Kuznetsov's first bell-type furnace was built in the 60s of the last century. The unique development belongs to Igor Kuznetsov, whose main activity is the design and improvement of brick stoves for heating.
Kuznetsov heating stoves are efficient and reliable designs that use a variety of fuel materials.
Currently, over 150 types of furnaces have been invented, each of which has a high efficiency factor - from 80 to 94%.
Features of the Kuznetsov furnace
Engineer Kuznetsov's stoves have been known not only at home, but all over the world since the 60s of the last century.
Moreover, the relevance of the developments half a century ago has not diminished in the least, but on the contrary - Kuznetsov's furnaces are becoming more and more popular.
The purpose of modernizing the old design of the Russian stove with a not so significant change in its internal structure was to create a heating unit with a higher efficiency while saving fuel.

Bell-type furnaces are one of the most common and in terms of characteristics are in no way inferior to channel furnaces.
This stove is the latest development in the conservative field: the installation and design of stoves. This stove features a fundamentally new method of using hot gas.
In a standard type design, the movement of cold and hot gas occurs due to the draft of air, which flows through the ash pan.
The bell-type furnace is very similar in principle to the operation of rocket furnaces, where hot gases move not under the influence of the chimney draft, but due to the gravity of the gases themselves.
What explains the high efficiency of the furnaces
The reasons why bell-type furnaces are so efficient compared to traditional devices are as follows:
- Correct distribution of flue gases according to the heating temperature outside the combustion chamber.
- The large number of hoods contributes to the trapping of hot gas and more efficient heat storage inside the device.
- Correct positioning of the hood helps to contain hot gases and maintain high temperature conditions. This leads to the collection of fuel combustion products in one place and a decrease in the level of soot formation in the chimney. For this reason, "blacksmiths" do not require frequent cleaning of soot.
- The heat exchanger is located in the bell, therefore it does not retain the heat produced by the furnace and does not reduce the level of efficiency.
It's not so easy to build a Kuznetsov oven with your own hands, but all that is required from the master is to follow clear step-by-step instructions.


Oven advantages and disadvantages
Benefits:
- high rate of efficiency of 75-85% (efficiency);
- fuel burns at high temperatures;
- the furnace runs on all types of solid fuels - wood, coal and brown coal, briquettes, etc .;
- ease of maintenance, there is no need to clean long channels (low soot formation);
- durability of the furnace;
- aesthetic, original appearance;
- high efficiency, versatility;
- profitability;
- long-term preservation of heat;
- the shape and design of the stoves may vary depending on the purpose;
- with the frequency of fuel inserts in the blacksmithing room only twice a day, you can have a thermal regime in the house, which compares favorably even with the regime of apartments with central heating.
An apartment in a high-rise building has more frequent temperature fluctuations than a private house heated by a Kuznetsov stove, which gives a uniform heat output between the fireboxes;


- combining a Kuznetsov oven and water heating at home is not difficult and is often used in practice.
A tubular heat exchanger is installed inside the firebox and connected to the heating circuit pipeline. The main plus is that the heat engineering and heat transfer of the furnace during modernization remain unchanged, without the slightest decrease in efficiency;
- the design of the blacksmithing allows you to arrange low chimneys, and there is no reduction in draft at the same time. This fact is somewhat surprising for those who first get acquainted with the design and operation of these furnaces;
- the features of the internal design of Kuznetsov's furnaces allow the unit to be installed in almost any room of any size, regardless of what the room is intended for.
Both in kitchens and in common rooms, the stove looks solid and aesthetically pleasing, and organically fits into many interiors;
- the most interesting and unusual feature of blacksmithing in the context of a house stove: you don't have to close the view. This most important part of the furnace and one of the conditions for safe daily operation is needed for the Kuznetsov furnace only if an emergency situation arises.
The fact is that when the process of fuel combustion comes to an end and cooling begins, the thrust in the channels of the furnace is redistributed spontaneously, “automatically”.


