Why is it needed
What are the functions of pumps for a heating system?
System with radiators and underfloor heating
The further you go, the higher the temperature. When heat is received from the earth, it must be regenerated, i.e. heated. Regeneration up to 1.8 m is possible mainly due to solar radiation, rain and melt water. The regeneration, thanks to the heat emanating from the deeper layers of the earth, is so small that it doesn't matter. From the earth collector, heat is most absorbed in winter, while it is recovered mainly in spring and summer. Soil regeneration is mainly driven by solar radiation as well as precipitation, which ensures that the soil accumulates heat during the next winter season.
It is clear that they are pumping a coolant; but heating without a pump can also work?
- Forced circulation equalizes the temperature of the coolant in different parts of the circuit, sharply accelerating the circulation. One of the main problems is that the radiators closest to the boiler are always much hotter than the distant ones. The reason is precisely the slow movement of water through the pipes.
- The pump for the heating system makes it possible to dispense with a smaller filling diameter
... With natural circulation, the problem of hydraulic resistance is very acute; one of the methods for solving it is the use of a deliberately overestimated pipe diameter. However, a contour made with a pipe with a cross section of 32-50 millimeters will be quite expensive and spoil the aesthetics of the room. - Forced circulation will allow filling without a slope
, necessary both to accelerate circulation and to displace air into the open. - Finally, in systems with high hydraulic resistance (for example, with radial distribution), a heating pump is a must. Without it, the difference created by heating will be insufficient for circulation in principle.
Important: some types of boilers do not work in gravity systems. When purchasing, be sure to read the instructions for supported configurations.
The accumulated parameters and thermal conductivity are higher than water and minerals, and the lower the porosity. They do not need a large surface area because the pipes run vertically into the ground. Usually it is up to 100 meters deep. Then you need to obtain permission from the Water Management Board. If the pipes are more than 100 meters deep, we need to obtain permission from the Mining Authority. A special assembly probe is inserted into the hole. The free space is then filled with filling material. The distance between these elements must be at least 6 meters.

The photo shows a Dakon Pyro pyrolysis boiler, capable of working only in forced circulation systems.
How to choose a circulating pump?
We got acquainted with the design features of the pumps and their varieties, but it's too early to rush to the store to buy. You should also decide on the parameters that you need to pay attention to when choosing a particular model. "Why the pump is often turned on in the well, you can read in our article."
Marking
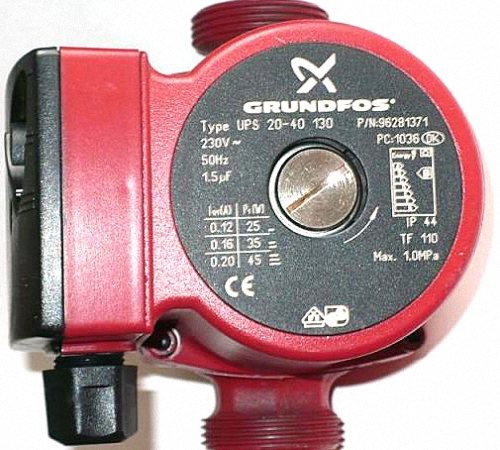


Body markings
The first thing we should see, picking up the model we like, is the marking, which will be located under the name. This could be, for example, 32-50. The first number here is the connection dimensions, 32 mm or 1.25 inches. Often, the pumps are equipped with nuts of the required size, making it possible to quickly assemble / disassemble it.
The second number is the pump lift.In our case, this is 5 m of water column or 0.5 atmosphere. There are pumps designed for higher or lower heights.
You may be interested in information on which pump to choose for a fountain
In addition, there should be a plate on the body, which indicates what the maximum load should be and under what parameters. The parameters mean the capacity - there are three positions for its adjustment in the pump. This is the second criterion for choosing a pump.
Performance
All requirements for a circulation pump are closely related. The capacity is the volume of the coolant distilled by the pump at a minimum load on it. The higher the performance, the better the model.
In order to find out the required performance, we will use the popular formula:
N / (T2-T1) = Q, Where
- T1 is the temperature of the coolant in the return pipeline;
- T2 is its temperature in the supply pipeline;
- N is the average power of the heating boiler;
- Q is the performance that we need to calculate.

Performance calculation
The average value of the water temperature in the "return" (Т1) is taken at 65–70 ° С, while the temperature in the supply pipeline (Т2) will be approximately 95 ° С. So we can approximately select the required parameters for the pump. It is believed that for every 10 m of the pipeline, 0.6 m of head, or pump lift, is needed.
In addition, there are ready-made thermal standards. According to them, for every 10 m² of heated area, only 1 kW of power is needed. And if, for example, the power of one radiator battery is 200 W, then for 10 m² you will need five sections. But this number of sections is relative, since in most cases there are more of them, "with a margin". Therefore, we need to take into account the fact that the circulation pump must cope with the supply of coolant to each radiator in the house.
Required power
The electrical power required to operate the pump is another parameter that you should pay attention to when buying. Often this power is insignificant - no more than 200 watts. It is only relevant in cases where permanent use of the pump is planned.
Costs
Could the heating pump cause any problems?
Do forced circulation systems have disadvantages?
