The construction of residential, commercial and industrial facilities is carried out using various tools, building mixtures and blocks. Some of them are classified as flammable, which emit toxic gas compounds when heated, spread the flame. According to their technical characteristics, they are flammable, which is reflected in state standards for production and in other documentation. The other class includes non-combustible materials. By definition, they are non-flammable, non-smoldering, and do not spread open combustion. The use of this type of construction products provides increased fire safety at the facility being built.
What is it NG materials
What materials and substances are non-flammable? These are those that, when exposed to a source of ignition, are incapable of smoldering, igniting, spreading fire or charring.


Non-combustible panels for interior decoration
According to Art. 12 of the "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements", classifying materials by fire hazard, GOST 12.1.044-89 on their fire and explosion hazard, the flammability group is a qualification characteristic for the combustion of any substances by origin, method of materials production, while:
About this topic ▼
Fire triangle and fire tetrahedron


- Non-combustible / non-combustible materials and substances that are incapable of burning in the surrounding air are classified as non-combustible.
- Some non-flammable substances that emit flammable vapors upon contact with each other, water, O2 air, as well as strong oxidants, are classified as explosive and fire hazardous. Therefore, to establish the real incombustibility of substances, materials obtained from them, the primary task is to determine their chemical composition and properties.
The laboratory, certification test results of materials and substances obtained during the assessment of the flammability group are used in the future for their classification, include data in GOST, technical production conditions; and also used in determining the category of explosion and fire hazard of protected objects, in the development of fire-prevention measures.
Aluminosilicate refractory materials
Alumina-silica refractories are refractories made mainly of A12O3 and SiO2.
Depending on the amount of A12O3 content, such refractories are: - semi-acidic (A12O3 content - from 14 to 28%); - fireclay (A12O3 content - from 28 to 45%); - high-alumina (A12O3 content - from 45 to 95%).
Semi-acid refractories are aluminosilicate refractories with a mass fraction of А12О3 from 14 to 28%.
Their properties make it possible to use such refractories only in insignificant areas of the lining of coke ovens and in some other steel-making units, but as fire insulation, this type of refractory has great prospects.
Where are applied
Most of these non-combustible materials are used in the construction of construction projects, for filling, ennobling the adjacent land plots, and some substances as heat carriers, fire extinguishing agents.
The most important area of application of non-combustible materials is the construction of facilities, equipping them with external, internal engineering communications, because only their use in a greater ratio with products made from combustible substances, for example, wood, can increase the fire resistance of buildings, structures, including those with an increased risk fire due to the peculiarities of technological processes, fire load.
If not long ago the floor in multi-storey residential buildings and public facilities was made of wooden boards, now they have been replaced by cement-sand screeds covered with fire-resistant non-combustible linoleum, and the wall, ceiling, partitions of the room for leveling their surfaces are sheathed with fire-resistant fireproof cardboard on a gypsum base ...
Chimneys, pipes of stoves of residential buildings, baths are made mainly of solid bricks, and fire-prevention cuts in the places where they intersect ceilings, roofs of buildings are compacted, separated from combustible wood structures with fire-retardant mastics, pastes, and plasters.
For the construction of objects, piece building materials are most often used - bricks, foam concrete blocks, reinforced concrete finished products; for external, internal decoration, insulation, both sheet and roll, loose finishing, heat-insulating materials.
Given the cold climate in most regions of our country, non-combustible fibrous heat insulators are in demand in the construction, repair of construction projects, utilities of settlements - from the usual mineral wool for fire-retardant basalt material, which are widely used for the following purposes, for:
- thermal insulation with rolled, semi-cylindrical foil-clad elements of pipeline systems transporting water and its solutions, including water, foam fire extinguishing installations;
- insulation of floors of upper, technical floors; window doorways, floors, roofs;
- thermal insulation of attic floor structures;
- sound insulation of premises, buildings related to entertainment establishments, catering establishments.


Thermal insulation of pipelines with non-combustible materials
The scope of application of various metals, their alloys is wide:
About this topic ▼
Fire safety during construction


- Steel - for the production of building bearing structures, as reinforcement for reinforced concrete prefabricated, monolithic structures of building objects.
