How to determine the cube of firewood (cubic capacity) or volume when buying
Last update: 20-07-2018
Method of calculating the volume of firewood when buying
4.2 (83.38%) 77 vote [s]
The purchase of firewood is always associated with the determination of the volume. Sellers have several ways to sell.
In the warehouse, firewood can be stacked, but it is sold in bulk to the end customer directly from the truck. This makes it difficult to accurately determine the volume of brought firewood.
The likelihood of paying money for a larger amount of firewood than actually brought in increases. Unscrupulous sellers often take advantage of this.
To determine the approximate volume of purchased firewood, you need to know the measurement methods.
At the end there is a calculator for calculating the volume of firewood.
How is the volume of firewood measured?
- Real cubic meter - for wood stacked without gaps.
- Folded cubic meter - for round timber, takes into account the gaps.
Methods for calculating the volume of firewood
- Solid wood volume lumberthat is neatly stacked in a stack can be easily determined by routine measurements of the length, width and height of the stack. The multiplication of the obtained values is the volume of firewood in cubic meters.
- For round wood volume is calculated as the product of the length of the log and its average diameter.
- To determine the volume of chopped wood or wood in chocks a foldable cubic meter is applied. This volume is determined by measuring the length, width and height of the stacking logs, but a correction factor is applied when recalculating. It is usually 0.7.
If we take 5 stacked cubic meters of firewood and 5 cubic meters of laid lumber, then they should be approximately the same in terms of the amount of wood.
Very often, firewood is sold without stacking, and it is much more difficult to determine the volume of bulk wood. For this, the concept is used
bulk or bulk cubic meter... This measure of measurement is used when transporting firewood in bulk in the back of a car or other vehicle.
In this case, the volume of firewood is determined as follows:
- It is necessary to calculate the volume of the body (by multiplying its length, width and height) and thereby determine the volume in folded cubic meters.
- Multiply by the correction factor.
This will be the volume of firewood in bulk cubic meters.
The dependence of the coefficient on the length of the logs is summarized in the table:
| Log length in meters | Conversion factor |
| 0,25 | 0,8 |
| 0,33 | 0,78 |
| 0,50 | 0,75 |
| 0,75 | 0,73 |
Also, firewood is sold by such volumetric measures as cart, lawn, KamAZ. At the same time, not a single seller will tell you the true volume of firewood in the back.
It would be much more convenient and easier to buy firewood by weight, but this also raises the issue of humidity, which is even more difficult to assess.
An example of calculating the amount of firewood without a calculator
Given:
- House area = 100 m2.
- Ceiling height (standard) = 2.8 m.
- The efficiency of heating equipment (boiler or stove) = 70%.
- Heat loss of walls, ceiling, floor is minimal.
To heat such a house for 1 cold month, on average, you will need:
- Raw birch logs (humidity 50%) - 2.8 m3.
- Dry birch logs (moisture content 20%) - 1.7 m3.
- Raw oak logs (humidity 50%) - 2.6 m3.
- Dry oak logs (moisture 20%) - 1.6 m3.
- Raw pine logs (humidity 50%) - 3.4 m3.
- Dry pine logs (moisture content 20%) - 2.1 m3.
If the efficiency of the furnace is lower or higher than the heat loss, then more firewood will need to be stored.
How to calculate one cubic meter of firewood: stacked, in bulk and in nets
How to calculate one cubic meter of firewood: stacked, in bulk and in nets
Surely every person who at least once ordered firewood wondered if the suppliers had cheated him? How to determine exactly how much firewood they brought you? Perhaps you have come across a villager or an experienced forestry worker who, from one meaningful glance at a pile of firewood, said an almost correct result. In fact, there is nothing difficult in determining the volume of firewood, and this can be done both by eye, with due experience, and with high accuracy, using the calculation method. Let's dwell on it in more detail.

The first thing you need to pay attention to when preparing for the calculation is the type of stacking of firewood. Let's start with the most common - in bulk. In this case, the firewood is thrown into the body or a pile; at first glance, it is rather difficult to estimate the volume, because the logs are not dense. First, you need to calculate the total amount of imported firewood. For this purpose, it is necessary to measure the piled firewood. If you have a cone-shaped pile, then we find out its diameter and height, if the firewood is in the body, we measure the length, height and width, it is better to level the slide first, for more accurate calculations. Having calculated the volume, you should translate it into storage meters, for this we use the coefficients. Usually, an average of 0.7 is taken, since this number is used in further calculations, but if an accurate calculation is required, the normative document GOST 3243-88 should be used. It specifies the exact coefficients, which depend on the type of wood, its condition, the length and thickness of the logs.
