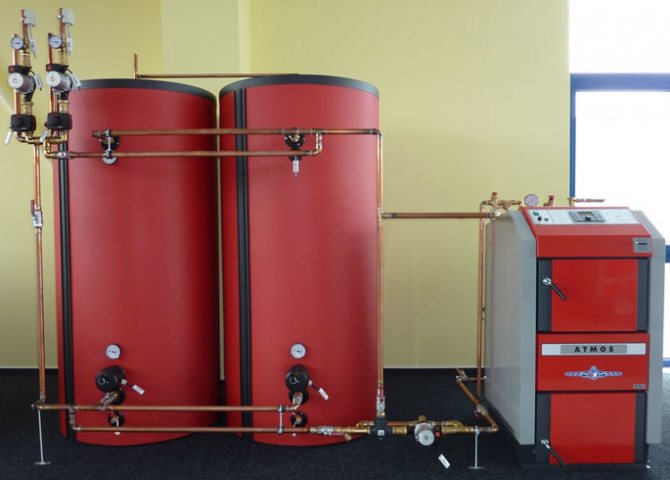
Posted in Tips Published 02/21/2016 · Comments: · Read: 4 min · Views: Post Views: 4 555
Hello, friends! Have you ever thought about how reliably your boiler is protected from overheating? Sometimes, when firing a solid fuel boiler, the temperature of the coolant has reached a critical value, and the fuel still continues to burn. At the same time, a significant amount of heat is released, which threatens with serious consequences both for the boiler and for the entire heating system as a whole.

The heating system with a solid fuel boiler is inertial. This positive quality of solid fuel boilers with excessive heating of the coolant can play a fatal role. In this case, it will not work to immediately stop the ongoing heating of the coolant. A particularly disastrous situation arises if the heating system contains polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes. Their operation is not designed for such a high temperature that it will inevitably lead to depressurization of the system.
In this case, it is no longer necessary to rely on a security system consisting of an expansion tank, a drain valve, an automatic air vent. It only protects the system from overpressure. But, when the resource of the expansion tank has already been exhausted, the increasing pressure in the system leads to the operation of the drain valve, and part of the coolant is discharged from the system.
It seems that the situation should improve, but it is only getting worse, because a decrease in the volume of the coolant leads to a more intense boiling of water in the boiler. The temperature continues to rise, and now…. But it is not all that bad. Boiler manufacturers have foreseen this scenario as well. Modern boilers are equipped with devices that prevent the boiler from overheating. But how effective they are, let's try to figure it out in this article.
Safety valve use
It is not the same as a safety valve. The latter simply relieves pressure in the system, but does not cool it. Another thing is the boiler overheating protection valve, which takes hot water from the system, and instead supplies cold water from the water supply. The device is non-volatile, it is connected to the supply and return mains, water supply network and sewerage system.


At a coolant temperature above 105 ºС, the valve opens and, due to a pressure in the water supply system of 2-5 bar, hot water is displaced from the jacket of the heat generator and cold pipelines, after which it goes into the sewage system. How the solid fuel boiler protection valve is connected is shown in the diagram:
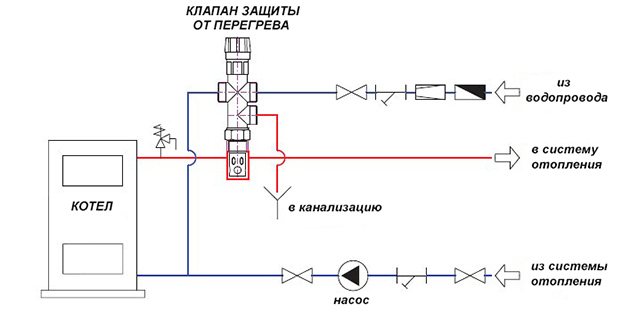