- Copper, aluminum - as conductors of wires, cables, current-carrying elements of power supply systems.
- Cast iron, steel - for the manufacture of cases of industrial, engineering equipment, pipes of various diameters, shaped elements for their connection.
Although for some water supply systems, for example, water, foam fire extinguishing systems, water mist extinguishing systems, it is permissible to replace steel pipeline products with fire-resistant plastic pipes, in general, there is no alternative to the use of non-combustible metal products.
Fireclay refractory materials
Fireclay refractories - contain 28-45% А12О3 and 50-70 SiO2 in their composition. The technology for the production of molded chamotte refractories includes: firing clay (kaolin) at 1300-1500 ° C in rotary or shaft kilns, grinding the resulting chamotte, mixing with binding clay and water (sometimes with the addition of other binders), molding, drying and firing at 1300 -1400 ° C.
Fireclay refractories are used for lining blast furnaces, steel-pouring ladles, heating and roasting furnaces, boiler furnaces, etc., as well as for the manufacture of siphon products for steel casting. Unshaped chamotte refractories are made from crushed chamotte and binding materials and are used in the form of mortars, ramming masses, powders, concrete aggregates when performing and repairing refractory linings of various thermal units.
A distinctive feature of high-alumina refractory products is the increased Al2O3 content, which exceeds 45%. The refractoriness of high-alumina products is about 1750 ° C and higher.Together with the high temperature of the onset of softening and increased chemical resistance against acidic and alkaline melts, they can be used in the main heating units of the metallurgical industry.
The most common units for the use of high-alumina refractory products are: the upper part of the walls and domes of air heaters, the laying of the bottom and hearth in blast furnaces, with continuous casting of steel; in furnaces with an operating temperature of 1400 ° C-1500 ° C, steel-pouring ladles during steel processing by vacuum treatment, as fillers for refractory concrete, mortars, etc.
These refractory products are of three types:
- Mullite-siliceous (А12О3 - 45-62%), MKR, have a chamotte base of clays and bauxites; are characterized by Al2O3 content up to 62%. They are produced by melting aluminum and silicon oxides in an electric furnace.
- Mullite (А12О3 -62-72%);
- Mullite-corundum (А12О3 - 72-90%) MK, as well as ML, have a base of alumina, low-iron bauxite and electrocorundum.
High-alumina corundum refractories. These include refractories with A12O3 content> 95%. For the manufacture of such a refractory, electrofusible corundum powder and technical alumina are used. After shaping, it is fired at a temperature of 1600 ° C - 1750 ° C. The fire resistance of the resulting material allows it to be used in processes with a temperature of 1750 ° C - 1800 ° C, corundum refractory is able to stably contact with liquid metal and slags, acids, alkalis and molten glass.
Corundum refractories are used to make corundum plates for slide gates of steel-pouring ladles, products for lining steel vacuum chambers, nozzles for high-temperature air heaters, thermocouple covers, crucibles for melting glasses, metals, etc.
Unshaped corundum refractories - mortars and concretes with corundum aggregates are used for lining the branch pipes of steel vacuum tubes, and masses and coatings - for the manufacture and repair of refractory linings with an operating temperature> 1700 ° C.
Fiber refractories (fibrous refractories) - heat-insulating refractories consisting of fibers in the form of molded (plates, blocks, sheets, etc.) with an inorganic or organic bond and unformed (cotton wool, felt, etc.) products. Fibrous refractories are made mainly from high-alumina and alumina glass fibers and from corundum, polycrystalline fibers, as well as from ZrO2 and other oxides.
Fibrous refractories are used for thermal insulation and lining of heating units, as well as for filling expansion joints.
Dinas Refractories - contain> 93% SiO2 or 80-93% SiO2 (when manufactured with additives) and are made from quartzite. Lime milk and ferrous additives are added to the quartzite powder, the products are molded on presses of a given size and fired at 1430-1460 ° C.
