Why is the air in the heating system dangerous?
When air appears in the heating system, a plug is formed. Because of this, one part of the pipeline remains cold, and the other too overheats. When air accumulates from all heating circuits in one place, the movement of the coolant completely stops. What does it threaten:
- When an air blockage appears in a closed loop, pressure builds up in the system. This triggers the safety valve.
- It will constantly work and remove water from the system until the heating equipment burns out.
- Sometimes, this pressure will rupture pipes.
To prevent this and eliminate the problem, an air vent is installed. In addition to these difficulties, the presence of air in the circuit will lead to oxidation of the pipe, the occurrence of rust and a decrease in the service life.
Where does the air in the heating system come from?
There are several reasons for airing the line:
- When the water heat carrier is heated, oxygen is released from the liquid. Portions of small bubbles accumulate and provoke the appearance of traffic jams.
- Filling the circuits with liquid under high pressure leads to the fact that the gases do not have time to be vented and remain (accumulate) in the pipelines. The circuits with branches must be filled slowly, within 1-2 hours, applying a jet with a low pressure - only in this way all air bubbles will come out.
- Depressurization of the system is a common cause of airing. Loosely screwed connections, slots, caverns are channels for the flow of gases into the tunnels.
- The formation of a network from a polymer pipe without an anti-diffusion coating will lead to rapid and frequent airing. The absence of a protective film on the parts allows oxygen to enter inside.
- A broken technology for laying pipes without a slope, the wrong diameter also leads to the formation of plugs. It is especially important to monitor the level of inclination in gravity lines, where air can stagnate, not to flow into the valves for bleeding gases.
Advice! To avoid the appearance of plugs in the repaired heating networks, after checking for leaks, release excess gases with valves and taps.
Purpose and types of air vents
The air vent is designed to discharge air from the heating system and to avoid the appearance of air pockets. Air accumulation occurs during system operation or due to malfunctions. Sometimes this happens when the pipeline is filled with a coolant or when there is a loss of tightness in one of the mechanisms. There are 2 types of air vents, which differ from each other in design features:
- Mayevsky's hand cranes;
- automatic air valves.
Each device consists of a shell and a valve. The body has a threaded connection and a gasket, thanks to which it is attached to any part of the heating system. The outlet port is closed by a valve, which consists of a rubber gasket or is in the form of a cone. Depending on the model, the valve can operate in either automatic or manual mode.
Each product is suitable for installation anywhere in the system and works the same way. The solenoid valves for air have a straight and angular configuration, and the Mayevsky valves are made in a radiator and simple design.
How the device works
An air valve (or several) is installed in the heating system, in places most likely for the accumulation of air bubbles. This prevents the formation of a large congestion, the heating works smoothly.
Mayevsky crane
Such devices are named after the surname of their developer. The Mayevsky crane has a thread and dimensions for a pipe with a diameter of 15 mm or 20 mm. It is arranged simply:
- In the body of the valve body, 2 through holes are made, which, in the open position of the Mayevsky crane, are connected to the heating system.
- These holes are sealed with a taper threaded screw.
- Air is discharged through a small (2 mm) opening directed upwards.
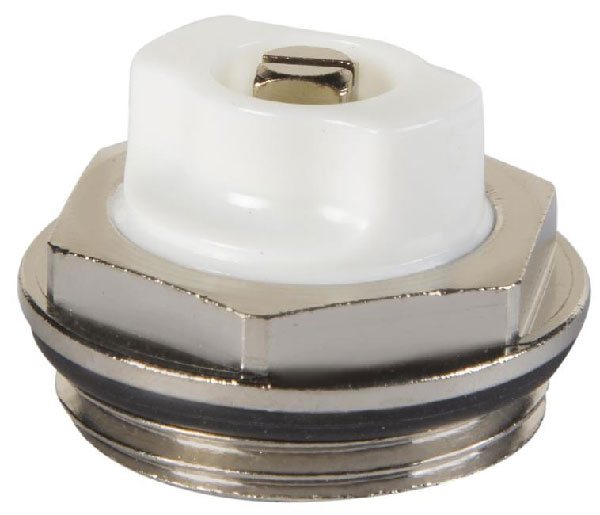

In order to bleed air from the system, unscrew the screw 1.5-2 turns. Air blows out with a whistle as communications are under pressure. The end of the airlock outlet is characterized by a drop in pressure and the appearance of water.
Note! The Mayevsky crane is a simple and reliable device for bleeding air accumulations. It does not clog or break because it has no moving parts. Its design is simple and reliable.
