flame takes up to 20% of the total gas consumed.
Another useful feature that gas non-volatile heating boilers are deprived of is the ability to control the weather and control by an external thermostat that removes the temperature, for example, in a remote room. Of course, we are not talking about programming the temperature regime for a day or a week either.
Solarium
Everything is simple here: solar boilers are COMPLETELY identical to gas boilers with electronic ignition. Only the burners differ. Actually, a lot of dual-fuel plants are produced.
It is clear that devices simply cannot work without a forced draft fan and electronic ignition.


Dependence of systems on electricity

Natural circulation circuit can work without electricity
Energy dependence of systems is defined as the ability to operate with or without electricity. Non-volatile communications are mounted in conditions of prolonged light off. For the normal functioning of heating, several methods are used:
- Installation of an electric generator or inverter batteries. The devices start up power after the mains are de-energized.
- Providing non-volatile heat generation. You will need an automatic boiler - pellet, liquid fuel or gas. The equipment operates without electricity, but it is uneconomical for the main fuel.
- Creation of gravitational pressure. The liquid moves through the difference in density when heated and cooled. The heated water masses go up, the cooled ones go down. Gravitational pressure is created by installing the boiler at the lowest point, the slope of the horizontal pipeline along the movement of water.
For gravitational heating, pipes with a diameter of 35 to 50 mm will be needed.
When implementing circulating or volatile heat supply, you will need a circulating pump.The system is connected to pipes of any diameter; special convectors and underfloor heating also work for heating. The water temperature is maintained at a predetermined level. In the event of a power outage, generators are installed.
Safety and efficiency of independent heating systems
To be able to save money on heating, several conditions must be met:
- Develop and approve the project in the licensing authorities. Without an approved by the GUI and agreed with all instances of the project, all modifications will be illegal. Therefore, it will not be possible to take advantage of the results.
- Carry out installation or reconstruction of existing equipment in accordance with the design solution.
- Install a heat energy meter. This will allow you to pay for the heat energy received exactly in the volume in which it was consumed.
- Provide the required level of automation or manual regulation. The CHP plant does not react very quickly to temperature changes in weather conditions and can continue to burn their boilers to the fullest. And through the heat exchange tank, unclaimed energy will be transferred to the networks of consumers who open windows and vents from excessive heat.
Installation and connection of an independent heating system
Installation work in its complexity is not much more difficult than the gravity track. Of the additional activities, it is worth noting the need to organize an uninterruptible power supply. This will make it possible not to be left without heat in the event of a power outage and is realized by automatically turning on an uninterruptible power supply battery or a liquid-fueled electric generator.
In addition, the existing centralized routes are also subject to modernization by separating coolants with a heat exchange tank, installing a forced circulation pump and an uninterruptible power supply. In this case, replacement or dismantling of pipelines with radiators is not required.


The schemes according to which heating devices are connected are of two types. Depending on the use of the scheme, two types of heat supply systems are distinguished - dependent and heat supply.
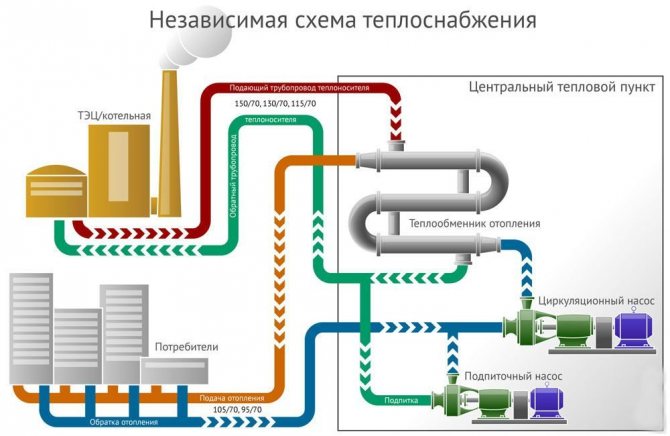
The meaning of an independent heat supply system is that the subscribers' equipment is hydraulically isolated from the heat energy supplier. And in order to provide subscribers with heat, auxiliary exchangers of central heating points are needed.
In the case of using a dependent system, it must be permanently connected to the energy carrier. Such a system consists of pipes and a boiler, which are interconnected into one whole. The meaning of a dependent heat supply system is to circulate hot water in a circle in a continuous mode. Due to the fact that the dependent system is completely tied to the heating main, which is the main source of thermal energy, when using it, it is impossible to adjust the water temperature or even, in case of warming, turn off the heating.