It was the bell-type stoves that became the basis for the creation of many household, heating and cooking stoves of a new type, which give a significantly better effect with less fuel consumption.
What can be said about the disadvantages of the oven.
Technically, they are not there, but you still need to take into account something.
The Kuznetsov furnace cannot have massive walls - this would negate many of its advantages. But at the same time, it is exposed to rather high thermal loads.
Therefore, this unit must be carefully calculated and verified at the development stage and built just as carefully, with scrupulous observance of all technology requirements. With the slightest deviations from the technical regulations, the "blacksmithing" will turn out to be very short-lived.
A bit of theory
Traditional home ovens with hobs, "Dutch" and "Swedish", despite the design differences, have one common feature. It affects the efficiency of these heating devices - this is the natural draft of the chimney. None of the most famous furnaces will function without traction; solid fuel boilers are not far from this regard.
Let's make a reservation: none, except for Kuznetsov's, because only the brainchild of Igor Vladimirovich do not require natural traction for their work.
The secret of effective work, which distinguishes Kuznetsov's two-bell furnaces from all others, lies in the principle of free flow of gases, which does not require additional energy from the outside.
Very detailed and accessible about this theory is set out in the articles posted by the inventor on the pages of his own web resource www.stove.ru. There, in the public domain, there are designs of furnaces that have already been put into operation. We will look at the theory in a nutshell, comparing the traditional method of burning solid fuel with the processes occurring in a bell-type furnace. So, in a conventional or channel furnace of the "Dutch" type, the movement of air and combustion products is due to the presence of draft in the chimney.
Natural cravings are external factors influencing:
- the difference in height between the blower entrance and the upper cut of the pipe;
- temperature differences between outside air and flue gases;
- wind load.
That is, the thrust is present even when the heater is inactive, as long as the damper is open. In the operating mode of the furnace, the thrust is increased many times, the speed of the gases increases sharply. As a result, a lot of air enters the furnace, the combustion temperature drops, and the efficiency of firewood combustion decreases.By limiting air access with a damper, we make the fuel smolder with a lack of oxygen, which is also not the optimal mode for extracting heat energy from wood.
The correct stove with high efficiency should take away the maximum heat from the combustion products so that it does not fly out into the chimney. In practice, this is not so easy to implement, and here's why:
- when the damper is open, the incandescent gases move quickly through the brick channels, not having time to transfer heat to the walls;
- if the damper is closed, then the flow rate will decrease, but the material of the channels is not able to absorb all the released heat and transfer it into the room, therefore, part of the energy nevertheless flies out into the pipe.
For these reasons, the efficiency of almost all existing furnaces rarely reaches 60%. In the developments of Kuznetsov, both problems have been successfully solved, the efficiency of fuel combustion and the efficiency of using the released heat are at the level of about 80%. Not every boiler operating on solid fuels can give such an indicator. I.V. Kuznetsov outlined the basics of designing furnaces in accordance with the principle of free flow of gases, which we will consider below.