Dinas refractories are used for the lining of coke ovens, glass melters, furnaces, air heaters, as well as a number of smelting units in CM, etc. Unshaped dinas refractories are mortars, materials for coatings, etc. are made from ground broken dinas, refractories and quartzites, used in the execution and repair of masonry.
1. Lime-periclase (dolomite) - refractory products made of dolomite, incl. with the addition of periclase powder with a mass fraction of MgO - 10-50% and CaO - 45-85%. Lime-periclase refractory products are stable when interacting with basic slags.
Unshaped lime-periclase refractories (masses of baked dolomite with a binder) are used for packing block and monolithic linings of electric arc furnaces, converters, steel-pouring ladles, etc.
2. Non-fired lime-periclase - refractory products made on the basis of SiC (> 70%).Non-fired calcareous periclase refractory products are made by molding fired dolomite powders on an organic bond (coal tar, pitchfork or with heat treatment at 300-600 ° C); their refractoriness is> 2000 ° C. Lime-periclase products are also produced, fired at 1500-1750 ° C and retaining partially free CaO.
3.Silicon carbide - refractory products with SiC content> 70%. Silicon carbide refractories are used for the manufacture of muffles, recuperators, thermocouple sheaths, etc .; linings for electric heating wells, zinc and aluminum production units, pipeline cyclones, etc.
Silicon carbide refractories on nitride and oxynitride bonds are also used for lining the lower part of the blast furnace and furnaces. Unshaped silicon carbide refractory products are used to coat the shield screens of boiler furnaces, in the form of mortars and masses when performing refractory masonry.
Classification
Classification, according to GOST 30244-94 on fire test methods, is used when dividing all building materials into classes according to flammability groups:
- NG - non-flammable.
- D - flammable.
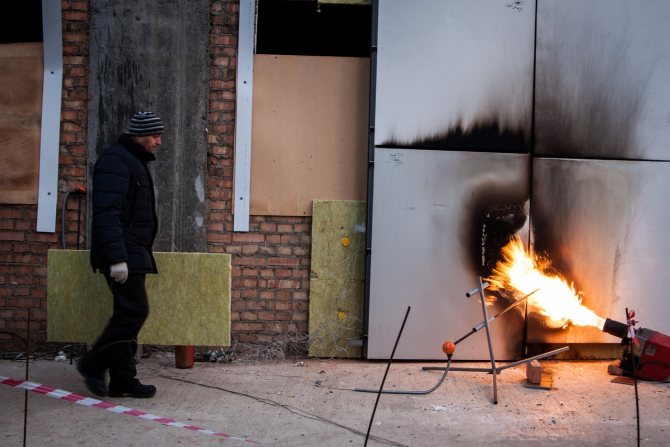
Non-combustible includes building materials that fully meet the following test conditions:
- The temperature rise in the oven is no more than 50%.
- Reducing the mass of the test material - no more than 50%.
- The period of stable burning with an open flame is no more than 10 s.
The same materials used in construction, insulation, decoration of objects that do not satisfy at least one indicator according to the test results are referred to as combustible.
There is also a classification of any building objects for their purpose according to the degree of fire resistance:
About this topic ▼
Determination of the fire resistance of building structures
- I - all elements are made of non-combustible materials, while the load-bearing elements of buildings and structures have a fire resistance limit of at least 2 hours.
- II - the same, but with a fire resistance limit of the supporting structure of 1.5 hours, while when creating non-attic coatings of objects - trusses, beams, flooring, it is allowed to use elements made of metal alloys that have not passed the fire protection of metal structures.
It is precisely the objects belonging to these two classes, completely made of non-combustible materials, substances used for their insulation, sound insulation, that are most resistant not only to the occurrence of a fire inside them, but also to external anomalous influences - earthquakes, floods.
In addition, there is the following classification of non-combustible materials, substances used in the construction, repair of objects.
By appointment:
- Ready-made building structures, including various types of bricks, concrete blocks.
- Heat and sound insulation molded materials; free-flowing substances, such as perlite, expanded clay.
- Decorative materials for finishing the premises of buildings, for example, marble, ceramic tiles.
