The technology of wall insulation with expanded polystyrene is as simple as possible if you understand a large number of working factors. An important significant point when choosing a material is the correct calculation of the thickness of wall insulation. When purchasing a product, you need to pay attention to mats, sheet sizes, and rolls.
The thickness of polystyrene foam for wall insulation directly depends on the materials that are endowed with individual characteristics and features:
Thermal conductivity and insulation:
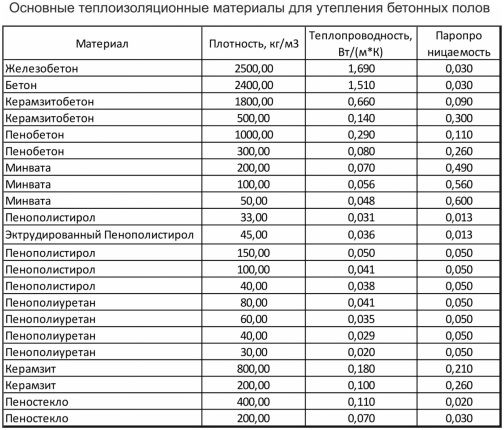
- URSA glass wool with values of 0.044 W / m * K;
- Polyfoam with indicators of 0.037 W / m * K;
- Ecological wool with indicators of 0.036 W / m * K;
- PPU insulation with indicators of 0.03 W / m * K;
- Expanded clay with indicators of 0.17 W / m * K;
- Brickwork with indicators of 0.520 W / m * K.

Minimum parameters of permissible thickness:
- URSA glass wool with indicators of 189 millimeters;
- Polyfoam with indicators of 159 millimeters;
- Ecological wool with indicators of 150 millimeters;
- PPU insulation with indicators of 120 millimeters;
- Expanded clay with indicators of 869 millimeters;
- Brickwork with indicators of 1460 millimeters.
Do not forget about other important factors:
- A certain thickness of expanded polystyrene for wall insulation provides individual operational reliability and strength;
- Structural wall load;
- Environmentally friendly composition;
- Biochemical resistance;
- Interactive chemical properties;
- Insulation for walls expanded polystyrene with a certain thickness must be resistant to corrosion;
- The appearance of condensation;
- Fire safety;
- Resistant to moisture;
- Air and vapor permeability and so on.
Insulation for walls polystyrene based on the above data allows you to calculate a significant value, that is, resistance at the time of heat transfer. For a simpler calculation, there is a special formula:
R = wall thickness: wall thermal conductivity coefficient.
Consequently, the thickness of polystyrene foam for wall insulation also depends on the material properties and finish.
The thickness of the material used for the outer side of the walls cannot be less than an already determined and established value. If the indicators are rejected, then it is pointless to carry out computational work:
- There will be a need for speculation and assumptions;
- You will not be able to find suitable dimensional indicators. They are either standard or discrete;
- In cold weather, you will have to look for additional heat;
- The amount of material used will increase.

Influence of weather conditions
The climatic conditions of a particular region directly affect the insulation for the walls of expanded polystyrene and the choice of thickness.
After determining the individual material, it is imperative to figure out the place of its correct use. Usually this information is provided by the direct manufacturers.
Insulation for walls polystyrene has its own recommendations with appointments. This is a roof, wall, foundation or floor.


Inside and outside
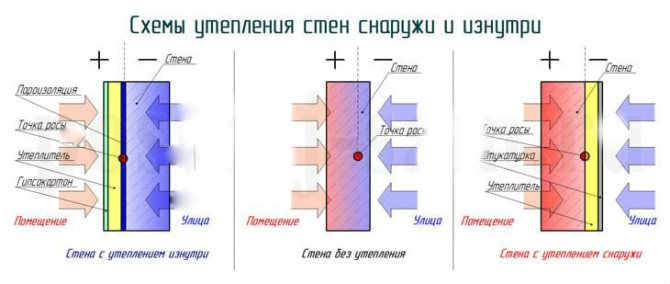
Now let's talk about the thickness of the extruded polystyrene foam used for wall insulation. Walls can be insulated both from the outside and from the inside, therefore insulation, respectively, is divided into internal and external.
For internal insulation, it is not necessary to use foam thicker than twenty to thirty millimeters, as this can lead to excessive condensation of moisture, which will provide wall phlegm, fungus and mold. A good vapor barrier must be thought out.Some craftsmen generally avoid insulating the walls inside with extruded polystyrene foam and replace it with more moisture-absorbing materials.
A more acceptable option than internal insulation is insulation of the walls with extruded foam from the outside.