Some features of connecting the pump to heating
Usually, the type and structure of the soil can be determined exactly after the first well drilled. Based on this data, it is determined whether the calculated probe length will be sufficient or whether a deeper hole will need to be drilled. Earth is water. Groundwater is also an excellent solar heat pump. Then the cold water is drained into the absorption well. Groundwater contains many minerals, but also many impurities. For this reason, additional heat exchangers are required to protect the evaporator in the heat pump.
- Electricity consumption
... It is small, but noticeable when working around the clock. An electric pump with a capacity of 100 watts will consume 72 kilowatt-hours per month during round-the-clock operation, which at current Russian tariffs will cost about 250-300 rubles. - System volatility
... It is clear that this is not a problem of a specific device, but of a project as a whole. However, it should be borne in mind that if you rely only on forced circulation, a wire breakage or theft will prepare you an extremely unpleasant surprise.
Tip: the problem of short-term blackouts can be solved by installing a UPS for a heating pump. Even a budget device will allow, with a consumption of 50-100 watts, to hold out for a couple of hours on a battery.
Keep in mind that even if the water test has shown that it does not exceed the manufacturer's approved standards, we are not 100% sure that the composition will not change in the future. A factor to consider when planning the depth of a well interacting with a heat pump is the level of the groundwater table, but this is variable. Modern heat pumps are used, for example, for cooling rooms in the summer, when the temperature inside buildings is usually higher than the temperature in the ground or in deep water. Free Cooling is a function that allows you to use a natural source of cooling, ie earth or water, to effectively reduce indoor heat.
Classification
What technical characteristics allow you to classify these devices into groups?
Rotor type
Remember in general terms the device of the electric motor? The rotor, equipped with permanent magnets, rotates in the continuously changing electromagnetic field of the stator winding. Bearings provide a minimum coefficient of friction.
It is very important that this is the most economical way to obtain the refrigerant, as in this case it is not necessary to use the compressor of the heat pump. The use of "free cooling" equipment provides additional significant benefits. First of all, the heat from the building, which merges with the ground, has a positive effect on the regeneration of the soil after winter and its cooling after being used for heating purposes.
Speed control
Main advantages: Integrated mixer for continuous operation without dew point temperature limitation. The "free cooling" mode has a positive effect on soil regeneration during the summer. The purpose of a circulation pump installed in a heating system is to provide a heating medium - most often to all receivers in this installation. In order for the pump to perform the task, it must be properly adjusted to the size of the installation. Some central heating boilers are factory installed with circulation pumps, especially for liquid fuels and gas.
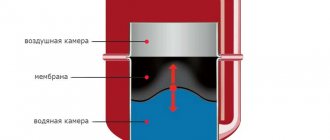
Now let's mentally separate the rotor from the stator with a thin stainless steel glass and fill it with water. Yes, the steel will partially shield the electromagnetic field; in addition, the induced eddy currents will heat the glass.
However, we will get an extremely fault-tolerant system, devoid of the main problem of centrifugal pumps - constant leaks of the stuffing box between the motor itself and the impeller.
In other cases, the circulation pump is installed in the heating system with return or supply. Older gravity heating systems did not use circulation pumps. The distribution of water in the system is automatic. The heated water flows to the upper part of the circuit, while the cold flow falls down. Pipes with large cross-sections are used for heating, and there is a large amount of liquid in the system. As the distance from the boiler increases, the water flow rate decreases.
By installing a circulation pump in the heating system that makes the water move, the aforementioned drawbacks of the gravity system are eliminated and the heaters can be installed below the boiler. The circulation pump can be installed in a gravity heating system without having to recycle the entire system.
This is how the so-called wet rotor heating pump works:
- The impeller is fixed directly to the rotor;
- The cooling function is performed by the heat carrier. The small amount of heat generated inside the pump by the induced currents serves to heat the house.
- The same coolant also performs the function of lubricating the bearings.
The use of modern materials (including ceramics) makes malfunctions of this class of devices extremely rare.
Pump characteristics. The characteristic is a graph of the dependence of the lift height and flow rate - this corresponds to the efficiency of the pump. Both of these values determine the suitability of a given pump for the system in which it is to be installed.
In principle, these values should be indicated in the design of the heating system, but often, especially old systems, are carried out without a project, and then the feeling and experience of the installer remains. Electronically controlled circulation pump. Pay attention to the direction of water flow, which should correspond to the arrow on the body when installing the pump. Install shut-off valves upstream and downstream of the pumps, which can be removed in the event of an emergency without draining the water supply system. For long-term pumps, the quality of the water in the heating system is recommended, therefore it is recommended to install a filter that will capture any contamination.
However, if you need a large head and high performance, you need a powerful electric motor, in which the rotor uses its own winding instead of permanent magnets. It is powered by contact brushes with replaceable graphite contacts. It will no longer be possible to place this entire structure in a conductive liquid.
How to properly operate the circulation pump
Clean the filter periodically. Closed-loop circulation pumps, where there is less water loss, less corrosion and less boiler stone, are more robust than those that operate in open systems such as solid fuel boilers. Also make sure the pump does not run dry without water. This can happen if the heating system heats up. This can be prevented by bleeding.