By the form of release of finished products:
- Structural elements - from reinforced concrete slabs, trusses to metal sandwich panels with non-combustible insulation.
- Sheet, roll, plate materials.
- Loose substances.
Parameters and characteristics of heaters
The oxygen index characterizes the fire safety properties by displaying the minimum volume of oxygen per unit volume of the thermal insulation material. According to the values of the oxygen index, there are three flammability thresholds of heaters:
- 40% - composite polymers;
- 31% - non-combustible heat-insulating materials made of fibrous and cellular components;
- 20% - combustible insulation.

Fire safety requirements according to Federal Law No. 123
Fibrous heat insulators are mainly represented by non-combustible mineral insulators, for example, glass or basalt.Such high-temperature thermal insulation is able to withstand temperatures of ˃ + 500 ° С, therefore its use is recommended for highly specialized places and structures:
- For insulation of various kinds of pipelines with cylindrical foil-clad elements;
- For thermal insulation of PVC window and door frames with thin mats or plates using the stitching method;
- For insulation of walls, ceilings, floors and roofs with basalt materials.
According to GOST 4640-93, heat-resistant mineral wool can be stone, glass, slag, and according to the oxygen index (30%) it should belong to the NG class - non-combustible materials.
Views
According to the state of aggregation, there are three types of non-combustible substances, both natural and artificial.
Solid, which can be in the form of building structures, heat-insulating, sound-insulating, finishing materials, bulk substances:
About this topic ▼
Means, methods of fire protection


- Rocky rocks - granite, diabase, marble, diorite, flint, gneiss, dolomite; as well as softer sandstones, limestones.
- Gravel, crushed stone, screenings, sand.
- Chalk, cement, clay.
- Asbestos, gypsum, lime, mortars, plasters.
- Concrete, reinforced concrete products.
- Cast iron, various types of rolled steel - from large I-beams, channels to sheets.
- Copper, brass, bronze, aluminum.
- Various types of glass products, including fire resistant glass.
- Textile materials - fireproof non-combustible fabric, basalt roll materials.
- Various types of mineral wool.


Non-combustible mineral wool mats
Liquid:
- Water used for drinking, watering plants, as well as a heat carrier in heat supply systems, a fire extinguishing agent in outdoor and indoor fire extinguishing networks.
- Aqueous solutions of salts, acids, alkalis.
- Solutions of detergents, foaming agents.
- Non-flammable synthetic fluids.
Gaseous:
- Nitrogen.
- Carbon dioxide.
- Argon.
- Freons.
Scope of application
The main purpose of determining the degree of flammability of substances lies in the practical field. The results of these activities are usually used in the construction and landscaping industry. The combined use of flammable and non-flammable substances will ensure high fire safety in combination with a moderate amount of production costs.
The materials used in the construction industry make it possible to make the safe operation of buildings after the completion of construction. Non-combustible materials for the bath can reduce the risk of fire to acceptable values. An example is the active use of hollow materials in construction.
Especially often a brick with voids inside the structure is used in this capacity. In addition, it is used as a non-combustible material for stoves in low-rise structures. It should be remembered that the contact points of chimneys and stoves docked with combustible structures must be insulated with fire retardants: mastic, plaster, sealant.
Non-combustible material for the chimney must be insulated at the junction with flammable elements. In the construction industry, hazardous materials are actively changing to formulations that are stable and resistant to fire. The traditional wooden floor structure is almost completely replaced by a conventional screed combined with floor ceramics or non-combustible linoleum. Non-combustible materials for walls and ceilings are widely used both in low-rise construction and in apartment buildings.
Materials based on wood and wood shavings are consistently being replaced from the construction industry. Usually, these materials are changed to block elements, for example, tuff blocks or foam concrete products.As finishing panels, both internal and external, non-combustible sheet material is used.


