A heating system is a complex of technical elements for generating heat, transferring it and transferring it to all heated rooms. Heating can be local or central. In the first case, the heating equipment and the pipeline are structurally combined into one device and installed in a heated room. Local heating is not quite suitable for warehouses due to the specifics of the terminals themselves.
Here, the central system will be optimal, in which the boiler or heat generator is placed in a separate room. When drawing up a warehouse heating project, special attention is paid to the calculation of the fire hazard category and the location of the main equipment. All instruments must be accessible for maintenance and repair.
Types of heating systems with different heat carriers
By the type of coolant, steam, air and water are distinguished. warehouse heating... In some cases, the systems are combined, arranging steam-air, steam-water or water-air heating. Everything in order.
Steam systems
The heat carrier is dry saturated steam with a temperature not exceeding 130 ° С. The system can be open-loop, when the condensate is transferred to the heat exchanger by a pump, or closed, when the condensate moves by gravity. Main advantages:
- minimal heat loss in heat exchangers;
- fast heating of radiators and other heating devices;
- low inertia;
- the possibility of heating multi-storey buildings;
- compactness of equipment;
- low hydrostatic pressure in the system.
Disadvantages:
- high heat losses in steam lines, as a result - a decrease in efficiency;
- noisiness;
- you cannot make the temperature of the coolant below 100 ° C;
- intensive corrosion of the metal elements of the circuit.
Steam heating is permitted for terminals with non-flammable and non-toxic dust, non-flammable and non-flammable vapors and gases. Steam lines are installed separately from the ventilation and air conditioning system.
Air systems
Air heating systems for warehouses are the most common today. The heat carrier is air that heats up when passing through the generating set. The heated air is distributed evenly throughout the storage volume through a duct system. The units are mounted on the roof and along the walls. The system is well suited for heating large high-rise buildings.
Main advantages:
- the possibility of combining the heating circuit with ventilation for the flow of fresh air into the room;
- high efficiency up to 95%;
- rapid heating of the air due to the absence of an intermediate heat carrier;
- the ability to automate the heating system, adjust the exact parameters.
Warm air outlets are designed so that there are no massive building structures in the path of the air flow. At a warehouse height of less than 8 meters, the release is carried out with covering jets, at a height of more than 8 meters - with non-covering jets. The air jet, when the air is discharged, is applied to the ceiling at a height equal to 0.85 times the height of the terminal (H). Non-overlapping jets are formed at a height of 0.35-0.65 N from the floor. The distance between the diffusers when installed in a row is no more than three room heights.
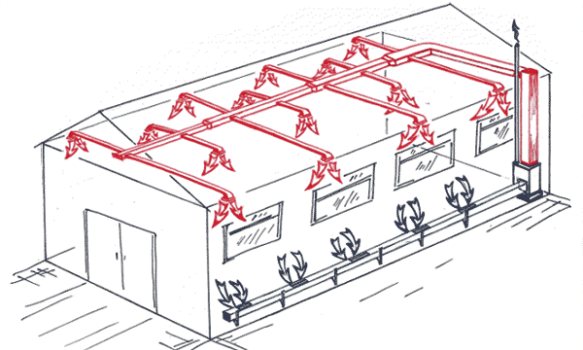

Air heating of a warehouse is economical in operation, pays off quickly, and can be installed with or without air ducts. The system works effectively in terminals with high ceilings, it allows you to evenly heat the entire volume of air.Combining heating with ventilation and air conditioning reduces the financial costs of the project.
If there is no need for constant heating of warehouses, but a strong drop in temperature cannot be allowed, heat guns are used as more compact devices. The equipment is placed around the perimeter of the terminal and connected to the thermostat sensors. When the temperature drops to the set value, the equipment turns on and starts generating heat. The device of such heating does not require drawing up a project, it allows you to quickly warm up the room. But after turning off the heat gun, the air cools down just as quickly.
Water systems
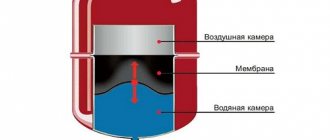
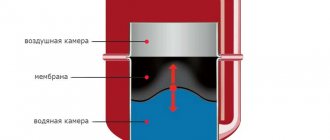
The heating medium in the water heating system can be water or water-based antifreeze. For small rooms, arrange a circuit with natural circulation. The pipes are angled so that the water moves by gravity. For warehouses of a large area, such a solution will not be effective; installation of pumps is required. Forced circulation systems are highly efficient but require electricity.