Now we know how many cubic meters they brought to us, but we ordered cubic meters, which means solid wood without gaps. On average, one fold meter is considered to be equal to 0.7 cubic meters of solid wood. It is this coefficient that is used in most cases, although for accurate calculations, you should return to the translation table set out in GOST 3243-88.


Another popular method of delivering firewood is in nets or stacked in rows. In this case, it is quite easy to determine the amount of imported cubic meters. We do not have to convert the bulk volume to the storage one, the only thing that needs to be done is to measure the woodpile, calculate the volume, and then use the coefficient already known to you to make calculations.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated in the calculations. To accurately determine the number of cubic meters, it is enough just to find out the volume of brought firewood, convert it to fold meters, and then, using the coefficient, find out the number of cubes.
And if you are interested in the weight of firewood, then after reading our article, you will know the many parameters that need to be taken into account when calculating the mass of wood: How much does firewood weigh?
We work without cheating! We always bring the exact amount of firewood ordered by you!
It is very easy to order firewood in Moscow and the Moscow region!
drova-mo.ru
What you need to know when buying firewood in cubes?
What is a cubic meter of firewood and how to calculate it?
When it comes to buying firewood in cubes, it is important to understand exactly how much firewood you buy, what is meant by cubic meters of firewood and how to correctly calculate a cubic meter of firewood on the spot. Basically, there are two types of cubic meters that are used to measure the volume of firewood supplied:
- Real cubic meter
- Bulk cubic meter
What is the difference between a real cubic meter and a bulk cubic meter?
Real cubic meter
A real cubic meter is the base point of reference in the measurement of firewood or the volume of other materials. Take a cube that has equal edges (1 meter long, 1 meter wide and 1 meter high). This will give us a real cubic meter. The space inside this cube has a volume of 1 cubic meter. Real cubic meters of firewood are measured by densely stacked firewood. If we put chopped firewood tightly into a cube with dimensions of 1m x 1m x 1m, we get a cubic meter of firewood.
Let's give an example of calculating the volume of firewood supply. Let's say we have a pile of densely packed chopped firewood measuring 2 mx 3 mx 1.5 m. Multiply the dimensions to calculate the number of cubic meters of firewood. 2m x 3m x 1.5m = 9 cubic meters.
Bulk cubic meter
Bulk cubic meters are used to measure chopped firewood that is not stacked, but simply poured at random. In order to calculate the amount of real cubic meters of bulk firewood, you need to recalculate them using special coefficients.
The most common coefficients for converting bulk cubic meters of chopped firewood into real cubic meters are as follows:
- 0.8 (with a length of chopped wood 25 cm)
- 0.78 (with chipped wood length 33 cm)
- 0.75 (with a length of chopped wood 50 cm)
The coefficients are taken from the materials of GOST 3243-88. Firewood. Technical conditions.
Let's give an example. Let's imagine that we have ordered a car of 25 cm long, unloaded, chopped firewood, which is simply poured into the back. Let's say we measured the dimensions of the body and got a volume of 10 cubic meters. It turns out that there are 10 bulk cubic meters of firewood in the back. Now we translate bulk cubic meters into real cubic meters: 10 x 0.8 = 8. That is, in 10 bulk cubic meters of chopped firewood 25 cm long - 8 real cubic meters of firewood.
How to calculate the price of a real cubic meter of firewood?
Most often, sellers of firewood indicate the price for a real cubic meter of firewood, and not for bulk. It is convenient for both the seller and the buyer. The unloaded firewood can be measured immediately, the scope of delivery and the cost can be calculated.
If the seller of firewood indicates the price for a bulk cubic meter of firewood, and not for a real one, you can calculate the price of a real cubic meter of firewood by dividing the price of a real cubic meter of firewood by the conversion factor of a bulk cubic meter into a real cubic meter. Let's say, in our example, the cost of a bulk cubic meter of firewood is 1500 rubles. In order to find out the price of a real cubic meter of firewood, we divide 1500 rubles by 0.8. It turns out that a real cubic meter of firewood, in our example, costs ~ 1875 rubles.