For insulation of walls, ceilings, floors, roll and sheet material based on basalt and other mineral fibrous compositions is used. These products are distinguished by high fire safety and are used:
- for thermal insulation of technical openings for windows and doors;
- to ensure thermal insulation of the outer floors, roof structures, floor of the room;
- for insulation of upper superstructures and attic floors;
- in order to ensure thermal insulation of pipelines for various purposes, including water pipelines, gas pipes, wastewater discharge system, cylindrical structures or roll samples are used as heat-saving elements;
- fibrous mineral compounds are also used for sound insulation in premises for various purposes.
Various metal structures also have a high degree of fire safety. This number includes:
1.
Cast iron and steel used to create pipe products, industrial and construction equipment, fittings for pipelines. From these metals casings are cast for machine tools and equipment for various purposes, they are used for the production of engineering equipment.
2.
Conventional steel is actively used for the production of fittings for structural fittings. Elements of supporting structures for structures for various purposes are created from steel.
3.
Copper, aluminum and various alloys based on them are used as conductive materials in the energy sector.
Requirements
They are set out in many regulations governing fire hazard, fire resistance of building structures, materials made of non-combustible materials. Among them:
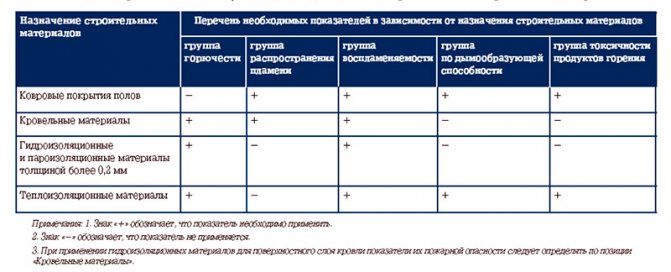
- GOST 30244-94 - on the regulations for testing the flammability of building materials, classification by flammability groups. The standard does not apply to paints and varnishes, as well as other building materials produced by solutions, powders, granules.
- NPB 244-97 - on indicators of fire hazard of facing, decorative and finishing, roofing, heat and waterproofing materials, floor coverings.
- GOST 4640-2011 - on the technical conditions for the production of mineral wool from melts of rocks, sedimentary rocks, volcanic, metallurgical slags, silicate waste, intended for the production of heat and sound insulation building materials. The obtained commercial wool is used in construction, as well as for thermal insulation of surfaces of industrial equipment, pipelines with temperatures ranging from - 180 to 700 ºC.
- GOST 21880-2011 - on the technical conditions for the production of stitched heat-insulating mats made of mineral wool intended for thermal insulation of the enclosing structure of construction objects, storage tanks for water, hydrocarbons, oil products; water supply systems, industrial pipelines.
- GOST 32313-2011 - on rigid, semi-rigid plates, mats, including those reinforced with a metal mesh, foil-clad, cylinders, and other industrial mineral wool products used to insulate engineering communications of construction facilities, process plants operating at temperatures from 0 to 1000 ºC.
- GOST 32314-2012 - on products from various types of mineral wool used in construction.
- GOST 32603-2012 - on TU for the production of metal panels with mineral wool insulation, used as enclosing structures in the construction of civil and industrial construction projects.
In addition to resistance to fire, for non-combustible materials and substances, other technical requirements are also put forward by the norms for:
- bending strength, tensile strength;
- moisture resistance;
- hygroscopicity;
- density;
- specific viscosity;
- thermal conductivity;
- deformational changes when heated, wet.
Many non-combustible materials, substances are used not only in construction, during finishing works, equipping facilities with utilities, but also in the production of fire extinguishers, stationary fire extinguishing systems, smoke protection, therefore, the requirements for them in each specific case are regulated by the relevant codes of practice, standards.
Shaped and unshaped refractory materials
Refractory products can be molded and unshaped.
Unshaped refractories - refractories made without specific shapes and sizes in the form of lumpy, powder and fibrous materials, as well as pastes and suspensions. Unshaped refractory materials are usually strengthened by the addition of mineral (eg water glass) or organic (polymers) binders.
These include metallurgical filling powders, aggregates and fine-grained components for refractory concretes, refractory cements, concrete mixtures and ready-to-use masses, mortars, coating materials (including shotcrete masses), and some types of fibrous refractories.