The disadvantage of this protection method is that it is not suitable for systems filled with antifreeze liquid. In addition, the scheme is not applicable in conditions where there is no centralized water supply, because together with a power outage, the supply of water from a well or a pool will also stop.
Chimney requirements
To determine what characteristics the manufacturer himself presents, you need to read the instructions, because there are specific data given, what is the minimum pipe section needed, height, temperature regime - these factors in a particular case are fundamental and you need to focus on them. writes which chimney is better for a solid fuel boiler and what technical parameters need to be taken into account. The above listed characteristics, such as the height, the length of the chimney, will allow you to choose a reliable, and most importantly functional channel from the point of view of this particular model.
Take into account the diameter of the chimney for a solid fuel channel, because not every channel will be able to remove the generated amount of gas in a certain time, and the accumulated fumes and gases can enter the room through non-tight joints and cracks.
Technological requirements
The following technical requirements must be observed:
- A dedicated area should be provided to disperse the smoke. It is a vertical pipe installed behind the nozzle of a solid fuel boiler. The accelerating section is made one meter high.
- The chimney is installed only vertically. A deviation of no more than 30 degrees is allowed.
- The presence of deflections is prohibited.
- Length is very important (3 - 6 meters).
- Three horizontal sections are allowed. Moreover, the length of each should not exceed half a meter.
- The height of the head over the roof must exceed 100 cm.
- Fastening the pipe to the wall is carried out in 1.5 meter increments.
- To create a sealed joint, the pipes are abundantly lubricated with a heat-resistant sealant.
To obtain ideal draft, it is necessary that the chimney design has a minimum number of turns. A flat pipe is considered the best.
The chimney can be installed inside or outside the building. For the first option, it is necessary to protect the pipe so that it does not come into contact with combustible materials. A special metal screen is used, installed in the place where the pipe passes through the ceiling. The chimney must be at a distance of more than 25 cm from the wall.
Outdoor structures look much safer. They are much easier to maintain. Masters consider this method to be the most preferable one.
Overheating reasons
The only reason for overheating is that the boiler produces more heat than is consumed by the heating system. But if earlier everything was fine, but now the boiler overheats, then the problem is not that the boiler is very powerful, but the problem lies elsewhere.
It is possible that your dirt filter in front of the circulation pump is simply clogged. In this case, you need to unscrew and clean it and the problem will be solved. With such a problem, your return will be cold.
There is an option that the circulation pump just broke down. With such a problem, your return will also be cold. Change the pump.
But the most common problem is overheating as a result of a power outage. Everything is perfect for you - a clean filter, a working pump, but it simply cannot work. And overheating occurs. The problem can be solved by extinguishing the boiler or pulling out the burning fuel from the boiler furnace - but this is far from the best option. The best option is to make the heating system insensitive to power outages - to make it self-flowing or to install an uninterruptible power supply.
Watch the video with the appearance of boiler overheating when the supply voltage is turned off.
And here is a video with a way to solve the problem of overheating of the boiler and the heating system.


A real boiler repair technician is hard to find
Therefore, it is important to understand them on your own, because the master is really not always required and many problems can be eliminated by yourself. Consider a list of boiler malfunctions, which covers as much as possible all possible breakdowns
The article is intended for a layman, but for an ordinary person who is capable of eliminating such problems.
Installing a thermostatic draft regulator
Owners of solid fuel boilers, especially in rural areas where power outages are frequent, have appreciated their advantages. The boiler is not picky about fuel, non-volatile, inexpensive. All modern solid fuel boilers are equipped with a thermostatic draft regulator that prevents the boiler from overheating.
When the set temperature is reached, the draft regulator lowers the blower flap through the chain, preventing air from entering the combustion zone. The fuel starts to smolder. Heat generation is reduced.
The draft regulator is maintenance-free. In the event of its failure, it can be easily replaced.
But such a system has one significant drawback, leading to a loss of boiler power. As you know, the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler reaches its maximum value only in the mode of active fuel combustion. In the smoldering mode, this indicator is almost halved.
Heat storage circuit
In a number of EU countries, rules have been introduced, according to which schemes for connecting solid fuel boilers to the heating system must necessarily include a heat accumulator. Without it, the operation of such heaters is simply prohibited. The reason is the high content of carbon monoxide (CO) in emissions during the limitation of oxygen supply to the furnace to reduce the intensity of combustion.
With normal air access, harmless carbon dioxide (CO2) is formed, therefore the firebox must operate at full capacity, giving energy to the heat accumulator. Then the CO content will not exceed environmental standards. In the post-Soviet space, there are still no such requirements, respectively, we continue to block air access in order to achieve slow smoldering of wood, for example, in a long-burning boiler.
Heat accumulators are commercially available as a finished product, although many craftsmen make their own. Basically, this is a tank covered with a layer of thermal insulation. In the factory version, it can have a built-in DHW circuit and a heating element for heating water. Such a solution allows you to accumulate heat from a wood-burning boiler, and during the moments of its downtime - to provide heating of the house for some time. The connection diagram of the boiler with the heat accumulator is shown in the figure:
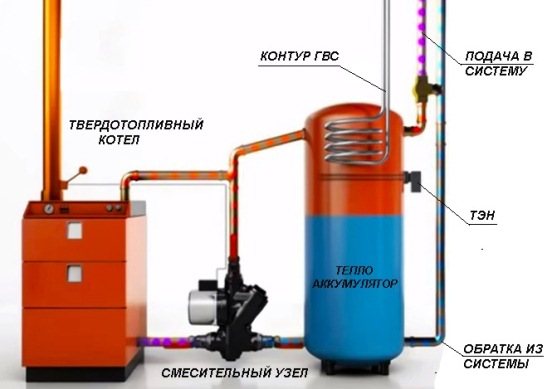