Circulation pump with regulator. Circulation pumps are equipped with manual or automatic speed control. The pump is expected to run at maximum speed as it provides maximum efficiency. In heating systems where the heater controls thermostatic valves, pressure fluctuations occur due to the closing or opening of valves on the radiators. This can cause serious operation of the heating system. By using electronically controlled, infinitely variable speed circulation pumps, you obtain constant system pressure, which eliminates the need for system operation.
A typical powerful pumping station for heating is the most ordinary centrifugal pump with a separate volute and an impeller in it. The motor shaft transmits torque to the impeller shaft; to compensate for vibrations and possible axial displacement, the coupling between them can be elastic.
The station is mounted on its own bed and requires a separate foundation.
Heat pump manufacturers are constantly working to improve them. The heat pump system is a very dependent three chains, which can be compared to three gears. When one of them stops, the whole system will stop working. The first scheme is the bottom source, that is, the solar energy battery located in the environment. Such a natural battery of energy can be crushed, ground water or air. The heat pump receives heat from the environment and transfers it to the heating system.
The point is that heat always flows from a "source" to a "heat source". The heat pump uses the natural flow of heat from cold to cold in a closed refrigerant circuit with an evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion valve. A heat pump "pumps" heat from the environment to a higher temperature that can be used for heating.
Advice: the simplest way to make the joint between the motor and the volute elastic literally on the knee is to connect the flanges at the ends of the shafts not with bolts, but with segments of a reinforced rubber belt.
Actually, it is precisely this scheme of the device that is called a pump with a dry rotor.
The conversion of air from outside air to heating the building takes place in three circuits. In the return loop, free heat is extracted from the environment and transported to the heat pump. In the refrigerant circuit, the heat pump increases the low temperature of the heat generated to the high temperature. In the circulation of the coolant, heat is distributed around the building.
Outside air is drawn by the fan into the heat pump's evaporator. Here the air gives off heat to the refrigerant and the air temperature drops. Cold air is discharged from the heat pump. Refrigerant - the gas that circulates in the closed loop of the heat pump also flows through the evaporator. The refrigerant has a very low boiling point. In the evaporator, the refrigerant receives heat from the air and begins to boil. The boiling gas is sent to a compressor powered by electricity or heat.
Pressure
As a rule, it is measured in meters and means the height of the water column that this pump for the heating system can create.
The typical understanding of this parameter by managers boils down to the fact that the head should be obviously greater than the variation in height between the lowest and highest points of the contour.
This point of view is simple, clear, logical and ... absolutely wrong.
Types of circulation pumps
From the compressor, the gas is fed to a heat exchanger, which transfers heat to the heating system and then cools and condenses. Since the pressure is still high, the refrigerant is pushed through the expansion valve, where a pressure drop occurs, so that the refrigerant returns to its original temperature. The refrigerant is redirected to the evaporator and the process is repeated.
The heating medium circulates in a closed loop and transfers the heat energy of the heated water to the hot water heater and inside the building heating system. Cooling agents used in air pumps. From the above description, it is clear that the physical and thermodynamic properties of the refrigerant have a dominant influence on the size and mutual proportions between energy flows.
It will be necessary to overcome the resistance of the water column in height into the house only in one case: if there is an air lock at the top of the circuit, which the pump will have to push through a narrow pipe to the very bottom of the heating system.
The situation is, frankly, far-fetched. Simply because in a well-designed circuit at its top point, an air vent is mandatory - a Mayevsky valve, a valve or an automatic air vent.
All refrigerants used in heat pumps comply with the requirements of the Kyoto Protocol, Montreal Convention. Efficiency, which is the parameter that tests a potential customer. The efficiency of a heat pump depends on the temperature difference between the bottom heat source and the heat sink, therefore, in the case of air source heat pumps, the shortening of the heating season significantly reduces the average annual efficiency of such heaters. When the heat pump is heavily used and its efficiency and heating capacity decrease as the air temperature drops, it is usually necessary to use an additional heat source.
The pressure generated by the heating pumps only has to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the circuit. More is not required of them. Moreover, the excess pressure created by the pump is harmful: at any throttling point with an overestimated pressure difference, water noise will appear.
The capacity of heat pumps with modulated heat output is different, where we usually deal with the minimum, maximum and nominal values at a given frequency of the compressor controlled by the inverter. The values given in the letters are the temperature in degrees Celsius, respectively, of the outside air, which in this case is the lower source of the heat pump and heating water, which is the heating medium in the internal installation of the building.
Air source heat pumps use energy stored in the ambient air or discharged air to heat, cool or prepare hot water. They can be installed as compact devices inside or outside the home. Close-coupled heat pumps are devices in which the condenser, evaporator, compressor, expansion valve and circulation pump are located in one housing.
Performance
This parameter, unlike the previous one, is simple and understandable to the most illiterate seller. This is just the volume of water in cubic meters that the device can pump over within an hour.
What depends on him? The uniformity of the distribution of the temperature of the coolant along the circuit.
However, overestimated performance is no less harmful than pressure:
- Electricity consumption will increase, and it is absolutely unjustified.
- Again, there will be noise. And not only on throttles, but also on all valves.
