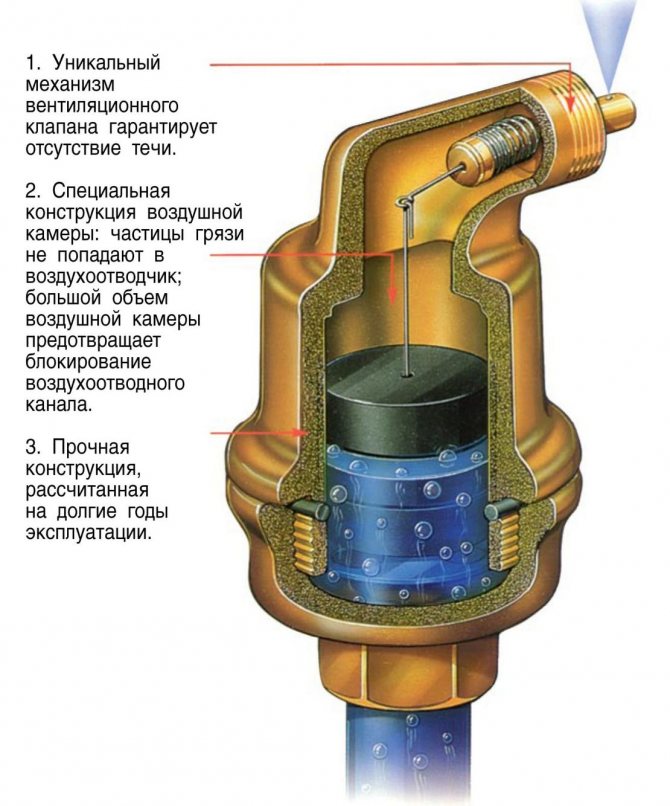
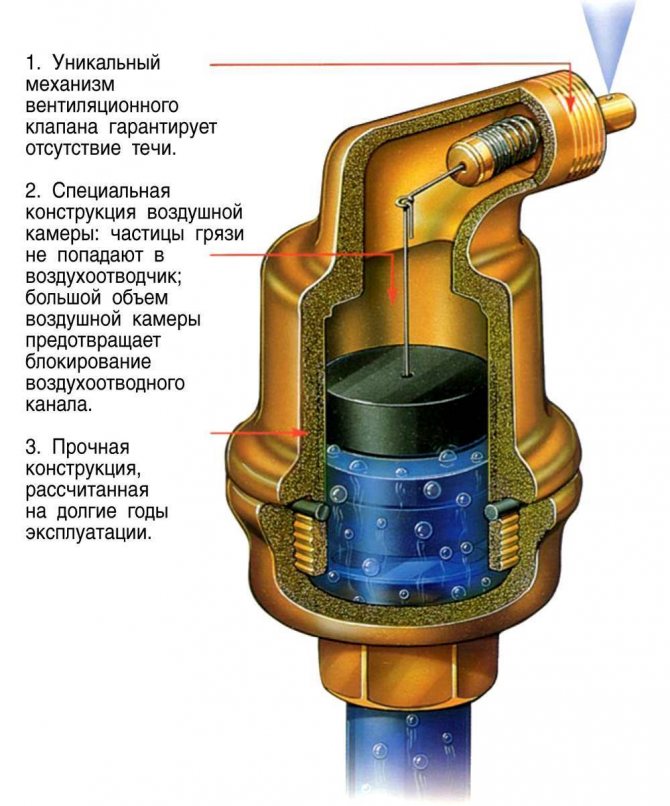
Air vent valves (in a simple way, "air drains") are used in pressure water aeration systems to remove excess air from the aeration column.
For proper operation of the aeration column, high performance air vents are required that are resistant to contamination with iron hydroxide and light debris: such as:
- plastic shavings from HDPE and PP pipes,
- pieces of plumbing thread, fuma, flax,
- plant particles - leaves, roots
The air relief valve also acts as an air intake to the aeration system, compensating for negative pressure in cases of draining the water purification system.
The most famous brands on the Russian market: ARI, RACI, UNIRAIN
The air vent is automatic and operates on the principle of a float mechanism.
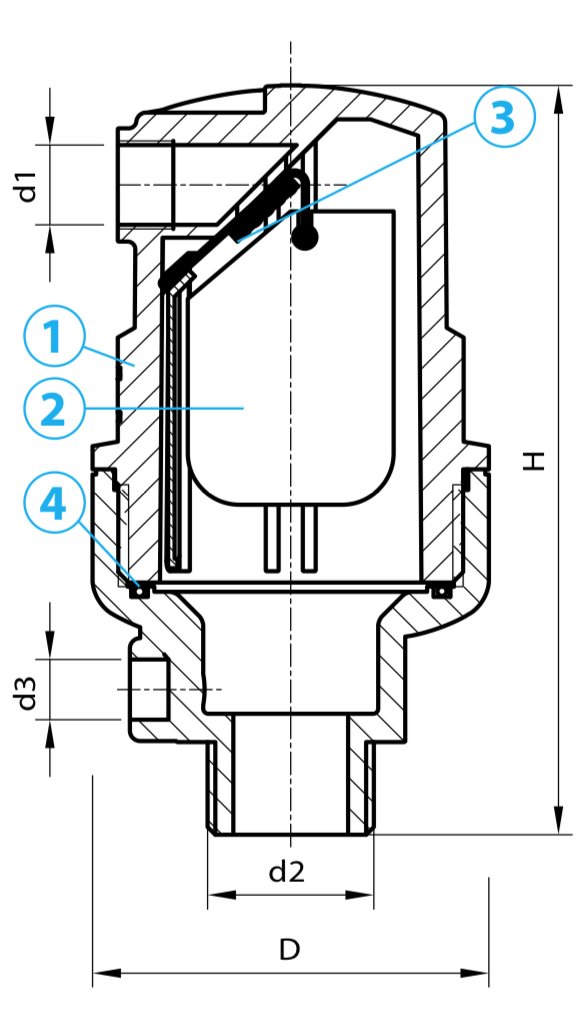
RACI air vent device diagram


Air vent RACIVENT
The diagram shows the RACI automatic air vent device from RACIVENT (Italy).
The valve body is made of fiberglass reinforced nylon. Very durable, withstands high pressure (up to 16 atm). Inside there is a polypropylene float and an E.P.D.M. rubber gasket.
Simple design and quality of parts guarantees durability of work with water of any chemical composition.
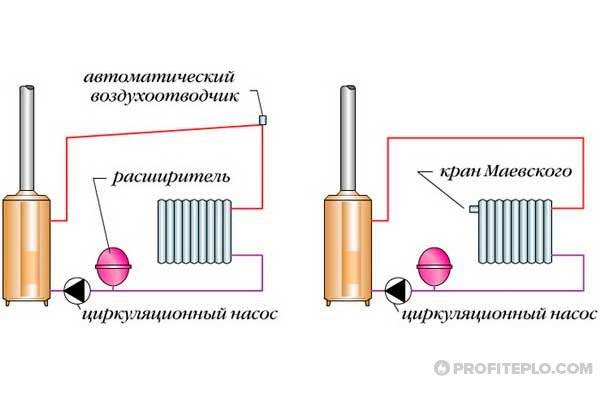
Design and operation of the manual air valve