Now you know the basic formulas for calculating the volume of supplied firewood. They were invented for the convenience of manufacturers and buyers and will help you more objectively compare suppliers' offers, measure the volume of ordered firewood and protect yourself from unscrupulous sellers. Bookmark this article or share it on social networks with your friends. Perhaps this information will help your friends save time, money and nerves.
drovoroob.ru
How much firewood is required to heat a house
We always look at the quality of the firewood that we buy. Softwood burns quickly, but does not give much heat. Preference is given to hard rocks, which, although they burn slowly, give a lot of heat to the venture. Rotten firewood is often on sale. When you harvest firewood yourself, this will never happen. And most often they sell raw wood.
It turns out that for a private house or summer cottage, it is best to find about 10 cubic meters of firewood per season. In order not to spend money on the purchase of chopped firewood, you can start harvesting them yourself. Moreover, there will always be a forest near the summer cottage, where there is an old fallen tree. A great way to harvest firewood is to take advantage of the moment when someone is taking apart an old wooden house.
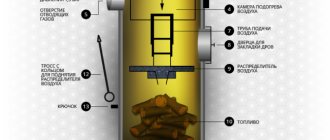
Equipment for preparing firewood for the winter
You cannot prepare a lot of firewood with a hacksaw or an ax. It also takes a lot of effort.
In order to carry out procurement work, you need to buy special tools, of which there are not so many.
In order to cut a tree trunk in the forest, you need to choose a good chainsaw. The best option is a device with a capacity of up to two kilowatts. If the work will be carried out near the house, then there is an option to use an electric saw. There are such types of saws on sale that are equipped with batteries. If the work will be carried out very often, then it is recommended to buy semi-professional saws. Their power is more than two kilowatts, and the price is higher.


Then, in order to chop wood, you need to buy a high-quality horizontal type log splitter. For the home, this is the best device that works safely. Working with a wood splitter is simple: you need to turn on the device that works on electricity, then put the log, and then wait until the knife separates it.
There will be rubbish after work. And then you need a shredder that can process waste. Slivers, shavings, leaves can be quickly turned into fertilizer for the garden.
If you want to buy quality equipment, you will have to pay a lot of money. However, the tools will last for a long time. After a while, they will pay off in full. For those who believe that buying ready-made firewood is cheaper, they are deeply mistaken. For example, what is it worth only one delivery of ready-made firewood, and then they still need to be stored. Firewood is stored under special sheds or in woodpiles.
Do-it-yourself firewood shed in the country, photo
Sheds for storing firewood in the winter in the country


shed for storing firewood in winter


Experts have proven that self-logging is much cheaper for the owner, even if he spent significant funds to buy garden equipment.
How to calculate the cubic capacity of chopped firewood
Wood has unique characteristics as it can be used not only as a building material, but also as a source of energy. Firewood is considered one of the cleanest fuels today.


Many companies sell similar goods, which may differ in quality. You can find out how to choose the right firewood on the website https://drovam.rf/drova-kolotye.html.
We count the folded firewood
The volume of wood is considered fairly easily if it is lumber, which is tightly stacked in stacks. But the wood cannot be folded so that there are no gaps between the logs. The calculation of these stacked materials can be broken down into several sequential steps:
- Initially, you need to calculate how many cubic meters are located on a heap or in the back of a car. To do this, simply multiply the width, height and length of a particular object. You can measure all this with an ordinary tape measure.
- To get the real volume of firewood in one heap, the previously obtained value should be multiplied by a factor of 0.7. For example, if you counted 10 cubic meters on a folded heap, then, taking into account the amendment, the volume of wood will be only 7 cubic meters.


Bulk firewood
But firewood is not always neatly folded into the correct structure. Many people want to know how much the bulk heap occupies. This task is more difficult, especially if the wood is non-standard and differ in the size of the log.
If you chopped a certain volume at home, then you can calculate it using approximately the following method:
- We need to find the size of the heap. To do this, you need to calculate its approximate form, on the basis of which this value can be obtained. The simplest option is the car body, where firewood was simply poured. The calculation algorithm involves multiplying the height, width and length of the frame.
- The resulting volume in the first step must be converted to warehouse meters. For this, special coefficients are also used, which depend on the length of the log. For example, if you counted 10 cubic meters on a heap, then with a log height of 0.5 m, the number of storage meters will be equal to 100.75 = 7.5 cubic meters.
- To translate the warehouse measurements obtained at the second step into real volume, you need to multiply the data obtained by a factor of 0.7 (7.50.7 = 5.25 cubic meters).