Dependent heating system diagram
When using an independent heating system, different types of fuel can be used. It should be noted that the installation of such a system is quite expensive. Unlike the dependent system, the independent water can be used for other needs. It is also an advantage that the independent one is much easier to install in the building.
Among other things, such a system provides an opportunity to save money due to the fact that it requires a small amount of fuel to operate. The amount of fuel can be adjusted at will, thereby creating a comfortable environment in the premises.
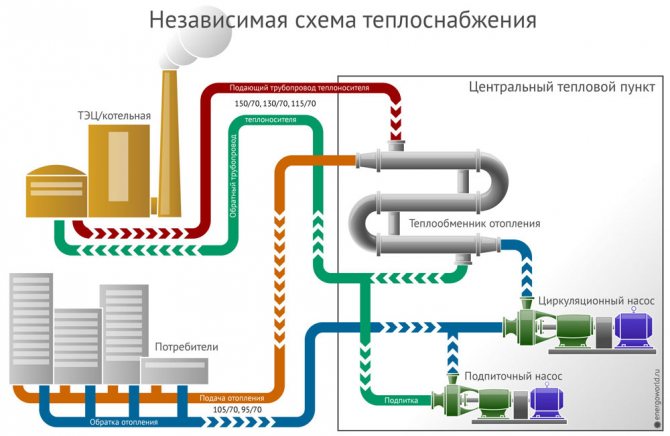