Unshaped refractories can be dry, semi-dry, ductile and flowable.
Unshaped refractories used for making and repairing lining of steel-pouring ladles (rammed and bulk silica, high-alumina and magnesia masses); converters (shotcrete mass), heating and roasting furnaces (chamotte, and high-alumina mass), induction furnaces (corundum and periclase mass), coke ovens (coating), hearth hearth, and electric arc furnaces (filling powders), etc.
Molding of refractory materials is carried out by methods of semi-dry and hot pressing, plastic molding, casting (vibration casting) from flowing masses or material melt, as well as by sawing prefabricated blocks or rocks.
Shaped refractories used for the manufacture of refractory masonry walls, arches, hearths and other structures of coke oven, open-hearth and blast furnaces, furnaces for smelting various alloys, for the lining of nuclear reactors, MHD generators, aircraft and rocket engines; unshaped - for filling joints when laying molded refractories, applying protective coatings on metals and refractories.
By the nature of heat treatment, non-fired and fired refractory materials are distinguished.
Non-fired refractories - products made of refractory materials and binder, acquire the required properties when dried <400 ° C (after heating the products from 400 to 1000 ° C, they are called heat-treated). A binder can be clays, ceramic suspensions, phosphate solutions, alkaline silicates (liquid glass), thermoplastic and thermosetting resins, elastomers and other non-fired refractories are not inferior in strength and ductility, and surpass fired refractories in heat resistance.
The following non-firing refractories are most widely used: silica concrete blocks (for heating wells), chamotte and high-alumina (for firing units), magnesia-lime based on resin (pitch) binder (for steel-making converters), periclase and periclase-chromite glasses (for steel pouring) ...
For fired refractory materials, the firing temperature exceeds 600 ° C and is determined by the achievement of the required physical and chemical properties of the material. Firing of refractory materials is carried out in plasma or electric furnaces of periodic or continuous operation - chamber, ring, tunnel, shaft, etc.
Other important properties of refractory materials are porosity, thermal resistance, thermal conductivity, temperature of the onset of deformation under load, and chemical resistance in various environments.
According to porosity (volume fraction of pores in%), they are distinguished: - extra dense refractory materials (porosity less than 3%),
- high-density (3-10%), - compacted (16-20%), - materials of increased porosity (20-30%), - lightweight (45-75%) - refractories with high (45-85%) porosity. Depending on the raw materials of manufacture, there are chamotte, dinas, alumina and others. - ultra-lightweight (75-90%), which usually include fibrous refractory materials.
According to the chemical and mineral composition, refractories are divided into types (silica, aluminosilicate, alumina, alumina-lime, magnesia, calcareous, chromium, zircon, oxide, carbon, silicon carbide and oxygen-free), into types into groups. With the compositional composition, the predominant component (for example, periclase-chromite and chromite-periclase) is put in the first place in the name of refractories.
Parameters that determine the safety of the material
In addition to the flammability class, additional parameters are used to classify the safety level of a building material, which are determined through tests. This includes toxicity, which has 4 subsections:
- T1 - low degree of danger.
- T2 - moderate degree.
- T3 - increased hazard indicators.
- T4 - extremely dangerous degree.
The smoke-generating factor is also taken into account, containing 3 classes in regulatory documents:
- D1 - low ability.
- D2 - average ability.
- D3 - high ability.


Flammability is also important:
- В1 - hardly flammable.
- B2 - moderately flammable.
- B3 - flammable.
And the final criterion that makes up the safe use of products is their ability to spread the flame over the combustion surface:
- RP-1 - non-proliferating.
- RP-2 - weakly spreading.
- RP-3 - moderately spreading.
- RP-4 - highly propagating.
Non-combustible electrical wiring
Electrical wires must comply with the following rules:
- Stow in non-combustible metal trays, cable channels, corrugated hoses or in non-combustible fabric;
- The connection is done only by soldering, as well as by using connectors or contact plates;
- In rooms with high humidity, heat-resistant moisture-proof lamps are installed;
- Wiring is done with a fireproof cable or wire.
