Some solid fuel boilers can operate on any fuel, but not all. Therefore, before buying coal, look at the passport of your unit. The brands for which the boiler was calculated should be indicated there. If there is no such information, you can go by the trial method. Most companies selling this type of fuel have bagged coal. You will need to take a bag of different grades and fractions, and alternately drown with each of them. Try to use the same amount of coal and evaluate the following parameters: amount of heat, duration of burning and amount of ash residue.
Firewood
These are sawn or chopped pieces of wood, which, when burned in furnaces, boilers and other devices, generate heat energy.

For the convenience of loading into the firebox, the wood material is cut into separate elements up to 30 cm long. To increase the efficiency of their use, the wood should be as dry as possible, and the combustion process should be relatively slow. In many respects, firewood from hardwoods such as oak and birch, hazel and ash, and hawthorn are suitable for heating premises. Due to the high resin content, increased burning rate and low calorific value, conifers are significantly inferior in this regard.
How to compare the cost of fuel briquettes with the cost of firewood?
As you know, firewood is most often sold in bulk or stacked. If firewood was brought to you on pallets in stacking, then a cubic meter of such firewood is equivalent to 0.7 cubic meters in terms of dense wood. If firewood was brought to you in bulk in the back of a truck, then with a length of firewood of 30-35 cm a cubic meter will contain only 52% of dense wood.
In other words, in order to compare the cost of bulk firewood for solid wood with the cost of fuel briquettes, the cost of firewood should be doubled.
So let's compare prices. Bulk firewood in the Leningrad Region costs 1,500-1,600 rubles. per cubic meter. In terms of dense wood, a cubic meter of firewood will cost 3,000-3,200 rubles. In neighboring areas, firewood can cost about one and a half times cheaper. Thus, a cubic meter of Ruf-type fuel briquettes costs the buyer, depending on the area, 2-3 times more expensive than firewood.
We decided to find out whether such a difference in price is worth the declared advertising advantages of fuel briquettes in the form of convenience, increased heat transfer and increased burning time of fuel briquettes. An amateur experiment was conducted, which, although it does not claim to be scientifically reliable, can clarify some aspects of using fuel briquettes instead of firewood.
Reference by topic: Types of heating systems and their arrangement in a country house - which design to choose
Coal
It is a natural plant material extracted from sedimentary rock.
This type of solid fuel contains carbon and other chemical elements. There is a division of the material into types depending on its age. Brown coal is considered the youngest, followed by hard coal, and anthracite is older than all other types. The age of a combustible substance is also determined by its moisture content, which is more present in the young material.
In the process of burning coal, environmental pollution occurs, and slag forms on the grates of the boiler, which, to a certain extent, creates an obstacle to normal combustion. The presence of sulfur in the material is also an unfavorable factor for the atmosphere, since this element is converted into sulfuric acid in the air.
However, consumers should not be concerned about their health.Manufacturers of this material, taking care of private customers, strive to reduce the sulfur content in it. The heat of combustion of coal can differ even within the same type. The difference depends on the characteristics of the subspecies and the content of minerals in it, as well as the geography of extraction. Not only pure coal is found as a solid fuel, but also low-enriched coal slag, pressed into briquettes.
| Coal type | Specific heat of combustion of material | |
| kJ / kg | kcal / kg | |
| Brown | 14 700 | 3 500 |
| Stone | 29 300 | 7 000 |
| Anthracite | 31 000 | 7 400 |
Varieties of coal and their characteristics
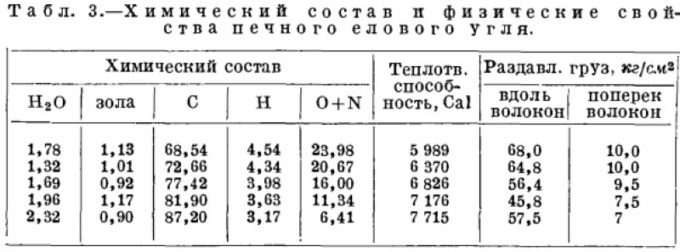
The economy and efficiency of operating a solid fuel boiler directly depends on the type of fuel used. In addition to wood waste, various types of coal are often used as the main energy source. That is why those who use it as their main fuel need to know its specific calorific value.
First of all, coal is distinguished by its origin... It contains various remains of ancient plants and bituminous masses, which underwent specific changes during submersion. The transformation of all these substances into efficient fuel took place at high temperatures and in conditions of a lack of oxygen. Experts note that fossil fuels include bituminous and brown coals, as well as anthracite.
In this video you will learn the process of burning brown coal:
Natural stone material
This type of fuel appeared much earlier than brown coal. Large layers of material are located underground at a depth of 3 kilometers. Its composition contains up to 97% of pure carbon, but the amount of volatile impurities is within 35%. As for the moisture content, in coal it is not more than 15%. And this has a positive effect on the thermal efficiency of the fossil.
Under ideal conditions, the specific heat of combustion of coal is in the range of 2100 ° C. But in a conventional heating furnace, such material is burned at a maximum of 1000 ° C.
The level of heat transfer varies within 7 thousand kcal / kg. It should be noted that this type of fuel difficult to ignite, since for these purposes it is necessary to heat the oven to 400 ° C.