A needle manual air valve is also called a Mayevsky valve. Its device:
- Brass body (plug) with 1/2 // or 3/4 // male thread for connection to the radiator. There are two Ø 2 mm air outlet holes in the casing - one at the end of the casing, the other on the side wall;
- Brass locking screw. On one side of the screw there is a slot for a slotted screwdriver; on the other side, the screw is machined for a cone that closes the air hole (position "closed");
- Plastic cover.
On sale you can find the so-called "arm crane". To use it, neither a key nor a screwdriver is needed - the plug can be easily unscrewed by hand.
Unscrew the screw to vent air from the housing. To do this, you can, of course, use a screwdriver, but there are special keys that most often come with the kit. After several turns, the screw cone comes out of the end hole and air enters the body cavity, which is immediately released through the second side hole. The main thing is not to rush to turn off the tap. About 30 - 40% of the air should come out with water, so you need to stock up on time, a basin and rags. After the air is released, you need to add the lost water to the system.


In modern aluminum or bimetallic heating radiators, a hole is already provided for the installation of a Mayevsky crane. It can be found on the side opposite to the coolant supply, from above. Most likely, there is already a nut for installation. A plastic plug is screwed into it. After removing it, an air valve is mounted in this place. Before this, the tap threads must be sealed with a rubber or silicone gasket.
Installing a Mayevsky crane on a cast iron battery is much more difficult. Let's start with the fact that these valves are much more powerful than those on aluminum radiators - they can withstand pressures up to 16 atmospheres and temperatures of 150 ° C. Sequencing:
- 1 Drain the water from the radiator;
- 2 Cut a hole in the upper plug of the cast-iron battery and cut a thread corresponding to the external thread of the air vent;
- 3 Screw in the Mayevsky tap;
- 4 Add water to the system.
Malfunctions and remedies