As you can see, the process of calculating the volume of chopped firewood is a fairly simple operation that will take you a little time.
stroybud.com
Wood moisture
What should be wood moisture for heating stoves and fireplaces. In order for the house to receive heat, we saved money, and the stove served for a long time and pleased us with warmth, light, created a cozy atmosphere in the house, did not require repairs and did not collapse, the moisture content of the firewood should be 17-20 percent.Then the question arises: how to measure wood moisture? If it is not enough for you to determine the moisture content of firewood by eye, you want to make sure that the firewood is properly dried, then you can use devices to check the moisture content of the wood. Such devices can be ordered online or bought in specialized stores. Such devices are called "moisture meters".
How many cubes are in the warehouse meter are important parameters in the calculation. Click!
All over the world there are uniform measurement systems: kilograms for determining weight, meters for the size of things, etc.
When harvesting and transporting firewood and forests, cubic meter and warehouse meter measurements are usually used - there is some difference between these values, which not everyone knows about.
What is a cubic meter
As the name implies, a cubic meter or cubic meter (m3) is the volume of a cube whose sides are equal to a meter. This value is usually measured in gas, water, snow, sand and other bulk and liquid materials.
However, this value is only suitable for measuring one whole piece of wood, for example, pine: after all, if you add a cube of separate firewood and boards, there will still be a distance between them, albeit a few millimeters.
Therefore, when buying firewood, boards and other "non-whole" pieces, cubic meters are not suitable: you would have to measure each block from all sides and try to fit them into the specified parameters. This is too long and can still lead to errors.
How to count a cube of firewood
To simplify the counting process and reduce the possibility of fraud, another term was coined - stock meter.
It is easiest to imagine it in the form of a woodpile measuring 1 mx 1 mx 1 m, into which the logs were folded, fitting them as tightly as possible to each other. There is still some distance between them - small, but significant when buying a large amount of firewood.
To convert the scadometer to a cubic meter, it is necessary to calculate the dimensions of the stack (length, height and width) and multiply by a special factor indicated in the table below. This will help to get the volume of firewood close to the truth.
The value of the coefficient can be found in special tables and in the photo: they depend on the type of wood, the length of the log and its volume.
For deciduous trees
For conifers
In other words, the shorter the logs, the more space they can take up in the package, while round firewood takes up more volume than chopped firewood.
The easiest way to see the meaning of a warehouse meter is with an example:
A pile of thin birch woods 0.75 meters long was purchased. The dimensions of the stack itself were 1.5 meters * 3 meters * 2.5 meters. It is necessary to calculate the total amount of firewood used using a calculator:
- It is necessary to calculate the volume of the stack itself by multiplying its sides: 1.5 * 3 * 2.5 = 11.25 cubic meters. meters;
- Then you need to determine the coefficient of the firewood itself: for birch it is 0.65;
- Both numbers are multiplied again: 11.25 * 0.65 = 7.3125 - this is the specific gravity.
The total difference is almost 4 cubic meters. meters. If there was no scadometer value, the buyer would have to overpay significantly for the purchase.
Calculation and weight
To calculate the weight of a stack, you need to multiply the number of storage meters by a coefficient, and then check the coincidence of the number using tables that are easy to find on the Internet.
They indicate the approximate weight of 1 cubic meter of different breeds. For example, fresh oak weighs 1000 kg, and with a natural moisture content of 15% - only 710 kg.
Example:
We bought 4 storage meters of dry chopped oak logs 0.25 meters long and 15% moisture. You need to check their weight:
- The ratio of such firewood is 0.76: 0.76 * 4 = 3.04 cubic meters. meters;
- 3.04 * 710 kg = 2158.4 kg - this is approximately how much the purchased firewood should weigh. If the difference is unduly deviated in one direction, then the seller is trying to cheat.
Note: When buying a tree, it is important to know not only its volume, but also its weight: if stored improperly, the tree can swell and become much heavier than it was, but the buyer will still have to pay for this.
If the tree was brought in the back of a car, for example, a Gazelle or a dump truck, not in a woodpile, but having thrown it somehow, it is necessary to multiply the volume of the body by 0.8 with a log length of 0.25 meters and by 0.75 with a length of 0, 5 meters. These are the average values of the occupied air for this type of installation.
How to calculate the cubic capacity, see an example of calculation in the following video:
6sotok-dom.com
Which firewood is better
Wood, which serves as a raw material for firewood, is far from the same in its properties.
Hard tree species such as birch, oak, hornbeam, beech, yew burn hotter, have a high fiber density, and burn more slowly.