The correct term is flame retardant or flame retardant cable. Fire-resistant cable (wire) can work not only in the wiring of buildings, but also in all kinds of fire extinguishing systems. The table contains a short list of the names of such products:
Conditions for growing cannabis in a grow box
Inside the growbox, its own microclimate is created, on which the growth and yield of the planted plants directly depends. Therefore, it is necessary to create the best growing conditions suitable specifically for cannabis.
Temperature.
The temperature in the grow box must always remain constant and be between +18 and +27 degrees. When the light is off, the temperature can drop to the lower mark, when it is on, it is advisable to keep it at +24 degrees. This temperature is considered to be the most favorable for cannabis.
Light mode
The required light regime depends on the variety. If the cannabis variety is autoflowering, then during the entire life cycle, the day should be 18 hours, and the night - 6 hours. Photoperiodic varieties require different light conditions for the growing and flowering stages - 18/6 and 12/12, respectively.
Air humidity
The optimum humidity is considered to be 40-60%. However, to reduce the risk of bud formation during the flowering stage, it is best to keep buds between 45% and 55%.
Plant feeding
For plants to grow healthy and enjoy a bountiful harvest, they need minerals and trace elements. The main minerals for feeding are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
Phosphorus is essential for marijuana during the flowering stage.It influences the formation of cones, promotes the growth of roots and inflorescences.
Nitrogen is essential during the growing season - it contributes to the development and growth of the plant.
Potassium is responsible for plant immunity, promotes the movement of nutrients, and improves the quality of the crop.
PH and EC
The acidity (pH) indicator monitors the available amount of ionic elements that cannabis needs for healthy growth. Cannabis grows well at a pH of 5.5-6.5.
The conductivity index (EC) is used to determine the concentration of nutrients (salts) in the soil. This indicator must be maintained at a stable level so that the plant does not suffer from an overabundance of nutrients. The EC value must be between 0.75 and 2.0.
Finally, I would like to add that not every grower wants to spend time and effort creating a growbox. Especially if you don't have the materials you need at hand. In this case, a ready-made solution will come to the rescue - growbox 80-250 Cocos. Along with the awning itself, the set includes lamps, ventilation, automation, a tissue pot with a substrate, devices for monitoring pH and EC levels, fertilizers, calibration solutions and special additional equipment. It has everything a gardener needs to start a carefree grower's career.
* All information provided is for informational purposes only and is not a guide or call to action.
** We remind you that the use of marijuana seeds as a seed (growing hemp in order to obtain a plant) is prohibited by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. You can learn more about the law here.
Fire-fighting pastes and plasters
Flame retardant coatings can be applied by coating, spraying or other mechanical means. They can be pastes or plasters, the layer of which usually does not exceed 5-10 mm, in plasters - 20-45 mm. The main difference between these materials from simple cement-sand putties and dry building mixtures is the absence of Portland cement and quartz sand in the composition. This is due to the fact that these two materials begin to decompose when exposed to temperatures above 500 ° C. When trying to extinguish a fire with water, a reverse chemical reaction occurs - the slaked lime breaks through the top layer, resulting in cracks and swelling, which contribute to the ingress of flame into the structures.
Fire retardant pastes and plasters are made on the basis of:
- silicate glass;
- gypsum;
- alumina and pozzolanic cements;
- vermiculite, perlite, tripoli, diatomite, pumice and others (as filler);
- kaolin wool, asbestos and various types of mineral fibers (binders).
The simplest pastes are made using local "lean" clay mixed with aqueous solutions of sulphite-yeast lye (SDS). Those pastes that contain vermiculite, perlite or kaolin wool are more effective - they are therefore added to fire doors as a fire-resistant filler.
As for the aesthetic side of the issue, unlike the same impregnations and varnishes, they hide the texture of the wood, therefore they are practically not used in the interior. However, wooden houses are not only interiors: there are many structures hidden from view. Therefore, pastes are most often used in attics, basements, utility rooms and others.
Tip: as already mentioned, they do not contain Portland cement and quartz sand. Therefore, if the seller in the store assures that the composition is suitable for wood, but contains the specified substances, such a product is not suitable for wood.