In the event of a valve malfunction, a leak appears. There may be several reasons for this:
- Manufacturing defects. One in fifty taps does not hold pressure at all. The only way out is replacement;
- Screw too short.In this case, its conical part cannot completely cover the hole, so a certain effort must be applied to screw in the screw all the way;
- Hard particles of debris getting between the screw and the housing can damage the internal threads. One-time fum tape can help here, but later you still have to change the tap.
What signs indicate the need to install an air valve
In order to prevent air accumulation, heating engineers propose to use an air valve for heating from the very beginning of the circuit's operation, therefore, heating engineers in the compiled heating scheme give recommendations as to which air vent is suitable for a specific heating system.
However, in some cases, trying to save money on the purchase of this type of control valve, the owners refuse to install devices and thereby provoke a number of problems. To solve them, they have to install an air valve for the heating system after the circuit has been tied and connected to the boiler.
The following signs indicate the presence of air pockets and indicate the need to integrate an air vent into the heating circuit:
- uneven heating of batteries;
- the appearance of "cold spots" on the pipeline;
- poor circulation in the heating system;
- noise in heating devices;
- poor quality heating of the house.
Finding a suitable installation location in the system
Taking into account the principle of operation of an automatic air vent for heating, it is usually used in such areas:
- Highest point of the heating circuit (tops on vertical pipes, etc.). This is where the internal air of the system usually collects.
- End areas of dead-end pipelines.
- Boiler piping safety group. This is especially needed by solid fuel boilers. In this case, an automatic air vent is included in the instrument kit, which also has a pressure gauge and an emergency valve. Thanks to the air vent, air is released as the coolant fills the boiler water jacket. In addition, the appliance increases the water drainage rate when the heat generator is disconnected from the general system.
- Together with a circulation pump, which allows to optimize its operation. This option is used only for those models of pumping equipment, the design of which provides for the installation of an air vent. If a coolant with air is pumped, a noticeable deterioration in the quality of the pump will occur, up to its shutdown. All this leads to rapid wear of the impeller and bearings. With the help of a bleeder, you can also remove steam from the coolant in case of overheating.
- Areas of the heating circuit where constant airing of the system is observed. One of the reasons for such phenomena is the incorrectly calculated angle of inclination of the pipe.
- Heating devices.
Solenoid valves for steam, steam-water mixture and oil
For steam, water, gases and high-pressure liquids up to 15 MPa (PN150), special electromagnetic solenoid valves are used, made of brass and SS304 stainless steel (AISI 304).
The solenoid solenoid valve SMART SA5576 is normally closed, SMART SA5578 is normally open. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam, oil, etc. Maximum pressure 25 bar, differential pressure 0.5 to 25 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 185 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SA55762 | G 3/8 " | DN10 | |
| SA55763 \ SA55783 | G 1/2 " | DN15 | |
| SA55764 \ SA55784 | G 3/4 " | DN20 | |
| SA55765 \ SA55785 | G 1 " | DN25 | |
| SA55766 \ SA55786 | G 1 1/4 " | DN32 | |
| SA55767 \ SA55787 | G 1 1/2 " | DN40 | |
| SA55768 \ SA55788 | G 2 " | DN50 |
Electromagnetic valve SMART SA5576F is normally closed, SMART SA5578F is normally open.High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam, oil, etc. Maximum pressure 25 bar, differential pressure 0.5 to 25 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 185 ° С.
| vendor code | Join. | Diameter | |
| SA55765F \ SA55785F | Flanges isp. one | DN25 | |
| SA55766F \ SA55786F | Flanges isp. one | DN32 | |
| SA55767F \ SA55787F | Flanges isp. one | DN40 | |
| SA55768F \ SA55788F | Flanges isp. one | DN50 |
Solenoid valve SMART SB5502 normally closed. Direct acting solenoid valve for water, air, solutions, alcohol, diesel fuel, freon, oil, glycol, etc. Maximum pressure 20 bar, differential pressure 0 to 20 bar. Working environment temperature -10 .. + 120 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SB55024 | G 1/4 " | DN10 | |
| SB55025 | G 3/8 " | DN10 | |
| SB55026 | G 1/2 " | DN10 |
Solenoid solenoid valve SMART SB5552 normally closed. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, alcohol, diesel fuel, freon. Maximum pressure 150 bar, differential pressure from 1 to 150 bar. Working environment temperature -20 .. + 110 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SB55524 | G 1/4 " | DN8 | |
| SB55525 | G 3/8 " | DN8 |
Valve electromagnetic steel SMART SB5562-S normally closed. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam, fuel, freon, alcohol. Maximum pressure 90 bar, differential pressure 0.5 to 90 bar. Working environment temperature 0 .. + 110 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SB55623-S | G 1/4 " | DN8 | |
| SB55624-S | G 3/8 " | DN8 | |
| SB55625-S | G 1/2 ″ | DN8 |
The electromagnetic two-way valve SMART SB5572 is normally closed. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam. Maximum pressure 75 bar, differential pressure from 1 to 75 bar. Working environment temperature -20 .. + 110 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SB55725 | G 3/8 " | DN15 | |
| SB55726 | G 1/2 " | DN15 | |
| SB55727 | G 3/4 " | DN20 | |
| SB55728 | G 1 " | DN25 |
Electromagnetic valve 2-way SMART SB5592 normally closed with tapered thread. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam. Maximum pressure 50 bar, differential pressure 1 to 50 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 150 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SB55926 | Rc 1/2 " | DN15 | |
| SB55927 | Rc 3/4 " | DN20 | |
| SB55928 | Rc 1 " | DN25 |
Pilot solenoid valve SMART SL5575 normally closed. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam, oil, petroleum products, fuel, etc. Maximum pressure 25 bar, differential pressure 1 to 15 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 180 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SL55751 | G 1/2 " | DN15 | |
| SL55752 | G 3/4 " | DN20 | |
| SL55753 | G 1 " | DN25 | |
| SL55754 | G 1 1/4 " | DN32 | |
| SL55755 | G 1 1/2 " | DN40 | |
| SL55756 | G 2 " | DN50 |
Electromagnetic valve normally closed SMART SL5595. High pressure solenoid valves for water, air, solutions, steam, oil, petroleum products, fuel, etc. Maximum pressure 10 bar, differential pressure 0 to 8 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 185 ° С.
| vendor code | Thread | Diameter | |
| SL55951 | G 1/2 " | DN15 | |
| SL55952 | G 3/4 " | DN20 | |
| SL55953 | G 1 " | DN25 | |
| SL55954 | G 1 1/4 " | DN32 | |
| SL55955 | G 1 1/2 " | DN40 | |
| SL55956 | G 2 " | DN50 |
Valve two-way flanged solenoid SMART SL7555F normally closed, Solenoid valves for water, alkalis, air, solutions, diesel fuel, oil, freon, carbon dioxide, steam, steam-water mixture, oil products, etc. Maximum pressure 10 bar, differential pressure 0 to 8 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 185 ° С.
| vendor code | Join. | Diameter | |
| SL75553F | Flanges isp. one | DN25 | |
| SL75554F | Flanges isp. one | DN32 | |
| SL75555F | Flanges isp. one | DN40 | |
| SL75556F | Flanges isp. one | DN50 |
Flanged solenoid valve SMART HF6752. Solenoid valves for superheated water, steam, oil, air, solutions, oil, freon, carbon dioxide, etc. Maximum pressure 16 bar, differential pressure from 1 to 16 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 185 ° С.
| vendor code | Join. | Diameter | |
| HF67523 | Flanges isp. one | DN65 | |
| HF67524 | Flanges isp. one | DN80 | |
| HF67525 | Flanges isp. one | DN100 | |
| HF67527 | Flanges isp. one | DN150 | |
| HF67527 | Flanges isp. one | DN150 |
Stainless steel solenoid valve SMART HX5571 for coupling connection normally closed, SMART HX5571F for flange connection normally closed. Solenoid valves for water, alkalis, air, solutions, diesel fuel, oil, freon, carbon dioxide, steam, steam-water mixture, oil products, etc. Maximum pressure 16 bar, differential pressure 0.5 to 16 bar. Working environment temperature -30 .. + 250 ° С.
| vendor code | Join. | Diameter | |
| HX55713 | G 1/2 " | DN15 | |
| HX55714 | G 3/4 " | DN20 | |
| HX55715 \ HX55715F | G 1 ”\ Flanges isp. one | DN25 | |
| HX55716 \ HX55716F | G 1 1/4 ”\ Flanges isp. one | DN32 | |
| HX55717 \ HX55717F | G 1 1/2 ”\ Flanges isp. one | DN40 | |
| HX55718 \ HX55718F | G 2 ”\ Flanges isp. one | DN50 |
Solenoid valves are equipped with electromagnetic coils of a given voltage, by default AC220V. The cost of the coil is included in the price of the valve.
Types of automatic air dumpers
In total, there are three types of these devices - despite this, the operation of the automatic air vent, or rather its principle, remains unchanged. In all cases, the same needle valve and the same float that opens and closes it are used - the only difference is in the position of the body relative to the connecting pipe, i.e. threaded connection.
- Direct automatic air valve for heating. The most common automatic venting device. It is intended only for vertical installation - in the sense that if you suddenly decide to use it for a battery, then you will additionally need a corner at 90 degrees. The optimal area of their application is pipelines, or rather their upper points, where, according to all the laws of physics, the air formed in heating rushes. If it were not for such devices, then it would be very inconvenient to discharge air at the highest points of heating systems. In addition, some heating system equipment is equipped with automatic dumpers with straight connecting pipes. For example, the automatic air valve is an integral part of the boiler safety group, which also includes a pressure gauge and an explosion valve. Air vents are also equipped with indirect heating boilers and other equipment, at the top of which there is a possibility of air accumulation.
- Corner air vent. In short, angle vending machines are used where it is not possible to install its direct counterpart - it may either not fit in the right place, or the equipment has a threaded side outlet. In general, there are many different situations, and it makes no sense to list them all, especially since the essence and principle of operation remain unchanged - only the location of the threaded outlet connecting pipe changes and, as a result, the appearance of the Mayevsky automatic crane. A very important condition for the correct functioning of the vending machine for venting is a strictly vertical installation of its body. Horizontally and even at an inclination with a small angle, the machine will not be able to work adequately - the float will get stuck and, as a result, air removal will be untimely or it will not be performed at all.
- Automatic air vent for radiators. In fact, this is a kind of angle vending machine for air removal, although from the outside you cannot tell - all these nuances are hidden inside the case. The outer part of the battery vent is designed for aesthetic reasons. In addition, these devices also differ in the diameter of the connecting pipe - on modern radiators, they are installed directly into the battery, without the use of foot nuts. On old batteries, they are mounted through a case with a threaded through hole, and for steel convectors, special machines with a half-inch pipe are used.
This and all the varieties that the automatic air valve for heating systems can boast of. In principle, more is not needed, since regardless of the various installation conditions, one of them will still work.
Types of air vents in the heating system