Diagram of an independent heating system
Principle of operation
As noted above, for the operation of the dependent system, industrial water is used, which, during operation, leaves salt and sand in the pipes, which interferes with the permeability of water in the pipes.In the case of an independent one, it is possible to use a purified one. At the same time, the equipment can be shown to have a sufficiently long service life.
An independent heating system completely dispenses with electricity. It may be needed only if a bunker and a conveyor are mounted in order to supply fuel to the boiler.
It is also possible to use a boiler operated with. Such boilers are a structure consisting of mechanical, thermostat, and steel tanks. Such a system does not tie you to the gas main.
Schemes for connecting heating systems to heating networks
Normal operation of the elevator occurs at H / h = 8-12 (H is the available head at the inlet; h is the resistance of the heating system).
It should be borne in mind that the value of the design head in front of the elevator is directly proportional to the resistance of the heating system. Therefore, an increase in the resistance of the heating system, for example, by 1.5 times will cause an increase in the design pressure R also by 1.5 times.
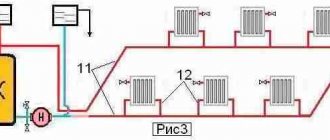
Connection with a pump on the jumper (c). In the event that water mixing cannot be performed using an elevator, a pump is installed on the jumper between the supply and return pipelines of the heating system. Mixing with the help of an elevator cannot be performed for the following reasons: the head at the connection point is insufficient for its normal operation; the required thermal power of the mixing unit is large and goes beyond the capacity of the manufactured elevators (usually more than 0.8 MW - 0.7 Gcal / h).
When installing mixing pumps in residential and public buildings, it is recommended to use a silent, foundationless pump. When installing mixing pumps designed for high flow, centrifugal type K and KM are used as mixing pumps. The pump flow is equal to G2 = 1.1G1, and the head should be equal to H = 1.15h (where h is the resistance of the heating system).
Connection with a pump on the supply pipe of the heating system (d). A pump on the supply line is installed if, along with mixing water, it is necessary to increase the pressure in the supply line at the point of connection of the heating system (the static height of the heating system is higher than the pressure in the supply line at the point of connection).
The pump flow is equal to G3 = 1.1 (1 + U) G1, and the head should be equal to:
Hsat = 1.15h + hn
where h is the resistance of the heating system; hn is the difference between the static height of the heating system and the piezometric height in the supply pipe of the heating network at the point of connection, m.
Connection with a pump on the return pipe of the heating system (e). A pump on the return pipe is installed if, along with mixing the water, it is necessary to reduce the pressure in the return pipe at the connection point of the heating system (the pressure is higher than the allowable pressure for the heating system). The pump flow in this case is equal to C3 = 1.1 (1 + U) G1 and the head must have a value that provides the required pressure in the return pipeline.
Independent affiliation (e). If the pressure in the return pipe in the heating network is higher than the permissible pressure for the heating system, and the building has a significant height or is located at a high place in relation to adjacent buildings, then the heating system is connected according to an independent scheme.
According to an independent scheme, it is allowed to connect buildings with a height of 12 floors or more. The independent scheme is based on the separation of the heating system from the heating network using a heat exchanger, as a result of which the pressure in the heating network cannot be transferred to the heating medium of the heating system. The circulation of the coolant is carried out using circulation pumps of the K and KM types. The pump flow is determined by the formula
G = Q / C (T11-T22)
where Q is the power of the heating system, kJ / h (Gcal / h); C is the heat capacity of water, J / (kg · h); T11, T22 - design water temperature, respectively, in the supply and return pipelines of the heating system, ° С
The required head of the pump should be equal to H = 1DM (psh k — resistance of the heating system). When choosing a head, one should strive for a minimum margin in flow rate and head. Otherwise, due to the increased water consumption in the heating system (speed is higher than the permissible), noise occurs. An independent heating system is usually equipped with an expansion vessel. Water leaks from the heating system are replenished from the network automatically according to the water level in the expansion tank.
Dependent heating system
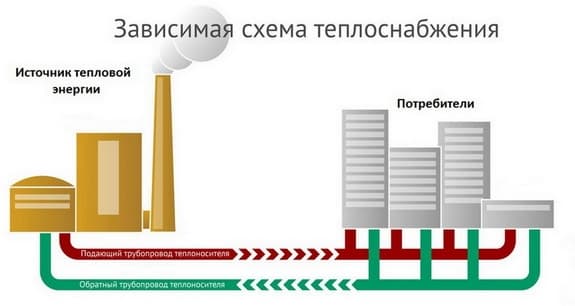
A dependent system is often called open. And it is called so, because the heat carrier is taken from the supply pipe to provide the house with hot water. The dependent scheme is often used in administrative, multi-apartment and other buildings that are intended for general use. The peculiarity of an open system is that the coolant flows through the main networks and enters the house immediately.
If the temperature of the heat carrier in the supply line is no more than 95 ° C, then it can be directed to heating devices. But if the temperature exceeds 95 ° C, then it is necessary to install an elevator unit at the entrance to the house. With its help, the water that comes from the heating radiators is mixed into the hot coolant to lower its temperature.