On the market, you can find several varieties of the Mayevsky crane, which are the same in design, but differ in the way of adjusting the locking screw. There are:
- with a comfortable handle for unscrewing by hand;
- with a regular head for a flat screwdriver;
- with a square head for a special key.
Where are the air release valves installed?
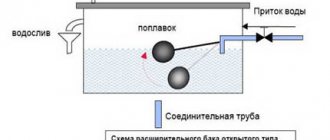
In open-type heating systems, air escapes through the expansion tank. But if the system is equipped with a pump for forced circulation of the coolant, then there is a possibility of air congestion. Therefore, in such systems, a manual or automatic air release device is installed. Installation locations of air vents, depending on different situations:
- On radiators, it is customary to install a manual air relief valve. It is mounted in this place because airing most often occurs at this point of the heating area. Therefore, they try to equip all radiators with devices.
- In the upper sections of the vertical risers (where bubbles are trying to penetrate), automatic devices of the direct type are installed. These are the most popular models and are also installed on underfloor heating collectors.
- If air has accumulated in a hard-to-reach place, such as the ends of dead-end branches, then corner and radiator models are used. The valve is connected to the system by means of a pipe.
- If the design of the circulation pump provides for the installation of an air vent, then it is mounted in order to improve the performance of the device. The airborne coolant is more difficult to pump over and slows down its operation. Because of this, it often stops, which leads to rapid wear of the bearings and impeller.
Causes and consequences of traffic jams in open heating systems with natural circulation
Situations when some radiators do not warm up at all or partially warm up are due to the air accumulated in the device. It is an obstacle to the complete filling of all sections of the battery with a coolant.


If the heating system is open type with natural circulation, then the reasons for the appearance of air jams in it can be:
- non-observance of pipe slopes during installation;
- filling the circuit with water using an expansion tank;
- measures to repair the system and drain water from it;
- too fast filling of the circuit with water when starting the system;
- water supply when filling the system was carried out from its upper point;
- poor performance of air vents or their absence;
- gradual release of air bubbles from water when heated, which is a natural physical phenomenon.
The negative consequences of airing the heating system can be:
- poor circulation of the coolant or its complete stop;
- decrease in the efficiency of heating the room;
- corrosive destruction of metal from the inside of devices under the influence of oxygen;
- the appearance of loud sounds in the form of gurgling and gurgling, which violates the comfortable acoustics in the home.
How to choose and install an air valve for heating?
Experts advise buying quality products from trusted suppliers, not cheap Chinese products. Air valve selection:
- products equipped with a shut-off valve are the best because they can be easily removed and replaced;
- in order not to use screwdrivers and keys, the Mayevsky crane is chosen with a handle;
- the best are those models that are equipped with additional functions;
- products covered with anodized protection are not subject to oxidation.
But before buying an air relief valve, you need to familiarize yourself with the technical characteristics of the heating equipment. For a two-story house, devices with an operating temperature of 100 ° C are used. They work efficiently at a pressure of 0.5-7 bar. Valve installation:
- The automatic air bleed device is mounted vertically on the radiators. In this case, the cap that closes the outlet is directed upward. This arrangement is used for straight and angled models.
- The ball valve is mounted in front of the drain valve. This is a prerequisite, thanks to which the air vent can be removed at any time without draining the water. Sometimes a shut-off valve is installed instead of a ball valve.
- Installation of the Mayevsky crane is carried out with a wrench. Unlike an adjustable wrench, this tool makes it easier to track the tightening level of a fastener. To prevent the device from breaking during screwing, it is held by the hexagon located under the camera, and not by the body.
If air accumulates in a multi-storey building after replacing the radiators, then the air vent is mounted on each radiator located in the upper manifold.
Valve installation location
There are points in the heating system where air is necessarily collected. So, Mayevsky's taps in the apartment should be installed on each radiator. In many modern radiator models, air bleed devices are installed at the manufacturing stage by the manufacturers themselves.
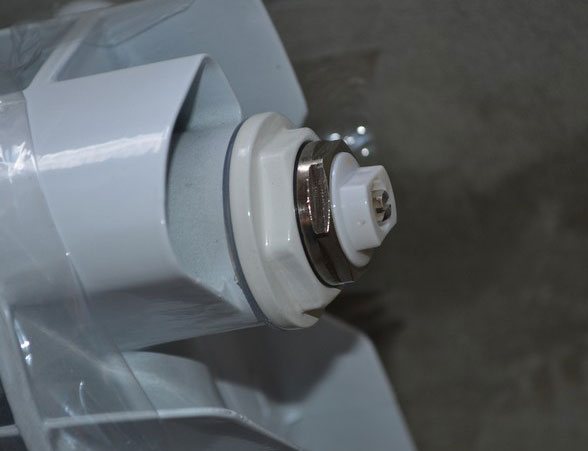


Note! If you have classic radiators, then the air valve should be installed in the upper part of it, which is located opposite the connection.