According to the principle of operation, ball and needle automatic devices are distinguished, according to the design - straight, angular and radiator. Despite the different areas of use, the principle of operation of all air vents is the same.
Special devices of the float plan are very popular. It is an automatic air vent that provides lateral air discharge. The device operates at an operating pressure of 10 bar, while the maximum allowable temperature is 110 degrees.The device can work not only with water, but also with different glycol solutions in a concentration of up to 25%, and the connection thread is 1/2.
All modern automatic air vents are divided into several types, differing in general design. In total, there are three main types of such devices:
- Corner;
- Straight;
- Radiator
Direct air discharge
The most common is the first type with a straight pipe. It is indispensable at the highest points of the system, where, according to all the laws of physics, the maximum amount of gases accumulates, and manual air discharge in such places is often difficult.
The closed system, which is constantly under pressure, is provided by the boiler safety group. It is usually located on the supply line that exits the heat generator. In addition to a pressure gauge and a safety valve, this kit also includes an automatic air vent for heating, which bleeds air when the tank is filled with liquid. If the unit is installed correctly, then it can be separated from the system at any time and released for maintenance using a gas valve. For boilers operating on solid fuels, a safety group is mandatory.
You can find an air blower in circulating pumps. His task is to create conditions for them for an uninterrupted water supply. The problem is that the pumping unit can only work with an incompressible medium. Air penetration into the pump impeller threatens to stop it completely. Active liquid circulation and is controlled by a gas valve.
Corner air vent
If the space is too inaccessible to install a simple valve (for example, the pipe is horizontal), use the angle version of the valve. Its branch pipe, turned 90 °, can be connected to the horizontal part. It is worth noting that the angular modification with an external thread, in addition to the expanded pipe, practically does not differ from its counterparts, therefore these types are completely interchangeable.
Radiator automatic air vent

Sometimes an automatic angle valve is installed on radiators instead of the traditional Mayevsky crane. It is only slightly larger than its counterpart, a little more expensive (about $ 2), but does not require daily human participation. This choice is justified if gases in the battery accumulate regularly due to the chemical reaction of the aluminum alloy from which the section is made and hot water.
Although for such cases a special automatic device is produced with a diameter like a radiator plug (see photo). The device is specially designed for aluminum and partially bimetallic radiators, has a suitable type of connection.
For cast-iron batteries and old-type systems, the Mayevsky tap and drain pipe are more suitable.
Causes and consequences of air locks in a closed forced circulation heating system
H2_2
The reasons are the same as for an open system, and also:
- Loose impeller of the circulation pump can "grab" air during operation;
- If hot water is supplied to the expansion tank from above, air can enter the system through cracks or ruptures in the tank membrane.
An air lock in the closed loop will increase the pressure in the system and activate the safety valve. The valve will bleed water over and over again until the boiler burns out or the heating pipes burst. Therefore, the security requirements for closed systems are much stricter. In particular, for the release of air, a closed circuit is equipped not only with Mayevsky's manual taps, but also with automatic air vents. One of these automatic valves is included in the safety group. The group is placed on the water supply, immediately after the boiler.
Important! A leaky pipeline or radiator cannot cause an airlock. The working system, whether closed or open, is under pressure.The air will never go towards a higher pressure - this is contrary to all laws of physics.
Reasons for the appearance
Air in the heating system can appear for various reasons. If this is a one-time problem, you can simply delete it and not search for the source. If airing is required several times per season, you will have to look for the cause. The most common ones are:
- Repair, modernization of the heating system. During repair work, air almost always enters the pipeline. It is natural.
- Filling the system with a coolant. If you pour water into the system slowly, it carries a little air with it, simultaneously displacing the one that is in the pipes and radiators. This is also an understandable process, and does not require any special measures.
- Depressurization of joints and welds. This defect requires elimination, since airing will occur constantly. In individual heating systems, this phenomenon (leaking connections) is also accompanied by a drop in pressure. And this is another reason to look for faults. The most likely place is the joints of pipes and radiators. They may be leaky. It is very difficult to look for them, since they do not always appear outwardly. If you notice that some of the compounds "breaks in" everything is much easier - you eliminate the drops. But if everything is outwardly normal, and air accumulates all the time, you have to coat the joints and seams with soapy foam and observe whether new bubbles appear. After finding each "suspicious" connection, they are tightened, coated with sealant or repackaged (the method depends on the type of connections).

Air can accumulate in pipe bends
If the heating system already has air vents (air vent valves) and plugs begin to appear in it, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the valves, as well as the tightness of the connections. The appearance of air in the heating system may be due to a rupture of the expansion tank diaphragm. In this case, the membrane will have to be changed, and for this it is necessary to stop the entire system.
These are the most common places and ways in which air gets into radiators and batteries. It is necessary to expel it from there from time to time, but with the autumn start-up of heating it is necessary.
Valve device
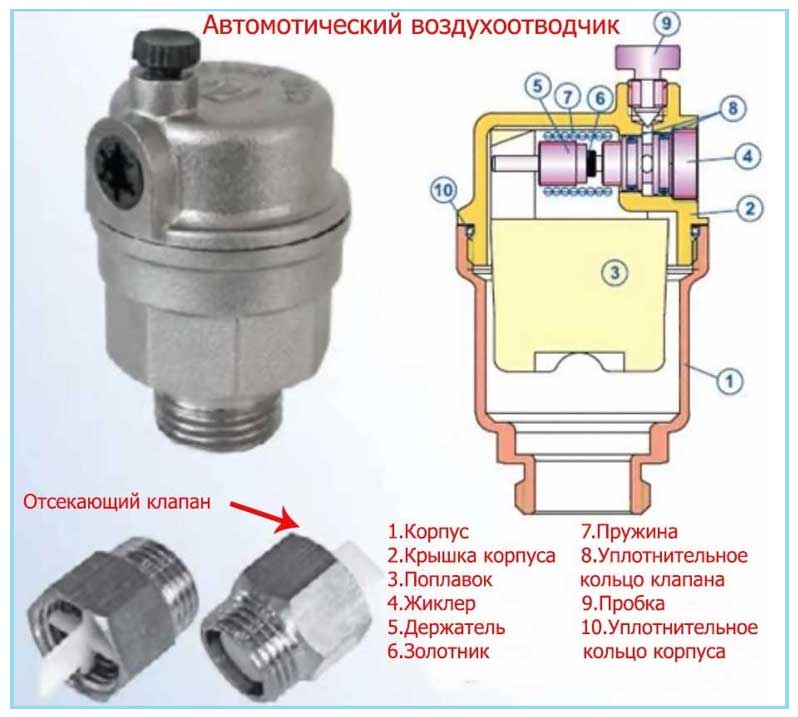