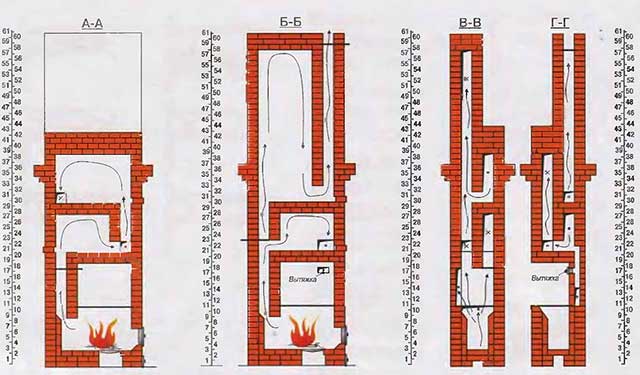
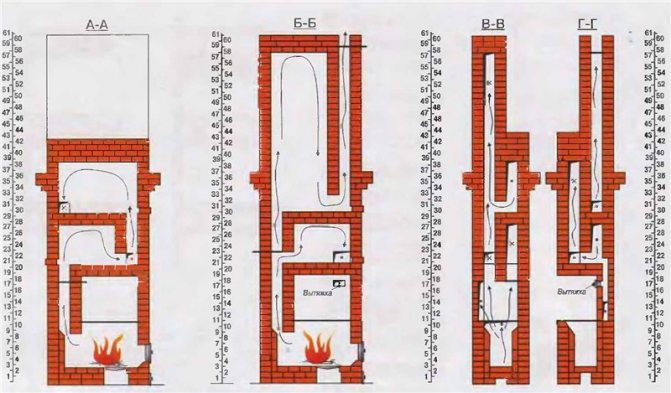
The principle of operation of the furnace
It is based on the principle of free movement of gases. For the circulation of air in a conventional furnace, the influence of external energy is necessary, that is, the creation of forced draft in the pipe.
When gases are in a confined space, in the presence of a constant source of heat, they separate under their own weight - the cold ones settle down, the hot ones rise up. At the same time, in the area of high temperatures, the pressure increases, and where it is cold, it drops and energy is generated.
It turns out that turbulent motion arises automatically due to the laws of physics. This means that if convection flows are correctly directed, then thermal energy will be carried by the masses of gas themselves.
With electrical heat supply, no draft tube is required. If the stove is heated with wood, then the combustion product must invariably come out.
Thanks to a clever design, it accumulates at the last stage of its path, as if under a hood. There it burns out again, giving up its heat to the end, and then, in the form of useless gas, is taken out into the street without cooling the system. Such ovens are also called bell-type ovens.
The fundamental feature of gas filling of cavities is that, no matter how many compartments the furnace has, they are all filled with gas evenly and the same physical processes take place in all. It is impossible to create something similar using traction, the principle of counterflow (widely used in Europe) or other convective methods.
That is why such stoves are an innovation in the stove heating system.
They regulate themselves and, no matter what configuration they give them, they always work according to a natural principle.
The principle of the furnace is quite simple: the lower tier and the firebox (also called the hearth) are combined into a single space - a bell, inside which the free movement of hot gases occurs.
The hottest, lighter gases move to the top of the bell, while the “heavier” cold gases are at the bottom. And between them, gases circulate with an intermediate temperature.
The heated air is held in the furnace for a long time, transferring heat to the walls of the bell, and the cooled air is discharged into the chimney through a special passage. The combustion temperature in the bell is very high. The efficiency of such a furnace is three times higher than that of a traditional Russian one.
Types of structures
The hoods inside the oven can be positioned in different ways, therefore there are many types of stoves... You can build a do-it-yourself stove for two-story houses, and both floors will be heated the same way.You can even make a building with a stove bench (heating of this type is convection) or you can put a heat exchanger inside. This type of construction is called a boiler, it has the KIK marking.
Exist type of building in the form of a fireplace, they are usually built in houses outside the city. Gas heating stoves have the designation IOC, and if they have a stove bench, the letter "L" is added. If there is also an oven in such structures, then the letter "D" is indicated.
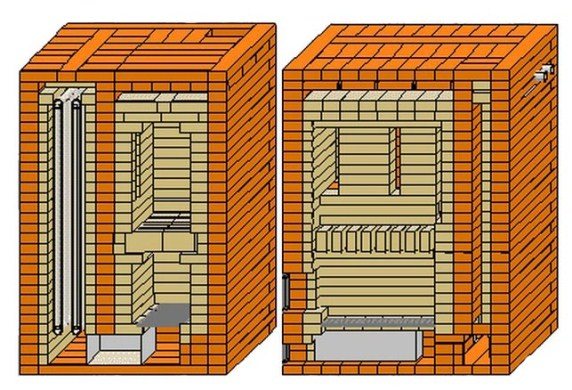
The real Russian bell-type furnaces of Kuznetsov are marked with RTIK, there are about 10 models, two of them have stove benches. Such stoves are most often built in baths. But it is difficult to install a massive brick stove there, so many people choose a metal structure for baths. Sauna stoves are marked with BIK, Kuznetsov designed them so that they are small, look presentable and take up a small area.
DIY greenhouse heating ideas
Varieties of Kuznetsov furnaces