- It will rise above the required return temperature, which means that the efficiency of the boiler will drop. The heat flux on the heat exchanger is linearly dependent on the delta of temperatures between the combustion products and the coolant.
Speed control
Now let's reveal a little secret. It is not so scary to miss the performance and head pressure if the pump control circuitry supports changing the impeller speed. Actually, the vast majority of modern devices are capable of this: only the most budget models remained single-speed.
Switching speeds can be stepped, with three or four fixed modes, and stepless. In the latter case, the price of the device at least doubles; but the savings in electricity relative to pumps with step switching of speeds can reach a very impressive 80 percent.
Purpose and scope
Hot water recirculation pumps have a very important function. With the help of such devices, it is possible to operate in the required mode of closed pipelines through which hot water is transported. By injecting liquid into the pipeline due to the rotation of special elements, recirculation electric pumps increase the pressure of the liquid medium pumped by them and, accordingly, the speed of its movement.
Most often, heating systems are equipped with recirculation pumps, which makes it possible to increase not only the efficiency, but also the economy of the latter. Most of these systems, as you know, work at the expense of a coolant, which, moving through the pipeline, gives off heat to the room. Heating of the coolant (in this case, before it is fed into the pipeline) is provided by a boiler, boiler or water heater. After passing through the entire heating circuit, the water must return to the heating equipment, where it is again given the required temperature.
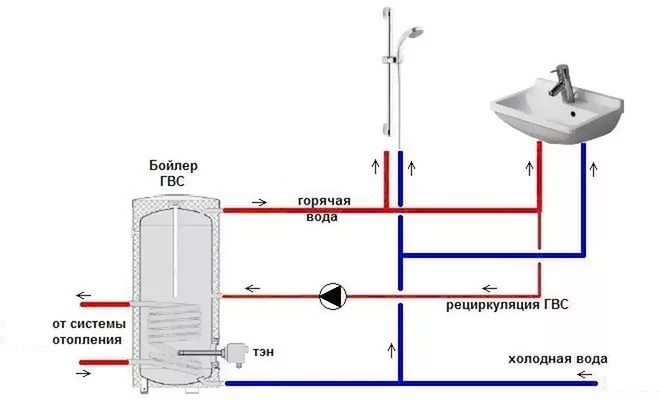

DHW recirculation circuit
Without the use of special pumping equipment, the circulation of water in the heating system will proceed slowly, and in some cases it may not flow at all, since the pressure of the coolant flow, which is not additionally increased in any way, will be extinguished by the elements of the pipeline. The result of this is unevenly heated heating pipes and, accordingly, an uncomfortable temperature in the premises of the house.
A circulation pump for hot water supply increases the head and pressure of a hot liquid moving along a closed pipeline loop. It is especially important to use circulation pumps for hot water in piping systems of houses with an area of more than 200 m2, in which there are several points of water intake, and the boiler is installed in a separate room or in the basement. Water in such pipelines (as a rule, rather long), if they do not have a recirculation system using a special pump, cools down quickly enough. This leads to the fact that when you open the tap, you have to wait a long time until the liquid heated to the required temperature flows out of it.
In addition, when opening some taps at the water intake points at once, the water pressure in them drops, because the pressure of the liquid moving through the pipeline by gravity is not additionally supported. To solve just such problems that private owners and residents of apartment buildings face, a hot water pump is designed to provide forced movement, as well as to create a stable water pressure and pressure in the hot water supply system.
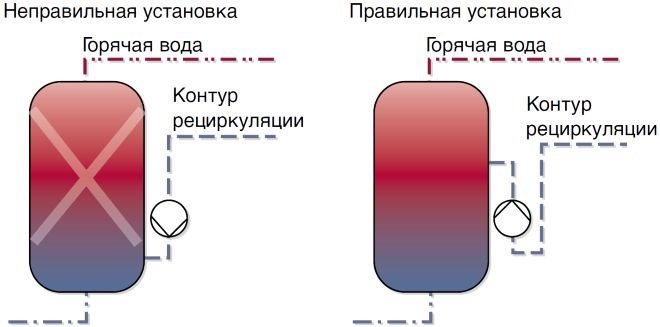

The recirculation pump should not be installed near tanks and water heaters, the heat from which can act on the thermostat
The use of a circulation pump for heating and hot water supply of a private house, in addition to the above advantages, allows you to save on energy costs. Since in systems with recirculation, water from the boiler is transported through pipes forcibly and reaches all points of water intake and heating radiators much faster, its temperature during such transportation decreases slightly. The boiler, if forced recirculation of water is provided in the pipeline it serves, it takes less time to heat it up, respectively, the consumption of energy carriers used to operate the heating equipment is reduced.
Pumps for circulation of hot water are actively used to equip systems "warm floor", the scheme of which assumes the presence of an extended pipeline circuit of a complex configuration, consisting of pipes of small diameter. The circulating pump in such cases ensures the constant movement of the coolant through the pipes.


The circulation pump is an essential element of the underfloor heating system
Selection by characteristics
How to choose a pump for a heating system?
