Characteristics of the substance
Propylene glycol is a dihydric alcohol, usually a colorless viscous liquid. It has a faint smell and a sweetish taste.
Propylene glycol, unlike its closest analogue, ethylene glycol, is considered a non-toxic substance, it is widely used in the perfumery and even in the food industry - in this case it is designated as E-1520.
The chemical formula of propylene glycol is C3H6 (OH) 2. The substance is extremely fluid in structure and can slowly seep through micro-holes and cracks. The ignition temperature is quite high, it is + 421 ° С.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Propylene Glycol as a Heat Transfer Fluid
You can clearly identify the advantages and disadvantages of propylene glycol by comparing it with water (which is also a heat transfer fluid in some heating systems):
- the density of dihydric alcohol is 1037 kg / m³, which is more than that of water (1000 kg / m³): the difference is 3.7%;
- the substance begins to boil at +187 ° С, and water at +100 ° С, the difference is 87%;
- alcohol freezes at -60 ° C, water already at 0 ° C;
- the specific heat capacity is equal to 2483 J / (kg · K), almost 2 times lower than that of water (4.187 J / (kg · K));
- thermal conductivity - 0.218 W / (m · K), which is three times lower than that of water 0.6 W / (m · K);
- dynamic viscosity of alcohol - 56 mPa · s, eight hundred times more than that of water (0.894 mPa · s).
Several conclusions can be drawn from this list.
- The density of propylene glycol is higher than that of water, so the static load and pressure in the heating system will also increase.
- The high boiling point of +187 ° C is not such an advantage. The specific heat of propylene glycol is two times lower than that of water. This means that you can bring these two liquids to a boil with the same amount of heat. Their temperature will reach its extreme point almost simultaneously, only water will boil at +100 ° C, and alcohol at +187 ° C.
- The freezing point of propylene glycol is noticeably lower. In addition, it practically does not expand during cooling, and this does not damage the heating system.
- A low specific heat capacity is a clear advantage, hence the rapid warming up of the heating system, however, propylene glycol is able to accumulate little heat - and this is already a disadvantage.
- High dynamic viscosity will add a load to the circulation pump, which moves the coolant through pipes and radiators.
However, in some situations, propylene glycol will do its job better than water:
- if you do not use the water heating system in winter and do not drain the water, the system may fail (even after complete draining, the water will still remain in the pipes, causing corrosion) - and propylene glycol can be used all year round and not drained in winter;
- antifreeze, which is based on propylene glycol, does not cause corrosion and does not form scale.
Such antifreezes also have disadvantages:
- the cost is higher than that of water;
- a complete fluid change is required every five years;
- there should be no parts in the heating system that contain zinc - propylene glycol quickly dissolves them;
- Propylene glycol is extremely fluid and can penetrate through small joints in the heating system.
Many manufacturers dilute antifreeze with water to correct some of the disadvantages of propylene glycol. What will it give:
- the cost of antifreeze will become noticeably lower;
- the viscosity will decrease;
- the heat capacity will increase;
- the heat transfer rate will increase;
- the boiling point will drop, but most boilers are still not designed for 160 ° C;
- freezing point is from -30 to -40 ° C degrees;
- antifreeze based on propylene glycol with water expands slightly, so the destruction of the heating system will not occur.
Using glycerin as a heat carrier
H2_2
To obtain a glycerin-based coolant, the pure substance is mixed with various impurities that allow it to remain liquid when used in cold conditions. The resulting composition is chemically inert, and chemical processes do not take place inside, which can have a detrimental effect on the elements of the entire system.
The ability to maintain a liquid state at subzero temperatures and absolute safety for humans makes it possible to use the coolant for heating systems in residential buildings, including for floor heating.
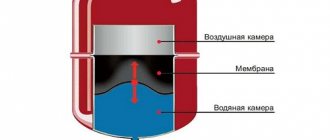
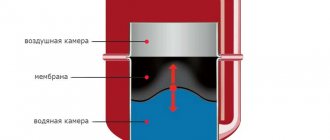
The operation of this heating system is based on one principle: there is a heater, heating elements and a coolant. In this case, the main characteristics of the coolant will affect the overall heating efficiency.
Important! It is necessary to determine which coolant will be used in the underfloor heating system at the stage of its design. This will affect the choice of equipment, pipe diameter and the length of the circuits.
Advantages of glycerin coolant
Compared to propylene glycol or ethylene glycol formulations, this antifreeze has the following advantages:
- It can be used in a wide temperature range from -30 to +105 ° C. Even when the substance is completely frozen, it does not expand and does not damage the pipes. After thawing, all its original properties are restored.