The automatic air vent consists of a cylinder with a built-in plastic float. The device is installed vertically, in normal operating mode its inner part will be tilted under the influence of the heat carrier. The air vent is equipped with a needle rod, to which the float is attached to the lever.
As soon as a plug forms in the pipe, the air will tend to the highest point of the heating circuit. If an automatically operating valve is installed in this place, the heat carrier will be pushed out by air. In the process of displacing water, the float will descend, opening the valve. As a result, air will escape from the pipes and radiator, and the space will be filled with water.
The air vent valve becomes scaled up during operation. This leads to disruption of its operation, loss of tightness. The automatic air release valve can only be replaced, it cannot be repaired.
Types of air vents
Automatic air vents differ in the type of installation, dimensions, thread diameters. according to the location of the nozzles, they are:
- Vertical;
- Radiator;
- Corner.
The angle automatic air vent is convenient for installation on the radiator. In the place where the heating pipe enters it. With such an installation, it will help to catch the air and gases formed in the radiator itself.
The vertical automatic air vent is best installed at the entrance to the heating system. When positioned this way, it will prevent air from entering the system.
The second option for installing a vertical model is at the top of the heating system. It is there that gases accumulate and interfere with the effective circulation of water or coolant.
Radiator air vents are installed instead of a plug or a Mayevsky valve in radiators. They are convenient, but it is advisable to install them on each radiator.
Solenoid valve classification
- By type of body material: brass, stainless steel, cast iron.
- By position in the absence of voltage on the induction coil: normally open solenoid valve (passes the flow of the working medium) and normally closed (closes the pipeline).
- By the type of connection: flanged, coupling.
- By type of working medium: solenoid valve for water, oil, air and steam.
- By the type of locking device: diaphragm and piston.
In our store you can buy any solenoid valve (including for water). We offer each client:
- Low prices. sells solenoid valves with minimal margins.
- Free consultation. Our experts will help you understand a wide range of models and choose a solenoid valve that suits your specific needs.
- Bonus programs. For regular customers and wholesale customers, we provide individual discounts for the purchase of solenoid valves.
- Quality service. We provide warranty and post-warranty service for any solenoid valve purchased from us.
- Delivery service. We will send your solenoid valves by transport companies, express mail or Russian post to any region of the country. In Moscow, for orders over 35 thousand rubles, delivery is FREE.
What is the threat of air in the heating system
Everyone, probably, more than once met with the fact that the heating is turned on, and some radiator or a whole group heats up badly or even stands cold. The reason for this is the air in the heating system. It usually accumulates at the highest point, displacing the coolant from this place. If enough of it accumulates, the circulation of the coolant may stop altogether. Then they say that an air lock has formed in the heating system. Professionals in this case say that the system is airborne.
To resume normal heating operation, the accumulated air must be removed. There are two options for this. The former is more commonly used in district heating systems. Cranes are installed on the extreme radiators in the branch. They are called drains. This is a conventional valve. After filling the system with a coolant, it is opened, kept open until an even stream of water without air bubbles comes out (then the water pours out in jerks). If we talk about multi-storey buildings, then during the start-up of the system, the air outlets on the risers must first open, and the remains can already be taken out to the apartments.
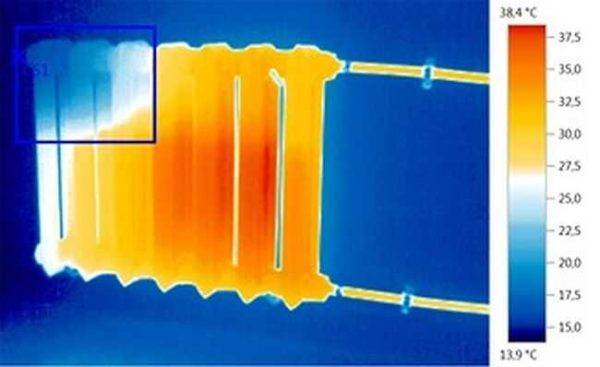

The air in the heating radiator interferes with the normal circulation of the coolant. This causes the battery to heat up poorly.
In private systems or after replacing radiators in apartments, not ordinary taps are installed to bleed air, but special air valves. They are manual and automatic. They are placed in the upper free manifold on each radiator (preferably) and / or at the highest point of the system.
What else threatens the air in the heating system? It contributes to a faster destruction of the components of the heating system. Although polymers are used more and more today, metal parts are still plentiful. The presence of oxygen promotes the activation of oxidation (ferrous metal rusts).
Installation of an automatic air vent


Before installation, a comprehensive check of the device is performed. The housing must be free from dirt, rust and scale, if present. Next, you need to do the following:
- The most convenient area for placing the air vent is calculated. It is advisable to think it over at the design stage of the heating system. The mounting point must be as high as possible, must collect air and gases from all circuits and must be accessible for maintenance.
- Using a shut-off channel or other connecting fittings (if necessary), tighten the automatic air vent valve so that the sealing material ensures the tightness of the joint. If an angle or radiator device is used, then the working part of the housing with the chamber and the float must always be facing upward for unhindered air release.
- The air vent can only be tightened with an open-end wrench - it is undesirable to use lever wrenches.
- The tightness of the connection is checked, after which the cap in the upper part of the device body is unscrewed. Next, you can fill the branch with a coolant.
What is an air valve
The air valve for heating is a sealed cone-shaped or cylindrical brass body. Inside it is a Teflon or polypropylene hollow float. This float is connected by a lever with a drain valve, which is equipped with a locking plug. This plug prevents leakage of the coolant in the event of a breakdown of the device.


Air vents for heating systems are of three types:
- Direct devices of the traditional type. They are only mounted vertically.
- Angle type devices that are installed at right angles. They are mounted on radiators instead of Mayevsky taps or in the event that a direct version of the air vent cannot be installed.
- Special models for installation on radiators.
According to the principle of operation, the air vent can be manual (Mayevsky's valve) and automatic. The last variety is the float type devices described above.
How the manual valve works
Let's figure out how a manual air vent for the heating system works. To understand the device of this variety, you need to look at the drawing of the Mayevsky crane. At the end of the body made of brass with an external thread there is a hole with a diameter of 2 mm. It is covered by a tapered screw. On the side of the same body there is a hole of a smaller diameter, which is used for air release.


The principle of operation of the manual air vent is as follows:
- In the operating mode of the heating circuit, the plug screw is tightly tightened. The outlet is hermetically sealed with a cone.
- To release the airlock, the screw is unscrewed a couple of turns. As a result of the pressure of the coolant, air begins to escape through a small hole, then enters the outlet channel and is discharged outside.
- Moreover, at first only air comes out of the hole, then an admixture of water appears. The tap must be closed when only a stream of water flows from the hole.
Since the manual air vent has no moving parts to clog, rust or wear, it is a reliable and trouble-free device. This valve is installed only on radiators.
Manual valves according to the unscrewing method are divided into the following types:
- a metal or plastic handle is used for opening;
- more often you can find a slot for a screwdriver with a flat working blade;
- for unscrewing with a special wrench, there is a screw with a four-sided tip.
Automatic valve working principle
The automatic air collector for the heating system works without human intervention. Basically, it is a vertical threaded brass cylinder with a plastic float inside. The float is connected by means of a lever with a spring-pressed air relief valve. This valve is built into the cover.
The principle of operation of the automatic air vent in the heating system is as follows:
- When the heating system is operating, the inner chamber of the device is filled with water, which pushes the float up.As a result, the air valve is spring-loaded and tightly closed.
- When air accumulates in the upper part of the chamber, the level of the heat carrier decreases, which causes the float to drop.
- When the liquid level drops to a critical value under the weight of the float, the spring compresses and opens the valve. As a result, the air begins to bleed away.
- Due to the increased pressure of the coolant in the system, all the air is displaced from the chamber of the device. The liquid takes the place of the displaced air and causes the float to rise, which pushes the valve upward and tightly closes the opening.