The recommended thickness of the material is from fifty to one hundred and fifty millimeters. Most of all expanded polystyrene is used for insulating plinths. If, according to calculations, it turns out that with a given thermal resistance the thickness of the insulation is less than three centimeters, then it is useless to insulate the building.
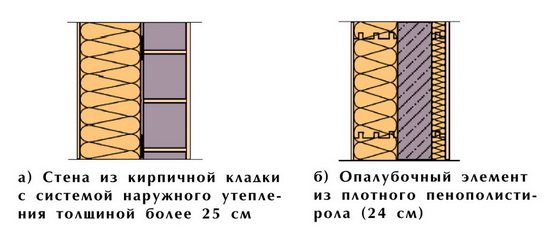
Wall construction
Wall construction plays a significant role in all universal thickness calculation instructions. The main parameters are:
- The number of layers;
- General composition;
- Order and priority;
- Immediate thickness.
There can be a great number of options. This is a bearing surface, glue composition, insulation, leveling layer, glass mesh, dowels, reinforcement layer, decorative layer. The thickness of polystyrene foam for wall insulation should also take into account the location of the heat insulator, waterproofer, vapor barrier, convection, infrared radiation, wind intensity, and so on.
The functions of insulation and purpose are also taken into account when calculating the parameters. It is always necessary to be reinsured and select the maximum thickness.

Types of expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene is a modern material, thanks to which excellent thermal insulation of the building is achieved. It is used both for insulating the walls of houses and for insulating the foundation (regardless of the level of groundwater).
But the scope of use of expanded polystyrene is not limited to this. Roof, floor, water pipes, transport routes, window and door openings - all these elements can be insulated with this material. Granular polystyrene foam can act as a filler for packaging or a decorative element for interior decoration of rooms.


There are the following types of insulation:
-pressless;
-extrusion;
- autoclave;
- press.
The most popular type of expanded polystyrene is non-pressed material. Moisture is removed from the granules through a drying process. Then the material is foamed at a temperature of 80-85 ° C, dried and reheated. The resulting mixture is placed in a special mold. When it cools, the material compresses itself. Pressless expanded polystyrene is the most fragile, since a minimum amount of isopentane is used for its manufacture (of course, it is also the cheapest product).
In the production of extruded polystyrene foam, special equipment is used - an extruder. The material is obtained after processing the final polymer product. In most cases, extruded polystyrene foam acts as a raw material for the manufacture of packaging containers.
The main difference between autoclaved polystyrene foam and extrusion material is the use of an autoclave. This equipment is used for foaming and high temperature exposure.
The most expensive item is the press material. The technology for the manufacture of granular polystyrene foam of this type occurs with the use of gas. This insulation has maximum durability.
Other conditions
The construction method is also important. Insulation for the walls of expanded polystyrene must be selected professionally.
All calculations must be carefully monitored and accurately calculated. If we are talking about the insulation of balconies or loggias, then you should be extremely careful.
The walls in these objects are very thin, and cold air is blown from all three sides. Batteries, as you know, are completely unacceptable there, they are absent.
Private construction does not involve calculating the thickness at all. In this case, the special climatic conditions of the area under consideration are taken as a basis and rounded up. In the shopping center at the time of purchase of the goods, similar indicators are found and are rounded up.
All additional insulation is endowed with different requirements. Therefore, they should not be compared with standard rules and indicators.
See more on this topic on our website:
- Do-it-yourself insulation of the walls of a frame house from the inside Manufacturers of SIP panels and people who understand how the walls of a frame house are insulated, say that well-mounted walls can fully replace a half-meter ...
- The thickness of the walls of a frame house for winter living - schemes What should be the thickness of the walls of a frame house for winter living in it? There is also an unequivocal answer to this question. at the same time, it is not. Why? Because…
- Correct installation of expanded polystyrene on external walls Due to a number of excellent qualities, extruded expanded polystyrene is readily used in construction or during renovation work. Installation of expanded polystyrene on the walls is not the only thing for which it serves ...
- External insulation for walls - insulation of the walls of the house outside with your own hands When analyzing heat loss in living conditions, about 40% falls on the walls, on the windows - 20%, on the roof - 25%, on the ventilation system - 15%. Thanks to ...
- Wall thickness of a frame house for permanent residence in it What should be the wall thickness of a frame house for permanent residence in it in an urban or suburban village? The answer to this question, on the one hand, is ...
Types and characteristics of EPS
For some time now, in Russia, extruded polystyrene foam has been called by the name of the company that produces this material. This is how Penoplex, Technoplex, TechnoNicol and Ursa appeared. Well-known "TechnoNikol", "URSA Eurasia" supply high-quality thermal insulation to the construction market.
Penoplex
Especially for underground structures and structures, the company produces a type of insulation "Penoplex Foundation". The manufacturer guarantees increased strength and ability to withstand loads for 50 years. The declared characteristics of this insulation are characteristic of EPS, however, the thermal conductivity coefficient is slightly higher - 0.03-0.032 W / m * ºС.
Sheets have dimensions of 1200x600 mm with a standard thickness of 20 to 150 mm. The average cost of one sheet with a thickness of 50 mm is 199 rubles.
Watch a video of how this type of material is used for insulation.
TechnoNicol
For the insulation of the slab foundation, the EPPS brand "TechnoNIKOL CARBON ECO SP" is produced. It is characterized by strength, stability in a biologically aggressive environment, thermal inertia. Service life - 40 years.
The company produces one standard size of this brand - 2360x580x100 mm. The price of one sheet fluctuates around 740 rubles.
We recommend watching a video on how to insulate the base using this material.
URSA Eurasia
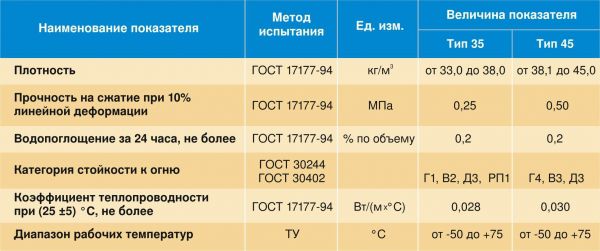
The company produces three grades of URSA XPS extruded polystyrene foam. The most suitable for basement insulation is URSA XPS N-V, since it has the highest compressive strength - 50 t / sq. m. However, the temperature regime is reduced: from -50 to +75.
URSA calls its products plates, and the dimensions of this material are as follows: 1250x600 with a thickness of 50.60, 80, 100 mm. The cost of one slab with a thickness of 50 mm is 192 rubles.
The use of expanded polystyrene for outdoor use requires a reliable seal with cement-based plaster mixes.
Advantages and disadvantages of expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene material is a porous air-containing raw material, is used in most cases as a heat-insulating material.
In industry, the material can also be used as electrical insulation and packaging material.
The material has gained widespread use due to its quality indicators:
- low level of water absorption;
- low thermal conductivity;
- ease;
- biological resistance;
- durability;
- compressive strength;
- not affected by temperatures;
- ease of installation;
- low price of the material.