Fire retardant pastes and plasters are applied using rollers, brushes and spray guns. As with varnishes, surfaces must be prepared very carefully.Even small amounts of dust can impair adhesion to wood, resulting in reduced efficiency. As a rule, they are applied in two layers - they are completely environmentally friendly and do not contain toxic substances.
How to cover the inside of the grow box Best reflective material


Growbox is a device designed for growing plants in different ways. It has its own distinctive design subtleties that must be taken into account if you decide to build a grow box with your own hands. Some craftsmen use for this any boxes at hand, lining of broken refrigerators, unnecessary cabinets, small storage rooms, etc. To make a grow box, you need to have some knowledge, be smart and not be afraid to fantasize. Even if you are a beginner, do not worry, feel free to pick up the instrument, and you will succeed.
Class confirmation


Samples of materials are tested in laboratories and in open areas according to standard methods separately for non-combustible and combustible building materials.
If the product consists of several layers, the standard provides for checking the flammability of each layer.
Determinations of flammability are carried out on special equipment. If it turns out that one of the components has high flammability, then this status will be assigned to the product as a whole.
The setup for carrying out experimental determinations should be located in a room with room temperature, normal humidity, and no drafts. Bright sunlight or artificial light in the laboratory should not interfere with the reading of the displays.
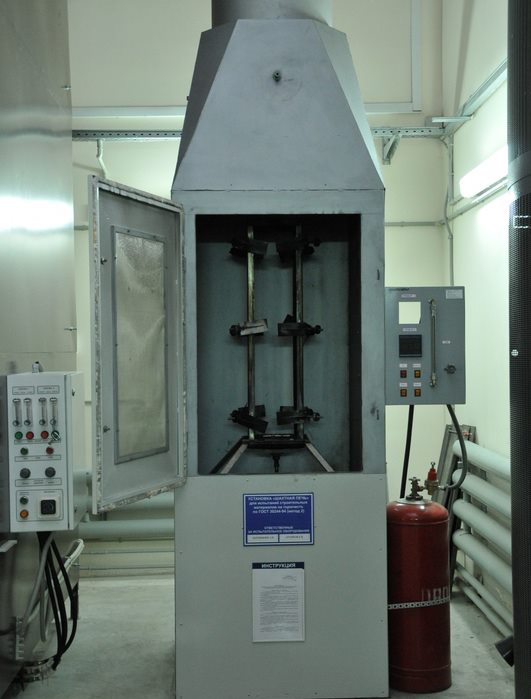


Before starting the study of the sample, the device is checked, calibrated, and heated. Then the sample is fixed in the holder of the inner cavity of the oven and the recorders are immediately turned on.
The main thing is that no more than 5 seconds have passed since the sample was placed. The determination is continued until the temperature balance is reached, at which within 10 minutes the changes do not exceed 2 ° C.
At the end of the procedure, the sample together with the holder is taken out of the oven, cooled in a desiccator, weighed and measured, reckoning them to the flammability group NG, G1, and so on.
Adjusting the height of the handle
The mechanism of the door handles is obvious: we turn the handle - the "tongue" is hidden in the door. Therefore, the first step in how to install a door handle is to drill holes for the handles and prepare a groove for the tongue. To do this, you need to decide on the installation height of the handles. Experts recommend installing at belt level, taking into account that the arm is bent at an angle of 90 degrees. Usually it is about 90-100 cm from the floor level.
Attention! In accordance with GOST 6629-88, the installation height of the door handles is exactly 1 meter from the floor surface. However, in private households, you have the right to choose the most convenient location for the handle.
Height of installation of handles and hinges for the door
It should be noted that if the handles are being installed within premises that are in the immediate vicinity, for example, adjacent bedrooms, then think about observing a uniform height for installing the handles.
However, it should be noted that sometimes the texture of the door suggests the presence of fittings in certain places. In such cases, deviations from the intended installation location can have a negative effect. Also, if there are small children in the house, then on the doors to the toilet and children's room, it may be worth slightly lowering the mounting height of the door handles.