- The coolant is sold ready-made and does not require additional dilution with water. Glycolic formulations must be diluted;
- Antifreeze does not cause corrosion or other damage to floor heating elements, including galvanized pipes and rubber gaskets;
- The substance is absolutely safe for human health and the environment, which is very important in the event of leaks or damage to the system as a whole;
- At a relatively high price, the composition has a long term of use up to 8 years. Another type of antifreeze has been used for about 5 years;
- The coolant can be poured into the pipes after any other type of antifreeze; flushing is not required;
- Antifreeze is made only from high quality raw materials, which are also used in the food and cosmetic industries;
- Belongs to the class of non-flammable substances.
Advice! When filling the pipes, you can add some fluorescent dye to the antifreeze. In the event of a leak in the system, the dye will help to quickly locate the leak.
Disadvantages of a glycerin composition
A glycerin-based coolant has its drawbacks, which must be taken into account when designing a warm floor:
- Freezing increases the density and viscosity of the glycerin composition, which leads to a decrease in its heat capacity. In a heating system project, pipes of a larger diameter will have to be used than when using ordinary water;
- The high viscosity of the composition will require the installation of a more powerful circulation pump in the heating system;
- Glycerin-based antifreeze requires the use of reliable and expensive gaskets and seals during the heating installation process. Teflon or paronite gaskets are recommended;
- Antifreeze tends to foam, which can cause the warm floor to air out. Special additives help to partially reduce foaming;
- The composition based on glycerin has a density and mass greater than that of glycolic. The use of a glycerin composition in the underfloor heating system will increase the load on the floors and foundation of the building.
How to use propylene glycol fluids correctly
Propylene glycol based heat transfer fluids have a similar chemical composition, which differs in the percentage of alcohol. Most often, such compositions are named by the manufacturer's name.
If propylene glycol antifreeze contains about 30%, it freezes at -13 ° C, 35% alcohol solution crystallizes at -20 ° C, 40% at -25 ° C, 75% solution at -65 ° WITH.
When replacing water with a propylene glycol-based composition, it is necessary to take into account some of the properties of antifreeze.
- Lower heat capacity and thermal conductivity. It is worth increasing the number of radiators, as well as purchasing a more powerful boiler. Heating systems are often installed in private houses that operate at half their capacity - in this case, you can do without replacing the boiler.
- High viscosity. Make sure the pipes have an inner diameter of at least 25 mm and install a larger circulation pump.
- Greater expansion ratio. If the expansion tank is less than 10 liters, then a larger one will need to be replaced.
- High fluidity. It is worth reducing the number of threaded connections, tie-ins and squeegees, and also provide free access to existing connections in case of leakage.
If the technical parameters of the existing heating meet the new requirements, you can proceed to the preparatory work:
- to seal squeegees, connections, tie-ins;
- completely drain the water from the heating system and rinse with caustic soda, it will remove rust and scale;
- remove all zinc parts;
- additives can be added to antifreeze that will protect copper parts;
- check the dirt trap twice as often;
- check the solution every two years for alcohol concentration;
- complete change of antifreeze every five years.
It is always worth flushing the system thoroughly if you are going to switch to another coolant.
Selection and use of glycerin coolant
Glycerine coolant is presented on the market by manufacturers Gulfstream, Eco-30, Teplocom, PRIMOCLIMA, Olga. Compositions of different brands differ in color and type of impurities.
For the convenience of consumers, antifreezes are sold packaged in cans of 10 or 20 kg, as well as in barrels of 50 kg. To fill a heating system with a volume of 100 liters, about 115 kg of coolant will be required.
When injecting the composition, specialized equipment is required. It is recommended to involve specialists to fill the heating complex. First of all, all heating equipment is cleaned.
To fill the complex with antifreeze, you will need a pump, a hose, a pressure gauge, a large container for the coolant and equipment for subsequent pressure testing. After filling the heating complex, it is pressurized.
Water
Benefits:
- environmentally friendly substance;
- sufficiently high heat capacity;
- circulates freely through the system;
- always at hand;
- extremely low cost.
Disadvantages:
- freezes at temperatures below 0 ° С;
- lack of operation in winter requires draining the system, which leads to corrosion;
- water hardness manifests itself at temperatures above 80 ° C, then decomposition of carbonate salts begins and scale deposits on the walls of the system, which reduces heat transfer and can break the system due to overheating.
Propylene glycol
- a more expensive option, supplied ready-made in canisters with a temperature of -30 degrees. Much less toxic.
Specific heat at 20 ° C, - 2483 J / (kg K). Density - 1.0363 g / cm³ Propylene glycol is used in electronic cigarettes as a tobacco preservative. Prevents the formation of mold, bacteria. Many boiler equipment manufacturers certify propylene glycol-based heat transfer fluids for use in boiler equipment.