So you yourself can always control the normal operation of your heating batteries and not depend on the desire of the housing office employees or the mood of the neighbors from above.
Points for installing air relief valves:
- radiators, bathroom coil, upper part;
- the top point of the pipeline;
- heating boiler safety system in individual communications;
- for hydraulic branching;
- on the collectors of the common manifold;
- on any U-shaped loops in communications, at the top point;
- for expansion joints in plastic heating systems.


It should be understood that air always accumulates in the upper part of the communications. An air lock can arise in the bend of the plastic pipe if the installation was carried out incorrectly and there was a temperature deformation.
The easiest way to get rid of the plug in the pipeline permanently is to cut a tee into the pipe. On the free vertical branch of the tee (the diameter of which is selected accordingly), a valve is installed to release air.
How to get rid of an airlock?
Sometimes, due to improper pipe laying and illiterate engineering design, air locks appear in hard-to-reach places. It is difficult to remove air from there. Air bleeding process:
- You can determine the location of the plug by the murmur and cold section of the pipe. If these signs are absent, then the pipes are tapped. A loud and loud sound indicates an accumulation of air.
- In a private house, air cushions are expelled from the pipes by increasing the temperature or pressure. To do this, open the drain valve closest to the jam and the make-up valve. The coolant will fill the pipes, the pressure will rise, the plug will begin to move and exit through the valve. After all the air has escaped, the hissing will stop and the water pressure can be shut off.
- If the plug remains, then it is necessary to raise the temperature and pressure at the same time. The indicators are raised to the maximum level (do not exceed it, since it is dangerous).
If designed incorrectly, the problem will appear regularly and in the same place. To remove it, an air vent is connected to this place. For large highways, a tee is mounted. A valve is mounted on a free entrance.
Air vents: the main task
The device for venting air from the heating system makes it possible to remove gases accumulated in the pipeline and radiators.
The airing of the system occurs for a number of reasons, including
:
- Due to the high content of dissolved gases in the coolant, which has not undergone special training - deaeration. The solubility of gases depends on the temperature of the medium, and when the coolant is heated, the air is separated from the water and accumulates, forming plugs.
- Due to the excessively rapid filling of the circuit with the coolant, the liquid in the branched network does not have time to displace the air in a natural way. The coolant must be poured from the lowest point so that air is forced upward and out through the open valve.
- Due to the penetration of air through the walls of the polymer pipeline, if it is made of a material without a special anti-diffusion coating. When choosing pipes, this point should be taken into account.
- In the course of repair work related to the replacement of elements without completely draining the coolant - in this case, the repaired heating device or circuit is cut off from the rest of the system, and then connected back.
- Loss of tightness.
- As a result of corrosive processes - when oxygen interacts with iron, hydrogen is released from the air molecule, which also accumulates in the system.
Why is the air in the heating system dangerous?
The air dissolved in the coolant gradually destroys steel pipes and radiators, elements of the boiler unit. The corrosive activity of air, which was first dissolved in water and then released during heating, significantly exceeds the parameters of atmospheric air due to the increased oxygen content.
Installation locations of air separators in the system
The gases accumulated in the pipeline not only provoke or accelerate the corrosion of metal elements, but also form air locks that prevent the heating system from fully functioning
:
- Due to gas plugs, the circulation of the coolant deteriorates; in serious cases, the movement of liquid through the pipes can be completely blocked. In such a situation, heating devices cool down quickly.
- Air locks work as a heat insulator, and if gases accumulate in the upper part of the battery, it warms up worse and gives less thermal energy to the room.
- In the presence of air locks, the movement of the coolant along the heating circuit is accompanied by loud gurgling sounds and gurgling, which violates the acoustic comfort in the house.
- Circulation pumps are not designed for pumping gases; when working with an air-filled coolant, the bearing and impeller of the pump unit wear out much faster.
Special air venting devices allow solving the problems associated with airing the heating system. It is important to choose the right valves for bleeding air and correctly determine the location of these elements.