Soft varieties have their advantages, for example: aspen, gives less heat than birch by 25%, but it perfectly maintains the heat in a melted oven. Alder also shares a delicious aroma, as do the conifers. Alder and aspen added to the stove at the end of the heating process remove soot deposits and soot in the chimney. But the formation of plaque, which can lead to clogging of the chimney, occurs when essential oils and resin of pine, fir, spruce are burned. Conifers are also inferior in calorific value to birch and oak, but they dry out faster and are more suitable for kindling. Only fir sparkles strongly, and larch at the end of combustion emits a lot of carbon monoxide and you need to be more careful with the damper.
Some types of fruit trees are medium-hard and have an average calorific value. They burn, emitting an aroma, they are easy to harvest, since firewood can be chopped without much effort.


Based on the above, it is difficult to advise any one type of wood for stove or fireplace firewood. As fuel - the most rational are hard deciduous tree varieties. Smooth flame, high heat output, less soot, ash. But the scent of conifers has a therapeutic effect, and is well suited to ignite. By combining several varieties, it is possible to maintain both the working condition of the chimney, the stove, and a comfortable microclimate during the entire cold period, subject to the initial investment in a good one. Otherwise, any heat, along with your funds, will fly into the pipe, evaporate through the cracks.
Wood volume calculation table: GOST, measurement method
The very method of calculating the volume of a round log, board or bar is simple, reduced to a mathematical problem of 5-6 grade. But in reality, everything is much more complicated: conical logs, boards are often measured in inches, the timber has chamfers, there are other subtleties and differences of real wood products. Therefore, tables are so convenient, which summarize the data on measuring the cubic capacity of the forest, taking into account such form errors as the taper of the logs, the presence of bark, escaping, the complexity of the shape of the slab and plate and other nuances.


Figure 1. Table for calculating the cubic capacity of edged sawn timber.
Tables of round timber volumes in accordance with GOST 2708-75
The most common, accurate and verified table for determining the volume of round timber is the one given in the official document, GOST 2708-75, without a validity period.
It contains data on the volume of round wood, diameter from 3 to 120 cm, length from 1 to 9.5 m, with a step in diameter of 1-2, and along the length - 10 cm.Additionally, specialized standard sizes of round logs are shown: 0.5-0.9 m and 10-13.5 m, and 6-15 cm and 8-38 cm thick, respectively. Their volumes have also been calculated. There are even more specific sizes.
Tab. 1. Cubic capacity of round wood 6-60 cm thick, 1-9 m long
| Thickness (diameter), cm | |||||||||
| 1,0 | 2,0 | 3,0 | 4,0 | 5,0 | 6,0 | 7,0 | 8,0 | 9,0 | |
| 6 | 0,0032 | 0,0073 | 0,0120 | 0,017 | 0,022 | 0,028 | 0,037 | 0,047 | 0,056 |
| 8 | 0,0053 | 0,0110 | 0,0170 | 0,026 | 0,035 | 0,045 | 0,057 | 0,071 | 0,084 |
| 10 | 0,0082 | 0,0170 | 0,026 | 0,037 | 0,051 | 0,065 | 0,082 | 0,100 | 0,122 |
| 12 | 0,0120 | 0,026 | 0,038 | 0,053 | 0,073 | 0,093 | 0,114 | 0,120 | 0,140 |
| 14 | 0,0160 | 0,035 | 0,052 | 0,073 | 0,097 | 0,123 | 0,150 | 0,179 | 0,21 |
| 16 | 0,0210 | 0,044 | 0,069 | 0,095 | 0,124 | 0,155 | 0,189 | 0,22 | 0,26 |
| 18 | 0,0270 | 0,056 | 0,086 | 0,120 | 0,156 | 0,194 | 0,23 | 0,28 | 0,32 |
| 20 | 0,0330 | 0,069 | 0,107 | 0,147 | 0,190 | 0,23 | 0,28 | 0,33 | 0,39 |
| 22 | 0,0400 | 0,084 | 0,130 | 0,178 | 0,23 | 0,28 | 0,34 | 0,40 | 0,46 |
| 24 | 0,0480 | 0,103 | 0,157 | 0,21 | 0,27 | 0,33 | 0,40 | 0,47 | 0,55 |
| 26 | 0,0570 | 0,123 | 0,185 | 0,25 | 0,32 | 0,39 | 0,46 | 0,54 | 0,63 |
| 28 | 0,0670 | 0,144 | 0,220 | 0,29 | 0,37 | 0,45 | 0,53 | 0,63 | 0,72 |