Glycerin-based heat carrier
Benefits:
- environmentally friendly;
- not hazardous by inhalation of vapors;
- does not cause poisoning if accidentally ingested;
- inert to galvanized parts;
- cheaper than propylene glycol-based coolant.
Disadvantages:
- the mass of the glycerin coolant gives an additional load on the equipment;
- the viscosity is higher than that of glycol solutions;
- thermally unstable;
- foams strongly, the risk of airing the system increases;
- when used, the requirements for gaskets (seals) and parts are increased.
We will not let your heating system defrost + 7-932-2000-535
In Russia, their share of the total volume of heat carriers sold is growing rapidly. At the state level, a ban has been introduced on the use of ethylene glycol coolants in refrigeration equipment and heating of railway cars.
WATER AS A HEAT CARRIER
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Water freezes in the system at temperatures below - 0 ° С and, as a result, puts the latter out of action / you cannot leave a house with a turned off, but filled heating system in winter /. In a matter of days and even hours, elements of the heating system / boiler; batteries; expansion tank; circulation pump / will simply be ruptured. Heating system corrosion. If, in order to avoid defrosting the heating system, the water is drained, the corrosion processes in the system filled with air proceed even faster than in water. The need to change the chemical composition of water before using it for heating. Natural water is characterized by such an indicator as hardness. At water temperatures above - 80,0 ° C, intensive decomposition of carbonate salts begins and scale deposits on the walls of the heat generator and pipes, which is the reason for the deterioration of heat transfer and failure of the heating elements due to their overheating. It is desirable that the water contains special additives that can extend the life of the heating system / corrosion inhibitors, etc. /. Ideally, additives are added to distilled water. Correction of specific electrical resistance of water during the heating season. Carrying out annual flushing of the system and boiler repair. |
SOLUTIONS OF SOME INORGANIC AND ORGANIC SALTS
AS A HEAT CARRIER
Saline solutions, although they freeze at lower temperatures than water, and are harmless to humans, are highly corrosive. Over time, they are “salted out” on the surface of pipes and heat exchangers. Such solutions also do not “cope” with Russian winter conditions due to insufficiently low freezing point.
Do not use ethyl / methyl alcohol or transformer oil as a heat carrier due to their high fire hazard.
At the present stage, antifreezes are increasingly used as coolants.
Antifreeze
Are low-freezing liquids used to cool internal combustion engines and various installations / including heating systems / operating at temperatures below -
0
° C.
GLYCERINE-BASED HEATING AGENT
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Due to the higher density, the mass of the glycerine coolant for filling the system of the same volume will be greater than the mass of the glycol coolant, which will create an additional load on the equipment. The viscosity of glycerin solutions, especially at low temperatures, is higher than that of glycol solutions, this accelerates the wear of some parts of the heating system, such as pumps and circulation pumps; more powerful pumps will be required. At the same freezing point, the glycerine coolant contains more organic component / glycerin / and less water than glycol / propylene glycol, ethylene glycol /. This leads to an additional increase in density and viscosity, to a decrease in heat capacity. Glycerin is thermally unstable: - with prolonged heating over - 90,0 ° C decomposes with the formation of volatile and carcinogenic substances, including acrolein. Decomposition products are also corrosive. During their polymerization, deposits form on the walls of the heating system, which worsen the heat dissipation and clog the system. - have a high freezing point. With the complete evaporation of water from the coolant, the base freezes at + 17,0 ° С, and, often, and at + Glycerin foams strongly, for this reason heat dissipation worsens, the risk of airing the system increases. When aqueous solutions of glycerin are used as heat carriers, the requirements for gaskets / seals / and parts made of non-polar rubbers and plastics are increased. |
| * - coolant that has not been in operation, moreover, does not contain additional components, except for glycerin, water and a package of additives. ** - coolant based only on glycerin, without additives | |
There are no state standards /GOST
/, establishing the requirements for glycerin-based antifreezes / coolants. Such coolants are produced according to technical conditions, in which product quality indicators are established by individual manufacturing firms.
Under the brand name of glycerin-based coolants, there are also mixed coolants containing propylene-glycol along with glycerin.
Currently, there is not a single large world or domestic manufacturer that has switched to the production of glycerin-based antifreezes and coolants.
The most reliable and proven are glycol-based heat transfer fluids.