Previously, no one paid special attention to the flow rate of the coolant, therefore such a scheme was often used. The dependent heating system does not require large installation costs
There is no need to lay additional pipes to provide the house with hot water.
But in addition to the above advantages, one can also highlight the disadvantage of a dependent heating system:
- It is problematic to adjust the temperature regime in the premises. The valves quickly fail due to the poor quality of the heat carrier.
- From the main pipes, various dirt and rust gets into the heating radiators. Steel and cast iron radiators continue to work without any changes. But in aluminum batteries, the ingress of rust and dirt has a detrimental effect on work.
- Although the coolant goes through all the required desalination and cleaning, it still passes through the rusty main pipelines. Accordingly, the coolant cannot be of good quality. This factor is a big disadvantage, since the coolant goes to water supply.
- Due to repair work, pressure drops in the system or even water hammer often occur. Such problems can seriously affect the operation of modern radiators.
Independent (closed) heating system
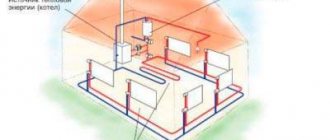
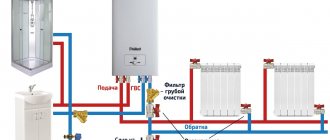
Currently, when constructing new boiler houses, an independent scheme for connecting the heating system has become more often used. It contains the main and additional circulation circuits, hydraulically separated by a heat exchanger. That is, the coolant from the boiler room or CHP goes to the central heating point, where it enters the heat exchanger, this is the main circuit. An additional circuit is a house heating system, the coolant circulates in it through the same heat exchanger, receiving heat from the network water from the boiler room. The scheme of operation of an independent system is shown in the figure:
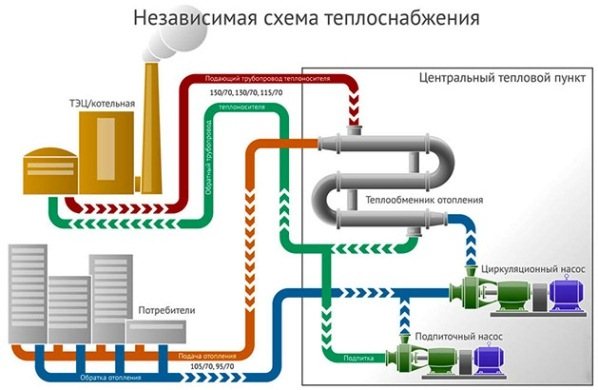

For reference. Previously, such systems used bulky shell-and-tube heat exchangers that took up a lot of space. This was the main difficulty, but with the advent of high-speed plate heat exchangers, this problem ceased to exist.


But what about the centralized supply of hot water, because now it is impossible to take it from the mains, the temperature there is too high (from 105 to 150 ºС)? It's simple: the independent connection scheme allows the installation of any number of plate heat exchangers connected to the main pipelines. One will provide heat to the heating system of the house, and the second can prepare water for household needs. How this is implemented is shown below:


To ensure that hot water always flows at the same temperature, the DHW circuit is made closed with the organization of automatic make-up in the return pipe.In apartment buildings, the DHW circulation return line can be seen in the bathroom, heated towel rails are connected to it.
It is obvious that operating an independent heating system has many advantages:
- the home heating circuit does not depend on the quality of the external heat carrier, the state of the main networks and pressure drops. The entire load is borne by the plate heat exchanger;
- it is possible to regulate the temperature in the premises using thermostatic valves;
- the coolant in a small circuit can be filtered and cleaned of salts, the main thing is that the pipes are in good condition;
- in the hot water supply system there will be drinking-quality water entering the house through the water main.
Nevertheless, due to the dirty coolant of poor quality in the central network, periodic flushing of an independent heating system, or rather, a plate heat exchanger, will be required. Fortunately, this is not so difficult to do. Another disadvantage should be noted the higher costs for the purchase of equipment, namely: heat exchangers, circulation pumps and shut-off and control valves. On the other hand, a closed system is safer and more reliable than an open one, it meets modern requirements better and is better adapted to new equipment.
Dependent open heating system
The main feature of the dependent system is that the coolant flowing through the main networks directly enters the house. It is called open because the coolant is taken from the supply pipeline to provide the house with hot water. Most often, such a scheme is used when connecting multi-apartment residential buildings, administrative and other public buildings to heating networks. The operation of the dependent heating system circuit is shown in the figure:
At a temperature of the coolant in the supply pipeline up to 95 ºС, it can be directed directly to the heating devices. If the temperature is higher and reaches 105 ºС, then a mixing elevator unit is installed at the entrance to the house, whose task is to mix the water coming from the radiators into the hot coolant in order to lower its temperature.