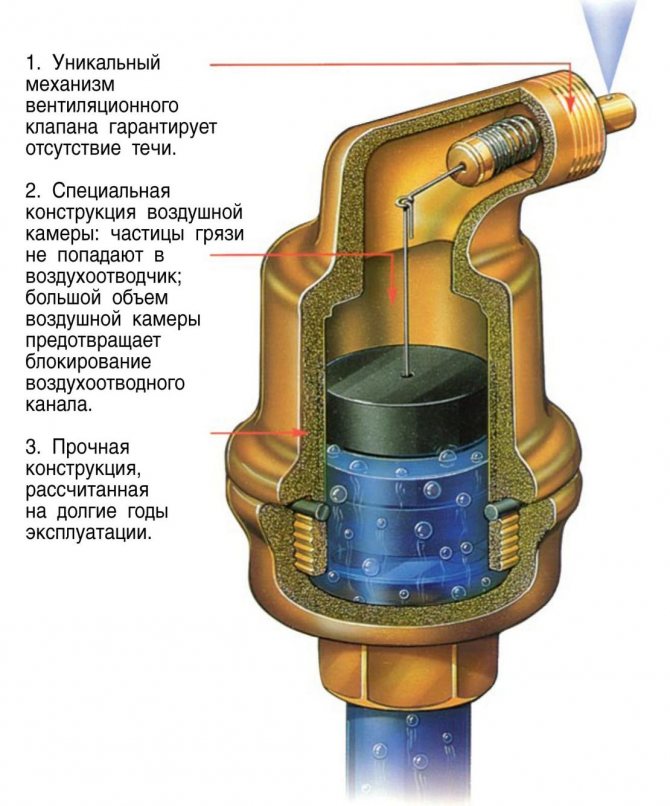
What is an air valve
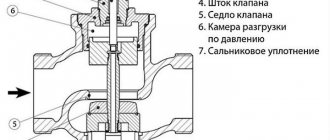
The air valve for heating is a sealed cone-shaped or cylindrical brass body. Inside it is a Teflon or polypropylene hollow float. This float is connected by a lever with a drain valve, which is equipped with a locking plug. This plug prevents the leakage of the coolant in the event of a breakdown of the device.
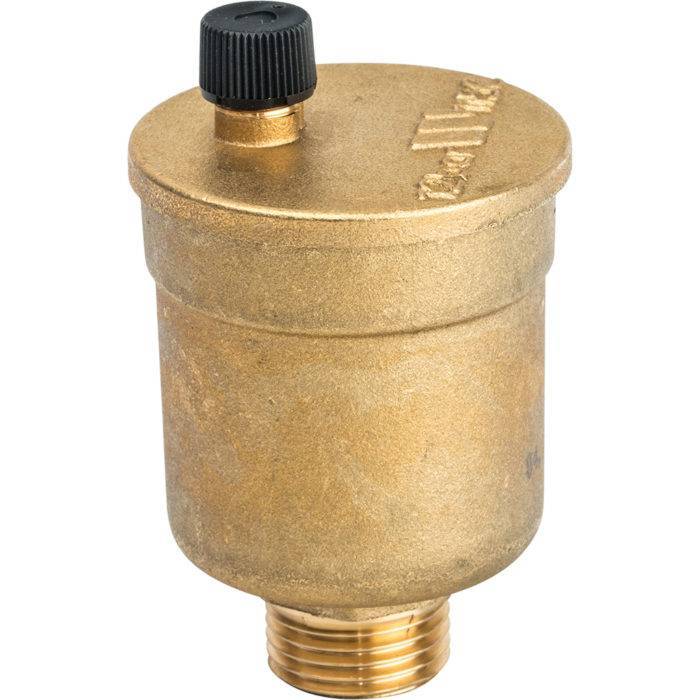


Air vents for heating systems are of three types:
- Direct devices of the traditional type. They are only mounted vertically.
- Angle type devices that are installed at right angles. They are mounted on radiators instead of Mayevsky taps or in the event that a direct version of the air vent cannot be installed.
- Special models for installation on radiators.
According to the principle of operation, the air vent can be manual (Mayevsky's valve) and automatic. The last variety is the float type devices described above.
How the manual valve works
Let's figure out how a manual air vent for the heating system works. To understand the device of this variety, you need to look at the drawing of the Mayevsky crane. At the end of the body made of brass with an external thread there is a hole with a diameter of 2 mm. It is covered by a tapered screw. On the side of the same body there is a hole of a smaller diameter, which is used for air release.