ETHYLENE GLYCOL BASED HEAT
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Ethylene glycol toxic, narcotic. It is absorbed into the body quickly. The degree of harm that ethylene glycol causes to a person depends on the amount of poison, the method of penetration and the individual state of the body. When swallowed, pulmonary edema occurs, and acute heart failure develops. Experts call different figures for the lethal dose of a substance: - 5,0 mg per kg of body weight; - Ethylene glycol is able to enter the body through the skin and by inhalation. Therefore, it is very dangerous to use ethylene glycol coolant in open systems - vapors will spread in the room; in double-circuit boilers, a poisonous coolant can be mixed into hot water. With prolonged exposure, chronic poisoning with damage to vital organs / vessels is possible; kidneys; nervous system/. The first signs of poisoning are depressed mood, lethargy. It is especially worth remembering that ethylene glycol does not have an unpleasant odor and has a sweetish taste, which poses an increased danger to children and animals in the event of coolant leaks from the system. With the complete evaporation of water from the antifreeze composition during subsequent cooling, ethylene glycol freezes at a temperature of minus - 13,0 ° C. Has a high viscosity at low temperatures. The spent heat transfer fluid based on ethylene glycol must not be poured into the open ground and into the sewer; it must be collected and sent for recycling. In the event of a spill in a residential building, floorboards, tiles, insulation impregnated with ethylene glycol coolant must be replaced. |
Heat transfer fluids based on ethylene glycol can be safely used in closed heating systems, with a closed expansion tank, for heating non-residential premises. For security reasons, constant monitoring of the system is required.
Antifreeze coolant, or antifreeze for cars?
Functionally in heat exchange systems it can be used - car antifreeze
, which was often practiced in Russia due to the insufficient availability of household
coolants-antifreeze
... The use of automotive fluids / antifreezes or Tosolov / in systems is possible if they are manufactured according to a technology that involves the use of liquid for cooling internal combustion engines, as well as as a working fluid in heat exchangers operating at low and moderate temperatures.
Conventional additive packages - automotive antifreeze
and
antifreeze
not designed for long-term and intensive operation in domestic heating systems. In some cases, the additives contained in modern
auto-fluids
and designed for car engine alloys may not be compatible with heating materials.
It should also be remembered that - automotive antifreeze
are inherent in all
environmental cons
coolants based on -
ethylene glycol
.
In addition, automotive antifreeze additives often include - toxic substances
that could pose a danger to -
human
and
animals
.
HEAT CARRIER BASED ON PROPYLENE GLYCOL
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Higher cost than other types of heat transfer fluids. The initial cost of a propylene glycol-based heat carrier is only an apparent high cost.It is justified by the minimal costs of repairing the system, low operating costs and labor costs, ensuring safety, and the absence of costs for connecting to centralized heating systems. It should also be borne in mind that the cost of a high-quality coolant is preferable to the cost of repairing expensive equipment. Heat carrier / antifreeze / "Comfort" brand "BUT ", Produced by PO" Khimprom ", Kemerovo, due to the manufacture |
It can be used in systems with heating elements outside the building or in the attic.
The wrong choice of antifreeze and non-observance of the operating rules can cause many problems during operation, up to a complete failure of the system.
Heating and water supply is a multifaceted engineering process,
requiring the knowledge and skills of a PROFESSIONAL.
Country house with autonomous heating system. The heat source is a gas, solid fuel or electric boiler. If the boiler suddenly breaks down and there is no information about the temperature in your country house (not installed), there is a high risk of defrosting the system. The water in the pipes and boiler will freeze and rupture (destroy) expensive equipment.
Recipe: pour non-freezing liquid into the heating system - a specialized coolant for heating systems. Currently, a heat transfer fluid of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and glycerin is common on the market. We will take into account when comparing the physical characteristics of the properties of water: Density - 1,000 g / cm³. Specific heat at 20 ° C, - 4218 J / (kg K)
Ethylene glycol heat transfer fluid
Benefits:
- the system is not defrosting;
- good thermophysical properties;
- slight deposits of salts and scale;
- average cost.
Disadvantages:
- belongs to the third class of danger, has a narcotic effect on the body, is toxic;
- quickly absorbed into the body, is able to penetrate the skin and by inhalation;
- does not have an unpleasant odor;
- poses an environmental hazard;
Component Specifications
Pure glycerin is a transparent liquid and belongs to trihydric alcohols. Mixes well with water or alcohols in any proportions. Under industrial conditions, the substance is synthesized from propylene. Under natural conditions, it is found in the base of oils or fats. Has the following technical characteristics:
- Colorless;
- Odorless;
- Transparent;
- Melts at 18 ° C, boils at 290 ° C;
- The density of the substance is 1.27 g / cm³;
- The refractive index is 1.473.
Propylene glycol based heat carrier
Benefits:
- insures the system against rupture;
- the volume during freezing increases by only 0.1%;
- provides the highest level of safety after water;
- not dangerous even with prolonged inhalation of vapors;
- non-corrosive;
- good thermophysical properties;
- possesses bactericidal and sterilizing properties.
Disadvantages:
- high cost (pays off with minimal repair costs, safety and the ability not to connect to central heating systems).