It is clear that class A energy efficiency and infinitely variable speed control are welcome. It is also clear that the repair of the German-made Wilo heating pump or the Danish Grundfos is required immeasurably less frequently than the Chinese Octopus. But what about the pressure and performance?
Pressure
The calculation of the pump for heating by pressure depends primarily on the length of the heating circuit. As already mentioned, the pump has to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipes, fittings and valves.
Experts from Wilo offer a fairly simple formula for calculating:
In it:
- H is the head that we calculate, in meters;
- R is the pressure drop per linear meter of the pipe, which is taken to be equal to 0.01-0.015 meters of pressure per linear meter of the circuit (the length of both flow and return is taken into account);
- ZF — correction factor for resistance of fittings and valves. It is taken equal to 1.3 for fittings and modern shut-off valves; the use of a throttle or thermostat in the main circuit increases the pressure loss by another 1.7 times.
Let's try, as an example, to calculate the pressure for two-pipe heating laid along the contour of a house measuring 8x10 meters.
The total length of the perimeter of the house is (8 * 2) + (10 * 2) = 36 meters.
Double-pipe heating forces you to multiply the length of the perimeter by 2.
We will not install the thermostat in the main circuit.
In total, we need a pump with a pressure of 0.015x72x1.3 = 1.4 meters.
Performance
What about the performance calculation?
Most of the sources suggest calculating the pump for heating using complex formulas tied to the specific heat capacity of water. However, in practice, the calculation can be greatly simplified:
Q = N / (T1-T2), where:
- Q is the required value in cubic meters per hour;
- N is the thermal power of the boiler in kilowatts;
- T1 and T2 — supply and return temperatures.
Let's give an example. A boiler with a capacity of 18 kilowatts, which has an outlet of 90 degrees, for a return temperature of 65 C needs a pump with a capacity of 18 / (90-65) = 0.72 m3 / h.
What is a heating pump
Heating designs with a natural whirlpool or recirculation supply can be quite effective, but only when servicing small areas. For private houses and apartments with a large area next to the boiler, it is necessary to install a special device for the forced movement of water through the system. The circulating sediment is a technological device that works in a ring heating, continuously moving water through pipes. Its main task is to ensure a continuous supply of heat and circulation of water in the system.
Circulation pump device
In a simplified version, the principle of operation of such a technological device is based on the interaction of a motor and a rotor, which is immersed in a coolant. The motor provides a continuous supply of fluid, and the rotor helps to convert kinetic energy into potential energy, thereby creating the necessary level of pressure in the system. However, in many respects, the high-quality and reliable operation of the circulation pump in the heating system depends on the type of device and its characteristics.
Types
Heating devices can be classified not only by brand names, but also by the characteristics and principle of operation of the device. So, the types of circulating sediments are conditionally subdivided into only two types:
- The dry type ejector is characterized by the fact that the rotor part of the device does not come into contact with water. Such a heating pump at the outlet gives an efficiency of up to 85%, but creates a fair amount of noise, which is why it is preferable to install the device in separate gas boiler rooms.
- Wet-type pumps are those devices in which the entire moving part is in constant contact with water. Warm liquid provides such technological devices with constant lubrication of parts and silent operation. The efficiency of wet circulating devices is only 50-65%, which is why it is preferable to install them in private houses.
Specifications
To buy a circulation pump for heating, it is important to be well versed in its technical parameters. There are not too many characteristics worth focusing on. In fact, only two will be important for a common man in the street:
- Head - hydraulic resistance of the system. The value is measured in meters and, as a rule, is set by the value of the highest point of the pipeline.
- Productivity is a parameter showing what volume of liquid the device can process per unit of time. Productivity is measured in cubic meters per hour.
It is worth knowing that these concepts are inversely proportional. So the maximum power of the electric pump will be achieved at zero pipeline height, and the head at the same flow. Thanks to these main characteristics, you can choose a model with the optimal parameters for yourself. At the same time, the principle of choosing a device - the more productive, the better - is not suitable for achieving high performance. Buying an incorrectly selected unit will lead to a decrease in heat transfer and an increase in electricity consumption.
Marking
Before choosing a pump for the heating system finally, it is worth reading and deciphering the alphanumeric designations on the unit label. As a rule, the following characteristics are added to the labeling of circulation pumps for heating systems:
- The letters UP indicate the type of unit. In this case, circulating.
- Then there are the letters S / E, denoting the control method: step change of speeds or smooth adjustment.
- After the letter characteristics are numerical ones. The first block indicates the inner diameter in millimeters of the narrow nozzles, the second part indicates the maximum head in decimetres.
- The third numerical block is the millimeter value of the installation length. This indicator is important in the case of a tie-in device.
- In addition, different manufacturers may indicate additional information on the label: type of housing material, method of connection to pipes, power or class of electricity consumption.
How to calculate the power of a circulation pump for heating
In order for the pump for circulating water in the system to fully meet the requirements, it is necessary to calculate the power for the motor before purchasing. If a unit with too high a performance index is supplied, the water in the pipes will make noise. Less power will not provide adequate heat. In fact, for the correct selection of the pumping device, it is necessary to calculate two quantities:
- engine performance;
- supply head.