This material is not suitable for kindling
As practice shows, it is coal that is most often used by ordinary citizens to heat houses, summer cottages and buildings for other purposes.
Universal brown look
Among all existing fossil coals, this species is considered the youngest. The fuel got its name due to its specific brown color. Among its main characteristics, it can be noted that it contains many volatile impurities and moisture - more than 40%. Despite this, the amount of pure carbon can reach 75%. Since brown coal contains a lot of moisture, it has low combustion temperature and a small percentage of heat transfer... Fuel starts to ignite at 260 degrees, but the combustion temperature can reach 2000 ° C. As for the calorific value, this figure is 3600 kcal / kg.
Of course, as the main energy source, brown coal is significantly inferior to ordinary firewood, which is why it is rarely used for solid fuel boilers and stoves, which are located in private houses.
It is interesting: firewood alder properties.


This material contains a lot of moisture.
But the briquetted form of this fossil, which has undergone special training in large-scale production, is very popular. Under artificial conditions, manufacturers reduce its moisture content, thereby significantly increasing energy efficiency. It should be noted that the heat transfer of briquetted brown coal is as much as 5 thousand kcal / kg.
This is one of the most ancient minerals, which contains practically no volatile impurities and moisture. But the amount of carbon exceeds 95%.Studies have shown that the specific heat of combustion of coal is in the range from 8500 to 9 thousand kcal / kg - this is the highest indicator among all existing coals. Under ideal conditions, such fuel burns at 2250 ° C, but ignites at 600 ° C. It should be noted that this indicator is typical for the lowest-calorie species. To ignite anthracite, you need to use dry wood, since it is necessary to create a certain heating of the boiler or stove.
This fossil material is classified as an industrial fuel. Use it in a regular boiler or oven very expensive and unprofitable... Despite the fact that anthracite compares favorably with its counterparts with low smoke and low ash content.


Besides, such material is expensive.
Pellets
Pellets (fuel pellets) is a solid fuel produced industrially from wood and plant waste: shavings, bark, cardboard, straw.
The raw material crushed to the state of dust is dried and poured into the granulator, from where it comes out in the form of granules of a certain shape. A plant polymer, lignin, is used to add viscosity to the mass. The complexity of the production process and high demand form the cost of pellets. The material is used in specially equipped boilers.
Calorific value of firewood
The amount of heat generated by burning wood depends on the type of wood and the moisture content of the wood. Humidity reduces the calorific value of firewood, since the evaporated water carries away part of the heat energy. Losses from moisture slightly depend on the initial temperature of the firewood (more precisely, the water in them) and are taken equal to 0.63 kWh per kilogram of water.
Absolutely dry deciduous firewood produces about 5 kWh of heat per kilogram of firewood. Absolutely dry coniferous firewood gives about 5.2 kWh of heat per kilogram of firewood, due to the chemical difference of their wood.
In real conditions, it is impossible to achieve ideal dryness, therefore, the table below shows the calorific value of firewood of different types of wood at a moisture content of 15% and for comparing other types of fuel:
| Type of fuel | Calorific value of the material, kWh / kg (MJ / kg) | Density of material, kg / dm³ | Loading density, kg / m³ | Calorific value of firewood, kWh / m³ |
| Beech, ash | 4,2 (15) | 0,74 | 480 | 2016 |
| Oak | 4,2 (15) | 0,69 | 470 | 1974 |
| Birch tree | 4,2 (15) | 0,65 | 450 | 1890 |
| Larch | 4,3 (15,5) | 0,58 | 420 | 1806 |
| Pine | 4,3 (15,5) | 0,52 | 360 | 1548 |
| Spruce | 4,3 (15,5) | 0,44 | 330 | 1419 |
| Fuel oil | 12 (43) | 0,84 | 840 | |
| Coal | 7,8-9,8 (28-35) | 0,6-1,9 |
Although the mass calorific value of coniferous wood is higher than that of deciduous wood, due to the lower density of wood, the specific volumetric calorific value of coniferous firewood is lower than that of deciduous wood. Coniferous wood takes up more space and burns faster.
A cubic meter of dry deciduous firewood can replace 200 liters of oil, 200 cubic meters of natural gas. The energy extracted from wood is also of solar origin. But at the same time, unlike oil, coal and gas, wood is a renewable resource. Firewood as a type of biofuel is a source of renewable energy.
Briquettes
Briquettes are solid fuels, similar in many respects to pellets. Identical materials are used for their manufacture: wood chips, shavings, peat, husks and straw. During the production process, the raw material is crushed and compressed into briquettes. This material is also classified as environmentally friendly fuel. It is convenient to store it even outdoors. Smooth, uniform and slow combustion of this fuel can be observed both in fireplaces and stoves, and in heating boilers.