Note. In the circuit, instead of a mixing unit consisting of several elements, a ready-made device is installed that performs the same functions - LADDOMAT 21.
Heat accumulator in a heating system with a solid fuel boiler
Fuel supply to solid fuel boilers is not amenable to automation. For this reason, solid fuel boilers are batch-type devices. They heat the coolant only during the combustion of the next portion of the fuel. The house is hot and cold.
In order to smooth out temperature fluctuations, it is necessary to load more fuel.
Solid fuel boilers for long burning have their advantages and disadvantages, but they do not solve the problem radically.
In the heating system of a house with a solid fuel boiler of intermittent action it is beneficial to have a heat accumulator, which accumulates heat energy during the operation of the boiler, and gives off heat to the room during a pause. The presence of such a heat accumulator stabilizes and optimizes the operating mode of heating the house with a solid fuel boiler. In a system with a heat accumulator temperature fluctuations in the house slow down, their amplitude decreases, the frequency of fuel loading increases. The boiler always works in the optimal mode of fuel combustion, with maximum efficiency, which saves fuel. The house itself is a kind of heat accumulator. All materials in the house have the ability to accumulate heat - heat capacity, and to give off heat when the air temperature in the room decreases. The higher the heat capacity of the structures of the house, the better - the slower the temperature changes in the rooms, the more comfortable it is in the house and less often you have to load fuel.
The greater the mass and density of building materials, the higher their heat capacity.
You may have noticed that buildings with thick stone walls are warm in winter and cool in summer.
Modern building technologies are going in the opposite direction.
Building structures are becoming lighter and the use of low density materials is increasing.
For example, a house built using frame or frame-panel technology can provide thermal comfort for residents only if the heating and air conditioning systems are almost continuous. After all, the heat capacity of such a house is minimal.
People have learned to use thermal energy accumulators for a long time in houses with low heat capacity. A Russian stove in a wooden house is a huge, heavy brick structure, a classic example of a heat accumulator in a house
with a small heat capacity of wooden walls.
In modern conditions, in order to increase the comfort of the house heating system with a solid fuel boiler, it is convenient and profitable to use other methods of heat accumulation.
What are the ways to protect heating equipment from overheating
Manufacturing companies try, in order to increase the consumer attractiveness of their products, to include any guarantees of its safety in the technical passport of boiler equipment. The uninitiated consumer does not have the slightest idea about the means of protecting the heating boiler from boiling.
There are currently the following ways to ensure the protection of solid fuel units used for autonomous heating systems. The effectiveness of each method is explained by the operating conditions of the boiler equipment, and the design features of the units.
In most cases, manufacturers recommend using tap water for cooling in the data sheet for a heater. In some cases, solid fuel boilers are equipped with built-in additional heat exchangers. There are models of boilers with external heat exchangers. Used by a safety valve to prevent overheating. The safety valve is designed only to relieve excessive pressure in the system, while the safety valve opens access to tap water when the boiler overheats.


If the temperature of the coolant exceeds the 100 ° C mark, it creates an excess pressure that opens the valve. Under the influence of tap water, which is supplied under a pressure of 2-5 bar, hot water is displaced from the circuit by cold water.
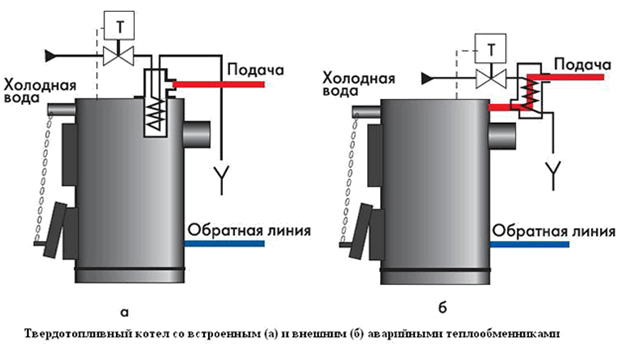