The operating power will be derived from the total heat output of the heating system. Simply put, the device must pump such a volume of liquid so that it is enough for the needs of all radiators in the house. To calculate this, it is necessary to know the exact resource requirement for complete heating of the building. For private houses with an area of 100 square meters, this value will be 10 kW. The calculation itself should be made according to the following scheme X = 3600U (a * b), where:
- У - heat consumption for heating;
- A - thermal conductivity of water = 4.187 kJ / kg;
- B - temperature difference between supply and return. As a rule, a value of 10-20 degrees is conventionally accepted.
Installation rules in the heating system
In order for the unit supplying water to serve for a long time, it was convenient to maintain it; when inserting, it is necessary to observe a number of rules:
- For ease of dismantling, ball valves must be installed on both sides of the unit.
- To create a barrier to fine mechanical particles, it is advisable to install a special filter in front of the device.
- It is advisable to install an automatic or manual air valve in the upper part of the bypass path, which will allow the accumulated oxygen to be removed from the system.
- Due to the fact that the installation of pumps in the heating system of different manufacturers has its own distinctive features, it is important to observe the installation direction indicated on the device case.
- It is always necessary to cut the pump for circulation of water in a wet-type heating system horizontally so as not to damage the electric motor during operation. In this case, the terminals of the unit must always point clearly upwards.
- Joints and threaded connections must be treated with sealants, and a gasket must be placed between the mating parts.
Connection
Let's not go into the jungle: we'd better leave the configuration and connection of powerful pumping stations to the engineers. Let's see what heating with a pump can be in a relatively small private house.
Open system
Yes, a small pump works great. Is he needed there? Let's put it this way: useful.
It can be used to speed up circulation in a fully working gravity heating system. In addition to a more uniform heating of radiators, as a bonus, we will get a much faster heating of the house after firing up the boiler.
The circuit design itself in this case remains quite typical:
- After the boiler, the filling rises sharply, forming the so-called booster manifold.
- An open expansion tank is mounted at its top point. It compensates for the change in the volume of the coolant when heated; all the air is displaced there.In addition, the tank can be used to feed the circuit.
Tip: the valve for filling the system with a centralized water supply, of course, is more convenient to put at the bottom. However, then it will be difficult to control the water level. It is better to drain the water supply directly into the tank.
- Further, the contour with a slope of several degrees goes down to the boiler. On the way, the water gives off heat to the radiators cut in parallel to the main circuit.
How and where to install the pump in this case?
In front of the boiler, on the return line. A lower water temperature will slightly increase the life of the device.
The connection diagram should be such as not to interfere with natural circulation:
- The main circuit is interrupted by a ball valve. When the pump is running, the bypass is closed so that the pump does not drive water in a circle.
- Pump connections are made with a smaller diameter before and after the valve in the main circuit.
- The tie-in is equipped with a pair of shut-off valves; in addition, a sump is placed in front of the impeller. In systems with a small volume, its function is successfully performed by a conventional coarse filter.
Before us is a perfectly executed modernization of the working gravitational heating system.
In normal mode, the heating works with forced circulation, but if the power supply is lost, and with the bypass valve open, the system starts to work like a normal gravitational one.
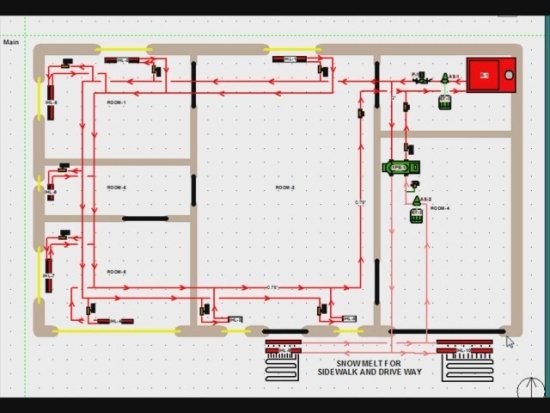
System with radiators and underfloor heating
How to design with your own hands a working system with two circuits - radiators and underfloor heating?
Of course, it is more convenient to make the contours independent. How to implement this?
Here's the instruction:
- After the boiler, a hydraulic arrow is mounted with several pairs of outputs. It is, in simple terms, a thick pipe between the supply and return. By taking the coolant from different pairs of nozzles, you can get different temperatures and differences.
- The main pump maintains circulation at a constant return temperature through a hydraulic switch. The additional one takes water (or other coolant) from a pair of hydraulic arrow terminals close to the return line and provides circulation inside the warm floor, maintaining a constant temperature in it. The radiator circuit is connected independently to a different pair of terminals.
As a result, radiators and underfloor heating can heat the house both together and independently.
Video
Units in building heating systems provide additional options for adjusting the mode. Despite the additional costs associated with the purchase and installation of a circular pump, the total costs quickly pay off, allowing you to optimize the heating mode.
Before choosing a circulation pump, the calculation of the basic parameters is highly desirable for the following reasons:
- insufficient power of the unit will make the heating system ineffective, and living in the house will be uncomfortable;
- excess capacity will lead to cost overruns for heating the home.
Thus, the selection of this specialized device largely determines the success of the heating of a residential building.
The pump for heating is in modern systems one of the decisive factors that ensure uniform movement of the coolant and, therefore, uniform heating of the fuel elements.