According to the functions performed, Kuznetsov's brick ovens can be divided into several main groups:
- Heating.
Their main task is to heat the premises.
- Cooking.
They are used for cooking. This group also includes bread ovens and stoves adapted for a cauldron.


- Bathrooms.
The principle of operation of Kuznetsov's sauna stoves remains unchanged - the natural movement of gases through two hoods. Another thing is that there is a heater here, which needs to be thoroughly warmed up to obtain high-quality steam.
The developer has proposed and is still using the optimal technical solution, where the stone filling is located in a heat-resistant steel oven. The oven is located directly above the firebox.
The heat energy accumulated in the lower and upper bells is used to heat water and heat not only the steam room, but also all adjacent rooms. The water coil is installed under the first hood so that it can be easily repaired or replaced.
The installation location can be determined by examining the drawings of the stoves.


- Fireplaces.
- Grills and barbecues.
- Combined structures, complexes.
- Perhaps the most popular are Kuznetsov's heating and cooking stoves. They will warm the house and will not leave hungry.


The heating and cooking option is most in demand both by summer residents and residents of rural areas. There is a simple practicality here: if there is already a fire, why not use it additionally for cooking.
Kuznetsov also has such projects.
Before you start building, make sure that this is exactly the option that you want to see at home.
Such stoves imply a convenient protrusion with a cast iron surface, with the possibility of partially opening the holes to increase the temperature. It is also possible to make a door for a cauldron, similar to the old Russian stoves.
Layout of heating and cooking stoves requires its own approach and individual drawings.
Bell-type furnaces can be erected in almost any room. This can be an apartment, a residential building, an outbuilding, or a bathhouse. For example, for a bathhouse, a bell-type stove will be an ideal replacement for a conventional standard stove.
By building this stove for a bath, you can solve several problems at once. This design is capable of heating several rooms: a sink and a steam room, as well as a relaxation room. In addition, it is very convenient to heat up water on the stove, simultaneously creating steam in the required amount.
The house can be equipped with two-bell heating with a stove, this installation is very functional. Before erecting such a structure, it is necessary to carefully study the project.
The system that burns raw fuel must be organized in the most optimal way.The oven must always be kept at the correct temperature, otherwise the gases that form after combustion can be transformed into harmful wastes of soot and tar.
Stoves with water heating
Modern Kuznetsov stoves with water heating of the KIK series (brick boilers) are of particular interest. In fact, this is a bell-type boiler, lined with bricks and having a good efficiency - about 70-80%, that is, similar to its iron "brothers". How such a high efficiency is achieved has been described above.
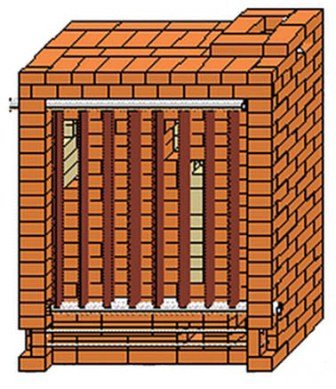

1 or 2 steel pipe registers are built into the furnace body (depending on the capacity). Ready-made modifications of boilers have a range of capacities of 17, 34 and 63 kW. In addition, the author also offers two-circuit models with the possibility of heating water for household needs. In his recommendations for the construction of such heaters, I.V. Kuznetsov points out that in order to increase the economy and efficiency of operation, the body of a brick boiler should be insulated with basalt fiber.