During the filling of the network with a coolant, air locks are constantly bleeding off, since the float lies at the bottom of the tank. When water fills the chamber, the spring mechanism lifts the valve. As a result, the bleeding process stops. However, some of the oxygen remains in the housing under the cover, but this in no way affects the operation of the heating circuit.
Automatic devices are available with angle and direct connection. The latter type throws vertically, and the first one - to the side. The corner option is appreciated for its reliability, but it collects air bubbles worse.
Installing air relief valves
To remove air from the heating, air vents are installed on the radiators - manual and automatic air valves. They are called differently: a vent, an air vent, a bleed or air valve, an air vent, etc. The essence does not change from this.
Mayevsky air valve
This is a small device for manually bleeding air from heating radiators. It is installed in the upper free radiator manifold. There are different diameters for different sections of the collector.
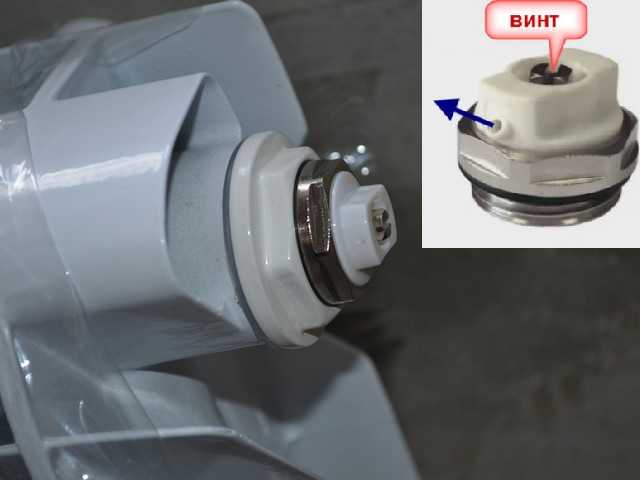


Manual air vent - Mayevsky crane
It is a metal disc with a conical through hole. This hole is closed with a tapered screw. By unscrewing the screw a few turns, we provide an opportunity for air to escape from the radiator.
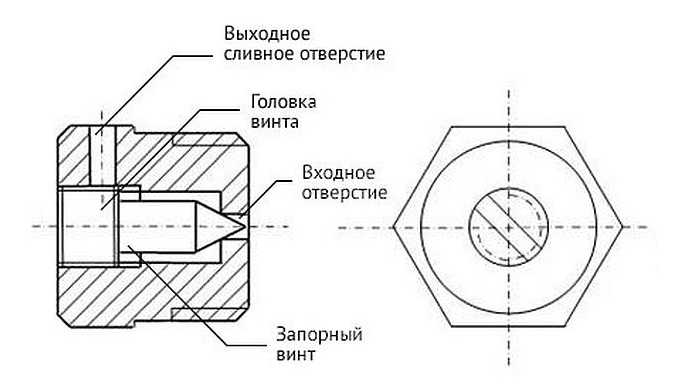

Device for venting air from radiators
To facilitate the air outlet, an additional hole is made perpendicular to the main channel. Through it, in fact, the air comes out. While airing with a Mayevsky crane, direct this hole up. After that, you can unscrew the screw. Unscrew a few turns, do not twist too much. After the hissing stops, return the screw to its original position, go to the next radiator.
When starting up the system, it may be necessary to bypass all air collectors several times - until the air stops coming out altogether. After that, the radiators should warm up evenly.
Automatic air relief valve
These small devices are installed both on radiators and elsewhere in the system. They differ in that they allow you to bleed air in the heating system in automatic mode. To understand the principle of operation, consider the structure of one of the automatic air valves.
The principle of the automatic escapement is as follows:
- In the normal state, the coolant fills the chamber by 70 percent. The float is at the top, presses the stem.
- When air enters the chamber, the coolant is displaced from the body, the float is lowered.
- He presses a ledge-flag on the jet, squeezing it out.

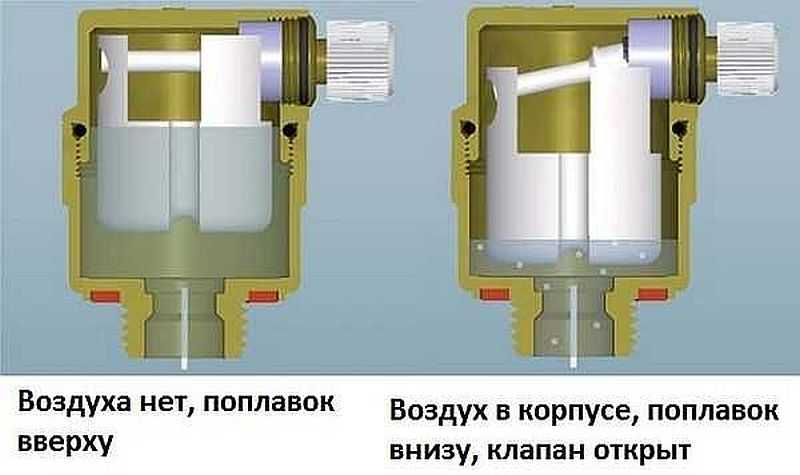
The principle of operation of the automatic air release valve
- The wrung out orifice opens a small gap, which is enough for the air that has accumulated in the upper part of the chamber to escape.
- As the water escapes, the air vent body fills with water.
- The float rises, freeing the stem. It is returned to its place by means of a spring.
Different designs of automatic air valves work according to this principle. They can be straight, angular. They are placed at the highest points of the system and are present in the security group.They can be installed in identified problem areas - where the pipeline has an incorrect slope, due to which air accumulates there.
Instead of Mayevsky's manual taps, you can put an automatic drain for radiators. It is only slightly larger in size, but it works in automatic mode.


Automatic air vent for venting
Salt cleaning
The main trouble with automatic valves for venting air from the heating system is that the air outlet is often overgrown with salt crystals. In this case, either the air does not come out or the valve starts to "cry". In any case, you need to remove and clean it.