Video
Such units are endowed with a set of advantages, defined as:
- Contribute to maintaining a constant temperature of the coolant.
- Low level of electricity consumption.
- High operational reliability.
- Ease of use.
Their main functional task is to level the resistance of the piping to the heating agent flow.
There are two main designs of circular pumps:
- with dry rotor;
- with a wet rotor.
The working chamber of the device with a dry rotor is separated from the electric motor by a sealed partition.Such units usually have higher power and performance, but they make noise during operation, therefore their use is limited to installation in isolated rooms or buildings.


Glandless pumps operate in a coolant environment, which increases their service life. For the same reason, they are low-noise, which allows their use inside serviced buildings.
A significant disadvantage of such units is their low efficiency
, which limits their use in large heating systems, however, in small private houses they are used very widely due to the above-mentioned low noise and durability.
It should be noted that the selection criteria are not limited to taking into account their positive and negative qualities. The choice of a circulation pump for heating necessarily includes its calculation according to several criteria.
Differences between devices with "dry" and "wet" rotors
Depending on whether the rotor is in contact with liquid, there are two types of pumps - "dry" and "wet". Each of the types has its own design features and scope.
"Wet" circulation pump: advantages and disadvantages
The "wet" rotor is in the liquid, and its stator is protected from contact with moisture by a special stainless steel sleeve. The disadvantage of models of this type is lower efficiency compared to "dry" designs. Advantages - relatively "quiet" operation, ease of maintenance and repair.
Modern models are equipped with reliable automation, thanks to which you can easily control their performance, select operating modes and thereby control power consumption. Circulating pumps with "wet" rotors are suitable for installation in systems where the amount of liquid is constant or slightly variable.
Design features of the model with a "wet" rotor
Features of the operation of models with "dry" rotors
"Dry" rotors do not come into contact with liquids, they are sealed with stainless steel, ceramic or carbon agglomerate O-rings. These elements are carefully adjusted; when they rotate, a water film appears, which protects the parts of the electric motor. The rings will gradually wear out as the device is used. A pressure spring is used to provide a seal. She clamps the parts, thus constantly adjusting to each other.
During operation, the pump creates air turbulences that lift fine dust particles into the air. If they get inside, they can compromise the tightness of the O-rings and damage the mechanism. A thin film of water is needed to prevent dust from entering between the parts of the device. The disadvantage of a dry rotor is noticeable noise during operation. These models are best placed in separate rooms.
Diagram of the design of the "dry" pump of the German brand Wilo
Cantilever, vertical and block dry models
Depending on the design features, there are three types of "dry" pumps:
- vertical;
- console (horizontal);
- block.
The suction nozzles of the cantilever models are located on the outside of the volute, the inlets are on the opposite side. The engine is mounted horizontally. The vertical models are so named because their motors are mounted vertically. The branch pipes in them are located on the same axis. The peculiarity of block pumps is that the liquid enters in the axial direction and exits in the radial direction.
Design features
For DHW circulation, centrifugal pumps with a "wet" rotor are mainly used. The principle of operation of such a circulation pump is quite simple.
- Water entering the recirculation pump chamber through the inlet pipe is captured by the impeller blades, the rotation of which is communicated from the drive motor shaft.
- Centrifugal force begins to act on the water, which throws it to the walls of the working chamber, where increased pressure is created.
- Under the influence of the pressure generated by the centrifugal force, the liquid is pushed into the pressure line of the recirculation pump.
- The suction of the next portion of hot water into the working chamber occurs due to the fact that in the central part of such a chamber during the course of the above processes, a rarefaction of air is created.


The device of a centrifugal circulation pump with a "wet" rotor
It should be borne in mind that a conventional centrifugal pump for water is not suitable for heating and hot water supply, since the operating conditions of such equipment do not provide for a high temperature of the pumped liquid. For the manufacture of pumps with which hot water is recirculated, materials are used that are resistant to increased loads and high temperatures. In addition, such electric pumps, which operate mainly indoors, should be distinguished by low noise so as not to make living conditions in a private or in an apartment building uncomfortable. No less important characteristics of electric pumps for DHW circulation are compactness and efficiency in terms of electricity consumption.
When choosing pumping equipment that will have to work with hot water, it should also be borne in mind that pumps for DHW recirculation differ in terms of operating conditions from the devices used to equip the heating system. So, models of pumps for a boiler room are designed to pump water, the temperature of which reaches 90 °, while devices that circulate hot water supply can work with a liquid medium heated to 65 °. Thus, they are not interchangeable, although, if necessary, the electric pump for heating can be used to circulate hot water in DHW systems. However, such devices cannot be replaced in the reverse order.


Domestic pumps are designed to recirculate water in small hot water systems
Why are circulating pumps installed in heating systems
Thanks to the forced circulation of the coolant, you can create a more comfortable microclimate in the house. Rooms are warmed up much faster and better. At the same time, the requirements for boiler power and energy consumption are reduced. The pumps are used both in radiator heating systems and in the arrangement of warm floors.
If the model is selected correctly, the efficiency of the system as a whole increases, and the cost of heating decreases. The only possible drawback is noise during operation, but most often extraneous sounds appear not due to the pump, but due to errors in the installation of the system or when air enters the pipes.