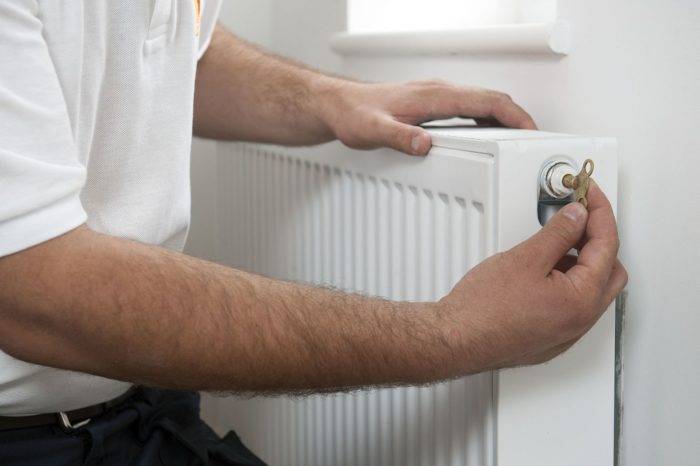


The principle of operation of the manual air vent is as follows:
- In the operating mode of the heating circuit, the plug screw is tightly tightened. The outlet is hermetically sealed with a cone.
- To release the airlock, the screw is unscrewed a couple of turns. As a result of the pressure of the coolant, air begins to escape through a small hole, then enters the outlet channel and is discharged outside.
- Moreover, at first only air comes out of the hole, then an admixture of water appears. The tap must be closed when only a stream of water flows from the hole.
Since the manual air vent has no moving parts to clog, rust or wear out, it is a reliable and trouble-free device. This valve is installed only on radiators.
Manual valves according to the unscrewing method are divided into the following types:
- a metal or plastic handle is used for opening;
- more often you can find a slot for a screwdriver with a flat working blade;
- for unscrewing with a special wrench, there is a screw with a four-sided tip.
Automatic valve working principle
The automatic air collector for the heating system works without human intervention. Basically, it is a vertical threaded brass cylinder with a plastic float inside. The float is connected by means of a lever with a spring-pressed air relief valve. This valve is built into the cover.
The principle of operation of the automatic air vent in the heating system is as follows:
- When the heating system is operating, the inner chamber of the device is filled with water, which pushes the float up. As a result, the air valve is spring-loaded and tightly closed.
- When air accumulates in the upper part of the chamber, the level of the thermal medium decreases, which causes the float to sink.
- When the liquid level drops to a critical value under the weight of the float, the spring compresses and opens the valve. As a result, the air begins to bleed away.
- Due to the increased pressure of the coolant in the system, all the air is displaced from the chamber of the device. The liquid takes the place of the displaced air and causes the float to rise, which pushes the valve upward and tightly closes the opening.
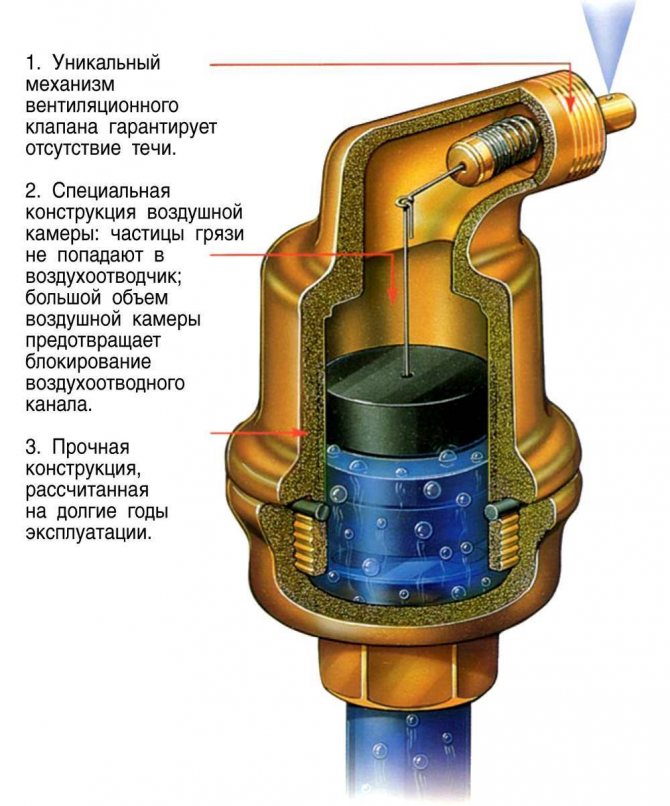

During the filling of the network with a coolant, air locks are constantly bleeding off, since the float lies at the bottom of the tank. When water fills the chamber, the spring mechanism lifts the valve. As a result, the bleeding process stops. However, some of the oxygen remains in the housing under the cover, but this in no way affects the operation of the heating circuit.
Automatic devices are available with angle and direct connection. The latter type throws vertically, and the first one - to the side. The corner version is appreciated for its reliability of operation, but it collects air bubbles worse.