Despite an impressive list of positive indicators, expanded polystyrene has disadvantages that must be taken into account during installation:
- low rate of sound insulation;
- instability to solvents and many chemicals;
- afraid of fire. When burning, it releases harmful toxic substances;
- poor resistance to ultraviolet light;
- easily lends itself to the influence of rodents and insects, which, making holes in the material, provoke its destruction;
- low vapor permeability;
- fragility.
However, the production technology of these materials is different.: expanded polystyrene is produced by extrusion, when granules melt when combined into a single structure, foam - by gluing granules with dry steam.

Foam thickness
As already mentioned, the quality of thermal insulation is very significantly affected by the thickness of the foam for insulating the wall from the outside. After all, if the insulation layer is of insufficient thickness, then it is possible that the building will freeze during the cold season. This is fraught with displacement of the "dew point" inside the dwelling, and, consequently, increased humidity and fogging of windows and walls.
Many novice builders believe that the thicker the foam, the better. This is an erroneous opinion, since there are also nuances here. For example, the desired effect will not be achieved, and material costs will increase significantly.
The best way is to correctly calculate the optimal thickness of the insulation. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the building material used in the construction of the dwelling, and the features of the climate.
Insulation will save on energy
The listed advantages will tell you how to choose foam:
- significant reductions in costs, material and installation work;
- saving heat for energy resources;
- there is no need to use additional heating devices, which also saves the family budget;
- due to the insulation of the walls with foam, it is possible to reduce the thickness of the walls from the main building material;
- stabilization of the temperature regime in the room;
- achieving the state of the ecology of the building;
- an increase in the service life of the structure, since the foam will reliably protect the walls from the influence of climatic factors.
Do-it-yourself foam insulation technology for outer walls
To insulate the walls is within the power of a master who is familiar with the basics of finishing work.
Let's consider in detail the method of insulation, called "wet facade".
Tools
For work, you will need hand and electric tools:
- level, plumb line, hammer, tape measure, pencil, hacksaw (knife), trowel and spatula;
- a bucket for mixing glue and plaster;
- hammer drill or hammer drill with bits or drills for concrete;
- drill nozzles for the preparation of solutions.
From consumables they purchase:
- adhesive for polystyrene based on cement or synthetic base;
- dowels with a rod length 4-5 cm more than the thickness of the foam;
- polyurethane foam or glue foam;
- foam gun.
Work progress step by step
Wall insulation begins with preparatory work:
- calculating the amount of insulation and purchasing it;
- preparation and testing of tools;
- purchases of consumables;
- installation of scaffolding (if necessary).