The types of environmentally friendly solid fuels discussed above are a good alternative to heat generation. In comparison with fossil sources of thermal energy, which have an adverse effect on the environment during combustion and are, moreover, not renewable, alternative fuels have clear advantages and relatively low cost, which is important for consumers of some categories.
At the same time, the fire hazard of such fuels is much higher. Therefore, it is required to take some safety measures regarding their storage and use of fire-resistant materials for walls.
The use of charcoal
Charcoal production is a promising direction. Its consumption is constantly growing, and it is used both in production and for domestic purposes. Usage in everyday life is familiar to everyone: cooking on the grill and in the barbecue today practically cannot do without charcoal. Many people prefer to lay charcoal in fireplaces: this fuel does not smoke, does not emit gases (in particular, carbon monoxide) and has a high calorific value.


Charcoal production is a promising direction
In industry, charcoal is used in metallurgy (in our country it is practically not practiced), for the manufacture of filters for various purposes. It is used in the smelting of some valuable metals, crystalline silicon, activated carbon. It is used in agriculture and medicine.
You can also use charcoal for heating. The peculiarity of its combustion is that there are no high tongues of flame. But there is a uniform steady heat. The combustion temperature of charcoal depends on several factors: on the density (different types of wood produce coal with different densities), on its quality (burning conditions) and on the amount of oxygen supplied during combustion. In an ordinary open hearth, the temperature can range from 400 ° C to 900 ° C, but under special conditions it is possible to reach 1200 ° C (forge). If we talk about average values, then the calorific value of charcoal is considered to be 30 MJ / kg.
| Fuel type for solid fuel boiler | Specific calorific value, MJ | Specific calorific value, kW / h |
| Lignite briquette | 21 | 5,84 |
| Raw brown coal | 14,7 | 4,09 |
| Pine firewood | 8,9 | 2,47 |
| Oak firewood | 13 | 3,61 |
| Birch firewood | 11,7 | 3,25 |
| Coal | 29,3 | 8,14 |
| Coke | 29 | 8,06 |
| Charcoal | 30-31 | 8,62 |
| Peat (dry) | 15 | 4,17 |
As you can see from the table, charcoal emits heat at least not less than coal and almost two and a half times more than the best firewood. Why is it almost never used for heating? First, in our country, charcoal is produced in very small volumes (the world produces 9 million tons per year, Russia accounts for 100 thousand tons) and has a high price. Even if you buy it from manufacturers, then when purchasing up to 5 tons, they ask for 180 rubles per 10 kg (18,000 per ton). Even with an economical expense, it turns out to be quite expensive. If you live in a place where there is a large number of forests, in which there is always enough dead wood, then securing a certain amount of charcoal is not very difficult even without equipment. You can use traditional charcoal technologies, which require only a metal barrel for the process, and even then it is not necessary. Of course, you cannot stock up in this way for the whole winter, but you can burn it up to put some amount into the boiler at night to maintain a comfortable temperature.


The calorific value of charcoal is slightly higher than the calorific value of high-quality coal