Water heating is often chosen by warehouse owners as the most optimal option. In places where there is a possibility of connecting to the central network, the task is simplified. In the absence of such an opportunity, the calculation of heating the warehouse should include the choice of a boiler and the device of a separate room for the boiler room. As a disadvantage of such a system, the aesthetic component is indicated - the pipes along the walls do not decorate the warehouse.
The advantage of water systems over steam systems is uniform heating of heating devices, the air does not dry out, and optimal conditions for goods are maintained. But such heating is not recommended for storage terminals higher than five floors. This is because warm air rises and collects at the top, increasing heat leakage through the roof and leaving areas of the ground floor cold. In warehouses with high tops and hot water heating, specialists install ceiling fans to increase efficiency. The rotation of the propellers in winter allows warm air to circulate throughout the warehouse, while in summer it provides some coolness.
Water infrared panels
Today, another very profitable way is known, with the help of which it is possible to equip the heating of a hangar or any other large utility room - the use of water IR panels.
In this case, the heat transfer fluid is heated to 160 ° C and enters the radiating tubes located under the ceiling. The infrared radiator effectively dissipates heat throughout the entire volume of the heated room. Thus, the equipment operates not on the convective, but on the radiant principle.
The uniqueness of such equipment lies in the fact that the air in the room is not heated. Various types of surfaces are subject to heating, including the surface of equipment, goods, shelving, walls, floors, ceilings, and even people in the room.
With the help of IR water panels, it is possible to effectively organize the heating of the workshop, in which welding, carpentry and other production work is carried out.
In this case, the purpose of the method is not to heat the room itself or raw materials, but to provide heat to the working personnel.
Main advantages
- quick and easy installation of the necessary equipment;
- the possibility of heating certain local areas of storage facilities;
- minimum heat losses;
- durability, reliability and safety;
- additional functions of noise absorption, lighting and ventilation.
In addition, heating a warehouse, workshop or hangar with such a radiator is an economically feasible process, since the savings reach 50% if we draw parallels with other methods of heating a warehouse.
Air-thermal curtains
Air curtains are required to separate zones with different temperature conditions. The equipment is mounted in the aperture of doors, windows, gates. The curtain is formed by the movement of a high-speed air flow. It is a kind of invisible barrier that does not allow warm air to escape and does not let cold air in from outside. In addition, the air curtain isolates the warehouse from exhaust gases, dust and other negative phenomena without interfering with the movement of special vehicles.
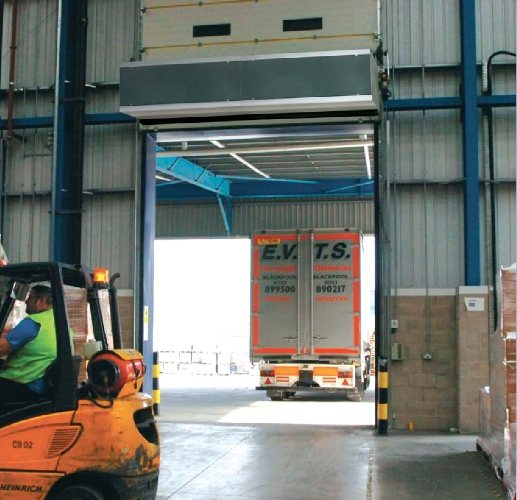


The curtain width is 0.6-2.5 meters. In wider openings, several devices are mounted close to each other. When calculating the heat curtain, the following factors are taken into account:
- the maximum temperature of the supplied air is 50 ° С at the entrance;
- temperature of air entering from outside 5-14 ° С;
- air speed no more than 8 m / s at the entrance and no more than 25 m / s at technological openings and gates;
- installation of thermal curtains is justified for entrance doors without vestibules that are opened five or more times a day or for 40 minutes per shift.
Types of heating systems by energy source
The energy source can be gas, electricity or solid / liquid fuels.
Gas heating of the warehouse
In gas heating systems, gas air heaters or boilers are used as a heat source. This is a fairly simple and economical heating method, especially if there is a central gas main. Special equipment is also inexpensive, but the device of such heating requires approval from the supervisory authorities and the preparation of a competent wiring project. Each gas boiler must have its own supply pipe and a separate chimney.