Disassembled automatic air vent
So that this can be done without stopping the heating, automatic air valves are paired with non-return ones. A check valve is installed first, an air valve is installed on it. If necessary, the automatic air collector for the heating system is simply unscrewed, disassembled (unscrewed the lid), cleaned and reassembled. The device is then ready to bleed air from the heating system again.
How the device works
An air valve (or several) is installed in the heating system, in places most likely for the accumulation of air bubbles. This prevents the formation of a large congestion, the heating works smoothly.
Mayevsky crane
Such devices were named after the name of their developer. The Mayevsky crane has a thread and dimensions for a pipe with a diameter of 15 mm or 20 mm. It is arranged simply:
- In the body of the valve body, 2 through holes are made, which, in the open position of the Mayevsky crane, communicate with the heating system.
- These holes are sealed with a taper threaded screw.
- Air is discharged through a small (2 mm) opening directed upwards.
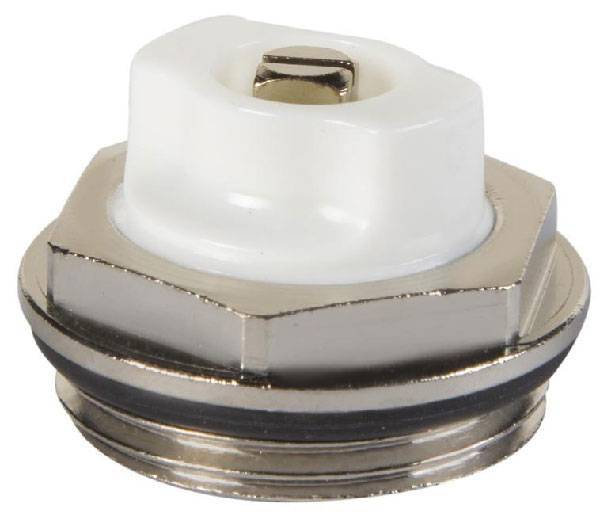


In order to bleed air from the system, unscrew the screw 1.5-2 turns. Air blows out with a whistle as communications are under pressure. The end of the airlock outlet is characterized by a drop in pressure and the appearance of water.
On the market, you can find several varieties of the Mayevsky crane, which are the same in design, but differ in the way of adjusting the locking screw. There are:
- with a comfortable handle for unscrewing by hand;
- with a regular head for a flat screwdriver;
- with a square head for a special key.
For an adult, the principle of unscrewing the locking screw does not matter. However, in a home with children, it is safer to use devices that must be unscrewed with a special device. Having unscrewed the usual tap with a comfortable handle, the child can scald with boiling water.
Automatic faucet
The automatic air relief valve is based on the principle of a float chamber, the design includes:
- vertical case with a diameter of 15 mm;
- float inside the body;
- a spring-loaded valve with a cover, which is connected and regulated by a float.
The automatic air valve for the heating system works without human intervention. Normally, when there is no air in the system, the float is pressed against the valve cover by the pressure of the liquid filler. At the same time, the lid is tightly closed.
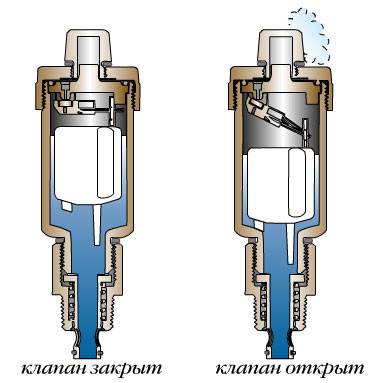

As air accumulates in the valve body, the float goes down. As soon as it drops to the critical level, the spring valve opens and bleeds out the air. Under the pressure of the carrier in the system, the space is again filled with liquid. The float rises to close the spring valve cover.
When there is no coolant in the communications, the float lies at the bottom of the valve. As the system fills, air leaves the tap in a continuous flow until the coolant reaches the float.
A distinction is made between the following configurations of automatic air valves for heating:
- with vertical air discharge;
- with lateral air discharge (through a special jet);
- with bottom connection;
- with corner connection.


For the layman, the design features of an automatic crane do not matter. However, for a professional, there is a difference in choosing between devices.
It is believed that:
- a device with a nozzle and a side hole is more reliable in operation than an automatic valve with a vertical air discharge;
- The bottom-connected valve is more effective at trapping air bubbles than the side-mounted valve.
If the design of the Mayevsky crane has not undergone changes for many years, then the device of automatic valves is constantly being improved and supplemented.
Manufacturers offer automatic valves with additional devices:
- with a membrane to protect against water hammer;
- with a shut-off valve, for the convenience of dismantling the device during the heating season;
- mini valves.
Automatic air valves for heating need frequent inspection and cleaning. The undoubted advantages of these devices include the ability to install them in hard-to-reach places.
Air and air valves in pipelines
- Home-
- Documents-
- Articles-
- Air and air valves in pipelines
Where does the air get into the pipelines?
When they say that "the pipe is empty," they mean that there is no water in the pipe. Usually, the pipeline is completely filled with air. When filling the pipeline, water displaces air from it.
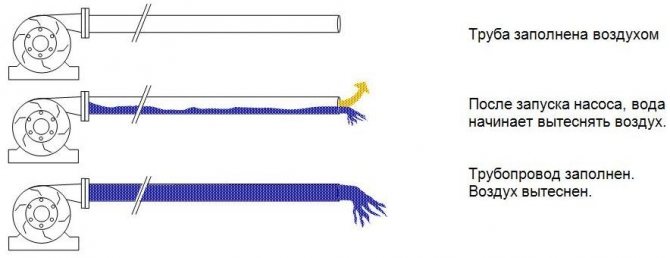

Example: A PVC pipe with a diameter of 250 mm has an inner diameter of 235 mm. In order to fill every 1000 m of such a pipeline, 43000 liters of water are needed. Accordingly, if the pipe is empty, 43,000 liters of air must be displaced.
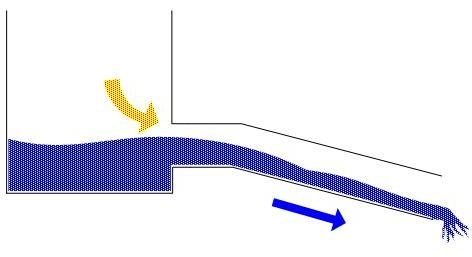

If the installation is incorrect, or if the level changes, there is a possibility of air entering the pipeline from the pump. In addition, dissolved air is always present in the water, which is released when pressure and temperature change.
What problems can air in pipelines cause?
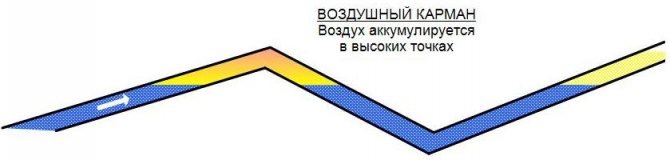
First of all, unlike water, air can be compressed. This means that as the pressure increases, the air decreases in volume. The sudden expansion of compressed air can lead to water hammer. Another undesirable effect of the presence of air in the piping is the danger of an “air pocket” when air collects at high points. "Air pockets" cover part of the flow area of the pipe. This effect is especially significant in "flat" systems with small slopes and low speed of water movement, when the water does not have time to take out the air. The presence of air increases the energy consumption of the pumps.