The first controversial aspect of tap water cooling is the lack of electricity to power the pump. The expansion vessel does not have enough water to cool the boiler.
The second aspect, which sweeps aside this cooling method, is associated with the use of antifreeze as a heat carrier. In the event of an emergency situation, up to 150 liters of antifreeze will go down the drain along with the incoming cold water. Is this protection method worth it?
The presence of a UPS will allow maintaining the operation of the circulating pump in a critical situation, with the help of which the coolant will evenly disperse through the pipeline, without having time to overheat. As long as there is enough battery capacity, an uninterruptible power supply ensures that the pump is running. During this time, the boiler should not have time to heat up to the critical parameters, the automation will work, starting the water along the spare, emergency circuit.
Another way to get out of a critical situation will be to install an emergency circuit in the piping of a solid fuel unit. Shutdown of the pump can be duplicated by the operation of the reserve circuit with natural circulation of the coolant. The role of the emergency circuit is not in providing heating of living quarters, but only in the ability to remove excess heat energy in an emergency.
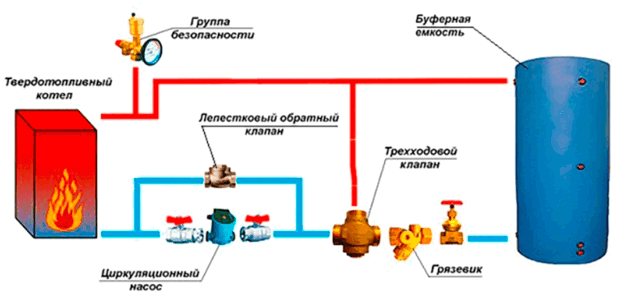

Such a scheme for organizing the protection of the heating unit from overheating is reliable, simple and convenient in operation. You will not need special funds for its equipment and installation. The only conditions for such protection to work are:
- the presence of an expansion tank or storage tank in the system;
- use of a check valve only of the petal type;
- the pipes in the secondary circuit must be of a larger diameter than the conventional heating circuit.
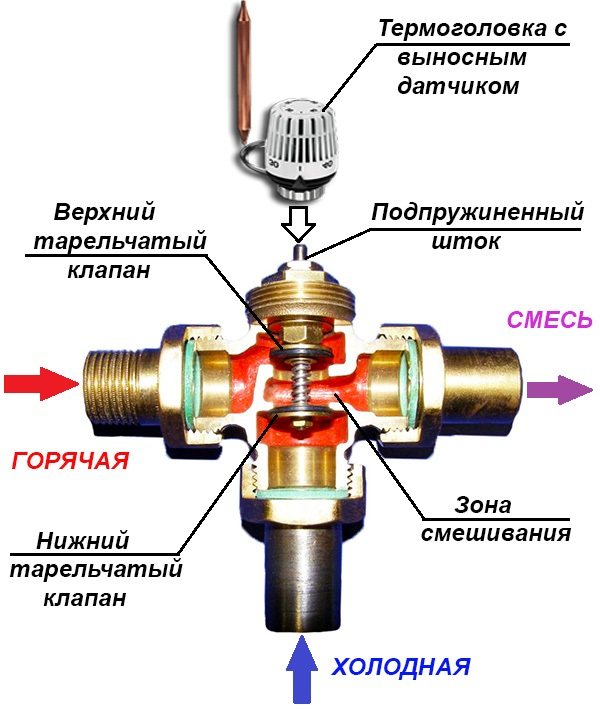
How the thermostatic diverter valve works
The thermostatic valve is installed on the flow in front of the bypass section (pipeline section) connecting the boiler flow and return in the immediate vicinity of the boiler. In this case, a small circulation loop of the coolant is formed. The thermo bulb, as mentioned above, is installed on the return pipeline in close proximity to the boiler.
At the moment of starting the boiler, the coolant has a minimum temperature, the working fluid in the thermowell occupies a minimum volume, there is no pressure on the stem of the thermal head, and the valve passes the coolant only in one direction of circulation in a small circle.
As the coolant heats up, the volume of the working fluid in the thermowell increases, the thermal head begins to press on the valve stem, passing the cold coolant to the boiler, and the heated coolant into the general circulation circuit.