| 30 | 0,0770 | 0,165 | 0,250 | 0,33 | 0,42 | 0,52 | 0,61 | 0,72 | 0,83 |
| 32 | 0,0870 | 0,190 | 0,28 | 0,38 | 0,48 | 0,59 | 0,70 | 0,82 | 0,94 |
| 34 | 0,10 | 0,210 | 0,32 | 0,43 | 0,54 | 0,66 | 0,78 | 0,92 | 1,06 |
| 36 | 0,11 | 0,230 | 0,36 | 0,48 | 0,60 | 0,74 | 0,88 | 1,02 | 1,18 |
| 38 | 0,12 | 0,260 | 0,39 | 0,53 | 0,67 | 0,82 | 0,97 | 1,13 | 1,30 |
| 40 | 0,14 | 0,28 | 0,43 | 0,58 | 0,74 | 0,90 | 1,07 | 1,25 | 1,44 |
| 42 | 0,15 | 0,31 | 0,47 | 0,64 | 0,81 | 1,00 | 1,18 | 1,38 | 1,58 |
| 44 | 0,16 | 0,34 | 0,52 | 0,70 | 0,89 | 1,09 | 1,30 | 1,51 | 1,73 |
| 46 | 0,18 | 0,37 | 0,57 | 0,77 | 0,98 | 1,19 | 1,41 | 1,65 | 1,90 |
| 48 | 0,19 | 0,41 | 0,62 | 0,84 | 1,06 | 1,30 | 1,54 | 1,80 | 2,07 |
| 50 | 0,21 | 0,44 | 0,67 | 0,91 | 1,15 | 1,41 | 1,67 | 1,95 | 2,26 |
| 52 | 0,23 | 0,48 | 0,73 | 0,99 | 1,25 | 1,53 | 1,81 | 2,12 | 2,45 |
| 54 | 0,25 | 0,53 | 0,80 | 1,07 | 1,35 | 1,65 | 1,96 | 2,29 | 2,63 |
| 56 | 0,27 | 0,57 | 0,86 | 1,16 | 1,46 | 1,78 | 2,11 | 2,46 | 2,83 |
| 58 | 0,29 | 0,61 | 0,92 | 1,25 | 1,57 | 1,91 | 2,27 | 2,63 | 3,03 |
| 60 | 0,31 | 0,66 | 0,99 | 1,33 | 1,68 | 2,05 | 2,42 | 2,81 | 3,23 |
This is a frequently used part of the table. Small graduation of the sizes of logs and cubic capacity allows using it both in industry and private individuals. Therefore, this table can be called universal. On its basis, a variety of techniques have been developed, for example, measuring standing timber in forestry, edging in transport at customs posts, and others (Fig. 1).
Back to the table of contents
Carriage: what is it? Determination of pine density. Dovetail: mount. More >>
Working with ready-made calculations of cubic capacity
Of course, not all standard sizes are given here, but for example, it can be seen that calculations of the cubic capacity of various logs have been made with great accuracy. In practice, the thickness (diameter) is measured, as indicated in GOST, then the length and cubic capacity is found from the table. Since the circumference of the cut of the log is not ideal in shape, 2 measurements of the diameter are carried out perpendicularly and its average value is found. It is this value that you need to look for in the string.


Figure 2. Using a caliper, you can measure the diameter and calculate the cubic capacity of the tree.
Example. A 6-meter log in the upper cut has 2 diameters (30 and 34 cm excluding bark), measured perpendicularly. We find the average value of the cut diameter of 32 cm. The length of the log is 6 m. From the table we find that at the intersection of a row with a value of 32 cm and a column of 6 m there is a volume value of 0.59 m³. If the log is rounded, then just one measurement of the diameter is enough. The error in the results is 2-4%, which is acceptable for most practical calculations.
When logging for a home, each log can be measured, but there is not always enough time and effort for this. Here, an industrial method of calculating the cubic capacity is used. The timber is sorted by length and then by equal upper diameters. Measurement is made in each group of one product.
And only after stacking in stacks or a car, the quantity is counted and the total cubic capacity is calculated by simply multiplying the number of logs by the volume of one of them.
Scheme for determining the diameter of the upper end.
In the forestry industry, for taxation (determination of the commodity stock of standing timber), in addition to simple tools, there are special electronic devices for measuring and calculating the parameters of standing trees.
Masser 2000 is a computerized measuring fork that allows not only to accurately measure the control diameter of a standing tree at a height of 1.3 m, but also to immediately determine the cubic capacity, taking into account the type, height and crown of the tree. Then the device outputs all the collected information to the computer (Fig. 2).
Back to the table of contents