The work is carried out in the following sequence:
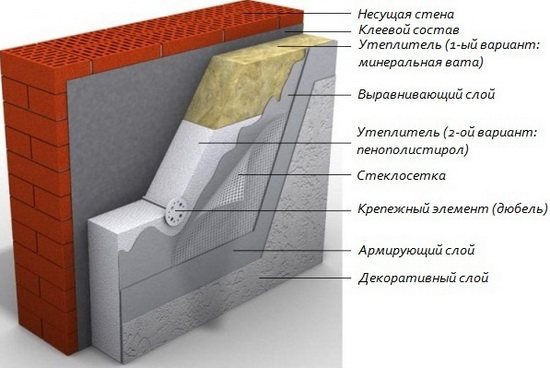
- The surface of the walls is being prepared, which are cleaned of dust and dirt.
- The voids in the seams (if any) are sealed with cement mortar or foam.
- Level the surface with plaster so that the irregularities do not exceed 1.5 - 2 cm.This will facilitate the adjustment of the sheets and reduce the amount of expensive glue during further finishing.
- At a level of 50 cm from the ground, the support bar is fixed strictly horizontally, if the foam is not placed to the ground, but finishing with another material is provided.
- With the help of a level and a plumb line, markings are made.
- A sheet is applied according to the marking and through it (so that there are no mistakes) a hole is drilled in the wall for a dowel.
- Starting from the center hole, fix the sheet to the wall.
- The second and subsequent sheets are placed with an offset (staggered).
- Seams are sealed with polyurethane foam. Remove excess sealant after complete hardening, usually after 12 hours and up to a day.
- With a special toothed roller or other improvised means, punctures are made up to 0.5 - 1 cm deep on the surface of the foam for better adhesion to the layer of glue-plaster.
- A 1 - 2 mm layer of specialized glue for expanded polystyrene is applied to the foam, which is leveled with a spatula.
- A fiberglass mesh is applied to the glue and "melted". The joints are overlapped, overlapping by 10 cm. The seams between the sheets and the edges of the nets should not overlap.
- Spread the glue with a spatula. By adding portions of glue in the right places, the final leveling of the surface is carried out, working as when using a putty.
Finishing

After the composition has dried, the surface is primed with means for outdoor use.
The final finishing is carried out with facade paint or plaster "bark beetle" is used. The latter option is preferable, since it hides inaccuracies and irregularities, which are especially clearly visible in side lighting.
With frame insulation, there are no tricks. Polyfoam is fastened with dowels with wide caps between the frame slats. The remaining voids are filled with polyurethane foam or foam glue. Then, without fail, a waterproofing membrane is nailed to the frame. It is convenient to do this with bars of counter-lattice, the thickness of which is 1-1.5 cm. After installing the siding or other material, there will be a gap between it and the foam, which will reduce the likelihood of dampness of the materials - the facade will become “ventilated”.
How to determine thickness
The thermal resistance of the material (R) plays a significant role in calculating the thickness of expanded polystyrene. The quality of the building's thermal insulation depends on it. This value is individual for each region. Some of them can be viewed in the table below.
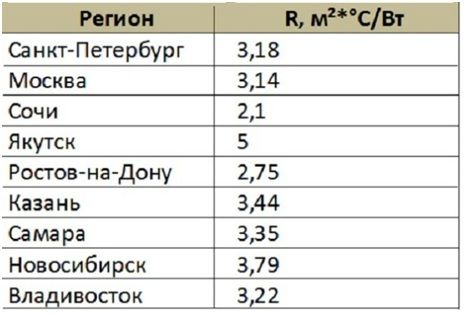

If the walls consist of several layers, then it is necessary to summarize the thermal resistance values for each material.
The calculation of the thickness of the foam is made by multiplying the indicators of thermal resistance and the coefficient of thermal conductivity, which can be found from the table.