As a result of mixing in cold water, the temperature in the return line decreases, which means that the volume of the working fluid in the thermowell decreases, which leads to a decrease in the pressure of the thermal head on the valve stem. This, in turn, leads to the termination of the supply of cold water to the small circulation loop.
The process continues until the entire coolant is heated to the required temperature. After that, the valve closes the movement of the coolant along a small circulation loop, and the entire coolant begins to move along a large heating circle.
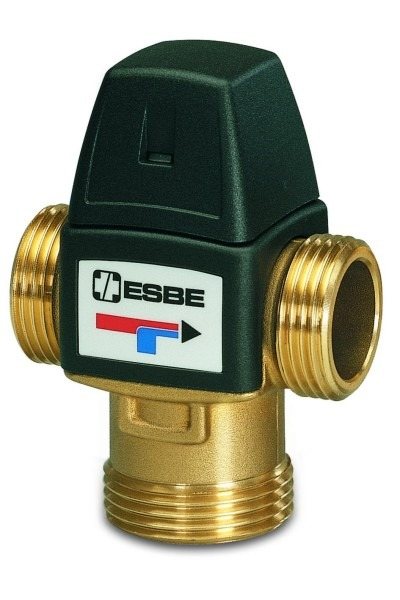


The thermostatic mixing valve works in the same way as a control valve, but it is not installed on the flow line, but on the return line. The valve is located in front of the bypass, which connects the supply and return and forms a small circle of coolant circulation. The thermostatic bulb is attached in the same place - on the section of the return pipeline in the immediate vicinity of the heating boiler.
While the coolant is cold, the valve passes it only in a small circle. As the heat carrier heats up, the thermal head begins to press on the valve stem, passing part of the heated heat carrier into the general circulation circuit of the boiler.