In most of the dome models of furnaces, a modern technical solution has been introduced, which ensures the afterburning of the combustible component of the flue gases. For this purpose, a secondary air supply is organized under the roof of the upper bell or in another place, depending on the design. When using wood of the appropriate quality, such a heating device will function as a pyrolysis oven.
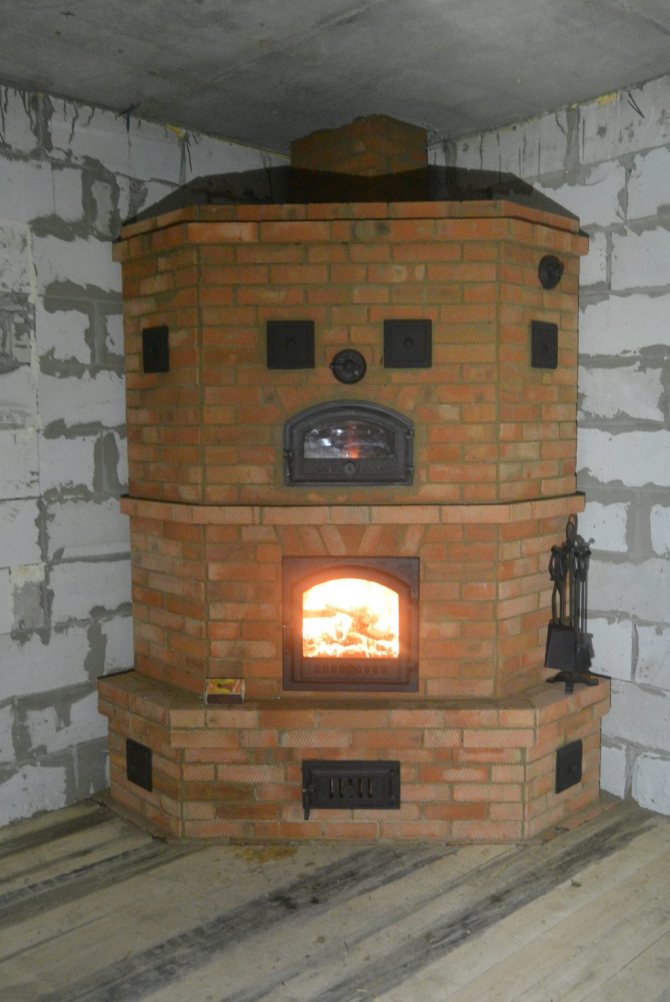
Do-it-yourself Kuznetsov stove
Building a blacksmithing requires not so much skill as having good diagrams and blueprints, as well as utmost care. Not even a stove-maker, but a skilled householder can master this task.
It will be easier for those who already have precious experience in brickwork, then the only thing you will need to quietly and peacefully lay the rows, observing the scheme.
Having decided to build a furnace according to one of Kuznetsov's orders with your own hands, get ready for careful and scrupulous work.


On the diagrams that can be easily found on the Internet, you will see a graphic image of each row, however, before starting laying, you need to get acquainted with the features of the technique, in particular:
- selection and preliminary processing of bricks;
- purchase of metal parts (plates, dampers, doors, latches);
- determining the most suitable place;
- preparation of the base and foundation;
- the possibility of equipping a chimney, etc.
Fireclay refractory bricks (Ш-5, ШБ-8) were recognized as the best material for the internal masonry of "blacksmiths", and ceramics (М-150) for external decoration.
To strengthen the brick walls, metal elements (reinforcement, wire) are used.
In order for the stove to function with maximum heat transfer, experienced craftsmen hone not only their skills, but also every brick - in the literal sense. They polish every detail, which is why projects made by professionals look flawless.