The scheme was very popular in the days of the USSR, when few people were concerned about energy consumption. The fact is that the dependent connection with the elevator mixing units works quite reliably and practically does not require supervision, and installation work and material costs are quite cheap. Again, there is no need to lay additional pipes to supply hot water to houses when it can be successfully taken from the heating main.
But this is where the positive aspects of the dependent scheme end. And there are much more negative ones:
- dirt, scale and rust from the main pipelines safely gets into all consumer batteries. Old cast-iron radiators and steel convectors did not care about such trifles, but modern aluminum and other heating devices were definitely not good enough;
- due to a decrease in water intake, repair work and other reasons, there is often a pressure drop in the dependent heating system, and even water hammer. This threatens with consequences for modern batteries and polymer pipelines;
- the quality of the coolant leaves much to be desired, but it goes directly to the water supply. And, although in the boiler house water goes through all stages of purification and desalination, kilometers of old rusty highways make themselves felt;
- it is not easy to regulate the temperature in rooms. Even full bore thermostatic valves quickly fail due to poor quality of the coolant.
Dependent and independent heat supply scheme - zhkhportal.rf
Dependent and independent heat supply systems differ in the way they are connected and have fundamental differences.In further publications, we will dwell on their differences in more detail, offer detailed, schematic calculations. Now we will present to you only the basic, conceptual definitions of the differences between systems.
Dependent heat supply systems
In dependent heat supply systems, there are no intermediate heat exchangers, heating points. These are systems in which the coolant flows directly into the consumer's heating system. The main advantage of such systems is its simplicity from a constructive point of view. The main disadvantage of a dependent heat supply system is the extremely low efficiency of the system. The great difficulty in regulating the temperature of the coolant during sharp temperature changes in the weather leads to overheating or underheating of the premises (decrease in comfort), as well as to excessive consumption of consumed energy resources.
The use of this system during construction has now been abandoned.
Independent heating systems
The transition from a dependent heat supply system to an independent one allows you to save consumed resources by 10-40% per year. Independent heat supply systems are systems in which the heating system of consumers is separated from the heat producer through the use of hydraulically isolated circuits. Heat exchangers of various designs (tubular, plate, etc.) are used in the role of hydraulic circuit insulators. This is a classic heat supply scheme using central heating points and is currently most widespread in the construction of new microdistricts. FINDINGS:
An independent heat supply system has the following important advantages in comparison with a dependent one, these are 1. The ability to accurately adjust the amount of heat supplied to the consumer (by regulating the temperature of the heat carrier in the consumer's circuit);
comment: in this case, it becomes possible to adjust the temperature of the coolant depending on the outside temperature, which in turn makes it possible to achieve a stable, comfortable air temperature in the room (20-22 degrees C) at any sharp, temperature, weather changes.
2. High reliability of the system is ensured by an integrated approach to the design of the heat supply system of the settlement and is provided by looping systems with the possibility of emergency switching of consumers from various sources of heat supply.
comment: the importance of the concept of reliability of heat supply systems is currently acquiring the greatest relevance (recall the case with the defrosting of heating systems of residential buildings in the settlement of Tomilino, Moscow region)
3. Obtaining an energy-saving effect (heat saving 10-40%) is carried out through the use of modern, electronic temperature controllers for the coolant, circulation pumps with variable speed, metering devices for consumed thermal energy, etc. - a set of measures to improve energy saving systems; 4. The possibility of using a coolant of different chemical composition - allows you to improve the performance of the system as a whole, increasing the protection of boiler installations. 5. The possibility of efficient organization of the heat supply system with a significant distance and territorial dispersion of consumers and many others ... Currently, independent heat supply systems have all the advantages of modern heat supply systems and are most often used in the design and construction of modern settlements. Despite serious financial costs and investments, the transition to independent heating systems is taking place everywhere.
________________________