As you can see, the scheme is extremely simple, but at the same time effective and reliable.
The thermostatic valve and thermal head do not need electrical energy to operate, both devices are non-volatile. No additional devices or controllers are needed either. To heat the coolant circulating in a small circle, 15 minutes are enough, while heating the entire coolant in the boiler can take several hours.
This means that using a thermostatic valve, the duration of condensate formation in a solid fuel boiler is reduced several times, and with it the time for the destructive effect of acids on the boiler is reduced.
To protect the solid fuel boiler from condensate, it is necessary to correctly pip it using a thermostatic valve and at the same time creating a small coolant circulation circuit.
When buying and installing a solid fuel boiler, it is imperative to take into account the peculiarities of its operation, namely, the high probability of overheating in emergency situations, which can result in a serious accident and even destruction of the unit's water jacket (explosion). Also, considerable harm can be caused by the formation of condensation on the walls of the combustion chamber, which happens under certain operating modes. To eliminate such troubles, the solid fuel boiler must be protected from overheating and condensation, which will be discussed in our article.
Ways to reduce heat loss
The above information will help to be used to correctly calculate the temperature of the coolant and tell you how to determine the situations when you need to use the regulator.
But it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is influenced not only by the temperature of the coolant, outside air and the strength of the wind. The degree of insulation of the facade, doors and windows in the house should also be taken into account.
To reduce the heat loss of housing, you need to worry about its maximum thermal insulation. Insulated walls, sealed doors, plastic windows will help reduce heat leakage. It also reduces heating costs.
With a large temperature difference between the supply and return of the boiler, the temperature on the walls of the boiler combustion chamber approaches the temperature of the "dew point" and condensation is possible. It is known that during the combustion of fuel various gases are released, including CO 2, if this gas combines with the "dew" that has fallen on the walls of the boiler, an acid is formed, which corrodes the "water jacket" of the boiler furnace. As a result, the boiler can be quickly damaged. To prevent dew loss, it is necessary to design the heating system in such a way that the temperature difference between the supply and return is not too large. This is usually achieved by heating the return coolant and / or including a hot water boiler with a soft priority in the heating system.
To heat the coolant between the return flow and the boiler supply, a bypass is made and a circulation pump is installed on it. The power of the recirculation pump is usually chosen as 1/3 of the power of the main circulation pump (the sum of the pumps) (Fig. 41). In order to prevent the main circulation pump from “pushing” the recirculation loop in the opposite direction, a check valve is installed downstream of the recirculation pump.
Fig. 41. Return heating
Another way to heat the return flow is to install a hot water supply boiler in the immediate vicinity of the boiler. The boiler is "set" on a short heating ring and positioned in such a way that hot water from the boiler after the main distribution manifold immediately enters the boiler, and from it returns back to the boiler. However, if the demand for hot water is small, then both a recirculation ring with a pump and a heating ring with a boiler are installed in the heating system. With proper calculation, the recirculation pump ring can be replaced with a system with three- or four-way mixers (Fig. 42).
Fig. 42. Heating the return flow using three- or four-way mixers On the pages "Control equipment of heating systems" were listed almost all technically significant devices and engineering solutions present in classic heating circuits. When designing heating systems on real construction sites, they should be fully or partially included in the project of heating systems, but this does not mean that exactly the heating fittings that are indicated on these pages of the site should be included in a specific project. For example, on the make-up unit, shut-off valves with built-in check valves can be installed, or these devices can be installed separately. Mud filters can be installed instead of mesh filters. An air separator can be installed on the supply pipelines, or it is possible not to install it, but to mount automatic air vents instead of it at all problem areas. On the return line, you can install a deslimator, or you can simply equip the collectors with drains. Adjustment of the temperature of the coolant for the "warm floor" circuits can be done with a qualitative adjustment with three- and four-way mixers, or you can make a quantitative adjustment by installing a two-way valve with a thermostatic head. Circulation pumps can be installed on a common supply pipe or vice versa, on the return.The number of pumps and their location can also vary.
Can the water in the well freeze? No, the water will not freeze. both in the sandy and in the artesian well, the water is below the freezing point of the soil. Is it possible to install a pipe with a diameter of more than 133 mm in a sand well of a water supply system (I have a pump for a large pipe)? sand well productivity is low. The "Kid" pump is specially designed for such wells. Can a steel pipe in a water supply well corrode? Slowly enough. Since when arranging a well for a suburban water supply, it is pressurized, there is no access to oxygen in the well and the oxidation process is very slow. What are the pipe diameters for an individual well? What is the productivity of the well with different pipe diameters? Pipe diameters for the arrangement of a well for water: 114 - 133 (mm) - well productivity 1 - 3 cubic meters / hour; 127 - 159 (mm) - well productivity 1 - 5 cubic meters ./ hour; 168 (mm) - well productivity 3 - 10 cubic meters / hour; REMEMBER! It is necessary that ...
The efficient operation of the heating system determines how comfortable the temperature will be in the cold season in the house. Sometimes there are situations when hot water is supplied to the system, and the batteries remain cold. It is important to find the cause and eliminate it. To solve the problem, you need to know the design of the heating system and the reasons for the cold return during hot supply.
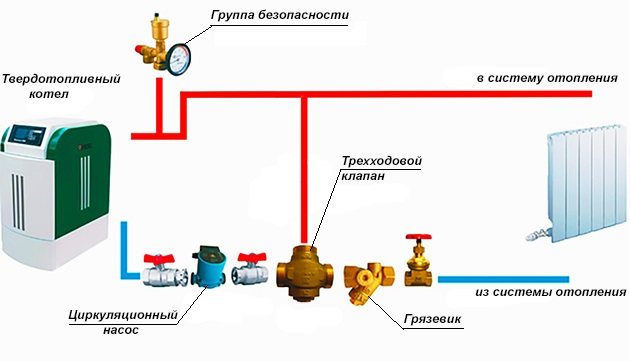
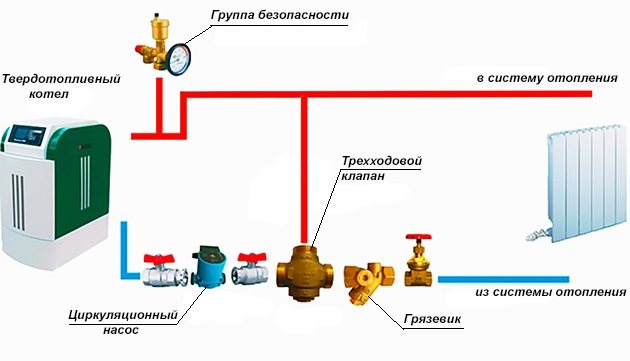
Basic scheme for piping a solid fuel boiler
For a better understanding of the processes that occur during the operation of the heat generator, we will show its piping in the figure, and then we will analyze the purpose of each element. In the event that the heating unit is the only source of heat in the house, then it is recommended to use the following basic scheme to connect it:
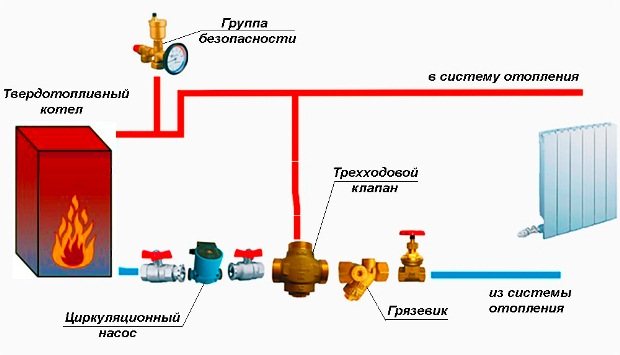