The main purpose of any stove is heating, its place should be chosen to provide heat in the most efficient way.
Kuznetsov's stoves are infrared heaters that provide the most heat through direct radiation.
Thus, maximum power is achieved when positioned correctly.
Therefore, the center of the room is always the right choice. A wise decision is to place as a separator of functional spaces such as kitchen and living room or living room and bedroom.
Try to avoid placing the stove masonry next to an outside wall, or worse, place it in a niche in the outside wall (typical for conventional fireplaces) if you want to keep warm indoors.
The choice of a stove of one type or another and its location in the house, in addition to the owner's preferences, depends on the intended purpose of the stove, the size of the house and the level of its thermal insulation, the number and size of windows.
In addition, for normal operation and repair, access to the stove must be free from all sides, that is, none of the sides of the stove should simultaneously enter any of the outer walls of the house.
To complete the construction process, you need to stock up on a bayonet and shovel, as well as the following materials:
- sand (3 parts), cement (1 part) and water for solution preparation;
- reinforcing rod of medium section;
- plastic wrap;
- board for the construction of formwork.
Construction stages:
- It all starts with the foundation. It should be unconnected with the main foundation of the bath. Its size is 10-15 cm larger than the estimated dimensions of the oven. The height of the foundation for the stove is selected based on the height of the bath's foundation: they must end at the same level.
On top of the finished base for the oven, waterproofing (roofing felt, roofing material) is laid in two layers. The floor around the future stove must have a fireproof covering. There are options: these are metal sheets, ceramic or ceramic tiles, natural or artificial stone, brick, etc.
- To determine the required number of bricks for building a furnace, we count the number of bricks in the first row of the order, multiply by 0.8 (the average fill factor of the rows) and by the number of rows.
This amount of bricks will be enough for the oven for sure, even taking into account broken and rejected ones. For a brick pipe, add 4-6 bricks per row.
- After the concrete foundation has completely solidified, you can proceed to the brickwork. Kuznetsov's stove is built correctly only if the order proposed by the inventor is observed.
- Before starting laying, it is worth considering the location of the chimney inside the room and outside on the roof, which must meet certain requirements. Recall that any Kuznetsov furnace has ready-made drawings, in accordance with which construction work is carried out.
- For the laying of the first two rows, fireclay fire-resistant bricks are used. To connect the bricks, a special masonry mortar is prepared. It is not recommended to use a mixture prepared for arranging the foundation base.
- After completing the masonry of the 1st row, the corners are checked, each of which should be 90 degrees. Arrangement of chimney ducts begins from the 2nd row.
- To improve the heat transfer of the device, it is recommended to install 4 duct cleaners - in the back, in the blower and on the sides. The sizes of the cleaning are selected on an individual basis. At this stage, the horizontalness of all surfaces is checked using a corner.
- From the 2nd row, an ash pan and a blower are formed. These working chambers are designed to clean ash and create the necessary combustion draft. Brickwork is staggered with a 6 mm seam. A mortar based on refractory clay is used to fix the bricks.
- Further, partitions for the internal compartments are installed, a wall is formed between the blower and the working part of the furnace.
- When laying the 5th row, the grate is installed, the thickness of which is determined by the degree of loading the chamber with fuel.
- When installing the grate, the technological gaps of 7 mm are observed between the grate for the grate and the outer wall of the stove. The grille is installed at a slight angle in relation to the door.
The door for the firebox is also installed here. When arranging the combustion chamber, it is additionally lined with fireclay bricks, which are laid with an edge. This ensures reliable protection of the outer walls of the furnace against high temperatures.
- Up to the 16th row, laying is carried out similarly to the previous rows.
- A cap is installed from the 17th row, after which you can start arranging the second chamber located above the first. It will be the second cap. At this stage, the cap is overlapped, and on the 21st row, passages are arranged, which are directed along the inner walls on both sides.
- The work is carried out in accordance with the proposed order up to the 26th row, after the completion of which the upper part of the hood is reliably closed with brickwork.
After making the foundation, you need to attend to the preparation of the mortar for laying the furnace. For the construction of a brick oven, not cement, but clay is used. And not any, but only the one that lies at a depth of at least 2 meters. The clay is sieved and washed out, preparing a solution of the desired viscosity.
- 24 hours after completion of the laying, a test run of the furnace can be performed with the addition of a small amount of fuel material. This will allow you to check the finished structure for leaks and the absence of gaps between the bricks.
- If even minor flaws are found, they should be eliminated immediately.
- The furnace is made of fireclay bricks, and the body of the furnace is made of ceramic, which means that they behave differently when heated and cooled. Therefore, the firebox itself must be floating; for this purpose, a special dry seam is made around it.
This is done so that fireclay and ceramic bricks, different in physical characteristics, do not break during operation. "Dry joint": between the fireclay and ceramic bricks, the masonry mortar must be removed, and mineral cardboard must be inserted into the resulting void.
- One more rule must be strictly observed - the projections from the fireclay masonry should not enter the recesses of the ceramic masonry, and vice versa. Thus, we get an absolutely independent firebox.
Materials and tools
For arranging a brick "blacksmithing" for a house or a bath, first of all, you should prepare working drawings and orders. The author himself has developed over a hundred different furnaces with step-by-step instructions for their construction.
Stove ordering is a complete guide that clearly explains the correct laying of each individual row in the intended sequence. Novice craftsmen are advised to strictly adhere to the order of Kuznetsov's furnaces, which will allow them to build a reliable and durable structure.
To carry out construction work, it is necessary to prepare the basic materials and working tools:
- solid red fire-resistant brick;
- fireclay brick;
- fire-resistant clay of medium fraction;
- mountain sand (twice the volume of clay);
- steel wire;
- metal corner;
- constructive elements: doors for the blower, firebox, grate for the grate, latch, stove for the hearth.
Attention! If desired, instead of clay and sand, you can purchase a ready-made masonry mixture, which is sold in specialized stores. All the necessary proportions of the main components are observed in it.
When buying a brick, it is recommended to check the material for defects and mechanical damage.
Do-it-yourself Kuznetsov stoves have their own subtleties of construction, therefore, before starting work, the layout of the device must be carefully studied.