Heating the warehouse with electricity
Here we will not talk about using electric boilers. Due to the high cost of electricity, the installation of such equipment is not always economically viable. The operation of electric boilers will be very expensive for owners of large storage areas.
A relatively new method of creating comfortable conditions for warehouse employees is the installation of infrared heat emitters. Special panels are mounted on the ceiling, directly above the workplace. There is a local heating of people, floors, furnishings. At the same time, the air does not heat up and does not circulate. The main advantages of infrared emitters:
- compact placement on the ceiling;
- light weight;
- simple installation.
This heating method is suitable for warehouses of any purpose and area. With constant use, infrared panels consume a lot of electricity, but this is almost half the amount of electric boilers.


Installation of radiators is justified in cases where it is not possible to arrange water, steam or air heating, for example, in the absence of fuel. The choice of infrared equipment depends on the fire hazard group of the room
Technical standards
Various SNiP, PPB and PUE regulate the rules for the installation of heating systems in warehouses, but only a specialist can understand the jungle of technical terminology. Here are some excerpts from the regulations:
- SNiP 2.11.01-85, clause 5.3 says that it is allowed to install air heating or combine air heating with local heating devices in warehouses.
- PUE clause 7.4.25: if in a fire hazardous zone of any class (which includes warehouses) heating is possible only with the help of electric heating devices, then the heating surfaces must be protected from contact with flammable substances. A stand made of non-combustible material should be arranged under the devices. For protection, fireproof screens are used that do not allow thermal radiation to pass through. It is prohibited to use electric heating devices in fire hazardous areas of warehouses, museums, archives, libraries, etc.An exception is specially designed rooms, for example, a dining room.
- SNiP 41-01-2003 clause 7.9.1. It is not allowed to place heating equipment in serviced warehouses of categories A, B, B1-B4. In terminals of category B2, B3, B4, it is possible to place heating equipment if several conditions are met:
- heating devices must have a degree of protection not lower than IP-54;
- the warehouse must be equipped with an automatic fire alarm that can turn off the equipment in case of fire.
- SNiP 41-01-2003 clause 12.2. Electrical receivers for heating systems must be of the same category as electrical receivers of engineering and technological equipment of the warehouse.


- SNiP 41-01-2003 clause 12.18. When using air heaters for heating a warehouse, it is necessary to provide protection against overheating.
- SP 31-110-2003 clause 15.7. It is forbidden to use heating devices with direct conversion of electrical energy into heat in warehouses with combustible materials. Such equipment can be installed in utility rooms and rooms for service personnel, which are separated from the warehouse terminal by a wall.
- SNiP 2.04.05-91. In rooms of category A, B, C, without the release of aerosols and dust, you can arrange water and steam heating with a maximum steam temperature of 130 ° C, water - 150 ° C. If dust or aerosol is emitted in a warehouse of category A or B, then the maximum temperature is taken to be 110 ° С, in rooms of category B - 130 ° С. If the warehouse stores substances that, when interacting with water and steam, form flammable, spontaneously igniting or explosive substances, then steam and water heating is prohibited.
- For heating auxiliary and utility rooms, you can use oil radiators powered by an independent electrical network and having thermostats.
In general, all the standards speak about the device of gas heating for warehouses, but the use of electrical equipment is also allowed. The electric boiler must be installed in a separate room or in an annex with walls made of non-combustible materials.
Heating of warehouses
Warehouse premises can be conditionally subdivided into "warm" and "cold". Such products of human activity as paints and varnishes and alcoholic beverages, chocolate, juices and much more, as a rule, are stored in "warm warehouses" equipped with a heating system, because it allows not only to heat the air, but also to maintain the necessary values of air humidity, and a certain temperature.
Warehouse heating systems can be divided into local and central. The first of the systems under consideration is a single device in which heat pipes, a heat generator, heating and other devices are structurally combined. Its work can be carried out by electricity, as well as liquid, solid, or gaseous fuels. Local heating systems have not found their widespread use in warehouses, because the central heating system for warehouses is much more efficient.
Central heating systems for warehouses are systems in which the heat generator is removed outside the heated premises, and the coolant is supplied through pipes from the generator to the places of consumption. Central heating systems for warehouses can be found mainly in large premises.