Note. The basic scheme, where there is a small boiler circuit and a three-way valve, shown in the figure, is mandatory for use when working together with other types of heat generators.
So, the first on the path of movement of the coolant from the boiler plant is the safety group. It consists of three parts mounted on one manifold:
- pressure gauge - to control the pressure in the network;
- automatic air relief valve;
- safety valve.
When operating a solid fuel boiler, there is always a risk of overheating of the coolant, especially at modes close to maximum power. This is due to some inertia of fuel combustion, because when the required water temperature is reached or a sudden power outage, it will not be possible to immediately stop the process. Within a few minutes after stopping the air supply, the coolant will still heat up, at this moment there is a risk of vaporization. This leads to an increase in pressure in the network and the danger of destruction of the boiler or burst of pipes.
To exclude emergencies, the piping of the solid fuel boiler must necessarily include a safety valve. It is adjusted to a certain critical pressure, whose value is indicated in the heat generator's passport. As a rule, the value of this pressure in most systems is 3 bar, when it is reached, the valve opens, releasing steam and excess water.
Further, in accordance with the diagram, for the correct operation of the unit, it is necessary to organize a small circulation circuit of the coolant. Its task is to prevent the ingress of cold water from the house heating system into the heat exchanger and the boiler water jacket. This is possible in 2 cases:
- when heating starts up;
- when, due to a power outage, the pump stops, the water in the pipelines cools down, and then the voltage supply resumes.
Important! The situation with a power outage poses a particular danger to cast iron heat exchangers.Sudden pumping of cold water from the system can lead to its cracking and loss of tightness.
If the firebox and heat exchanger are made of steel, then connecting the solid fuel boiler to the heating system through a three-way valve protects them from low-temperature corrosion. The phenomenon occurs if condensation forms on the inner walls of the combustion chamber due to temperature differences. Mixing with volatile fractions and ash, moisture forms a scale layer on the steel walls, which is very difficult to clean off. This corrodes the metal and shortens the service life of the product as a whole.
The scheme works according to the following principle: while the water in the boiler jacket and in the system is cold, the three-way valve allows it to circulate along a small circuit. After reaching the temperature of 60 ºС, the unit begins to mix the coolant from the network at the unit inlet, gradually increasing its consumption. Thus, all the water in the pipes warms up gradually and evenly.
How to get rid of condensate in the boiler furnace?
In solid fuel boilers, moisture can form on the inner walls of the combustion chamber. This happens when the wood is already on fire and the blower fan (if there is one) is working at full capacity, and the water in the heating system is still cold.


From the temperature drop, condensate arises, which, mixing with the combustion products, settles on the walls of the chamber. This deposit corrodes the metal, as a result of which the service life of the boiler is significantly reduced.
Note. Boilers with a cast-iron heat exchanger are not afraid of corrosion, but, in turn, are sensitive to sudden changes in the temperature of the coolant.
It is not difficult to solve this problem, you just need to include a three-way thermostatic valve in the piping scheme, set for a coolant temperature of 55-60 ºС, as shown in the figure below. The protection of the solid fuel boiler against condensation works as follows: until the water in the boiler heats up to the set temperature, it circulates along a small circuit. After sufficient heating, the three-way valve gradually mixes in water from the system. Thus, there is no temperature drop or condensation in the furnace.