Simplified diagram of connecting the circulation pump to the heating system
Performance calculation
One of the control parameters is the performance of the pumping equipment, which is calculated from the ratio:
- the amount of thermal energy consumed in a particular room;
- the value of the pumping device capacity;
- specific heat capacity, if water is used as a heat carrier, for other types (transformer oil, antifreeze, etc.), the corresponding data are applied;
- the temperature difference between the direct and return branches of the heating system, which can be:
- 20 o C - with a normal heating system of residential areas;
- 10 о С - temperature level in non-residential areas with low-temperature heating;
- 5 о С is the temperature of the heat carrier in the underfloor heating system.
The performance indicator is a passport characteristic, in the technical documentation it is reflected as cubic meters per hour. In order for the result of the calculation to correspond to the form we are accustomed to, it must be divided by the value of the specific gravity of water.
Video
Let's give an example of calculation: the area of the heated room is 200 square meters, therefore, in order to heat it, energy costs of 20,000 watts are needed. The room is equipped with a normal heating system with a temperature difference of 20 ° C. Using these numerical values in the above formula, we get:
20,000 / (1.16 x 20) = 862 kg / hour,
recalculation into the usual values gives the result
862 / 971.8 = 0.887 m 3 / hour.
To heat the specified room, you will need a pump with a capacity of at least 0.9 m 3 / hour. This indicator must be looked for in the passport.
To calculate this characteristic, you can apply the following formula:
G = 3.6Q / (c x dT) kg / h, where
с - specific heat of the carrier used in heating.
It is easiest to select a pump if the boiler output is already known. In this case, you can apply the ratio:
Q = N x dT, where
Q - unit performance;
N - boiler power;
dT is the temperature difference at the outlet from the boiler and at the return.
Important! The rotor is only horizontal! The direction of flow is indicated by an arrow on the body.
Where else are circulating pumps used?
- In cold and hot water supply systems
Installing a pump allows you to achieve a stable hot water temperature and a good pressure in the system. You don't have to pour cold water down the drain while waiting for hot water to come out of the tap. This saves resources.
- In innovative heating systems
Solar and geothermal heating technologies are not yet very common, but pumps are also installed in them to circulate the coolant.
- In air conditioning systems
Circulation pumps can handle more than just hot liquids for heating homes. They are equally well used for refrigeration and air conditioning.
- In heat recovery systems
The recuperator is a unit that heats the supply air due to the removed air. A pump is needed to circulate ethylene glycol in such a system.
Hot water pump
What do circulating pumps consist of, their varieties
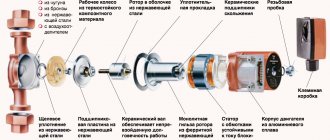
All such pumps consist of the following components:
- corpson which the "snail" is installed;
- loop pipesattached to the "snail";
- electric motor, which has terminals for connecting to the network;
- rotor - a rotating structural element (on one side, the rotor sucks in the coolant, after which it pumps it into the loop pipes, as a result, the required pressure is formed at the pump outlet).
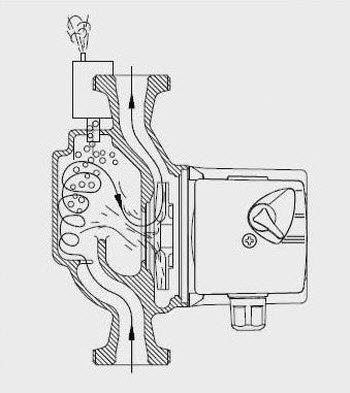

Circulation pump sectional view
The use of a circulation pump eliminates a number of problems. So, if during natural circulation the water in the last radiator is cold, and in the nearby it is a little warm, then with the return flow, the coolant with a low temperature forces the boiler to work more intensively, sometimes even at the peak of its capabilities. Moreover, if mistakes were made in the design of the heating system, then the difference in temperature will be even more noticeable.
You may be interested in information about what the pumping station consists of


Installed pump
Can I use a circulation pump for irrigation
Difficulties with watering plants is an urgent problem for many gardeners. The circulation pump is universal, therefore it helps to solve it too. As a rule, the "root of evil" is a weak water pressure. Large volumes of water are needed, but the water supply system is often not able to pump it at the required speed and pressure. By installing a pump, you can provide the desired head.
The pumps are used in drip irrigation systems that require an operating pressure of 0.2-4 atmospheres. To organize such a system, storage tanks are installed on a hill and circulating pumps are turned on for several hours a day. This allows you to achieve greater irrigation efficiency than when installing gravity systems, which often do not live up to expectations.
When choosing a model, pay attention to the main parameters: power, maximum pressure, volume and lifting height of the pumped liquid. If there are difficulties with the calculation, you do not need to buy a pump "by eye", consult a specialist. As for the manufacturers, the trade marks Halm, Wilo (Germany), Grundfos (Denmark), Pedrollo (Italy), AlfaStar (Poland) have proven themselves well in the pumping equipment market. The products of these brands have won the trust of buyers all over the world. If the budget allows, it is better to purchase models from these manufacturers.