What problems can arise due to the presence of a vacuum in the pipeline?
When we say rarefaction, we mean below atmospheric pressure. When emptying the pipeline (planned or in the event of an accident), the air does not have time to take the place of water. At the same time, the pressure in the pipe decreases and can fall below atmospheric, which in turn can lead to the destruction of the pipe. This phenomenon is especially common in plastic pipelines with thin walls and large diameters.
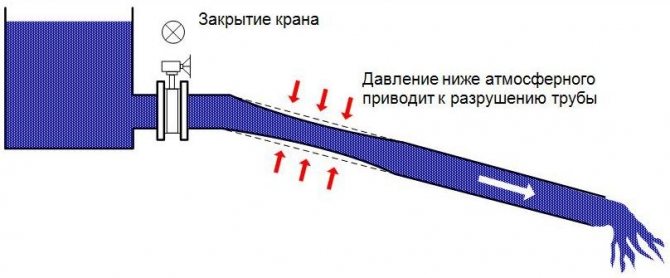

The damaged pipeline may not collapse immediately, but will be weakened. If the joint seals are made of rubber gaskets, they can move into the pipe, causing leaks when pressure is restored. Investigating leaks in low-pressure pipelines with rubber seals, it was found that most of them are caused by pipe deformations due to the occurrence of vacuum.
What kinds of air valves are there?
There are 3 types of air valves: - Kinetic valve - Automatic valve - Combination valve
Kinetic air valve
| They are also called anti-vacuum valves. The valves operate at low pressure (several meters of water column).They are used to remove large volumes of air from the system while it is filling with liquid and allow large volumes of air to take the place of water in the pipeline when it is drained. The kinetic function is undoubtedly one of the main functions of air valves. When the pipeline is filled with water and under pressure, the valve is closed and does not release air. The valve only works when filling and emptying the pipelines. Traditional kinetic valve designs have hollow ball-shaped floats. The characteristic features of this design: • The flow area is less than the nominal • The hollow float is deformed upon impact, regardless of the material (plastic or stainless steel). As a consequence, during the next operations, it does not fit tightly to the seat and the valve leaks. This part requires periodic replacement. • If the pipeline is under pressure for a long time, the float can stick. In this case, the valve will not operate the next time the pipeline is emptied, and a vacuum may develop and damage the pipeline. • Due to the light weight of the ball, there is a risk of premature closing of the valve at low pressure. |
Automatic air valve
| These valves remove air trapped in pressurized lines. The flow area of the automatic valve is very small and only serves to release small amounts of air. This valve cannot replace the kinetic valve, since it is not designed for more air volumes. Traditional automatic valve design: • Has a hollow float • Has moving parts that are prone to deformation and wear |
Combined air valve
| They are also called three function valves. Combined air valves provide kinetic and automatic functions in one unit. • Exhausting a large amount of air from the system during filling of the pipe, when the internal pressure is still low (several meters of water column). • Introducing a large amount of air during emptying of the pipe, which prevents the pressure from falling below atmospheric pressure. • Bleeding of air from the pipeline under pressure. Conventional combination valve design: • Separate body for kinetic valve • Separate body with automatic valve at the top |
More on the topic:
Prevent water hammer - prevent pipeline rupture!
Air valves - the magic wand for pipelines!
Air relief valves - choose the right one!
Air Valve Installation Recommendations
Dorot water hammer absorbers
Design and principle of operation
The automatic air valve for heating systems has a simple and reliable design. The hollow metal body is equipped with a connecting pipe, which is located at the bottom or on the side, depending on the version of the product. A float made of polymer resin is located in the inner chamber of the device. The float is connected by a link rod to a needle valve that closes the hole in the upper part of the air vent cover.
Removing the plug with a manual valve, it is required to control the process in order to shut off the device in time - the air will be completely vented when a stream of coolant flows through the vent. Installing an automatic air vent eliminates the hassle of servicing the heating system.
The principle of operation of the device is based on the use of gravity - a hollow float is lighter than water, but heavier than air. In the normal state, the air vent is filled with a coolant, due to which the float is in the upper position, pressing the needle valve. Over time, the coolant is displaced from the inner chamber of the device by the accumulating gas.
As a result, the float under the influence of gravity falls down, opening the valve slightly. The accumulated air under the pressure of the liquid in the heating system goes out through the hole in the body of the drain, and the chamber is again filled with a coolant, which raises the float, automatically closing the valve.
Float air vents are used to remove air locks, and also help to speed up the drainage of the coolant from the system during maintenance or repair work. Due to a decrease in the level of the coolant in the circuit, the valves automatically open, and the air entering through them forces the liquid to drain faster.
Reasons for airing the system
Air in the heating circuit negatively affects the function and durability of the system. Oxygen reacts with steel and is corrosive. Air locks interfere with the normal movement of the coolant, block the heating of the upper part of radiators or entire heating devices. The presence of air bubbles in the coolant leads to premature wear of the moving parts of the circulation pumps.

Ventilated heating system
There are several reasons for the formation of air locks.
:
- Use of water from a water supply system as a heat carrier, which has not undergone special treatment to remove dissolved air. When heated, gases leave the liquid medium and accumulate in the upper points of the pipeline and batteries.
- Excessively fast filling of the system with a coolant or its supply from a non-low point. In such a situation, the liquid does not have time to displace air from all corners of the mounted system.
- Loss of tightness by the system due to installation errors or damage to elements.
- The use of polymer pipes that do not have a barrier coating, which prevents the penetration of oxygen molecules into the coolant.
- Errors in the development of the project or arrangement of the system (incorrectly selected angle of inclination of pipes, etc.).
- Air ingress into the system during repairs requiring the dismantling of circuit elements.
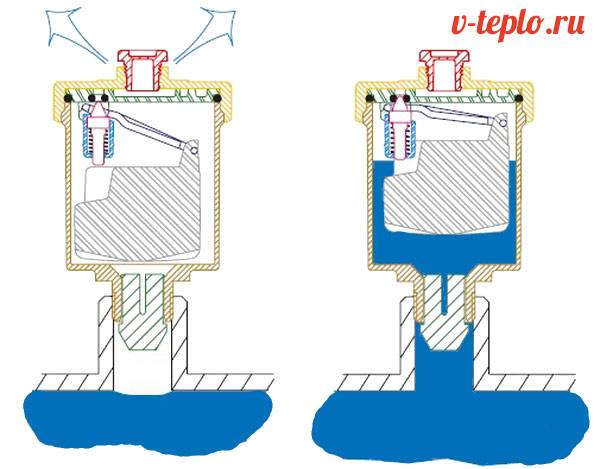
How an automatic air vent works
When the water supports the float from below, it pushes the rubber gasket and the pressure of the water pushes the gasket into the valve body. This closes the hole. When the water leaves, the float sinks and pulls the rubber gasket along with it, the hole for air inlet and outlet opens.
During operation, the automatic air vent spits water. Why is this happening? Because air bubbles hit the float mechanism from below rather sharply and this causes an impulse operation of the air vent. To prevent the air vent from splashing dirty water at its outlet, a thread with a diameter of 1/4 to 1/2 is provided (depending on the model of the air vent valve RACI, A.R.I., Unirain,
This video shows how the RACI air vent valve works