The introduction of a mixing unit into the circuit also protects the cast-iron heat exchanger from the temperature drop of the coolant, since the valve will not allow cold water to enter the heat generator.
Basic principle of boiler protection against condensation
To protect the solid fuel boiler from condensation, it is necessary to exclude a situation in which this process is possible. To do this, you must not allow the cold heat carrier to enter the boiler. The return temperature should be less than the flow temperature by 20 degrees. In this case, the supply temperature must be at least 60 C.
The easiest way is to heat a small amount of coolant in the boiler to the nominal temperature, create a small heating circuit for its movement and gradually mix the rest of the cold coolant with hot water.
The idea is simple, but it can be implemented in various ways. For example, some manufacturers offer to purchase a ready-made mixing unit, the cost of which can be 25 000
and more rubles. For example, the FAR company (Italy) offers similar equipment for
28,500 rubles
and the company
Laddomat
sells a mixing unit for
25,500 rubles
.
A more economical, but at the same time no less effective way to protect a solid fuel boiler from condensate is to regulate the temperature of the coolant entering the boiler using a thermostatic valve with a thermal head.
Protecting solid fuel boilers from overheating with a heating radiator
A type 22 steel panel radiator with a size of 500x600 mm is used as a cooling radiator.


I decided to conduct a test: to check how long it takes the boiler to boil if the circulation pump is turned off.We have Stropuv's boiler, and it burns for about a day.
Why it is imperative to do heating pressure testing after installation
Therefore, our test will take place in two stages:
- Day 1. We melt the boiler, wait for it to reach a temperature of 60 degrees and turn off the circulation pump. We note the time during which the coolant in the boiler will heat up to 100 degrees.
- Day 2. We remove the radiator from the piping scheme, heat up the boiler and turn off the circulation pump. We note the time during which the coolant in the boiler will heat up to 100 degrees.
About the heating system in this house
There is no boiler room in this house. The customer decided to place the boiler in the kitchen. I tried several times to dissuade him, but, as they say, "the owner is the master." I think after a while he will change his mind.
Get a heating system project for 100 rubles. per m²
The customer chose the wood-fired version of the Stropuva boiler with a capacity of 15 kW. Behind the boiler there is a cooling radiator and a copper piping of the boiler.
A three-way thermostatic valve is installed in the piping, which protects the boiler return from cooling. The boiler piping consists of three circuits. The first circuit serves radiators. Collector piping for radiators is implemented here. The collector group is located behind the wall, in the bathroom.
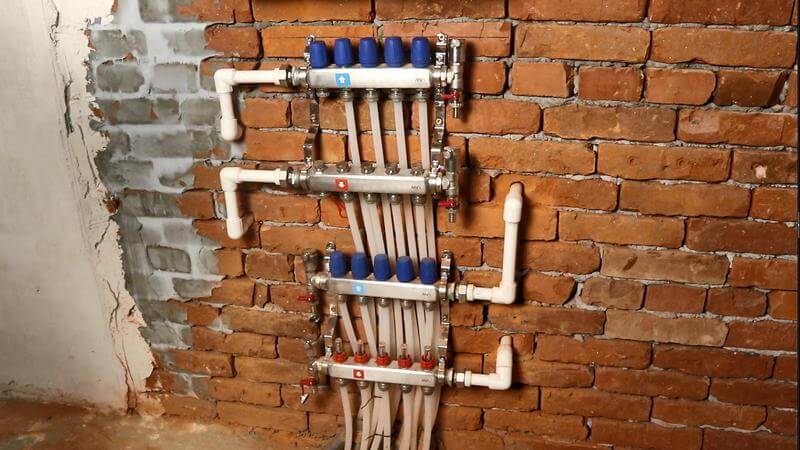


The second circuit is warm floors. The pump-mixing unit is located behind the boiler, below the cooling radiator. The underfloor heating collector group is also located in the bathroom. The third circuit - loading the indirect heating boiler.
It hasn't been installed yet. But for him, there are special taps in the boiler piping. We placed collector groups in the bathroom. Warm floors cover the kitchen, bathroom, corridor and hallway. Radiators are installed in the bedrooms and living room.
Day 1. Testing the boiler with a radiator
The boiler warmed up to 60 degrees, I turned off the circulation pump and waited for the temperature in the boiler to rise to 100 degrees. In half an hour, the temperature on the boiler rose to 95 degrees and stopped.
3 hours have passed since the pump was turned off, and the temperature on the boiler did not rise above 95 degrees. He did not wait any longer, he started the circulation pump in normal mode.
Day 2. Testing the boiler without a radiator
The boiler warms up to 60 degrees, I turn off the circulation pump and wait for the temperature in the boiler to rise to 100 degrees. Without a radiator, the temperature in the boiler rose to 100 degrees in a little more than 30 minutes. He turned on the circulation pump.
It turns out that a radiator connected to the boiler by gravity protects against boiling. You can watch our experiment in the video.